Nitrogen Surplus—A Unified Indicator for Water Pollution in Europe?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Nitrogen Budgets and Relation to Water Quality
1.2. Nitrogen Surpluses as a Result of Budgets and as Indicators for Measures and Policies
1.3. Nitrogen Budgets for Investigating Farm Performance and as Tool for Farm Advice
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Framework
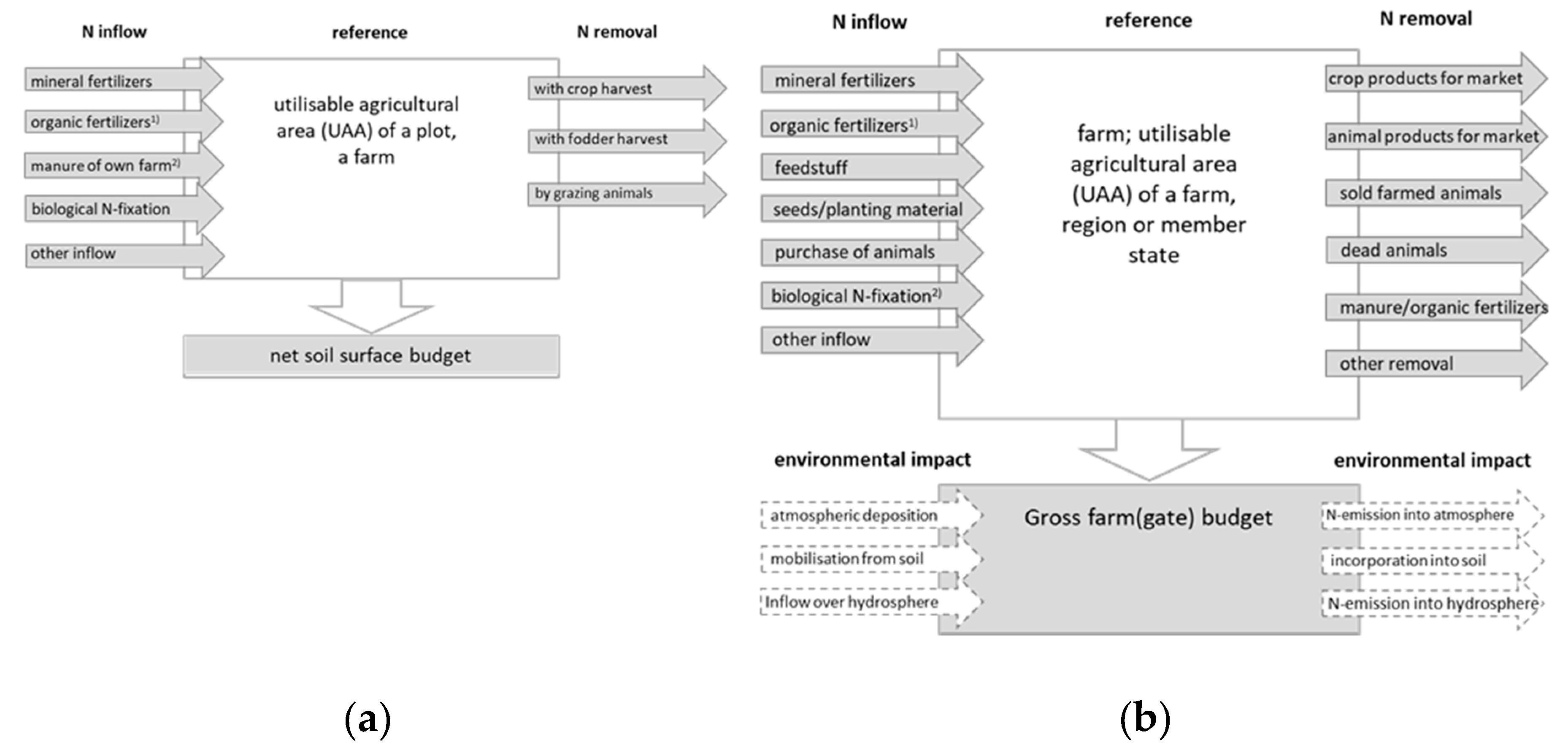
2.1.1. Budget Type
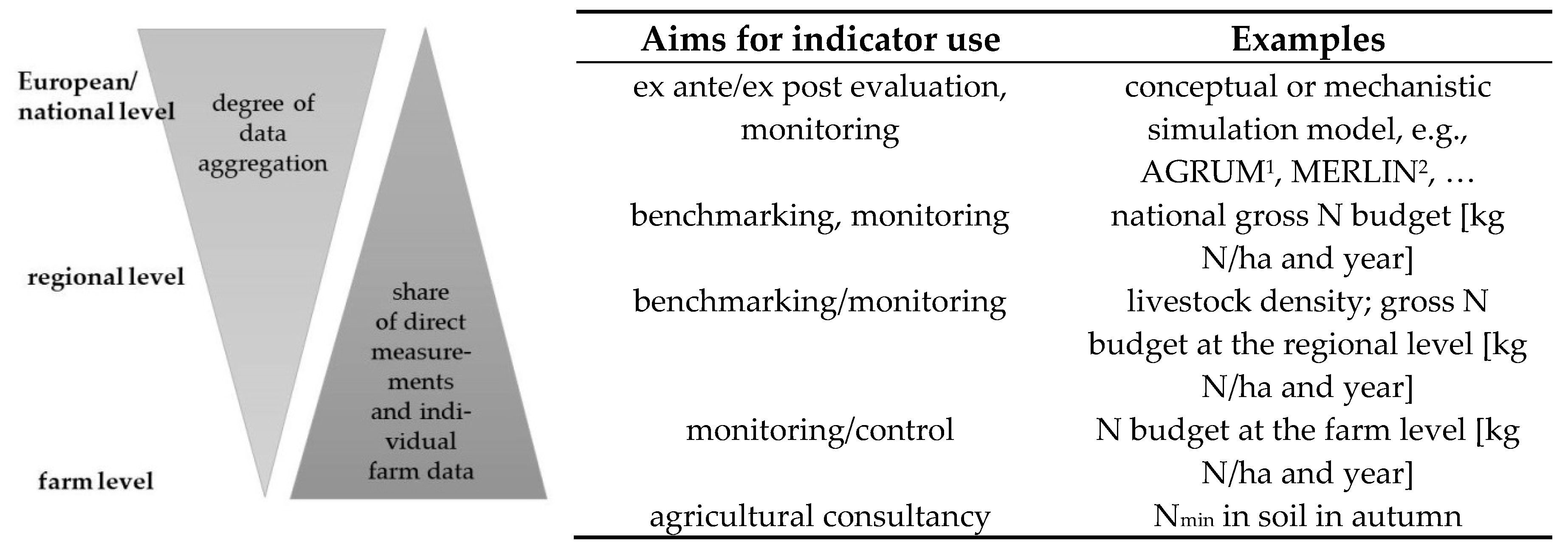
2.1.2. Level of Application of Budget
2.2. Survey on Nitrogen Budgets at the Farm Level
- The type and elements of fertilization plans and budgets used at the farm and plot levels,
- The type and elements of budgets used at the regional or national levels,
- The legally binding procedures in connection with the use of fertilization plans and budgets,
- The informative value of budgets, according to budget type, and
- The barriers in the use/implementation of budgets according to the individual experience and the experience in the FAIRWAY case studies.
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of Fertilization Planning and Budgeting at the Farm Level
3.2. Results on Fertilization Planning
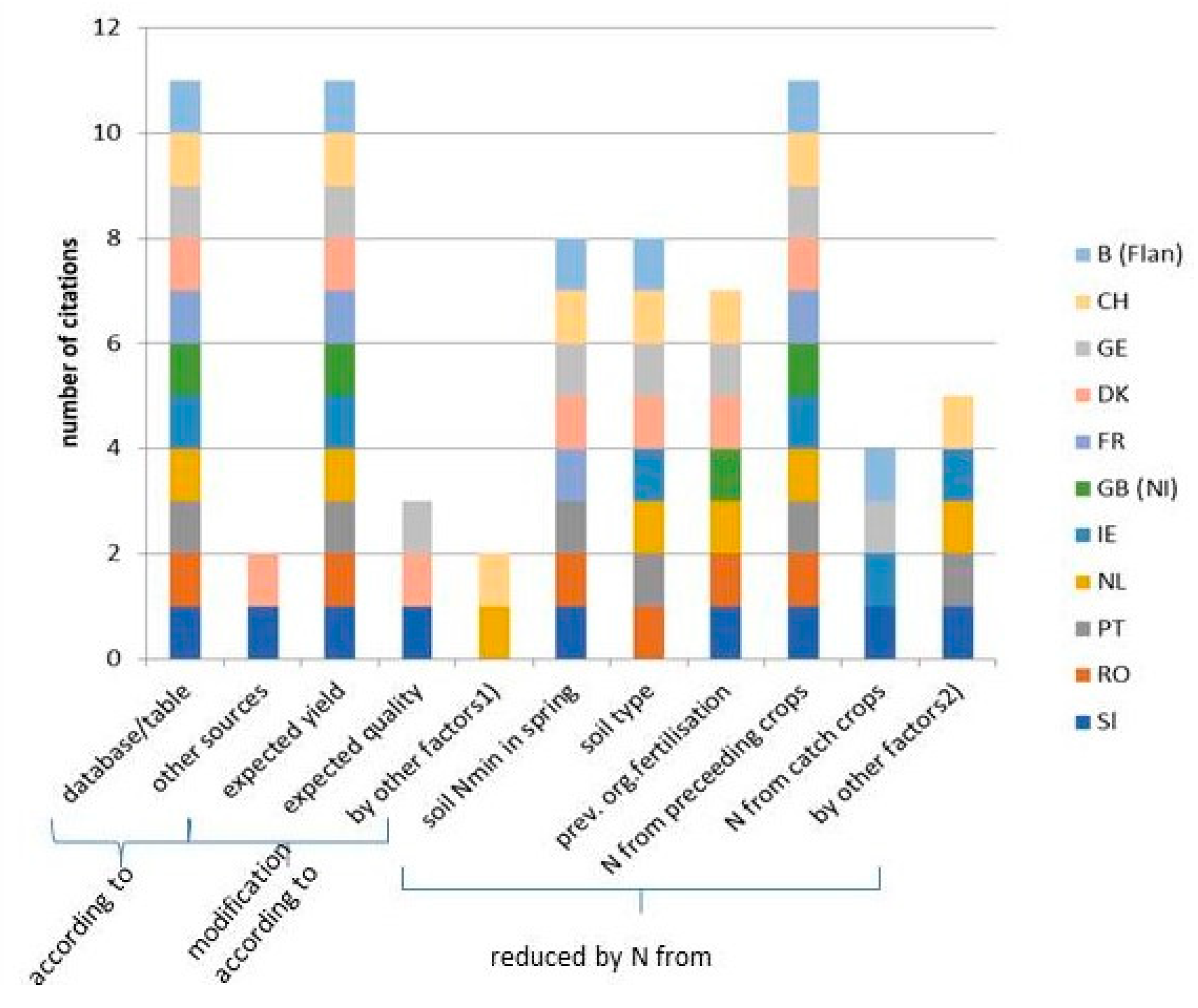
3.2.1. Factors Considered in Fertilization Planning
3.2.2. Impact of Technical Progress on Nitrogen Requirement of Crop
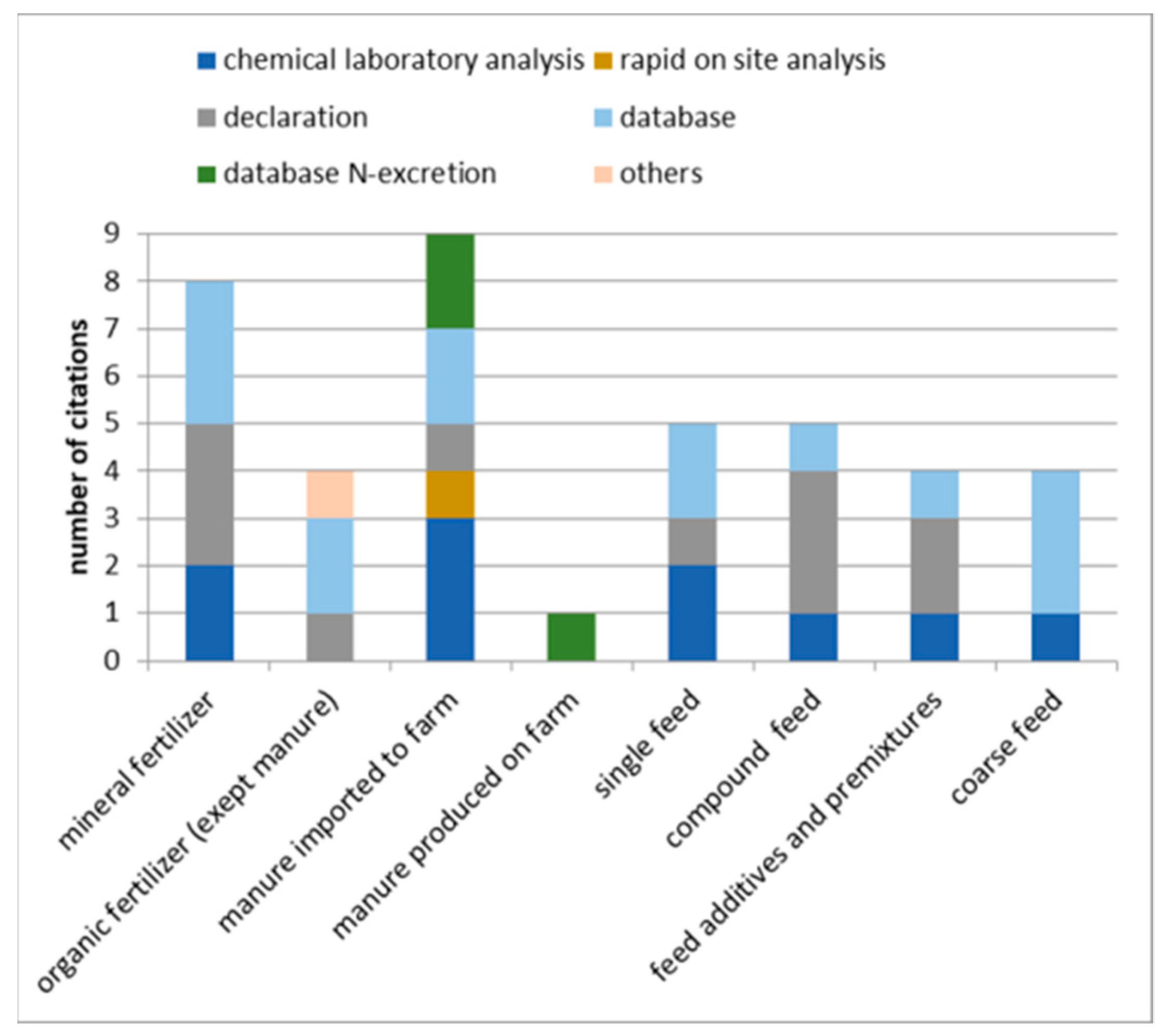
3.2.3. Factors Used to Estimate Plant-Available Nitrogen in Manure and Other Organic Fertilizers
3.2.4. Emission Factors for Nitrogen
3.2.5. The Plant Availability of Nitrogen in Manure
3.3. Elements of Soil Surface Budgets
3.4. Elements of Farm Budgets
3.5. Comparison of Budgets in Different Countries
3.5.1. Germany
3.5.2. Switzerland
3.5.3. The Netherlands
- A farm with a high individual herd NUE produces less N in manure, and thus reduces the need for N-export;
- A farm with a high individual herd NUE consumes less feedstuff;
- A high NUE with respect to soil indicates a low farm N surplus;
- A high NUE of grassland indicates a high N yield;
- A high N input goes along with a lower NUE;
- A high NUE, in turn, results in substantial savings for the farmer (expenses for fertilizer, feedstuff and for manure export) [46].
3.5.4. Romania
4. Discussion
4.1. Prevalence of N Fertilization Planning and N Budgeting at the Farm Level
4.2. Need for the Standardization of Data Collection
4.2.1. Nitrogen Concentration in Different Manure Types
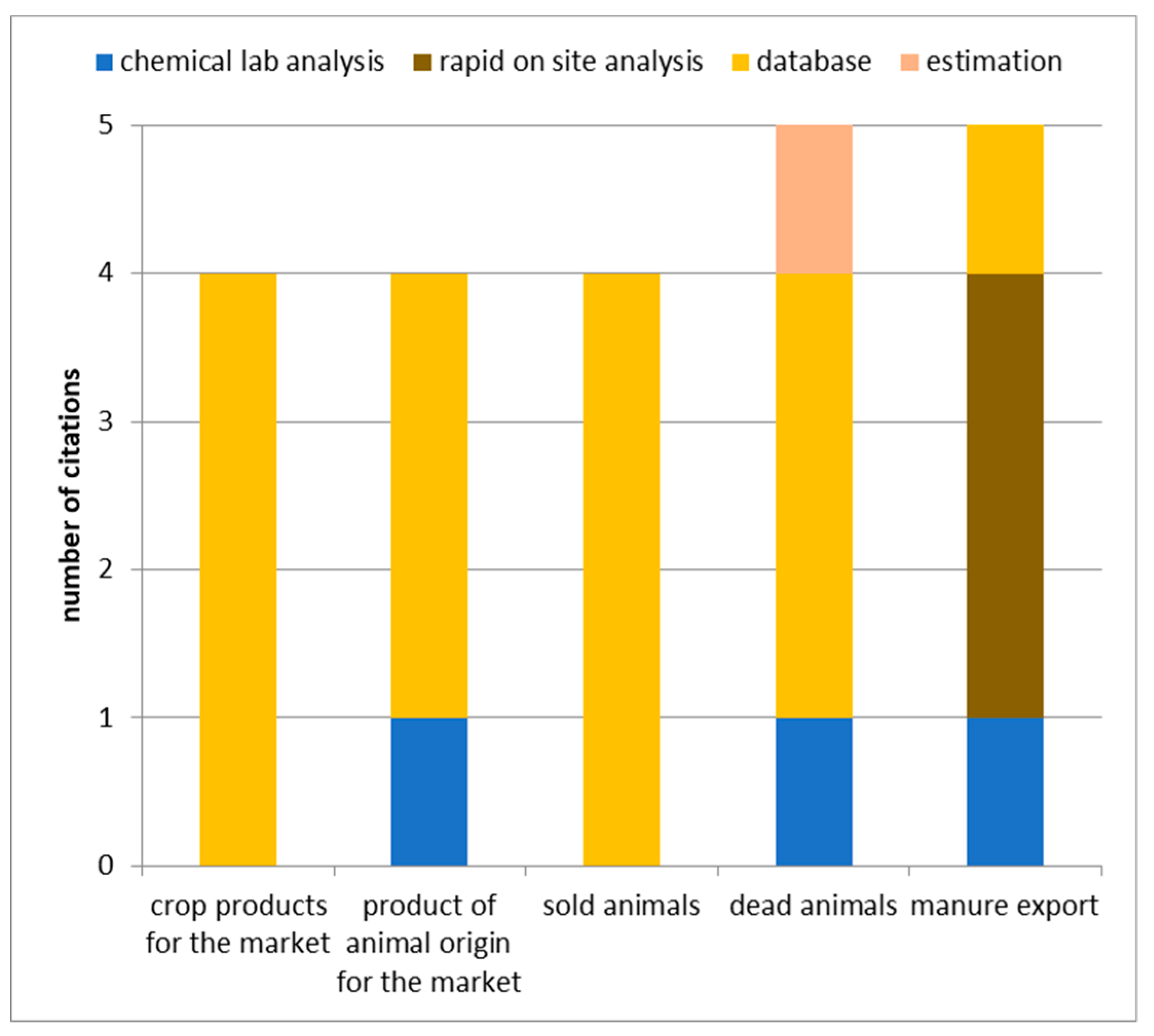
4.2.2. Analyses and Measurements versus Standard Data and Estimations
4.3. Detection of “Hidden” Surpluses Using N Budgets
4.3.1. Nitrogen Losses during Housing and Storage and during/after Manure Application
4.3.2. The Plant Availability of Nitrogen in Organic Fertilizers and Soil Conditioners
4.4. Evaluation of the Presented Budget Types
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OECD. OECD Core Set of Indicators for Environmental Performance Reviews. A Synthesis Report by the Group on the State of the Environment; Environment Monographs No 83; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kremer, A.M.; Methodology and Handbook—Eurostat/OECD—Nutrient Budgets EU-27, Norway, Switzerland. European Commission, Eurostat. 2017, 112p. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/documents/2393397/2518760/Nutrient_Budgets_Handbook_%28CPSA_AE_109%29_corrected3.pdf/4a3647de-da73-4d23-b94b-e2b23844dc31 (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Eurostat Nutrient Budgets—Methodology and Handbook; Version 1.02.; Eurostat and OECD: Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 2013.
- Düngeverordnung (DüV) vom 26. Mai 2017. Verordnung über die Anwendung von Düngemitteln, Bodenhilfsstoffen, Kultursubstraten und Pflanzenhilfsmitteln nach den Grundsätzen der guten fachlichen Praxis beim Düngen. BGBl.I, 1305 pp. Available online: https://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/d_v_2017/D%C3%BCV.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Leip, A.; Britz, W.; Weiss, F.; de Vries, W. Farm, land, and soil budgets for agriculture in Europe calculated with CAPRI. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3243–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, K.; Heumesser, C.; Schmid, E. Groundwater nitrate contamination: Factors and indicators. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Ruijter, F.J.; Boumans, L.j.M.; Smit, A.L.; von den Berg, M. Nitrate in upper groundwater on farms under tillage as affected by fertilizer use, soil type and groundwater table. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2007, 77, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, I.; Antony, S.G. Agricultural nitrogen balances and water quality in the UK. Soil Use Manag. 2002, 18, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieling, K.; Kage, H. N balance as an indicator of N leaching in an oilseed rape—Winter wheat—Winter barley rotation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 115, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczko, U.; Kuchenbuch, R.O. Environmental indicators to assess the risk of diffuse nitrogen losses from agriculture. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankinen, K.; Salo, T.; Granlund, K.; Rita, H. Simulated nitrogen leaching, nitrogen mass field balanes and their correleation on four farms in south-western Finland during the peeriod 2000–2005. Agric. Food Sci. 2007, 16, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, B.; Thorling, L.; Schullehner, J.; Termansen, M.; Dalgaard, T. Groundwater nitrate response to sustainable nitrogen management. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgaard, T.; Bienkowski, J.F.; Bleeker, A.; Dragosit, U.; Drouet, J.L.; Durand, P.; Frumau, A.; Hutchings, N.J.; Kedziora, A.; Magliulo, V.; et al. Farm nitrogen balances in six European landscapes as an indicator for nitrogen losses and basis for improved management. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 5303–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andelov, M.; Kunkel, R.; Uhan, J.; Wendland, F. Determination of nitrogen reduction levels necessary to reach groundwater quality targets in Slovenia. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1806–1817. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1001074214000734 (accessed on 16 April 2020). [CrossRef]
- Spiess, E. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium balances and cycles of Swiss agriculture from 1975 to 2008. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 91, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisvert, C.; Curie, F.; Moatar, F. Annual agricultural N surplus in France over a 70-year period. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2017, 107, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oenema, O.; Kros, H.; de Vries, W. Approaches and uncertainties in nutient budgets. Implications for nutrient management and environmental policies. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 20, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameira, M.R.; Rolim, J.; Valente, F.; Faro, A.; Dragosits, U.; Cordovil, C.M.d.S. Spatial distribution and uncertainties of nitrogen budgets for agriculture in the Tagus river basin in Portugal—Implications for effectiveness of mitigation measures. Land Use Policy 2019, 84, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourley, C.J.P.; Aarons, S.R.; Powel, M. Nitrogen use efficiency and manure management practices in contrasting dairy production systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 147, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Haene, K.; Magyar, M.; Mulier, A.; De Neve, S.; Pálmai, O.; Nagy, J.; Németh, T.; Hofman, G. Comparison of N and P farm gate balances between the intensive agriculture in Flanders and the extensive agriculture in Hungary. In Proceedings of the 14th World Fertilizer Congress of the International Centre for Fertilizers, CIEC Chiang Mai, Thailand, 22–27 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mulier, A.; Hofman, G.; Baecke, E.; Carlier, L.; De Brabander, D.; De Groote, G.; De Wilde, R.; Fiems, L.; Janssens, G.; Van Cleemput, O.; et al. A methodology for the calculation of farm level nitrogen and phosphorus balances in Flemish agriculture. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 20, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Haene, K.; Salomez, J.; De Neve, S.; De Waele, J.; Hofman, G. Environmental performance of the nitrogen fertiliser limits imposed by the EU Nitrates Directive. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 192, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waele, J.; D’Haene, K.; Salomez, J.; Hofman, G.; De Neve, S. Simulating the environmental performance of post-harvest management measures to cope with the Nitrates Directive. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, J. ZA-AUI: Jüngste Entwicklungen und Resultate. BLW, Fachbereich Agrarumweltsysteme und Nährstoffe, 2017. Available online: https://2017.agrarbericht.ch/de/umwelt/agrarumweltmonitoring/agrarumweltindika torenaui (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- CORPEN Des Indicateursd’azotepourgérer des Actions de Maîtrise des Pollutions à L’échelle de la Parcelle, de L’exploitation et du Territoire. Ministère de l’Écologieet du Développement Durable, Paris, France, 2006. Available online: http://www.developpement-durable.gouv.fr/IMG/pdf/DGALN_2006_09_azote_indicateur.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2018).
- Schröder, J.J.; Aarts, H.F.M.; van Middelkoop, J.C.; de Haan, M.H.A.; Schils, R.L.M.; Velthof, G.L.; Fraters, B.; Willems, W.J. Permissible manure and fertilizer use in dairy farming systems on sandy soils in The Netherlands to comply with the Nitrates Directive target. Eur. J. Agron. 2007, 27, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klages, S.; Osterburg, B.; Hansen, H.; Betriebliche Stoffstrombilanzen für Stickstoff und Phosphor—Berechnung und Bewertung. Dokumentation der Ergebnisse der Bund-Länder-Arbeitsgruppe "Betriebliche Stoffstrombilanzen" und der Begleitenden Analysen des Thünen-Instituts 2017. Johann Heinrich von Thünen-Institut, Braunschweig, Germany, 108p. Available online: https://literatur.thuenen.de/digbib_extern/dn059490.pdf. (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Eurostat—Agri-Environmental Indicator—Gross Nitrogen Balance. 2018. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Agri-environmental_indicator_-_gross_nitrogen_balance#Key_messages (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- Brandt, J. Review Report of Agri-Drinking Water Quality Indicators and IT/Sensor Techniques, on Farm Level, Study Site and Drinking Water Source; Brandt, J. FAIRWAY Project Deliverable 3.1; 2018; 180p, Available online: https://fairway-is.eu/index.php/farm-management/workpackages/agri-drinking-water-quality-indicators (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- Hirt, U.; Mahnkopf, J.; Venohr, M.; Kreins, P.; Heidecke, C.; Schernewski, G. How can German river basins contribute to reach the nutrient emission targets of the Baltic Sea Action Plan. In Environmental Science and Technology: Proceedings from the Fifth International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Houston, TX, USA, 25–29 June 2012; Sorial, G.A., Hong, J., Eds.; American Science Press: Houston, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aimon-Marie, F.; Angevin, F.; Guichard, L. MERLIN: Une Méthode Agronomique Pour Apprécier les Risques de Pollution Diffuse par les Nitrates D’origine Agricole; Agrotransfert: Lusignan, France, 2001; 27p. [Google Scholar]
- Häußermann, U.; Bach, M.; Klement, L.; Breuer, L. Stickstoff-Flächenbilanzen für Deutschland mit Regionalgliederung Bundesländer und Kreise—Jahre 1995 bis 2017; Methodik, Ergebnisse und Minderungsmaßnahmen. Abschlussbericht TEXTE 131/2019. 2019. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/publikationen/stickstoff-flaechenbilanzen-fuer-deutschland (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- BLW Weisungen und Erläuterungen 2019. Verordnung über die Direktzahlungen an die Landwirtschaft (Direktzahlungsverordnung, DZV; SR 910.13; Bundesamt für Landwirtschaft: Bern, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Richner, W.; Sinaj, S. Grundlagen für die Düngung landwirtschaftlicher Kulturen in der Schweiz (GRUD 2017). Agrarforschung Schweiz 2017, 8, 276. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, J.; Soerensen, P.; Velthof, G.; Amon, B.; Pinto, M.; Rodhe, L.; Salomon, E.; Hutchings, N.; Burczyk, P.; Reid, J. An assessment of the variation of manure nitrogen efficiency throughout Europe and an appraisal of means to increase manure-N efficiency. Adv. Agron. 2013, 119, 371–441. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, P.; Frydendahl Hellwing, A.L.; Børsting, Ch.F. (Eds.) Normtal for husdyrgødning 2019, 38.Institut for husdyrvidenskab, Aarhus Universitet, Tjele, Denmark. Available online: http://anis.au.dk/normtal/ (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Anonymous Decree on the Protection of Waters against Pollution Caused by Nitrates from Agricultural Sources. 2009. Available online: http://www.pisrs.si/Pis.web/pregledPredpisa?id=URED5124 (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- Velthof, G.L.; Hou, Y.; Oenema, O. Nitrogen excretion factors of livestock in the European Union: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 3004–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verordnung zur Änderung der Düngeverordnung und Anderer Vorschriften. Bundesrat Drucksache 98/20,20.02.20. Available online: https://www.bundesrat.de/SharedDocs/drucksachen/2020/0001-0100/98-20.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=2 (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Stoffstrombilanzverordnung (StoffBilV) vom 14. Dezember 2017. Verordnung über den Umgang mit Nährstoffen im Betrieb und betrieblichen Stoffstrombilanzen. BGBl.I, pp. 3942; 2018 I pp. 360. Available online: https://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/stoffbilv/StoffBilV.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- BMEL Stoffstrombilanz: Mehr Transparenz über Nährstoffe in Landwirtschaftlichen Betrieben. Available online: https://www.bmel.de/DE/Landwirtschaft/Pflanzenbau/Ackerbau/_Texte/Stoffstrombilanz.html (accessed on 27 January 2020).
- Avater-Esper, S.; Neue Düngeverordnung soll ab April 2020 Gelten. Top Agrar. Available online: https://www.topagrar.com/acker/news/neue-duengeverordnung-soll-ab-april-2020-gelten-11837988.html (accessed on 27 January 2020).
- Agrida, B.L.W. Wegleitung Suisse-Bilanz; Auflage 1.13; Agridea und Bundesamt für Landwirtschaft: Bern, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bosshard, C.; Spiess, E.; Richner, W. Überprüfung der Methode SuisseBilanz; Schlussbericht. Forschungsanstalt Agroscope, Reckenholz-Tänikon ART: Zurich, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gassner, A. Gewässerschutzbestimmungen in der Landwirtschaft. Ein internationaler Vergleich. In Umwelt-Wissen 2006, Nr. 0618; Bundesamt für Umwelt: Bern, Switzerland, 2006; 76p. [Google Scholar]
- Poppe, K.J. MINAS—The Dutch Mineral Accounting System For the California Department of Food and Agriculture. LEI Wageningen, 2013. Available online: https://www.cdfa.ca.gov/is/ffldrs/frep/pdfs/6_Poppe.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- EEA (2005): Agriculture and Environment in EU-15—The IRENA Indicator Report. Agriculture and Environment. p. 128. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/eea_report_2005_6 (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- Menzi, H. Manure management in Europe: Results of a recent survey. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference of the RAMIRAN Network, High Tatras, Strbské Pleso, Slovak Republic, 14–16 May 2002; pp. 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kaasik, A.; Lund, P.; Damgaard Poulsen, H.; Kuka, K.; Lehn, F.; Kuoppala, K.; Rinne, M.; Nousiainen, J.; Perttilä, S.; Koivunen, E.; et al. Overview of Calculation Methods for the Quantity and Composition of Livestock Manure in the Baltic Sea Region. Report on Current National Manure Calculation Systems Produced in Manure Standards Work Package 3: Guidelines for Calculated Manure Systems. 2019. Available online: https://www.luke.fi/manurestandards/wp-content/uploads/sites/25/2019/06/WP3-report_ManureStandards_Final2.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Luostarinen, S.; Kaasinen, S. Manure Nutrient Content in the Baltic Sea Countries; Natural Resource Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2016; 45p, Available online: http://urn.fi/URN:ISBN:978-952-326-272-0 (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Snauwaert, E.; Forrestal, P.; Bonmati, A.; Riiko, K.; Klages, S.; Brandsma, J.; Provolo, G.; Bernard, J.-P.; Mini-Paper—On Farm Tools for Accurate Fertilization. EIP-AGRI Focus Group—Nutrient Recycling. 2016. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eip/agriculture/sites/agri-eip/files/2_mp_on_farm_tools_final.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Daatselaar, C.H.; Reijs, J.R.; Oenema, J.; Doornewaard, G.J.; Aarts, F.M. Variation in nitrogen use efficiencies on Dutch dairy farms. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 3055–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oenema, J. ANCA: The Dutch way. Wageningen University & Research Denmark cattle congress, Herning, Denmark, 26.02. 2019. Available online: https://www.landbrugsinfo.dk/Kvaeg/Dansk-Kvaeg-kongres/Filer/kk19_57_Jouke_Oenema.pptx (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Shah, G.M.; Shah, G.A.; Groot, J.C.J.; Oenema, O.; Raza, A.S.; Lantingal, E.A. Effect of storage conditions on losses and crop utilization of nitrogen from solid cattle manure. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 154, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthof, G.L.; Lesschen, J.P.; Webb, J.; Pietrzak, S.; Miatkowski, Z.; Kros, J.; Pinto, M.; Oenema, O. The Impact of the Nitrates Directive on Gaseous N Emissions—Effects of Measures in Nitrates Action Programme on Gaseous N Emissions; Final Report 2010. Contract ENV.B.1/ETU/2010/0009; Alterra: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2011; 58p. [Google Scholar]
- Reidy, B.; Dämmgen, U.; Döhler, H.; Eurich-Menden, B.; van Evert, F.K.; Hutchings, N.J.; Luesink, H.H.; Menzi, H.; Misselbrook, T.H.; Monteny, G.-J.; et al. Comparison of models used for national agricultural ammonia emission inventories in Europe: Liquid manure systems. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 42, 3452–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidy, B.; Webb, J.; Monteny, G.-J.; Misselbrook, T.H.; Menzi, H.; Luesink, H.H.; Hutchings, N.J.; Eurich-Menden, B.; Döhler, H.; Dämmgen, U. Comparison of models used for national agricultural ammonia emission inventories in Europe: Litter-based manure systems. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, W.-G.; Pfister, P.; Schaaf, H.; Homm-Belzer, A.; Fischer, S. Humus—Chancen und Risiken für den Grundwasserschutz (Ergebnisse aus der Praxis). In Verbraucherschutz als Herausforderung für die landwirtschaftliche Produktion; VDLUFA Kongress, Kurzfassungen; Verband Deutscher Landwirtschaftlicher Untersuchungs- und Forschungsanstalten e.V.: Darmstadt, Germany, 2019; pp. 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Schimmelpfennig, S.; Heidecke, C.; Beer, H.; Bittner, F.; Klages, S.; Krengel, S.; Lange, S. Klimaanpassung in Land- und Forstwirtschaft—Ergebnisse eines Workshops der Ressortforschungsinstitute FLI, JKI und Thünen-Institut. In Thünen Working Paper 2018, 86; Johann Heinrich von Thünen-Institut: Braunschweig, Germany, 2018; 110p. [Google Scholar]
- Klages, S.; Heidecke, C.; Osterburg, B. The impact of agricultural production and policy on water quality during the dry year 2018. Water 2020. under review. [Google Scholar]



| Country | Fertilization Plan (y/n) | Legally Bound (y/n) | N Budgets (y/n) | Legally Bound (y/n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B (Flan) | (y) | (y)(1) | (y) | (y)(2) |
| CH | (y) | (y)(3) | y | y |
| DK | y | y | N(4) | - |
| FR | y | (y)(5) | n | - |
| GE | y | y | y | y |
| NL | y | (y)(6) | y | n |
| PT | (y) | (y)(5) | n | - |
| IE | y | (y)(7) | n | - |
| RO | y | y | y | y |
| Sl | y | y | (y)(8) | - |
| UK-NI | y | y | n | - |
| N emissions From Stables and Storages | Availability of Applied N in Soil for Crops | N Emissions during/after Organic Fertilizer Application | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % of N excretion | % of applied N | % of N excretion | % of applied N | |
| B (Flan)(1) | y | y | n | n |
| CH | y | y | n | n |
| DK | y(4) | y(3,4) | n | n |
| FR | n | n.a.(2) | n | n |
| GE | y | y | y(5) | y(6) |
| IE | n | y | n | n |
| NL | y | y | n(7) | y(8) |
| PT | n | y | n | y |
| RO | y | y | y | n |
| Sl | y | y | n | y |
| UK-NI | n | y | n | n |
| Crop Available % of Total Nitrogen (=Manure N Efficiency) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | Pigs | Layer | Broiler | Sheep | ||||
| Country | Slurry | Solid | Slurry | Solid | Slurry | Solid | ||
| AT | 50 | 5/15 | 65 | 5/15 | 60 | 30 | 30 | |
| B(Flan) | 60 60 | 60 30 | 60 60 | 30 30 | 60 60 | 30 30 | 30 30 | 30 30 |
| BG | 20–35 | 20 | 40–45 | 20 | 40–50 | 40–50 | 40–50 | |
| CH(1) | 45 | 20 | 50 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 30 | |
| CZ | 60 | 40 | 60 | 40 | 60 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| DK(2) | 70 | 65 | 75 | 65 | 70 | 65 | 65 | 65 |
| EE | 50 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| GE(2) | 50 60 | 25 35 | 60 70 | 30/40 40 | 60 70 | 60 70 | 25 35 | |
| FR | 45 | 10/15 | 60 | 20/30 | 45 | 45 | 35 | 10 |
| GR | 20–35 | 10 | 20–45 | 10 | 20–30 | 20–30 | 20–30 | 10 |
| IE | 40 | 30 40 | 50 | 50 50 | 50 | 50 50 | 50 50 | 30 40 |
| IT(3) | 24–62 | 24–62 | 28–73 | 28–73 | 32–84 | 32–84 | 32–84 | |
| LV | 50 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 30 | 25 | 25 | |
| LT | 35 | 35 | 35 | |||||
| LU | 25–50 | 30–50 | 30–60 | 30–50 | 50 | 50 | ||
| NL | 60/40 | 40/25 | 60–70 | 55 | 60/70 | 55 | 55 | |
| PL | 50–60 | 30 | 50–60 | 30 | 50–60 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| PT | 55–75 60 | 30–60 20 | 50–80 80 | 40–60 | 50–70 | 40–60 90 | 40–60 90 | 40–60 |
| RO | 50 | 30 | 50 | 30 | 30 | 50 | ||
| SE | 40–50 | 36–41 | 57 | 47 | 48 | 47/57 | ||
| SI | 50 75–85 | 30 50–70 | 50 75–85 | 30 50–70 | 30 75–85 | 50 50–70 | 50/ 50–70 | |
| SK | 50 | 30 | 50 | 30 | 30 | 50 | 50 | |
| UK | 20/35 | 10 | 25/50 | 10 | 20/35 | 20/30 | 10 | |
| UK-NI | 38 | 30 30 | 50 50 | 30 | 30 30 | 30 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klages, S.; Heidecke, C.; Osterburg, B.; Bailey, J.; Calciu, I.; Casey, C.; Dalgaard, T.; Frick, H.; Glavan, M.; D’Haene, K.; et al. Nitrogen Surplus—A Unified Indicator for Water Pollution in Europe? Water 2020, 12, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041197
Klages S, Heidecke C, Osterburg B, Bailey J, Calciu I, Casey C, Dalgaard T, Frick H, Glavan M, D’Haene K, et al. Nitrogen Surplus—A Unified Indicator for Water Pollution in Europe? Water. 2020; 12(4):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041197
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlages, Susanne, Claudia Heidecke, Bernhard Osterburg, John Bailey, Irina Calciu, Clare Casey, Tommy Dalgaard, Hanna Frick, Matjaž Glavan, Karoline D’Haene, and et al. 2020. "Nitrogen Surplus—A Unified Indicator for Water Pollution in Europe?" Water 12, no. 4: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041197






