Response of Salt Transport and Residence Time to Geomorphologic Changes in an Estuarine System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
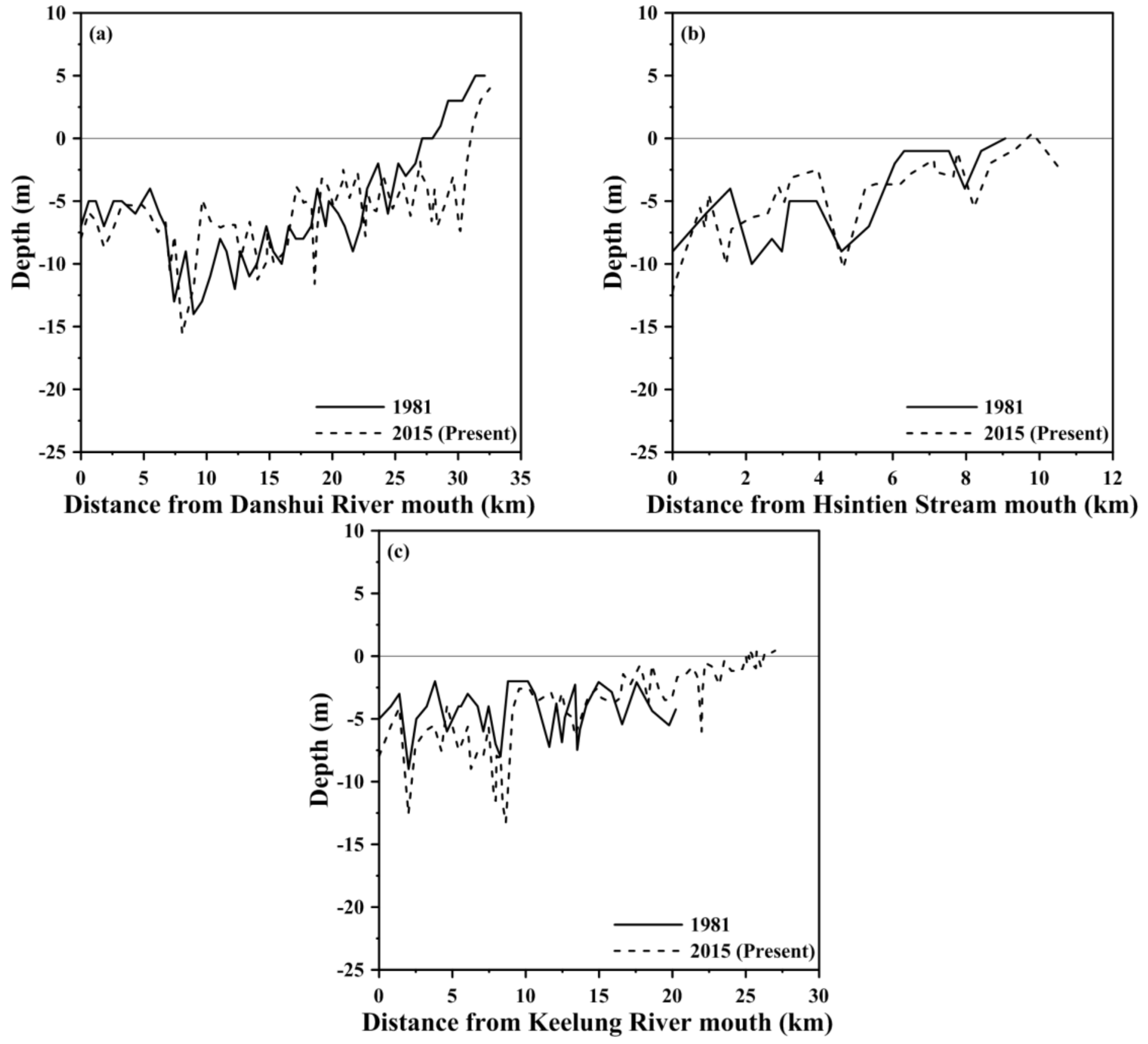
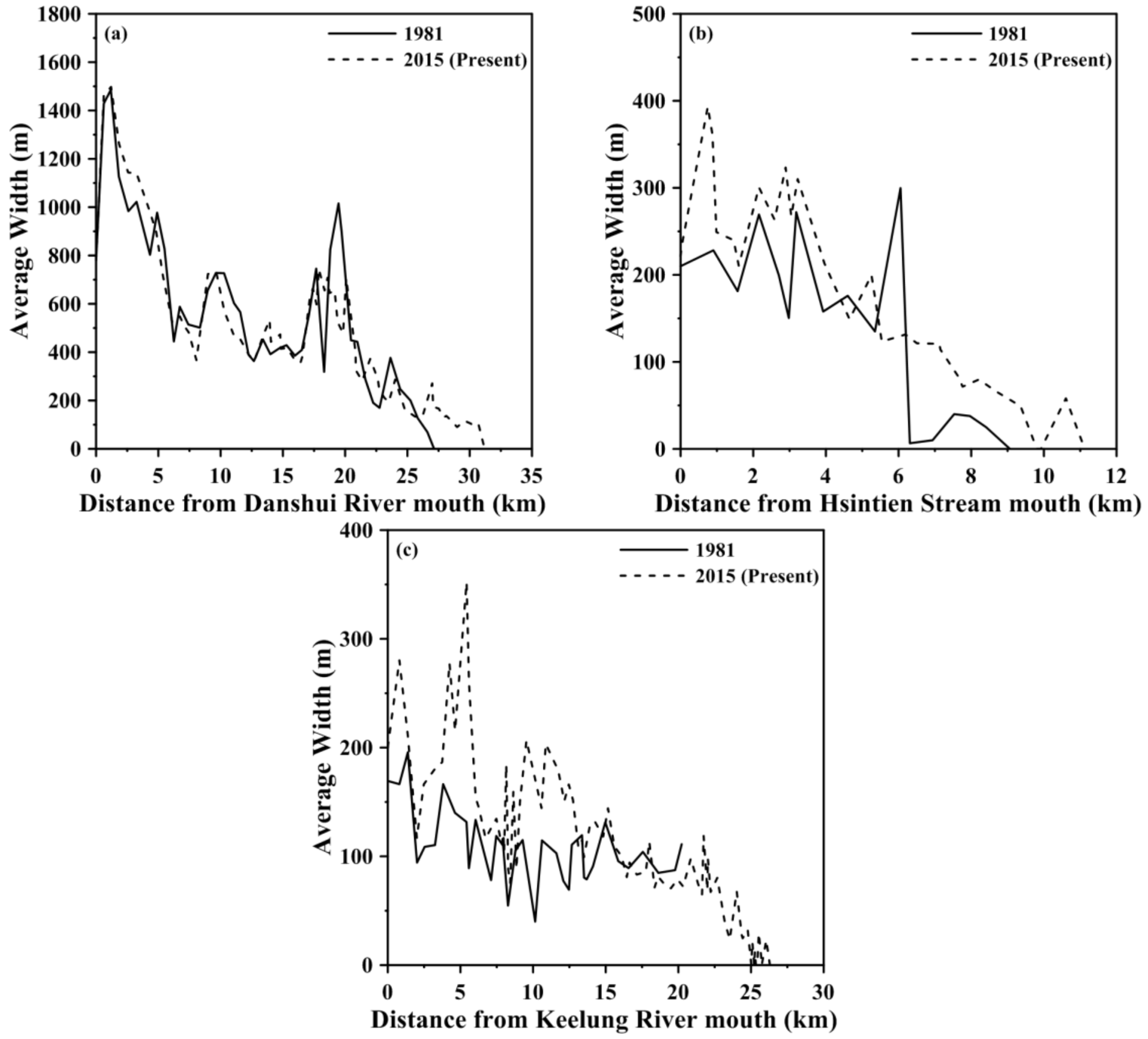
2. Site Description
3. Methods
3.1. Hydrodynamic Model
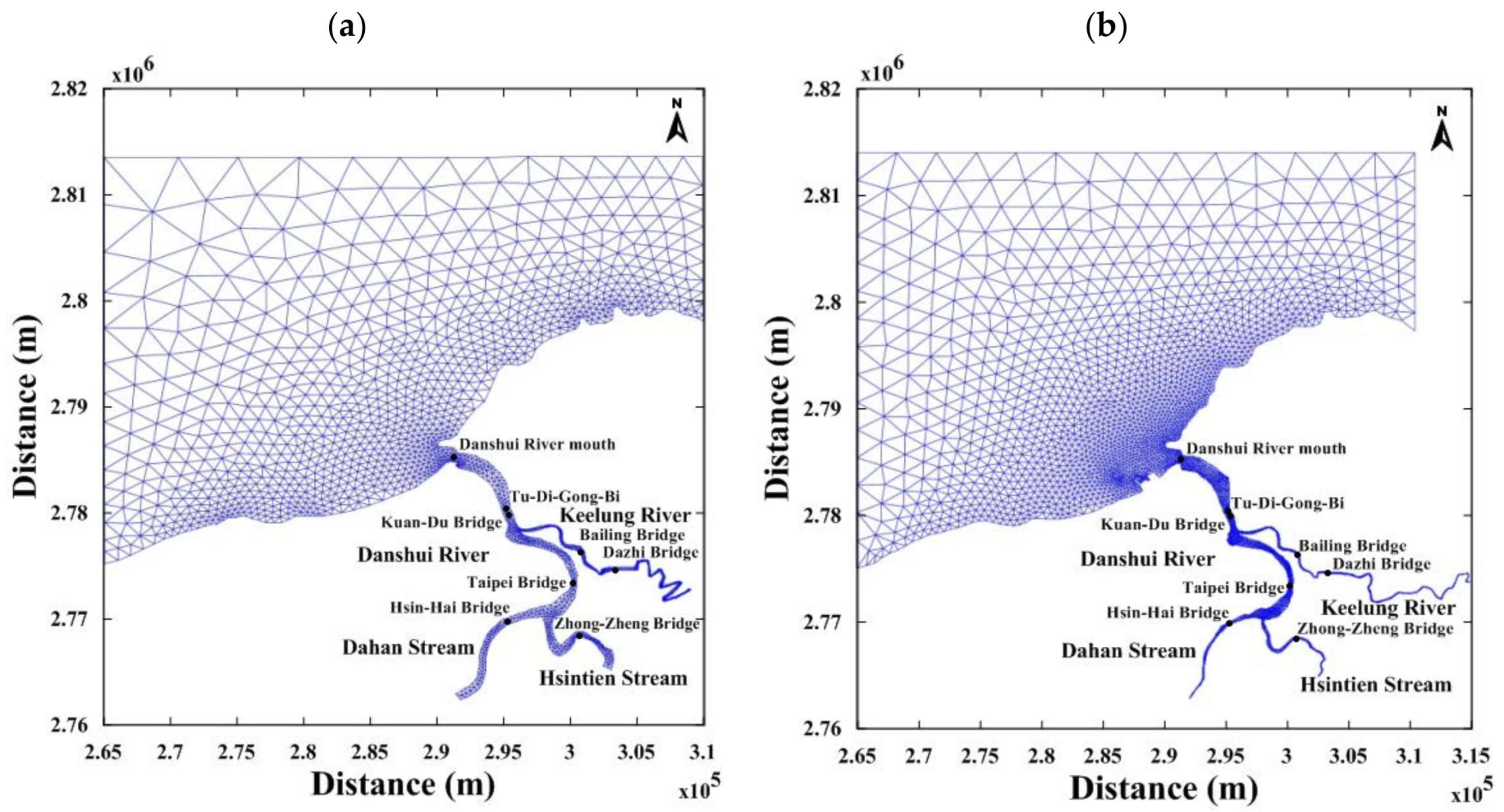
3.2. Grid Establishment for Computation
3.3. Boundary and Initial Conditions
3.4. Criteria for Model Performance
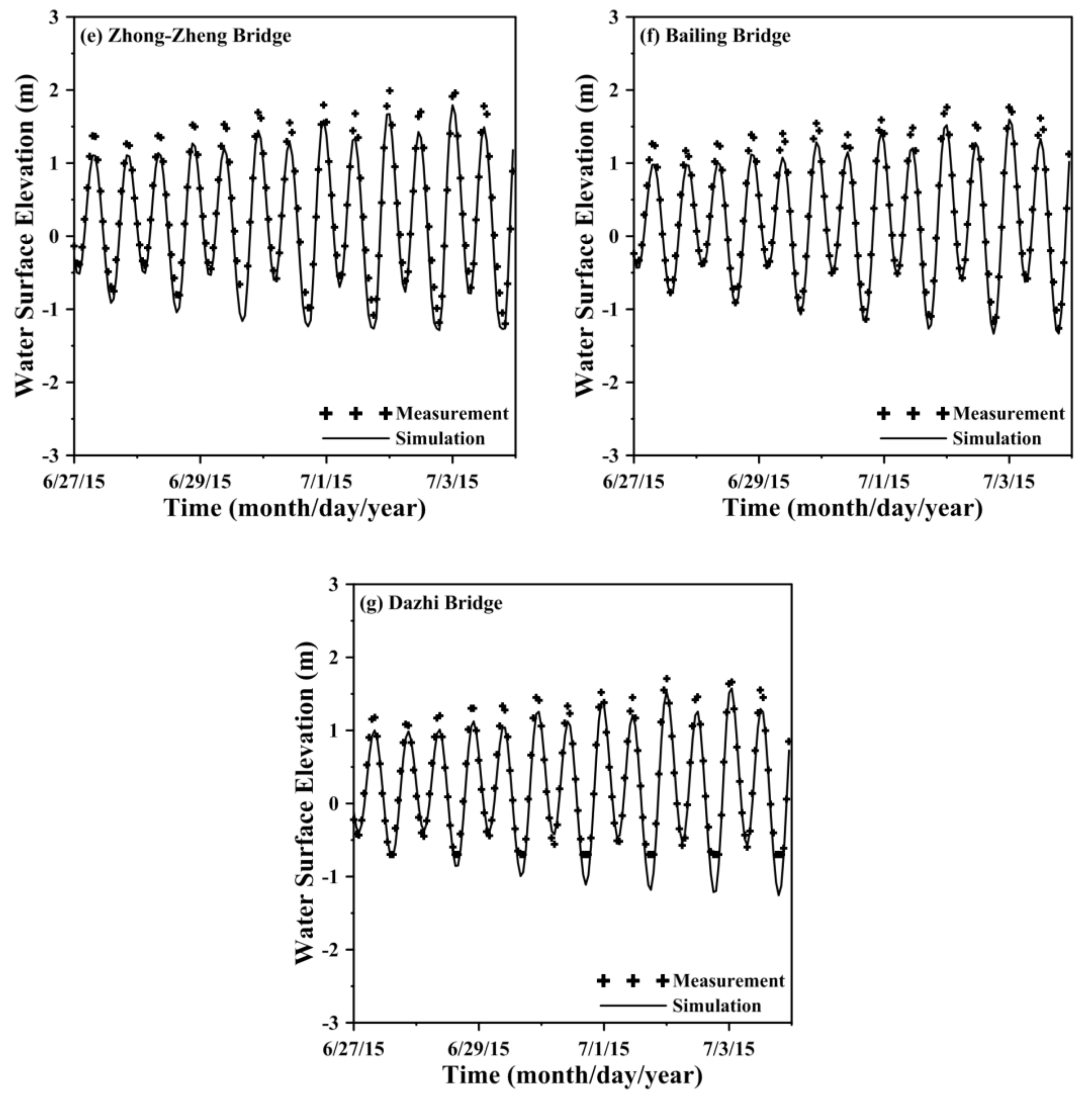
4. Model Calibration and Validation
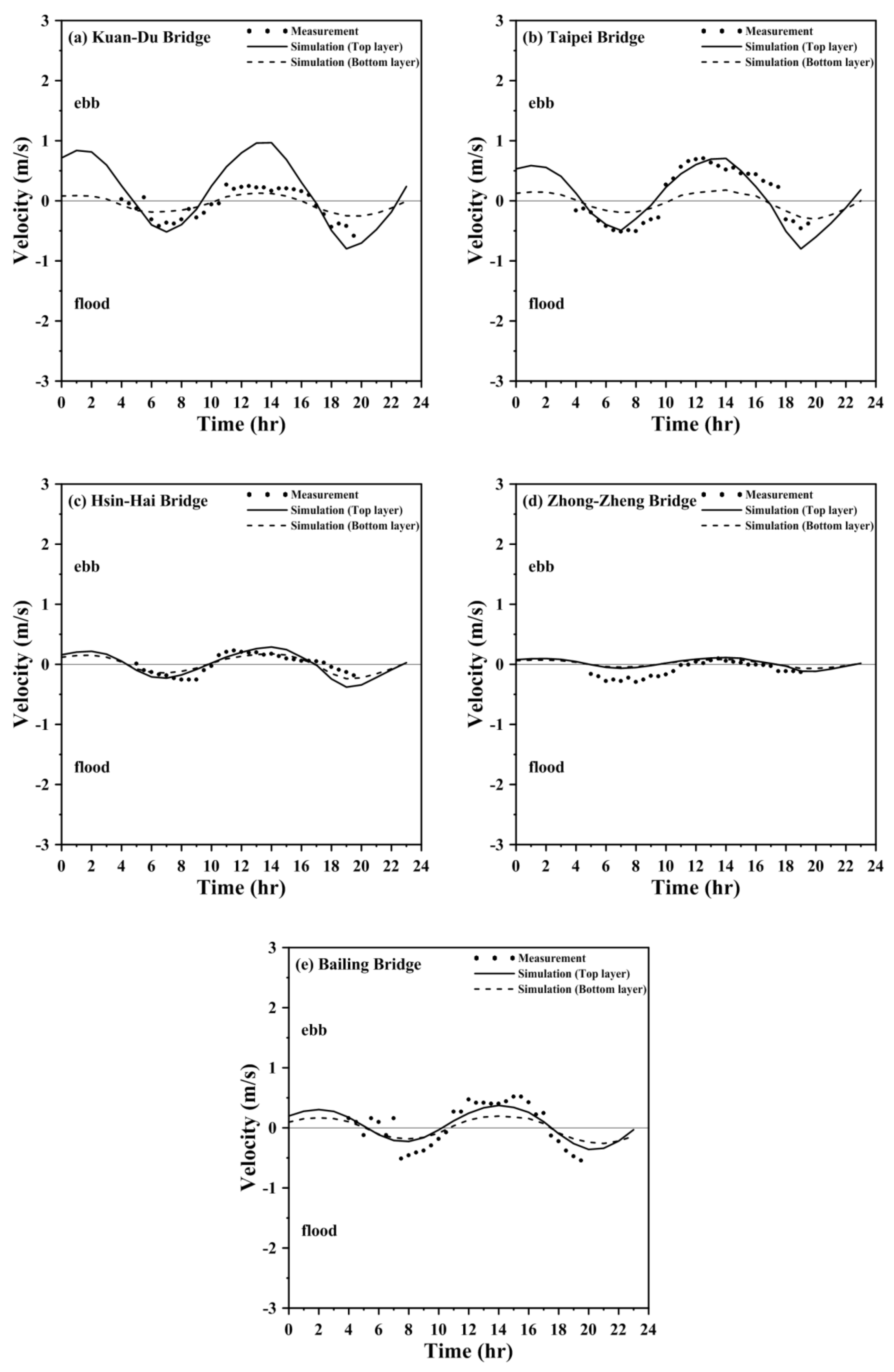
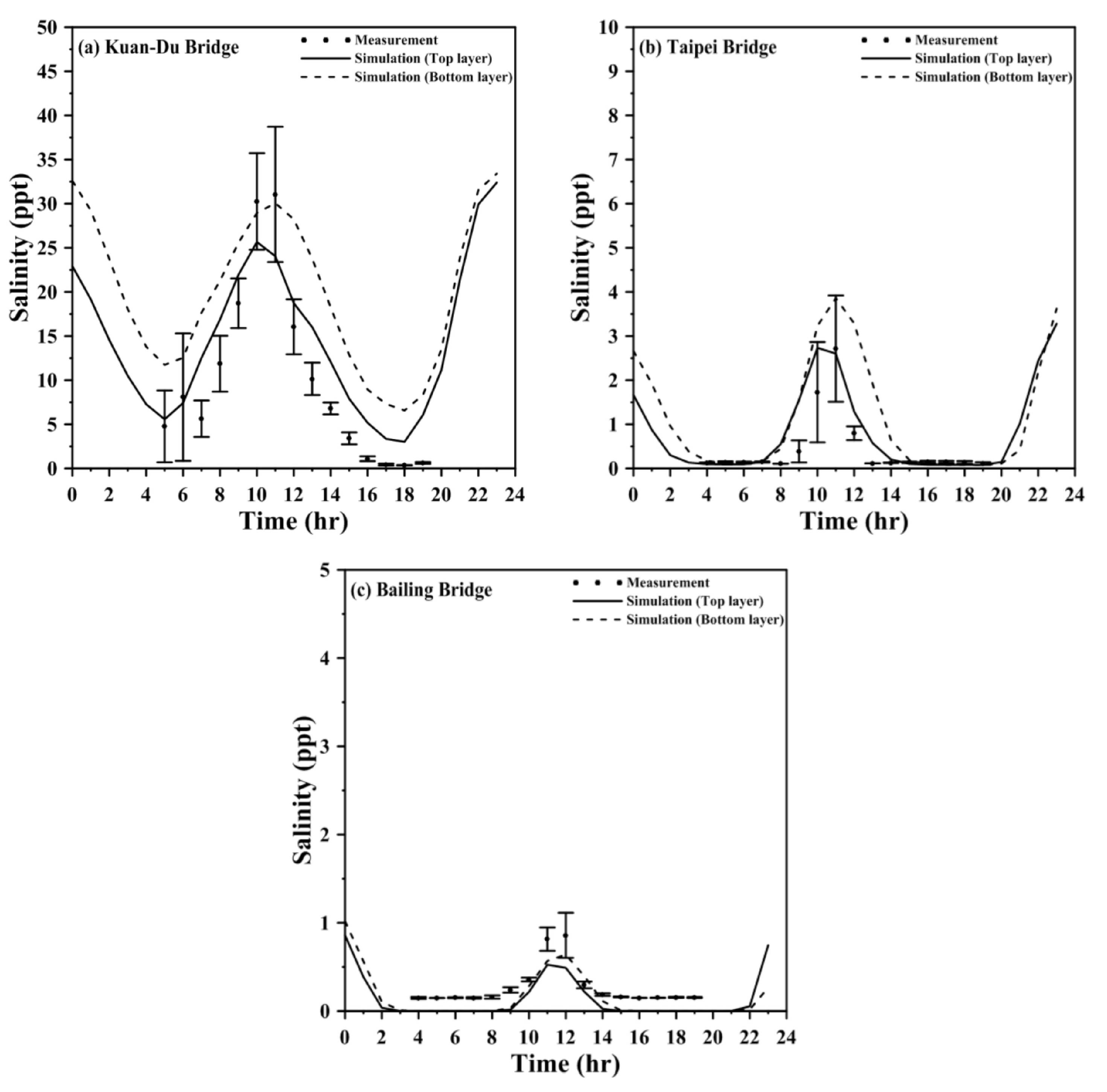
4.1. Model Calibration
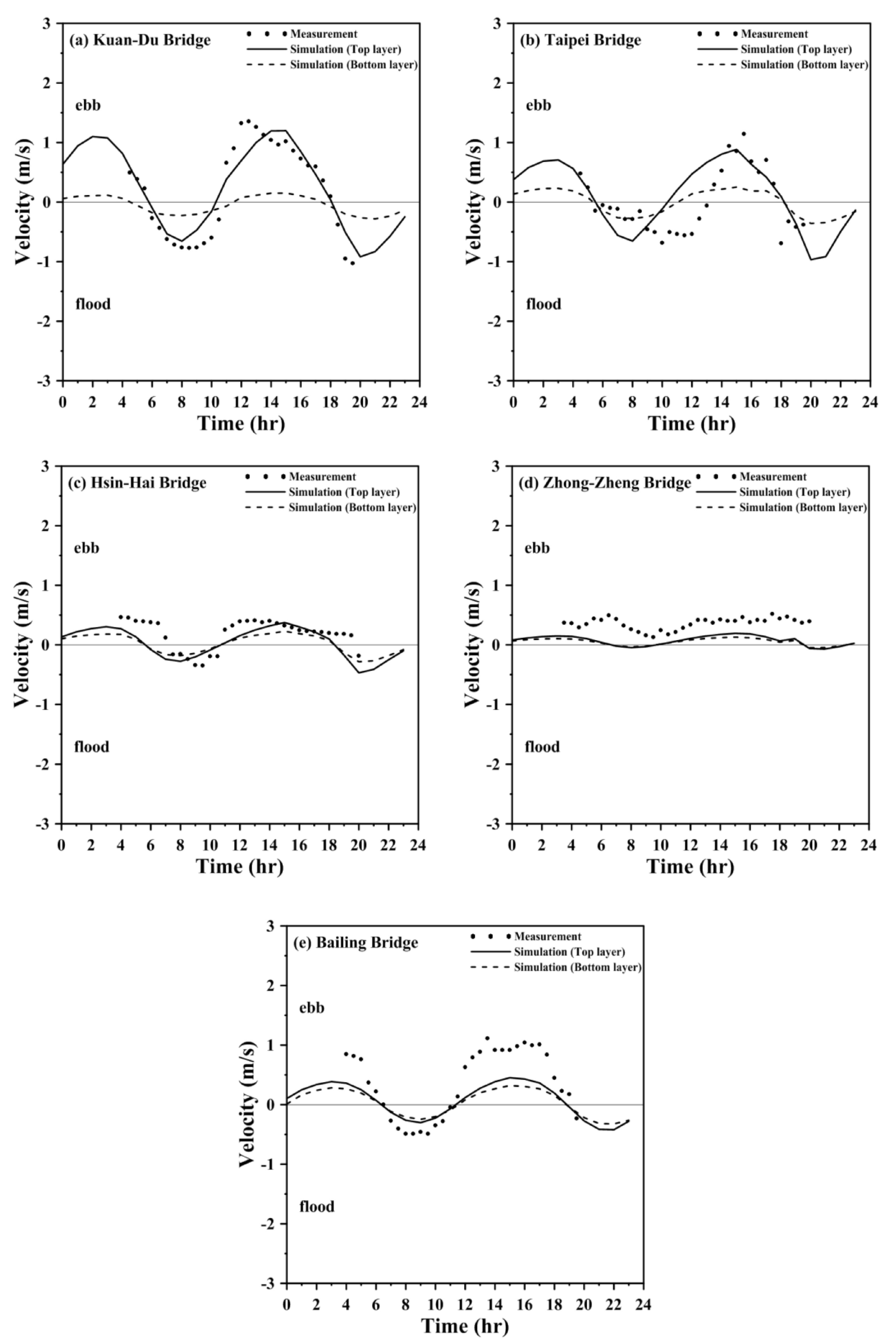
4.2. Model Validation
5. Results
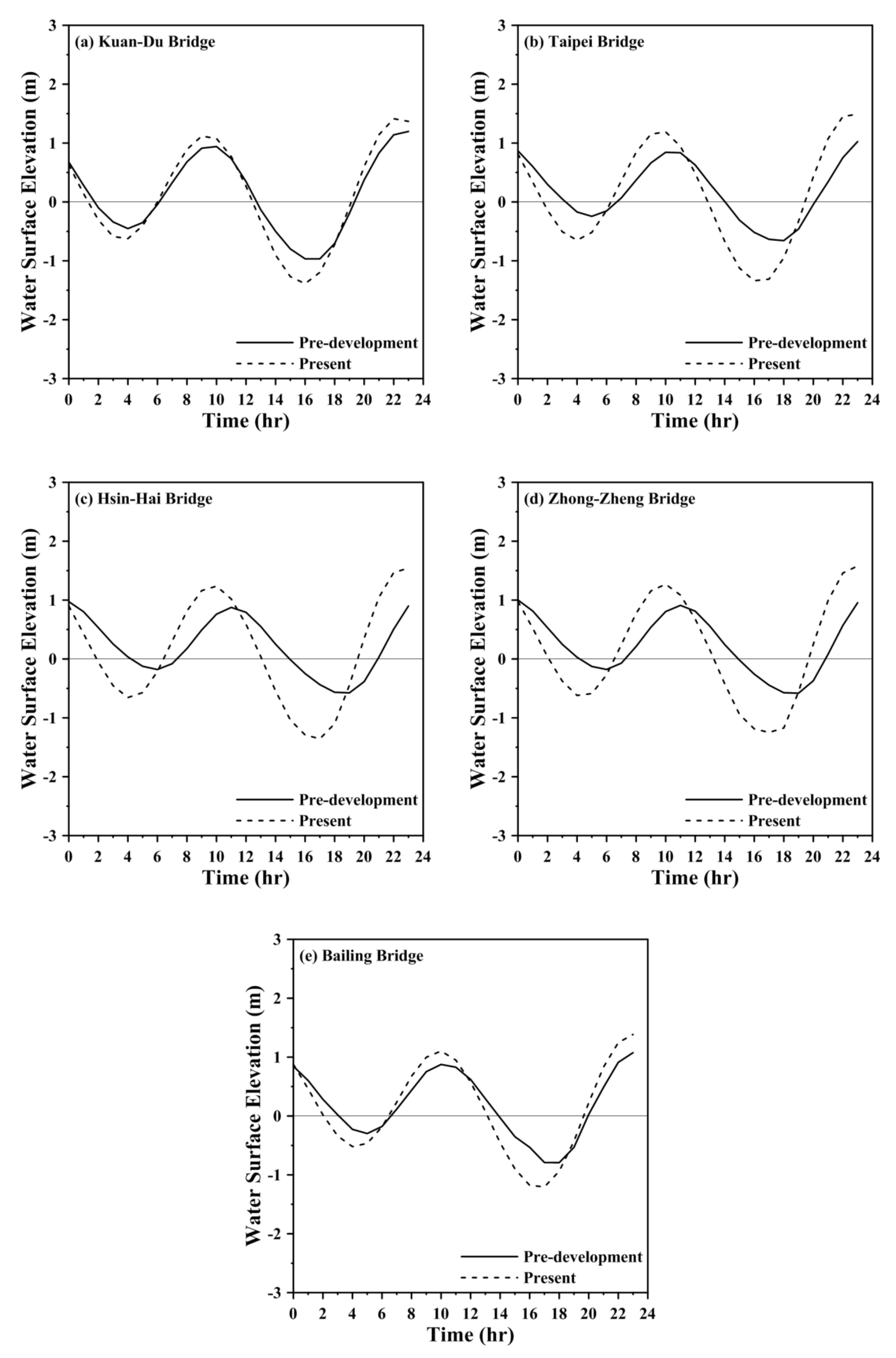
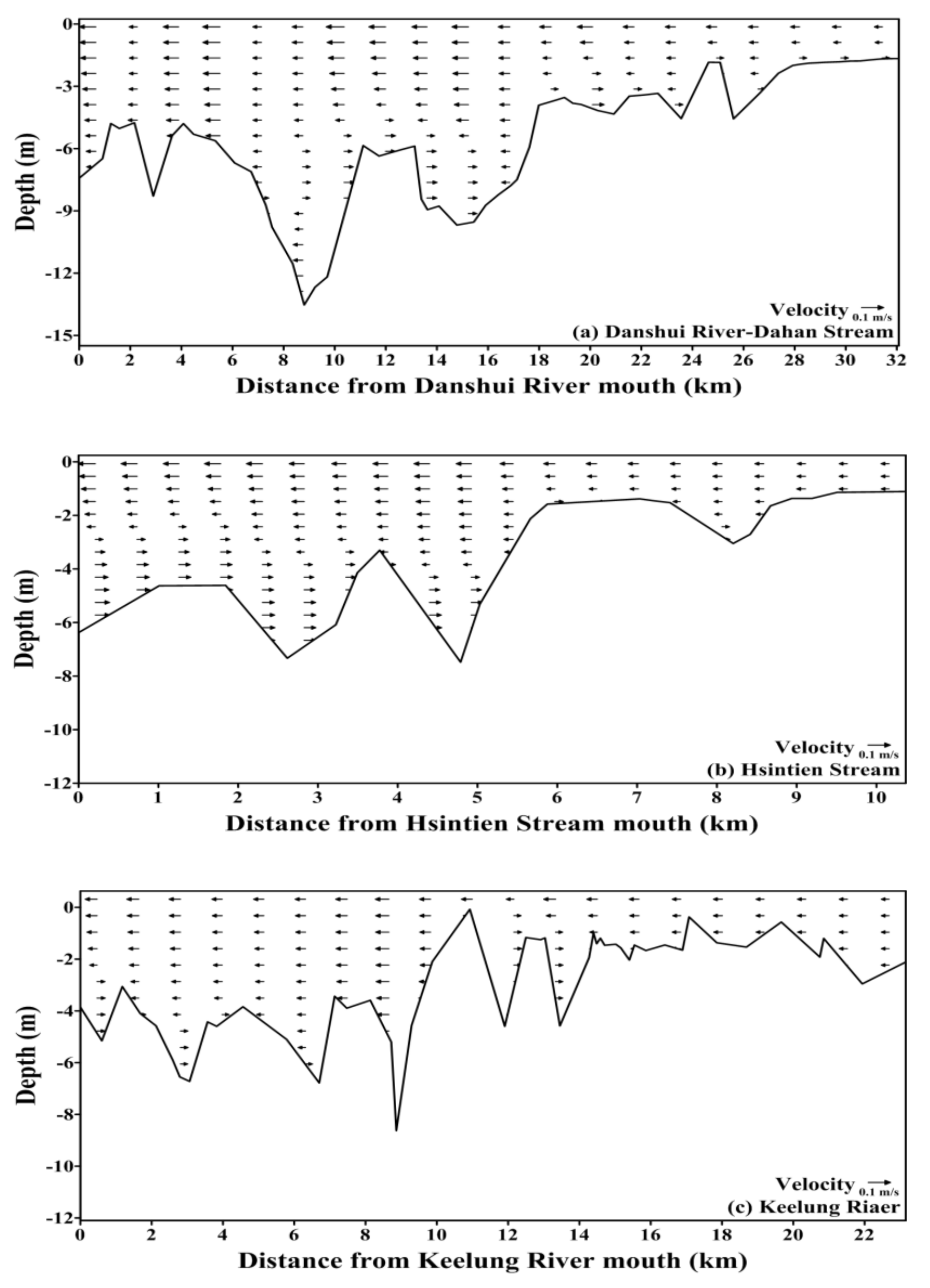
5.1. Water Levels and Residual Currents
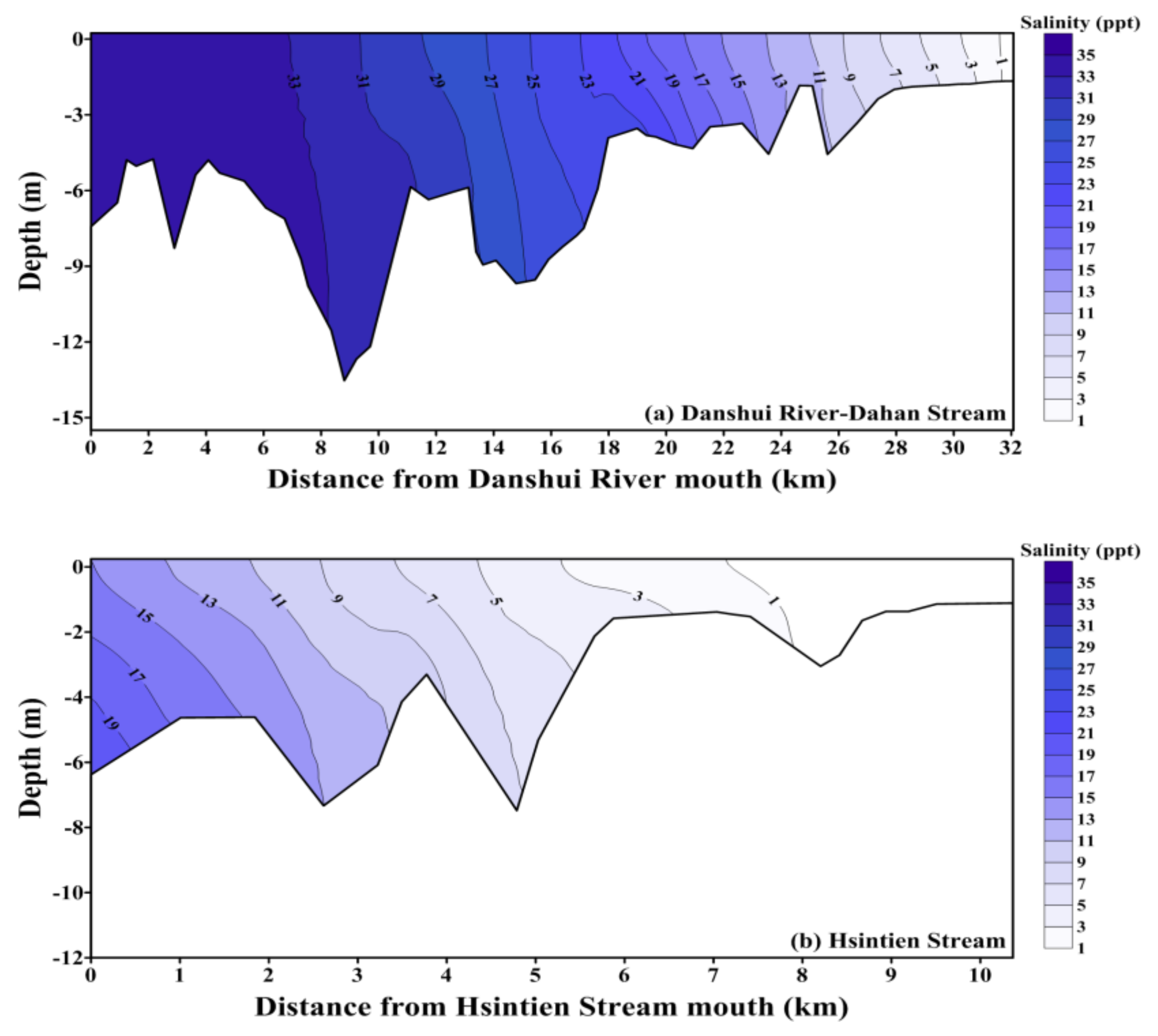
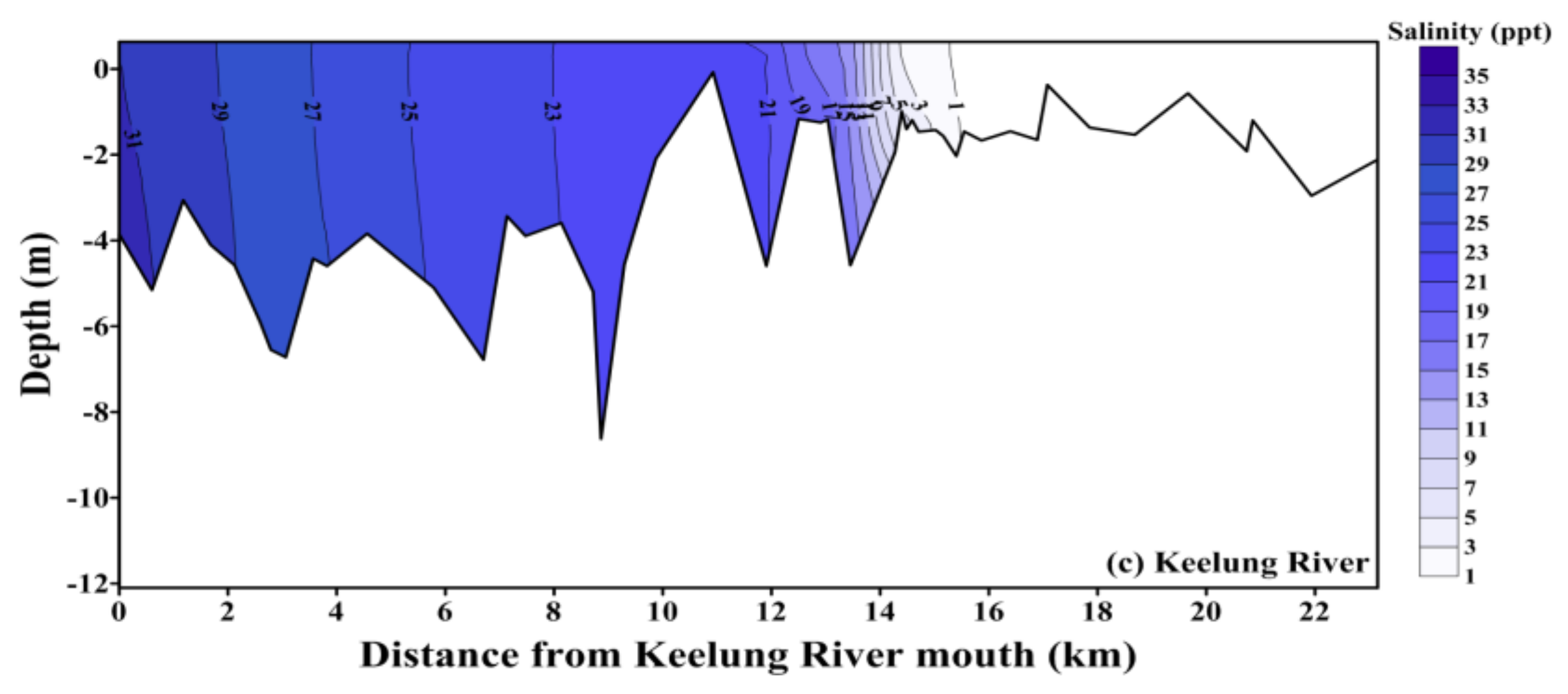
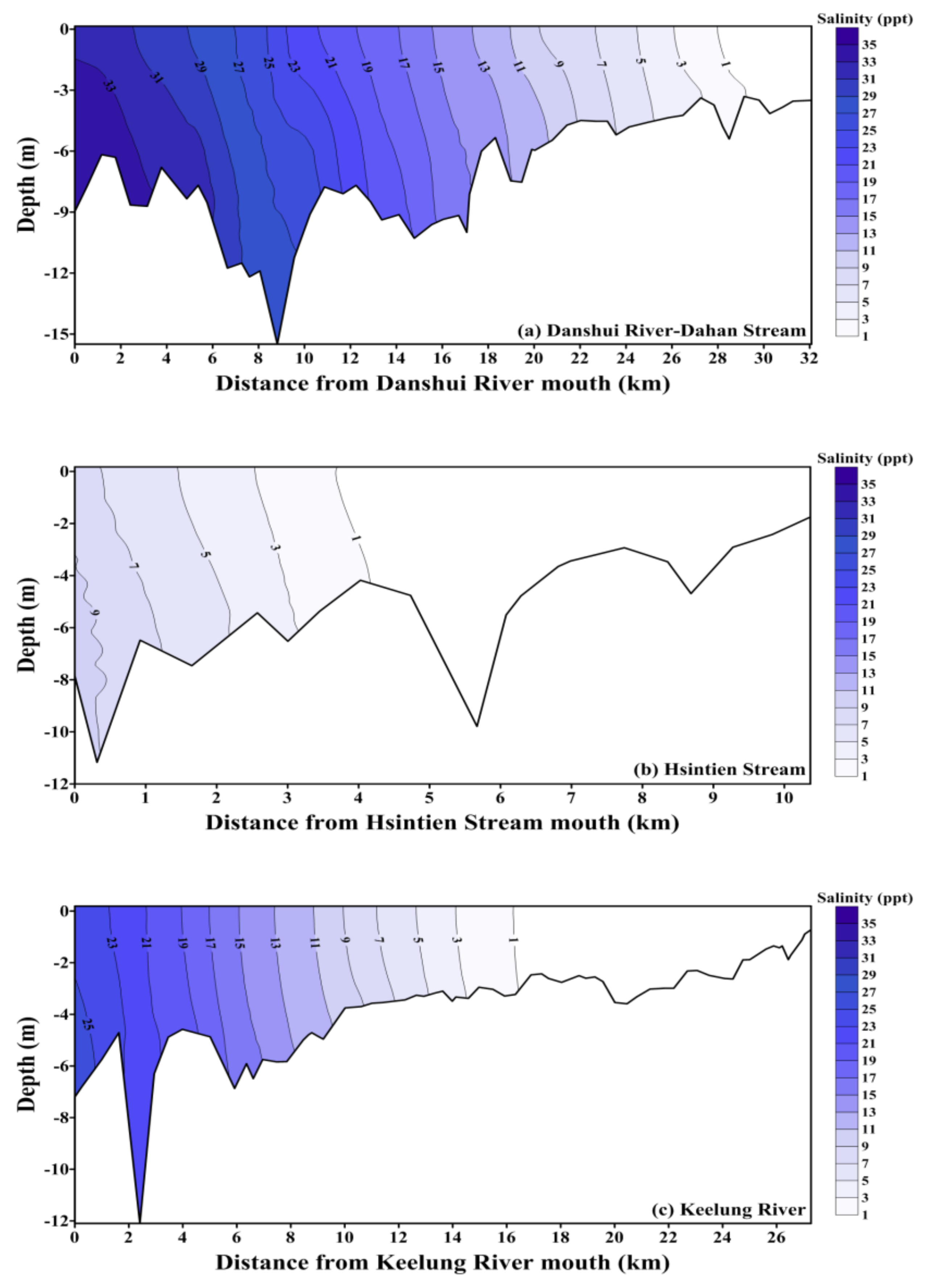
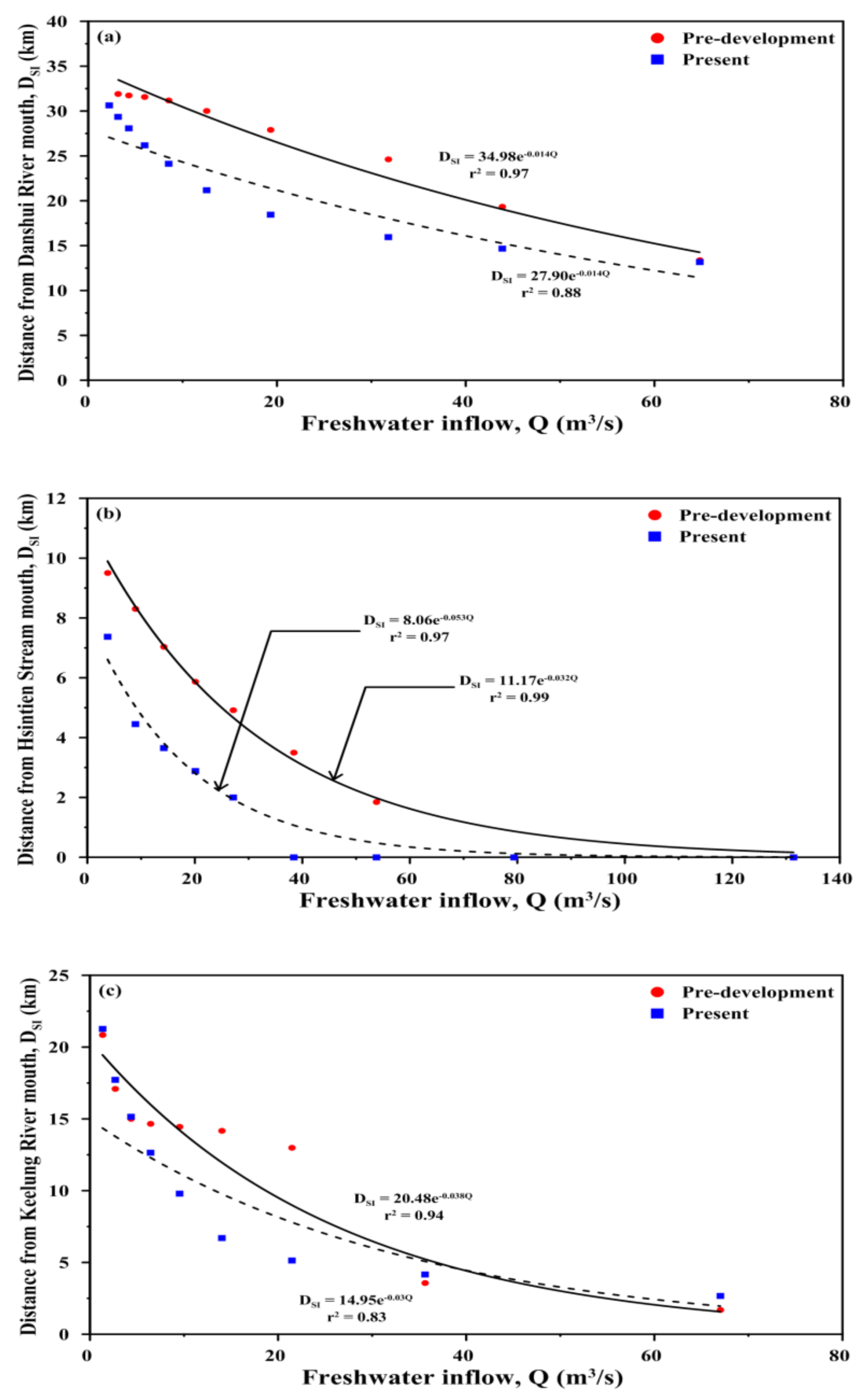
5.2. Saltwater Intrusion
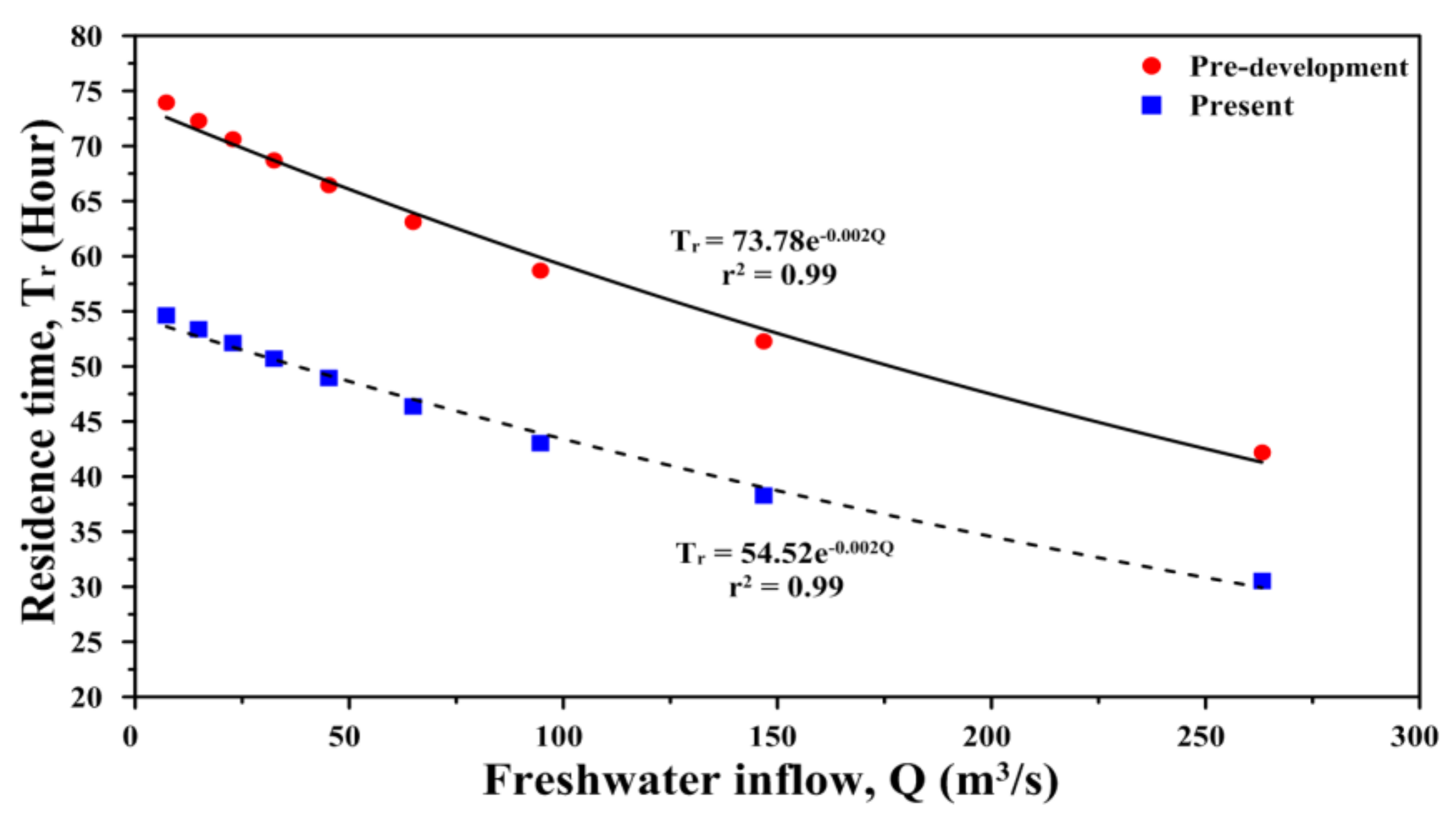
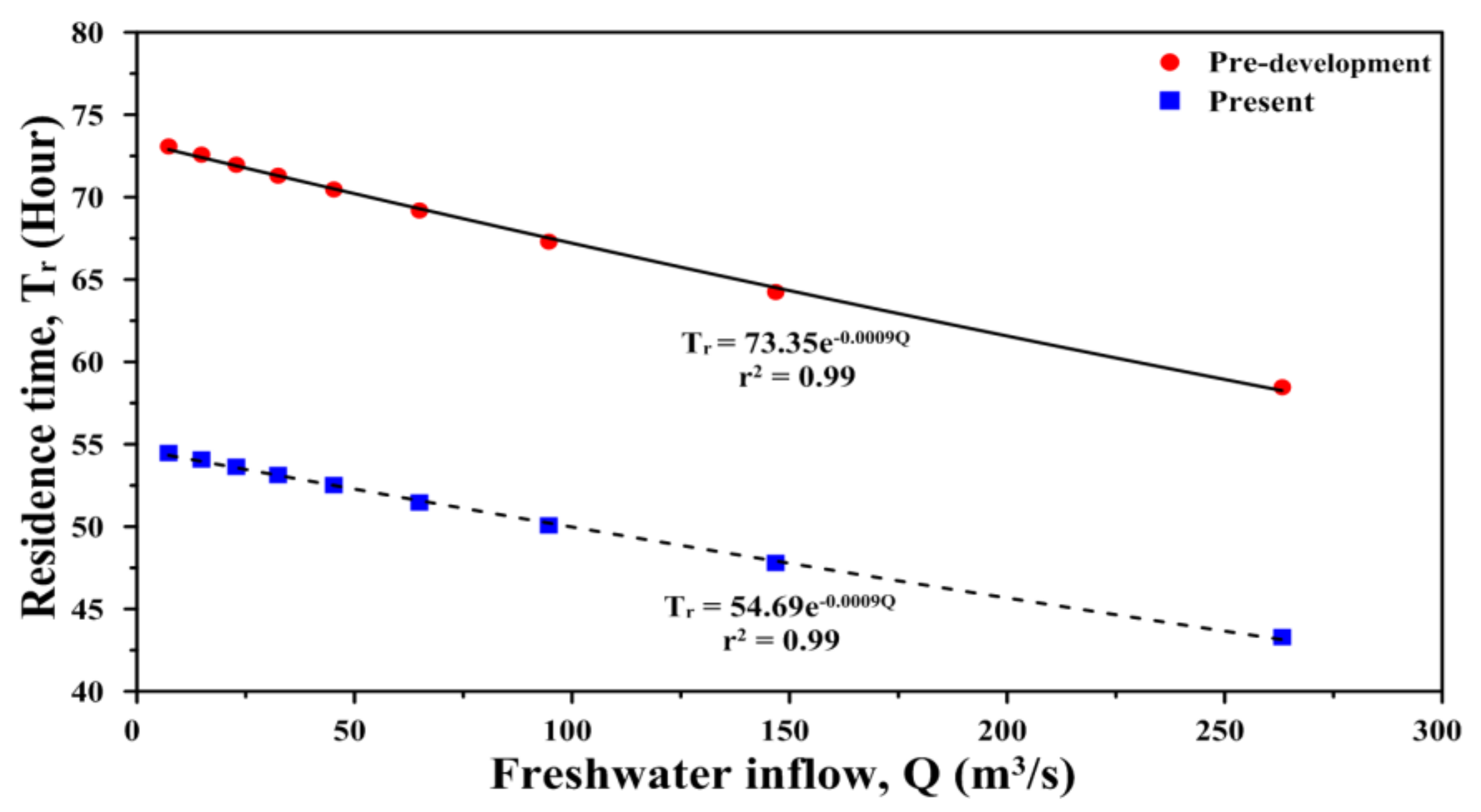
5.3. Residence Time
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dyer, K.R. Estuaries: A Physical Introduction; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997; p. 195. [Google Scholar]
- Valle-Levinson, A. Definition and classification of estuaries. In Contemporary Issues in Estuarine Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X. A sensitivity analysis of low salinity habitats simulated by a hydrodynamic model in the Manatee River estuary in Florida, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 104–105, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyr-Koller, R.C.; Kernkamp, H.W.J.; van Dam, A.; van der Wegen, M.; Lucas, L.V.; Knowles, N.; Jaffe, B.; Fregoso, T.A. Application of an unstructured 3D finite volume numerical model to flows and salinity dynamics in the San Francisco Bay-Delta. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 192, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Fortunato, A.B.; Regom, J.R.L. Effect of morphological changes on the hydrodynamics and flushing properties of the Obidos Lagoon (Portugal). Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 917–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Levinson, A. Density-driven exchange flow in terms of the Kelvin and Ekman numbers. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Shen, J.; Jia, J. The impact of human activities on the flushing properties of a semi-enclosed lagoon: Xiaohai, Hainan, China. Mar. Environ. Res. 2008, 65, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchard, H.; Hetland, R.D.; Schulz, E.; Schuttelaars, H.M. Diverse of residual estuarine circulation in tidally energetic estuaries: Straight and irrotational channels with parabolic cross section. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2011, 41, 548–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.; Whitefield, A.K. Challenging paradigms in estuarine ecology and management. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 94, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, G.M.E.; Perez, D.E.; Piccolo, M.C.; Palma, E.D.; Cuadrado, D.G. Geomorphologic and physical characteristics of a human impacted estuary: Quequen Grdnde River estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 62, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, A.J.; Uncles, R.J.; Villena-Lincoin, A.; Widdows, J. An assessment of the potential impact of dredging activity on the Tamar estuary over the last century: I. Bathymetric and hydrodynamic changes. Hydrobiologia 2007, 588, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Chen, W.B.; Wu, C.H. Modelling effects of realignment of Keelung River, Taiwan. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Mar. Eng. 2008, 161, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picado, A.; Dias, J.M.; Fortunato, A.B. Tidal changes in estuarine systems induced by local geomorphological modifications. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 1854–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Weisberg, R.H.; Zheng, L.Y.; Han, S.Z. Influences of channel deepening and widening on the tidal and nontidal circulations of Tampa Bay. Estuar. Coast. 2015, 38, 132–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velamala, S.N.; Thomas, J.; Bari, S.; Kachave, S. The impact of dredging on residence time in the Amba estuary, west coast of India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, S.D.; Moss, A.J.; Luther, M.E. Changes in residence time due to large-scale infrastructure in a coastal plain estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 33, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.; Meire, P.; Temmerman, S. Changing tidal hydrodynamics during different stages of ecogeomorphological development of a tidal marsh: A numerical modeling study. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 188, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Huang, W.C. Modeling the transport and distribution of fecal coliform in a tidal estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 431, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Jia, L.; Shen, J.; Liu, T.J. Sediment transport in response to changes in river discharge and tidal mixing in a funnel-shaped micro-tidal estuary. Cont. Shelf. Res. 2014, 76, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Shen, J. Decoupling the influence of biological and physical processes on the dissolved oxygen in the Chesapeake Bay. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Park, K.; Shen, J.; Dzwonkowski, B.; Yu, X.; Yoon, B., II. Role of baroclinic processes on flushing characteristics in a highly stratified estuarine system, Mobile Bay, Alabama. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 4518–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.C.; Ken, P.J.; Liu, H.M. Transport and distribution of manganese in tidal estuarine system in Taiwan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 510–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhadas, M.S.; Silva, A.; Leitao, P.C.; Neves, R. Effect of the bathymetric changes on the hydrodynamic and residence time in Obidos Lagoon (Portugal). J. Coast. Res. 2009, SI 56, 549–553. [Google Scholar]
- Passeri, D.L.; Hagen, S.C.; Medeiros, S.C.; Bilskie, M.V. Impacts of historic morphology and sea level rise on tidal hydrodynamics in a microtidal estuary (Grand Bay, Mississippi). Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 111, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Wan, Y.S.; Qiu, C. Three dimensional model evaluation of physical alternations of the Caloosahatchee River and Estuary: Impact on salt transport. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 173, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, A.R.; Plomaritis, T.; Reyns, J.; Ferreira, O.; Roelvink, D. Tidal circulation patterns in a coastal lagoon under sea-level rise. Ocean Dyn. 2018, 68, 1121–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, H.V.; Huang, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, X. Cross-scale baroclinic simulation of the effect of channel dredging in an estuarine settling. Water 2018, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, S.W.; Gross, E.S.; Hutton, P.H. Modeling salt intrusion in the San Francisco Estuary prior to anthropogenic influence. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 146, 58–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, M.; Jia, L.; Cai, H.; Chen, X. Impacts of physical alterations on salt transport during the dry season in the Modaomen Estuary, Pearl River Delta, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 227, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.H.; Kuo, A.Y.; Kuo, J.T.; Liu, W.C. Procedure to calibrate and verify numerical models of estuarine hydrodynamics. J. Hydrau. Eng. ASCE 1999, 125, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.S.; Jiann, K.T.; Liu, K.K. Seasonal variation and flux of dissolved nutrients in the Danshuei Estuary, Taiwan: A hypoxic subtropical mountain river. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 78, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.B.; Liu, W.C. Modeling investigation of asymmetric tidal mixing and residual circulation in a partially stratified estuary. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2016, 16, 167–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C. Modelling circulation and vertical mixing in estuaries. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Mar. Eng. 2006, 159, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemad-Shahidi, A.; Shahkolahi, A.; Liu, W.C. Modeling of hydrodynamics and cohesive sediment processes in an estuarine system: Study case in Danshui River. Environ. Model. Assess. 2010, 15, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Baptista, A.M. SELFE: A semi-implicit Eulerian-Lagrangian finite element model for cross-scale ocean model. Ocean Model. 2008, 21, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Haidvogel, D. A semi-implicit ocean circulation model using a generalized topography-following coordinate system. J. Comput. Phys. 1994, 115, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umlauf, L.; Buchard, H. A generic length-scale equation for geophysical turbulence models. J. Mar. Res. 2003, 61, 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodi, W. Turbulence Models and Their Applications in Hydraulics: A State of the Art Review; International Association for Hydraulics Research: Delft, The Netherlands, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Canuto, V.M.; Howard, A.; Cheng, Y.; Dubovikov, M.S. Ocean turbulence. Part I: One-point closure model-momentum and heat vertical diffusivities. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the validation of models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karna, T.; Baptista, A.M. Evaluation of long-term hindcast simulation for the Columbia River estuary. Ocean Model. 2016, 99, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Li, L.; He, Z.; Kalhoro, N.A.; Xu, D. Numerical modelling study of seawater intrusion in Indus River Estuary, Pakistan. Ocean Eng. 2019, 184, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, K.; Kuang, C.; Zhu, D.Z.; He, L.; Mao, X.; Liang, H.; Song, H. Influence of sea level rise on saline water intrusion in the Yangtz River Estuary, China. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 54, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, W.R.; MacCreeady, P. The estuarine circulation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2014, 46, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmerer, W.J. Effects of freshwater flow on abundance of estuarine organisms: Physical effect or trophic linkage? Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 243, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, L.P.; Boicourt, W.C.; Rives, S.R. Model for estimating tidal flushing of small embayments. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1992, 118, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luketina, D. Simple tidal prism model revisited. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1998, 46, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W. Hydrodynamic modeling of flushing time in a small estuary of North Bay, Florida, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 74, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Flannery, M.S. Critical flow for water management in a shallow tidal river based on estuarine residence time. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 2367–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhan, V.C. Advances in Coastal Modeling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 67. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, A.; Baptista, A.M. Diagnostic modeling of residence time in estuaries. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1935–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Shen, J.; Bilkovic, D.M.; Hershner, C.H.; Sisson, M. A numerical modeling approach to predict the effect of a storm surge barrier on hydrodynamics and long-term transport processes in a partially mixed estuary. Estuar. Coast. 2017, 40, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.D.; Linville, A.J.; Luther, M.E. Alteration of residual circulation due to large-scale infrastructure in a coastal plain estuary. Estuar. Coast. 2014, 37, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monismith, S.G.; Kimmerer, W.; Burau, J.R.; Stacey, M.J. Structure and flow-induced variability of salt intrusion in San Francisco Bay. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 3003–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hetlands, R.; Geyer, W. An idealized study of the structure of long, partially mixed estuaries. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 2677–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Khangaonkar, T. Modeling tidal circulation and stratification in Skagit River estuary using an unstructured grid ocean model. Ocean Model. 2009, 28, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacWilliams, M.L.; Bever, A.J.; Gross, E.S.; Ketefian, G.S.; Kimmerer, W.J. Three-dimensional modeling of hydrodynamic and salinity in the San Francisco Estuary: And evaluation of model accuracy, X2, and the low salinity zone. San Franc. Estuary Watershed Sci. 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.F.; Hsu, M.H.; Kuo, A.Y. Residence time of the Danshui River estuary, Taiwan. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganju, N.K.; Jaffe, B.E.; Schoellhamer, D.V. Discontinuous hindcast simulations of estuarine bathymetric change: A case study from Suisun Bay, California. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



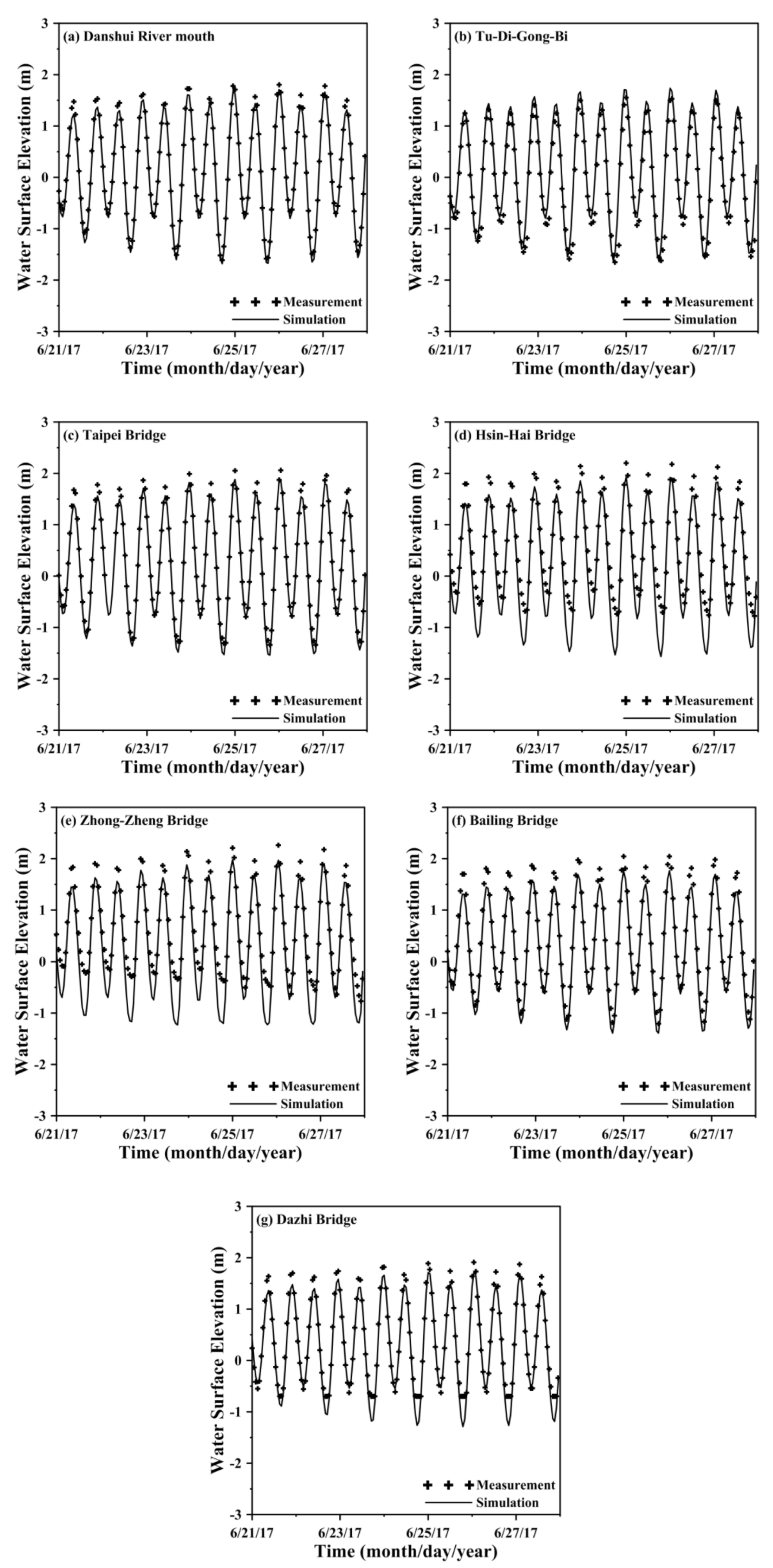

| Date (Period) | Error Index | Model Calibration | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Danshui River Mouth | Tu-Di-Gong-Bi | Taipei Bridge | Hsin-Hai Bridge | Zhong-Zheng Bridge | Bailing Bridge | Dazhi Bridge | ||
| 27 June ~ 3 July 2015 | MAE (m) | 0.041 | 0.263 | 0.106 | 0.258 | 0.188 | 0.142 | 0.142 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.051 | 0.323 | 0.130 | 0.316 | 0.219 | 0.164 | 0.178 | |
| r | 0.998 | 0.952 | 0.994 | 0.956 | 0.987 | 0.995 | 0.982 | |
| Skill | 0.999 | 0.960 | 0.994 | 0.964 | 0.983 | 0.989 | 0.985 | |
| 1 ~ 7 July 2016 | MAE (m) | 0.052 | 0.153 | 0.078 | 0.440 | 0.435 | 0.134 | 0.172 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.063 | 0.235 | 0.097 | 0.596 | 0.655 | 0.163 | 0.211 | |
| r | 0.999 | 0.970 | 0.997 | 0.927 | 0.877 | 0.985 | 0.970 | |
| Skill | 0.999 | 0.985 | 0.998 | 0.883 | 0.830 | 0.991 | 0.984 | |
| 21 ~ 27 June 2017 | MAE (m) | 0.081 | 0.240 | 0.111 | 0.367 | 0.343 | 0.195 | 0.142 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.096 | 0.307 | 0.136 | 0.443 | 0.425 | 0.219 | 0.190 | |
| r | 0.998 | 0.968 | 0.995 | 0.953 | 0.961 | 0.995 | 0.985 | |
| Skill | 0.998 | 0.975 | 0.996 | 0.946 | 0.946 | 0.986 | 0.988 | |
| Date | Error Index | Model Calibration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kuan-Du Bridge | Taipei Bridge | Hsin-Hai Bridge | Zhong-Zheng Bridge | Bailing Bridge | ||
| 30 June 2015 | MAE (m/s) | 0.113 | 0.188 | 0.082 | 0.110 | 0.193 |
| RMSE (m/s) | 0.159 | 0.211 | 0.098 | 0.136 | 0.208 | |
| r | 0.950 | 0.922 | 0.822 | 0.859 | 0.867 | |
| Skill | 0.926 | 0.917 | 0.901 | 0.672 | 0.827 | |
| 4 July 2016 | MAE (m/s) | 0.128 | 0.302 | 0.232 | 0.239 | 0.337 |
| RMSE (m/s) | 0.162 | 0.331 | 0.262 | 0.260 | 0.383 | |
| r | 0.961 | 0.898 | 0.764 | 0.703 | 0.965 | |
| Skill | 0.957 | 0.828 | 0.642 | 0.501 | 0.742 | |
| 24 June 2017 | MAE (m/s) | 0.398 | 0.347 | 0.189 | 0.293 | 0.385 |
| RMSE (m/s) | 0.450 | 0.426 | 0.223 | 0.304 | 0.444 | |
| r | 0.950 | 0.613 | 0.755 | 0.429 | 0.980 | |
| Skill | 0.849 | 0.739 | 0.769 | 0.341 | 0.741 | |
| Date | Error Index | Model Calibration | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kuan-Du Bridge | Taipei Bridge | Bailing Bridge | ||
| 30 June 2015 | MAE (ppt) | 4.544 | 1.238 | 0.498 |
| RMSE (ppt) | 4.995 | 1.655 | 0.648 | |
| r | 0.931 | 0.968 | 0.942 | |
| Skill | 0.842 | 0.918 | 0.955 | |
| 4 July 2016 | MAE (ppt) | 5.508 | 0.155 | 0.251 |
| RMSE (ppt) | 6.404 | 0.287 | 0.326 | |
| r | 0.885 | 0.883 | 0.939 | |
| Skill | 0.825 | 0.836 | 0.812 | |
| 24 June 2017 | MAE (ppt) | 5.942 | 0.425 | 0.148 |
| RMSE (ppt) | 6.414 | 0.691 | 0.157 | |
| r | 0.928 | 0.899 | 0.974 | |
| Skill | 0.880 | 0.860 | 0.881 | |
| Flow Condition | Dahan Stream (m3/s) | Hsintien Stream (m3/s) | Keelung River (m3/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q10 | 64.78 | 131.36 | 67.00 |
| Q20 | 31.79 | 79.40 | 35.66 |
| Q30 | 19.33 | 53.80 | 21.50 |
| Q40 | 12.55 | 38.37 | 14.00 |
| Q50 | 8.52 | 27.10 | 9.53 |
| Q60 | 5.98 | 20.08 | 6.46 |
| Q70 | 4.32 | 14.22 | 4.38 |
| Q80 | 3.19 | 9.01 | 2.72 |
| Q90 | 2.19 | 3.76 | 1.33 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.-C.; Ke, M.-H.; Liu, H.-M. Response of Salt Transport and Residence Time to Geomorphologic Changes in an Estuarine System. Water 2020, 12, 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041091
Liu W-C, Ke M-H, Liu H-M. Response of Salt Transport and Residence Time to Geomorphologic Changes in an Estuarine System. Water. 2020; 12(4):1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041091
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wen-Cheng, Min-Hsin Ke, and Hong-Ming Liu. 2020. "Response of Salt Transport and Residence Time to Geomorphologic Changes in an Estuarine System" Water 12, no. 4: 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041091
APA StyleLiu, W.-C., Ke, M.-H., & Liu, H.-M. (2020). Response of Salt Transport and Residence Time to Geomorphologic Changes in an Estuarine System. Water, 12(4), 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041091






