Experimental Evaluation for the Impacts of Conservation Agriculture with Drip Irrigation on Crop Coefficient and Soil Properties in the Sub-Humid Ethiopian Highlands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
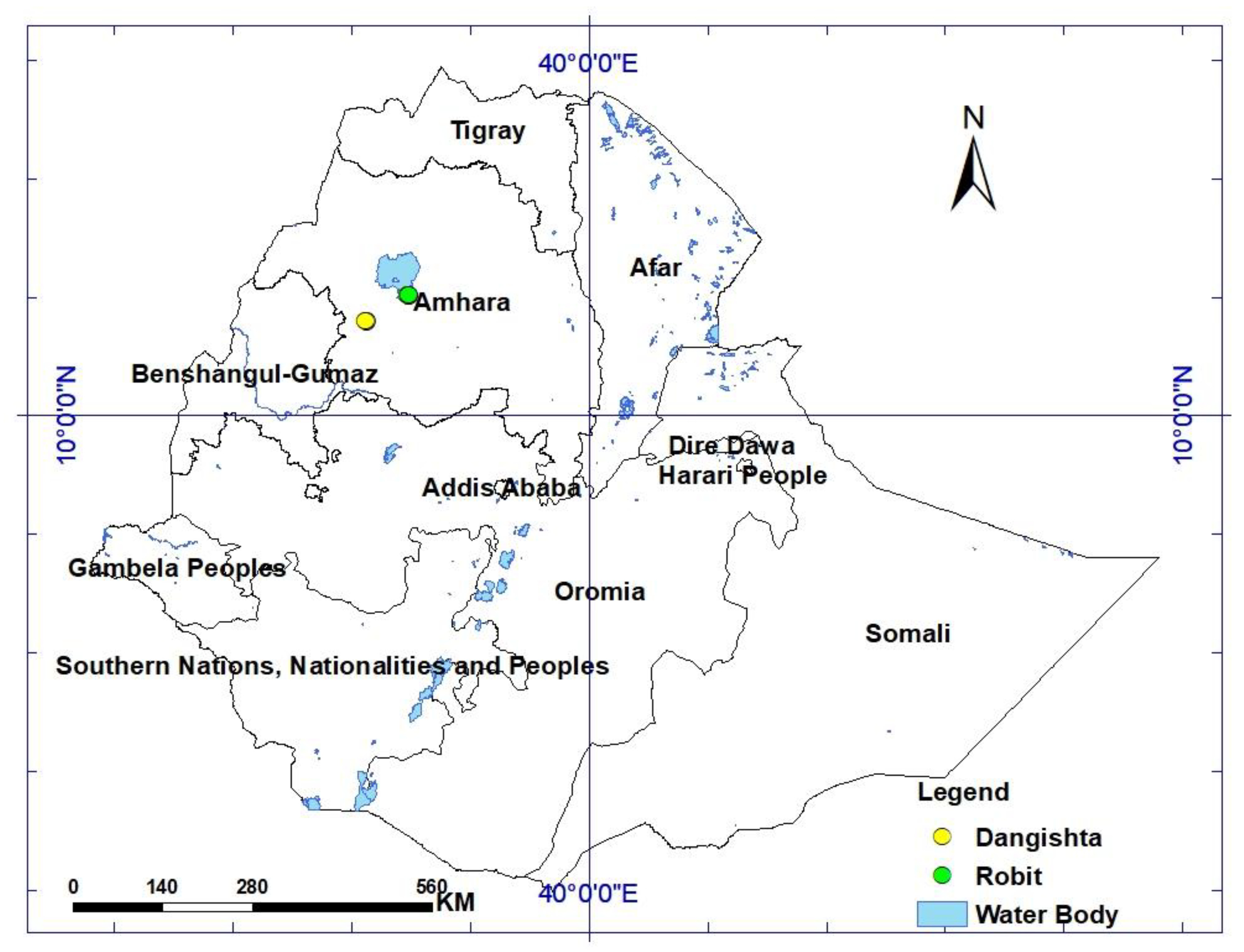
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design and Field Setup Procedures
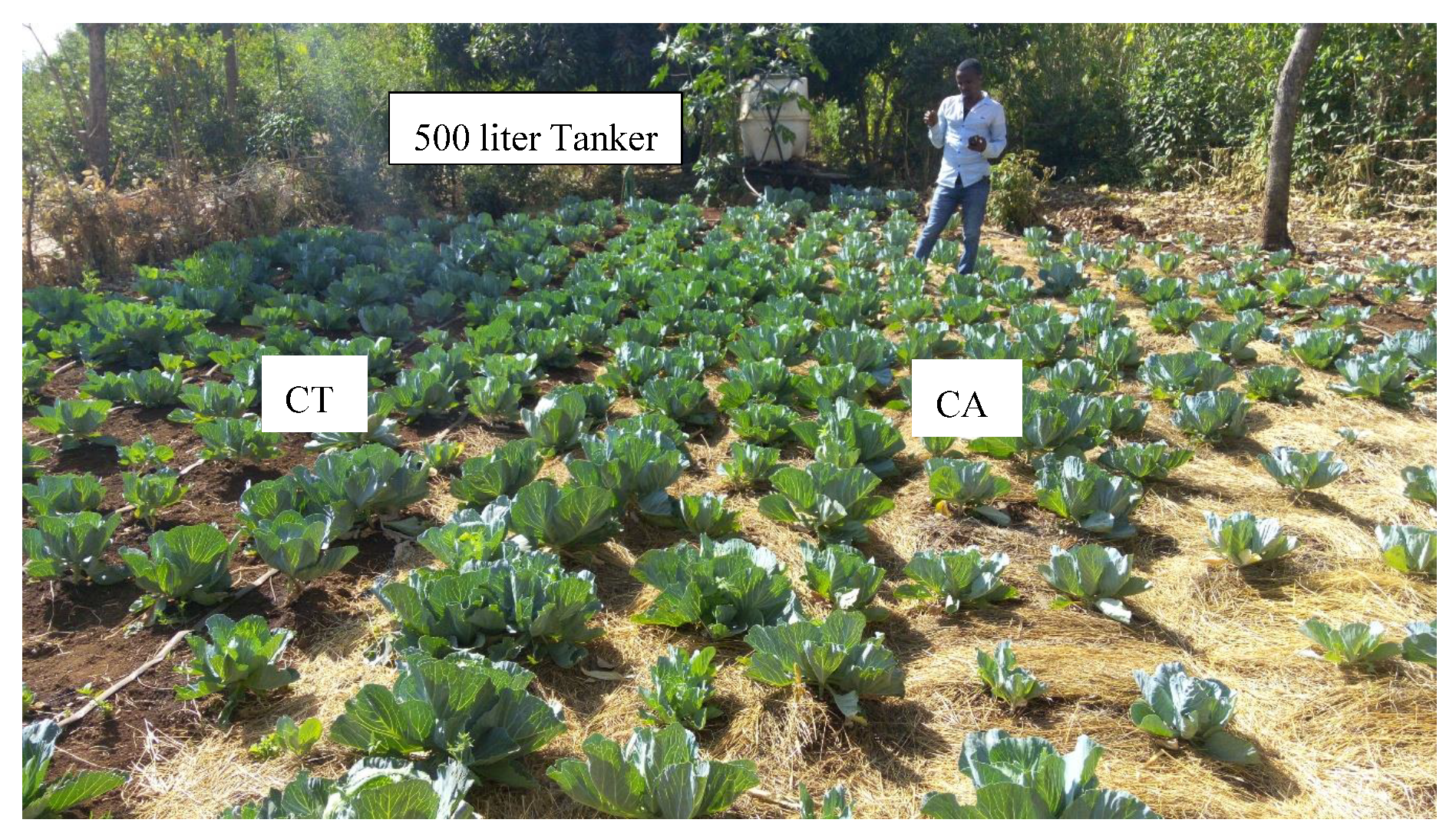
2.2.1. Experimental Design
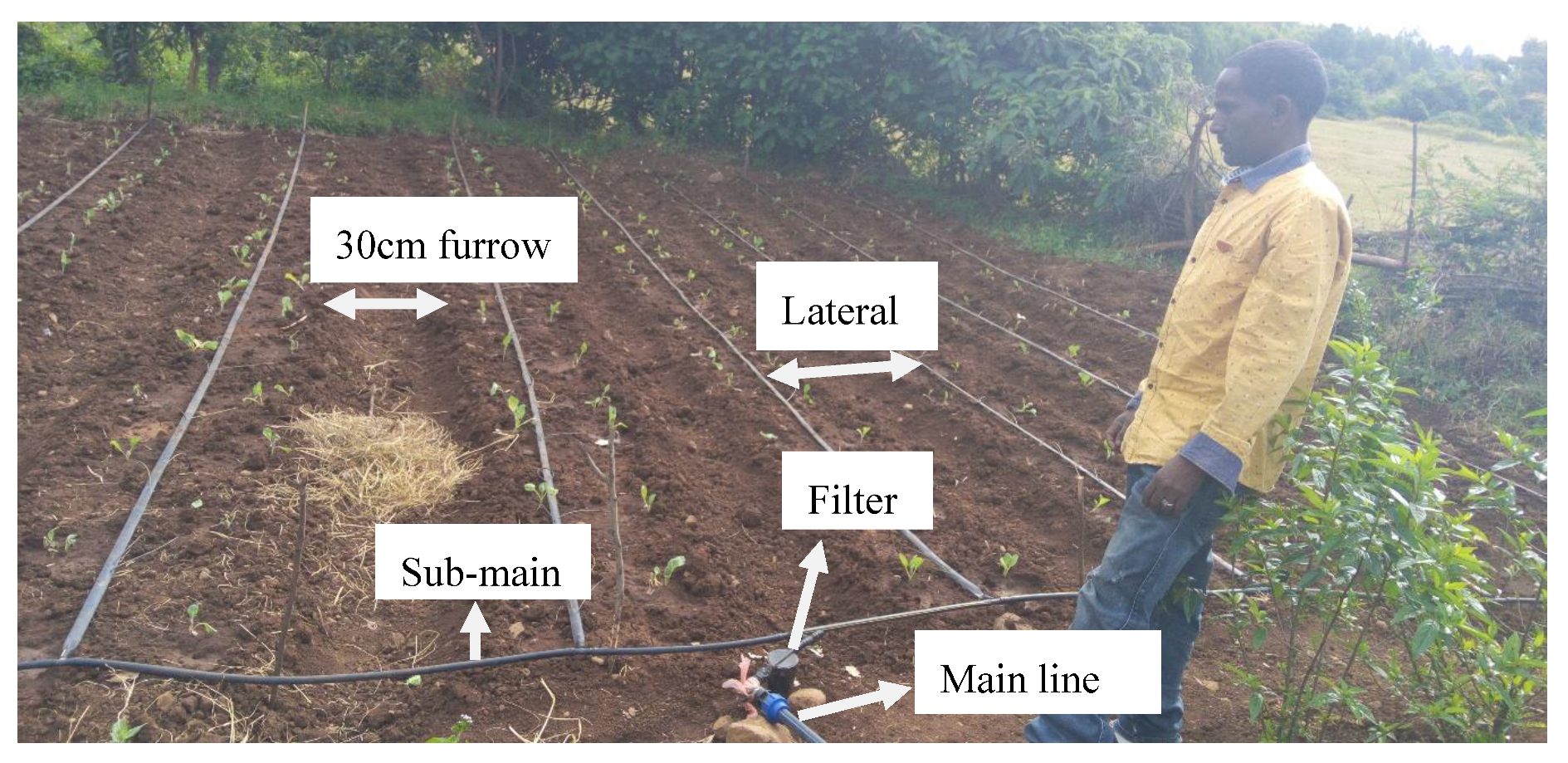
2.2.2. Field Setup Procedures
2.3. Data Monitoring and Collection
2.3.1. Soil Physio-Chemical Property
2.3.2. Meteorological Data
2.3.3. Agronomic and Water Use Data
2.4. Crop Coefficients
3. Results and Discussion
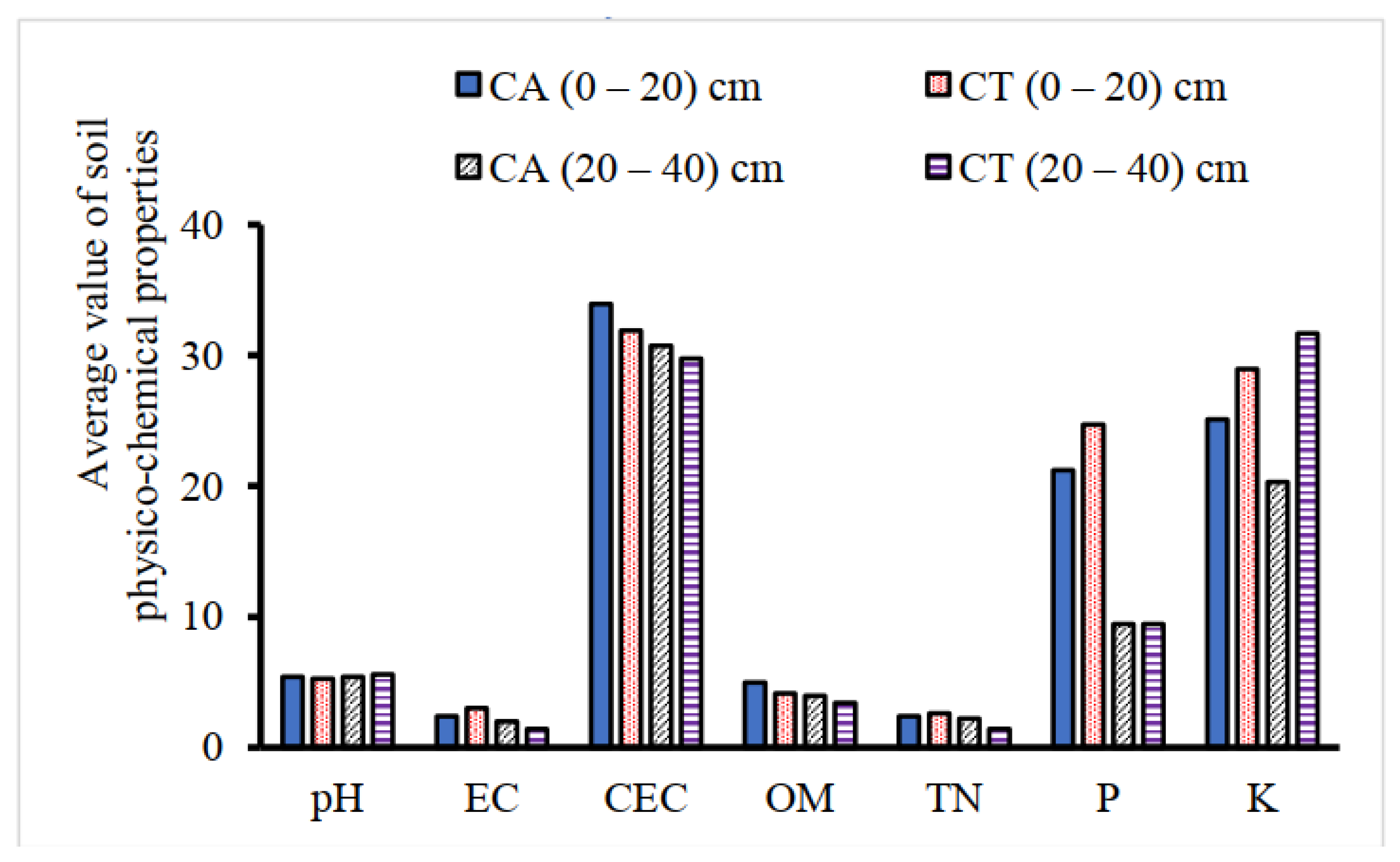
3.1. Effects of CA with Drip Irrigation on Soil Physico-Chemical Properties
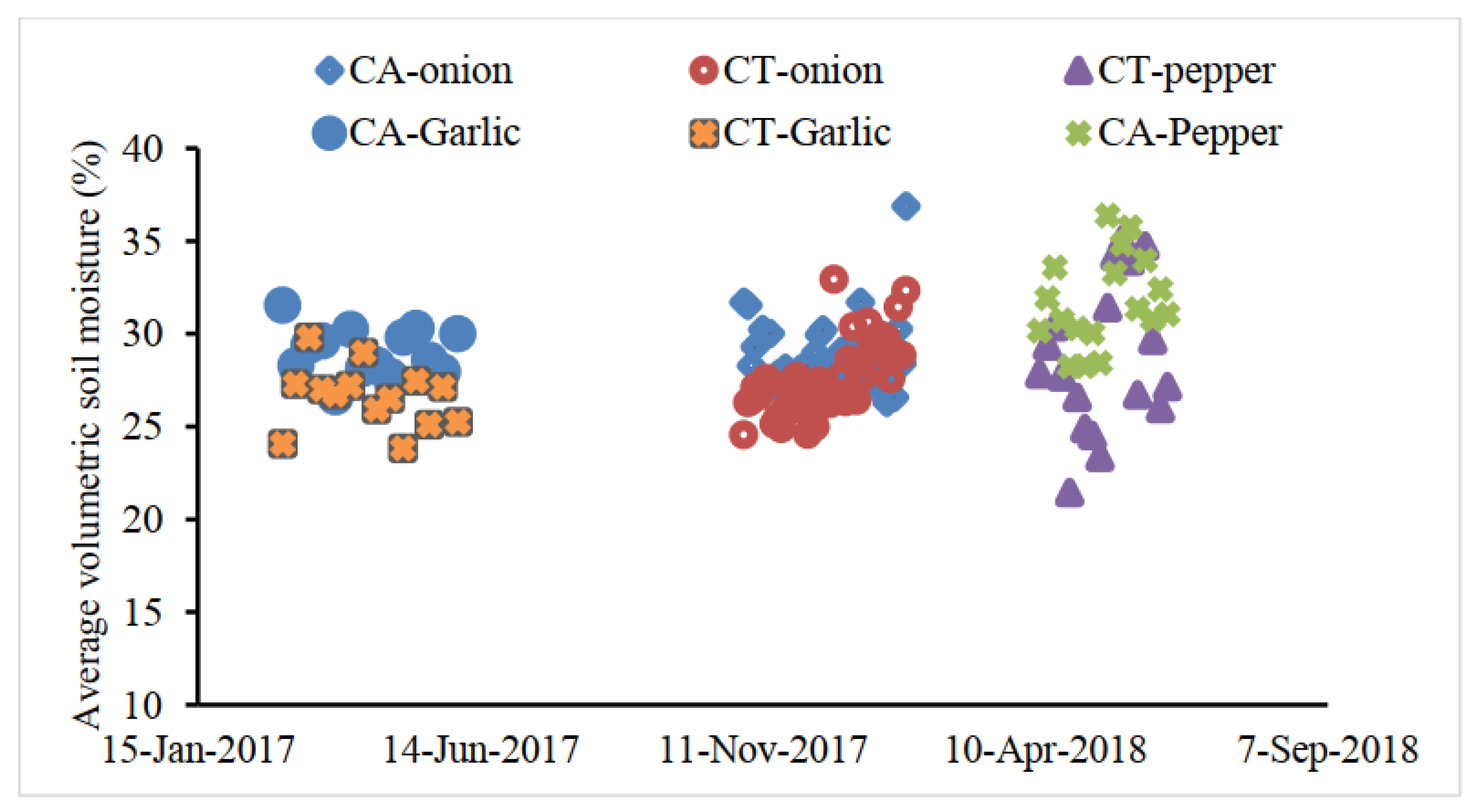
3.2. Amount of Water Used and Soil Moisture Content
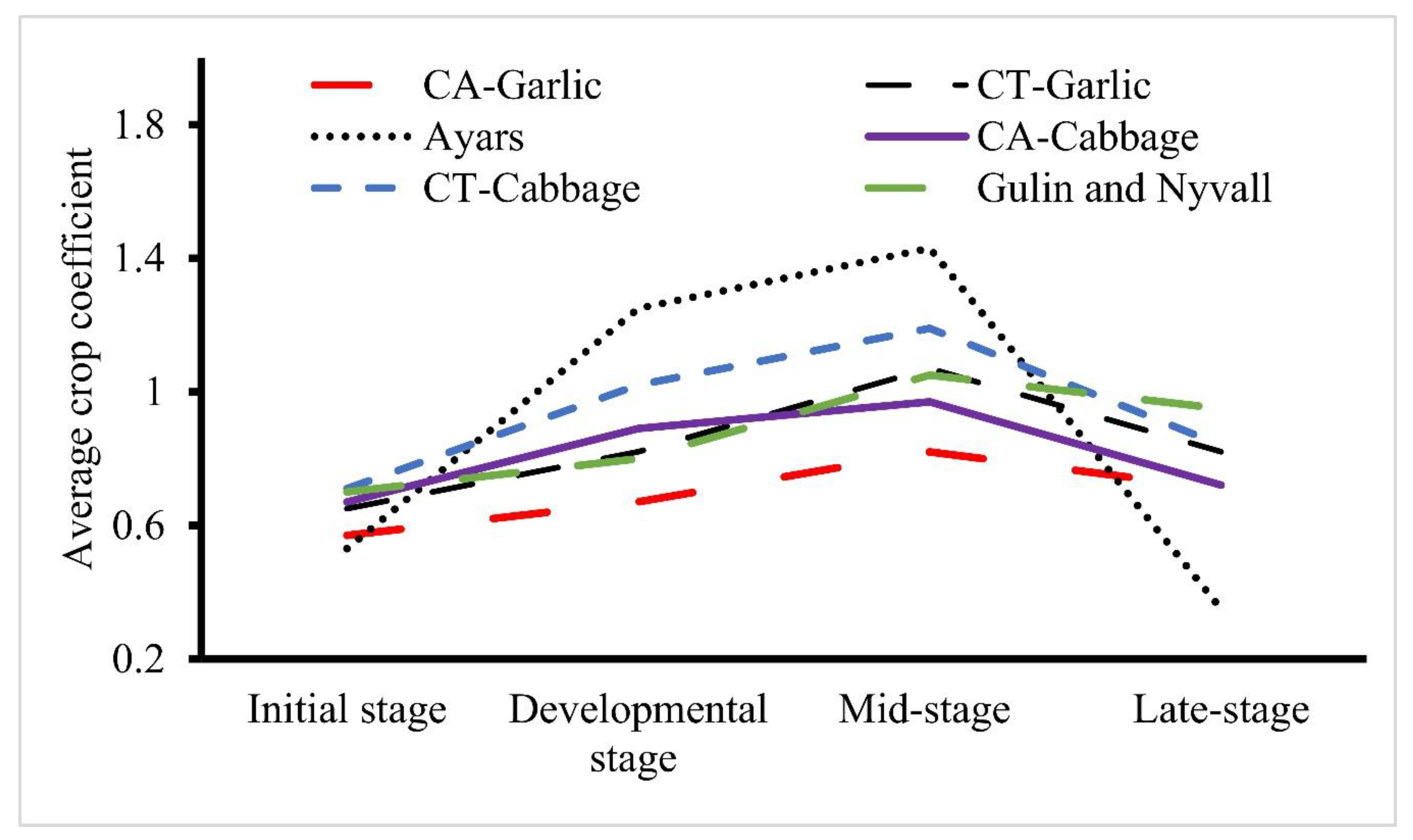
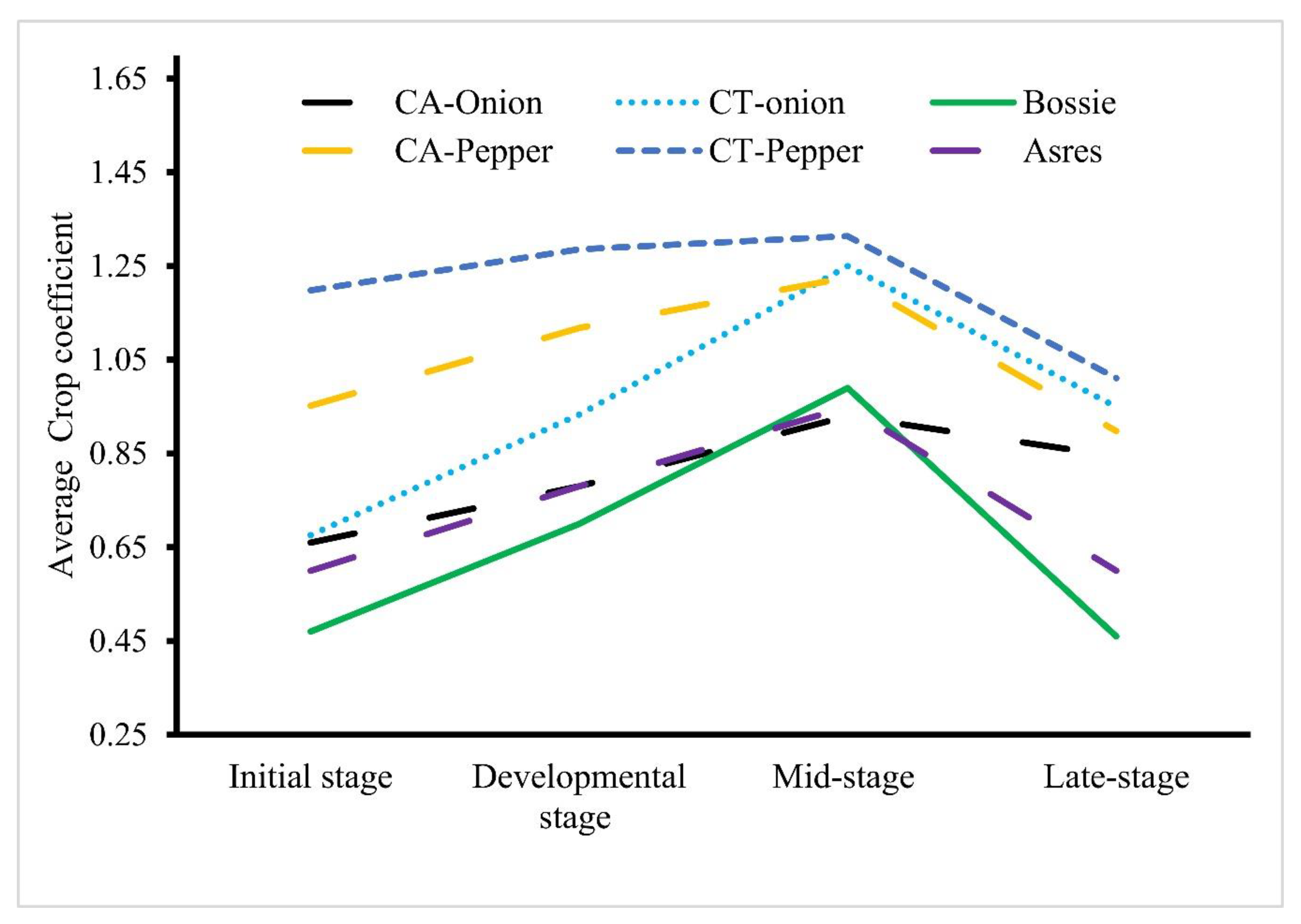
3.3. Effect on Crop Coefficient (Kc)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Soil Physico-Chemical Properties
| Items | pH | OM (%) | EC (ds/m) | TN (%) | Av. k (ppm) | Av. P (ppm) | Av. FC (%) | Av. Pwp (%) | Fe (%) | Av. CEC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 5.9 | 4.8 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 1349 | 24.7 | 36.8 | 24.2 | 18.5 | 21.5 |
| CT | 5.8 | 4.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1411 | 25.4 | 35.5 | 25 | 18.4 | 17.4 |
| N | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| p-value | 0.15 **,a | 0.01 *,a | 0.5 **,a | 0.05 **,a | 0.3 **,a | 0.4 **,a | 0.08 **,a | 0.37 **,a | 0.4 **,a | 0.06 **,a |
| CA | 6.4 | 4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1118 | 32.2 | n.a | n.a | n.a | 25.8 |
| CT | 6.2 | 3.7 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 997 | 24.2 | n.a | n.a | n.a | 23.3 |
| N | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |||
| p-value | 0.09 **,b | 0.02 *,b | 0.2 **,b | 0.03 *,b | 0.2 **,b | 0.24 **,b | 0.02 *,b | |||
| CA | 5.1 | 3.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 305.6 | 21.6 | 32.8 | 22.2 | 12.9 | 25.6 |
| CT | 5.2 | 3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 496.3 | 13.7 | 32.7 | 22.2 | 12 | 27 |
| N | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| p-value | 0.15 **,c | 0.24 **,c | 0.11 **,c | 0.35 **,c | 0.18 **,c | 0.07 **,c | 0.43 **,c | 0.5 **,c | 0.04 *,c | 0.16 **,c |
| CA | 5.5 | 4.9 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 454.4 | 18.3 | 34.5 | 26.8 | 16.9 | 28 |
| CT | 5.6 | 4.8 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 415.5 | 19.1 | 24.6 | 24.5 | 13.6 | 32.8 |
| N | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| p-value | 0.15 **,d | 0.4 **,d | 0.35 **,d | 0.38 **,d | 0.45 **,d | 0.44 **,d | 0.1 **,d | 0.13 **,d | 0.03 *,d | 0.06 **,d |
| Items | pH | OM (%) | EC (ds/m) | TN (%) | Av. k (ppm) | Av. P (ppm) | Av. CEC (%) | Fe (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 5.388 | 4.982 | 0.222 | 0.228 | 250.92 | 21.204 | 33.92 | 30.094 |
| CT | 5.268 | 4.156 | 0.28 | 0.238 | 289.34 | 24.684 | 31.88 | 31.186 |
| N | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| P-value | 0.3 **,a | 0.005 *,a | 0.25 **,a | 0.21 **,a | 0.27 **,a | 0.13 **,a | 0.08 **,a | 0.36 **,a |
| CA | 5.406 | 3.932 | 0.192 | 0.204 | 203.04 | 9.426 | 30.72 | 26.516 |
| CT | 5.582 | 3.42 | 0.142 | 0.17 | 316.76 | 9.432 | 29.76 | 26.592 |
| N | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| P-value | 0.14 **,b | 0.06 **,b | 0.16 **,b | 0.05 **,b | 0.05 **,b | 0.49 **,b | 0.37 **,b | 0.48 **,b |
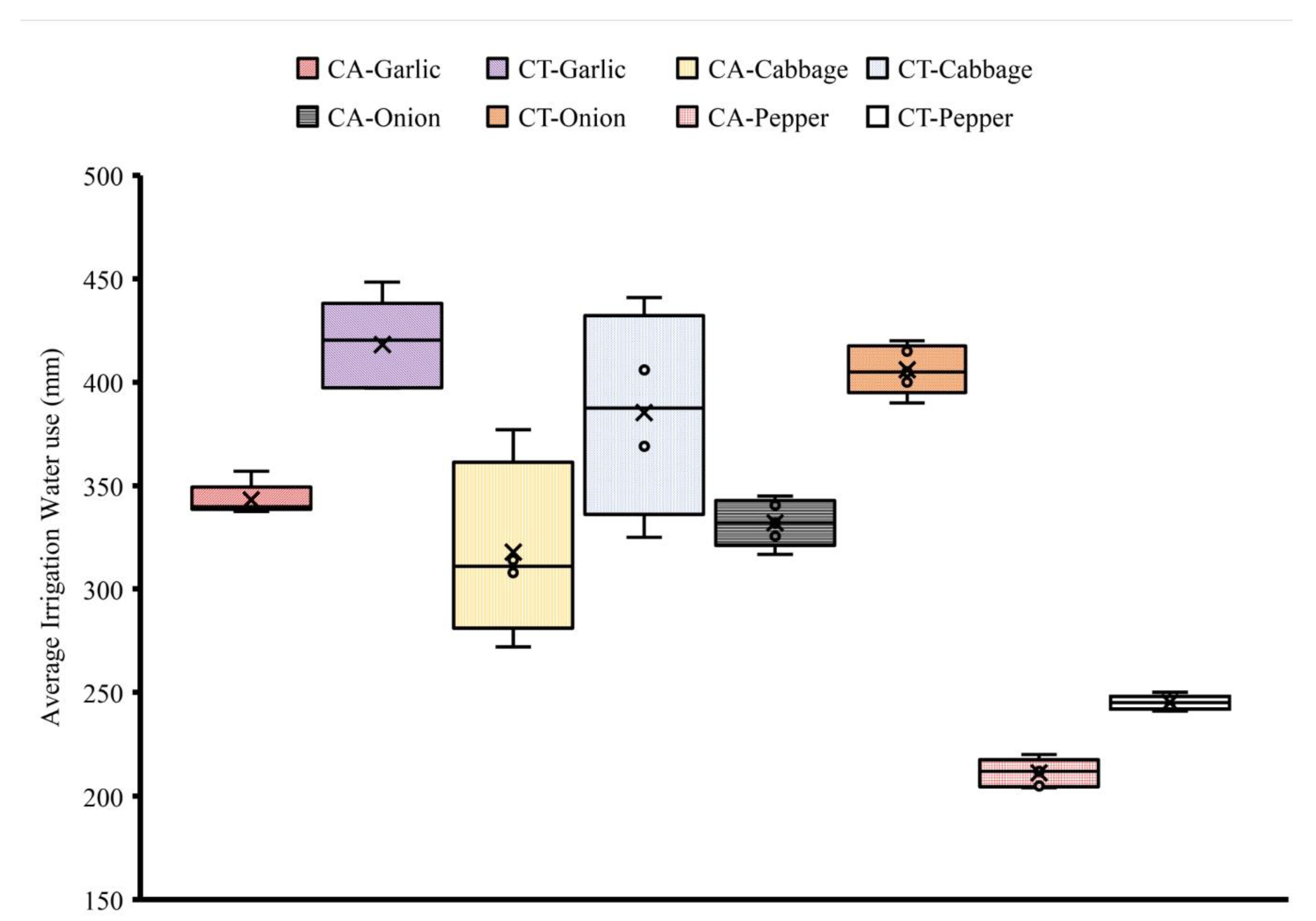
Appendix B. Average Irrigation Water Use and Crop Coefficient
| Items | Cabbage | Garlic | Onion | Pepper |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 318.1 | 199.2 | 332.4 | 211.4 |
| CT | 385.2 | 275.4 | 406.4 | 245.4 |
| N | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| P-value | 0.006 *,a | 0.0000236 *,b | 0.00074 *,b | 0.0074 *,b |
| A, Initial stage | B, Mid-stage | ||||||||
| Item | Cabbage | Onion | Garlic | Pepper | Item | Cabbage | Onion | Garlic | Pepper |
| CA | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.59 | CA | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.82 | 1.22 |
| CT | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.65 | 0.65 | CT | 1.19 | 1.24 | 1.07 | 1.31 |
| N | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | N | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| p-value | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.26 | 0.12 | p-value | 0.04 | 0.003 | 0.02 | 0.27 |
| C, Developmental stage | D, Late-stage | ||||||||
| Item | Cabbage | Onion | Garlic | Pepper | Item | Cabbage | Onion | Garlic | Pepper |
| CA | 0.89 | 0.78 | 0.67 | 1.12 | CA | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.89 |
| CT | 1.02 | 0.93 | 0.82 | 1.28 | CT | 0.84 | 0.95 | 0.82 | 1.01 |
| N | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | N | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| p-value | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.26 | p-value | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.04 |
| Item | Cabbage | Onion | Garlic | Pepper |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.71 | 1.05 |
| CT | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.84 | 1.20 |
| N | 16 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| p-value | 0.007 * | 0.005 * | 0.003 * | 0.054 ** |
References
- Awulachew, S.B. Irrigation potential in Ethiopia: Constraints and opportunities for enhancing the system. Gates Open Res. 2019, 3, 12–58. [Google Scholar]
- Gebremariam, M.; Kebede, F. Land use change effect on soil carbon stock, above ground biomass, aggregate stability and soil Crust: A case from Tahtay Adyabo, North Western Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. J. Drylands 2010, 3, 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Zegeye, H.; Rasheed, A.; Makdis, F.; Badebo, A.; Ogbonnaya, F.C. Genome-wide association mapping for seedling and adult plant resistance to stripe rust in synthetic hexaploid wheat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mhiret, D.A.; Dagnew, D.C.; Assefa, T.T.; Tilahun, S.A.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Steenhuis, T.S. Erosion hotspot identification in the sub-humid Ethiopian highlands. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2019, 19, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, T.T. Experimental and Modeling Evaluation of Conservation Agriculture with Drip Irrigation for Small-Scale Agriculture in Sub-Saharan Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University, Greensboro, NC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Assefa, T.; Jha, M.; Reyes, M.; Srinivasan, R.; Worqlul, A.W. Assessment of Suitable Areas for Home Gardens for Irrigation Potential, Water Availability, and Water-Lifting Technologies. Water 2018, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Worqlul, A.W.; Jeong, J.; Dile, Y.T.; Osorio, J.; Schmitter, P.; Gerik, T.; Srinivasan, R.; Clark, N. Assessing potential land suitable for surface irrigation using groundwater in Ethiopia. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 85, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassenrath, G.; Lin, X.; Shoup, D. Identification of Yield-Limiting Factors in Southeast Kansas Cropping Systems. Kans. Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Rep. 2015, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abittew, A.B.; Fufa, B. Determinants of Farmers’ Willing Ness to Pay for the Conservation Strategy of National Parks: The Case for Simen Mountains National Park; Haramaya University: Haramaya, Ethiopia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Abebe, T.H.; Bogale, A. Willingness to pay for rainfall based insurance by smallholder farmers in Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia: The case of Dugda and Mieso Woredas. Asia Pac. J. Energy Environ. 2014, 1, 121–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, P.R. Conservation agriculture: What is it and why is it important for future sustainable food production? J. Agric. Sci. Camb. 2007, 145, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fereres, E.; Soriano, M.A. Deficit irrigation for reducing agricultural water use. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 58, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lal, R. Soil degradation by erosion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2001, 12, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, T.T.; Jha, M.K.; Tilahun, S.A.; Yetbarek, E.; Adem, A.A.; Wale, A. Identification of erosion hotspot area using GIS and MCE technique for Koga watershed in the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beddington, J.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Clark, M.; Fernández, A.; Guillou, M.; Jahn, M.; Erda, L.; Mamo, T.; Van Bo, N.; Nobre, C.A.; et al. Achieving Food Security in the Face of Climate Change: Final Report from the Commission on Sustainable Agriculture and Climate Change; CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, F.A.; Pulido-Velazquez, M. Water conservation in irrigation can increase water use. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18215–18220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wada, Y.; Wisser, D.; Bierkens, M.F. Global modeling of withdrawal, allocation and consumptive use of surface water and groundwater resources. Earth Syst. Dyn. Discuss. 2014, 5, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assefa, T.; Jha, M.; Reyes, M.; Tilahun, S.; Worqlul, A.W. Experimental Evaluation of Conservation Agriculture with Drip Irrigation for Water Productivity in Sub-Saharan Africa. Water 2019, 11, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assefa, T.; Jha, M.; Reyes, M.; Worqlul, A. Modeling the Impacts of Conservation Agriculture with a Drip Irrigation System on the Hydrology and Water Management in Sub-Saharan Africa. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Challinor, A.J.; Simelton, E.S.; Fraser, E.D.; Hemming, D.; Collins, M. Increased crop failure due to climate change: Assessing adaptation options using models and socio-economic data for wheat in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 034012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Gourdji, S.M. The influence of climate change on global crop productivity. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosegrant, M.W.; Cline, S.A. Global food security: Challenges and policies. Science 2003, 302, 1917–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrett, C.B.; Reardon, T.; Webb, P. Nonfarm income diversification and household livelihood strategies in rural Africa: Concepts, dynamics, and policy implications. Food Policy 2001, 26, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worqlul, A.W.; Collick, A.S.; Rossiter, D.G.; Langan, S.; Steenhuis, T.S. Assessment of surface water irrigation potential in the Ethiopian highlands: The Lake Tana Basin. Catena 2015, 129, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelkoff, T.; Clemmens, A.; El-Ansary, M.; Awad, M. Surface-irrigation evaluation models: Application to level basins in Egypt. Trans. Asae 1999, 42, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzema, H. Drain for Gain: Managing salinity in irrigated lands—A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, L.S.; Cordery, I.; Iacovides, I. Improved indicators of water use performance and productivity for sustainable water conservation and saving. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 108, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, T.T.; Jha, M.K.; Reyes, M.R.; Schimmel, K.; Tilahun, S.A. Commercial Home Gardens under Conservation Agriculture and Drip Irrigation for Small Holder Farming in sub-Saharan Africa. In Proceedings of the 2017 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 16–19 July 2017; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, P. Conservation agriculture (CA), defined as minimal soil disturbance (no-till) and permanent soil cover (mulch) combined with rotations, is a more sustainable cultivation system for the future than those presently practised. J. Agric. Sci 2007, 145, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thierfelder, C.; Wall, P.C. Effects of conservation agriculture techniques on infiltration and soil water content in Zambia and Zimbabwe. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 105, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowler, D.; Bradshaw, B. Farmers’ adoption of conservation agriculture: A review and synthesis of recent research. Food Policy 2007, 32, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, A.; Friedrich, T.; Shaxson, F.; Pretty, J. The spread of conservation agriculture: Justification, sustainability and uptake. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2009, 7, 292–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivenge, P.; Murwira, H.; Giller, K.; Mapfumo, P.; Six, J. Long-term impact of reduced tillage and residue management on soil carbon stabilization: Implications for conservation agriculture on contrasting soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, D.; Manjunatha, M.; Rajkumar, G.; Hebbara, M.; Minhas, P. Comparative effects of drip and furrow irrigation on the yield and water productivity of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) in a saline and waterlogged vertisol. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 83, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisiri, N.; Senzanje, A.; Rockstrom, J.; Twomlow, S. On farm evaluation of the effect of low cost drip irrigation on water and crop productivity compared to conventional surface irrigation system. Phys. Chem. Earthparts A/B/C 2005, 30, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edralin, D.; Sigua, G.; Reyes, M. Dynamics of soil carbon, nitrogen and soil respiration in farmer’s field with conservation agriculture Siem Reap, Cambodia. Int. J. 2016, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Assefa, T.; Jha, M.; Worqlul, A.W.; Reyes, M.; Tilahun, S. Scaling-Up Conservation Agriculture Production System with Drip Irrigation by Integrating MCE Technique and the APEX Model. Water 2019, 11, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Gu, B.; Du, T.; Zhang, J. Crop coefficient and ratio of transpiration to evapotranspiration of winter wheat and maize in a semi-humid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 59, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesema, M.; Schmitter, P.; Nakawuka, P.; Tilahun, S.A.; Steenhuis, T.; Langan, S. Evaluating irrigation technologies to improve crop and water productivity of onion in Dangishta watershed during the dry monsoon phase. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on the Advancements of Science and Technology in Civil and Water Resources Engineering, Online, 13–29 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.; Parkin, G.; Schmitter, P.; Gowing, J.; Tilahun, S.A.; Haile, A.T.; Yimam, A.Y. Insights from a multi-method recharge estimation comparison study. Groundwater 2018, 57, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yimam, A.Y.; Bekele, A.M.; Nakawuka, P.; Schmitter, P.; Tilahun, S.A. Rainfall-Runoff Process and Groundwater Recharge in the Upper Blue Nile Basin: The Case of Dangishta Watershed. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances of Science and Technology, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 5–7 October 2018; pp. 536–549. [Google Scholar]
- Yiak, D.; Tilahun, S.; Schmitter, P.S.; Nakawuka, P.; Steenhuis, T. Groundwater recharge of Robit-Bata Experimental Watershed, Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on the Advancements of Science and Technology [ICAST], Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 8–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- De Winter, J.C. Using the Student’s t-test with extremely small sample sizes. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2013, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zotarelli, L.; Dukes, M.D.; Romero, C.C.; Migliaccio, K.W.; Morgan, K.T. Step by step calculation of the Penman-Monteith Evapotranspiration (FAO-56 Method); Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, M.G.; Kselik, R.A.; Allen, R.G.; Molden, D. Water Requirements for Irrigation and the Environment; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wellens, J.; Raes, D.; Traore, F.; Denis, A.; Djaby, B.; Tychon, B. Performance assessment of the FAO AquaCrop model for irrigated cabbage on farmer plots in a semi-arid environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 127, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration-Guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56. Faorome 1998, 300, D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Yoder, R.; Odhiambo, L.O.; Wright, W.C. Evaluation of methods for estimating daily reference crop evapotranspiration at a site in the humid southeast United States. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2005, 21, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, Y.; Yazar, A.; Gençel, B.; Sezen, M.S. Optimum lateral spacing for drip-irrigated corn in the Mediterranean Region of Turkey. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 85, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezen, S.M.; Yazar, A.; Eker, S. Effect of drip irrigation regimes on yield and quality of field grown bell pepper. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 81, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedeed, S.I.; Zaghloul, S.M.; Yassen, A. Effect of method and rate of fertilizer application under drip irrigation on yield and nutrient uptake by tomato. Ozean J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 2, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Tilahun, S.A.; Yilak, D.L.; Schmitter, P.; Zimale, F.A.; Langan, S.; Barron, J.; Parlange, J.Y.; Steenhuis, T.S. Establishing irrigation potential of a hillside aquifer in the African highlands. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Huo, Z.; Qu, Z.; Xu, X.; Huang, G.; Steenhuis, T.S. Modeling contribution of shallow groundwater to evapotranspiration and yield of maize in an arid area. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, A.; Edwards, D.; Asher, C. pH optima for crop growth. Plant Soil 1980, 54, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, A.; Jones, C.; Jacobsen, J. Soil pH and organic matter. Nutr. Manag. Modul. 2009, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Balesdent, J.; Chenu, C.; Balabane, M. Relationship of soil organic matter dynamics to physical protection and tillage. Soil Tillage Res. 2000, 53, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Singh, A.; Mal, P. Effect of drip irrigation on yield of cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata) under mulch and non-mulch conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 58, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossie, M.; Tilahun, K.; Hordofa, T. Crop coefficient and evaptranspiration of onion at Awash Melkassa, Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2009, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebal, N. Growth, yield and water use pattern of chilli pepper under different irrigation scheduling and management. Asian J. Agric. Res. 2011, 5, 154–163. [Google Scholar]
- Enku, T.; Melesse, A.M. A simple temperature method for the estimation of evapotranspiration. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 2945–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, F. Crop water requirement using single and dual crop coefficient approach. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol 2013, 2, 4493–4499. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Smith, M.; Raes, D.; Wright, J.L. FAO-56 dual crop coefficient method for estimating evaporation from soil and application extensions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhao, N.; Lei, B.; Rosa, R.D.; Paredes, P.; Paço, T.A.; Pereira, L.S. The dual crop coefficient approach to estimate and partitioning evapotranspiration of the winter wheat–summer maize crop sequence in North China Plain. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayars, J.E. Water requirement of irrigated garlic. Trans. Asabe 2008, 51, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulik, T.; Nyvall, J. Crop Coefficients for use in Irrigation Scheduling; Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Fisheries of British Columbia: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2001; pp. 1–6.
- Asres, S.B. Evaluating and enhancing irrigation water management in the upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia: The case of Koga large scale irrigation scheme. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 170, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, T.; Jha, M.; Reyes, M.; Worqlul, A.; Doro, L.; Tilahun, S. Conservation agriculture with drip irrigation: Effects on soil quality and crop yield in sub-Saharan Africa. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Site | Vegetable | Management Activity | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dangishita | Garlic (1st cycle) | Tillage 1 | 13 October 2015 and 16 October 2015 |
| Mulch application 2 | 25 October 2015 | ||
| Planting | 28 October 2015 | ||
| UREA application | 28 November 2015 | ||
| Irrigation Application | 6 November 2015–22 February 2016 | ||
| Harvesting | 3–4 March 2016 | ||
| Onion (2nd cycle) | Tillage 1 | 14 March 2016 and 16 March 2016 | |
| Mulch application 2 | 15 March 2016 | ||
| Planting | 17 March 2016 | ||
| Irrigation Application | 15 March–3 May 2016 | ||
| Harvesting | 24–26 June 2016 | ||
| Garlic (3rd cycle) | Tillage 1 | 15 February 2017 | |
| Mulch application 2 | 17 February 2017 | ||
| Planting | 17 February 2017 | ||
| DAP 3 application | 4 March 2017 | ||
| Irrigation Application | 17 March–3 June 2017 | ||
| Harvesting | 20–22 June 2017 | ||
| Pepper (4th cycle) | Tillage 1 | 12 March 2018 | |
| Mulch application 2 | 14 March 2018 | ||
| Planting | 15 March 2018 | ||
| Irrigation Application | 15 March–9 June 2018 | ||
| Harvesting | 12–20 July 2018 | ||
| Robit | Tomato (1st cycle) | Tillage 1 | 2 September 2015 |
| Mulch application 2 | 23 October 2015 | ||
| Planting | 24 October 2015 | ||
| Malathion 4 application | 22 November 2015 | ||
| Irrigation Application | 24 October 2015–12 March 2016 | ||
| Harvesting | 1–15 March 2016 | ||
| Garlic (2nd cycle) | Tillage 1 | 19 March 2016 | |
| Mulch application 2 | 21 March 2016 | ||
| Planting | 22 March 2016 | ||
| Irrigation Application | 23 March–21 June 2016 | ||
| Harvesting | 10–18 July 2016 | ||
| Cabbage (3rd cycle) | Tillage 1 | 27 October 2016 | |
| Mulch application 2 | 8 November 2016 | ||
| Planting | 9 November 2016 | ||
| UREA 3 application | 20 December 2016 | ||
| Dimeto 4 40% application | 15 November 2016 | ||
| Irrigation Application | 9 November 2016–25 February 2017 | ||
| Harvesting | 15–26 February 2017 |
| Experimental Site | Dangishta | Robit | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation Season | Beginning | End | Beginning | End | ||||
| Parameter\Treatment | CA | CT | CA | CT | CA | CT | CA | CT |
| Soil PH | 5.9 | 5.8 | 6.4 | 6.2 | 5.1 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.6 |
| Organic matter (%) | 4.8 | 4.3 | 4 | 3.7 | 3.2 | 3 | 4.9 | 4.8 |
| Electrical Conductivity (ds/m) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Total Nitrogen (%) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Average Potassium (ppm) | 1349 | 1411 | 1118 | 997 | 305.6 | 496.3 | 454.4 | 415.5 |
| Average phosphorous (ppm) | 24.7 | 25.4 | 32.2 | 24.2 | 21.6 | 13.7 | 18.3 | 19.1 |
| Average field capacity (%) | 36.8 | 35.5 | n.a | n.a | 32.8 | 32.7 | 34.5 | 24.6 |
| Sand (%) | 46.4 | 36.4 | 29.2 | 26 | 19.5 | 19 | 20.5 | 22.5 |
| Silt (%) | 24.6 | 29.4 | 34.4 | 32 | 29.5 | 28.5 | 27.5 | 29 |
| Clay (%) | 29 | 34.2 | 36.4 | 42 | 51 | 52.5 | 55 | 45.5 |
| Average Permanent wilting point (%) | 24.2 | 25 | n.a | n.a | 22.2 | 22.2 | 26.8 | 24.5 |
| Iron (%) | 18.5 | 18.4 | n.a | n.a | 12.9 | 12 | 16.9 | 13.6 |
| Average cation exchange Capacity (%) | 21.5 | 17.4 | 25.8 | 23.3 | 25.6 | 27 | 28 | 32.8 |
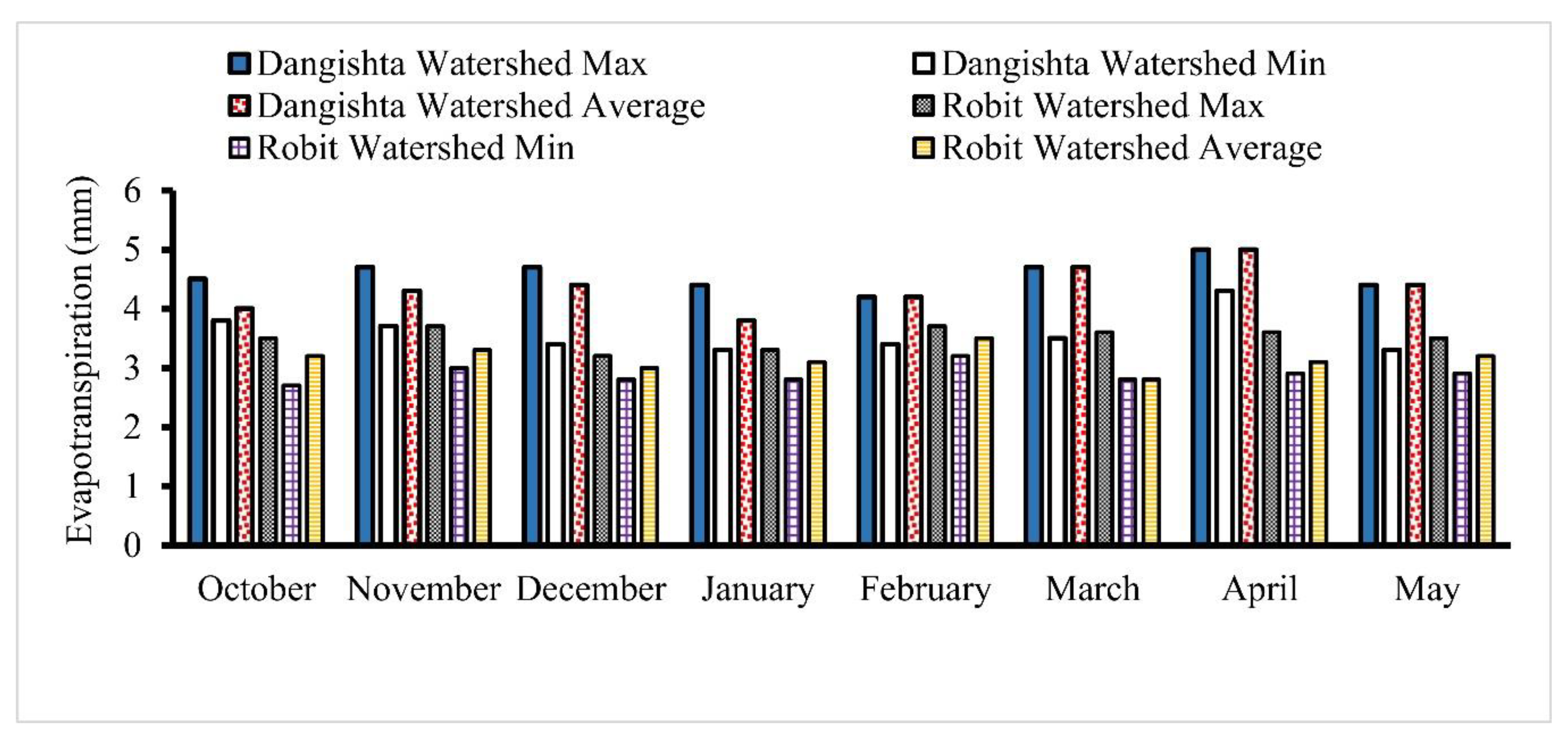
| Watershed | Treatment | Max | Min | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robit | CA | 4.0 | 2.8 | 3.4 |
| CT | 4.3 | 3.0 | 3.6 | |
| Dangishta | CA | 3 | 2.8 | 2.8 |
| CT | 3.75 | 3.3 | 3.5 |
| Treatment | Initial | Developmental | Mid | Late | Crop Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 0.67 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 0.72 | Cabbage |
| 0.59 | 0.67 | 0.82 | 0.75 | Garlic | |
| 0.95 | 1.12 | 1.22 | 0.89 | Pepper | |
| 0.66 | 0.78 | 0.93 | 0.84 | Onion | |
| CT | 0.71 | 1.02 | 1.19 | 0.84 | Cabbage |
| 0.65 | 0.82 | 1.07 | 0.82 | Garlic | |
| 1.19 | 1.28 | 1.31 | 1.01 | Pepper | |
| 0.67 | 0.93 | 1.24 | 0.95 | Onion |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yimam, A.Y.; Assefa, T.T.; Adane, N.F.; Tilahun, S.A.; Jha, M.K.; Reyes, M.R. Experimental Evaluation for the Impacts of Conservation Agriculture with Drip Irrigation on Crop Coefficient and Soil Properties in the Sub-Humid Ethiopian Highlands. Water 2020, 12, 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040947
Yimam AY, Assefa TT, Adane NF, Tilahun SA, Jha MK, Reyes MR. Experimental Evaluation for the Impacts of Conservation Agriculture with Drip Irrigation on Crop Coefficient and Soil Properties in the Sub-Humid Ethiopian Highlands. Water. 2020; 12(4):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040947
Chicago/Turabian StyleYimam, Abdu Y., Tewodros T. Assefa, Nigus F. Adane, Seifu A. Tilahun, Manoj K. Jha, and Manuel R. Reyes. 2020. "Experimental Evaluation for the Impacts of Conservation Agriculture with Drip Irrigation on Crop Coefficient and Soil Properties in the Sub-Humid Ethiopian Highlands" Water 12, no. 4: 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040947
APA StyleYimam, A. Y., Assefa, T. T., Adane, N. F., Tilahun, S. A., Jha, M. K., & Reyes, M. R. (2020). Experimental Evaluation for the Impacts of Conservation Agriculture with Drip Irrigation on Crop Coefficient and Soil Properties in the Sub-Humid Ethiopian Highlands. Water, 12(4), 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040947







