Nutrient Recovery from Anaerobically Treated Blackwater and Improving Its Effluent Quality through Microalgae Biomass Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture Media and Strain
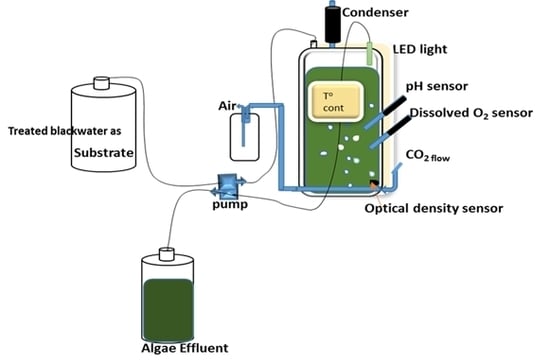
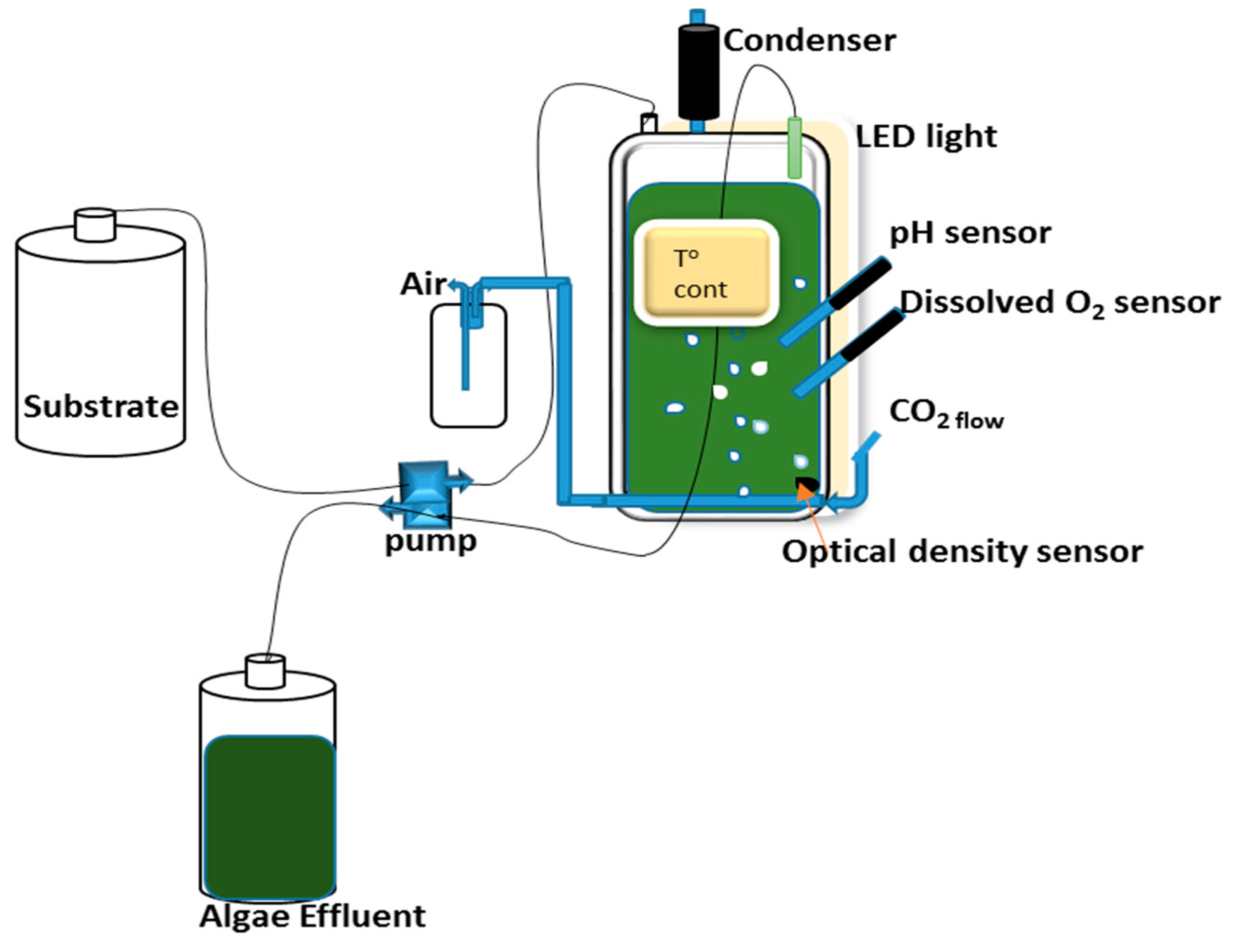
2.2. Photobioreactor (PBR) Set-Up and Culture Conditions
2.3. Nutrient Analysis and Algae Growth Determination
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
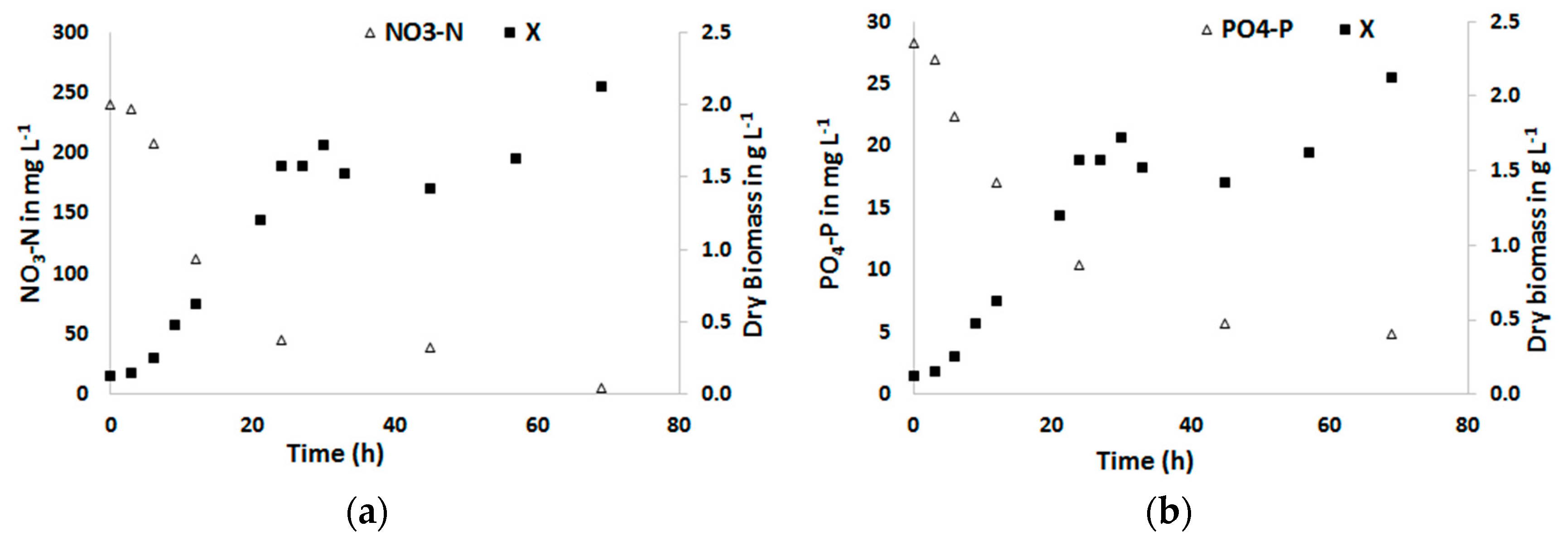
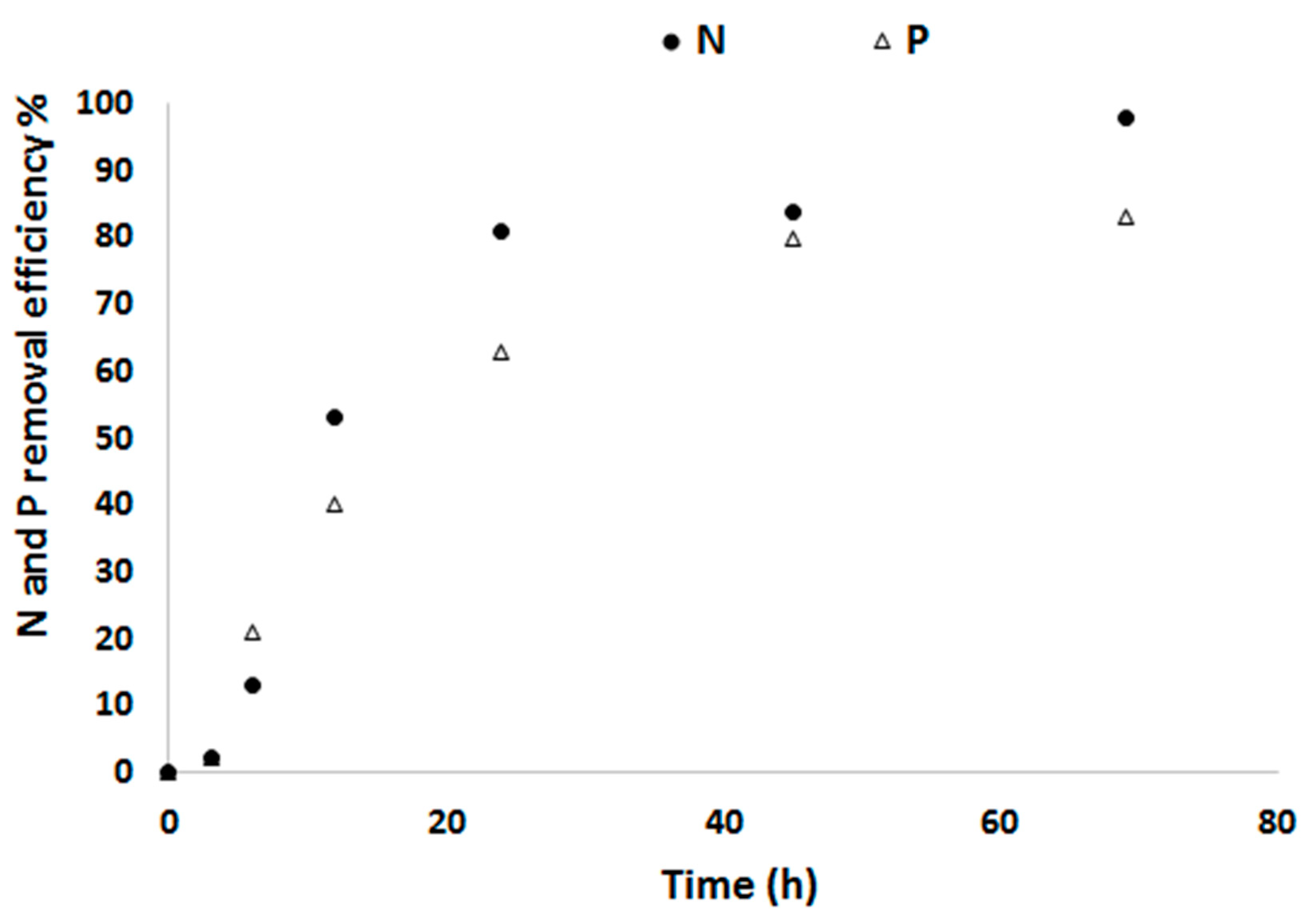
3.1. Biomass Productivity and Nutrient Removal with a Defined Medium
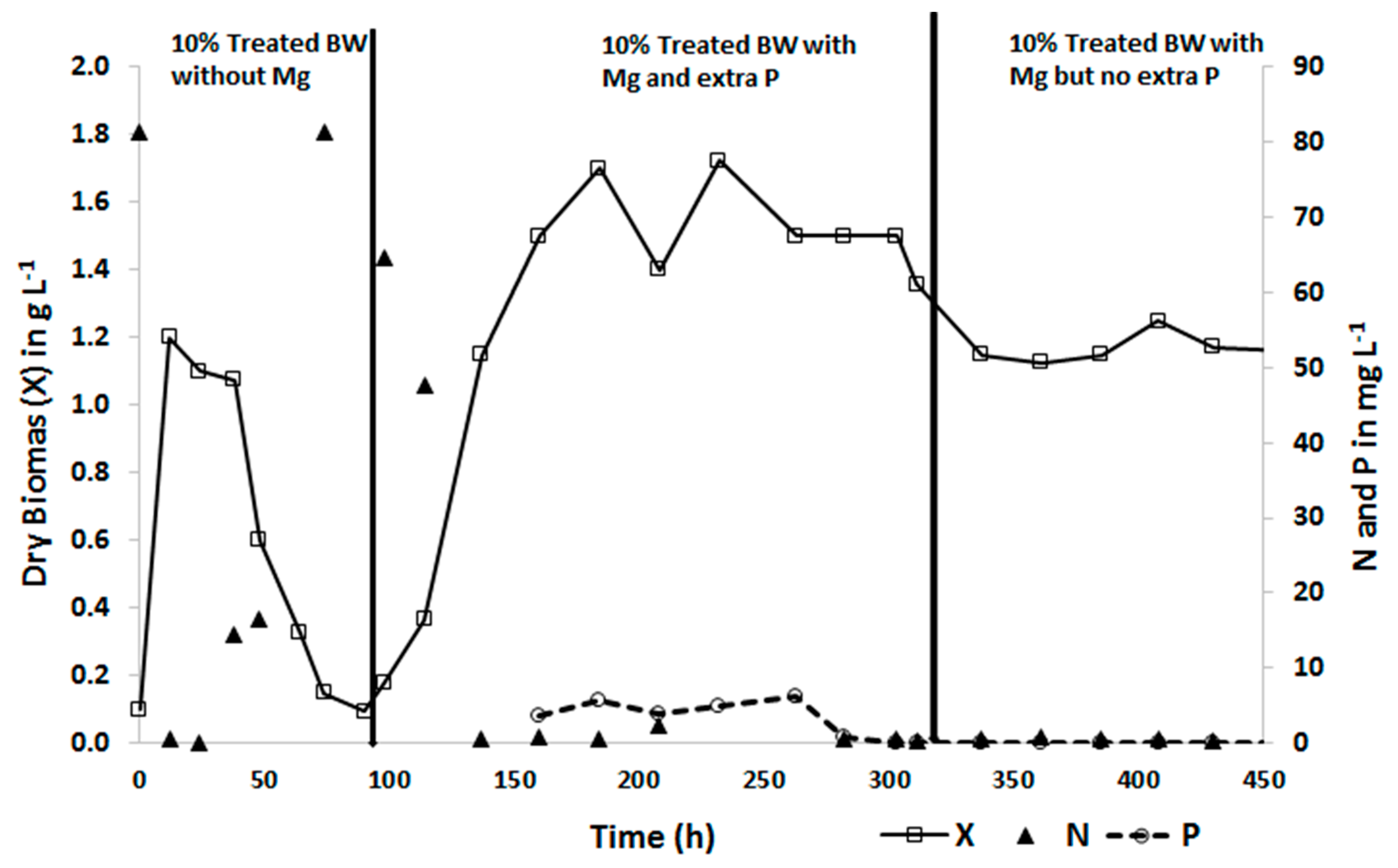
3.2. Biomass Productivity and Nutrient Removal with Treated Blackwater as a Substrate
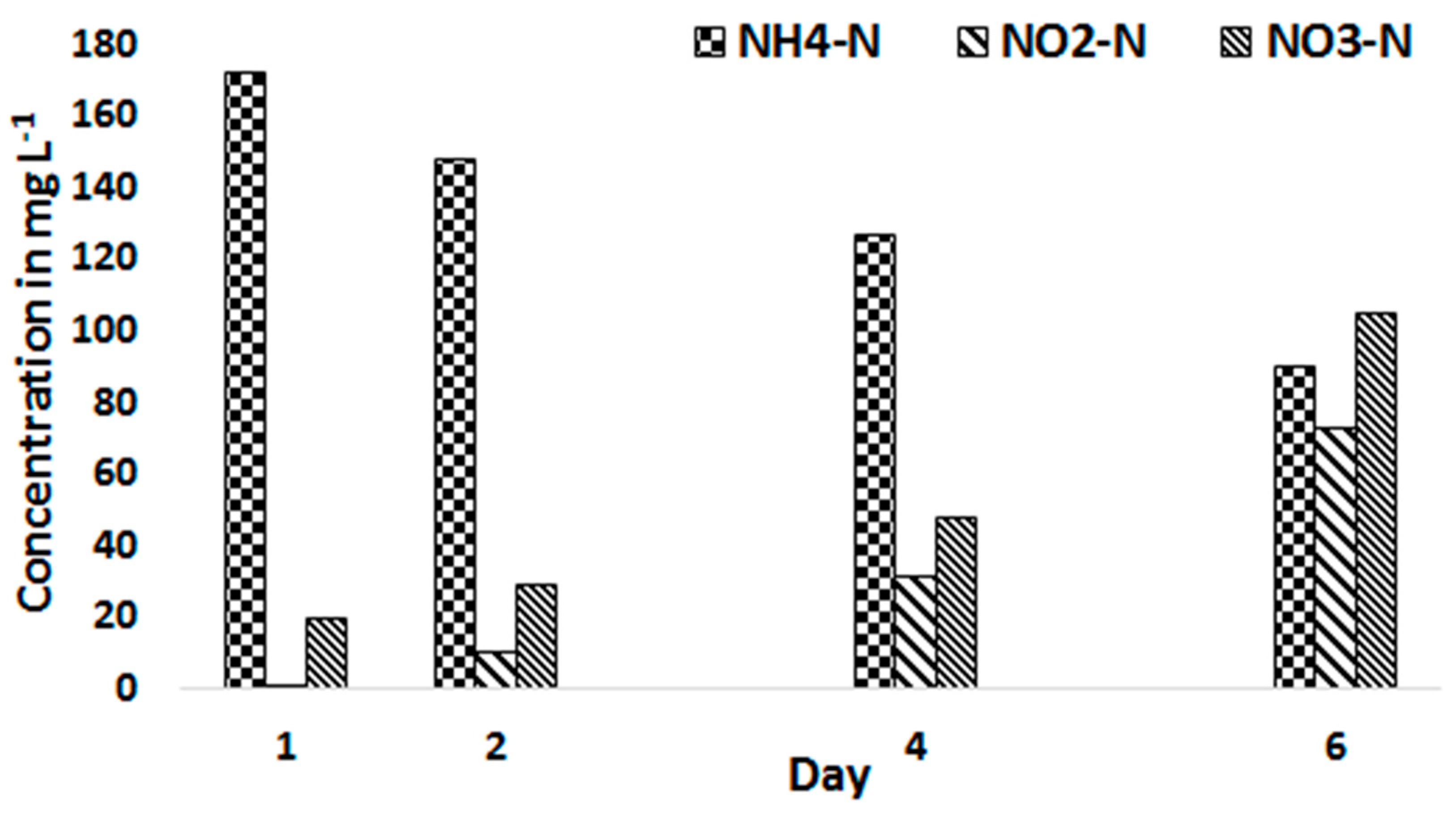
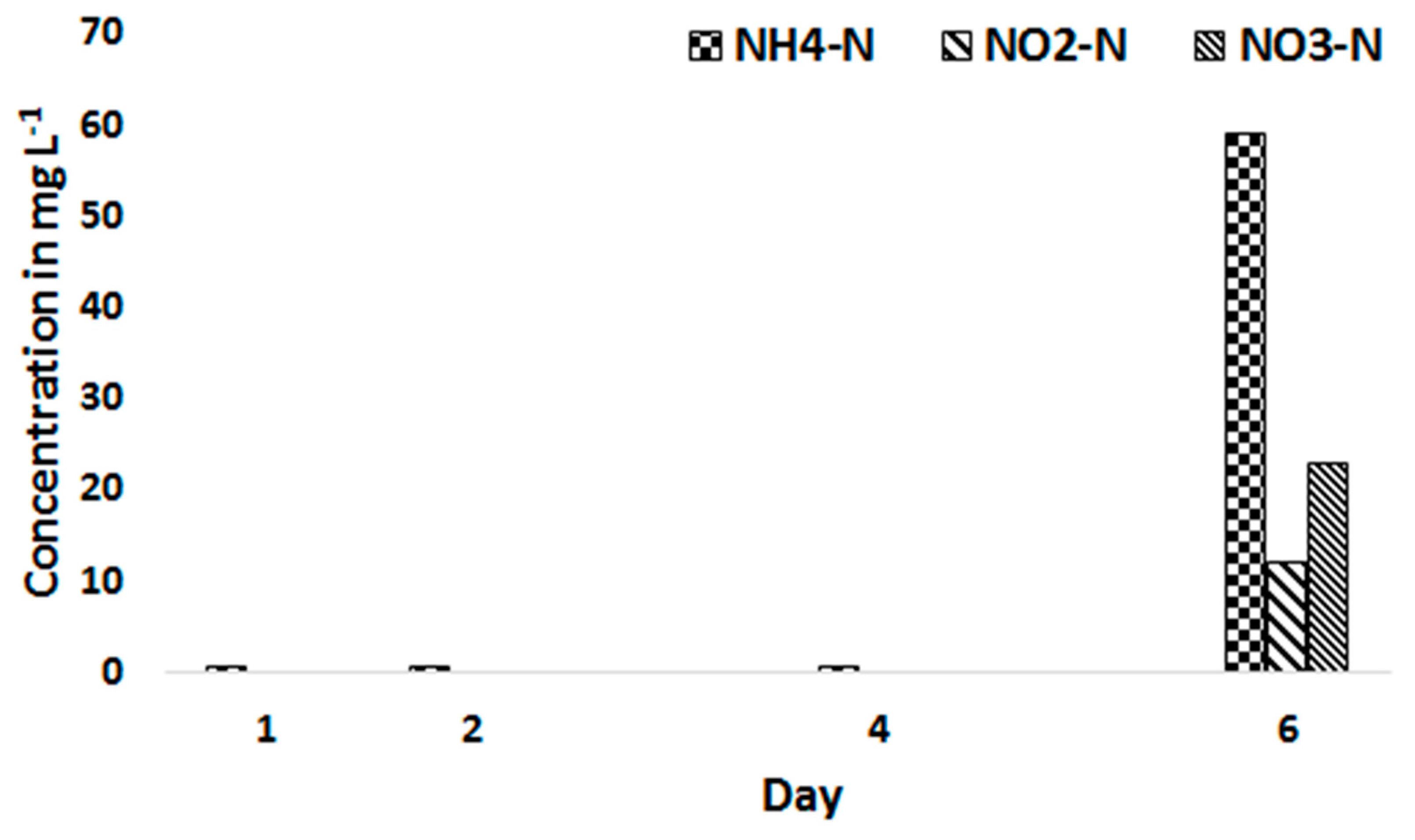
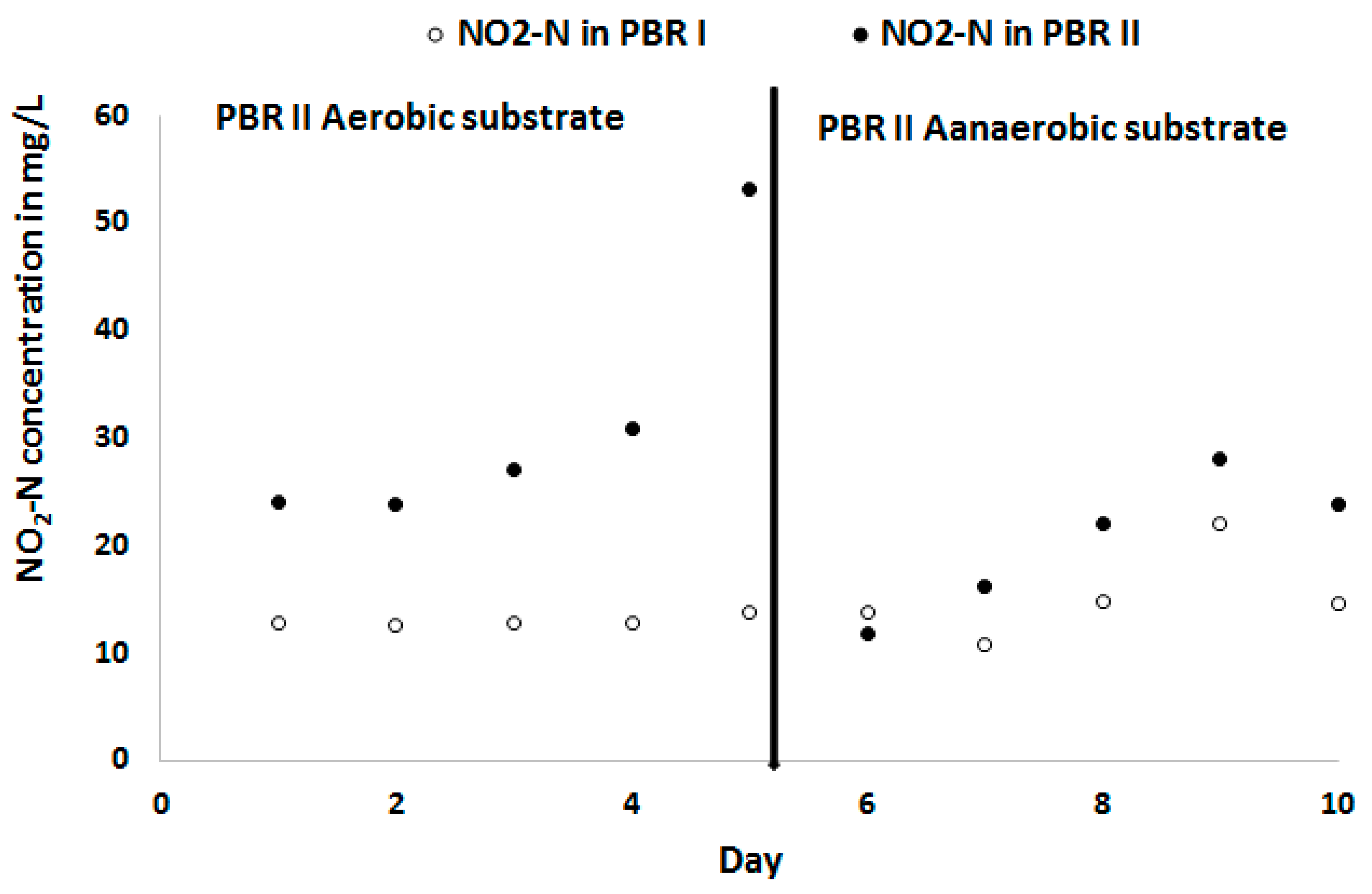
3.3. Effect of NO2-N on Chlorella Sorokiniana
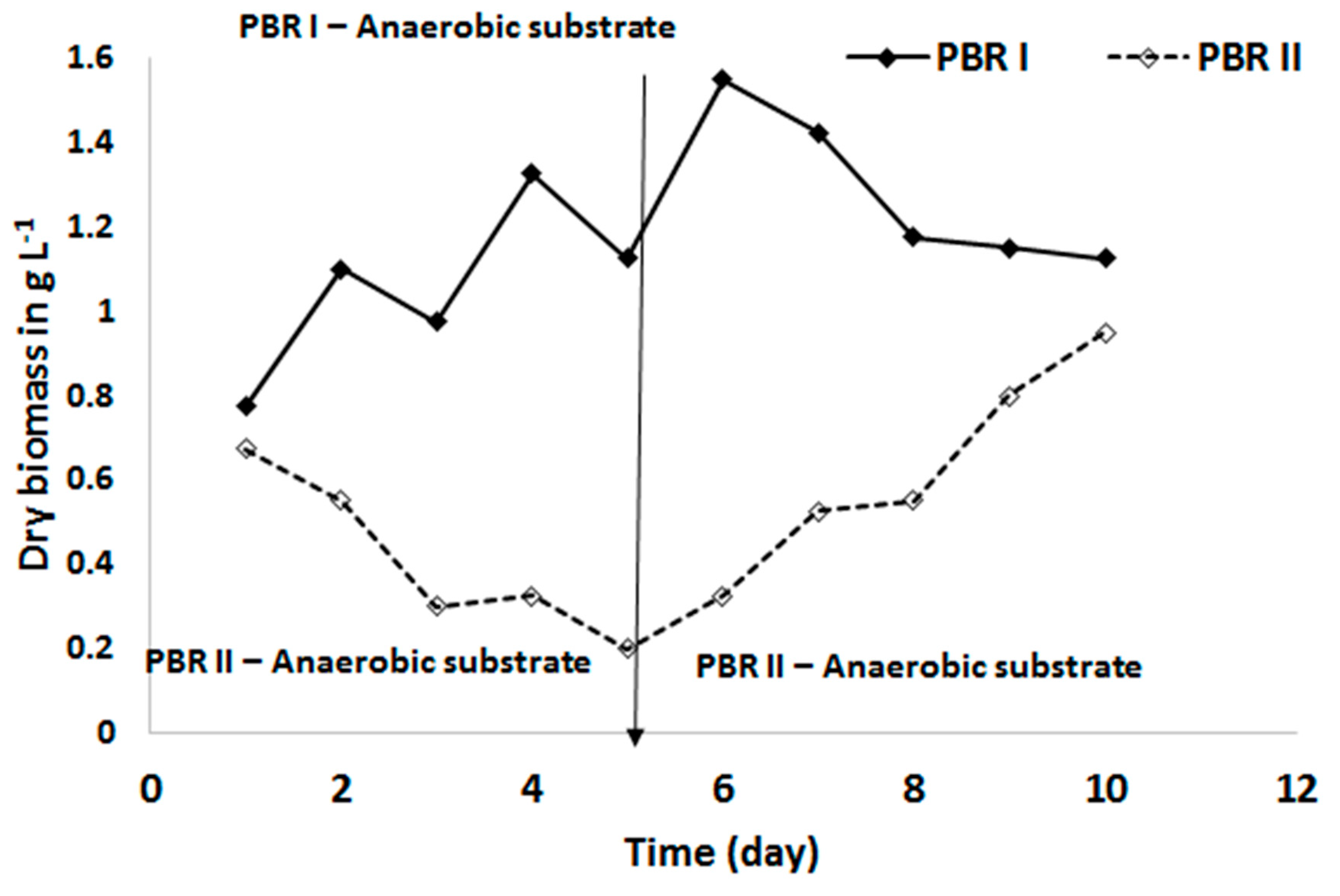
3.4. Effects of Reducing Substrate Retention Time, Stopping Stirring and Removing CaCl2 as a Supplement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kujawa-Roeleveld, K.; Zeeman, G. Anaerobic treatment in decentralized and source-separation-based. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol 2006, 5, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaff, M.S.; Temmink, H.; Zeeman, G.; Buisman, C.J. Anaerobic treatment of concentrated black water in a uasb reactor at a short hrt. Water 2010, 2, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaff, M.H.; Temmink, G.; Zeeman, C. Buisman. Energy and phosphorus recovery from black water. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 2759–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moges, M.E.; Todt, D.; Janka, E.; Heistad, A.; Bakke, R. Sludge blanket anaerobic baffled reactor for source-separated blackwater treatment. Water Sci. Technol 2018, 78, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeman, G.; Kujawa, K.; Mes, T.D.; Hernandez, L.; Graaff, M.D.; Abu-Ghunmi, L.; Mels, A.; Meulman, B.; Temmink, H.; Buisman, C.; et al. Anaerobic treatment as a core technology for energy, nutrients and water recovery from source-separated domestic waste (water). Water Sci. Technol 2008, 57, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, W.; Drosg, B. Assessment of the state of the art of technologies for the processing of digestate residue from anaerobic digesters. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1984–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Min, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ruan, R. Anaerobic digested dairy manure as a nutrient supplement for cultivation of oil-rich green Microalgae chlorella sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2623–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Padín, J.R.; Figueroa, M.; Fernández, I.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Campos, J.L.; Mendez, R. Post-treatment of effluents from anaerobic digesters by the anammox process. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.; Jeison, D.; Rubilar, O.; Ciudad, G.; Chamy, R. Nitrification–denitrification via nitrite accumulation for nitrogen removal from wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Peng, Y.; Li, B.; Liang, H. Shortcut nitrification–denitrification by real-time control strategies. Bioresour. Technol 2009, 100, 2298–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Peng, Y.; Wu, W.M. Kinetic model for biological nitrogen removal using shortcut nitrification-denitrification process in sequencing batch reactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5015–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmer, C.; Kunst, S. Simultaneous nitrification/denitrification in an aerobic biofilm system. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, G.; Lemaire, R.; Keller, J.; Yuan, Z. Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal from nutrient-rich industrial wastewater using granular sludge. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 100, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virdis, B.; Rabaey, K.; Rozendal, R.A.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J. Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and carbon removal in microbial fuel cells. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2970–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, C.; Boehler, M.; Huber, P.; Brunner, I.; Siegrist, H. Biological treatment of ammonium-rich wastewater by partial nitritation and subsequent anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) in a pilot plant. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 99, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, S.; Gilbert, E.M.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Joss, A.; Horn, H.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences–an application survey. Water Res. 2014, 55, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-P.; Nàcher, C.P.i.; Merkey, B.; Zhou, Q.; Xia, S.Q.; Yang, D.H.; Sun, J.H.; Smets, B.F. Effective biological nitrogen removal treatment processes for domestic wastewaters with low c/n ratios: A review. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2010, 27, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede-Westhead, E.; Pizarro, C.; Mulbry, W.W. Treatment of dairy manure effluent using freshwater algae: Elemental composition of algal biomass at different manure loading rates. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2004, 52, 7293–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Claxton, R.; Das, K.C. Biomass and bioenergy production potential of microalgae consortium in open and closed bioreactors using untreated carpet industry effluent as growth medium. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6751–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group 1 Contribution to the Fourth Assessment Report of the IPCC; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 212. [Google Scholar]
- Olguín, E.J. Phycoremediation: Key issues for cost-effective nutrient removal processes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2003, 22, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Hunt, R.W.; Das, K.C. Microalgae cultivation in a wastewater dominated by carpet mill effluents for biofuel applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3097–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.X.; Li, L.; Martinez, B.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Culture of microalgae chlamydomonas reinhardtii in wastewater for biomass feedstock production. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Min, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, R. Cultivation of green algae chlorella sp. In different wastewaters from municipal wastewater treatment plant. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuantet, K.; Temmink, H.; Zeeman, G.; Janssen, M.; Wijffels, R.H.; Buisman, C.J. Nutrient removal and microalgal biomass production on urine in a short light-path photobioreactor. Water Res. 2014, 55, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos Fernandes, T.; Shrestha, R.; Sui, Y.; Papini, G.; Zeeman, G.; Vet, L.E.; Wijffels, R.H.; Lamers, P. Closing domestic nutrient cycles using microalgae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12450–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Reynolds, D.L.; Das, K.C. Microalgal system for treatment of effluent from poultry litter anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10841–10848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Semi-continuous cultivation of chlorella vulgaris for treating undigested and digested dairy manures. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 2324–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshetu Moges, M.; Todt, D.; Heistad, A. Treatment of source-separated blackwater: A decentralized strategy for nutrient recovery towards a circular economy. Water 2018, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutner, S.H.; Provasoli, L.; Schatz, A.; Haskins, C.P. Some approaches to the study of the role of metals in the metabolism of microorganisms. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 1950, 94, 152–170. [Google Scholar]
- Redfield, A.C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am. Sci. 1958, 46, 205–221, 230A. [Google Scholar]
- NORCCA. Available online: https://niva-cca.no/shop/trebouxiophyceae/chlorella/niva-chl-176 (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- Becker, E.W. Micro-algae as a source of protein. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsukawa, R.; Hotta, M.; Masuda, Y.; Chihara, M.; Karube, I. Antioxidants from carbon dioxide fixing chlorella sorokiniana. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjånes, K.; Andersen, U.; Heidorn, T.; Borgvang, S.A. Design and construction of a photobioreactor for hydrogen production, including status in the field. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2205–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Camejo, J.; Barat, R.; Pachés, M.; Murgui, M.; Seco, A.; Ferrer, J. Wastewater nutrient removal in a mixed microalgae–bacteria culture: Effect of light and temperature on the microalgae–bacteria competition. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuaresma, M.; Janssen, M.; Vílchez, C.; Wijffels, R.H. Horizontal or vertical photobioreactors? How to improve microalgae photosynthetic efficiency. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5129–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuantet, K.; Janssen, M.; Temmink, H.; Zeeman, G.; Wijffels, R.H.; Buisman, C.J. Microalgae growth on concentrated human urine. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, T.V.; Suárez-Muñoz, M.; Trebuch, L.M.; Verbraak, P.J.; Van de Waal, D.B. Toward an ecologically optimized n: P recovery from wastewater by microalgae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguer, J.F.; L’Helguen, S.; Madec, C.; Labry, C.; Le Corre, P. Nitrogen uptake and assimilation kinetics in alexandrium minutum (dynophyceae): Effect of n-limited growth rate on nitrate and ammonium interactions. Eur. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hii, Y.S.; SOO, C.L.; Chuah, T.S.; Mohd-Azmi, A.; Abol-Munafi, A.B. Interactive effect of ammonia and nitrogen on the nitrogen uptake by Nannochloropsis sp. J. Sustain. Sci. Manage 2011, 6, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Camejo, J.; Barat, R.; Ruano, M.V.; Seco, A.; Ferrer, J. Outdoor flat-panel membrane photobioreactor to treat the effluent of an anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Influence of operating, design, and environmental conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Park, S.Y.; Li, Y. Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams by microalgae: Status and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podevin, M.; De Francisci, D.; Holdt, S.L.; Angelidaki, I. Effect of nitrogen source and acclimatization on specific growth rates of microalgae determined by a high-throughput in vivo microplate autofluorescence method. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Nutrient | Anaerobically Digested Blackwater | After Filtration and UV Treatment | 10% ** TreatedBW | Defined Medium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ntot mg L−1 | 1140–2360 | 1100–1980 | 110–198 | 247 |
| NH4-N mg L−1 | 580–1390 | 580–1200 | 58–120 | ND |
| NO3-N mg L−1 | 0–4.05 | 6–93.6 | 0.6–9.36 | 247 |
| NO2-N mg L−1 | 0–0.6 | 0.2–130 | 0.02–13 | ND |
| Ptot mg L−1 | 100–140 | 76–92.4 | 7.6–9.24 | 29.2 |
| PO4-P mg L−1 | 46–92.5 | 54–85.3 | 5.4–8.53 | 29.2 |
| Mg mg L−1 * | 11.3 | 9.4 | 0.94 | 9.8 |
| K mg L−1 * | 165.0 | 185.0 | 18.5 | 59.3 |
| Ca mg L−1 * | 38.8 | 31.8 | 3.18 | 13.6 |
| Na mg L−1 * | 191.7 | 195 | 19.5 | 411 |
| Al µg L−1 * | 22.0 | 15.5 | 1.55 | 0.0 |
| Fe µg L−1 * | 143.3 | 40.7 | 4.07 | 1.0 |
| Cu µg L−1 * | 30.7 | 6.9 | 0.69 | 0.4 |
| Mn µg L−1 * | 37.5 | 6.0 | 0.60 | 1.4 |
| Ni µg L−1 * | 11.1 | 3.7 | 0.37 | 0.0 |
| Zn µg L−1 * | 62.0 | 30.5 | 3.05 | 5.0 |
| Co µg L−1 * | 0.43 | 0.17 | 0.017 | 0.4 |
| Turbidity NTU | 80–160 | 0.15–2 | ND | ND |
| E. coli MPN/100 mL | 10^5 | <1 | <1 | ND |
| Unit | Defined Medium | 10% Treated BW without Extra P | 10% Treated BW with Extra P | 20% Treated BW with Extra P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ntot | mg L−1 | 247 | 54–85 | 54–85 | 177–212 |
| Ptot | mg L−1 | 29.2 | 4.5–6 | 33–35.2 | 18.8–21.3 |
| N:P ratio | 8.7 | 12–14 | 3.5 | 10 | |
| Volumetric biomass productivity PV | g L−1 d−1 | 2.17 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 1.9 |
| Areal biomass productivity PA | g m−1 d−1 | 52.21 | 36.18 | 50.43 | 46.04 |
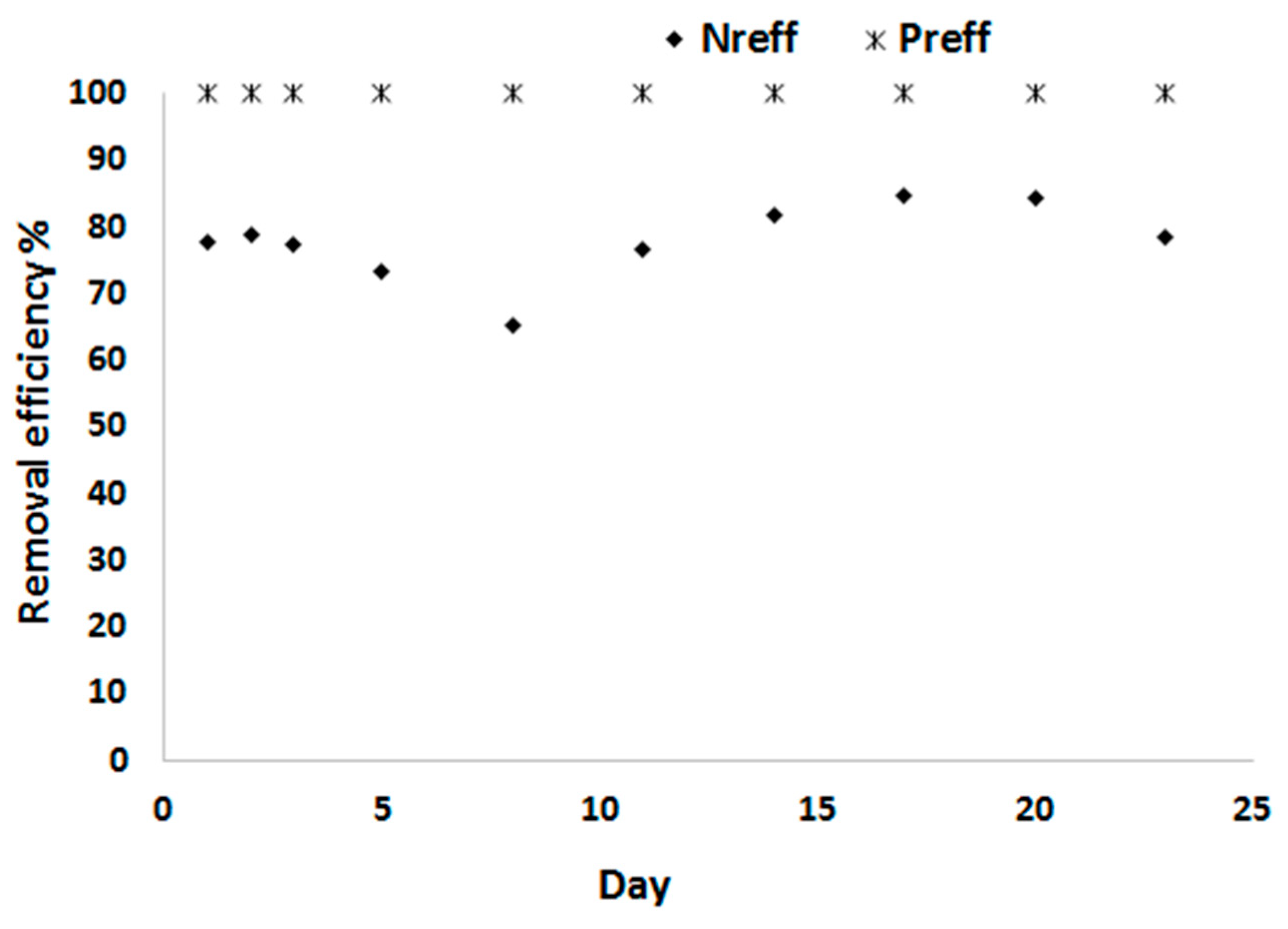
| N removal efficiency Nreff | % | 80–98 | 99.8 | 99.7 | 77.8 |
| P removal efficiency Preff | % | 63–83 | 99.2 | 86.1 | 99.5 |
| N removal rate Nr | mg N L−1d−1 | 291.1 ± 29.8 | 99.17 ± 0.3 | 110.46 ± 0.4 | 212.6 ± 23 |
| P removal rate Pr | mg P L−1d−1 | 29.5 ± 4.1 | 8.3 ± 04 | 42.7 ± 2.6 | 35.3 ± 0.6 |
| N removal yield on light YN/Ph | mg (mole photons)−1 | 55.9 ± 5.7 | 19.1 ± 0.3 | 20.9 ± 0.1 | 41.0 ± 4.1 |
| P removal yield on light YP/Ph | mg (mole photons)−1 | 5.7 ± 0.8 | 1.6 ± 0.01 | 8 ± 0.9 | 6.8 ± 0.1 |
| Biomass yield on light YX/Ph | mg (mole photons)−1 | 420 | 290 | 400 | 370 |
| Biomass yield on N YX/N | g g−1 | 7.9 ± 1.3 | 15.2 ± 0.2 | 18.9 ± 1.5 | 9 ± 1.1 |
| Biomass yield on P YX/P | g g−1 | 78.4 ± 9.0 | 187.9 ± 9.5 | 50.2 ± 4.5 | 54 ± 5.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moges, M.E.; Heistad, A.; Heidorn, T. Nutrient Recovery from Anaerobically Treated Blackwater and Improving Its Effluent Quality through Microalgae Biomass Production. Water 2020, 12, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020592
Moges ME, Heistad A, Heidorn T. Nutrient Recovery from Anaerobically Treated Blackwater and Improving Its Effluent Quality through Microalgae Biomass Production. Water. 2020; 12(2):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020592
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoges, Melesse Eshetu, Arve Heistad, and Thorsten Heidorn. 2020. "Nutrient Recovery from Anaerobically Treated Blackwater and Improving Its Effluent Quality through Microalgae Biomass Production" Water 12, no. 2: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020592
APA StyleMoges, M. E., Heistad, A., & Heidorn, T. (2020). Nutrient Recovery from Anaerobically Treated Blackwater and Improving Its Effluent Quality through Microalgae Biomass Production. Water, 12(2), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020592