Statistical Evaluation of the Latest GPM-Era IMERG and GSMaP Satellite Precipitation Products in the Yellow River Source Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
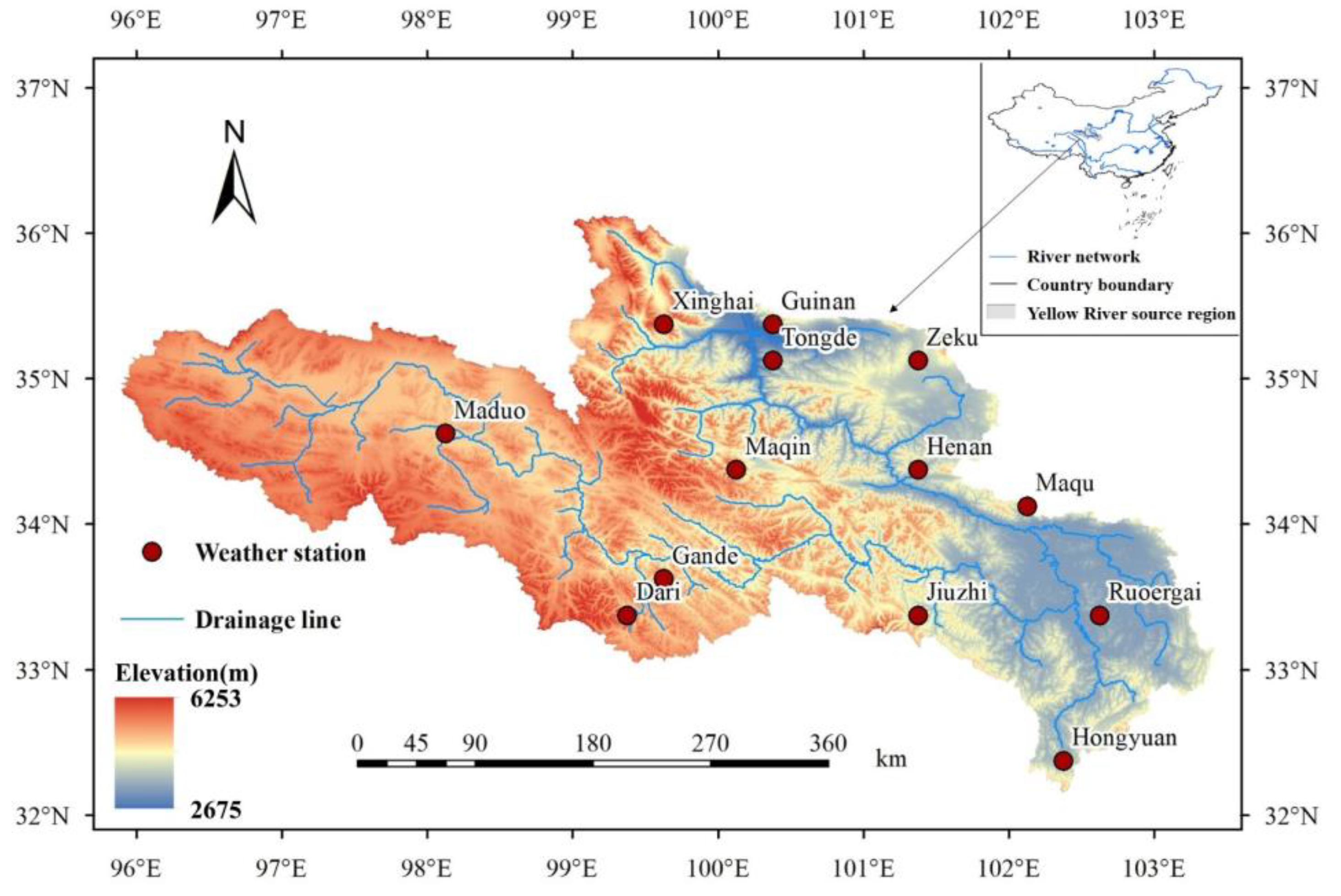
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Ground Precipitation Data
2.3. Satellite Precipitation Products
2.3.1. IMERG Products
2.3.2. GSMaP Products
3. Methodology
3.1. Statistical Metrics
3.2. Confusion Matrix for Daily Precipitation Evaluation
4. Results
4.1. Statistical Evaluation of IMERG SPPs
4.1.1. Statistical Indices at Multiple Temporal Scales
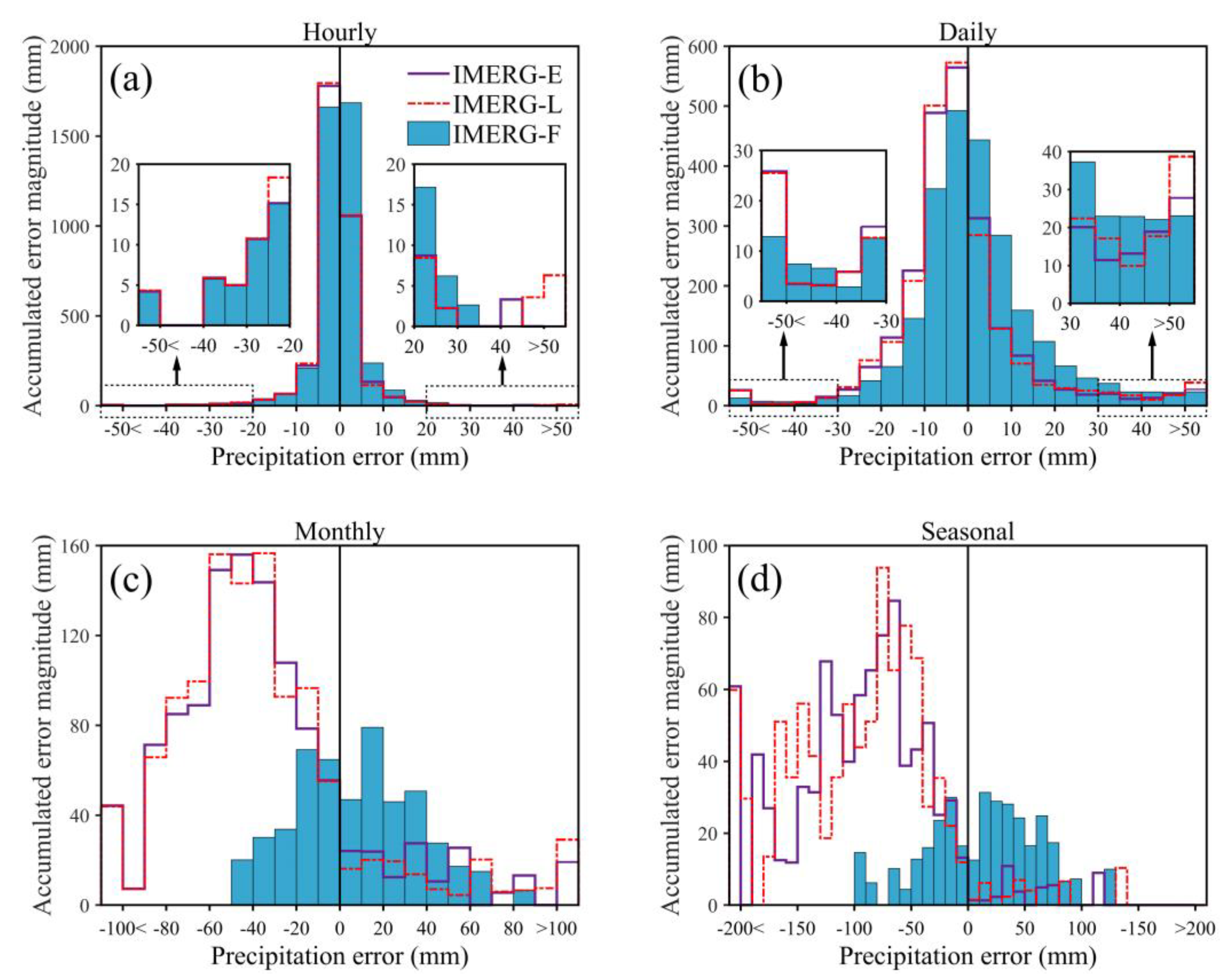
4.1.2. Precipitation Error Distribution
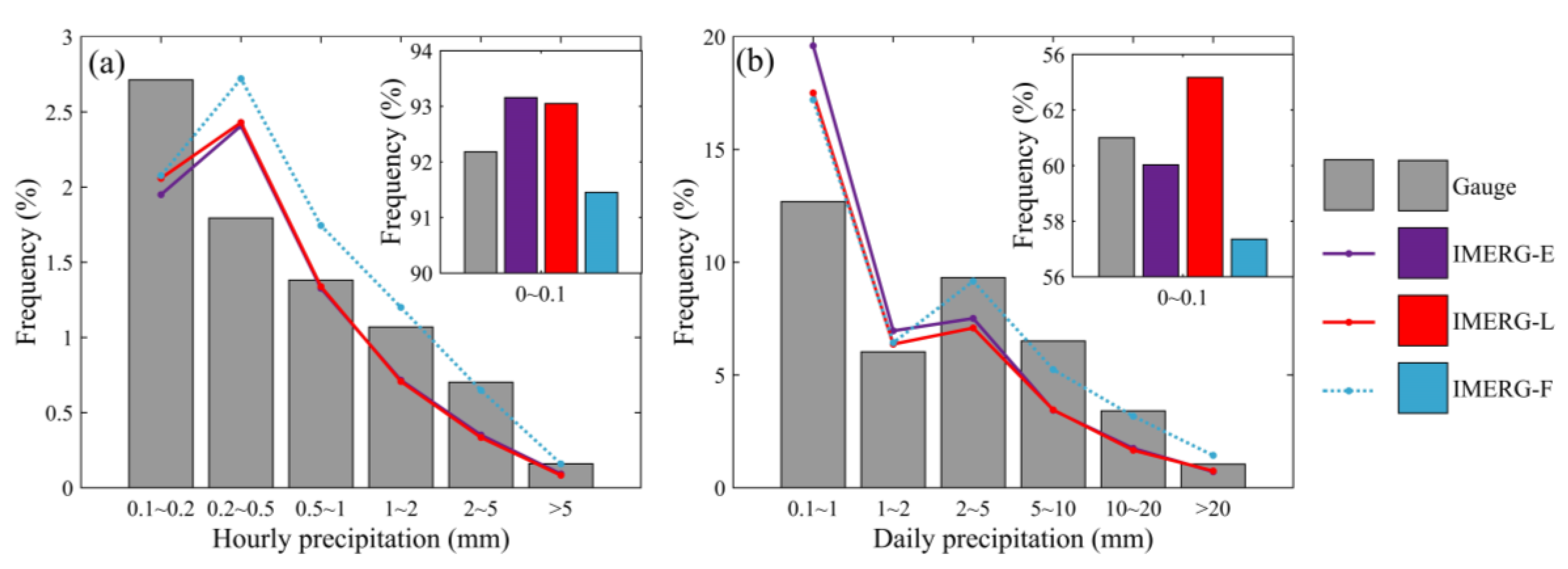
4.1.3. Precipitation Frequency Distribution
4.2. Statistical Evaluation of GSMaP SPPs
4.2.1. Statistical Indices at Different Temporal Scales
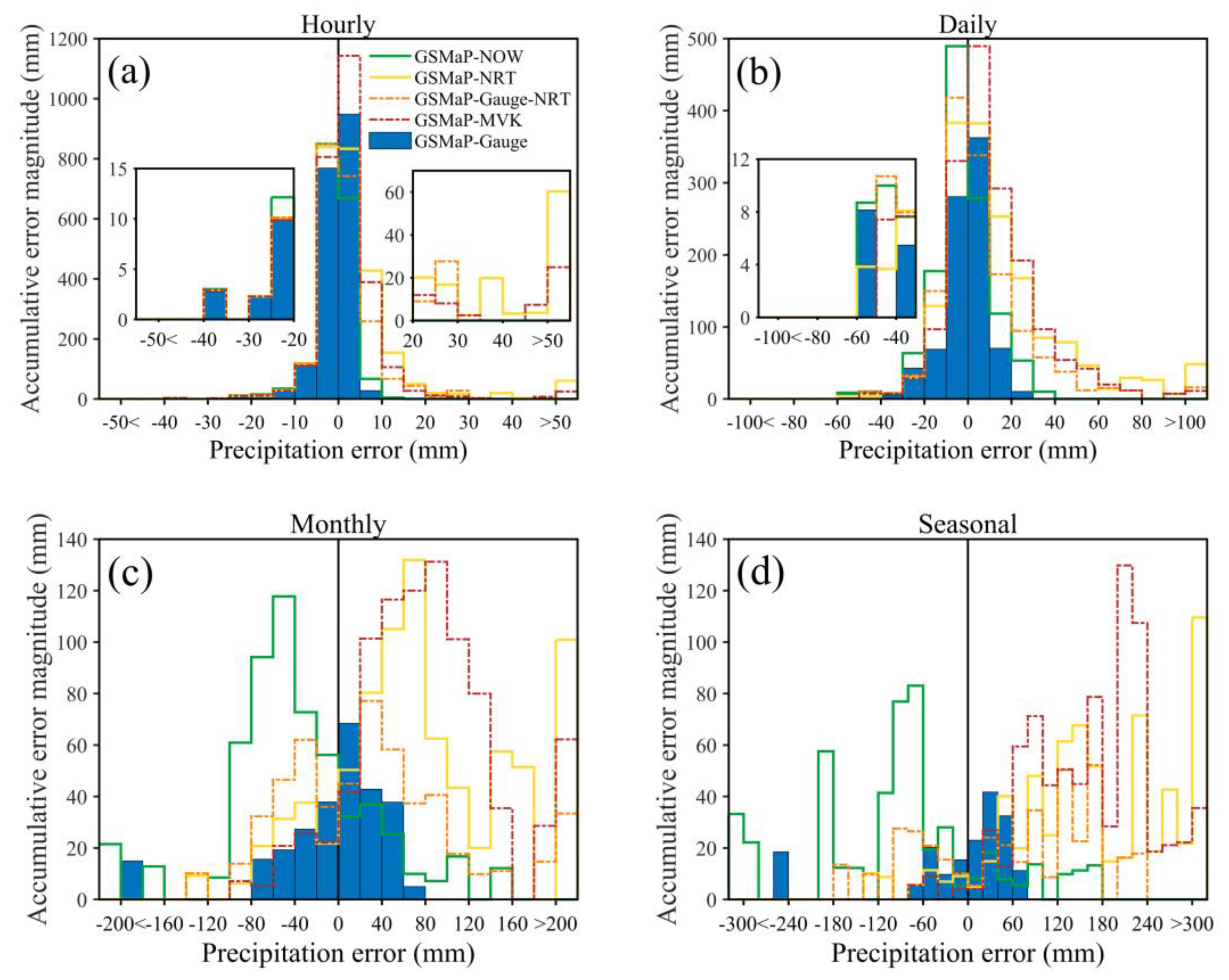
4.2.2. Precipitation Error Distribution
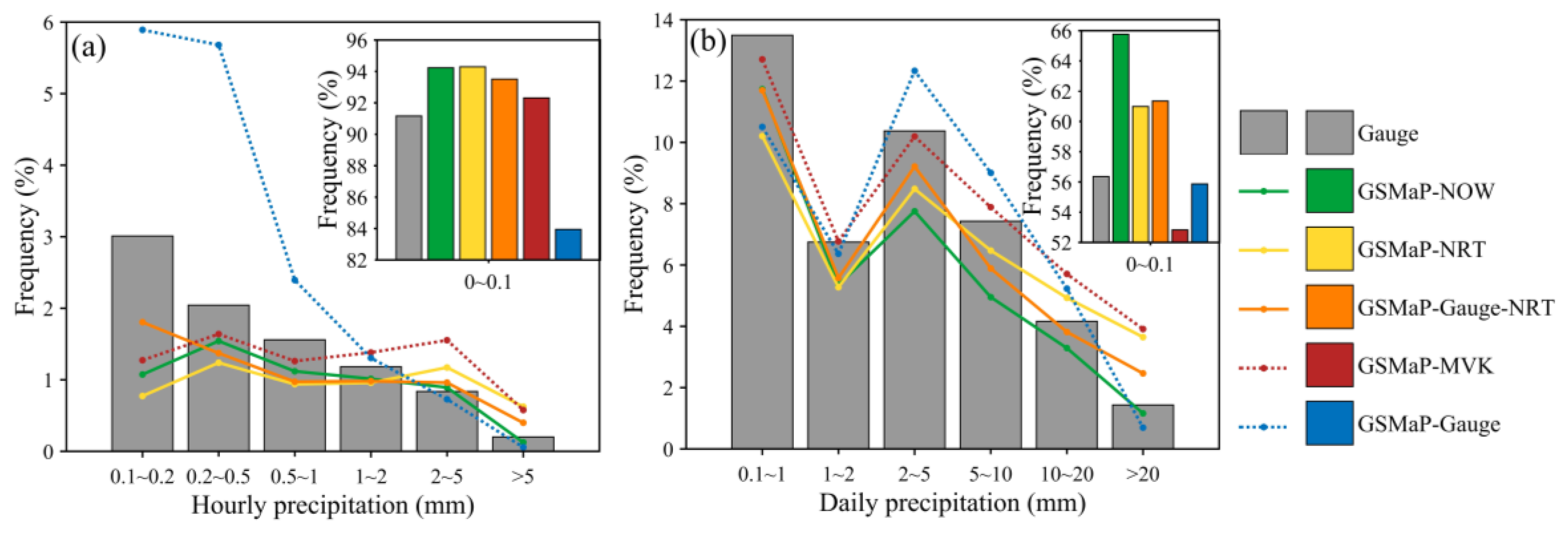
4.2.3. Precipitation Frequency Distribution
4.3. IMERG SPPs Versus GSMaP SPPs
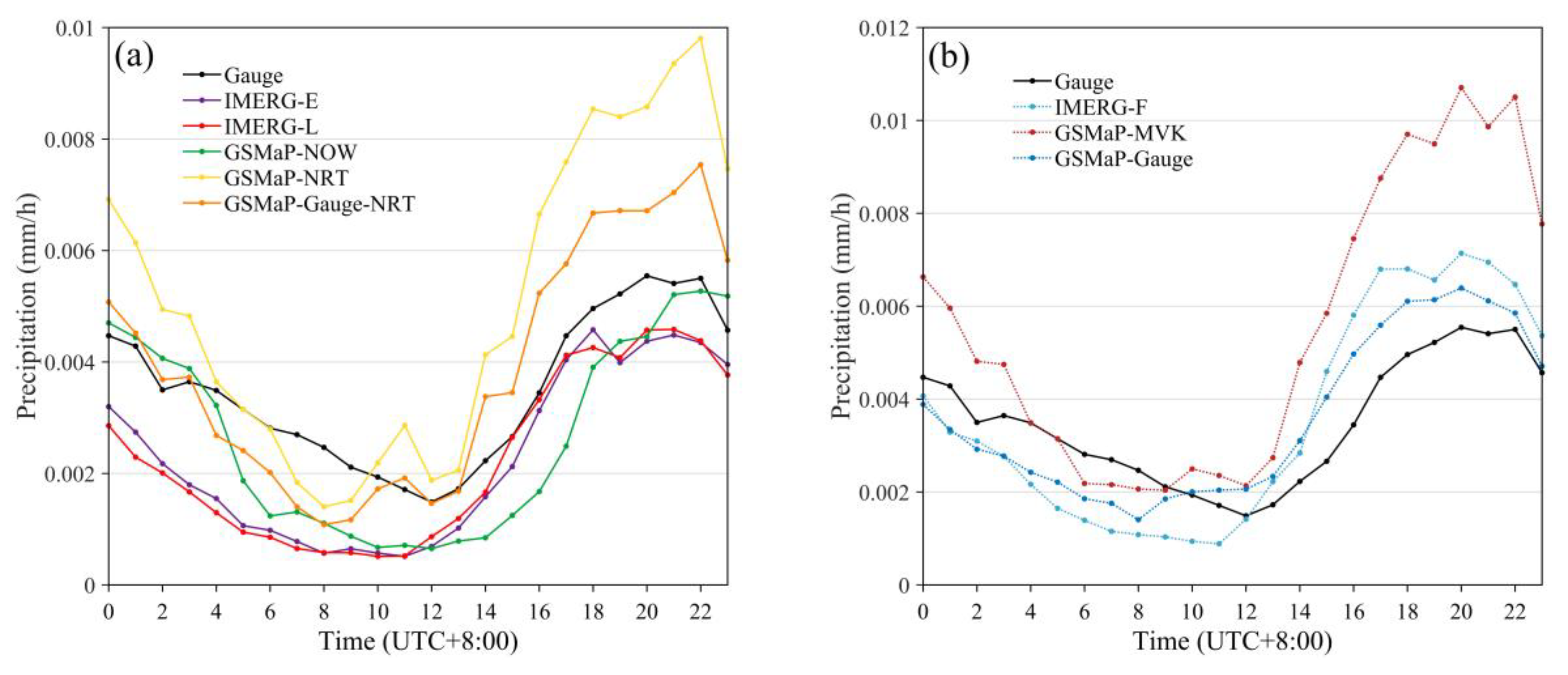
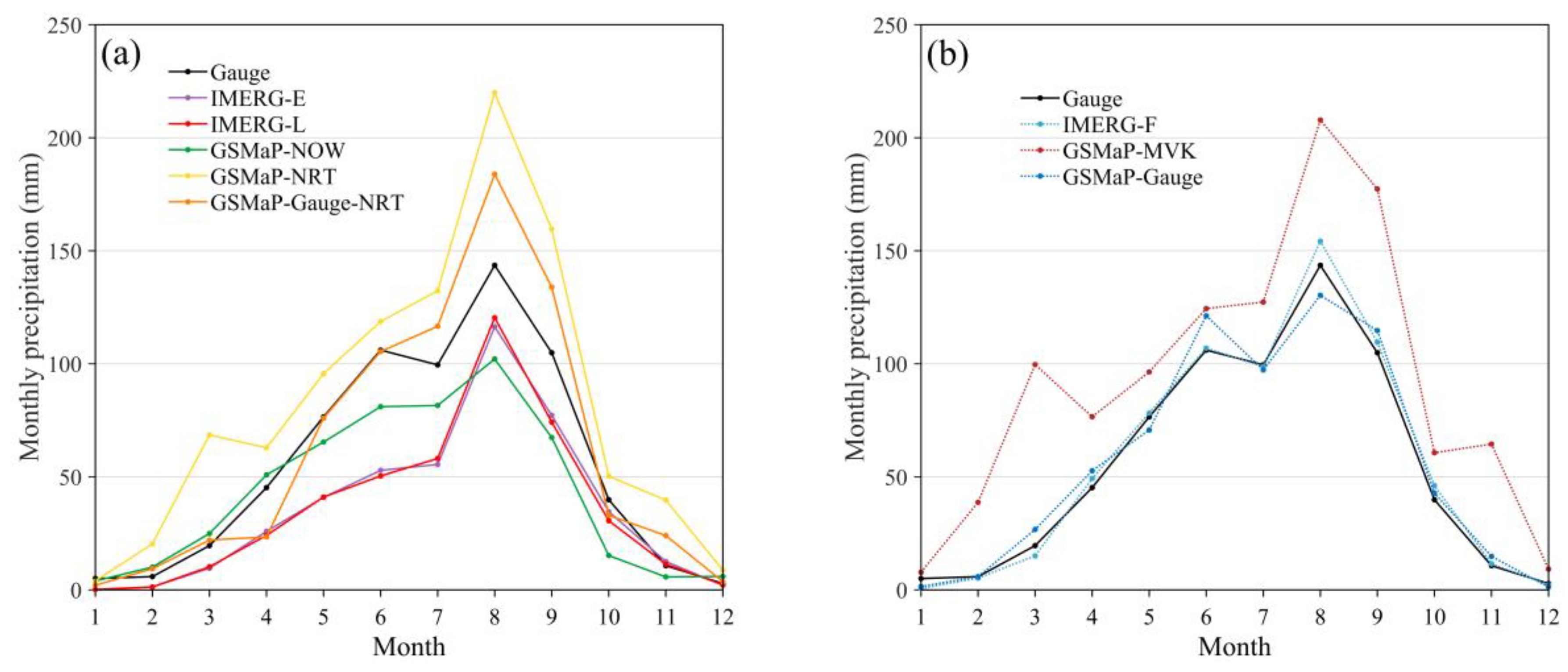
4.3.1. Temporal Variation of SPP-based Precipitation Estimates
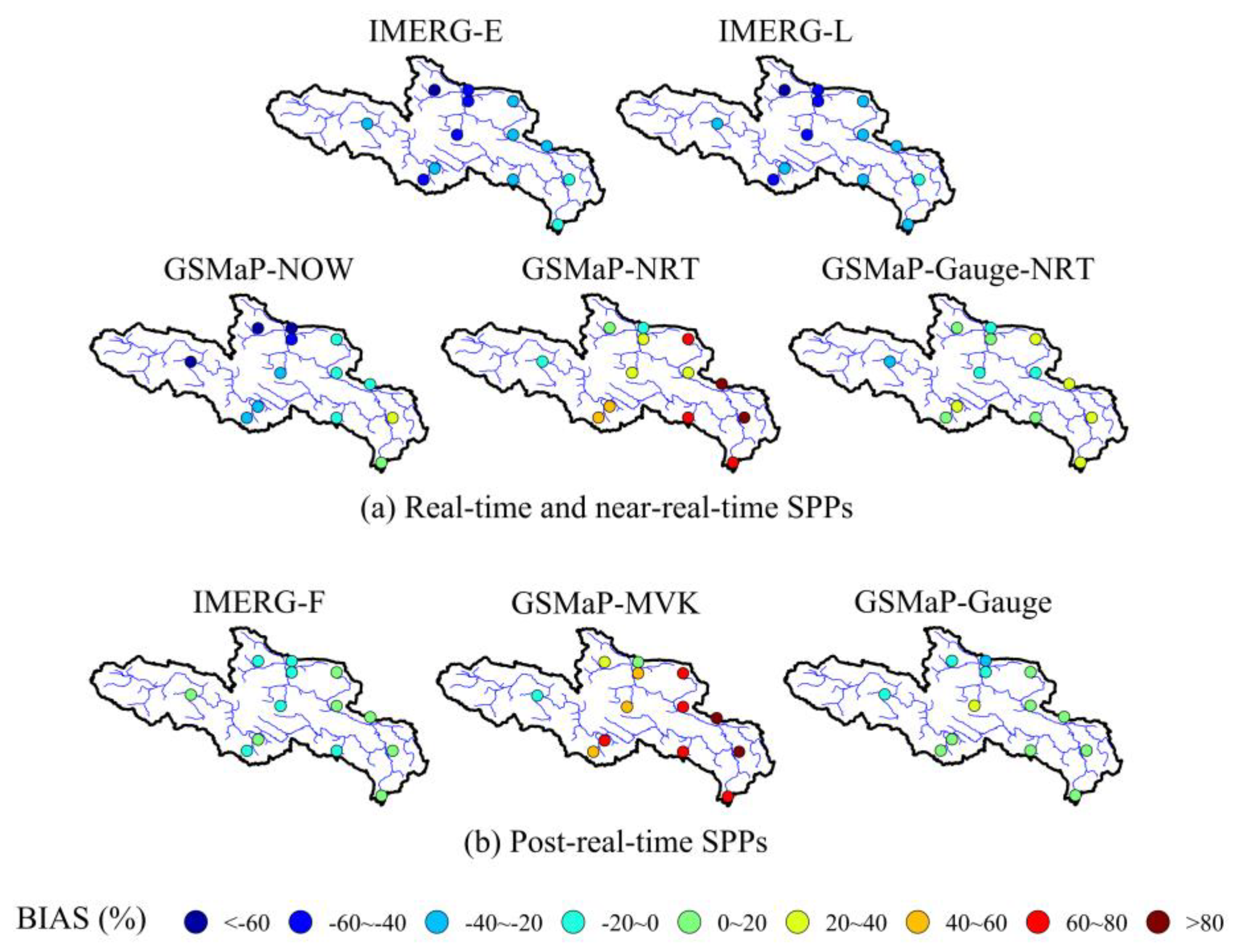
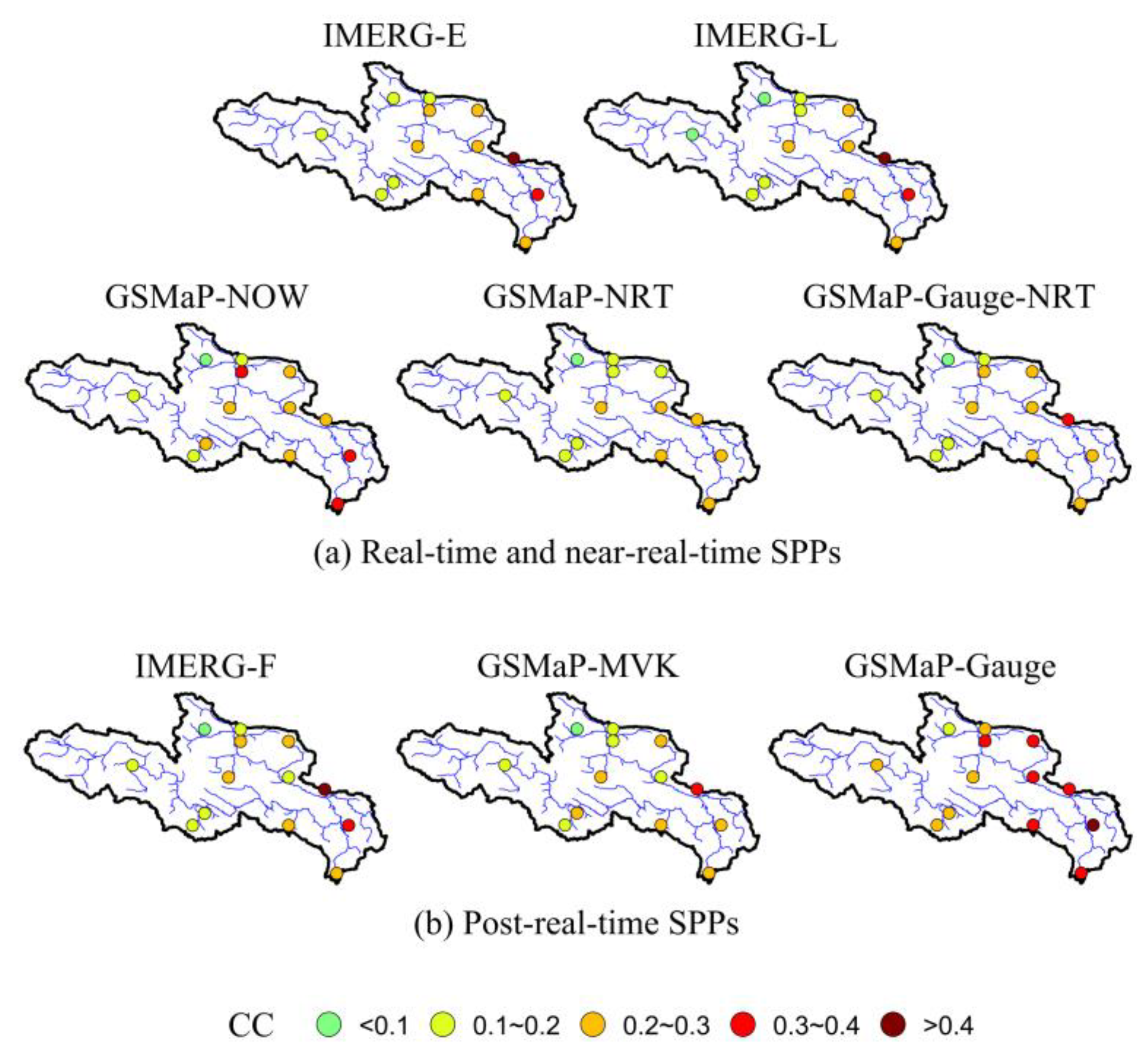
4.3.2. Spatial Pattern of Statistical Metrics
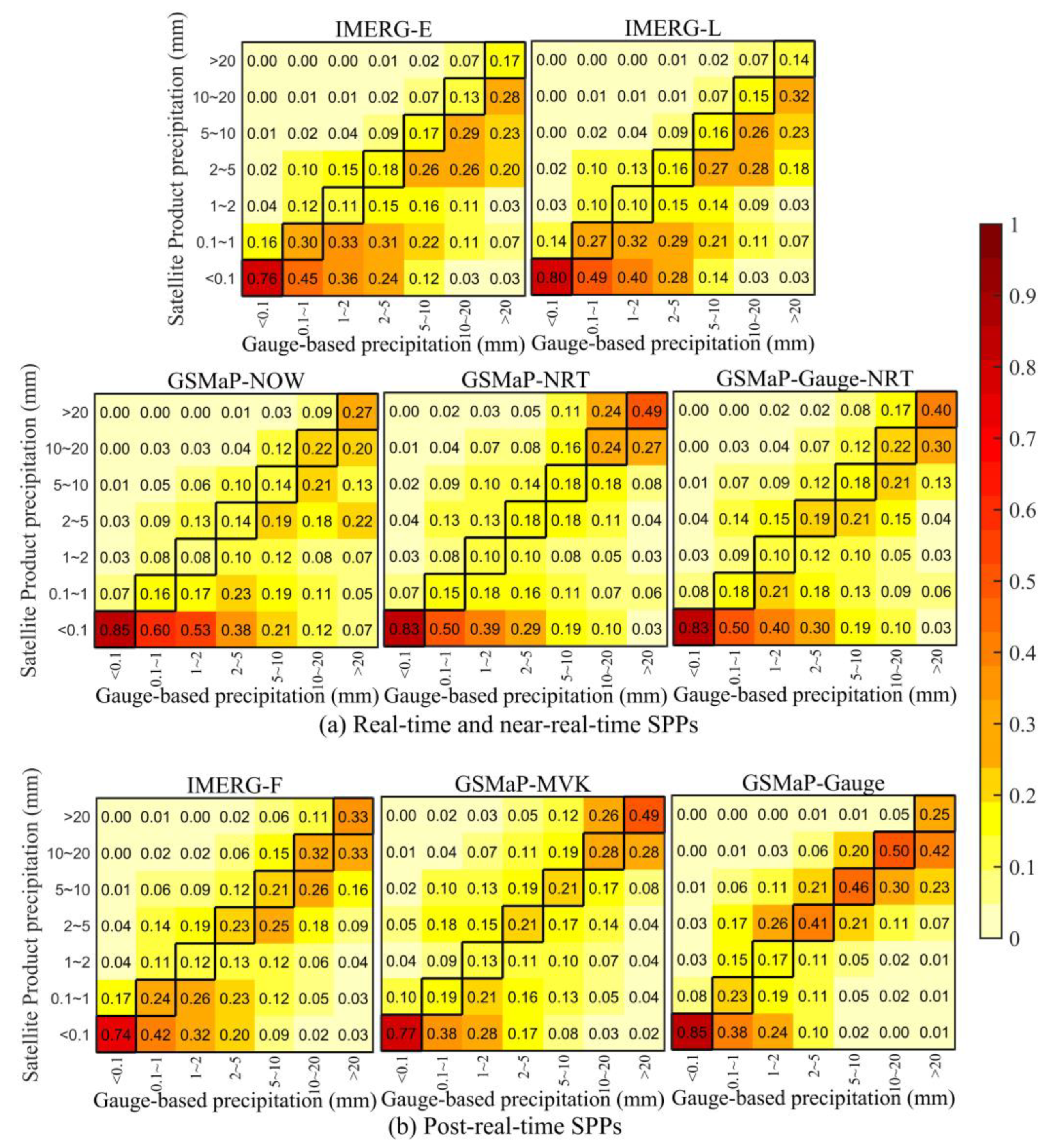
4.3.3. Confusion Matrix
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Owing to the gauge-based calibration with the GPCC dataset, IMERG-F generally performed better than IMERG-E and IMERG-L, presenting considerably lower systematic biases. IMERG-E and IMERG-L underestimated the occurrences of the no-rain and light-rain events but overestimated moderate and heavy rain.
- (2)
- Regarding the performance of the three GSMaP SPPs, GSMaP-Gauge outperformed the other four GSMaP SPPs in all statistical metrics, although numerous false precipitation detections were incurred at the hourly scale. However, GSMaP-Gauge excessively underestimated the precipitation under 0.1 mm and overestimated the precipitation ranging from 0.1 to 1 mm. GSMaP-Gauge-NRT was ranked as the second after GSMaP-Gauge with evident improvement over GSMaP-NRT. GSMaP-MVK and GSMaP-NRT showed significant overestimations, and GSMaP-NOW notably underestimated total precipitation.
- (3)
- By comparing the performance of IMERG and GSMaP SPPs, GSMaP-Gauge-NRT presented better characteristics of the diurnal and monthly cycles most of the time among all real- and near-real-time SPPs. For post-real-time SPPs, GSMaP-Gauge presented the highest capability for the quantification of daily precipitation events, whereas IMERG-F resulted in the best precipitation estimates at the monthly scale. Considering the estimation accuracy of SPPs in complex elevation and topography, the evaluation metrics (BIAS and CC) at the hourly scale presented distinct spatial pattern. The BIAS and CC were higher in the southeastern part (the lowlands) of the basin than in the northwestern part (the highlands). In the application of confusion matrix, GSMaP-Gauge performed the best and showed the most stable quality results among all post-real-time SPPs, followed by IMERG-F.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kidd, C.; Huffman, G. Global precipitation measurement. Meteorol. Appl. 2011, 18, 334–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Ingram, W.J. Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle. Nature 2002, 419, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Hong, Y.; Limaye, A.S.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Khan, S.I.; Dorji, C.; Chen, S. Statistical and hydrological evaluation of TRMM-based Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis over the Wangchu Basin of Bhutan: Are the latest satellite precipitation products 3B42V7 ready for use in ungauged basins? J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Aonashi, K.; Takahashi, N.; Seto, S.; Hirose, M.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K. Global precipitation map using satellite-borne microwave radiometers by the GSMaP project: Production and validation. IEEE T. Geosci. Remote. 2007, 45, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhang, C.; Fu, G.; Sweetapple, C.; Zhou, H. Evaluation of global fine-resolution precipitation products and their uncertainty quantification in ensemble discharge simulations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sc. 2016, 20, 903–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falck, A.S.; Maggioni, V.; Tomasella, J.; Vila, D.A.; Diniz, F.L. Propagation of satellite precipitation uncertainties through a distributed hydrologic model: A case study in the Tocantins–Araguaia basin in Brazil. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Amarnath, G. Applications of satellite-based rainfall estimates in flood inundation modeling—A case study in Mundeni Aru River Basin, Sri Lanka. Remote Sens.-Basel. 2017, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yong, B.; Ren, L.L.; Hong, Y.; Wang, J.H.; Gourley, J.J.; Jiang, S.H.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. Hydrologic evaluation of Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis standard precipitation products in basins beyond its inclined latitude band: A case study in Laohahe basin, China. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y.; Yong, B.; Yang, X.; Yuan, F.; Ma, M. Comprehensive evaluation of multi-satellite precipitation products with a dense rain gauge network and optimally merging their simulated hydrological flows using the Bayesian model averaging method. J. Hydrol. 2012, 452, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Y.; Duan, Z.; Disse, M.; Chiogna, G. Evaluation of precipitation input for SWAT modeling in Alpine catchment: A case study in the Adige river basin (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Adler, R.F.; Huffman, G.J.; Pierce, H. Applications of TRMM-based multi-satellite precipitation estimation for global runoff prediction: Prototyping a global flood modeling system. In Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Springer Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 245–265. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Tan, J.; Xie, P. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) Version 4.5: NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG); NASA: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Xie, P. GPM Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) Version 4.4; PPS, NASA/GSFC: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2014; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. B. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Tan, T.; Xie, P. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) Version 5.2 NASA—NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG); NASA: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L.; Lu, H.; Yang, K.; Chen, Y. Evaluation of GPM IMERG Precipitation Products in the South Tibetan Plateau and Central Himalaya; AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Yong, B. Evaluation and hydrological utility of the latest GPM IMERG V5 and GSMaP V7 precipitation products over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens.-Basel. 2018, 10, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, G.; Ma, Y.; Long, D.; Zhong, L.; Hong, Y. Evaluation of GPM Day-1 IMERG and TMPA Version-7 legacy products over Mainland China at multiple spatiotemporal scales. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Lü, H.; Crow, W.T.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Su, J. Comprehensive Evaluation of GPM-IMERG, CMORPH, and TMPA Precipitation Products with Gauged Rainfall over Mainland China. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. How do GPM IMERG precipitation estimates perform as hydrological model forcing? Evaluation for 300 catchments across Mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beria, H.; Nanda, T.; Bisht, D.S.; Chatterjee, C. Does the GPM mission improve the systematic error component in satellite rainfall estimates over TRMM? An evaluation at a pan-India scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozante, J.; Vila, D.; Barboza Chiquetto, J.; Fernandes, A.; Souza Alvim, D. Evaluation of TRMM/GPM blended daily products over Brazil. Remote Sens.-Basel. 2018, 10, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gosset, M.; Alcoba, M.; Roca, R.; Cloché, S.; Urbani, G. Evaluation of TAPEER daily estimates and other GPM-era products against dense gauge networks in West Africa, analysing ground reference uncertainty. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2018, 144, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dezfuli, A.K.; Ichoku, C.M.; Mohr, K.I.; Huffman, G.J. Precipitation characteristics in West and East Africa from satellite and in situ observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1799–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Tian, F.; Yang, L.; Hu, H.; Lu, H.; Hou, A. Ground validation of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42V7 rainfall products over southern Tibetan Plateau based on a high-density rain gauge network. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmospheres. 2017, 122, 910–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhong, R.; Lai, C.; Chen, J. Evaluation of the GPM IMERG satellite-based precipitation products and the hydrological utility. Atmos. Res. 2017, 196, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Liu, J.; Tuo, Y.; Chiogna, G.; Disse, M. Evaluation of eight high spatial resolution gridded precipitation products in Adige Basin (Italy) at multiple temporal and spatial scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1536–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Adler, R.F.; Kubota, T.; Ushio, T. Evaluation of GSMaP Precipitation Estimates over the Contiguous United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Hu, J.; Gebregiorgis, A.; Xue, X.; Zhang, X. Inter-Comparison of High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Products over Central Asia. Remote Sens.-Basel. 2015, 7, 7181–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, S.; Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Ishidaira, H. Assessment of the Latest GPM-Era High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Products by Comparison with Observation Gauge Data over the Chinese Mainland. Water 2016, 8, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Lü, H.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X. Evaluating the hydrological utility of latest IMERG products over the Upper Huaihe River Basin, China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 225, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Yong, B.; Ren, L. Error features of the hourly GSMaP multi-satellite precipitation estimates over nine major basins of China. Hydrol. Res. 2018, 49, 761–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Soe, K.; Ren, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Applications of TRMM- and GPM-Era Multiple-Satellite Precipitation Products for Flood Simulations at Sub-Daily Scales in a Sparsely Gauged Watershed in Myanmar. Remote Sens.-Basel. 2019, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Eylander, J.B.; Joyce, R.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Hsu, K.; Turk, F.J.; Garcia, M.; Zeng, J. Component analysis of errors in satellite-based precipitation estimates. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, B.; Huang, Y. Assessment of the Two Successive GPM-Based V3 and V4 GSMaP Precipitation Products at Multiple Temporal and Spatial Scales Over China. IEE J.-Stars. 2019, 12, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Song, F.; Udmale, P.; Jin, J.; Thapa, B.R.; Ishidaira, H. Error Analysis and Evaluation of the Latest GSMap and IMERG Precipitation Products over Eastern China. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, M.V.; Mitra, A.K.; Momin, I.M.; Mitra, A.K.; Pai, D.S. Evaluation and inter-comparison of high-resolution multi-satellite rainfall products over India for the southwest monsoon period. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 4577–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Mo, K.; Li, Z.; Tang, G. Multiscale Comparative Evaluation of the GPM IMERG v5 and TRMM 3B42 v7 Precipitation Products from 2015 to 2017 over a Climate Transition Area of China. Remote Sens.-Basel. 2018, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Tang, G.; Long, D.; Yong, B.; Zhong, L.; Wan, W.; Hong, Y. Similarity and Error Intercomparison of the GPM and Its Predecessor-TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis Using the Best Available Hourly Gauge Network over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens.-Basel. 2016, 8, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, R.; Liu, C.; Sato, Y.; Fukushima, Y. Responses of streamflow to climate and land surface change in the headwaters of the Yellow River Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Maskey, S.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Zhao, H. Streamflow trends and climate linkages in the source region of the Yellow River, China. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3399–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.H.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.F.; Cao, L.J.; Yang, Y.R.; Zou, F.L.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zhao, H.M.; Chen, Z. Quality control procedures for hourly precipitation data from automatic weather stations in China. Meteorol. Mon. 2010, 36, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, B.; Shi, C.; Cui, W.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, T.; et al. Evaluation of hydrological utility of IMERG Final run V05 and TMPA 3B42V7 satellite precipitation products in the Yellow River source region, China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, T.; Kirschbaum, D.B.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F. Approximating long-term statistics early in the global precipitation measurement era. Earth Interact. 2017, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokolova, M.; Lapalme, G. A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Inform. Process. Manag. 2009, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visa, S.; Ramsay, B.; Ralescu, A.L.; Van Der Knaap, E. Confusion Matrix-based Feature Selection. MAICS 2011, 710, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Abera, W.; Brocca, L.; Rigon, R. Comparative evaluation of different satellite rainfall estimation products and bias correction in the Upper Blue Nile (UBN) basin. Atmos. Res. 2016, 178–179, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Xu, C.; Yong, B.; Yuan, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zeng, X. Statistical and hydrological evaluation of the latest Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) over a midlatitude humid basin in South China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A. Statistical comparison of satellite-retrieved precipitation products with rain gauge observations over Bangladesh. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2906–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Chang, Y.; Liu, P. Assessment of IMERG precipitation over Taiwan at multiple timescales. Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Bao, A.; Ndayisaba, F.; Liu, T.; Kurban, A.; De Maeyer, P. Systematical Evaluation of Satellite Precipitation Estimates Over Central Asia Using an Improved Error-Component Procedure. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 10906–10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foelsche, U.; Kirchengast, G.; Fuchsberger, J.; Tan, J.; Petersen, W.A. Evaluation of GPM IMERG Early, Late, and Final rainfall estimates using WegenerNet gauge data in southeastern Austria. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sc. 2017, 21, 6559–6572. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Tang, G.; Wei, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of multi-satellite precipitation products in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 7437–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Chidzambwa, S.; Ceccato, P.; Connor, S.J.; Ropelewski, C.F. Validation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products over complex terrain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacina, L.; Poulter, R.M.; Ashmore, S.E.; Manley, G.; BONACINA, L. Orographic rainfall and its place in the hydrology of the globe. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 1945, 71, 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.; Hall, A.; Fovell, R.G. Blocking in areas of complex topography, and its influence on rainfall distribution. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mega, T.; Ushio, T.; Takahiro, M.; Kubota, T.; Kachi, M.; Oki, R. Gauge-Adjusted Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation. Ieee, T. Geosci. Remote. 2019, 57, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Chen, B.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Z.; Hong, Y. Error-Component Analysis of TRMM-Based Multi-Satellite Precipitation Estimates over Mainland China. Remote Sens.-Basel. 2016, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.; Gao, X.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Y. Merging multi-source precipitation products or merging their simulated hydrological flows to improve streamflow simulation. Hydrolog. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z. Geographically weighted regression based methods for merging satellite and gauge precipitation. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Products | Resolution | Latency | Time Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| IMERG-E | 0.1°, 0.5 h | 4 h | 1 June 2014 to 31 December, 2018 |
| IMERG-L | 0.1°, 0.5 h | 14 h | 1 June 2014 to 31 December, 2018 |
| IMERG-F | 0.1°, 0.5 h | 3.5 months | 1 January 2014 to 31 December, 2018 |
| GSMaP-NOW | 0.1°, 0.5 h | Real time | 29 March 2017 to 31 December, 2018 |
| GSMaP-NRT | 0.1°, 1 h | 4 h | 17 January 2017 to 31 December, 2018 |
| GSMaP-Gauge-NRT | 0.1°, 1 h | 4 h | 17 January 2017 to 31 December, 2018 |
| GSMaP-MVK | 0.1°, 1 h | 3 days | 1 March 2014 to 31 December, 2018 |
| GSMaP-Gauge | 0.1°, 1 h | 3 days | 1 March 2014 to 31 December, 2018 |
| Categories | Statistic Metrics | Equations | Perfect Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pearson correlation coefficient (CC) | 1 | |
| 2 | Mean error (ME) | 0 | |
| Mean absolute error (MAE) | 0 | ||
| Root-mean-squared error (RMSE) | 0 | ||
| Relative BIAS (BIAS) | 0 | ||
| 3 | Probability of detection (POD) | 1 | |
| False alarm ratio (FAR) | 0 | ||
| Critical success index (CSI) | 1 | ||
| 4 | Coefficient of skewness (SK) | 0 |
| Time Scale | SPPs | CC | ME (mm) | MAE (mm) | RMSE (mm) | BIAS (%) | POD | FAR | CSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hourly | IMERG-E | 0.24 | −0.024 | 0.093 | 0.55 | −33.17 | 0.69 | 0.27 | 0.55 |
| IMERG-L | 0.22 | −0.025 | 0.094 | 0.56 | −34.45 | 0.69 | 0.27 | 0.55 | |
| IMERG-F | 0.24 | 0.001 | 0.111 | 0.60 | 2.04 | 0.71 | 0.32 | 0.53 | |
| Daily | IMERG-E | 0.53 | −0.558 | 1.499 | 3.93 | −33.17 | 0.77 | 0.25 | 0.61 |
| IMERG-L | 0.52 | −0.581 | 1.487 | 4.09 | −34.45 | 0.74 | 0.22 | 0.61 | |
| IMERG-F | 0.60 | 0.044 | 1.606 | 4.12 | 2.04 | 0.80 | 0.26 | 0.63 | |
| Monthly | IMERG-E | 0.82 | −16.744 | 23.306 | 33.76 | −33.17 | - | - | - |
| IMERG-L | 0.82 | −17.414 | 23.512 | 34.39 | −34.45 | - | - | - | |
| IMERG-F | 0.95 | 1.449 | 10.289 | 15.83 | 2.04 | - | - | - | |
| Seasonal | IMERG-E | 0.88 | −50.716 | 55.521 | 75.41 | −33.17 | - | - | - |
| IMERG-L | 0.88 | −52.745 | 57.422 | 77.03 | −34.45 | - | - | - | |
| IMERG-F | 0.97 | 4.529 | 21.069 | 30.12 | 2.04 | - | - | - |
| Time Scales | SPPs | SK |
|---|---|---|
| Hourly | IMERG-E | −0.26 |
| IMERG-L | −0.27 | |
| IMERG-F | 0.02 | |
| Daily | IMERG-E | −0.68 |
| IMERG-L | −0.70 | |
| IMERG-F | −0.10 | |
| Monthly | IMERG-E | −1.62 |
| IMERG-L | −1.78 | |
| IMERG-F | 0.28 | |
| Seasonal | IMERG-E | −1.56 |
| IMERG-L | −1.50 | |
| IMERG-F | 0.46 |
| Time Scales | SPPs | CC | ME (mm) | MAE (mm) | RMSE (mm) | BIAS (%) | POD | FAR | CSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hourly | GSMaP-NOW | 0.26 | −0.019 | 0.115 | 0.58 | −23.14 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.17 |
| GSMaP-NRT | 0.16 | 0.040 | 0.171 | 1.25 | 48.29 | 0.23 | 0.64 | 0.16 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge-NRT | 0.21 | 0.009 | 0.143 | 0.81 | 11.24 | 0.24 | 0.67 | 0.16 | |
| GSMaP-MVK | 0.19 | 0.049 | 0.175 | 0.98 | 58.77 | 0.29 | 0.67 | 0.18 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge | 0.31 | 0.002 | 0.125 | 0.54 | 2.88 | 0.53 | 0.71 | 0.23 | |
| Daily | GSMaP-NOW | 0.53 | −0.464 | 1.895 | 4.37 | −23.14 | 0.59 | 0.24 | 0.50 |
| GSMaP-NRT | 0.46 | 0.968 | 2.702 | 8.63 | 48.29 | 0.67 | 0.25 | 0.55 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge-NRT | 0.54 | 0.225 | 2.151 | 5.67 | 11.24 | 0.67 | 0.24 | 0.55 | |
| GSMaP-MVK | 0.54 | 1.178 | 2.642 | 6.84 | 58.77 | 0.78 | 0.28 | 0.60 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge | 0.73 | 0.058 | 1.321 | 3.19 | 2.88 | 0.82 | 0.19 | 0.68 | |
| Monthly | GSMaP-NOW | 0.75 | −14.480 | 27.866 | 42.33 | −23.14 | - | - | - |
| GSMaP-NRT | 0.78 | 29.425 | 41.294 | 67.99 | 48.29 | - | - | - | |
| GSMaP-Gauge-NRT | 0.84 | 6.857 | 26.003 | 41.58 | 11.24 | - | - | - | |
| GSMaP-MVK | 0.79 | 35.635 | 43.343 | 64.03 | 58.77 | - | - | - | |
| GSMaP-Gauge | 0.92 | 1.861 | 12.816 | 22.17 | 2.88 | - | - | - | |
| Seasonal | GSMaP-NOW | 0.78 | −43.440 | 27.866 | 94.68 | −23.14 | - | - | - |
| GSMaP-NRT | 0.85 | 88.276 | 41.294 | 142.32 | 48.29 | - | - | - | |
| GSMaP-Gauge-NRT | 0.89 | 20.571 | 26.003 | 78.20 | 11.24 | - | - | - | |
| GSMaP-MVK | 0.87 | 106.906 | 43.343 | 141.50 | 58.77 | - | - | - | |
| GSMaP-Gauge | 0.96 | 5.584 | 25.414 | 38.75 | 2.88 | - | - | - |
| Time Scale | SPPs | SK |
|---|---|---|
| Hourly | GSMaP-NOW | −0.17 |
| GSMaP-NRT | 0.27 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge-NRT | 0.07 | |
| GSMaP-MVK | 0.32 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge | 0.02 | |
| Daily | GSMaP-NOW | −0.31 |
| GSMaP-NRT | 0.49 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge-NRT | 0.15 | |
| GSMaP-MVK | 0.68 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge | 0.05 | |
| Monthly | GSMaP-NOW | −1.02 |
| GSMaP-NRT | 1.64 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge-NRT | 0.58 | |
| GSMaP-MVK | 1.93 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge | 0.23 | |
| Seasonal | GSMaP-NOW | −1.15 |
| GSMaP-NRT | 1.60 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge-NRT | 0.72 | |
| GSMaP-MVK | 1.82 | |
| GSMaP-Gauge | 0.30 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Yuan, F.; Shi, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Ren, L.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Statistical Evaluation of the Latest GPM-Era IMERG and GSMaP Satellite Precipitation Products in the Yellow River Source Region. Water 2020, 12, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041006
Shi J, Yuan F, Shi C, Zhao C, Zhang L, Ren L, Zhu Y, Jiang S, Liu Y. Statistical Evaluation of the Latest GPM-Era IMERG and GSMaP Satellite Precipitation Products in the Yellow River Source Region. Water. 2020; 12(4):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041006
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jiayong, Fei Yuan, Chunxiang Shi, Chongxu Zhao, Limin Zhang, Liliang Ren, Yonghua Zhu, Shanhu Jiang, and Yi Liu. 2020. "Statistical Evaluation of the Latest GPM-Era IMERG and GSMaP Satellite Precipitation Products in the Yellow River Source Region" Water 12, no. 4: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041006
APA StyleShi, J., Yuan, F., Shi, C., Zhao, C., Zhang, L., Ren, L., Zhu, Y., Jiang, S., & Liu, Y. (2020). Statistical Evaluation of the Latest GPM-Era IMERG and GSMaP Satellite Precipitation Products in the Yellow River Source Region. Water, 12(4), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041006





