Fatigue Life Study of Francis Pump under Reverse Generation Condition Based on Fluid Solid Coupling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
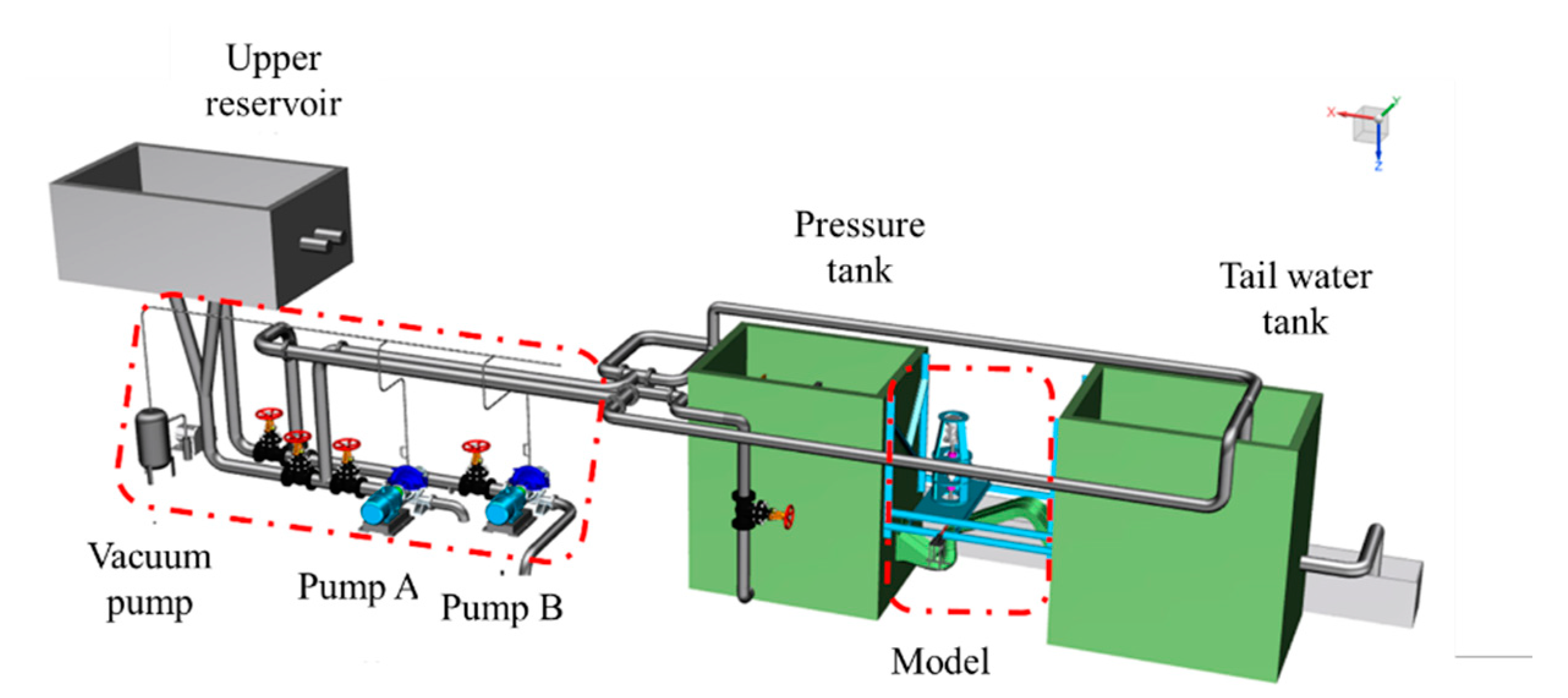
2. Model Establishment and Experiments
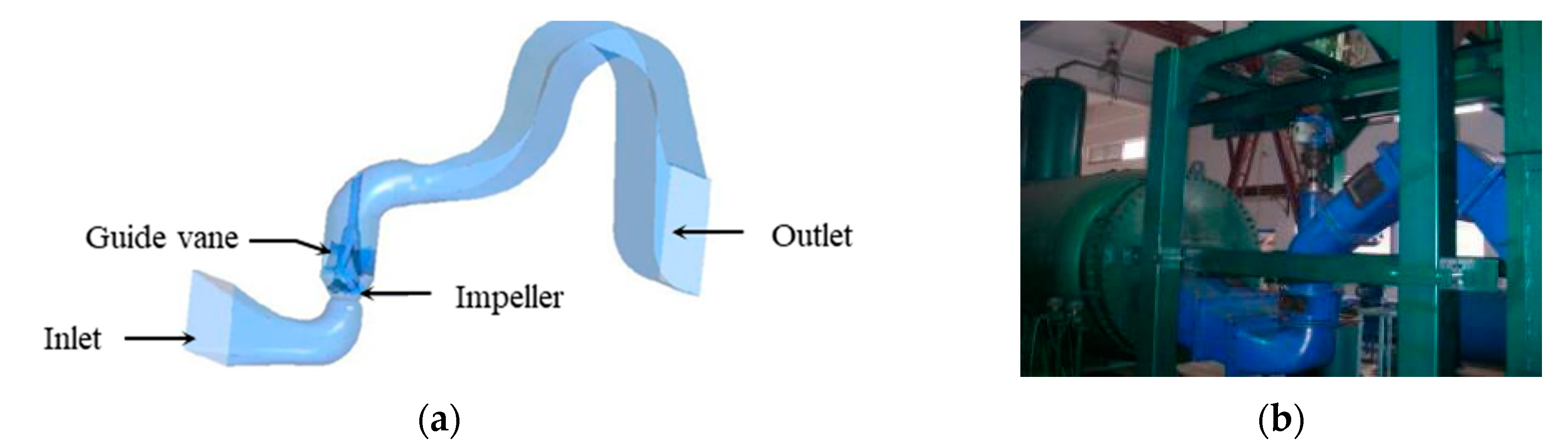
2.1. Modeling and Meshing
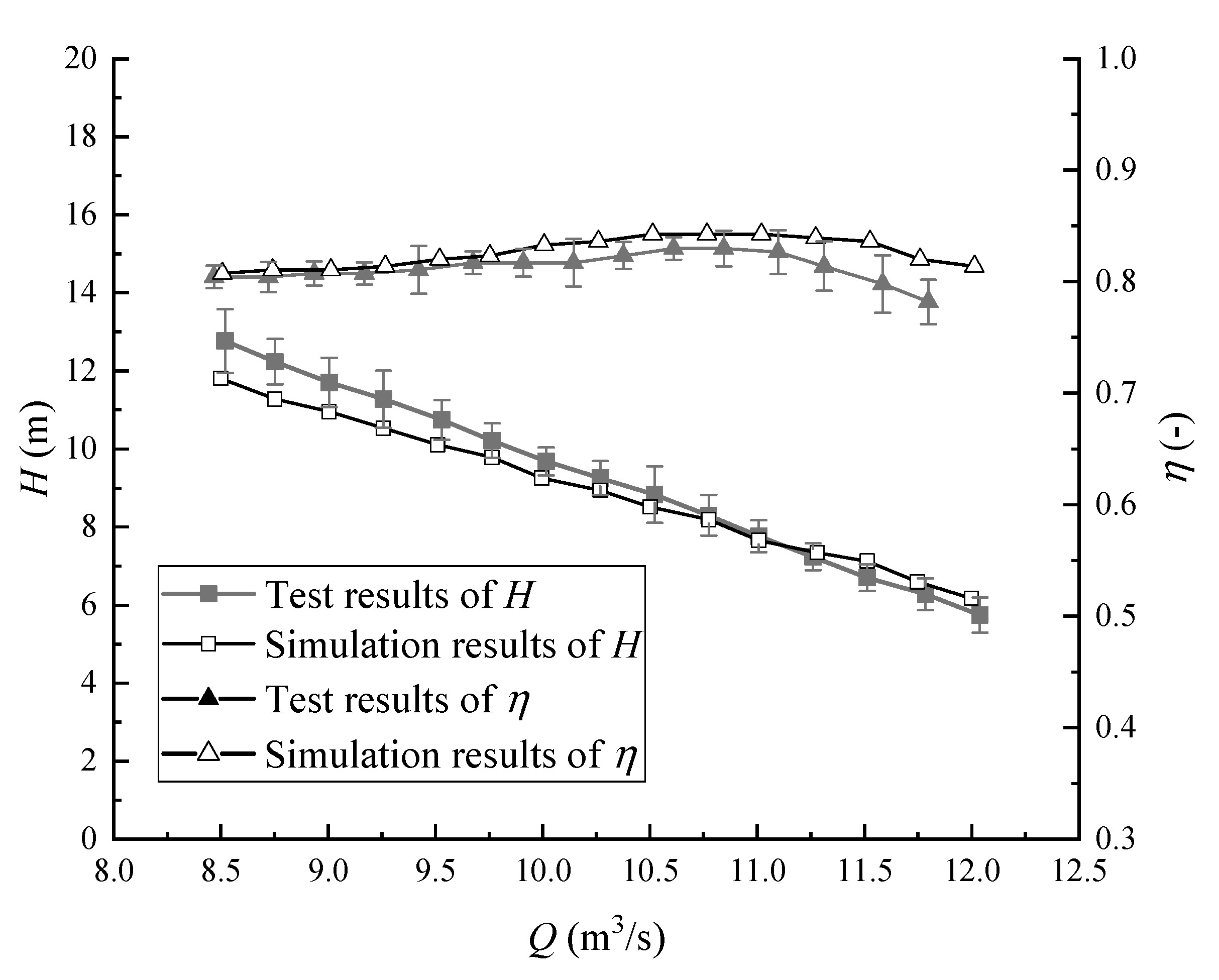
2.2. External Characteristics of the Francis Pump
3. Numerical Simulation Method
3.1. The Governing Equations
3.2. Settings of Structural Field
3.3. Settings of Flow Field
4. Analysis of the Numerical Results
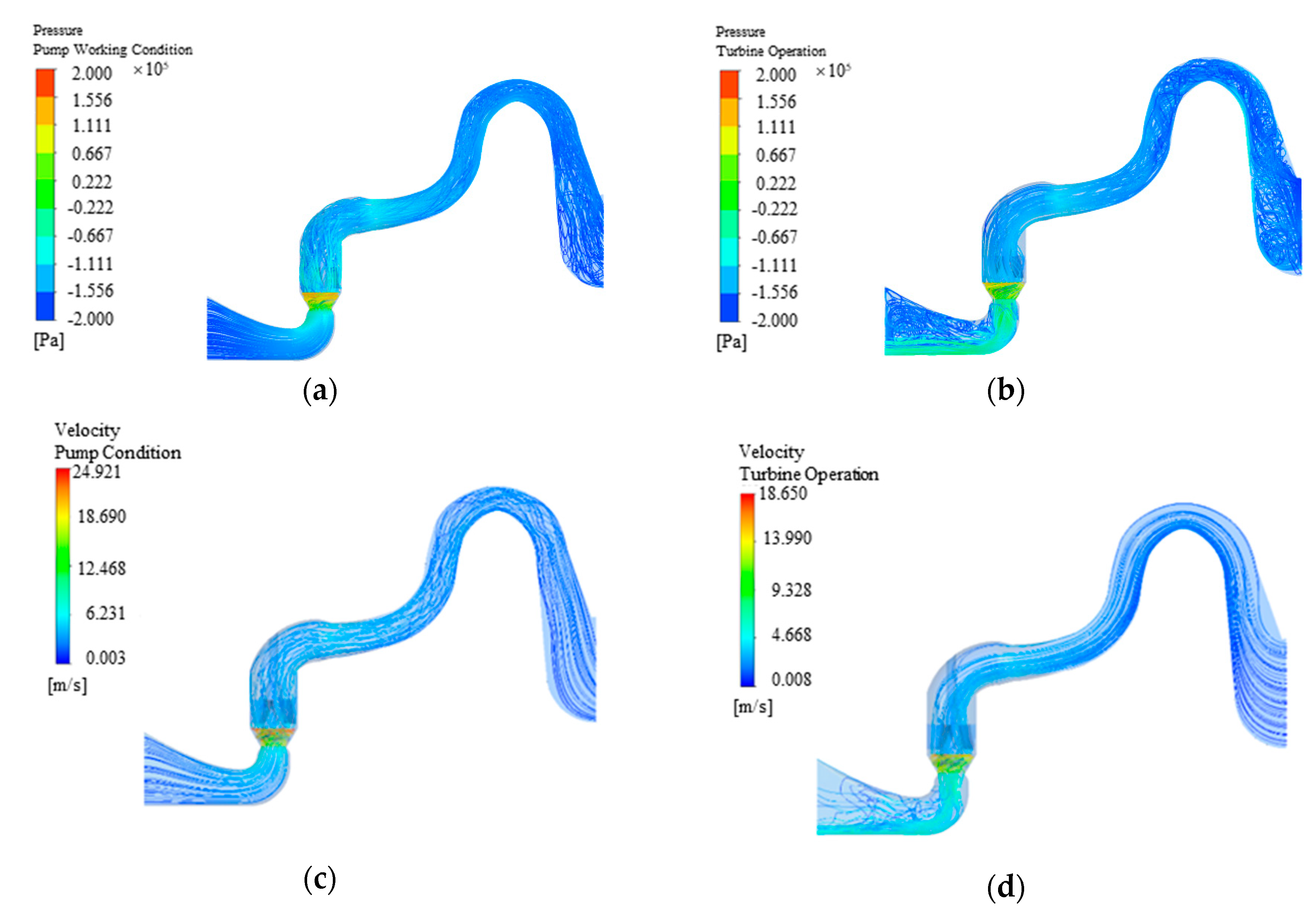
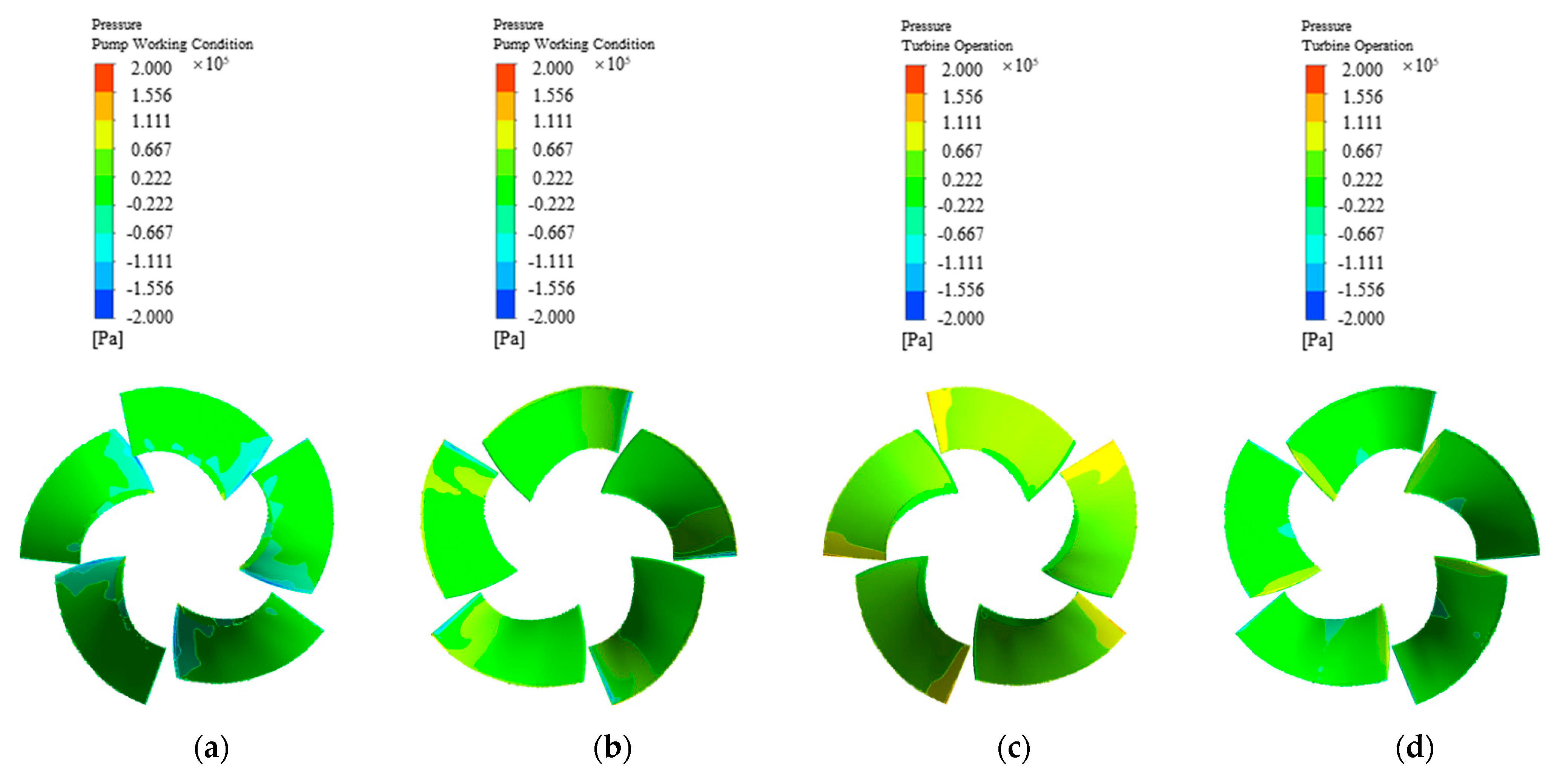
4.1. Comparison of the Streamline Graph and Blade Pressure Cloud Chart
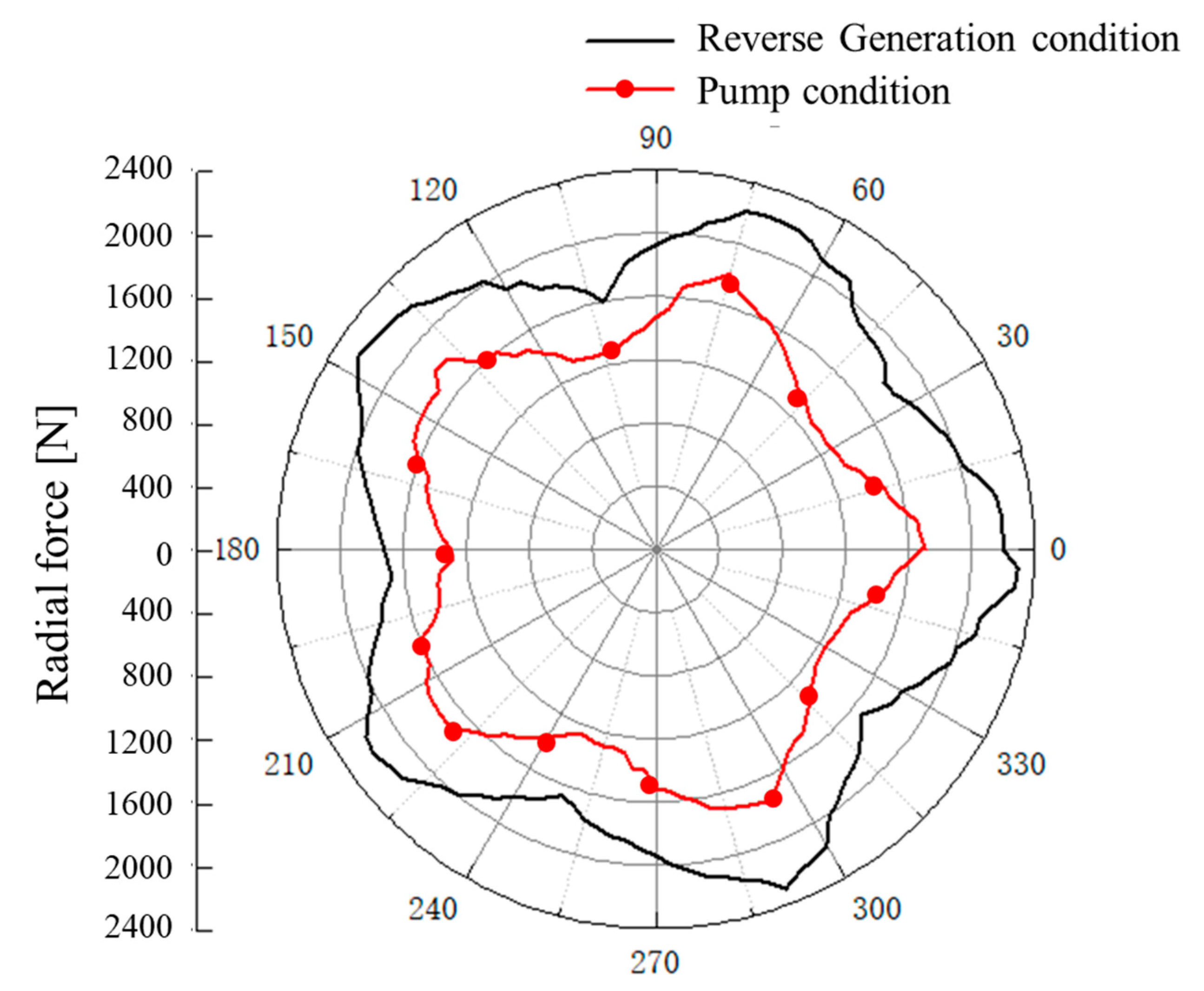
4.2. Force Analysis of the Blades
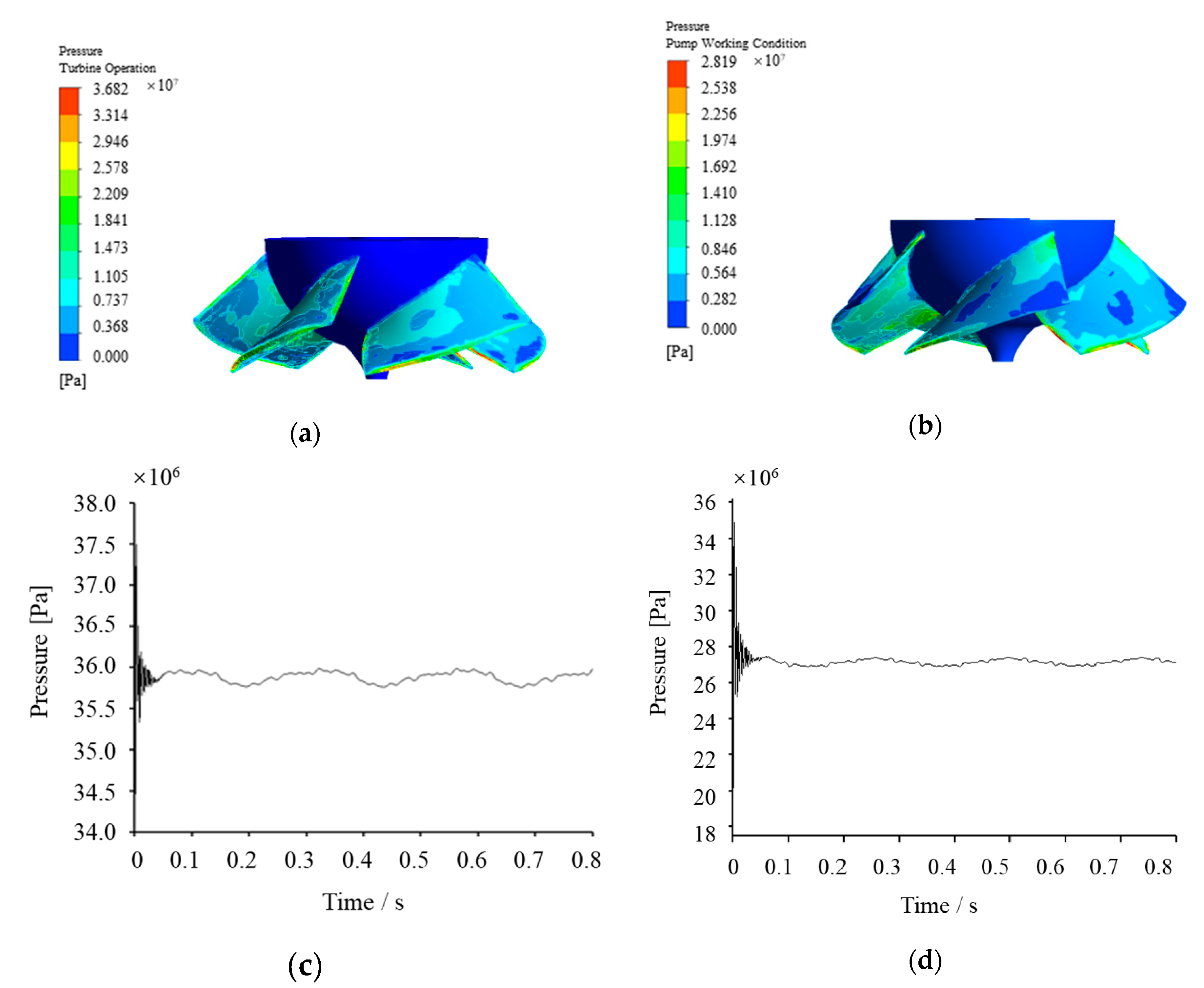
4.3. Stress Analysis of the Runner
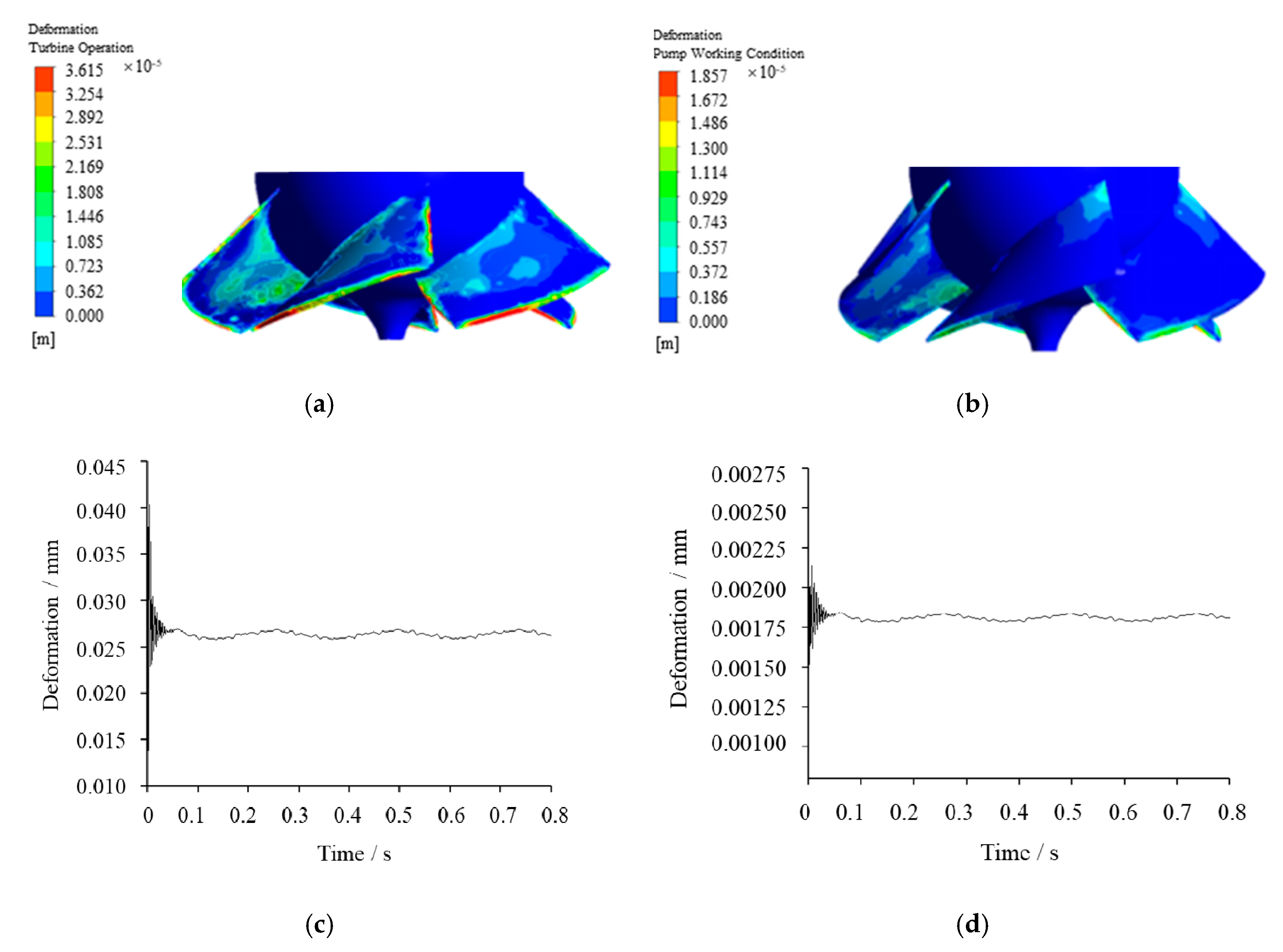
4.4. Deformation Analysis of the Runner
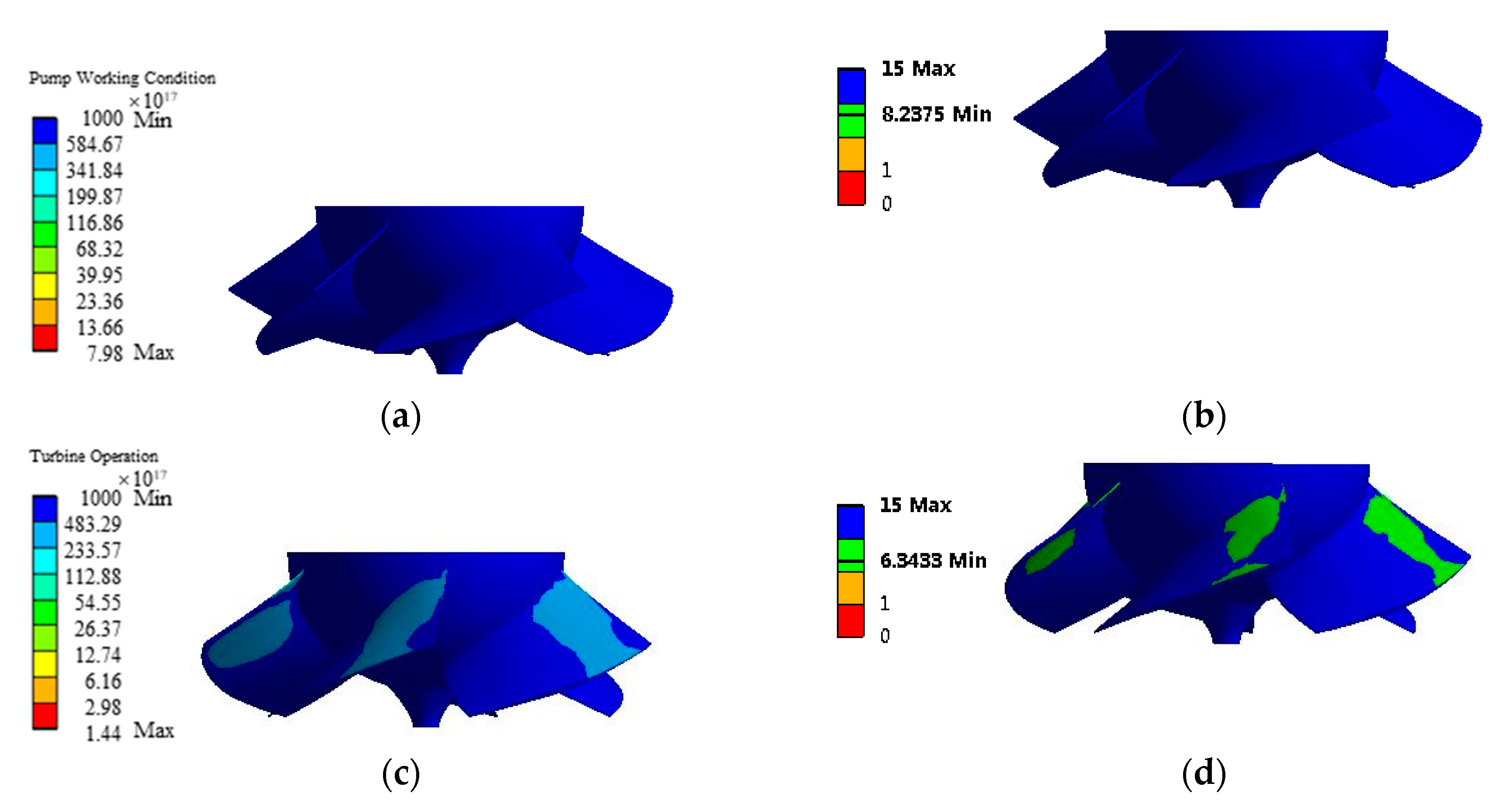
4.5. Estimation of Fatigue Life
4.5.1. Theoretical Calculation of Fatigue Life
4.5.2. Numerical Calculation of Fatigue Life
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Chen, D.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Leed, J.; Jung, K. Dynamic modeling and dynamical analysis of pump-turbines in S-shaped regions during runaway operation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 138, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Xiang, G.M.; Gong, R.; Wei, X.; Liu, Z. Unsteady simulation and analysis for hump characteristics of a pump turbine model. Renew. Energy 2015, 77, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Z.; Fan, H.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.L. S-shaped characteristics on the performance curves of pump-turbines in turbine mode—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höller, S.; Benigni, H.; Jaberg, H. Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the 4-Quadrant Behavior of Different Mixed Flow Diffuser Pumps. Int. J. Turbomach. Propuls. Power 2019, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giovanna, C.; Jean-Bernard, H.; Giorgio, P.; Olivier, T.; Guido, A. Unstable behaviour of pump-turbines and its effects on power regulation capacity of pumped-hydro energy storage plants. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 399–409. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammetoglu, A.; Karadirek, I.E.; Ozen, O.; Habib, M. Full-Scale PAT Application for Energy Production and Pressure Reduction in a Water Distribution Network. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanizzi, M.; Capurso, T.; Balacco, G.; Binetti, M.; Marco, T.; Camporeale, S. Pump as turbine for throttling energy recovery in Water Distribution Networks. Aip Conf. Proc. 2019, 2191, 20142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanizzi, M.; Capurso, T.; Balacco, G.; Marco, T.; Binetti, M.; Piccinni, A.F.; Fortunato, B.; Camporeale, S. Preliminary assessment of a pump used as turbine in a water distribution network for the recovery of throttling energy. In Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Turbomachinery Fluid dynamics & Thermodynamics, Stockholm, Sweden, 3–7 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, L.; Delgado, J.; Covas, D.I.C. Improved Assessment of Energy Recovery Potential in Water Supply Systems with High Demand Variation. Water 2018, 10, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celebioglu, K.; Altintas, B.; Aradag, S.; Tascioglu, Y. Numerical research of cavitation on Francis turbine runners. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 17771–17781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, B.; Weber, W.; Seidel, U. The role of fluid-structure interaction for safety and life time prediction in hydraulic machinery. Iop Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 49, 072007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Singh, P.M.; Choi, Y.D. The effect of runner blade loading on the performance and internal flow of a Francis hydro turbine model. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negru, R.; Muntean, S.; Marsavina, L.; Susan-Resiga, R.; Pasca, N. Computation of stress distribution in a Francis turbine runner induced by fluid flow. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 64, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Jin, X.L.; Ding, L. Stress Analysis of Tubular Turbine Based on Fluid-Structure Coupling. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 190–191, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.L.; Lin, Y.G.; Jin, Y.Z. Numerical Simulation of Flow in Centrifugal Pump with Complex Impeller. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Strength analysis on stamping and welding impeller in centrifugal pump based on fluid structure interaction theorem. Trans. Csae 2011, 27, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X. Blade Stress of the Reactor Coolant Pump of 300 MWe Nuclear Power Plant in China Based on Fluid-solid Coupling Method. J. Mech. Eng. 2010, 46, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Huang, W.; Suo, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Fluid-solid strong-interaction model of mechanical seals in reactor coolant pumps. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 2339–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shi, W.; Si, Q.; Zhou, L. Numerical calculation and finite element calculation on impeller of stainless steel multistage centrifugal pump. J. Vibroeng. 2014, 16, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y. Stress analysis of the canned nuclear coolant pump based on FSI. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering, Prague, Czech Republic, 7–11 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, K.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y. Numerical study on unidirectional fluid-solid coupling of Francis turbine runner. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Shi, W. Mechanical properties of mixed-flow pump impeller based on bidirectional fluid-structure interaction. J. Agric. Mach. 2015, 46, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Analysis of the structural strength of a multistage submersible pump based on fluid solid coupling. J. Agric. Mach. 2013, 44, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, L.; Weng, K. Dynamic characteristics analysis of tubular turbine based on bidirectional fluid solid coupling. Acta Agro Eng. 2016, 32, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Luo, X.; Feng, J. Analysis of cracks in Francis Runner Blades Based on transient fluid solid coupling. J. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, F.; Gui, Z. Fatigue cracks analysis and improvement scheme of the Francis turbine runner blades. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 42, 970–974. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Kong, D. Research on the fatigue life of a Francis turbine runner. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2006, 25, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Carpinteri, A.; Ronchei, C.; Scorza, D.; Vantadori, S. Fracture mechanics based approach to fatigue analysis of welded joints. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2015, 49, 67678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chamberland-Lauzon, J.; Oram, C.; Klopfer, A.; Ruchonnet, N. Fatigue analyses of the prototype Francis runners based on site measurements and simulations. Iop Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 22, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidel, U.; Mende, C.; Hübner, B.; Weber, W.; Otto, A. Dynamic loads in Francis runners and their impact on fatigue life. Iop Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 22, 032054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egusquiza, E.; Valero, C.; Presas, A.; Huang, X.; Guardo, A.; Seidel, U. Analysis of the dynamic response of pump-turbine impellers. Influence of the rotor. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 68, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Li, Y.; Shao, Y.; Pei, J.; Chen, J. Numerical calculation of effect of fluid-structure interaction on flow field in pumping stations with two way passages. China Rural Water Hydropower 2017, 1, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Wu, X. Strength analysis of guide vane centrifugal pump based on fluid solid coupling. J. Vib. Shock 2013, 32, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, S. Fluid solid coupling calculation of axial flow turbine runner. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2008, 29, 1673–1675. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E.; Sun, A.; Yang, C.; Wang, J. Multiobjective Optimization Design and Experimental Investigation on the Axial Flow Pump with Orthogonal Test Approach. Complexity 2019, 2019, 1467565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, H.; Soo-Hwang, A.; Yao, Y.; Fan, H. Numerical analysis of non-axisymmetric flow characteristic for a pump-turbine impeller at pump off-design condition. Renew. Energy 2017, 115, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E. Study on Propellers Distribution and Flow Field in the Oxidation Ditch Based on Two-Phase CFD Model. Water 2019, 11, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capurso, T.; Stefanizzi, M.; Pascazio, G.; Ranaldo, S.; Camporeale, S.; Fortunato, B.; Marco, T. Slip Factor Correction in 1-D Performance Prediction Model for PaTs. Water 2019, 11, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Density (kg/m3) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio (-) | Yield Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7730 | 203 | 0.291 | 550 |
| Condition | X-Direction Radial Force (N) | Y-Direction Radial Force (N) | Radial Resultant Force (N) | Axial Force (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pump condition | 1226.2 | 700.1 | 1412.0 | 88,679.7 |
| Reverse power generation condition | 1762.5 | 866.2 | 1963.9 | 67,654.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E.; Li, C.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, T. Fatigue Life Study of Francis Pump under Reverse Generation Condition Based on Fluid Solid Coupling. Water 2020, 12, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041162
Chen X, Zheng Y, Xu J, Zhang Y, Fernandez-Rodriguez E, Li C, Zhou Y, Jiang T. Fatigue Life Study of Francis Pump under Reverse Generation Condition Based on Fluid Solid Coupling. Water. 2020; 12(4):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041162
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaocui, Yuan Zheng, Junhui Xu, Yuquan Zhang, E. Fernandez-Rodriguez, Chengyi Li, Ying Zhou, and Tao Jiang. 2020. "Fatigue Life Study of Francis Pump under Reverse Generation Condition Based on Fluid Solid Coupling" Water 12, no. 4: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041162






