Transparent Exopolymer Particle (TEPs) Dynamics and Contribution to Particulate Organic Carbon (POC) in Jaran Bay, Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alldredge, A.L.; Passow, U.; Logan, B.E. The abundance and significance of a class of large, transparent organic particles in the ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part I 1993, 40, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passow, U. Transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in aquatic environments. Prog. Oceanogr. 2002, 55, 287–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Reche, I.; Pulido-Villena, E.; Agustí, S.; Duarte, C.M. Uncoupled distributions of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) and dissolved carbodydrates in the Southern Ocean. Mar. Chem. 2009, 115, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpezzi, M.A.; Sanford, L.P.; Crump, B.C. Abundance and distribution of transparent exopolymer particles in the estuarine turbidity maximum of Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 486, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, X.; Passow, U.; Migon, C.; Burd, A.B.; Legendre, L. Transparent exopolymer particles: Effects on carbon cycling in the ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2017, 151, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, Y.; Yokokawa, T.; Uchimiya, M.; Nishino, S.; Fukuda, H.; Ogawa, H.; Nagata, T. Transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in the deep oceaen: Full-depth distribution patterns and contribution to the organic carbon pool. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 583, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Precali, R.; Giani, M.; Marini, M.; Grilli, F.; Ferrari, C.R.; Pečar, O.; Paschinic, E. Mucilaginous aggregates in the northern Adriatic in the period 1999–2002: Typology and distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 353, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauvais, S.; Pedrotti, M.L.; Egge, J.; Iversen, K.; Marrasé, C. Effects of turbulence on TEP dynamics under contrasting nutrient conditions: Implications for aggregation and sedimentation processes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 323, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamanillo, M.; Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Nunes, S.; Rodríguez-Ros, P.; DalľOsto, M.; Estrada, M.; Sala, M.M.; Simó, R. Main drivers of transparent exopolymer particle distribution across the surface Atlantic Ocean. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passow, U.; Alldredge, A.L. Distribution, size and bacterial colonization of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in the ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 113, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passow, U.; Shipe, R.F.; Murray, A.; Pak, D.K.; Brzezinski, M.A.; Alldredge, A.L. The origin of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) and their role in the sedimentation of particulate matter. Cont. Shelf Res. 2001, 21, 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engel, A.; Passow, U. Carbon and nitrogen content of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in relation to their Alcian Blue adsorption. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 219, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mari, X.; Beauvais, S.; Lemée, R.; Pedotti, M.L. Non-Redfield C:N ratio of transparent exopolymetric particles in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 1831–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, A.; Thoms, S.; Riebesell, U.; Rochelle-Newall, E.; Zondervan, I. Polysaccharide aggregation as a potential sink of marine dissolved organic carbon. Nature 2004, 428, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De La Rocha, C.L.; Nowald, N.; Passow, U. Interactions between diatom aggregates, minerals, particulate organic carbon, and dissolved organic matter: Further implications for the ballast hypothesis. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gogou, A.; Repeta, D.J. Particulate-dissolved transformations as a sink for semi-labile dissolved organic matter: Chemical characterization of high molecular weight dissolved and surface-active organic matter in seawater and in diatom cultures. Mar. Chem. 2010, 121, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinos, C.; Gogou, A.; Krasakopoulou, E.; Lagaria, A.; Giannakourou, A.; Karageogis, A.P.; Psarra, S. Transparent Exopolymer Particles (TEP) in the NE Aegean Sea frontal area: Seasonal dynamics under the influence of Black Sea water. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 149, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passow, U.; Alldredge, A.L.; Logan, B.E. The role of particulate carbohydrate exudates in the flocculation of diatom blooms. Deep Sea Res. Part I 1994, 41, 335–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Claquin, P.; Pannard, A.; Napoléon, C.; Le Roy, B.; Véron, B. Dynamic of soluble extracellular polymeric substances and transparent exopolymer particle pools in coastal ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 427, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.C.; Wang, Y.S.; Li, Q.P.; Yue, W.Z.; Wang, Y.T.; Sun, F.L.; Peng, Y.L. Distribution characteristics of transparent exopolymer particles in the Pearl River estuary, China. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jennings, M.K.; Passow, U.; Wozniak, A.S.; Hansell, D.A. Distribution of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) asross an organic carbon gradient in the western North Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Chem. 2017, 190, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Marrasé, C.; Muñoz-Fernández, A.; Sala, M.M.; Simó, R.; Gasol, J.M. Seasonal dynamics of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) and their drivers in the coastal NW Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, B.E.; Passow, U.; Alldredge, A.L.; Grossart, H.P.; Simon, M. Rapid formation and sedimentation of large aggregates is predictable from coagulation rates (half-lives) of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP). Deep-Sea Res. Part II 1995, 42, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauvais, S.; Pedrotti, M.L.; Villa, E.; Lemée, R. Transparent exopolymer particle (TEP) dynamics in relation to trophic and hydrological conditions in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 262, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; Park, K. Eutrophication of bottom mud in shellfish farms, the Goseong-Jaran Bay. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1983, 16, 260–264. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, T.; Lee, W.C.; Kang, J.J.; Jo, N.; Lee, D.; Kim, K.; Min, J.; Kang, S.; et al. Monthly variations in the intracellular nutrient pools of phytoplankton in Jaran Bay, Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 85, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, H.H.; Atkins, R.G. Photo-electric Measurements of Submarine Illumination throughout the Year. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1929, 16, 297–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsons, T.R.; Maita, Y.; Lalli, C.M. A Manual of Biological and Chemical Methods for Seawater Analysis; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Passow, U.; Alldredge, A.L. A dye-binding assay for the spectrophotometric measurement of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP). Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Iwakuma, T.; Takahashi, M.; Otsuki, A.; Ichmura, S. Measurement of photosynthetic production of a marine phytoplankton population using a stable 13C isotope. Mar. Biol. 1983, 73, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, K.; Hare, C.E.; Feng, Y.; Berg, G.M.; DiTullio, G.R.; Neeley, A.; Benner, I.; Sprengel, C.; Beck, A.; Sanudo-Wilhemy, S.A.; et al. Distribution of calcifying and silicifying phytoplankton in relation to environmental and biogeochemical parameters during the late stages of the 2005 North East Atlantic Spring Bloom. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Duarte, C.M.; Reche, I. Significance of Bacterial Activity for the Distribution and Dynamics of Transparent Exopolymer Paticles in the Mediterranean Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wurl, O.; Miller, L.; Vagle, S. Production and fate of transparent exopolymer particles in the ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wetz, M.S.; Robbins, M.C.; Paerl, H.W. Transparent Exopolymer Particles (TEP) in a River-Dominated Estuary: Spatial-Temporal Distributions and an Assessment of Controls upon TEP Formation. Estuaries Coasts 2009, 32, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alldredge, A.L.; Passow, U.; Haddock, H.D. The characteristics and transparent exopolymer particle (TEP) content of marine snow formed from thecate dinoflagellates. J. Plankton Res. 1998, 20, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoderegger, K.E.; Herndl, G.J. Production of exopolymer particles by marine bacterioplankton under contrasting turbulence conditions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 189, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Yoon, Y.H.; Oh, S.J. Variational characteristics of phytoplankton community in the mouth parts of Gamak Bay, Southern Korea. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 27, 205–215. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.C.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, W.C.; Hong, S.; Kang, J.J.; Lee, D.; Jo, N.; Bhavya, P.S. Decoupling of Macromolecular compositions of particulate organic matters between the water columns and the sediment in Geoje-Hansan Bay, South Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2018, 53, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herndl, G.J. Microbial Dynamics in Marine Aggregates. In Seasonal Dynamics of Plankton Ecosystems and Sedimentation in Coastal Waters; Symposium Proceedings, NurmiPrint OY: Nurmijärvi, Finland, 1995; pp. 81–105. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, N.; Kawamura, T.; Mitamura, O.; Terai, H. Importance of extracellular organic carbon production in the total primary production by tidal-flat diatoms in comparison to phytoplankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 190, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chin, W.C.; Orellana, M.V.; Verdugo, P. Spontaneous assembly of marine dissolved organic matter in polymer gels. Nature 1998, 391, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.Y.; Ke, C.H.; Zhu, A.; Wang, W.X. Oyster-based national mapping of trace metals pollution in the Chinese coastal waters. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaiah, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Furuya, K. Temporal variations in transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) associated with a diatom spring bloom in a subarctic ria in Japan. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 212, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.M.; Prieto, L.; Vargas, M.; Echevarría, F.; García-Lafuente, J.; Ruiz, J.; Rubín, J.P. Hydrodynamics and the spatial distribution of plankton and TEP in the Gulf of Cádiz (SE Iberian Peninsula). J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corzo, A.; Rodríguez-Gálvez, S.; Lubian, L.; Sangrá, P.; Martínez, A.; Morillo, J.A. Spatial distribution of transparent exopolymer particles in the Branfield Strait, Antarctica. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhaskar, P.V.; Bhosle, N.B. Dynamics of transparent exopolymeric particles (TEP) and particle-associated carbohydrates in the Dona Paula bay, west coast of India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 115, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramaiah, N.; Furuya, K. Seasonal variations in phytoplankton composition and transparent exopolymer particles in a eutrophicated coastal environment. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 30, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Sun, X. Concentrations and distribution of transparent exopolymer particles in a eutrophic coastal sea: a case study of the Changjiang (Yangtze River) estuary. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2019, 70, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuculano, F.; Duarte, C.M.; Marbá, N.; Agustí, S. Seagrass as major source of transparent exopolymer particles in the oligotrophic Mediterranean coast. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 5069–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engel, A.; Meyerhöfer, M.; von Bröckel, K. Chemical and biological composition of suspended particles and aggregates in the Baltic Sea in summer (1999). Estuar. Coast. Shelf S. 2002, 55, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prieto, L.; Navarro, G.; Cózar, A.; Echevarría, F.; García, C.M. Distribution of TEP in the euphotic and upper mesopelagic zones of the southern Iberian coasts. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2006, 53, 1314–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, J.Y.; Radway, J.C.; Kilthau, W.P.; Bothe, D.W.; Wilson, T.W.; Vaillancourt, R.D.; Quinn, P.K.; Coffman, D.J.; Murray, B.J.; Knopf, D.A. Size-resolved characterization of the polysaccharidic and proteinaceous components of sea spray aerosol. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 154, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scoullos, M.; Plavšić, M.; Karavoltsons, S.; Sakellari, A. Partitioning and distribution of dissolved copper, cadmium and organic matter in Mediterranean marine coastal areas: The case of a mucilage event. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 67, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, A.; Piontek, J.; Metfies, K.; Endres, S.; Sprong, P.; Peeken, I.; Gäbler-Schwarz, S.; Nöthig, E.M. Inter-annual variability of transparent exopolymer particles in the Arctic Ocean reveals high sensitivity to ecosystem changes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, J.D.; Cottingham, S.D.; Billinge, J.; Cunliffe, M. Seasonal microbial community dynamics correlate with phytoplankton-derived polysaccharides in surface coastal waters. ISME J. 2014, 8, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreshchinskii, A.; Engel, A. Seasonal variations of the sea surface microlayer at the Boknis Eck Times Series Station (Baltic Sea). J. Plankton Res. 2017, 39, 943–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redfield, A.C.; Ketchum, B.H.; Richards, F.A. The Influence of Organisms on the Composition of Seawater, Comparative and Descriptive Oceanography; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1963; pp. 26–77. [Google Scholar]
- Dortch, Q.; Whitledge, T.E. Does nitrogen or silicon limit phytoplankton production in the Mississippi River plume and nearby regions? Cont. Shelf Res. 1992, 12, 1293–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justíc, D.; Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Dortch, Q. Changes in nutrient structure of river-dominated coastal waters: Stoichiometric nutrient balance and its consequences. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1995, 40, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo, A.; Morillo, J.A.; Rodríguez, S. Production of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in culture of Chaetoceros calcitrans under nitrogen limitation. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 23, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Mazuecos, I.P.; Reche, I.; Gasol, J.M.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Álvarez, A.; Montero, M.F.; Arístegui, J. Transparent exopolymer particle (TEP) distribution and in situ prokaryotic generation across the deep Mediterranean Sea and nearby North East Atlantic Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 173, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
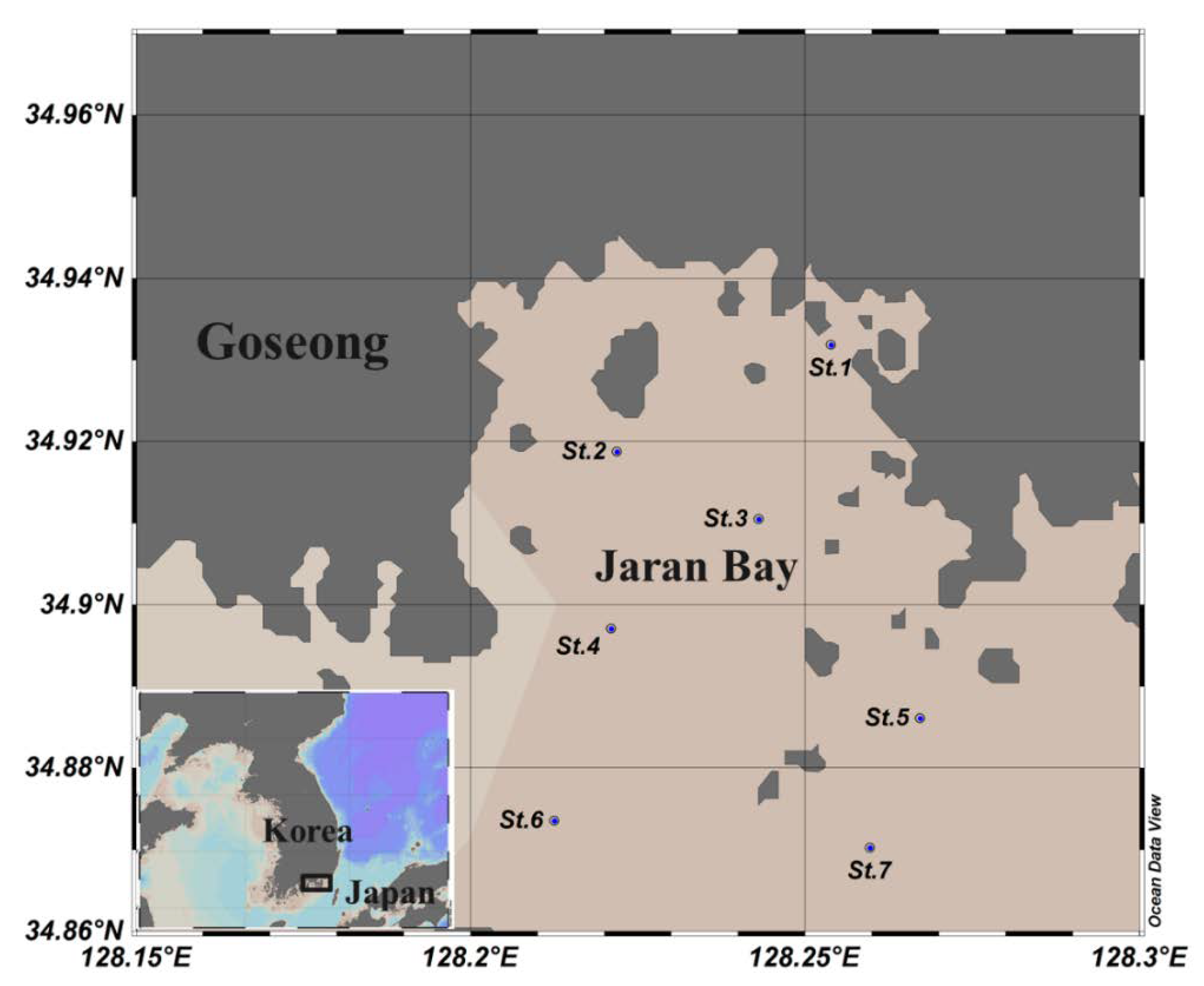
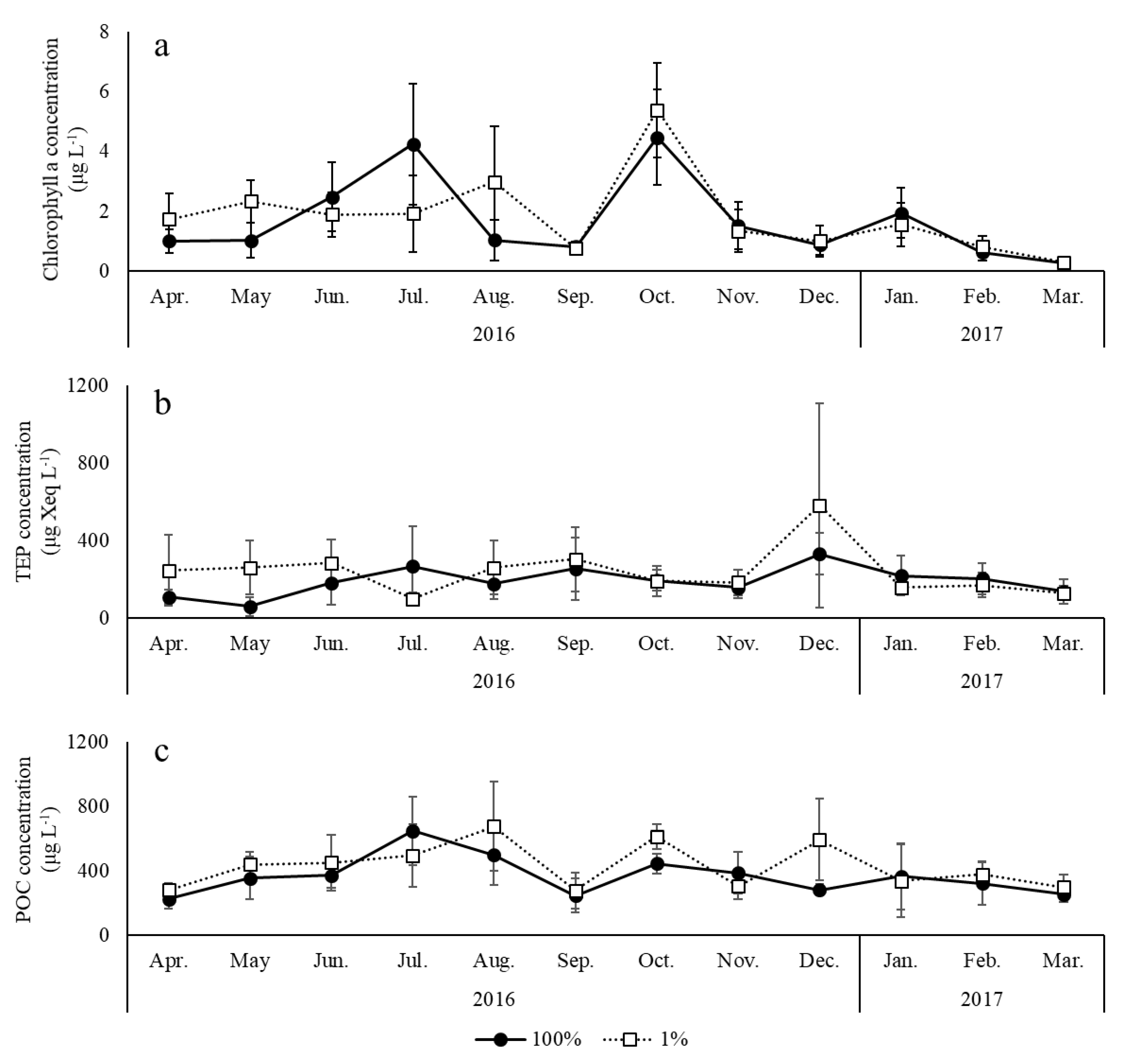
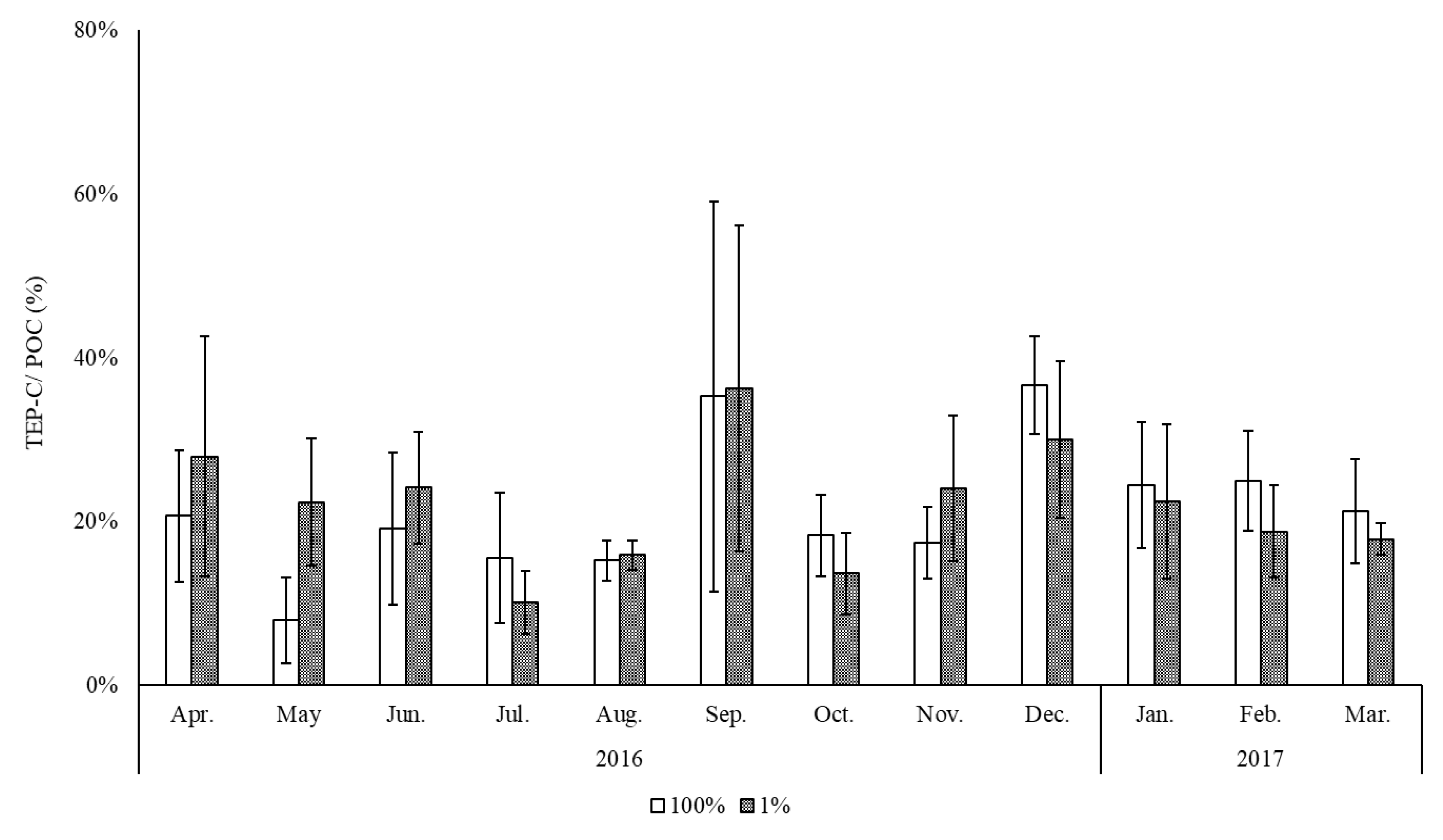
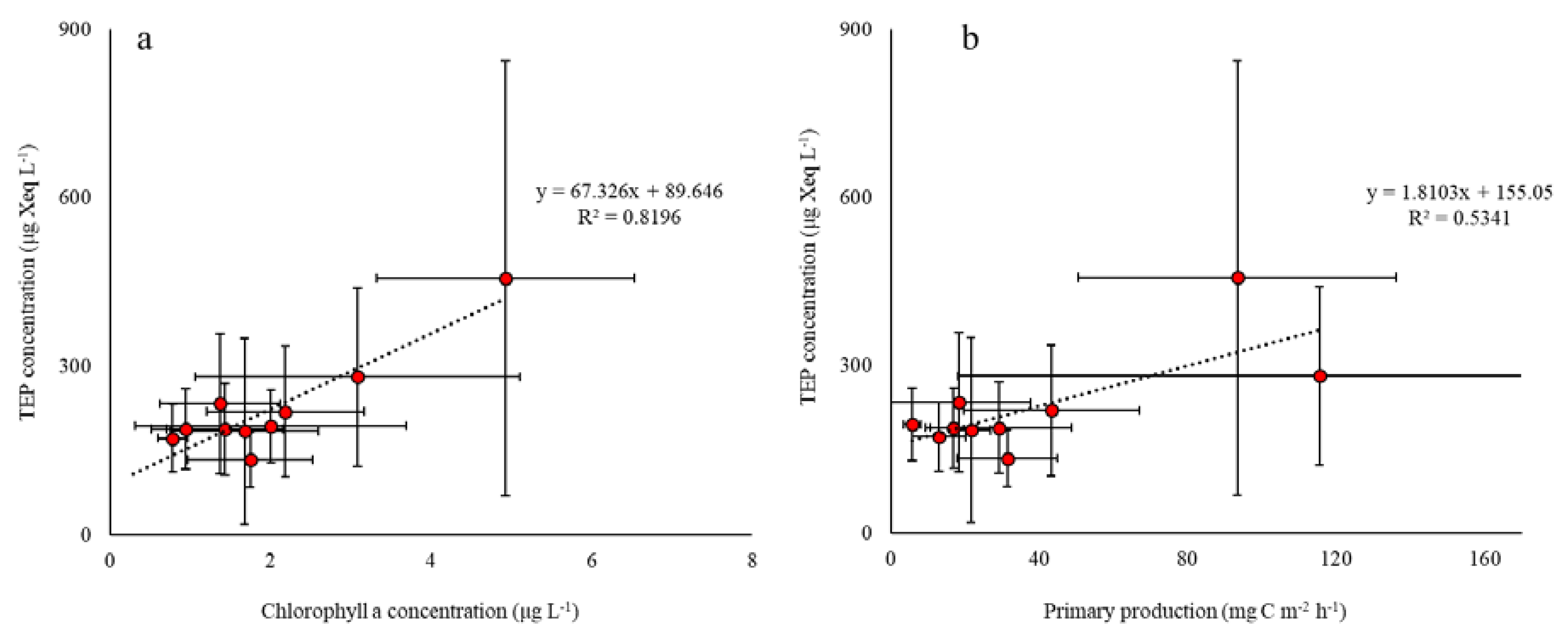
| Year | Month | Light Depth (%) | Temperature (°C) | Salinity | Secchi Depth (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Apr. | 100 | 13.0 ± 0.5 | 32.8 ± 0.6 | 6–10 |
| 1 | 11.8 ± 0.5 | 33.1 ± 0.3 | |||
| May | 100 | 20.8 ± 0.5 | 31.7 ± 0.6 | 5–9 | |
| 1 | 18.0 ± 0.3 | 32.4 ± 0.6 | |||
| Jun. | 100 | 23.6 ± 0.9 | 29.3 ± 1.9 | 5–8 | |
| 1 | 20.7 ± 0.7 | 30.5 ± 2.9 | |||
| Jul. | 100 | 23.7 ± 1.1 | 29.6 ± 3.3 | 2–5 | |
| 1 | 23.4 ± 0.6 | 32.7 ± 0.7 | |||
| Aug. | 100 | 28.7 ± 0.8 | 29.1 ± 1.0 | 6–10 | |
| 1 | 23.4 ± 0.6 | 29.5 ± 3.2 | |||
| Sep. | 100 | 23.9 ± 0.4 | N.D. | 2–4 | |
| 1 | 23.8 ± 0.3 | N.D. | |||
| Oct. | 100 | 21.7 ± 0.2 | N.D. | 3–5 | |
| 1 | 21.8 ± 0.3 | N.D. | |||
| Nov. | 100 | 16.8 ± 0.8 | 29.8 ± 2.5 | 3–5 | |
| 1 | 16.9 ± 1.0 | 28.7 ± 3.2 | |||
| Dec. | 100 | 12.2 ± 1.1 | 32.2 ± 0.4 | 5–7 | |
| 1 | 12.1 ± 1.1 | 32.0 ± 0.3 | |||
| 2017 | Jan. | 100 | 9.1 ± 0.6 | 32.0 ± 1.0 | 5–7 |
| 1 | 9.2 ± 0.5 | 32.2 ± 0.5 | |||
| Feb. | 100 | 6.4 ± 0.7 | 32.9 ± 0.8 | 6–7 | |
| 1 | 6.4 ± 0.8 | 33.4 ± 0.3 | |||
| Mar. | 100 | 9.6 ± 0.4 | 33.8 ± 0.1 | 4–8 | |
| 1 | 9.6 ± 0.6 | 33.6 ± 0.3 |
| Year | Month | Light Depth (%) | Specific Uptake Rate (h−1) | Absolute Uptake Rate (µg C h−1 L−1) | Integral Primary Production (mg C m−2 h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Apr. | 100 | 0.0125 ± 0.0114 | 3.6 ± 3.9 | 18.3 ± 19.4 |
| 1 | 0.0004 ± 0.0004 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | |||
| May | 100 | 0.0121 ±0.0112 | 3.9 ± 3.9 | 21.6 ± 5.2 | |
| 1 | 0.0010 ± 0.0014 | 0.4 ± 0.4 | |||
| Jun. | 100 | 0.0210 ± 0.0145 | 12.7 ± 10.4 | 43.2 ± 23.7 | |
| 1 | 0.0006 ± 0.0002 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | |||
| Jul. | 100 | 0.0532 ± 0.0407 | 52.8 ± 50.4 | 115.4 ± 97.3 | |
| 1 | 0.0010 ± 0.0004 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | |||
| Aug. | 100 | 0.0065 ± 0.0071 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 5.7 ± 2.3 | |
| 1 | 0.0007 ± 0.0003 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | |||
| Sep. | 100 | 0.0080 ± 0.0046 | 4.6 ± 2.8 | 12.9 ± 7.2 | |
| 1 | 0.0003 ± 0.0002 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | |||
| Oct. | 100 | 0.0458 ± 0.0127 | 28.0 ± 12.4 | 93.3 ± 42.7 | |
| 1 | 0.0011 ± 0.0006 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | |||
| Nov. | 100 | 0.0242 ± 0.0089 | 8.5 ± 3.8 | 29.1 ± 19.7 | |
| 1 | 0.0008 ± 0.0005 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | |||
| Dec. | 100 | 0.0091 ± 0.0034 | 2.9 ± 1.3 | 16.9 ± 6.4 | |
| 1 | 0.0005 ± 0.0002 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | |||
| 2017 | Jan. | 100 | 0.0198 ± 0.0046 | 6.3 ± 2.6 | 31.3 ± 13.5 |
| 1 | 0.0009 ± 0.0005 | 0.2 ± 0.2 | |||
| Feb. | 100 | 0.0047 ±0.0015 | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 15.2 ± 7.4 | |
| 1 | 0.0003 ± 0.0002 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | |||
| Mar. | 100 | 0.0048 ± 0.0015 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 10.5 ± 4.9 | |
| 1 | 0.0004 ± 0.0002 | 0.1 ± 0 |
| Region | Season | Depth (m) | TEP Range (Mean) (μg Xeq L−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western Arctic Ocean | Summer | 0–200 | 37–130 (120) | [6] |
| Eastern tropical and eastern subarctic, North Pacific Ocean | Summer | Above mixed layer depth | 78–970 | [33] |
| Western and central Pacific Ocean (subtropical and equatorial regions) | Summer and winter | 0–200 | 5–40 (25) | [6] |
| Northeast coast of Japan | Spring and winter | 0–15 | 136–2321 | [43] |
| Tokyo bay | All year | 0–20 | 14–1774 | [47] |
| Changjiang estuary | Spring, summer and autumn | 0–80 | 37–1227 | [48] |
| Mediterranean Sea | Spring | Upper mixed layer | 19–53 (29) | [32] |
| Coastal NW (rocky shore) Mediterranean Sea | All year | Surface | 5–91 | [49] |
| Baltic Sea | Summer | 40 | 145–322 | [50] |
| Bransfield Strait | Summer | 0–100 | 0–346 | [45] |
| Southern Ibrian coasts | Spring | Mixed layer | 507–560 | [51] |
| Neuse River estuary | All year | Surface | 805–1801 | [34] |
| Chesapeake bay | All year | 0–24 | 37–2820 | [4] |
| Northeast Atlantic Ocean | Spring | 0–10 | 20–420 | [31] |
| Western North Atlantic Ocean and Sargasso Sea | Spring | 2–5 | 100–200 | [52] |
| Jaran bay (Southern coast of Korea) | All year | Euphotic depth | 27–1695 (222) | This study |
| Region | Season | TEP-C/POC % | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| NE Aegean Sea | Early spring, summer and autumn | 70 | [17] |
| Coastal NW Mediterranean Sea | Early summer | 77 | [22] |
| Epipelagic Mediterranean Sea | Spring | 75 | [61] |
| Deep Mediterranean Sea | 50 | ||
| North East Atlantic Ocean | 85 | ||
| Open Atlantic Ocean | Spring and fall | 66 | [9] |
| Southwestern Atlantic Shelf | Spring | 73 | |
| Dona Paula Bay | All year | 7 | [46] |
| Chesapeake Bay | Early and late spring, fall and winter | 32 | [4] |
| Jaran bay (Southern coast of Korea) | All year | 22 | This study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.H.; Lee, W.C.; Kim, H.C.; Jo, N.; Jang, H.K.; Kang, J.J.; Lee, D.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.H. Transparent Exopolymer Particle (TEPs) Dynamics and Contribution to Particulate Organic Carbon (POC) in Jaran Bay, Korea. Water 2020, 12, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041057
Lee JH, Lee WC, Kim HC, Jo N, Jang HK, Kang JJ, Lee D, Kim K, Lee SH. Transparent Exopolymer Particle (TEPs) Dynamics and Contribution to Particulate Organic Carbon (POC) in Jaran Bay, Korea. Water. 2020; 12(4):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041057
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jae Hyung, Won Chan Lee, Hyung Chul Kim, Naeun Jo, Hyo Keun Jang, Jae Joong Kang, Dabin Lee, Kwanwoo Kim, and Sang Heon Lee. 2020. "Transparent Exopolymer Particle (TEPs) Dynamics and Contribution to Particulate Organic Carbon (POC) in Jaran Bay, Korea" Water 12, no. 4: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041057
APA StyleLee, J. H., Lee, W. C., Kim, H. C., Jo, N., Jang, H. K., Kang, J. J., Lee, D., Kim, K., & Lee, S. H. (2020). Transparent Exopolymer Particle (TEPs) Dynamics and Contribution to Particulate Organic Carbon (POC) in Jaran Bay, Korea. Water, 12(4), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041057







