Energy Dissipation of Type a Piano Key Weirs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. PK Weir Overview
1.2. Energy Dissipation
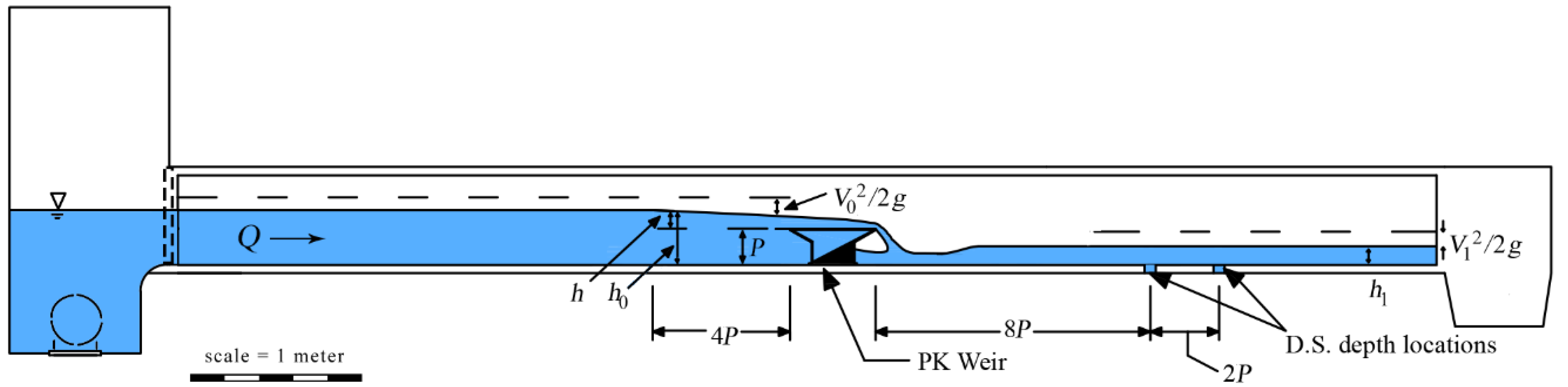
2. Experimental Setup
3. Results
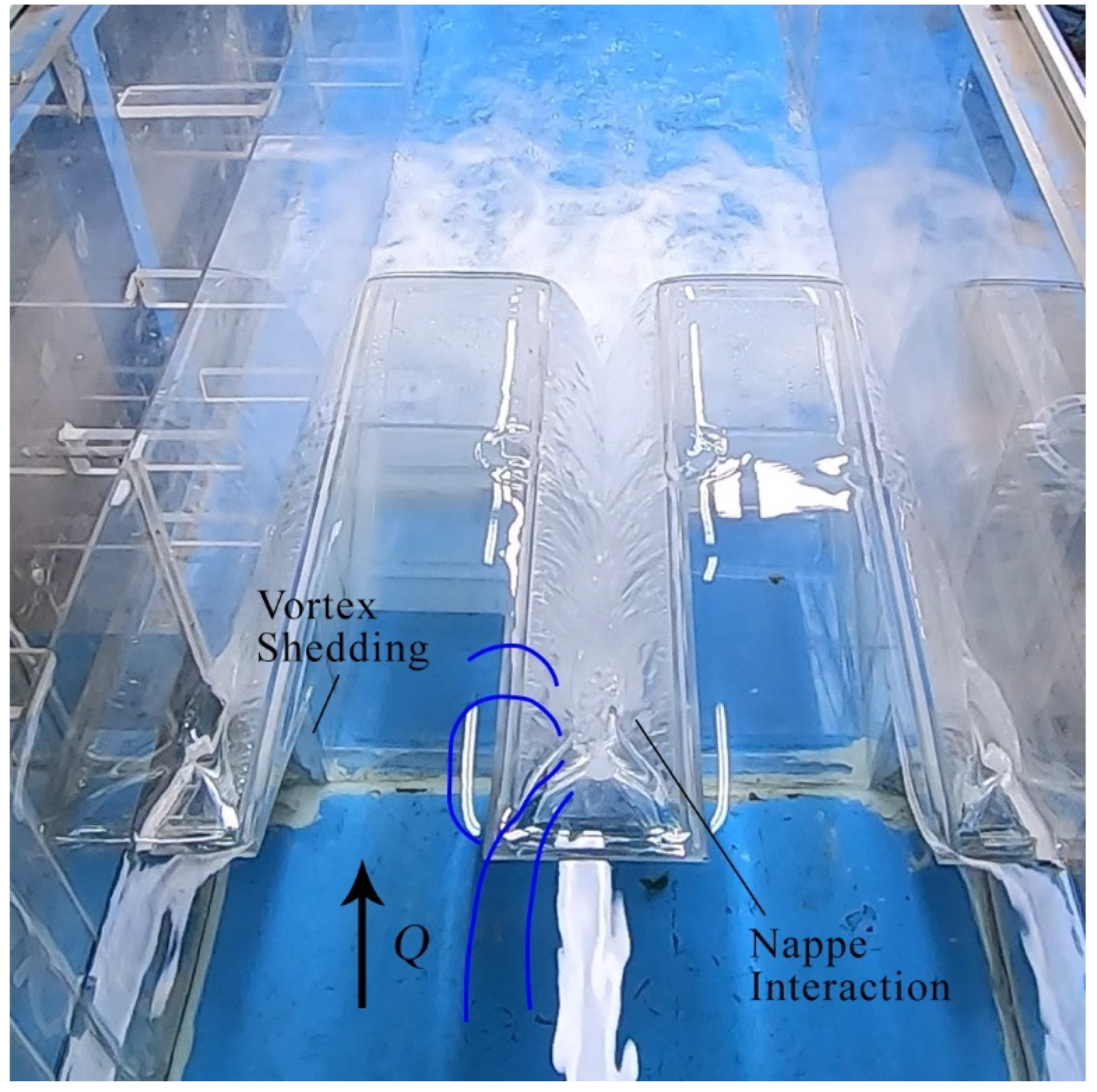
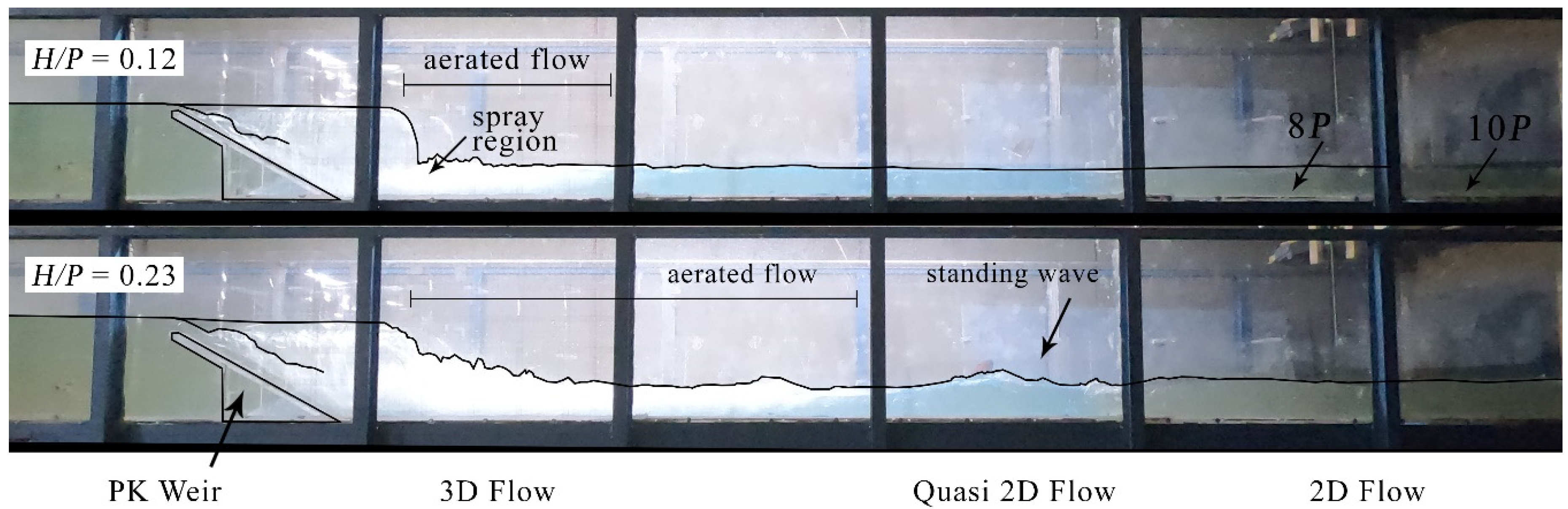
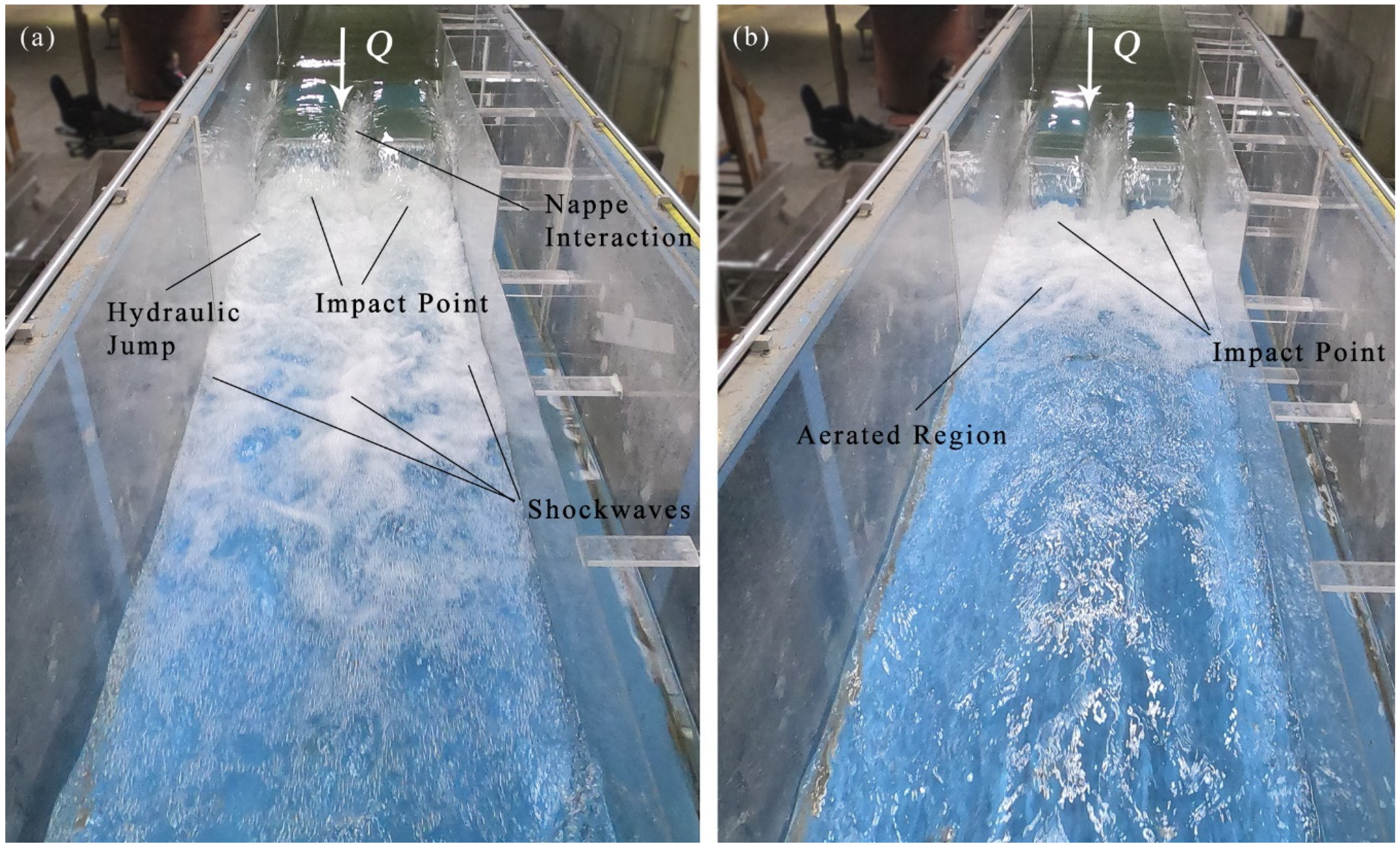
3.1. Type A PK weir Flow Features
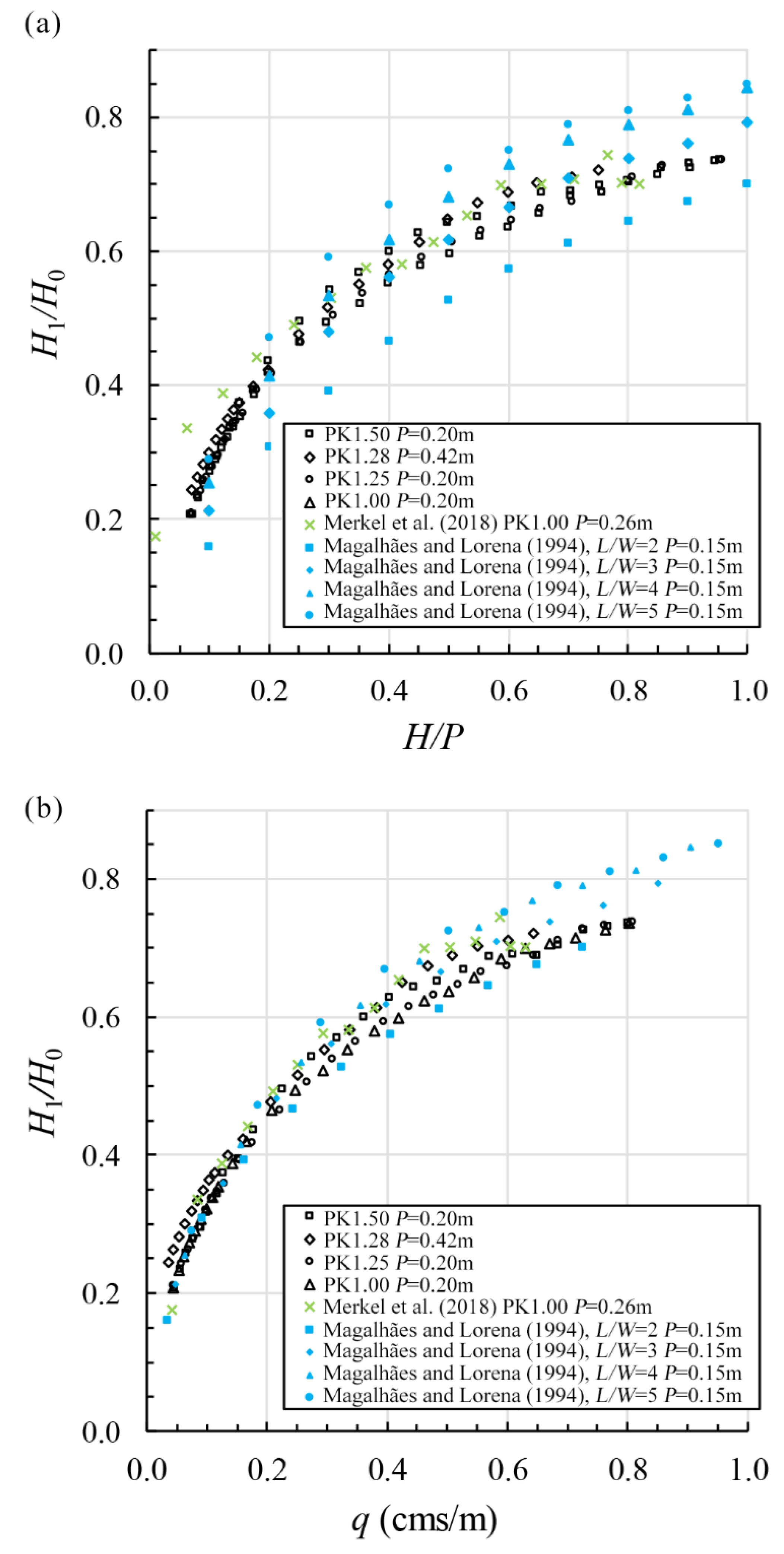
3.2. Dissipation of Energy
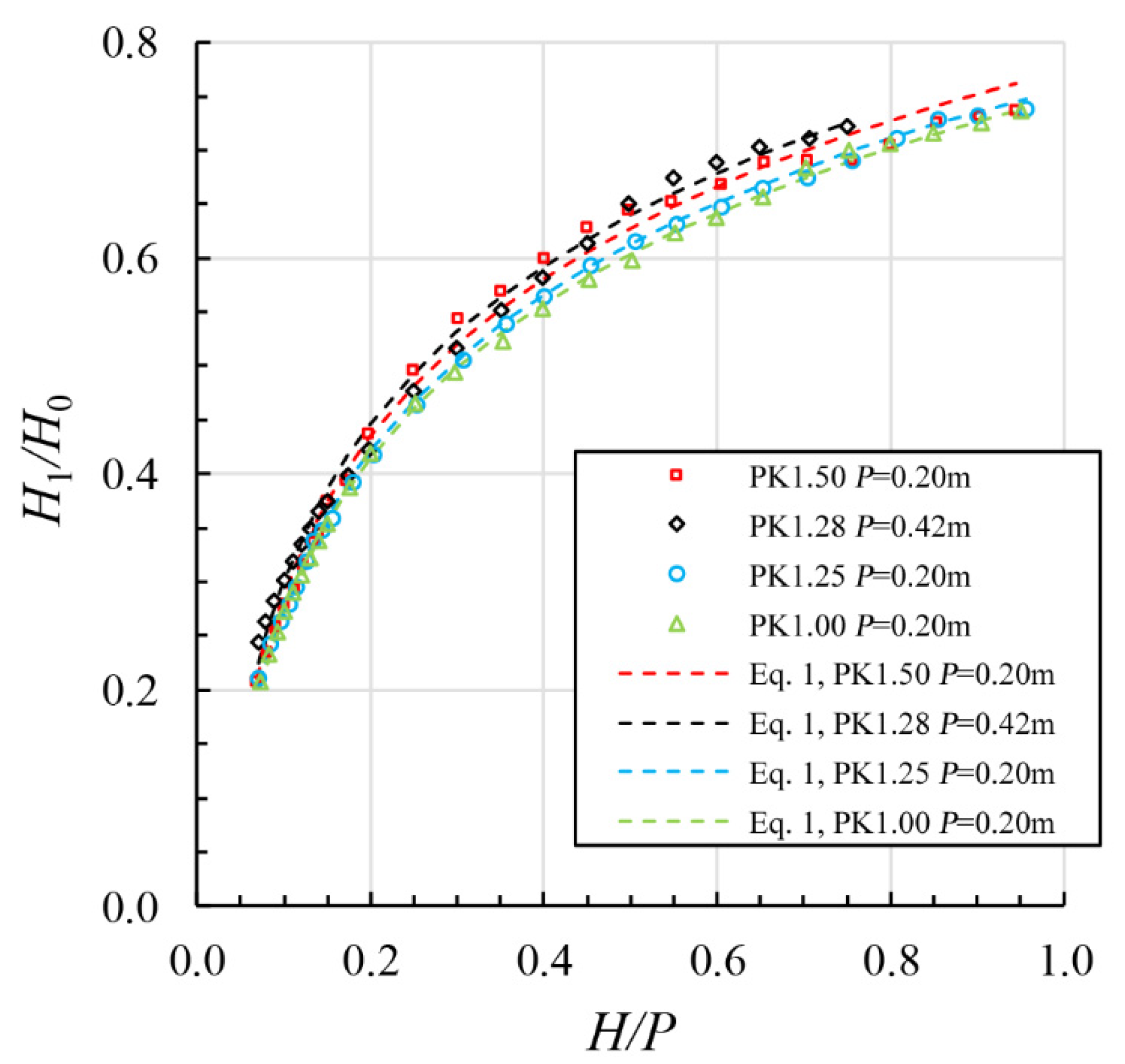
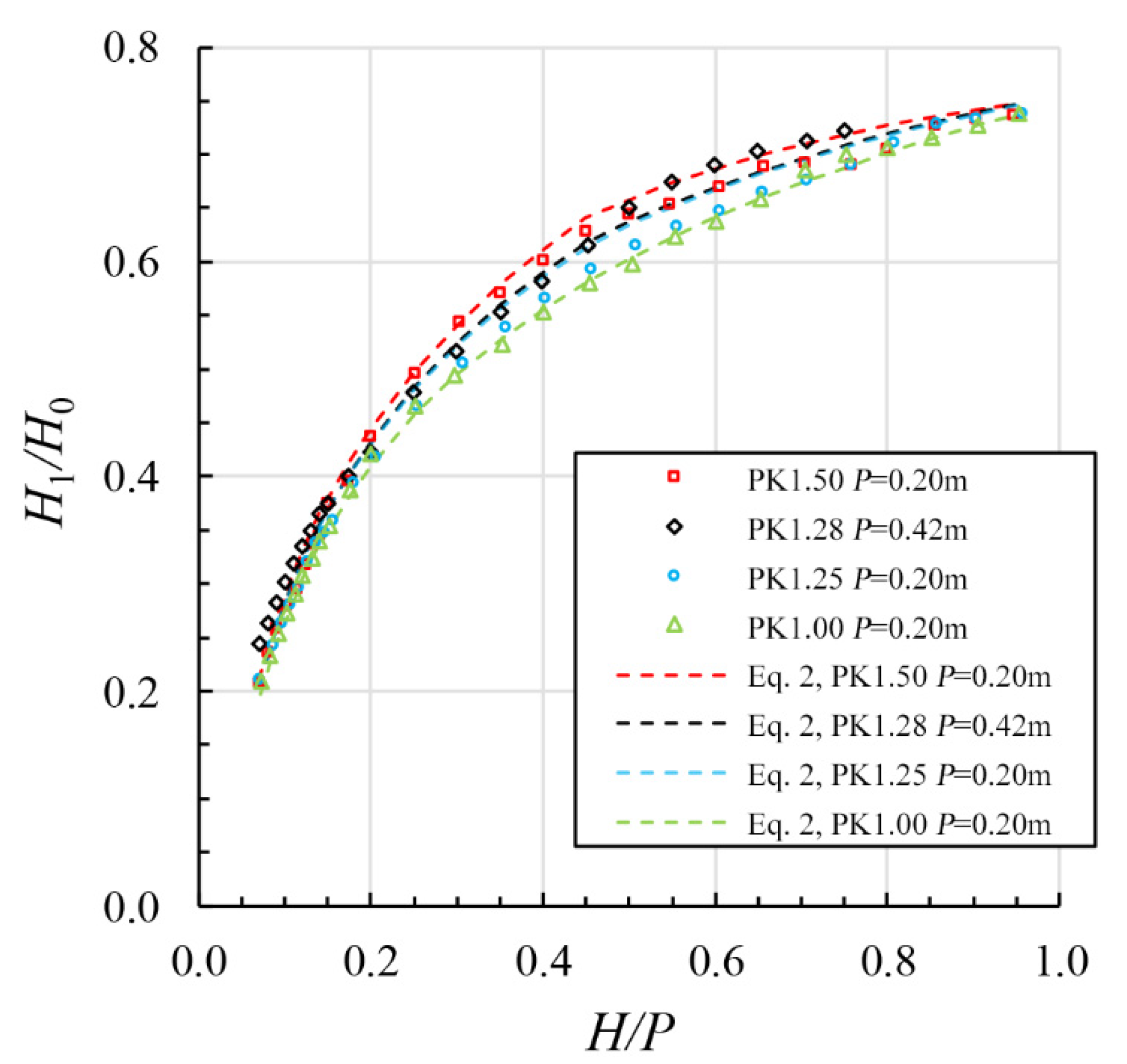
3.3. Residual Energy Estimation for Design
4. Discussion and Conclusions
- Similar to labyrinth weirs, PK weirs provide some energy dissipation that may be desirable in rehabilitation and new projects. The rate of energy dissipation is not linear and is greatest at low heads.
- Energy dissipation is in part provided by flow entering the structure with the front perpendicular faces of the PK weir beneath the upstream overhangs. Some vortex shedding is noted along with capillary waves. The nappes are considered as opposing planar jets producing turbulence, mixing, increasing aeration, and forming jets directed downstream at a trajectory mimicking the outlet cycle ramps. These jets expand and interact at the toe of the PK weir and with the tailwater.
- The parameter Wi/Wo appears to affect energy dissipation of a PK weir in the following range: 0.2 ≤ H/P ≤ 0.8. As Wi/Wo increases, the hydraulic efficiency also increases, resulting in decreased energy dissipations. At values of H/P ≤ 0.2 and H/P ≥ 0.8, energy dissipation appears to remain relatively constant, independent of the parameter Wi/Wo.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blanc, P.; Lempérière, F. Labyrinth spillways have a promising future. Hydropower Dams 2001, 8, 129–131. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, W.L. Energy loss at the base of free overfall. Trans. ASCE 1943, 108, 1343–1360. [Google Scholar]
- White, M.P. Discussion of moore. Trans. ASCE 1943, 108, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Rand, W. Flow geometry at straight drop spillways. Proc. ASCE 1953, 81, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, M.A. Hydraulics of rectangular vertical drop structures. J. Hydraul. Res. 1979, 17, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H. Comparison of energy dissipation between nappe and skimming flow regimes on stepped chutes. J. Hydraul. Res. 1994, 32, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H. Hydraulic Design of Stepped Cascades, Channels, Weirs, and Spillways; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chamani, M.; Rajaratnam, N. Energy loss at drops. J. Hydraul. Res. 1995, 33, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erpicum, S.; Laugier, F.; Boillat, J.L.; Pirotton, M.; Reverchon, B.; Schleiss, A.J. Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs—PKW 2011; CRC Press: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Erpicum, S.; Laugier, F.; Pfister, M.; Pirotton, M.; Cicero, G.; Schleiss, A.J. Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs II—PKW 2013; CRC Press: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Erpicum, S.; Laugier, F.; Ho Ta Khanh, M.; Pfister, M. Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs III—PKW 2017; CRC Press: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Crookston, B.M.; Erpicum, S.; Tullis, B.P.; Laugier, F. Hydraulics of labyrinth and piano key weirs: 100 years of prototype structures and future research needs. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2019, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crookston, B.M.; Anderson, R.M.; Tullis, B.P. Free-flow discharge estimations for piano key weir geometries. J. Hydro-environ. Res. 2018, 19, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite Ribeiro, M.; Pfister, M.; Schleiss, A.J.; Boillat, A.L. Hydraulic design of A-type piano key weirs. J. Hydraul. Res. 2012, 50, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lempérière, F.; Ouamane, A. The piano key weir: A new cost-effective solution for spillways. Int. J. Hydropower Dams 2003, 10, 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Machiels, O.; Pirotton, M.; Archambeau, P.; Dewals, B.J.; Erpicum, S. Experimental parametric study and design of piano key weirs. J. Hydraul. Res. 2014, 52, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, A.P.; Lorena, M. Perdas de Energiado do Escoamento Sobre Soleiras em Labirinto. (Energy Losses in Flow Over Labyrinth Weirs); SILUSBA: Lisboa, Portugal, 1994; pp. 203–211. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, R.; Matos, J.; Melo, J. Discharge Capacity and Residual Energy of Labyrinth Weirs. In Hydraulic Model Report No. CH61/06, Proceedings of the International Junior Researcher and Engineer Workshop on Hydraulic Structures (IJREWHS ‘06), Montemor-o-Novo, Portugal, 2–4 September 2006; The University of Queensland: Brisbane, Australia, 2006; pp. 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, R.; Matos, J.; Melo, J. Characteristic Depths and Energy Dissipation Downstream of a Labyrinth Weir. In Hydraulic Structures, Proceedings of the International Junior Researcher and Engineer Workshop on Hydraulic Structures (IJREWHS ‘08), Pisa, Italy, 20 July–1 August 2008; Pagliara, S., Ed.; Pisa University Press: Pisa, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, R.; Matos, J.; Melo, J.F. Flow Properties and Residual Energy Downstream of Labyrinth Weirs. In Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs; Erpicum, S., Laugier, F., Boillat, J.L., Pirotton, M., Reverchon, B., Schleiss, A., Eds.; CRC Press/Balkema: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Merkel, J.; Belzner, F.; Gebhardt, M.; Thorenz, C. Energy Dissipation Downstream of Labyrinth Weirs. In Proceedings of the 7th IAHR International Symposium on Hydraulic Structures, Aachen, Germany, 15–18 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shukur, A.-H.K.; Al-Khafaji, G.H. Experimental study of the hydraulic performance of piano key weir. Int. J. Energy Environ. 2018, 9, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Leite Ribeiro, M.; Boillat, J.L.; Schleiss, A.J.; Laugier, F.; Albalat, C. Rehabilitation of St-Marc Dam. Experimental Optimization of a Piano Key Weir. In Proceedings of the 32nd IAHR Congress, Venice, Italy, 1–6 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Leite Ribeiro, M.; Boillat, J.L.; Schleiss, A.J.; Laugier, F. Coupled Spillway Devices and Energy Dissipation Systems at St-Marc Dam (France). In Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs II—PKW 2013; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Bieri, M.; Federspiel, M.; Boillat, J.-L.; Houdant, B.; Faramond, L.; Delorme, F. Energy Dissipation Downstream of piano key weirs—Case study of Gloriettes Dam (France). In Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs—PKW 2011; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 120–130. [Google Scholar]
- Erpicum, S.; Machiels, O.; Archambeau, P.; Dewals, B.; Pirotton, M.; Daux, C. Energy dissipation on a stepped spillway downstream of a Piano Key Weir—Experimental study. In Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs—PKW 2011; CRC Press: London, UK, 2011; pp. 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Erpicum, S.; Silvestri, A.; Dewals, B.; Archambeau, P.; Pirotton, M.; Colombié, M.; Faramond, L. Escouloubre Piano Key Weir: Prototype Versus Scale Models. In Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs II—PKW 2013; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ho Ta Khanh, M.; Hein, T.C.; Hai, N.T. Main Results of the PK Weir Model Tests in Vietnam (2004–2010). In Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs—PKW 2011; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri, A.; Archambeau, P.; Pirotton, M.; Dewals, B.; Erpicum, S. Comparative Analysis of the Energy Dissipation on a Stepped Spillway Downstream of a Piano Key Weir. In Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs II; Erpicum, S., Laugier, F., Pfister, M., Pirotton, M., Cicero, G.M., Schleiss, A.J., Eds.; CRC Press/Balkema: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Jüstrich, S.; Pfister, M.; Schleiss, A.J. Mobil riverbed scour downstream of a piano key weir. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, M.; Jüstrich, S.; Schleiss, A.J. Toe-scour formation at Piano Key Weirs. In Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs III—PKW 2017; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Truong Chí, H.; Huynh Thanh, S.; Ho Ta Khanh, M. Results of Some Piano Keys Weir Hydraulic Model Tests in Vietnam. In Proceedings of the 22nd ICOLD Congress, Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Palermo, M.; Crookston, B.M.; Pagliara, S. Analysis of Equilibrium Morphologies Downstream of a PK Weir Structure. In Proceedings of the EWRI World Environmental and Water Resource Congress, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 17–21 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Crookston, B.M. Labyrinth Weirs. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Utah State University, Logan, Utah, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- SonTek. FlowTracker Handheld ADV Technical Manual, Firmware Version 3.3 Software Version 2.2; SonTek/YSI Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.M.; Tullis, B.P. Piano key weir hydraulics and labyrinth weir comparison. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.L. Size-Scale Effects of Nonlinear Weir Hydraulics. Master’s Thesis, Utah State University, Logan, Utah, 2018. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/etd/6926 (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Pagliara, S.; Palermo, M.; Carnacina, I. Scour process due to symmetric dam spillways crossing jets. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2011, 9, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crookston, B.M.; Tullis, B.P. Labyrinth weirs: Nappe interference and local submergence. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crookston, B.M.; Tullis, B.P. Hydraulic design and analysis of labyrinth weirs. II: Nappe aeration, instability, and vibration. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erpicum, S.; Tullis, B.P.; Lodomez, M.; Archambeau, P.; Dewals, B.; Pirotton, M. Scale effects in physical piano key weirs models. J. Hydraul. Res. 2016, 54, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tullis, B.P.; Crookston, B.M.; Young, N. Scale effects in free-flow nonlinear weir head-discharge relationships. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2019, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

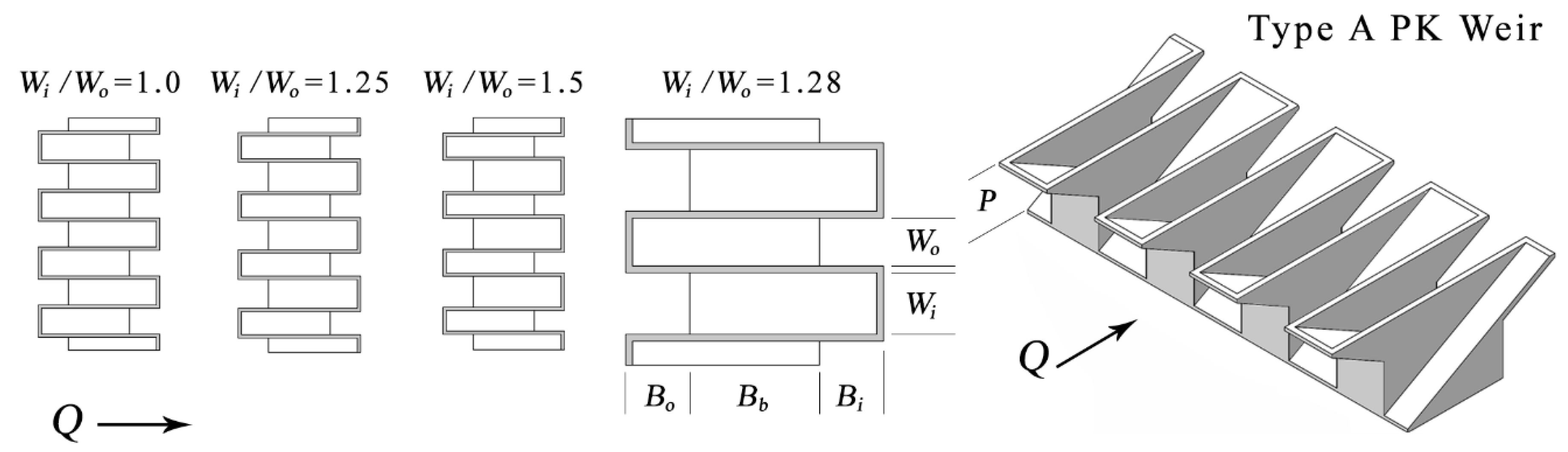

| Model | Range of H | Wi/Wo | Wi | P | L | B | N | Flume |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (mm) | (m) | (m) | (m) | ||||
| PK 1.50 | 0.014–0.186 | 1.50 | 124.7 | 0.20 | 4.82 | 0.50 | 4 | 2 |
| PK 1.28 | 0.020–0.211 | 1.28 | 248.4 | 0.42 | 5.15 | 1.04 | 2 | 1 |
| PK 1.25 | 0.014–0.188 | 1.25 | 115.6 | 0.20 | 4.75 | 0.50 | 4 | 2 |
| PK 1.00 | 0.014–0.187 | 1.00 | 103.9 | 0.20 | 4.81 | 0.50 | 4 | 2 |
| Geometry | Published Data | 0.2 ≤ H/P | 0.2 ≤ H/P ≤ 0.9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAPE 1 | RMSE 2 | MAPE 1 | RMSE 2 | ||
| PK 1.50 | Anderson and Tullis (2013) [36] | 3.12% | 0.0113 | 4.97% | 0.0327 |
| PK 1.28 | Young (2018) [37] | 1.79% | 0.0061 | 3.39% | 0.0226 |
| PK 1.25 | Anderson and Tullis (2013) [36] | 1.94% | 0.0086 | 3.01% | 0.0179 |
| PK 1.00 | Anderson and Tullis (2013) [36] | 1.15% | 0.0045 | 1.86% | 0.0103 |
| Geometry | A | B | C | R2 1 | MAPE 2 | RMSE 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PK 1.50 | 0.7699 | 0.2107 | 0.01 | 0.9931 | 2.83% | 0.0154 |
| PK 1.28 | 0.7835 | 0.2108 | 0.01 | 0.9954 | 2.27% | 0.0113 |
| PK 1.25 | 0.7528 | 0.2088 | 0.02 | 0.9994 | 1.29% | 0.0062 |
| PK 1.00 | 0.7478 | 0.2075 | 0.10 | 0.9993 | 0.75% | 0.0046 |
| Geometry | R2 1 | MAPE 2 | RMSE 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PK 1.50 | 0.9981 | 6.84% | 0.0313 |
| PK 1.28 | 0.9943 | 2.73% | 0.0146 |
| PK 1.25 | 0.9990 | 6.93% | 0.0320 |
| PK 1.00 | 0.9994 | 3.10% | 0.0150 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
R. Eslinger, K.; Crookston, B.M. Energy Dissipation of Type a Piano Key Weirs. Water 2020, 12, 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051253
R. Eslinger K, Crookston BM. Energy Dissipation of Type a Piano Key Weirs. Water. 2020; 12(5):1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051253
Chicago/Turabian StyleR. Eslinger, Kam, and Brian M. Crookston. 2020. "Energy Dissipation of Type a Piano Key Weirs" Water 12, no. 5: 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051253
APA StyleR. Eslinger, K., & Crookston, B. M. (2020). Energy Dissipation of Type a Piano Key Weirs. Water, 12(5), 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051253






