Use of Chemically Treated Human Hair Wastes for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Human Hair
2.3. Chemical Treatment of Human Hair
2.4. Characterization of Human Hair
2.5. Heavy Metal Ions Biosorption Experiments
2.6. Desorption, Regeneration and Reuse
3. Results and Discussion
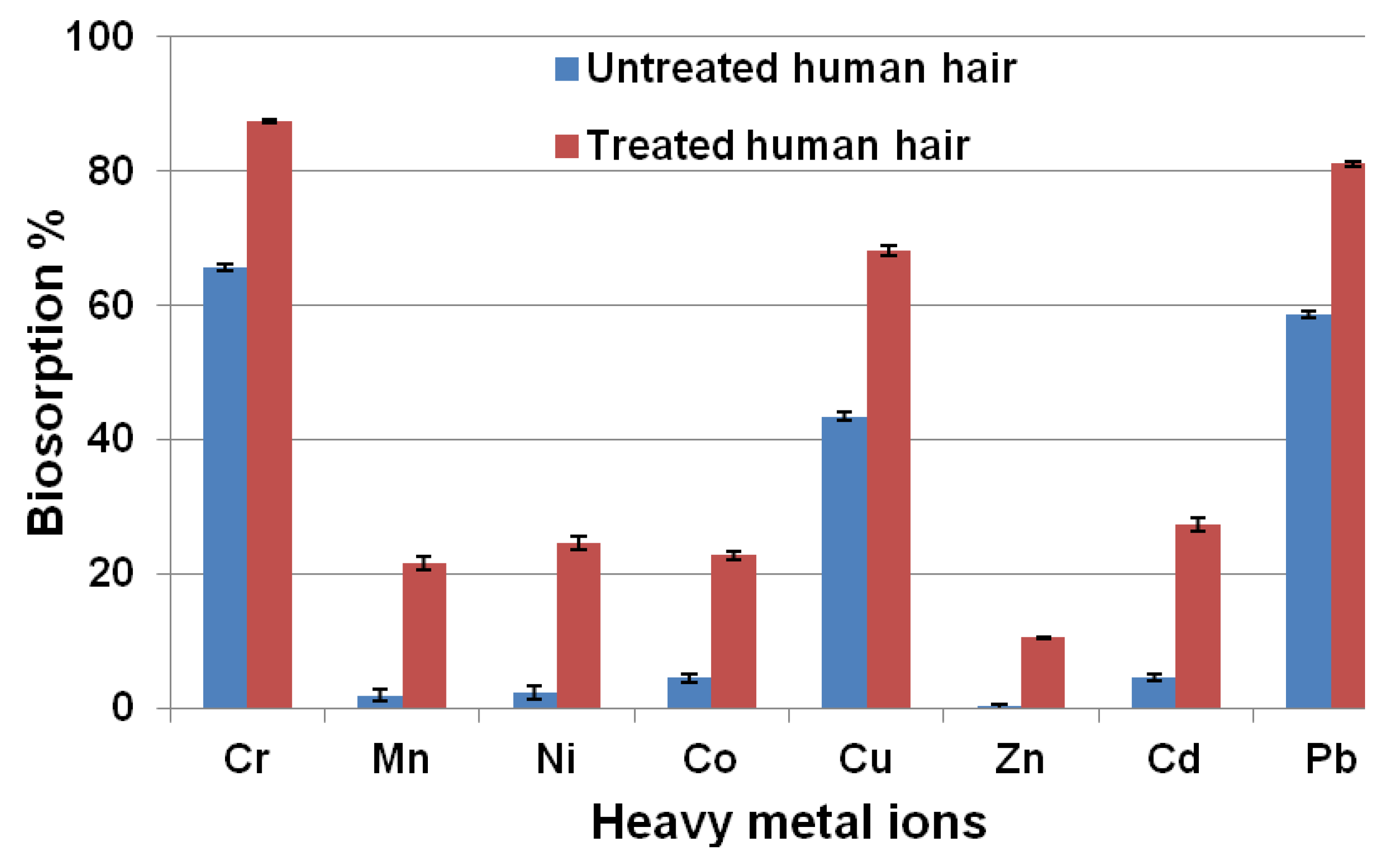
3.1. Comparison of Biosorption Efficacy between Untreated and Treated Human Hair
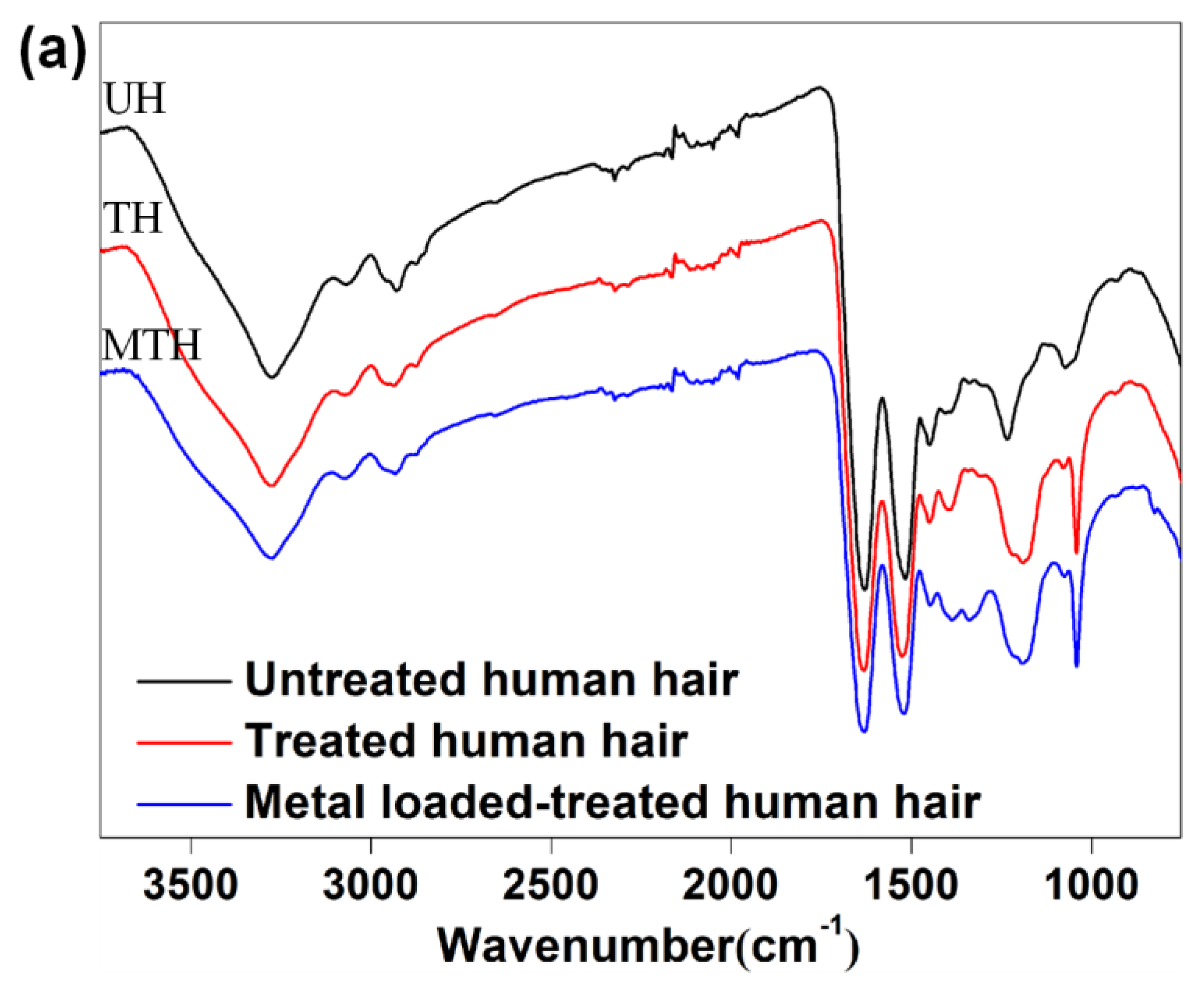
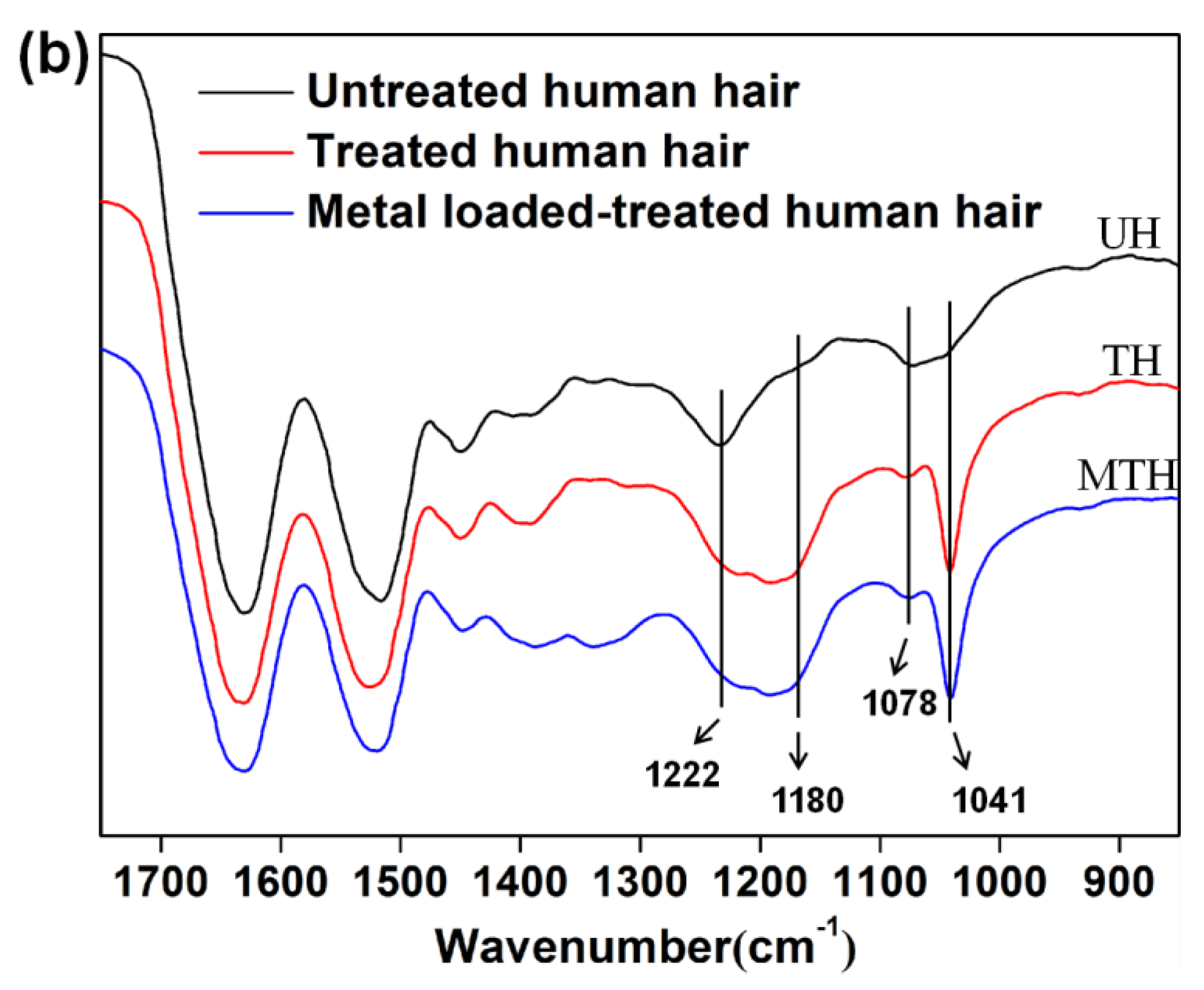
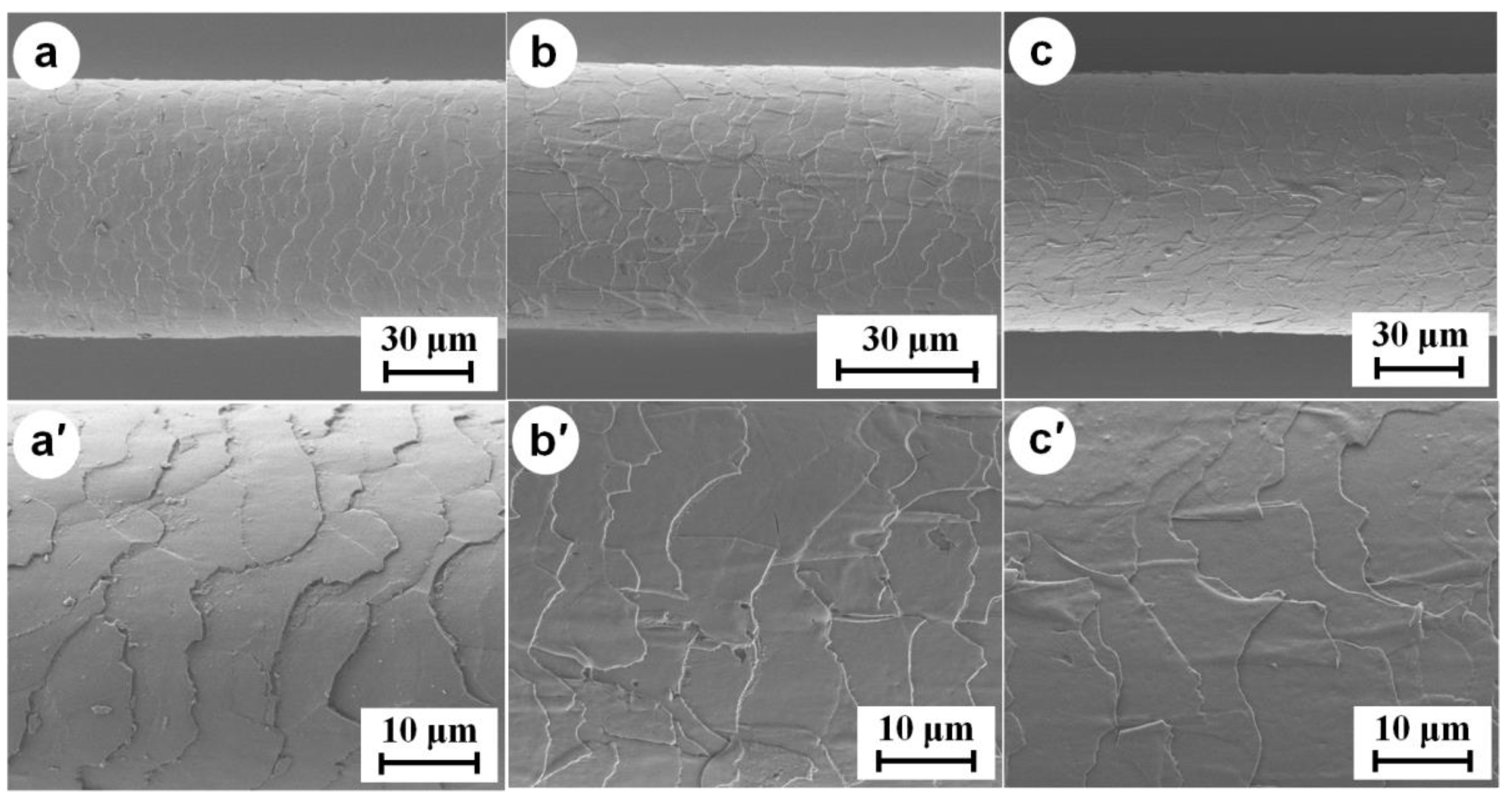
3.2. FT-IR and SEM Characterization
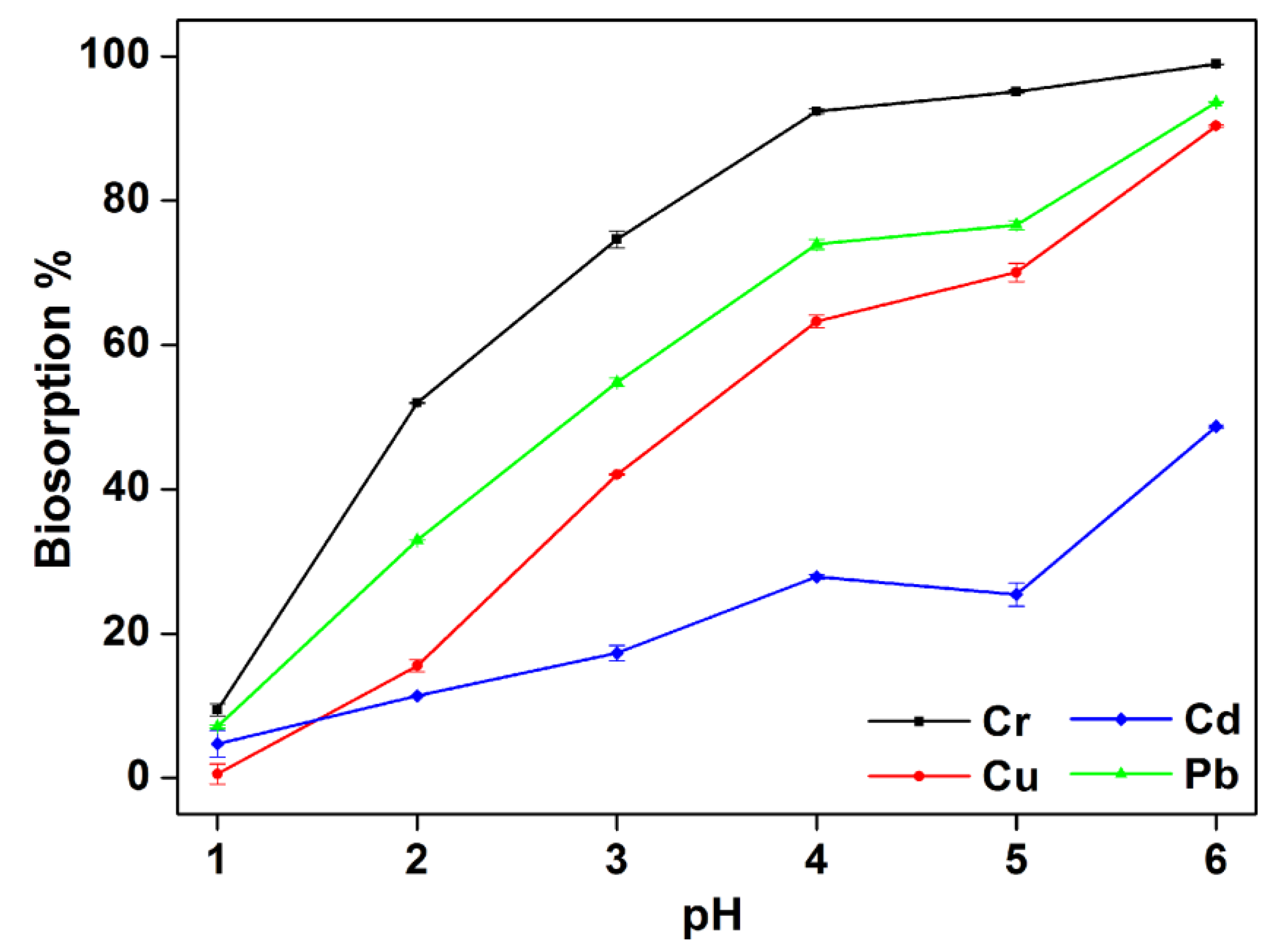
3.3. Effect of the pH in Multiple Metal System
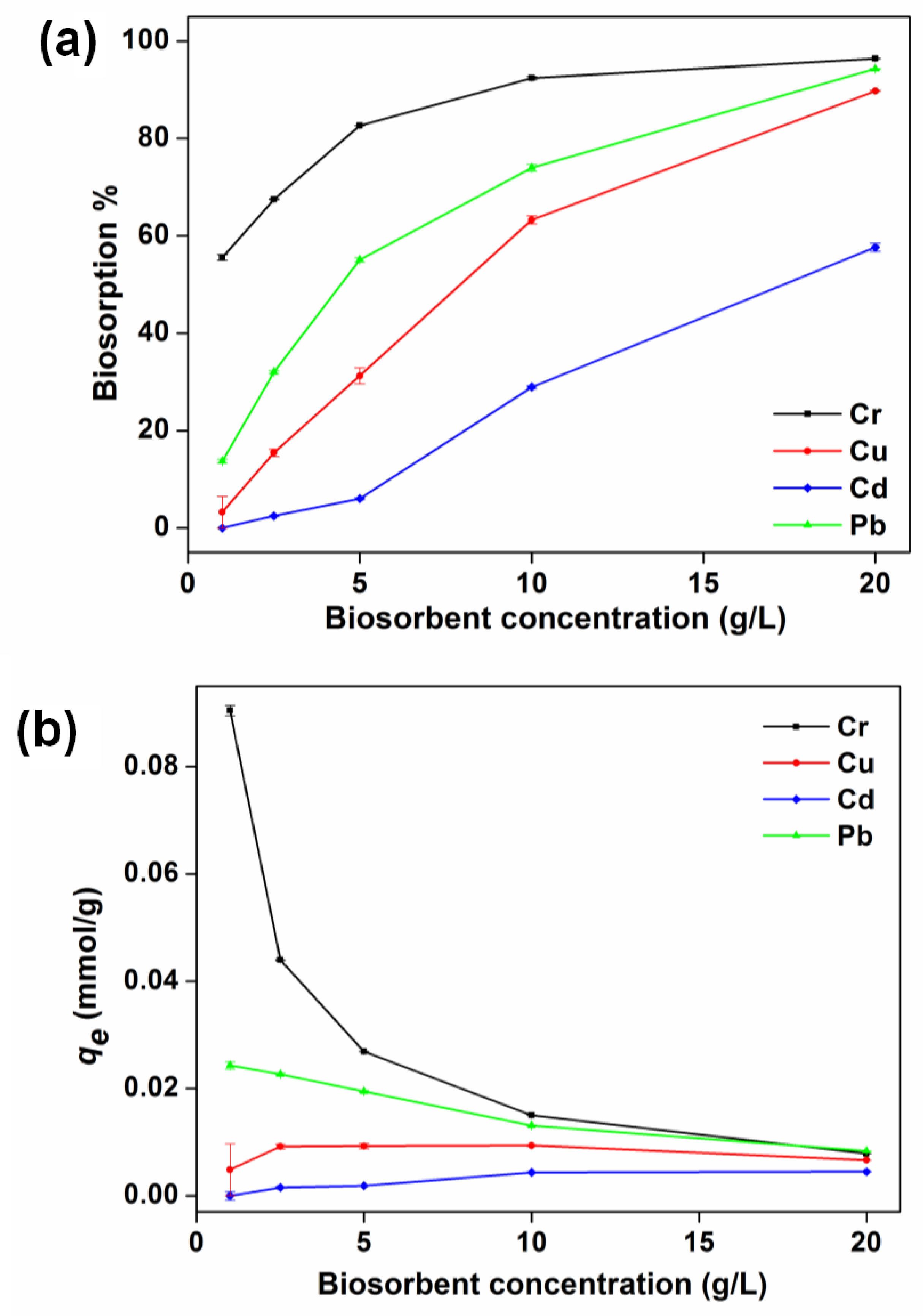
3.4. Effect of Biosorbent Concentration
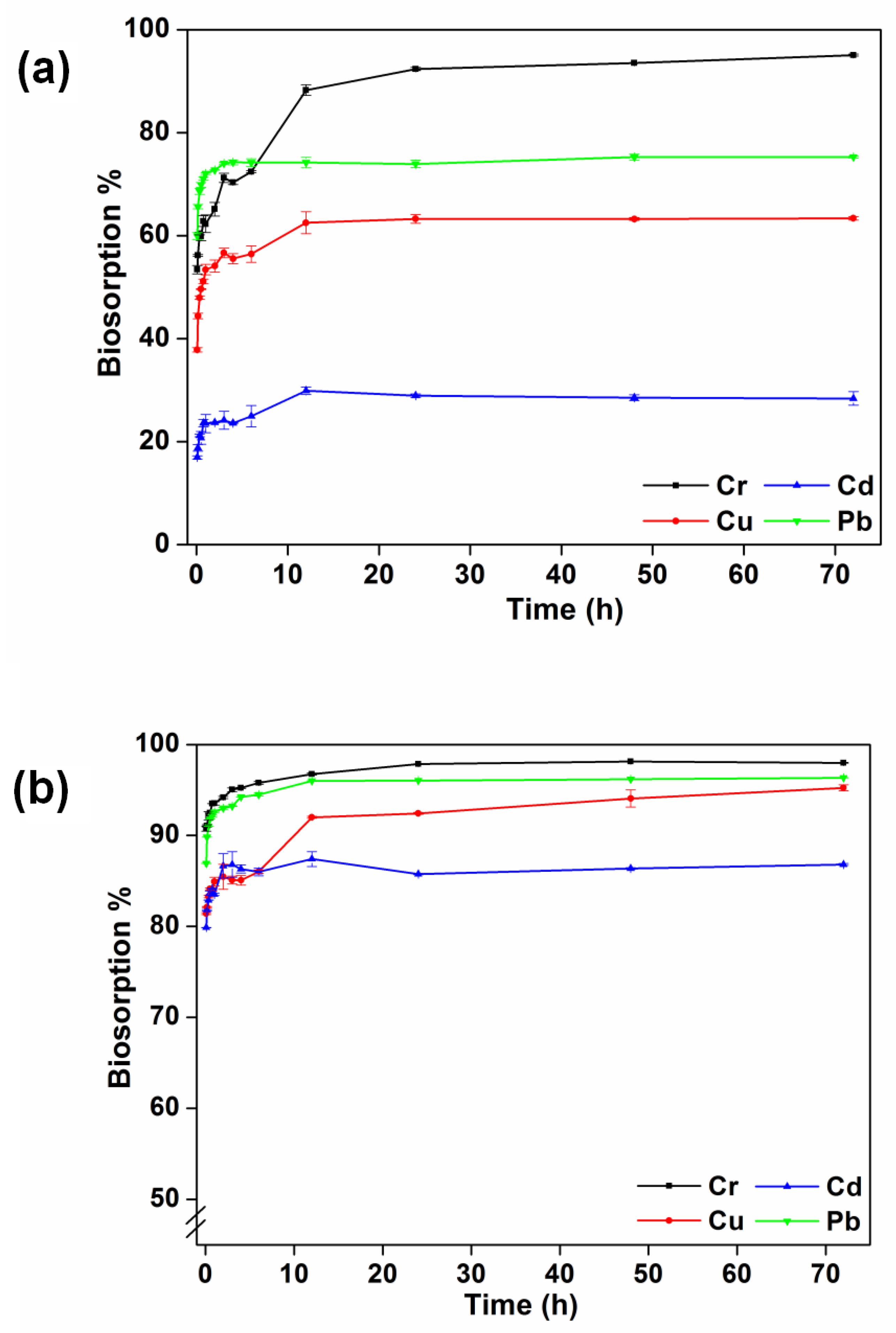
3.5. Effect of Contact Time
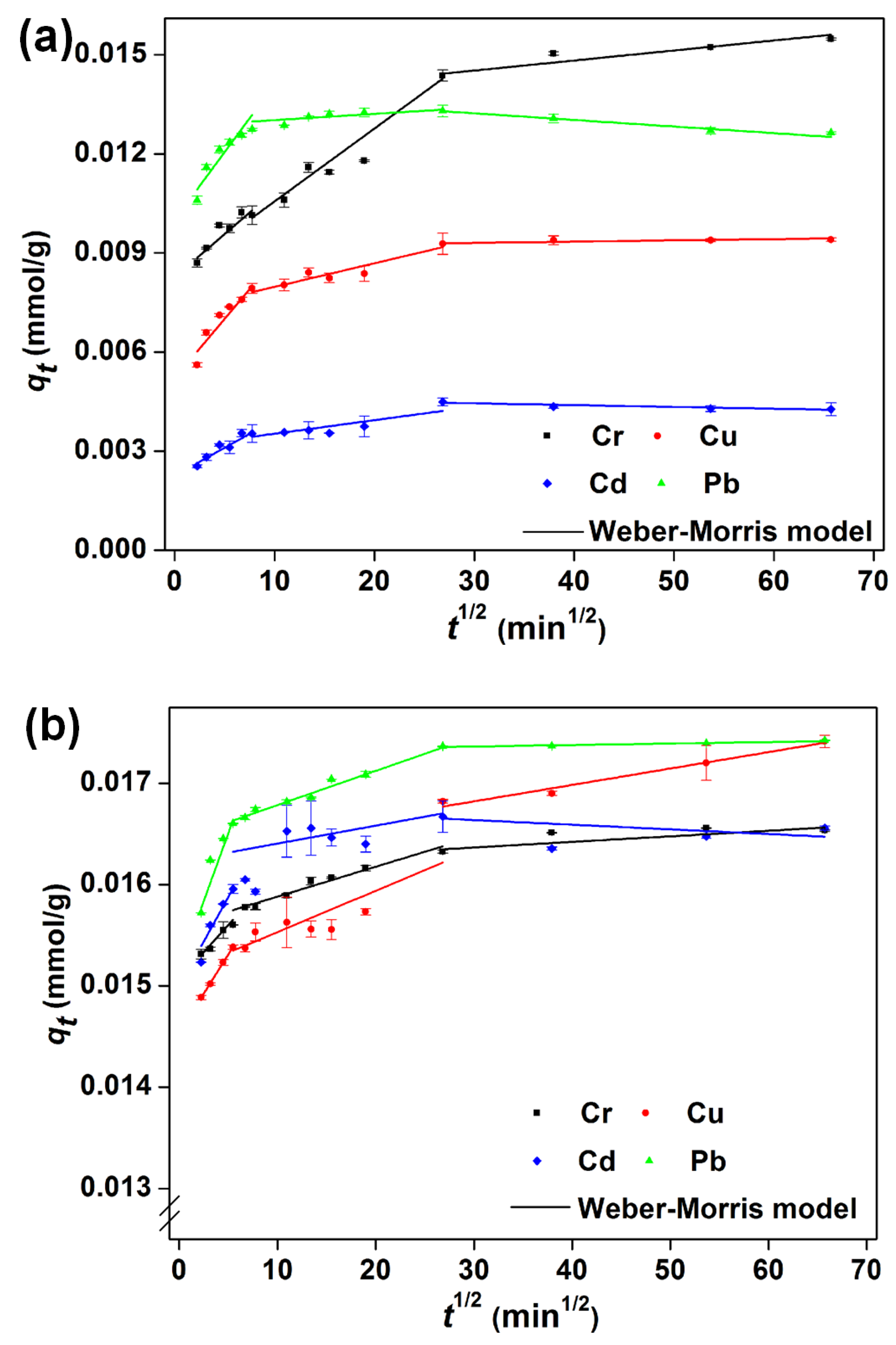
3.6. Kinetic Studies
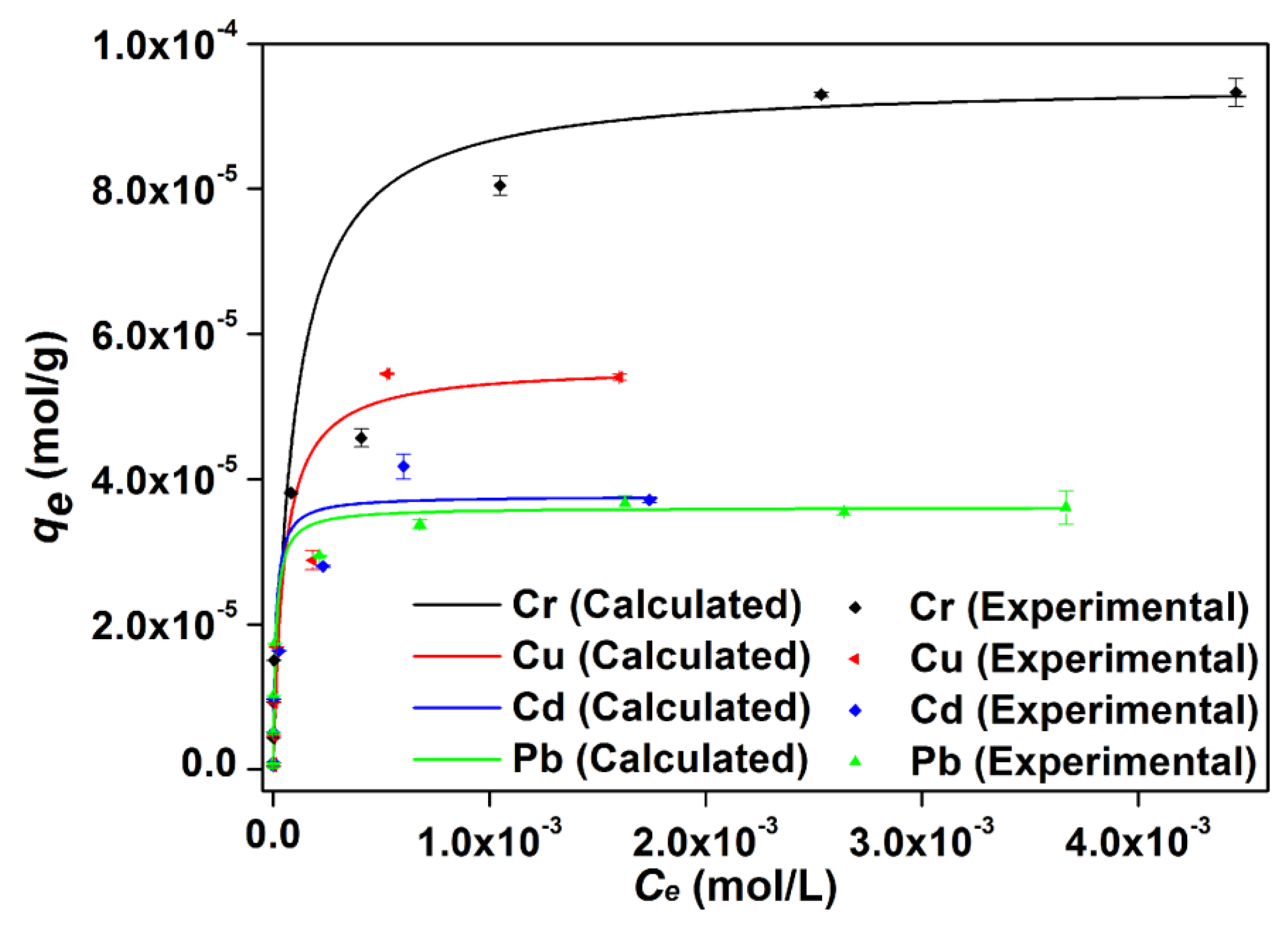
3.7. Thermodynamic Isotherm Characterization
3.8. Desorption, Regeneration, and Reuse Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beer, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilela, D.; Parmar, J.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sánchez, S. Graphene-Based Microbots for Toxic Heavy Metal Removal and Recovery from Water. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2860–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeed, A.; Iqbal, M.; Akhtar, M.W. Removal and recovery of lead(II) from single and multimetal (Cd, Cu, Ni, Zn) solutions by crop milling waste (black gram husk). J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 117, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostovaritalab, M.; Hayati-Ashtiani, M. Investigation of Cs(I) and Sr(II) removal using nanoporous bentonite. Part. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, Y.; Yassin, J.M.; Tedla, A. Removal of organic dye and toxic hexavalent chromium ions by natural clay adsorption. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 165, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohzad, E.; Jafari, D.; Esmaeili, H. Adsorption of lead and arsenic ions from aqueous solution by activated carbon prepared from tamarix leaves. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 12356–12367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, G.R.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Biosorption technology for removal of toxic metals: A review of commercial biosorbents and patents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19097–19118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.S.W.; Fatinathan, S. Pb(II) biosorption using chitosan and chitosan derivatives beads: Equilibrium, ion exchange and mechanism studies. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, D.; Mahajan, G.; Kaur, M.P. Agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent for sequestering heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6017–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, P.; Misra, M. Use of keratin fiber for separation of heavy metals from water. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Carrillo, F.; López-Mesas, M.; Palet, C. Valorization of keratin biofibers for removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Mesas, M.; Navarrete, E.R.; Carrillo, F.; Palet, C. Bioseparation of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution using cork waste biomass. Modeling and optimization of the parameters of the biosorption step. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfaksi, Z.; Azzouz, N.; Abdelwahab, A. Removalof cr(VI) from water by cork waste. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamal, M.H.M.A.; Azira, W.M.K.W.K.; Kasmawati, M.; Haslizaidi, Z.; Saime, W.N.W. Sequestration of toxic Pb(II) ions by chemically treated rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) leaf powder. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, W.S.W.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3935–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.; He, J.; Gao, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhu, X. Cosorption of Phenanthrene and Mercury(II) from Aqueous Solution by Soybean Stalk-Based Biochar. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12116–12123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm-Lehto, P.C. Biosorption of heavy metals by lignocellulosic biomass and chemical analysis. BioResources 2019, 14, 4952–4995. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Zubair, M.; Khosa, M.A.; Song, S.; Ullah, A. Keratin and chitosan biosorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1389–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, E.; Rintala, J. Anaerobic digestion of organic solid poultry slaughterhouse waste—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Rastogi, S.; Terry, A.E.; Popescu, C. Self-organization of Oligopeptides Obtained on Dissolution of Feather Keratins in Superheated Water. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asheh, S.; Banat, F.; Al-Rousan, D. Beneficial reuse of chicken feathers in removal of heavy metals from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2003, 11, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, C.S.; Gang, E.H.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H. Nanofibrous membrane of wool keratose/silk fibroin blend for heavy metal ion adsorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 302, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluigi, A.; Tonetti, C.; Vineis, C.; Tonin, C.; Mazzuchetti, G. Adsorption of copper(II) ions by keratin/PA6 blend nanofibres. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A. Human hair “waste” and its utilization: Gaps and possibilities. J. Waste Manag. 2014, 2014, 498018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freddi, G.; Arai, T.; Colonna, G.M.; Boschi, A.; Tsukada, M. Binding of metal cations to chemically modified wool and antimicrobial properties of the wool–metal complexes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 3513–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, L.; Squires, P.L.; Garry, M.; Tumosa, C.S. A measurement of human hair oxidation by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Forensic Sci. 1985, 30, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, W.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Farwell, D.W.; Nutbrown, M. Fourier-transform Raman spectroscopic study of human hair. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 1997, 53, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febrianto, J.; Kosasih, A.N.; Sunarso, J.; Ju, Y.-H.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Equilibrium and kinetic studies in adsorption of heavy metals using biosorbent: A summary of recent studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 616–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances, Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. The kinetics of sorption of divalent metal ions onto sphagnum moss peat. Water Res. 2000, 34, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption of carbon from solution, Journal of the Sanitary Engineering Division. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Onal, Y.; Akmil-Başar, C.; Sarici-Ozdemir, C. Investigation kinetics mechanisms of adsorption malachite green onto activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guechi, E.; Benabdesselam, S. Removal of cadmium and copper from aqueous media by biosorption on cattail (typha angustifolia) leaves: Kinetic and isotherm studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 173, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgen, M.D.R.M.; Vázquez, O.F.G.; Montoya, V.H.; Gómez, R.T. Removal of heavy metals using adsorption processes subject to an external magnetic field. In Heavy Metals; Intechopen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 253–280. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/heavy-metals/removal-of-heavy-metals-using-adsorption-processes-subject-to-an-external-magnetic-field (accessed on 28 April 2020).
| Metal | Cr | Cu | Cd | Pb | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System | Single | Multiple | Single | Multiple | Single | Multiple | Single | Multiple | |
| Pseudo first order | k1 × 103 (min−1) | 9.21 a | 4.19 b | 6.91 a | 15.0 b | 26.3 a | 12.9 b | 26.8 a | 27.3 b |
| qe (mmol/g) | 0.00132 | 0.00655 | 0.00263 | 0.00346 | 0.00151 | 0.00190 | 0.00173 | 0.00233 | |
| R2 | 0.9327 | 0.7343 | 0.9905 | 0.8794 | 0.9136 | 0.8592 | 0.8381 | 0.9030 | |
| Pseudo second order | k2(g/mmol min) | 15.4 | 1.51 | 3.83 | 6.75 | 38.2 | 16.2 | 17.8 | 16.6 |
| qe (mmol/g) | 0.0166 | 0.0155 | 0.0174 | 0.00945 | 0.0165 | 0.00429 | 0.0174 | 0.0133 | |
| R2 | 1.000 | 0.9993 | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | 1.000 | 0.9997 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| kd (mmol/g) | 0.0151 | 0.00831 | 0.0145 | 0.00517 | 0.0148 | 0.00223 | 0.0157 | 0.0103 | |
| Constant | Cr | Cu | Cd | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich | KF × 103 | 1.56 | 2.87 | 0.546 | 0.247 |
| n | 2.30 | 1.90 | 2.86 | 3.63 | |
| R2 | 0.8646 | 0.8402 | 0.9291 | 0.8607 | |
| Langmuir | Q0 × 105 (mol/g) | 9.47 | 5.57 | 3.77 | 3.61 |
| B × 10−4 (L/mol) | 1.07 | 2.06 | 8.64 | 8.04 | |
| KL (L/g) | 1.01 | 1.15 | 3.26 | 2.90 | |
| R2 | 0.9912 | 0.9905 | 0.9952 | 1.000 | |
| −ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | 22.8 | 24.4 | 27.9 | 27.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Carrillo-Navarrete, F.; López-Mesas, M.; Palet, C. Use of Chemically Treated Human Hair Wastes for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water. Water 2020, 12, 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051263
Zhang H, Carrillo-Navarrete F, López-Mesas M, Palet C. Use of Chemically Treated Human Hair Wastes for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water. Water. 2020; 12(5):1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051263
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Helan, Fernando Carrillo-Navarrete, Montserrat López-Mesas, and Cristina Palet. 2020. "Use of Chemically Treated Human Hair Wastes for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water" Water 12, no. 5: 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051263
APA StyleZhang, H., Carrillo-Navarrete, F., López-Mesas, M., & Palet, C. (2020). Use of Chemically Treated Human Hair Wastes for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water. Water, 12(5), 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051263






