Effects of Land Use on Stream Water Quality in the Rapidly Urbanized Areas: A Multiscale Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
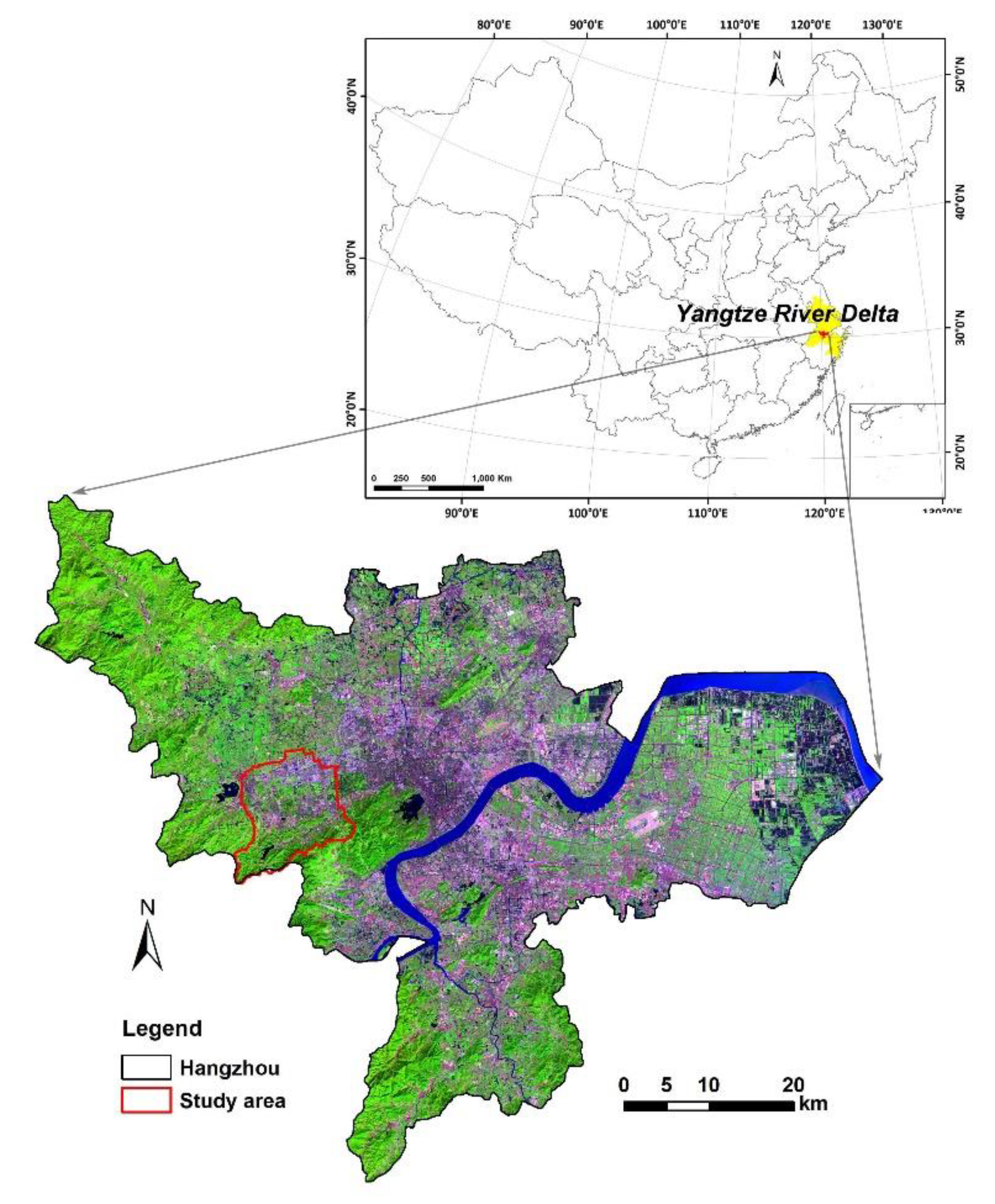
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Land Use Information Extraction
2.3. Water Sampling and Buffer Zone Delineation
2.4. Landscape Metrics
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Land Use Patterns
3.2. Characteristics of Water Quality
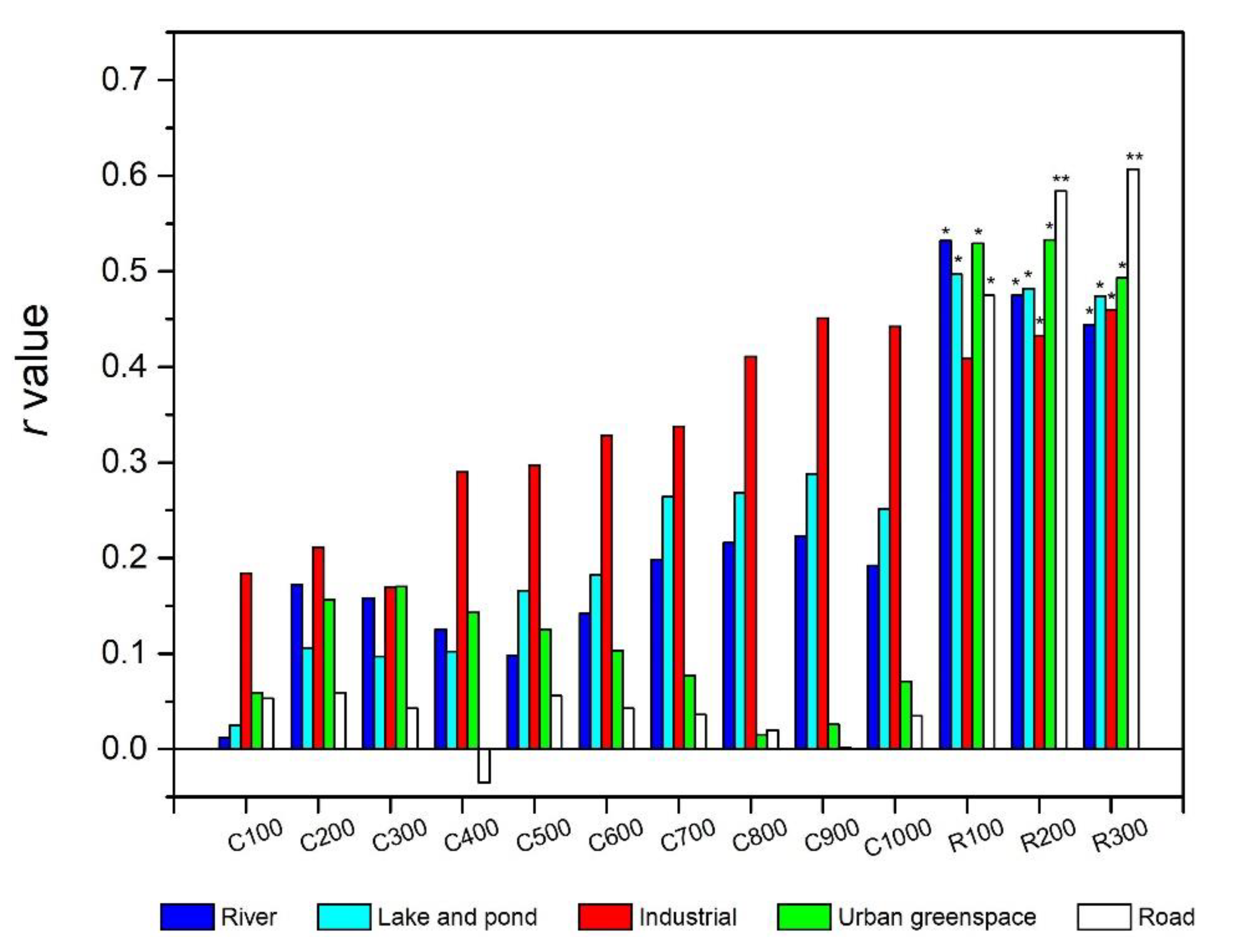
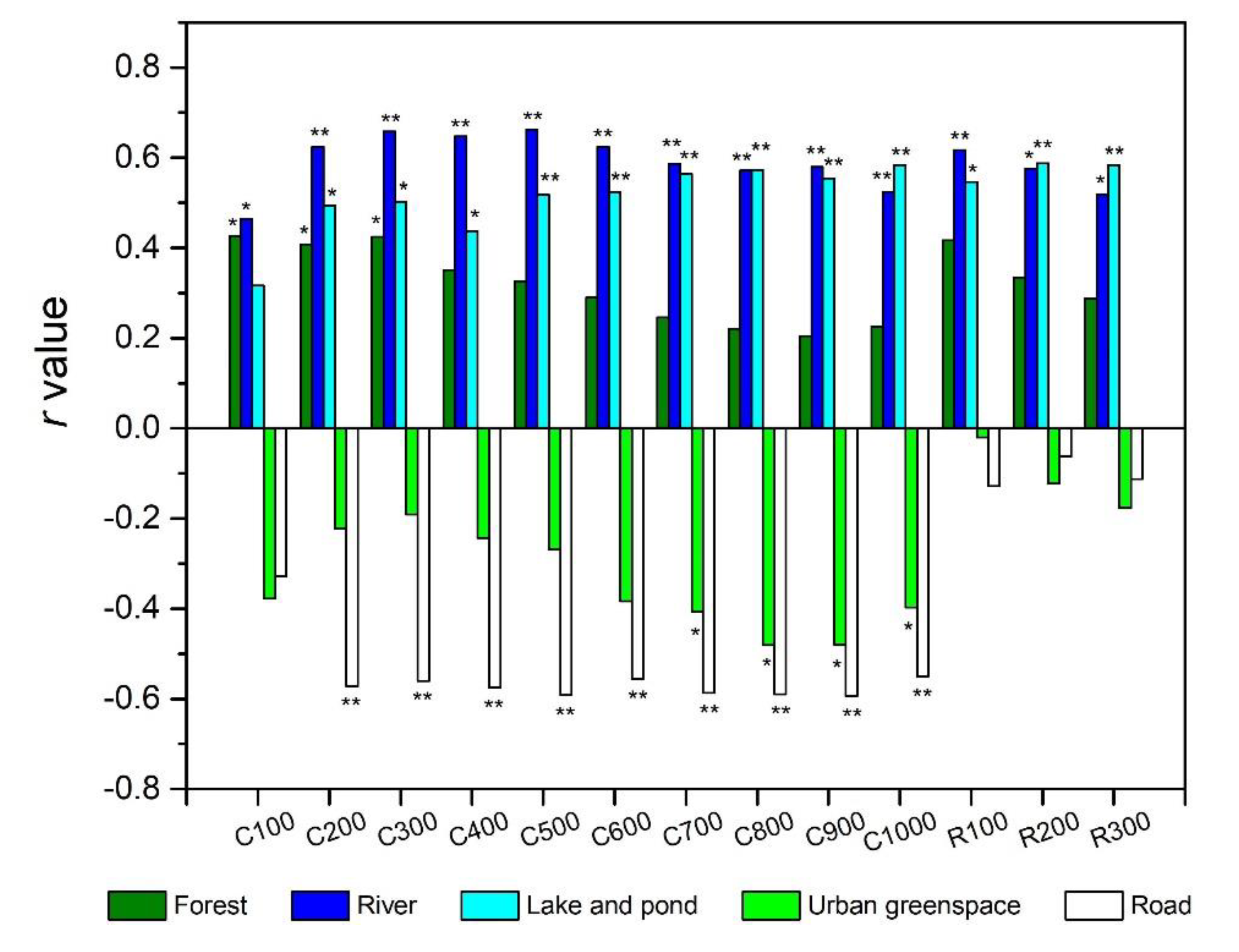
3.3. Land Use Types and Water Quality
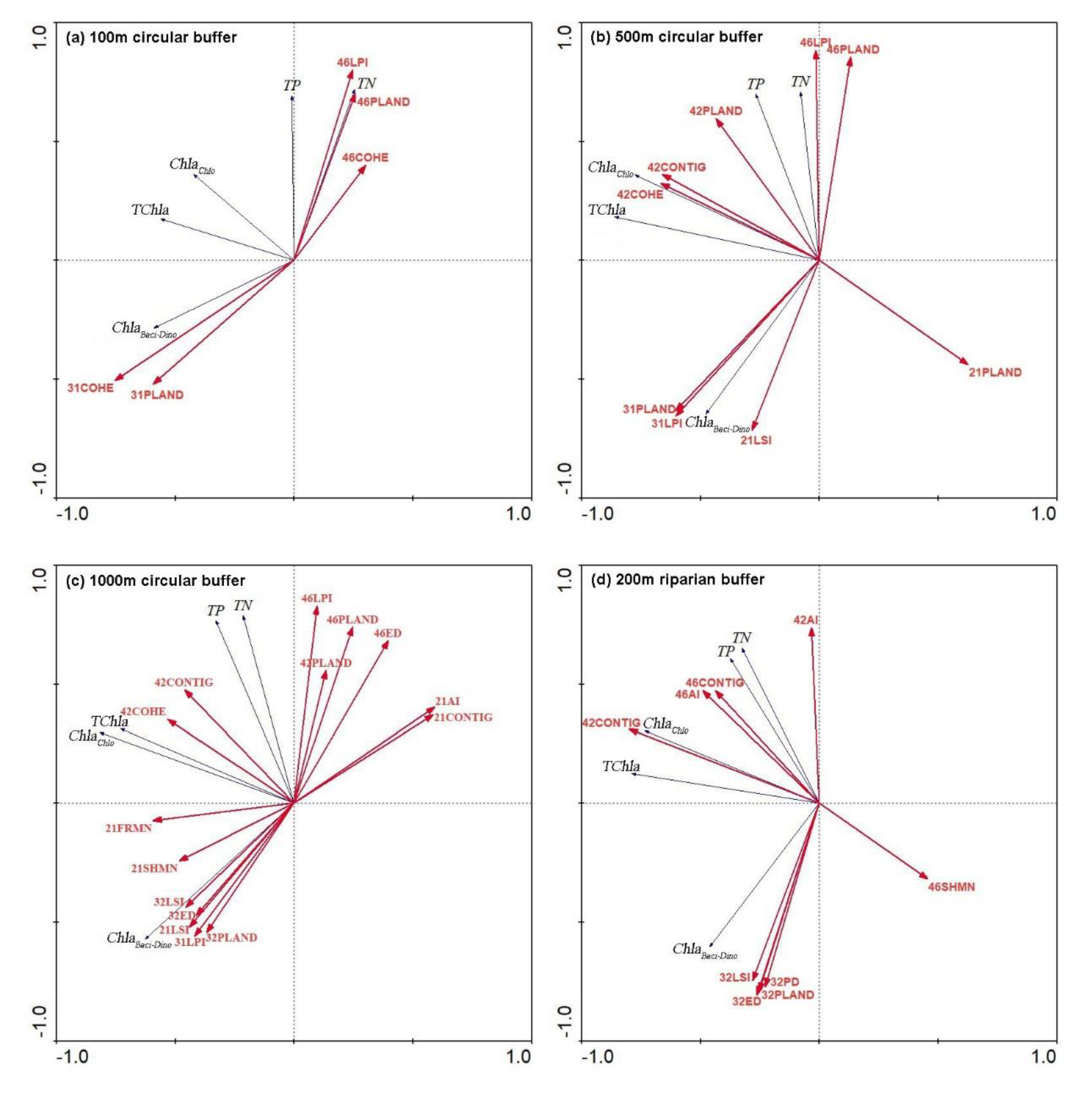
3.4. Land Use Patterns and Water Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Pollution in Urbanized Areas
4.2. Effects of Land Uses Types on Stream Water Quality
4.2.1. Nutrient and Heavy Metal Concentrations
4.2.2. Algae Biomass
4.3. Effects of Land Use Patterns on Stream Water Quality
4.4. Influence of Spatial Scale on Land Use-Water Quality Relationships
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, C.L., Jr.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious surface coverage: The emergence of a key environmental indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Qiu, Z. Understanding the relationship of land uses and water quality in Twenty First Century: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Land use and land cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: Using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Zhong, Y.; Meligrana, J.; Anderson, B.; Watt, W.E.; Chen, J.; Leung, H.-L. Urbanization, land use, and water quality in Shanghai: 1947–1996. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mei, K.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, T.; Gong, J.; Zhang, M. Impacts of land use and population density on seasonal surface water quality using a modified geographically weighted regression. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 450–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, S.T.; Chen, W. Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.S.; Wang, K.; Hong, Y.; Qi, J.G. Spatio-temporal dynamics and evolution of land use change and landscape pattern in response to rapid urbanization. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delphin, S.; Escobedo, F.; Abd-Elrahman, A.; Cropper, W. Urbanization as a land use change driver of forest ecosystem services. Land Use Policy 2016, 54, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Göbel, P.; Dierkes, C.; Coldewey, W. Storm water runoff concentration matrix for urban areas. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2007, 91, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrane, S.J. Impacts of urbanisation on hydrological and water quality dynamics, and urban water management: A review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 2295–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, P.R.; Lee, S.; Kanel, S.R.; Khan, S.P.; Lee, Y.-S. Spatial–temporal variation and comparative assessment of water qualities of urban river system: A case study of the river Bagmati (Nepal). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 129, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, D.B.; Roy, A.H.; Smith, B.; Capps, K.A. Global perspectives on the urban stream syndrome. Freshw. Sci. 2016, 35, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.-N.; Ding, H.-Y.; Dai, Y.; Ding, S.; Gao, X. Threshold Responses in the Taxonomic and Functional Structure of Fish Assemblages to Land Use and Water Quality: A Case Study from the Taizi River. Water 2019, 11, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brabec, E.; Schulte, S.; Richards, P.L. Impervious surfaces and water quality: A review of current literature and its implications for watershed planning. J. Plan. Lit. 2002, 16, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, R.; Benoit, G. Effects of Impervious Cover at Multiple Spatial Scales on Coastal Watershed Streams 1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 712–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampella, R.A.; Procopio, N.A.; Lathrop, R.G.; Dow, C.L. Relationship of Land-Use/Land-Cover Patterns and Surface-Water Quality in The Mullica River Basin. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.D. Urbanization and stream quality impairment. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1979, 15, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhou, L. Influence of spatial variation in land-use patterns and topography on water quality of the rivers inflowing to Fuxian Lake, a large deep lake in the plateau of southwestern China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.; Booth, D.; Hill, K.; Coburn, B.; Avolio, C.; Coe, S.; Spirandelli, D. The impact of urban patterns on aquatic ecosystems: An empirical analysis in Puget lowland sub-basins. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 80, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, O.; Niyogi, D.K.; Townsend, C.R. Scale-dependence of land use effects on water quality of streams in agricultural catchments. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 130, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.; Richards, C.; Host, G.; Arthur, J. Landscape influences on water chemistry in Midwestern stream ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 1997, 37, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliva, L.; Williams, D.D. Buffer zone versus whole catchment approaches to studying land use impact on river water quality. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3462–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, K.; Valente, R.A.; Randhir, T.O.; dos Santos, A.C.A.; Vettorazzi, C.A. Effects of land use and land cover on water quality of low-order streams in Southeastern Brazil: Watershed versus riparian zone. Catena 2018, 167, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wu, J.; Peng, S. Assessing the effects of landscape pattern on river water quality at multiple scales: A case study of the Dongjiang River watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, T.; Mazumder, A. Spatial scale of land-use impacts on riverine drinking source water quality. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Sun, D.; Zhou, L. A statistical assessment of the impact of agricultural land use intensity on regional surface water quality at multiple scales. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 4170–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolpin, D.W. Agricultural chemicals in groundwater of the midwestern United States: Relations to land use. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 26, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, L.; Yang, K.; Liu, Q.; Qian, G. Influences of land use on water quality in a reticular river network area: A case study in Shanghai, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 137, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Hou, X.; Li, W.; Aini, G.; Chen, L.; Gong, Y. Impact of landscape pattern at multiple spatial scales on water quality: A case study in a typical urbanised watershed in China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.M., Jr.; Mccutchan, J.R., Jr. Ecological responses to nutrients in streams and rivers of the Colorado mountains and foothills. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Jones, I.; Thackeray, S. Testing the sensitivity of phytoplankton communities to changes in water temperature and nutrient load, in a temperate lake. Hydrobiologia 2006, 559, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimet, F. Recent views on river pollution and diatoms. Hydrobiologia 2012, 683, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.-J.; Lee, S.-W.; Hwang, S.-J.; Park, S.-R.; Hwang, S.-A. Exploring the non-stationary effects of forests and developed land within watersheds on biological indicators of streams using geographically-weighted regression. Water 2016, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.H.; Dong, Y.X.; Zhou, G.H.; Zheng, W. Soil geochemical baseline and environmental background values of agricultural regions in Zhejiang province. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2007, 23, 81–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Standards. Current Land Use Classification (GB/T 21010-2017); China Quality and Standards Publishing & Media Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bu, H.; Wei, M.; Yuan, Z.; Wan, J. Relationships between land use patterns and water quality in the Taizi River basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Shi, Z.H.; Yin, W.; Huang, X. Spatial and seasonal patterns in stream water contamination across mountainous watersheds: Linkage with landscape characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Herlihy, A.; Kaufmann, P.; Wigington, J.; Van Sickle, J.; Moser, T. Linkages among land-use, water quality, physical habitat conditions and lotic diatom assemblages: A multi-spatial scale assessment. Hydrobiologia 2004, 515, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jin, G.; Tang, H.; Mo, Y.; Wang, Y.-G.; Li, L. Response of water quality to land use and sewage outfalls in different seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 134014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D. Landscapes and Riverscapes: The Influence of Land Use on Stream Ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damanik-Ambarita, M.N.; Everaert, G.; Goethals, P.L. Ecological models to infer the quantitative relationship between land use and the aquatic macroinvertebrate community. Water 2018, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-W.; Hwang, S.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Hwang, H.-S.; Sung, H.-C. Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Guhathakurta, S.; Dai, G.; Wu, L.; Yan, L. The control of land-use patterns for stormwater management at multiple spatial scales. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L. Correlation analysis between landscape metrics and water quality under multiple scales. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ter Braak, C.J.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider, R.A.; Kerekes, J.J. Eutrophication of Waters: Monitoring, Assessment and Control; OECD: Paris, France, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.-A.; Hwang, S.-J.; Park, S.-R.; Lee, S.-W. Examining the relationships between watershed urban land use and stream water quality using linear and generalized additive models. Water 2016, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tromboni, F.; Dodds, W. Relationships between land use and stream nutrient concentrations in a highly urbanized tropical region of Brazil: Thresholds and riparian zones. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulac, M.N.; Reckhow, K.H. An examination of land use—Nutrient export relationships. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1982, 18, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.J.; Meyer, J.L. Streams in the urban landscape. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2001, 32, 333–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Romero, A.J.; Rico-Sánchez, A.E.; Mendoza-Martínez, E.; Gómez-Ruiz, A.; Sedeño-Díaz, J.E.; López-López, E. Impact of changes of land use on water quality, from tropical forest to anthropogenic occupation: A multivariate approach. Water 2018, 10, 1518. [Google Scholar]
- Matteo, M.; Randhir, T.; Bloniarz, D. Watershed-scale impacts of forest buffers on water quality and runoff in urbanizing environment. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2006, 132, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogna, D.; Dufrêne, M.; Michez, A.; Latli, A.; Jacobs, S.; Vincke, C.; Dendoncker, N. Forest cover correlates with good biological water quality. Insights from a regional study (Wallonia, Belgium). J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 211, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caccia, V.G.; Boyer, J.N. Spatial patterning of water quality in Biscayne Bay, Florida as a function of land use and water management. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1416–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puckett, L.J. Identifying the major sources of nutrient water pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 408A–414A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, M.R.; Goldstein, R.M. Assessing water quality at large geographic scales: Relations among land use, water physicochemistry, riparian condition, and fish community structure. Environ. Manag. 2003, 31, 0504–0517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenat, D.R.; Crawford, J.K. Effects of land use on water quality and aquatic biota of three North Carolina Piedmont streams. Hydrobiologia 1994, 294, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalí, J.; Gastesi, R.; Álvarez-Mozos, J.; de Santisteban, L.; de Lersundi, J.D.V.; Giménez, R.; Larrañaga, A.; Goñi, M.; Agirre, U.; Campo, M. Runoff, erosion, and water quality of agricultural watersheds in central Navarre (Spain). Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 1111–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, L.; Liu, Q.; Peng, Q.; Kang, M. Impacts of land use on surface water quality in a subtropical River Basin: A case study of the Dongjiang River Basin, Southeastern China. Water 2015, 7, 4427–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skaggs, R.W.; Breve, M.; Gilliam, J. Hydrologic and water quality impacts of agricultural drainage. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 24, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yang, Z.; Cui, B.; Gao, H.; Ding, Q. Some heavy metals distribution in wetland soils under different land use types along a typical plateau lake, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 106, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; He, M.; Hao, F.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W. Heavy metal loss from agricultural watershed to aquatic system: A scientometrics review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindström, M. Urban land use influences on heavy metal fluxes and surface sediment concentrations of small lakes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 126, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. Low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios favor dominance by blue-green algae in lake phytoplankton. Science 1983, 221, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zelnik, I.; Balanč, T.; Toman, M.J. Diversity and Structure of the tychoplankton diatom community in the limnocrene spring Zelenci (Slovenia) in relation to environmental factors. Water 2018, 10, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teittinen, A.; Taka, M.; Ruth, O.; Soininen, J. Variation in stream diatom communities in relation to water quality and catchment variables in a boreal, urbanized region. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 530, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q. Influences of the land use pattern on water quality in low-order streams of the Dongjiang River basin, China: A multi-scale analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uuemaa, E.; Roosaare, J.; Mander, Ü. Landscape metrics as indicators of river water quality at catchment scale. Hydrol. Res. 2007, 38, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Integrating water-quality management and land-use planning in a watershed context. J. Environ. Manag. 2001, 61, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mander, Ü.; Tournebize, J.; Tonderski, K.; Verhoeven, J.T.; Mitsch, W.J. Planning and establishment principles for constructed wetlands and riparian buffer zones in agricultural catchments. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, R.F.V.; Varandas, S.G.; Pacheco, F.A.; Pereira, V.R.; Santos, C.F.; Cortes, R.M.; Fernandes, L.F.S. Impacts of land use conflicts on riverine ecosystems. Land Use Policy 2015, 43, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Level I | Level II | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Cropland | 11 Cropland | Cultivated land |
| 2 Forest | 21 Forest | A large area dominated by trees |
| 3 Water | 31 River | Natural-flowing watercourse and artificial canal |
| 32 Lake and pond | lake, reservoir and pond | |
| 4 Construction land | 41 Residential | Houses and apartment buildings |
| 42 Industrial | Land and buildings used for manufacturing, logistics, warehouse and mining | |
| 43 Commercial | Houses and buildings for businessman working, commercial retails, restaurants, lodging and entertainments | |
| 44 Public management and service | Lands used for administration, public services and municipal utilities, education and research | |
| 45 Urban greenspace | Parks and greenspace lands used for entertainments and environmental conservations | |
| 46 Road | Paved roads including freeways, major and minor city roads | |
| 47 Under construction | Under construction but not yet finished | |
| 5 Bareland | 51 Bareland | Bare soil and bare rock |
| Attributes | Name (Abbreviation) | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fragmentation | Edge density (ED) | m/ha | Total length of all edge segments divided by total area for the corresponding patch type |
| Patch density (PD) | n/km2 | Number of patches of the corresponding patch type per unit area | |
| Dominance | Percentage of landscape (PLAND) | % | Percentage of the landscape comprised of the corresponding patch type |
| Largest patch index (LPI) | % | Proportion of total area occupied by the largest patch of a patch type | |
| Shape complexity | Mean shape index (SHMN) | - | Mean patch perimeter divided by the minimum perimeter of the corresponding land use area |
| Mean fractal dimension index (FDMN) | - | Sum of 2 times the logarithm of the patch perimeter divided by the logarithm of the total area for the corresponding patch type divided by the number of patches | |
| Landscape shape index (LSI) | - | Perimeter-to-area ratio for the corresponding class, increasing with irregular shapes | |
| Connectedness and aggregation | Contiguity index (CONTIG) | - | Assessing patch shapes based on the spatial connectedness of cells within a patch |
| Cohesion index (COHE) | - | Indicates the physical connectedness of the corresponding patch type | |
| Aggregation index (AI) | % | Number of like adjacencies involving the corresponding class, divided by the maximum possible number of like adjacencies involving the corresponding land use type |
| Indicator | Maximum | Minimum | Mean (Std.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TN (mg/L) | 31.69 | 1.34 | 6.46 (6.73) |
| TP (mg/L) | 2.80 | 0.09 | 0.61 (0.62) |
| As (μg/L) | 8.20 | 0.00 | 4.48 (2.28) |
| Cd (μg/L) | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 (0.27) |
| Cr (μg/L) | 12.30 | 0.00 | 3.66(3.36) |
| Cu (μg/L) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 (0.00) |
| Mn (μg/L) | 676.40 | 0.00 | 30.40 (134.80) |
| Ni (μg/L) | 1.70 | 0.00 | 0.32 (0.43) |
| Pb (μg/L) | 5.40 | 0.00 | 1.98 (1.43) |
| Zn (μg/L) | 2.00 | 0.00 | 0.13 (0.46) |
| ChlaCyan (μg/L) 1 | 130.43 | 0.00 | 8.39 (26.52) |
| ChlaChlo (μg/L) 2 | 233.29 | 0.00 | 63.56 (69.46) |
| ChlaBaci-Dino (ug/L) 3 | 138.74 | 0.00 | 25.04 (31.18) |
| TChla (μg/L) 4 | 328.84 | 2.08 | 96.99 (83.75) |
| Scales | Explained Variation (%) | Explanatory Variables Selected (p < 0.05) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis 1 | Axis 2 | All Axes | ||
| 100-m circular buffer | 26.0 | 12.2 | 39.5 | 31COHE, 31PLAND, 46LPI, 46PLAND and 46COHE |
| 500-m circular buffer | 43.9 | 25.2 | 71.6 | 21LSI, 21PLAND, 31LPI, 31PLAND, 42COHE, 42CONTIG, 42PLAND, 46LPI and 46PLAND |
| 1000-m circular buffer | 47.4 | 23.7 | 80.9 | 21AI, 21CONTIG, 21FRMN, 21LSI, 21SHMN, 31LPI, 32ED, 32LSI, 32PLAND, 42COHE, 42CONTIG, 42PLAND, 46ED, 46LPI and 46PLAND |
| 200-m riparian buffer | 38.2 | 20.3 | 60.1 | 32ED, 32PD, 32LSI, 32PLAND, 42AI, 42CONTIG, 46AI, 46CONTIG and 46SHMN |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Song, X.; Shao, G.; Hu, T. Effects of Land Use on Stream Water Quality in the Rapidly Urbanized Areas: A Multiscale Analysis. Water 2020, 12, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041123
Song Y, Song X, Shao G, Hu T. Effects of Land Use on Stream Water Quality in the Rapidly Urbanized Areas: A Multiscale Analysis. Water. 2020; 12(4):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041123
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yu, Xiaodong Song, Guofan Shao, and Tangao Hu. 2020. "Effects of Land Use on Stream Water Quality in the Rapidly Urbanized Areas: A Multiscale Analysis" Water 12, no. 4: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041123
APA StyleSong, Y., Song, X., Shao, G., & Hu, T. (2020). Effects of Land Use on Stream Water Quality in the Rapidly Urbanized Areas: A Multiscale Analysis. Water, 12(4), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041123






