The Impact of Submerged Breakwaters on Sediment Distribution along Marsh Boundaries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
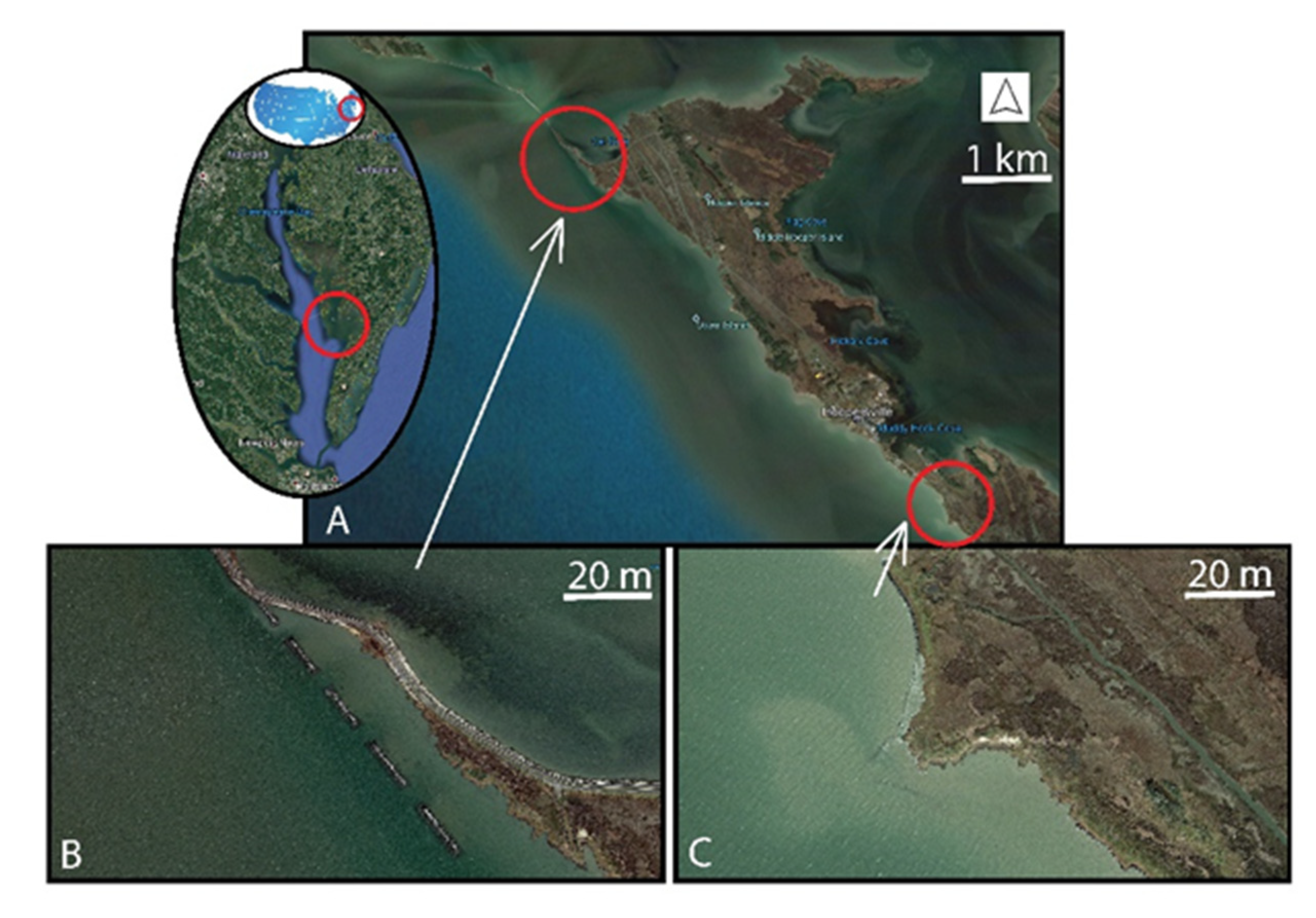
2. Materials and Methods
Model Description
3. Results
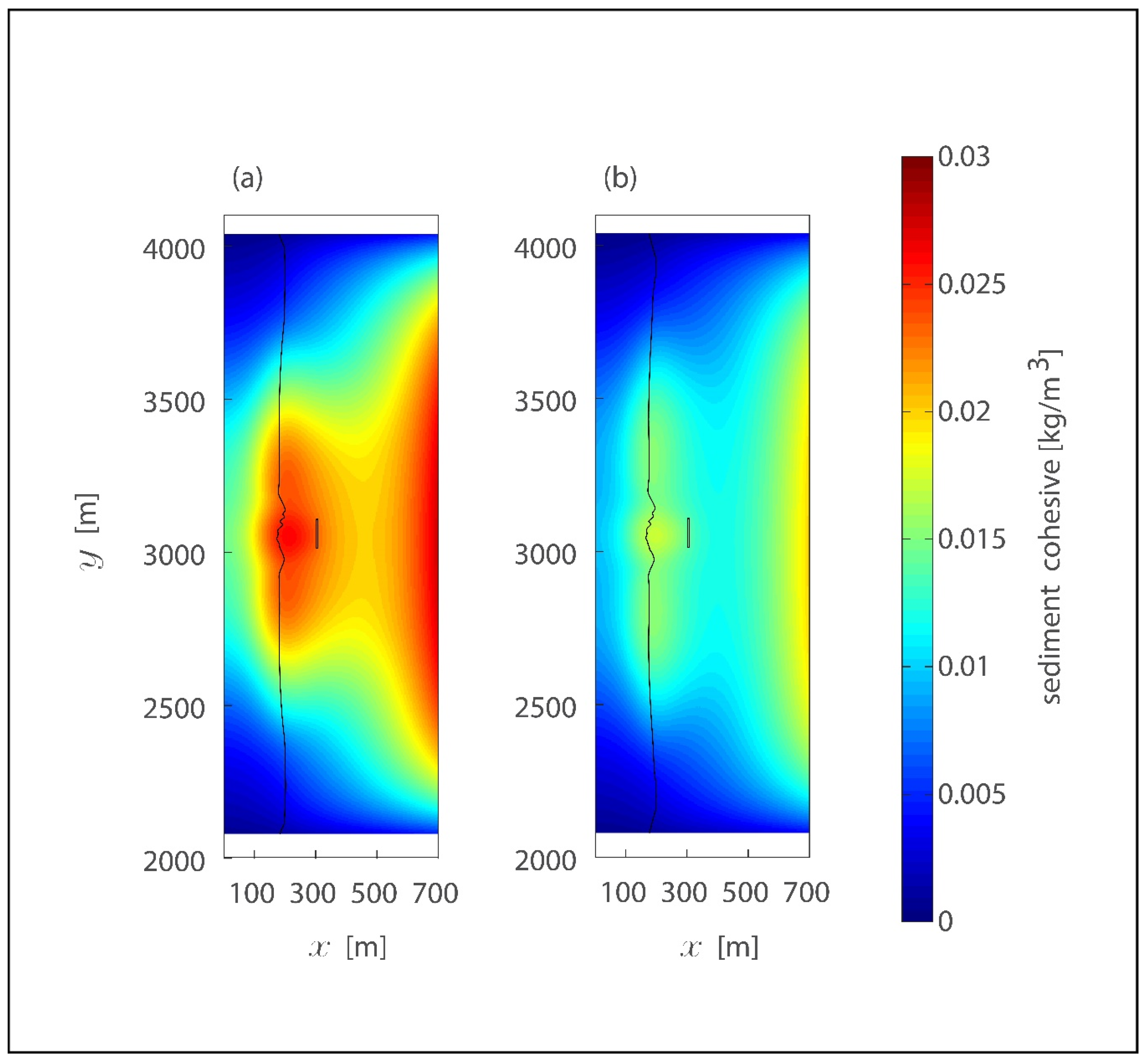
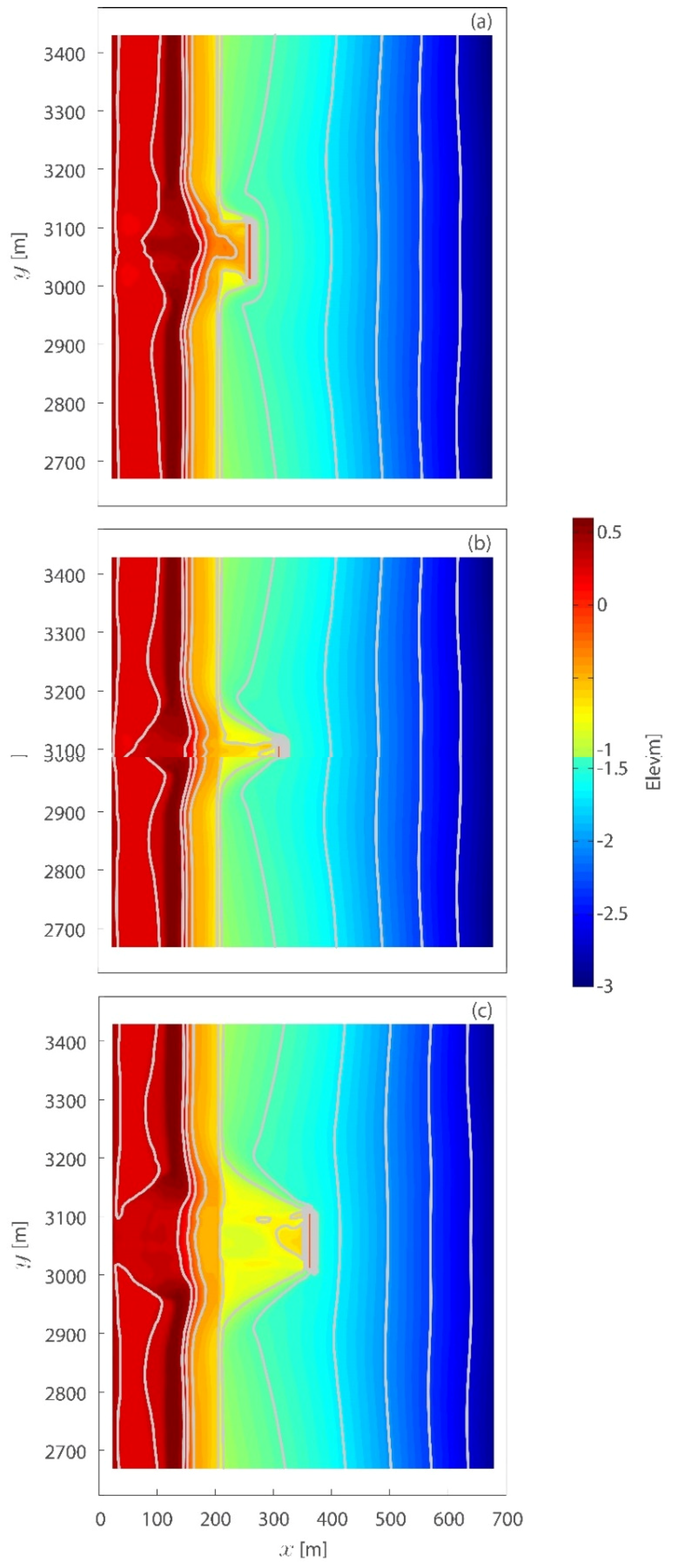
3.1. Hydrodynamic Results
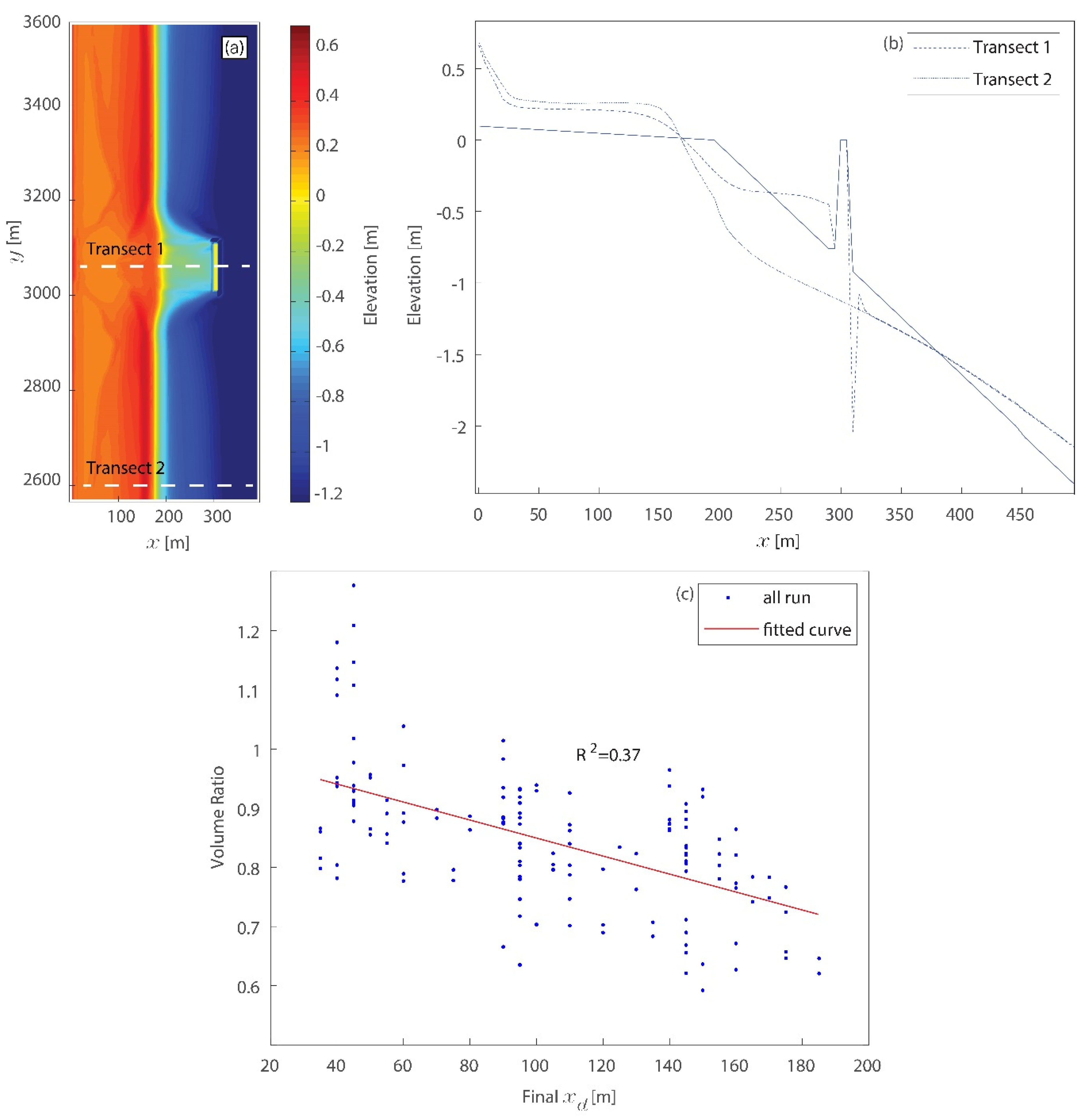
3.2. Morphodynamic Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kay, R.; Alder, J. Coastal Planning and Management, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Post, J.C.; Lundin, C.G. Guidelines for Integrated Coastal Zone Management; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Creel, L. Ripple Effects: Population and Coastal Regions; Population Reference Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Board, O.C.; National Research Council. Mitigating Shore Erosion along Sheltered Coasts; National Academic Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pilkey, O.H.; Wright, W. Seawalls versus Beaches. J. Coast. Res. 1988, 4, 41–64. [Google Scholar]
- Douglass, S.L.; Pickel, B.H. The tide doesn’t go out anymore-the effect of bulkheads on urban shorelines. Shore Beach 1999, 67, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kennish, M.J. Environmental threats and environmental future of estuaries. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airoldi, L. An ecological perspective on the deployment and design of low-crested and other hard coastal defence structures. Coast. Eng. 2005, 52, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borsje, B.W.; van Wesenbeeck, B.K.; Dekker, F.; Paalvast, P.; Bouma, T.J.; van Katwijk, M.M.; de Vries, M.B. How ecological engineering can serve in coastal protection. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broome, S.W.; Rogers, S.M., Jr.; Seneca, E.D. Shoreline Erosion Control Using Marsh Vegetation and Low-Cost Structures. 2015. Available online: https://tamug-ir.tdl.org/bitstream/handle/1969.3/28985/Broome-Rogers-Seneca-shoreline-erosion-control[1].pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Allen, J.R.; Pye, K. Saltmarshes: Morphodynamics, Conservation and Engineering Significance; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Boorman, L.A.; Garbutt, A.; Barratt, D. The Role of Vegetation in Determining Patterns of the Accretion of Salt Marsh Sediment; Special Publications; Geological Society: London, UK, 1998; Volume 139, pp. 389–399. [Google Scholar]
- Boorman, L.A. Salt marshes–present functioning and future change. Mangroves Salt Marshes 1999, 3, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scyphers, S.B.; Powers, S.P.; Heck, K.L. Ecological value of submerged breakwaters for habitat enhancement on a residential scale. Environ. Manag. 2015, 55, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiberg, P.L.; Taube, S.R.; Ferguson, A.E.; Kremer, M.R.; Reidenbach, M.A. Wave attenuation by oyster reefs in shallow coastal bays. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.S.N.; Walles, B.; Sharifuzzaman, S.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Ysebaert, T.; Smaal, A.C. Oyster breakwater reefs promote adjacent mudflat stability and salt marsh growth in a monsoon dominated subtropical coast. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschella, P.S.; Abbiati, M.; Åberg, P.; Airoldi, L.; Anderson, J.M.; Bacchiocchi, F.; Granhag, L. Low-crested coastal defence structures as artificial habitats for marine life: Using ecological criteria in design. Coast. Eng. 2005, 52, 1053–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palinkas, C.M.; Barth, N.; Koch, E.W.; Shafer, D.J. The influence of breakwaters on nearshore sedimentation patterns in Chesapeake Bay, USA. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 32, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraci, C.; Scandura, P.; Foti, E. Bottom profile evolution of a perched nourished beach. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2014, 140, 04014021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraci, C. Experimental investigation of the hydro-morphodynamic performances of a geocontainer submerged reef. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2018, 144, 04017045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumer, B.M.; Fredsøe, J.; Lamberti, A.; Zanuttigh, B.; Dixen, M.; Gislason, K.; Di Penta, A.F. Local scour at roundhead and along the trunk of low crested structures. Coast. Eng. 2005, 52, 995–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker-Urso, S.; Nixon, S.W.; Cochran, J.K.; Hirschberg, D.J.; Hunt, C. Accretion rates and sediment accumulation in Rhode Island salt marshes. Estuaries 1989, 12, 300–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuerch, M.; Spencer, T.; Temmerman, S.; Kirwan, M.L.; Wolff, C.; Lincke, D.; McOwen, C.J.; Pickering, M.D.; Reef, R.; Vafeidis, A.T.; et al. Future response of global coastal wetlands to sea-level rise. Nature 2018, 561, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, A.M.; Catherine, S.M.P. Effectiveness of mangrove forests in surface wave attenuation: A review. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 5, 4483–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadwalladr, D.A.; Owen, M.; Morley, J.V.; Cook, R.S. Wigeon (Anas penelope L.) conservation and salting pasture management at Bridgwater Bay National Nature Reserve, Somerset. J. Appl. Ecol. 1972, 9, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Howe, M.A.; Hahn, D.C.; Chase, J. Effects of tide cycles on habitat selection and habitat partitioning by migrating shorebirds. Auk 1977, 94, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiber, F.C. Salt marsh animals: Distributions related to tidal flooding, salinity and vegetation. In Ecosystems of the World; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Nardin, W.; Fagherazzi, S. The effect of wind waves on the development of river mouth bars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardin, W.; Larsen, L.; Fagherazzi, S.; Wiberg, P. Tradeoffs among hydrodynamics, sediment fluxes and vegetation community in the Virginia Coast Reserve, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 210, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, N.; Sun, T.; Fagherazzi, S. Modeling tidal bedding in distributary-mouth bars. J. Sediment. Res. 2014, 84, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lera, S.; Nardin, W.; Sanford, L.; Palinkas, C.; Guercio, R. The impact of submersed aquatic vegetation on the development of river mouth bars. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.H.; Mulligan, R.P. Application of a spectral wave model to assess breakwater configurations at a small craft harbour on Lake Ontario. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roelvink, J.A.; Van Banning, G.K.F.M. Design and development of DELFT3D and application to coastal morphodynamics. Oceanogr. Lit. Rev. 1995, 11, 925. [Google Scholar]
- Lesser, G.R.; Roelvink, J.V.; Van Kester, J.A.T.M.; Stelling, G.S. Development and validation of a three-dimensional morphological model. Coast. Eng. 2004, 51, 883–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K.; Barnett, T.P.; Bouws, E.; Carlson, H.; Cartwright, D.E.; Enke, K.; Ewing, J.A.; Gienapp, H.; Hasselmann, D.E.; Kruseman, P.; et al. Measurements of wind-wave growth and swell decay during the Joint North Sea Wave Project (JONSWAP). Ergänzungsheft 1973, 12, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Battjes, J.A.; Janssen, J.P.F.M. Energy loss and set-up due to breaking of random waves. Coast. Eng. 1978, 1978, 569–587. [Google Scholar]
- Rodi, W.; Scheuerer, G. Scrutinizing the k-epsilon-model under adverse pressure gradient conditions. In 4th Symposium on Turbulent Shear Flows; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lévêque, E.; Toschi, F.; Shao, L.; Bertoglio, J.P. Shear-improved Smagorinsky model for large-eddy simulation of wall-bounded turbulent flows. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 570, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Partheniades, E. Erosion and deposition of cohesive soils. J. Hydraul. Div. 1965, 91, 105–139. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Principles of Sediment Transport in Rivers, Estuaries and Coastal Seas; Aqua Publications: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; Volume 1006, pp. 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Russ, E.R.; Palinkas, C.M. Seasonal-scale and decadal-scale sediment-vegetation interactions on the subaqueous Susquehanna River delta, upper Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries Coasts 2018, 41, 2092–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlamont, J.; Ockenden, M.; Toorman, E.; Winterwerp, J. The characterisation of cohesive sediment properties. Coast. Eng. 1993, 21, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edmonds, D.A.; Slingerland, R.L. Significant effect of sediment cohesion on delta morphology. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardin, W.; Edmonds, D.A.; Fagherazzi, S. Influence of vegetation on spatial patterns of sediment deposition in deltaic islands during flood. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 93, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sumer, B.M.; Fredsøe, J. Experimental study of 2D scour and its protection at a rubble-mound breakwater. Coast. Eng. 2000, 40, 59–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birben, A.R.; Özölçer, İ.H.; Karasu, S.; Kömürcü, M.İ. Investigation of the effects of offshore breakwater parameters on sediment accumulation. Ocean Eng. 2007, 34, 284–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, M.; Fagherazzi, S.; Petti, M. Modeling wave impact on salt marsh boundaries. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castagno, K.A.; Jiménez-Robles, A.M.; Donnelly, J.P.; Wiberg, P.L.; Fenster, M.S.; Fagherazzi, S. Intense storms increase the stability of tidal bays. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 5491–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton-Grier, A.E.; Wowk, K.; Bamford, H. Future of our coasts: The potential for natural and hybrid infrastructure to enhance the resilience of our coastal communities, economies and ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 51, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleming, C.S.; Dillard, M.K.; Regan, S.D.; Gorstein, M.; Messick, E.; Blair, A. A coastal community vulnerability assessment for the Choptank Habitat Focus Area. NOAA Tech. Memo. NOS NCCOS 2017, 225, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Ridge, J.T.; Rodriguez, A.B.; Fodrie, F.J. Evidence of exceptional oyster-reef resilience to fluctuations in sea level. Ecol. Evolut. 2017, 7, 10409–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, A.B.; Fodrie, F.J.; Ridge, J.T.; Lindquist, N.L.; Theuerkauf, E.J.; Coleman, S.E.; Grabowski, J.H.; Brodeur, M.C.; Gittman, R.K.; Keller, D.A.; et al. Oyster reefs can outpace sea-level rise. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, H.; Kraus, N.C. Shoreline response to a single transmissive detached breakwater. Coast. Eng. 1990, 1991, 2034–2046. [Google Scholar]
- De Vincenzo, A.; Covelli, C.; Molino, A.J.; Pannone, M.; Ciccaglione, M.; Molino, B. Long-Term Management Policies of Reservoirs: Possible Re-Use of Dredged Sediments for Coastal Nourishment. Water 2019, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
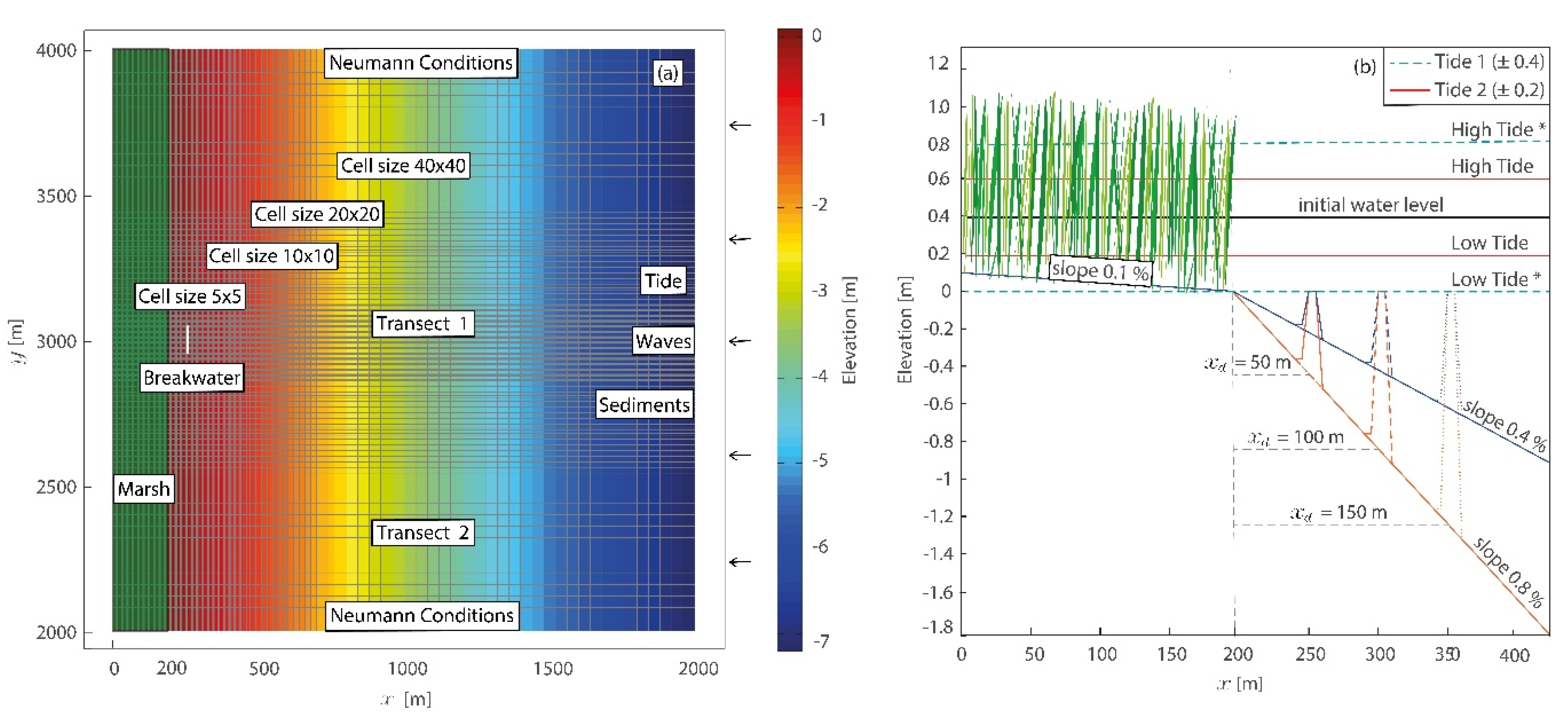
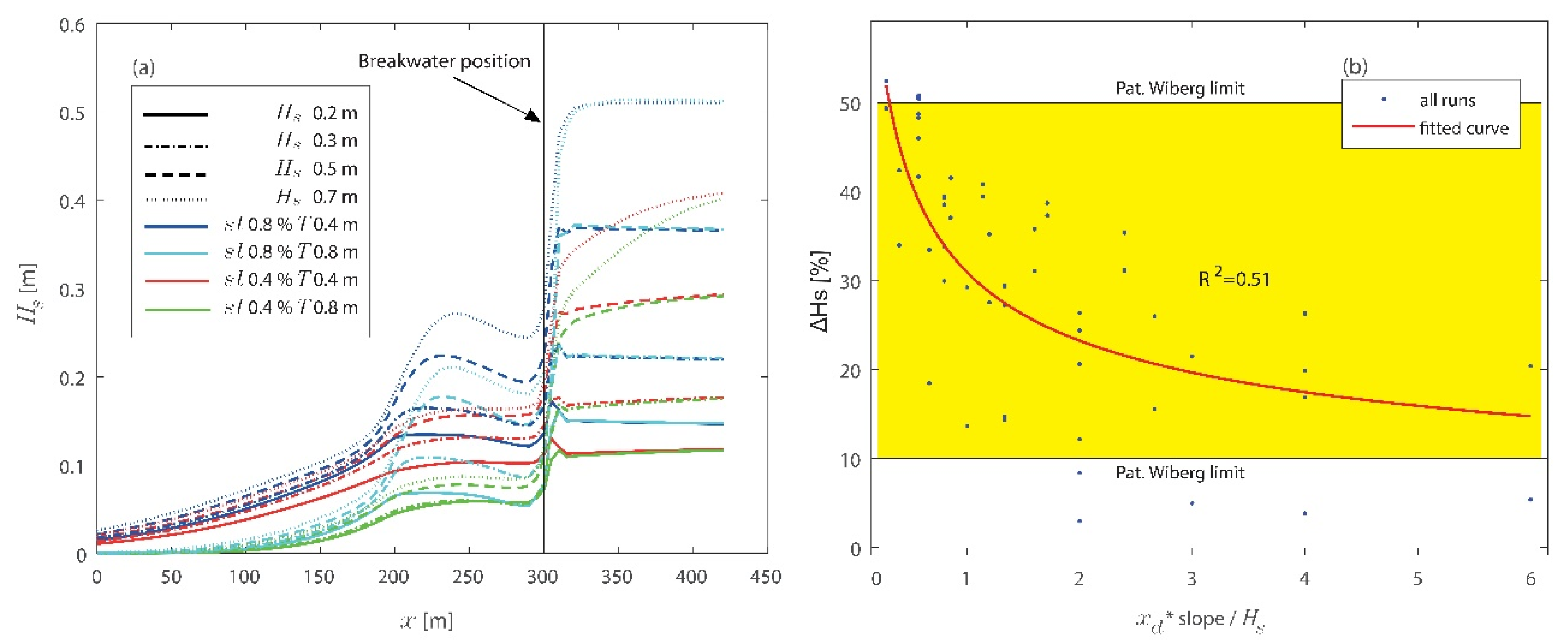
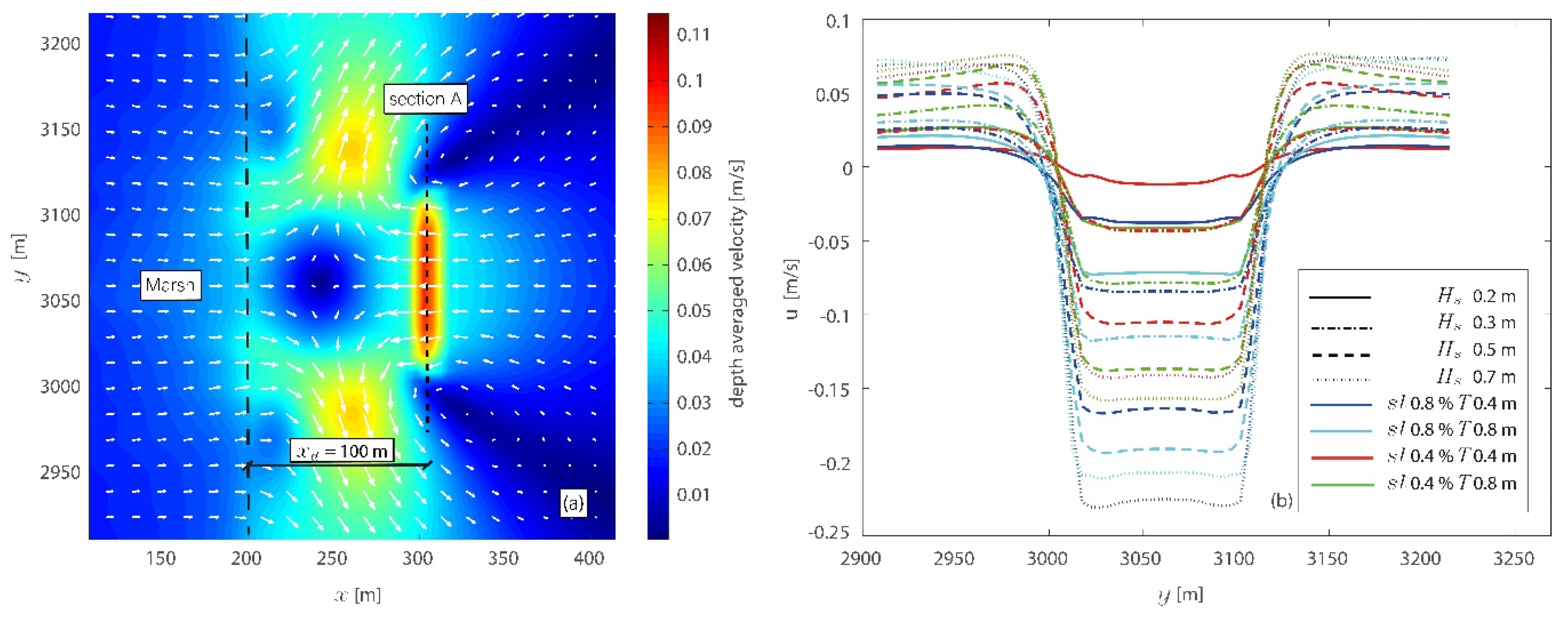
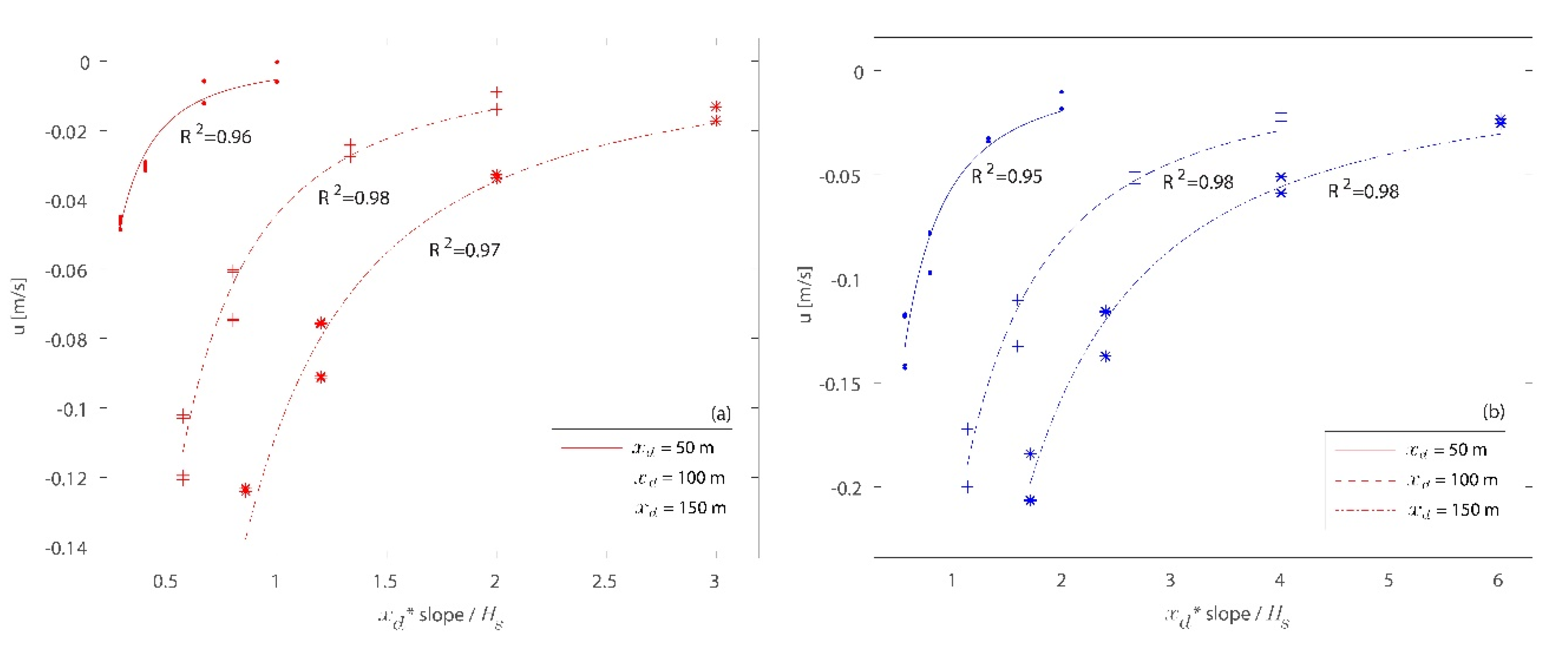
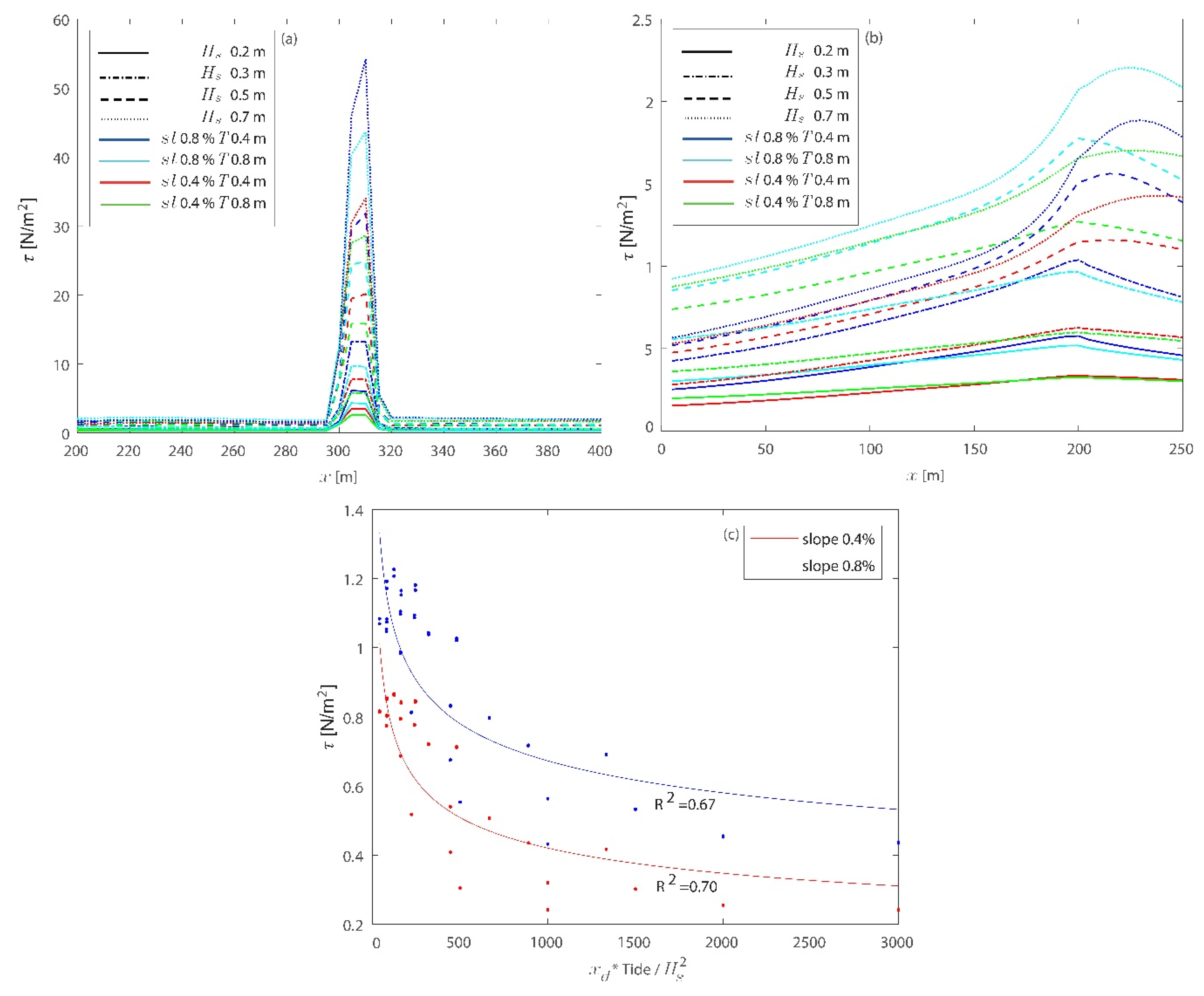
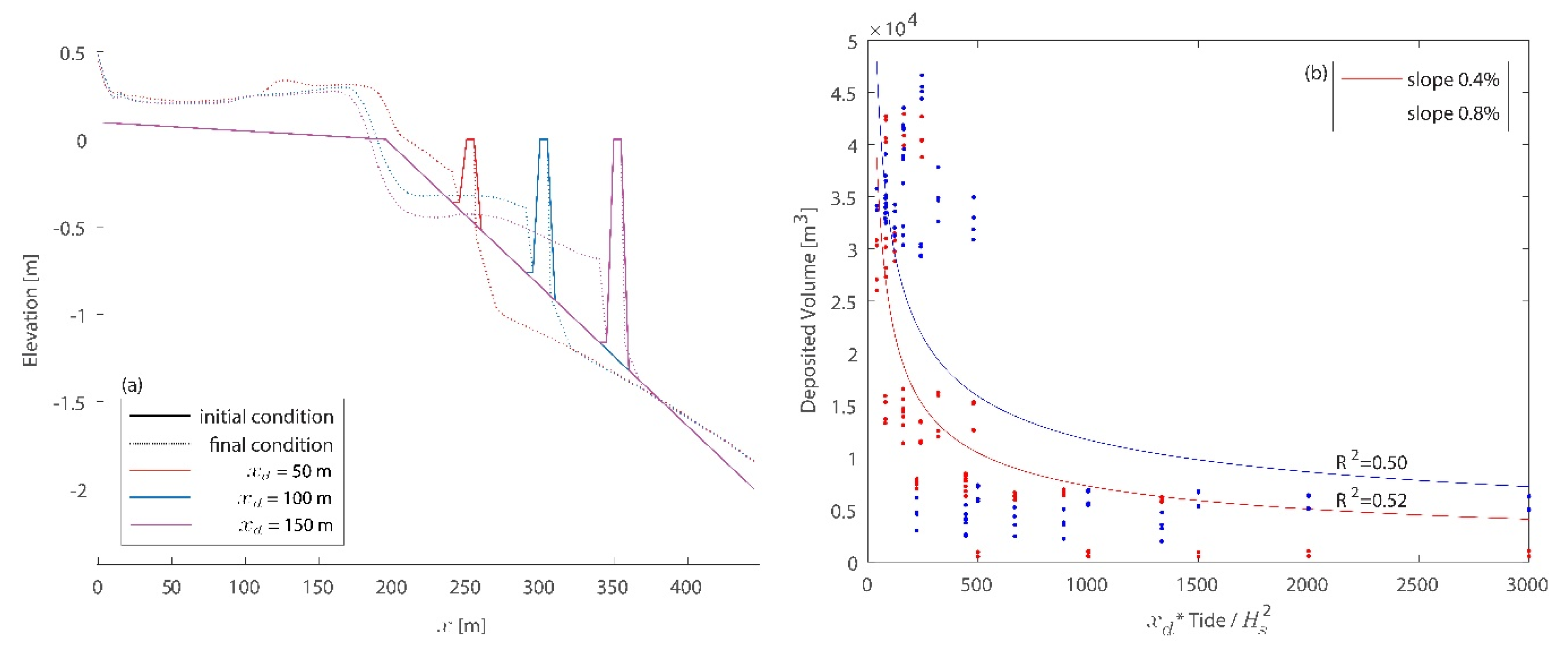
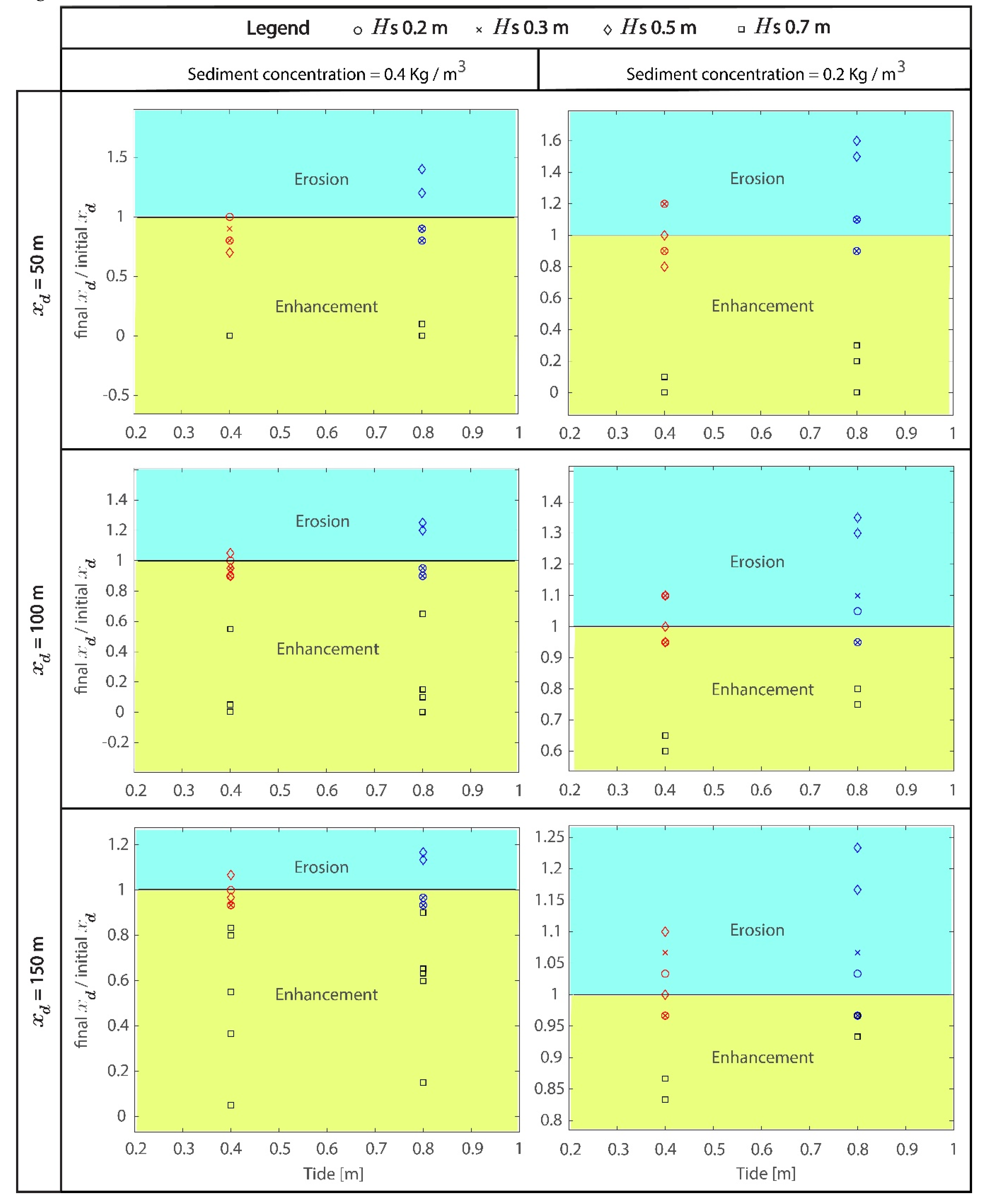
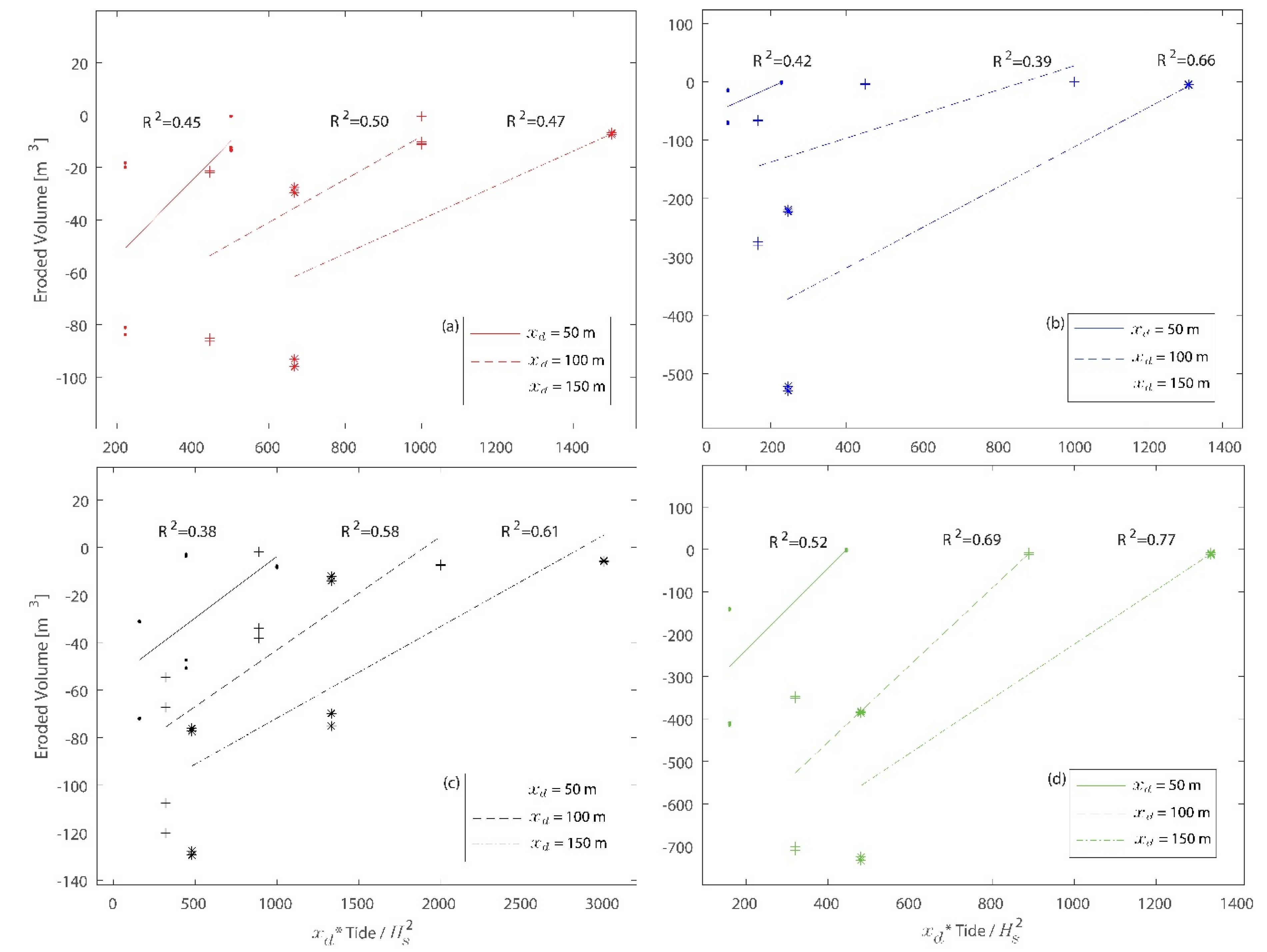
| Hs (m) | xd (m) | sl (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2 0.3 0.5 0.7 | 50 100 150 | 0.4 0.8 |
| D50 (µm) | T (m) | C (Kg/m3) |
| 100 150 | ±0.2 ±0.4 | 0.2 0.4 |
| C | Mass concentration of sediment fraction, kg/m3 | θ | Wave direction |
| Cx | Propagation velocity in the x-space, m/s | S | Source/sink term for the action Balance equation |
| Cy | Propagation velocity in the y-space, m/s | Sx | Total sediment transport in the x direction, m2/s |
| Cσ | Propagation velocity in the σ –space, m/s | Sy | Total sediment transport in the y direction, m2/s |
| Cθ | Propagation velocity in the θ –space, m/s | sl | Basin slope, % |
| D | Diffusion coefficient | τ | Fluid shear stress tensor |
| D50 | Median diameter, µm | t | Time, s |
| ɛpor | Bed porosity | Td | Deposition or erosion rate, m/s |
| g | Gravity acceleration, m/s2 | T | Tidal conditions, m |
| Hs | Wave height, m | V | Velocity field, m/s |
| N | Density spectrum | x | Longitudinal direction, m |
| p | Fluid pressure, N/m2 | xd | Breakwater distance from the coast |
| R | Source/sink term for the advection-diffusion equation | y | Transversal direction, m |
| ρ | Fluid density, kg/m3 | z | Elevation, m |
| σ | Frequency | zb | Bed level, m |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vona, I.; Gray, M.W.; Nardin, W. The Impact of Submerged Breakwaters on Sediment Distribution along Marsh Boundaries. Water 2020, 12, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041016
Vona I, Gray MW, Nardin W. The Impact of Submerged Breakwaters on Sediment Distribution along Marsh Boundaries. Water. 2020; 12(4):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041016
Chicago/Turabian StyleVona, Iacopo, Matthew W. Gray, and William Nardin. 2020. "The Impact of Submerged Breakwaters on Sediment Distribution along Marsh Boundaries" Water 12, no. 4: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041016
APA StyleVona, I., Gray, M. W., & Nardin, W. (2020). The Impact of Submerged Breakwaters on Sediment Distribution along Marsh Boundaries. Water, 12(4), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041016




