On the Hydrodynamic Behavior of the Changed River–Lake Relationship in a Large Floodplain System, Poyang Lake (China)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
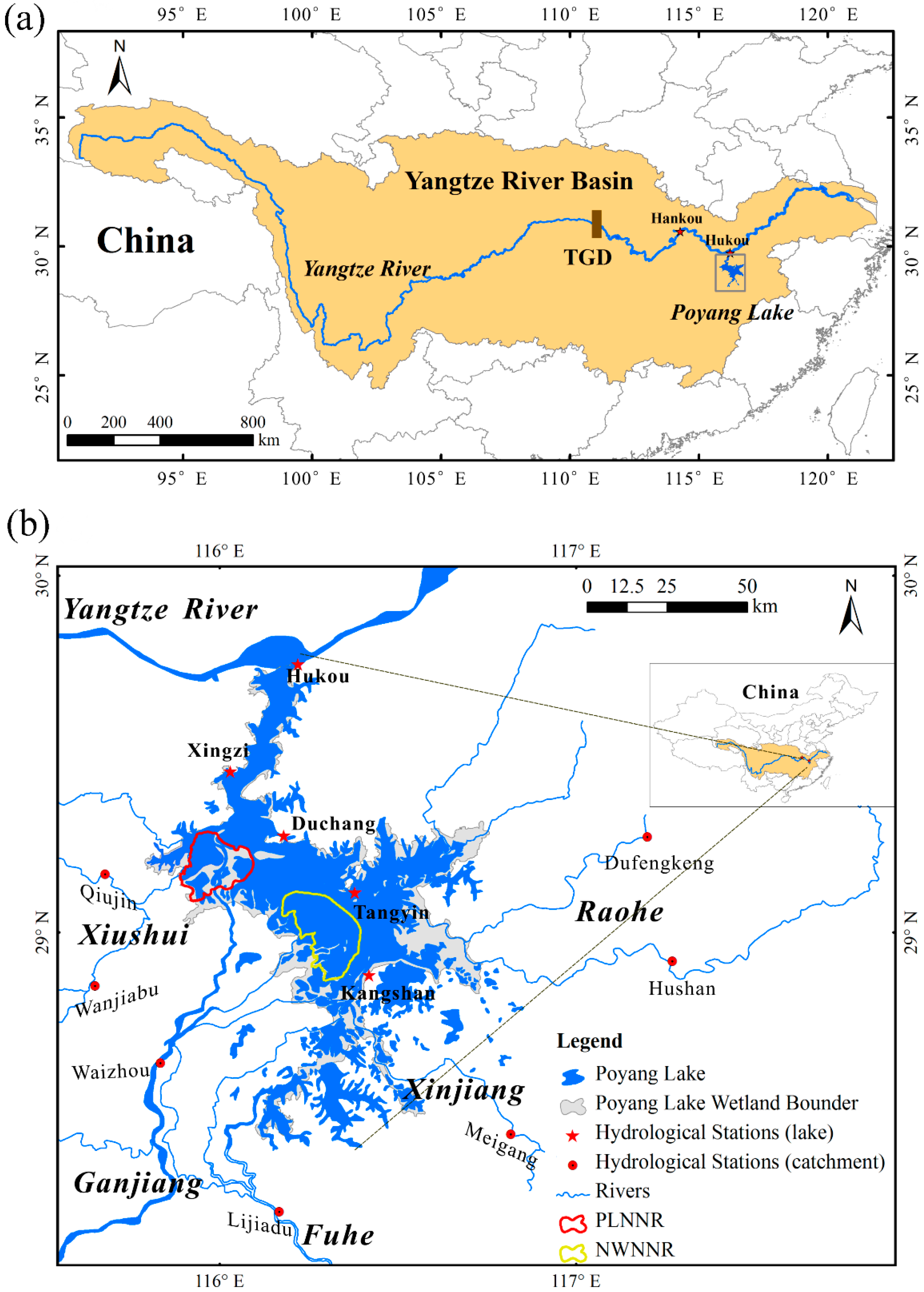
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Purpose
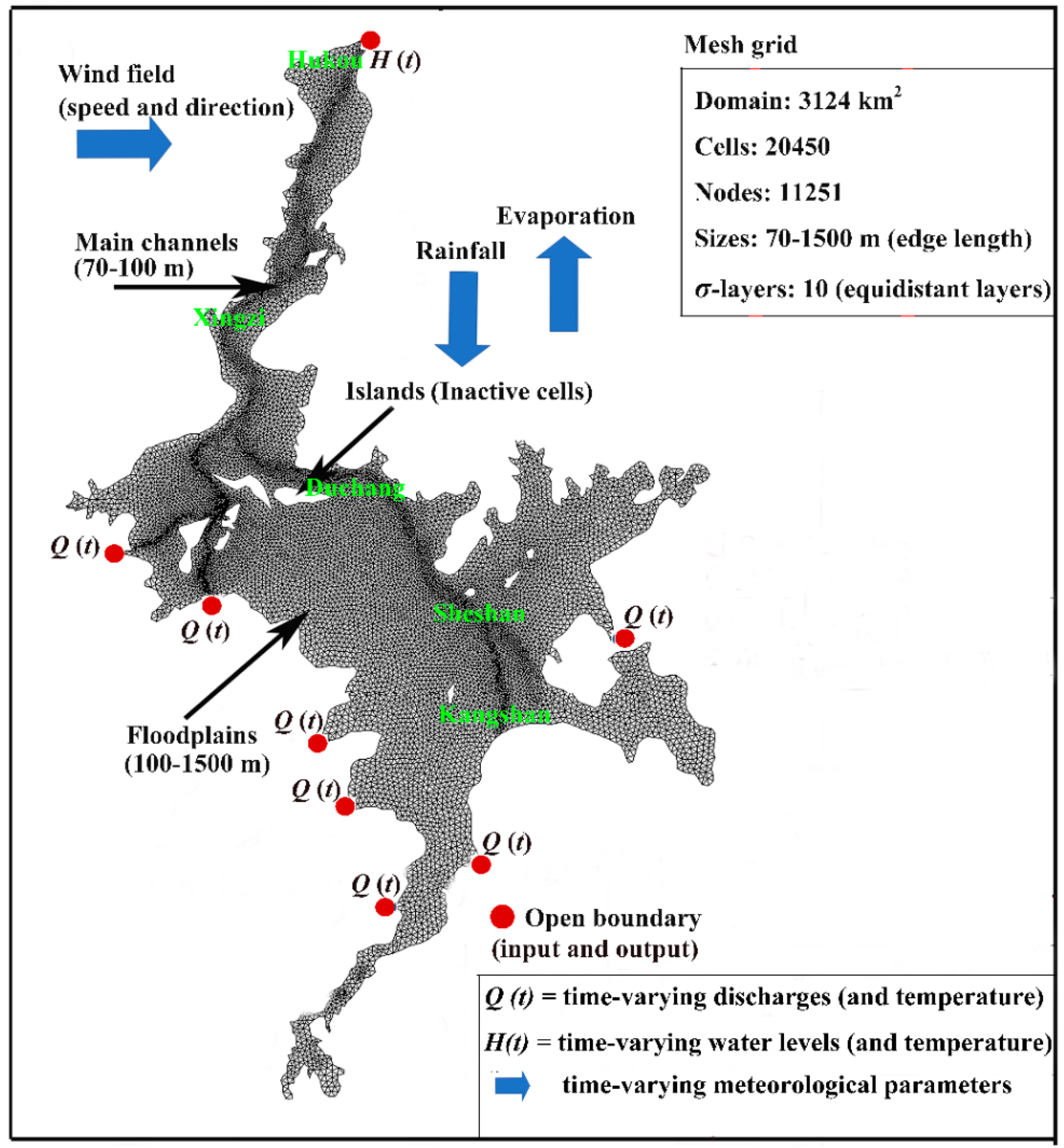
2.3. Floodplain Hydrodynamic Model
2.4. Model Validation
2.5. Scenario Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
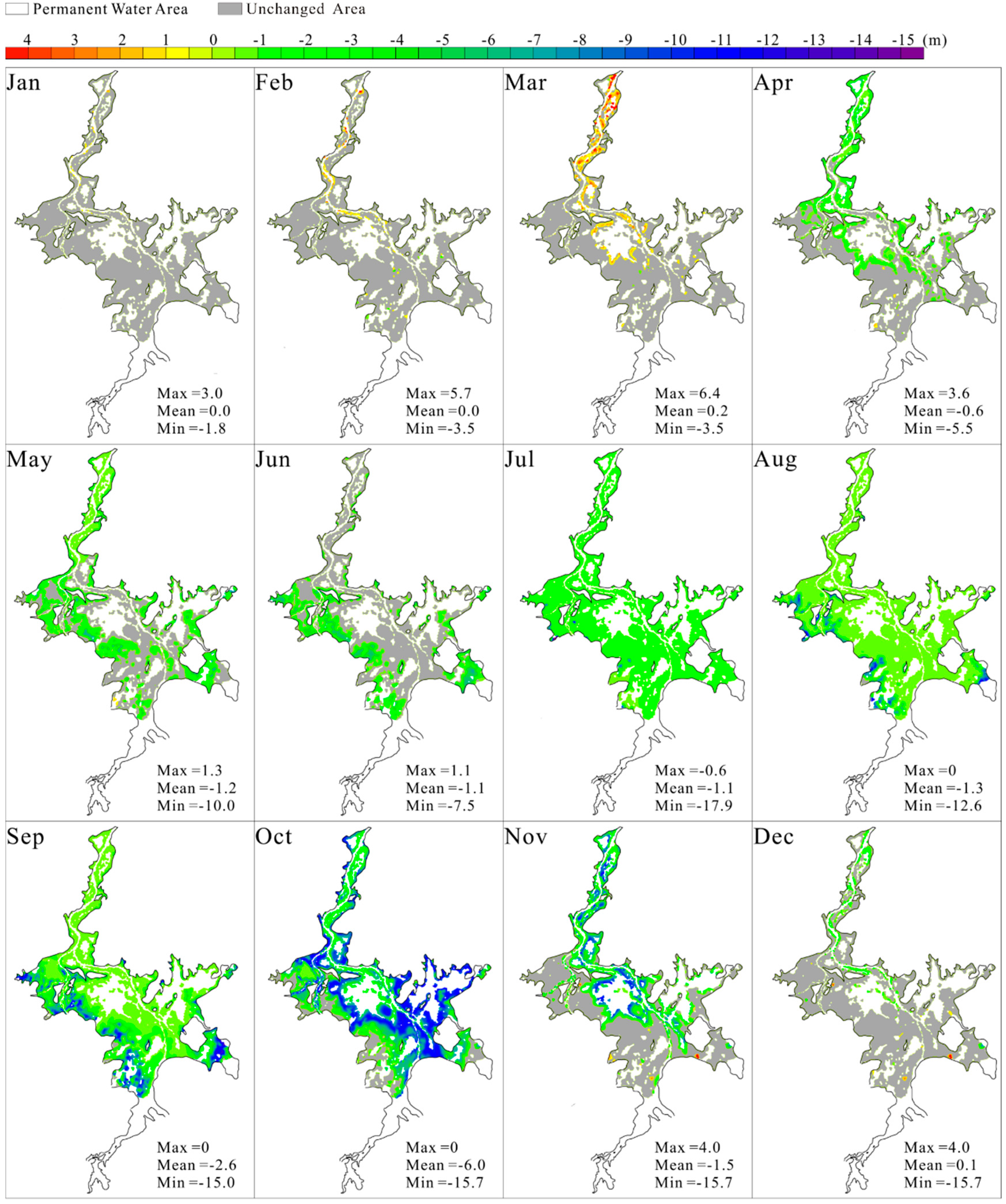
3.1. Spatiotemporal Changes in Water Level
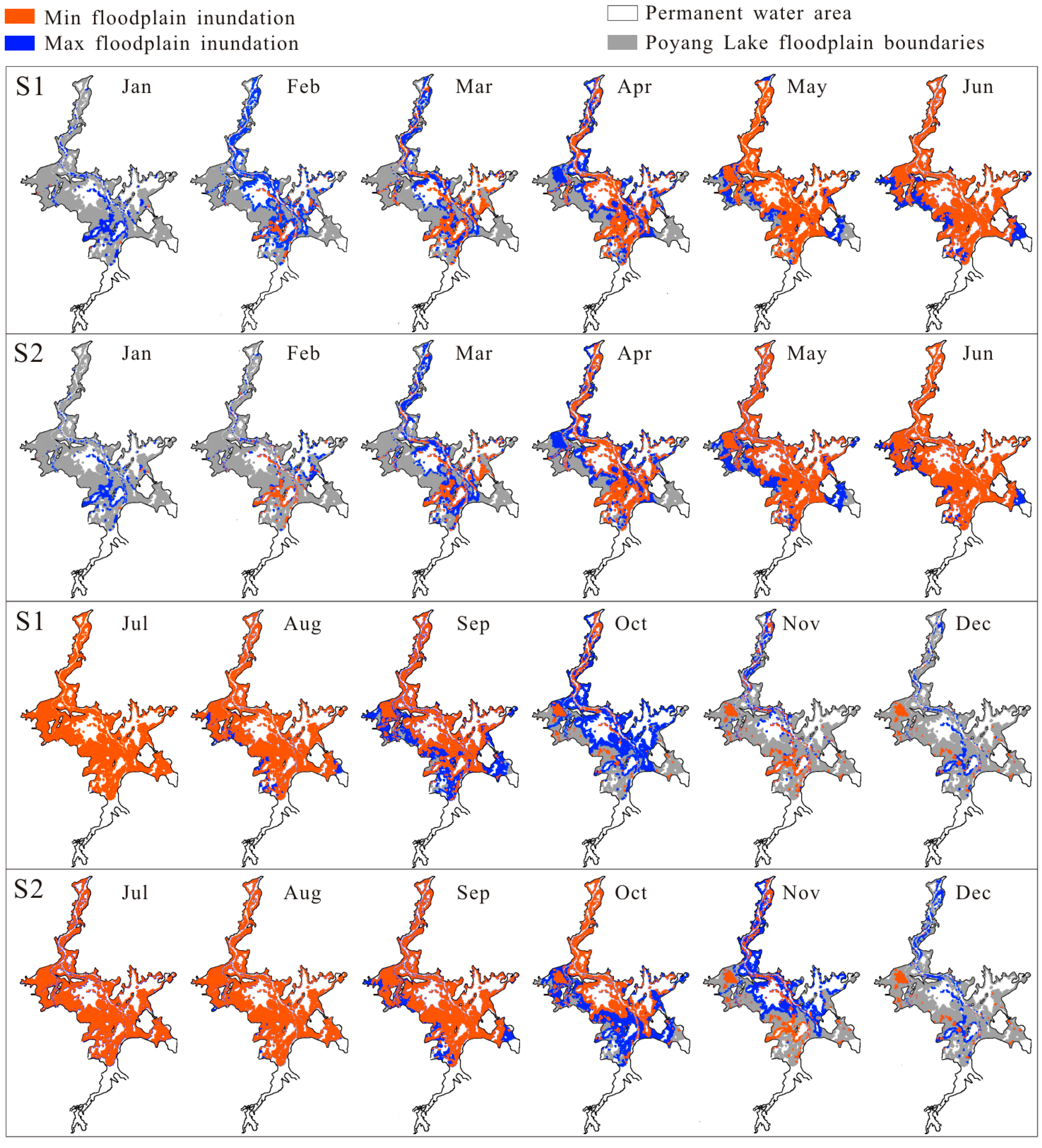
3.2. Changes in Inundation Extent
3.3. Changes in Inundation Duration
3.4. Limitations and Uncertainties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van der Most, M.; Hudson, P.F. The influence of floodplain geomorphology and hydrologic connectivity on alligator gar (Atractosteus spatula) habitat along the embanked floodplain of the Lower Mississippi River. Geomorphology 2018, 302, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entwistle, N.S.; Heritage, G.L.; Schofield, L.A.; Williamson, R.J. Recent changes to floodplain character and functionality in England. Catena 2019, 174, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melack, J.M.; Forsberg, B.R. Biogeochemistry of Amazon Floodplain Lakes and Associated Wetlands. In The Biogeochemistry of the Amazon Basin and Its Role in a Changing World; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 235–276. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet, M.P.; Barroux, G.; Martinez, J.M.; Seyler, F.; Moreira-Turcq, P.; Cochonneau, G.; Roux, E. Floodplain hydrology in an Amazon floodplain lake (Lago Grande de Curuaí). J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, Y.; Tan, Z.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Yao, J. Hydrodynamic investigation of surface hydrological connectivity and its effects on the water quality of seasonal lakes: Insights from a complex floodplain setting (Poyang Lake, China). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, R.J.; Leigh, C.; Sheldon, F. Mechanistic effects of low-flow hydrology on riverine ecosystems: Ecological principles and consequences of alteration. Freshwater Sci. 2012, 31, 1163–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helton, A.M.; Poole, G.C.; Payn, R.A.; Izurieta, C.; Stanford, J.A. Relative influences of the river channel, floodplain surface, and alluvial aquifer on simulated hydrologic residence time in a montane river floodplain. Geomorphology 2014, 205, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Werner, A.D. Hysteretic relationships in inundation dynamics for a large lake–floodplain system. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbitt, K.J. The relative importance of wetland size and hydroperiod for amphibians in southern New Hampshire, USA. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 13, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crase, B.; Liedloff, A.; Vesk, P.A.; Burgman, M.A.; Wintle, B.A. Hydroperiod is the main driver of the spatial pattern of dominance in mangrove communities. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray-Hudson, M.; Wolski, P.; Murray-Hudson, F.; Brown, M.T.; Kashe, K. Disaggregating hydroperiod: Components of the seasonal flood pulse as drivers of plant species distribution in floodplains of a tropical wetland. Wetlands 2014, 34, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray-Hudson, M.; Wolski, P.; Cassidy, L.; Brown, M.T.; Thito, K.; Kashe, K.; Mosimanyana, E. Remote Sensing-derived hydroperiod as a predictor of floodplain vegetation composition. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 23, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiang, J. A study of the relationship between wetland vegetation communities and water regimes using a combined remote sensing and hydraulic modeling approach. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 278–292. [Google Scholar]
- Legesse, D.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Gasse, F. Analysis of the hydrological response of a tropical terminal lake, Lake Abiyata (Main Ethiopian Rift Valley) to changes in climate and human activities. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Araneda, F.J.; Urrutia, J.; Soto-Mora, Y.; Figueroa, R.; Hauenstein, E. Effects of the hydroperiod on the vegetative and community structure of freshwater forested wetlands. Chile. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2012, 27, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Long, C.M.; Pavelsky, T.M. Remote sensing of suspended sediment concentration and hydrologic connectivity in a complex wetland environment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Tian, L.; Gan, W. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X. Dramatic inundation changes of China’s two largest freshwater lakes linked to the Three Gorges Dam. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9628–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilvear, D.; Bryant, R. Analysis of remotely sensed data for fluvial geomorphology and river science. In Tools in Fluvial Geomorphology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 103–132. [Google Scholar]
- Malinowski, R.; Höfle, B.; Koenig, K.; Groom, G.; Schwanghart, W.; Heckrath, G. Local-scale flood mapping on vegetated floodplains from radiometrically calibrated airborne LiDAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2016, 119, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Monitoring the impact of backflow and dredging on water clarity using MODIS images of Poyang lake, china. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P.A. Relationships between vegetation patterns and hydroperiod on the Roanoke River floodplain, North Carolina. Plant Ecol. 2001, 156, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerger, A.; Wealands, S. Beyond modelling: Linking models with GIS for flood risk management. Nat. Hazards 2004, 33, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, C.L.; Koseff, J.R.; Lucas, L.V.; Cloern, J.E.; Schoellhamer, D.H. Effects of spatial and temporal variability of turbidity on phytoplankton blooms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 254, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, C.; Foerster, S.; Bronstert, A. Comparison of hydrodynamic models of different complexities to model floods with emergency storage areas. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 4695–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Feng, S.; Guo, H. Interactions of the Yangtze river flow and hydrologic processes of the Poyang Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Q. Changes in hydrological interactions of the Yangtze River and the Poyang Lake in China during 1957–2008. Acta Geogr. 2011, 66, 609–618. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, S. Effects of the three gorges dam on Yangtze River flow and river interaction with Poyang lake, china: 2003–2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.G.; Werner, A.D.; Xin, P.; Jiang, T.; Barry, D.A. Has the Three-Gorges Dam made the Poyang Lake wetlands wetter and drier? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Ban, X.; Wang, X.; Cai, X. Assessment of hydrologic alterations caused by the Three Gorges Dam in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River, China. Water 2014, 6, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, C.Y.; Hong, Y.; Hardy, J.; Sun, Z. Examining the influence of river–lake interaction on the drought and water resources in the Poyang Lake basin. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rhoads, B.L.; Wang, D. Assessment of the flow regime alterations in the middle reach of the Yangtze River associated with dam construction: Potential ecological implications. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 3949–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Hong, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. Attribution of the changes in annual streamflow in the Yangtze River Basin over the past 146 years. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Liang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Huang, Q. Impoundment effects of the Three-Gorges-Dam on flow regimes in two China’s largest freshwater lakes. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 5111–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Liang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Lu, X.X. Numerical evaluation of flow regime changes induced by the Three Gorges Dam in the Middle Yangtze. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Q.; Zhan, L. Characteristics of low-water level changes in lake Poyang during 1952–2011. J. Lake Sci. 2012, 24, 675–678. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.; Werner, A.D.; Li, Y.L.; Yao, J.; Li, X. An investigation of enhanced recessions in Poyang lake: Comparison of Yangtze river and local catchment impacts. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wan, R.; Yang, G.; Wang, X. Temporal variation of hydrological rhythm in Poyang Lake and the associated water exchange with the Changjiang River. Sci. Geogr. 2014, 12, 1488–1496. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Factors influencing water level changes in china’s largest freshwater lake, Poyang lake, in the past 50 years. Water Int. 2014, 39, 983–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Hydrological evidence and causes of seasonal low water levels in a large river-lake system: Poyang Lake, China. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Chen, X.; Feng, L. Four decades of winter wetland changes in Poyang Lake based on Landsat observations between 1973 and 2013. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, J.; Du, Y.; Han, P.; Wang, J.; Huang, W. Monitoring wetland vegetation pattern response to water-level change resulting from the Three Gorges Project in the two largest freshwater lakes of China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wan, R.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Xu, L. Responses of wetland vegetation in Poyang Lake, China to water-level fluctuations. Hydrobiologia 2016, 773, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Scientists line up against dam that would alter protected wetlands. Science 2009, 326, 508–509. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, J.; Werner, A.D.; Li, X. Hydrodynamic and hydrological modeling of the Poyang Lake catchment system in China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Xu, C.Y. Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Satellite-based detection of water surface variation in China’s largest freshwater lake in response to hydro-climatic drought. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4544–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Capturing variations in inundation with satellite remote sensing in a morphologically complex, large lake. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ji, W. Study on Jiangxi Poyang Lake National Nature Reserve; Forest Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Danish Hydraulic Institute (DHI). Mike 21 Flow Model: Hydrodynamic Module User Guide; DHI: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, J. Investigation of residence and travel times in a large floodplain lake with complex lake-river interactions: Poyang Lake (China). Water 2015, 7, 1991–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Tan, Z. Inter-annual variations of Poyang Lake area during dry seasons: Characteristics and implications. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Werner, A.D.; Yao, J.; Ye, X. The influence of river-to-lake backflow on the hydrodynamics of a large floodplain lake system (Poyang Lake, China). Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, L.; Hu, Q. A modeling study of catchment discharge to Poyang Lake under future climate in China. Quat. Int. 2011, 244, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Tan, Z.; Yao, J. Investigation of water temperature variations and sensitivities in a large floodplain lake system (Poyang Lake, China) using a hydrodynamic model. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, H.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Q. Application of a distributed catchment model to investigate hydrological impacts of climate change within Poyang Lake catchment (China). Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Q. Evidences of hydraulic relationships between groundwater and lake water across the large floodplain wetland of Poyang Lake, China. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2018, 18, 698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Jiang, J.; Liang, Q.; Huang, Q. Large-scale hydrodynamic modeling of the middle Yangtze River Basin with complex river-lake interactions. J. Hydrol. 2013, 492, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.; Zhang, D.; Bai, P. Quantifying the impact of bathymetric changes on the hydrological regimes in a large floodplain lake: Poyang Lake. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Seasonal water exchanges between China’s Poyang Lake and its saucer-shaped depressions on river deltas. Water 2017, 9, 884. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, X.; Shankman, D.; Huber, C.; Yesou, H.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, J. Sand mining and increasing Poyang Lake’s discharge ability: A reassessment of causes for lake decline in China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Li, Y. On the Hydrodynamic Behavior of the Changed River–Lake Relationship in a Large Floodplain System, Poyang Lake (China). Water 2020, 12, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030626
Li M, Li Y. On the Hydrodynamic Behavior of the Changed River–Lake Relationship in a Large Floodplain System, Poyang Lake (China). Water. 2020; 12(3):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030626
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mengfan, and Yunliang Li. 2020. "On the Hydrodynamic Behavior of the Changed River–Lake Relationship in a Large Floodplain System, Poyang Lake (China)" Water 12, no. 3: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030626
APA StyleLi, M., & Li, Y. (2020). On the Hydrodynamic Behavior of the Changed River–Lake Relationship in a Large Floodplain System, Poyang Lake (China). Water, 12(3), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030626




