Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Water onto Activated Carbon by Surfactant Modification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
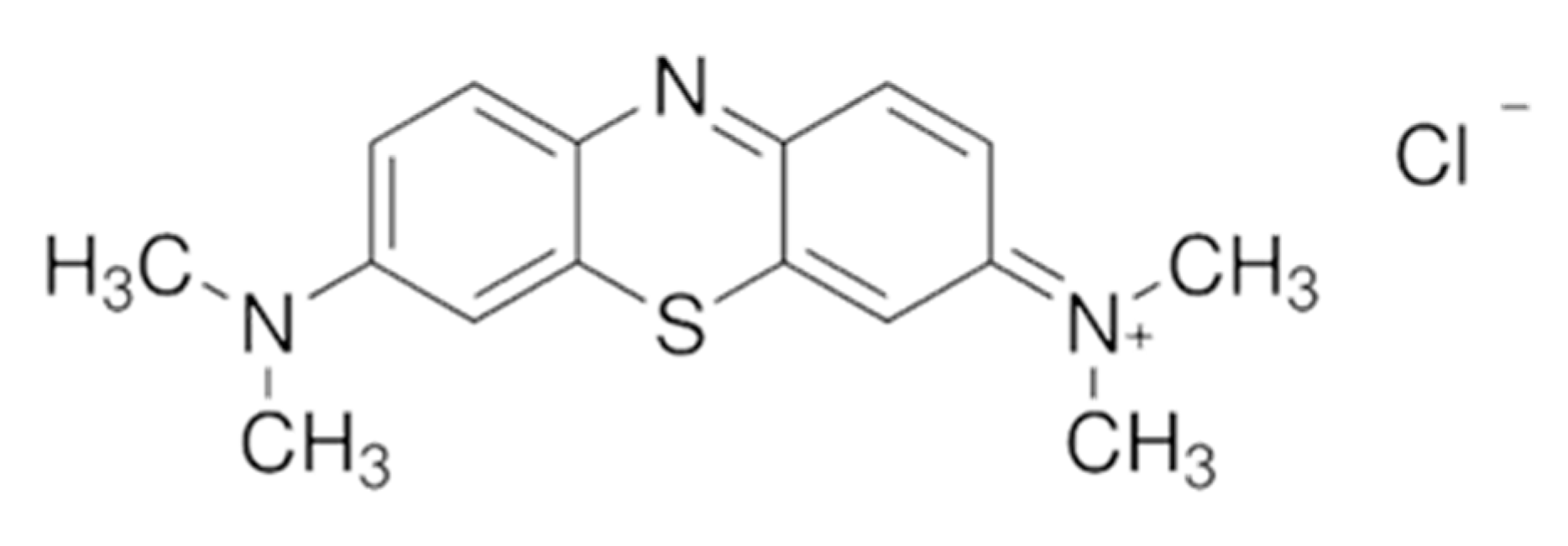
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Surfactant-modified Activated Carbon
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results
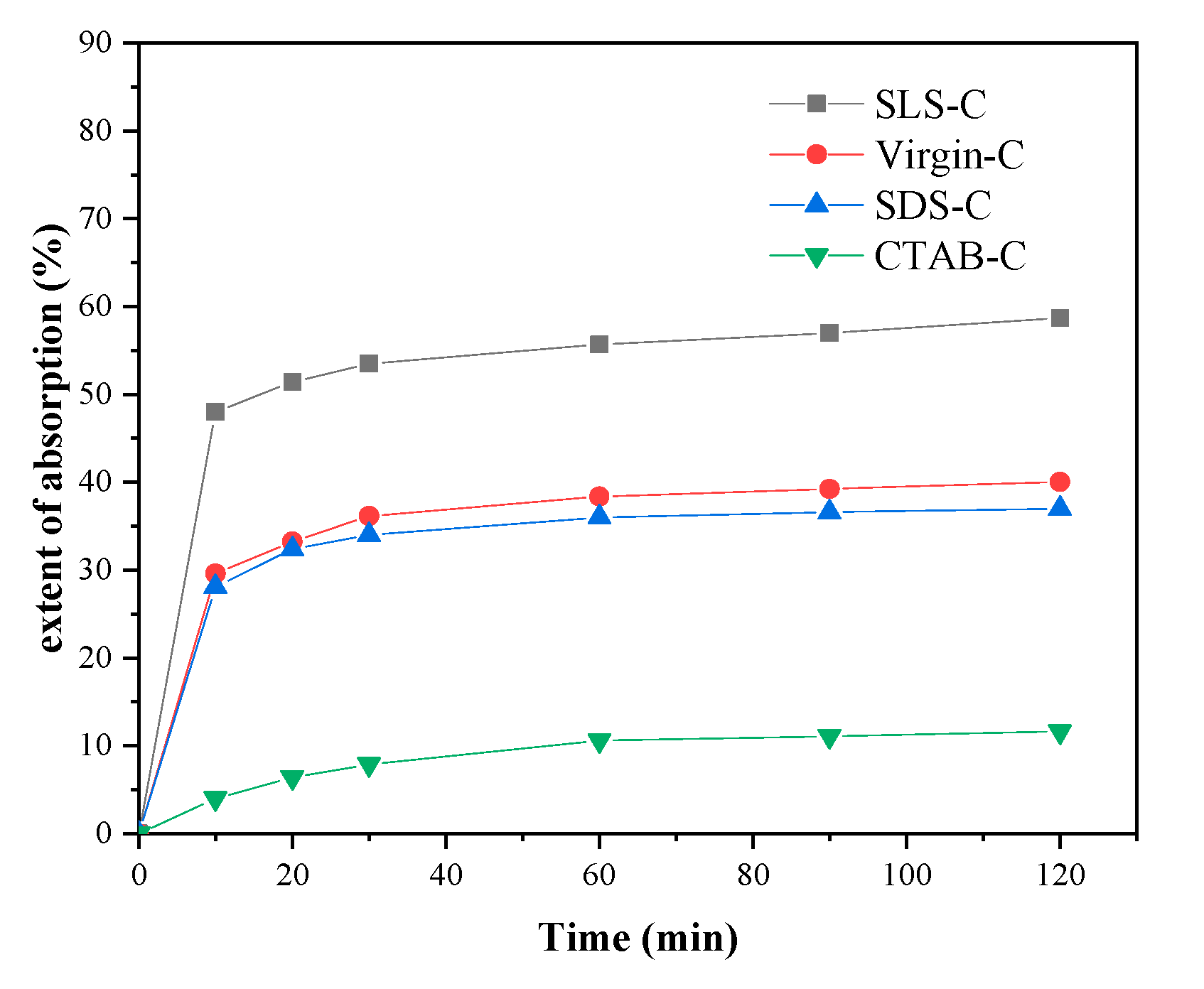
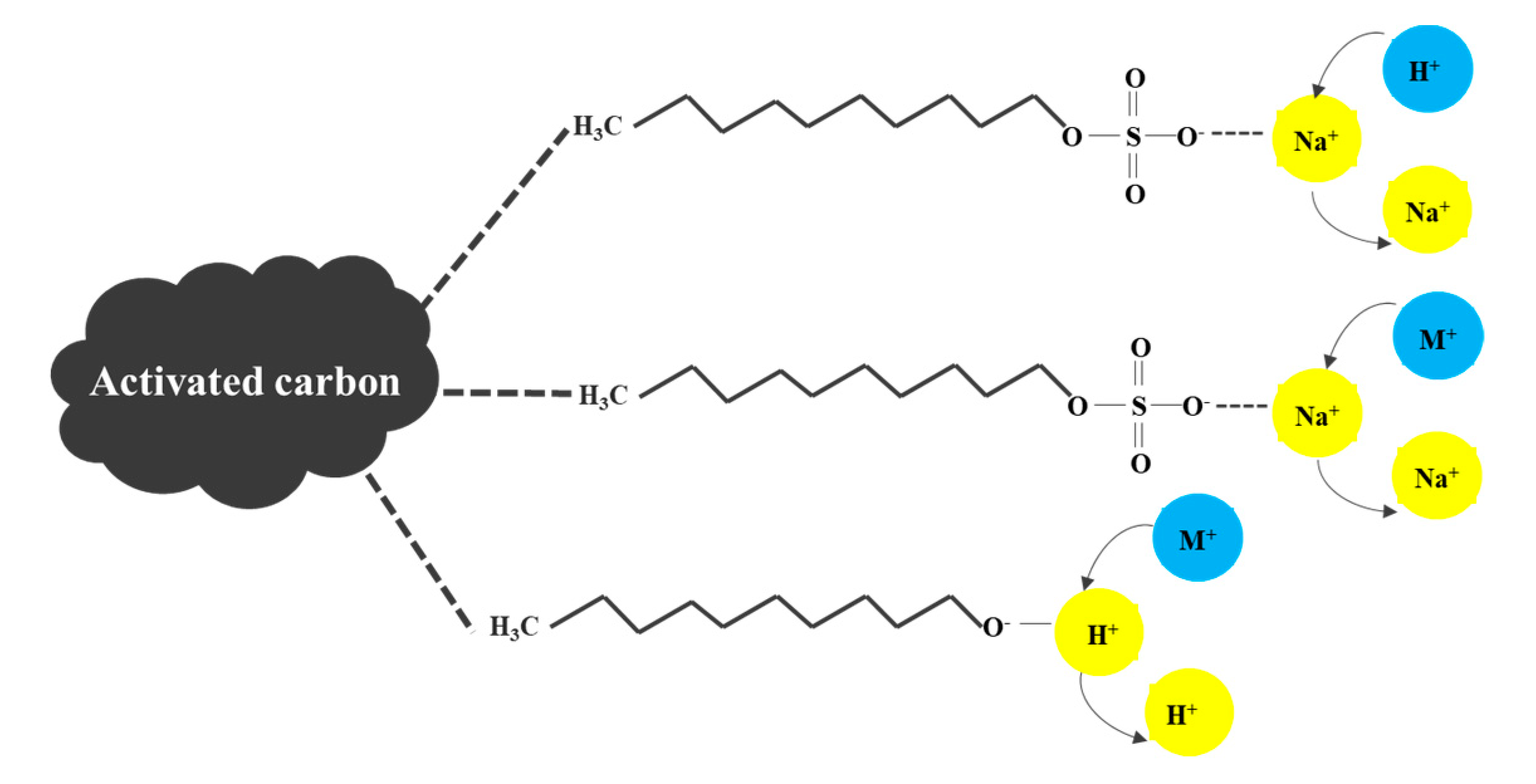
3.1. Effect of Different Surfactants
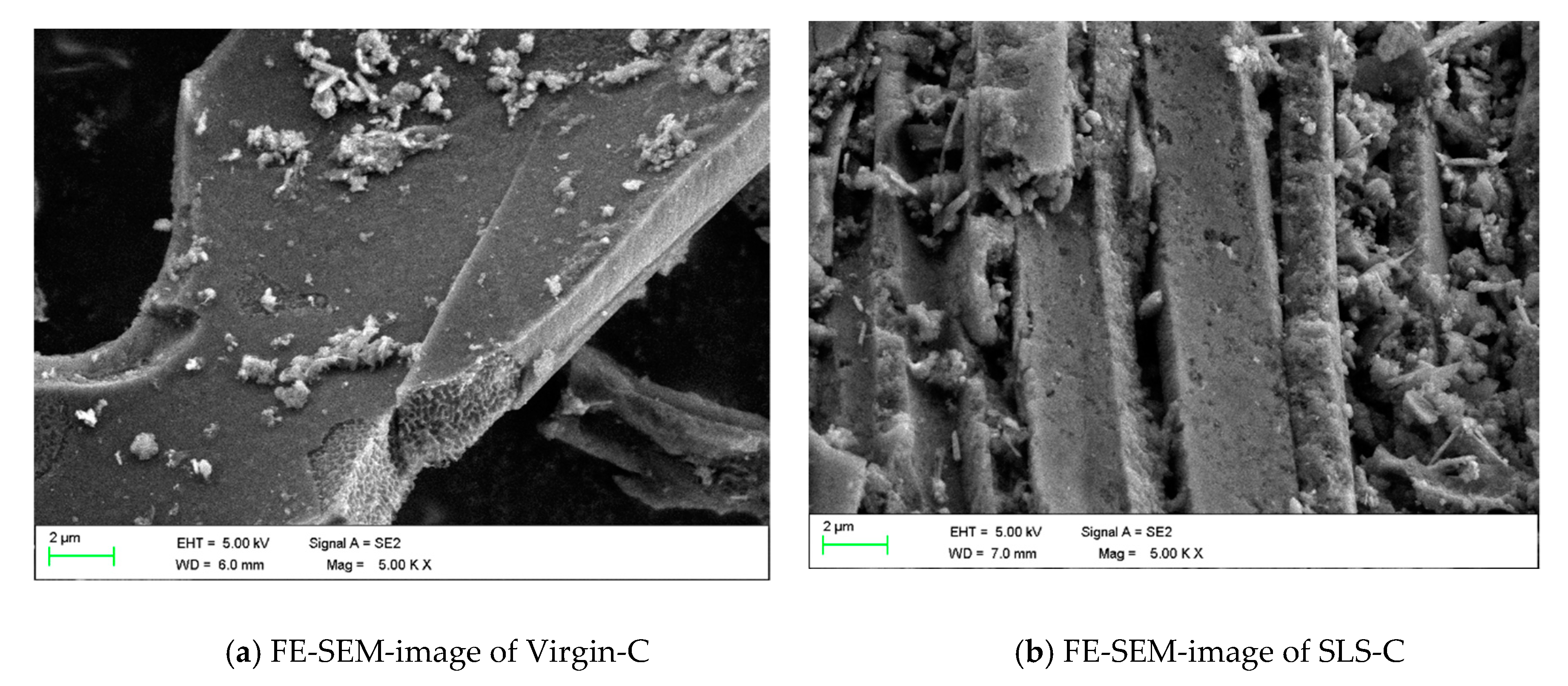
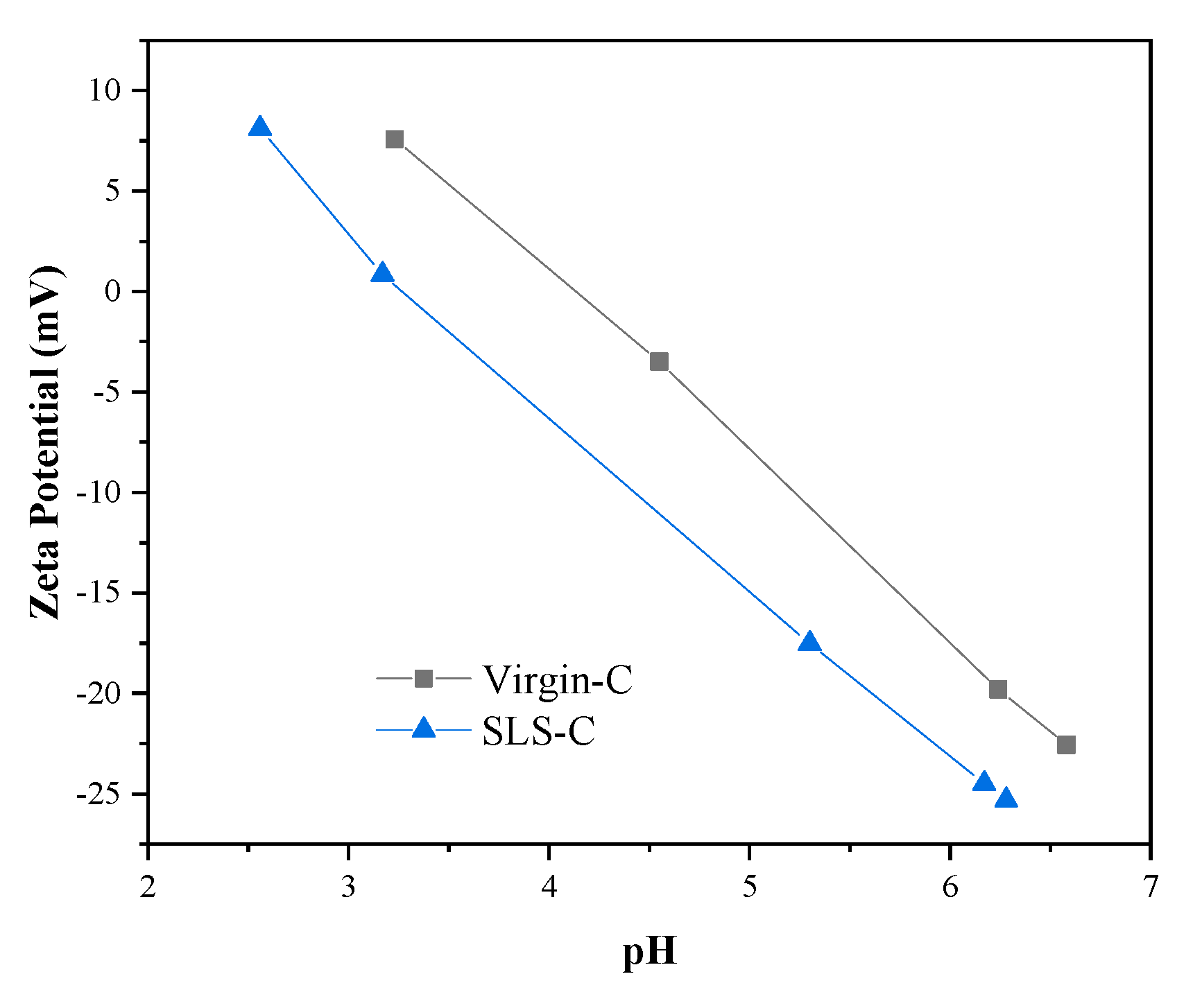
3.2. Characterization of SLS-C
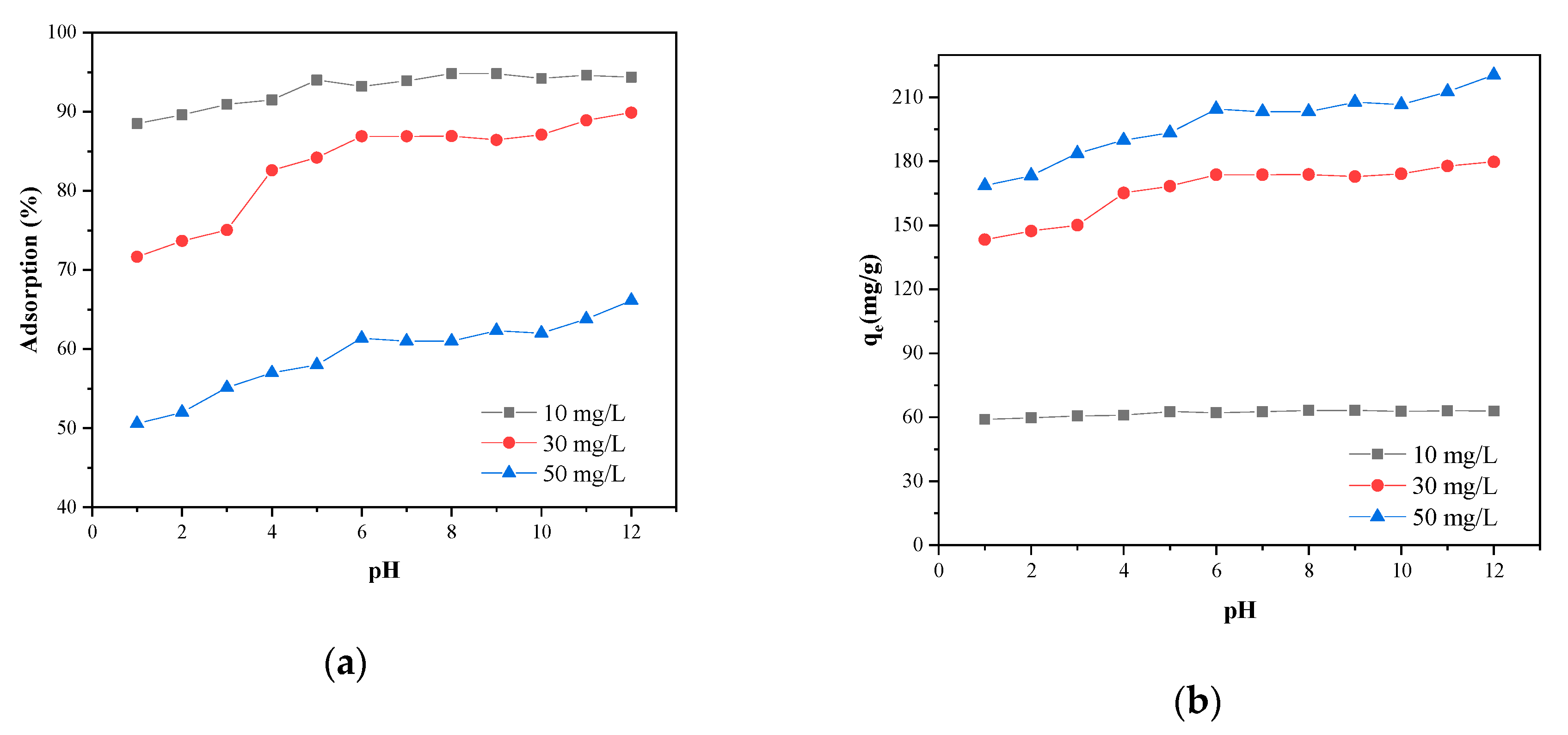
3.3. Effects of Initial Solution pH
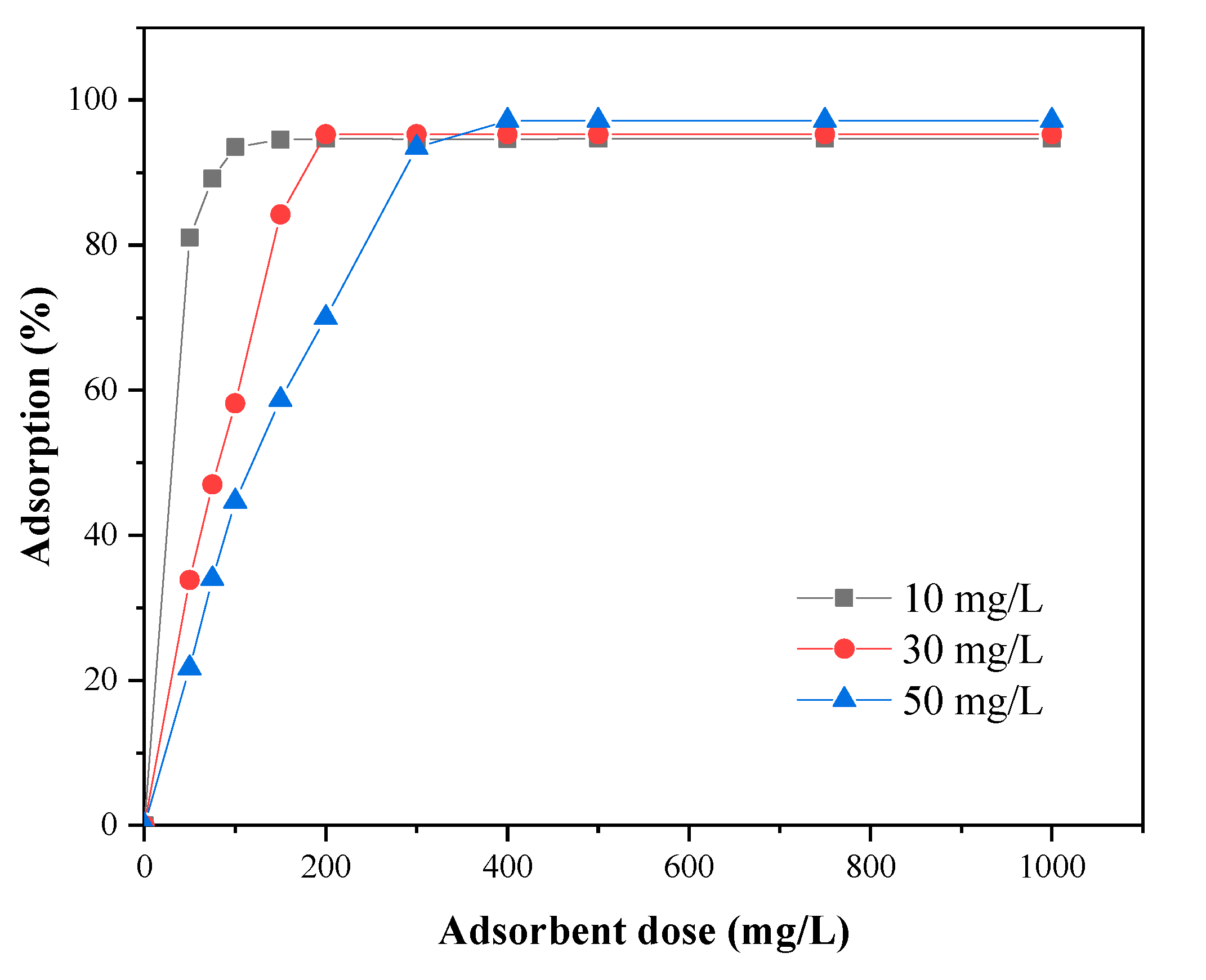
3.4. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
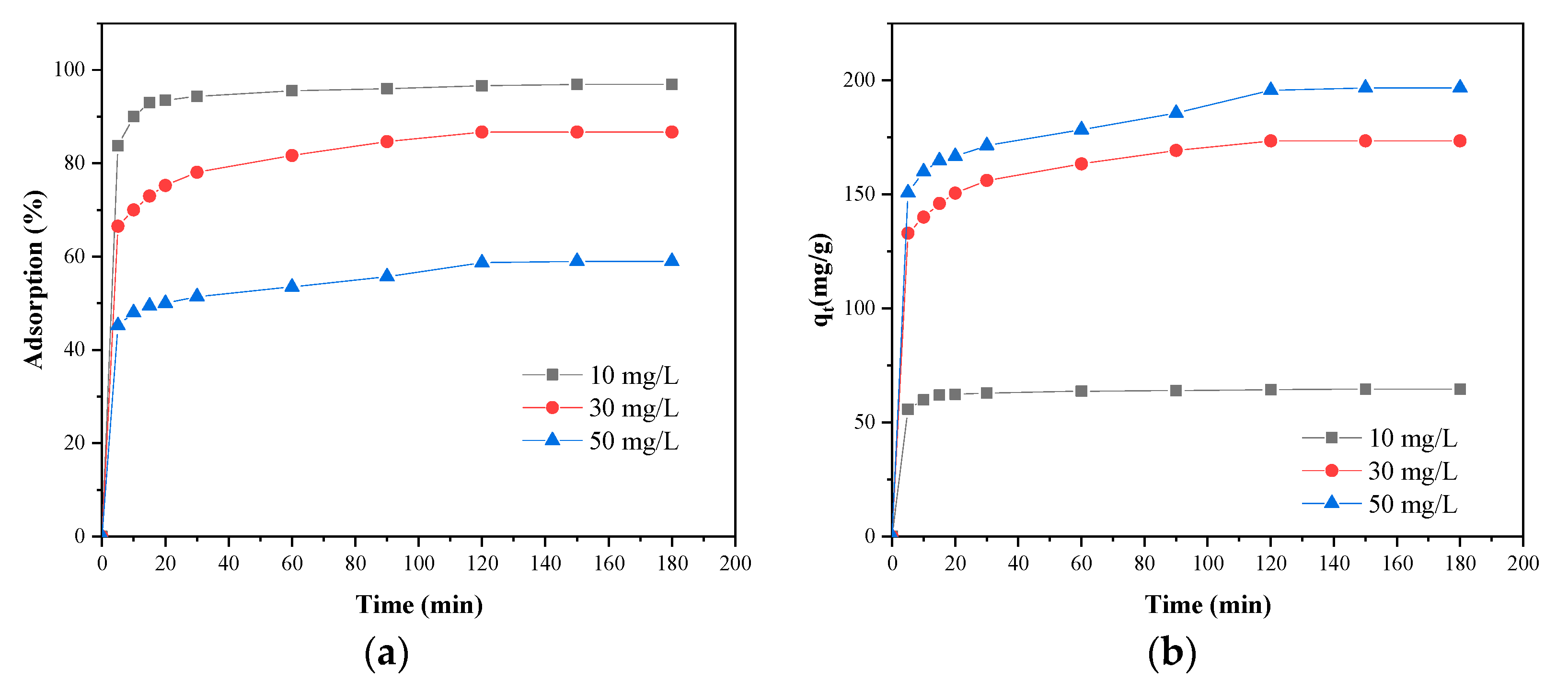
3.5. Effects of Contact Time
3.6. Effects of Initial MB Concentration
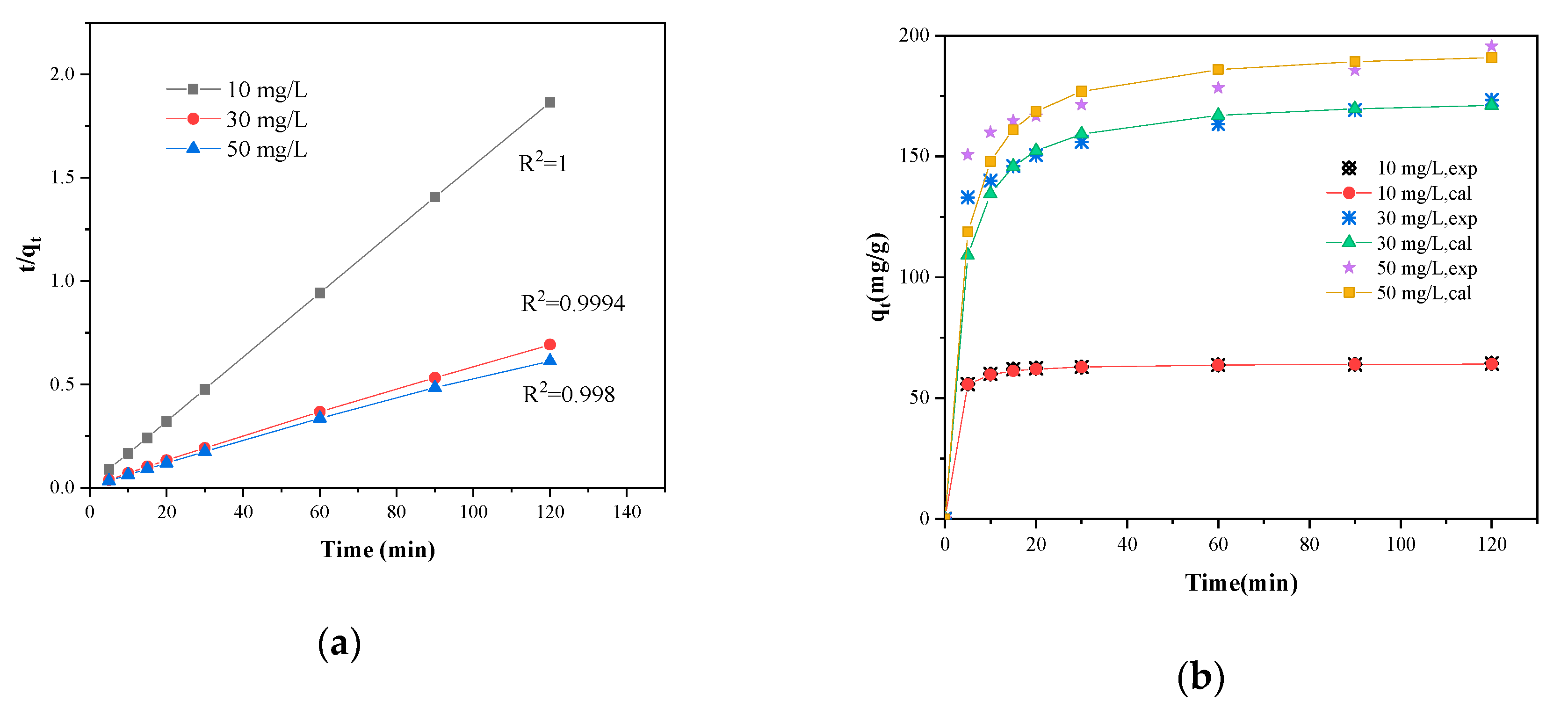
3.7. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm
3.7.1. Adsorption Kinetics
3.7.2. Adsorption Isotherm
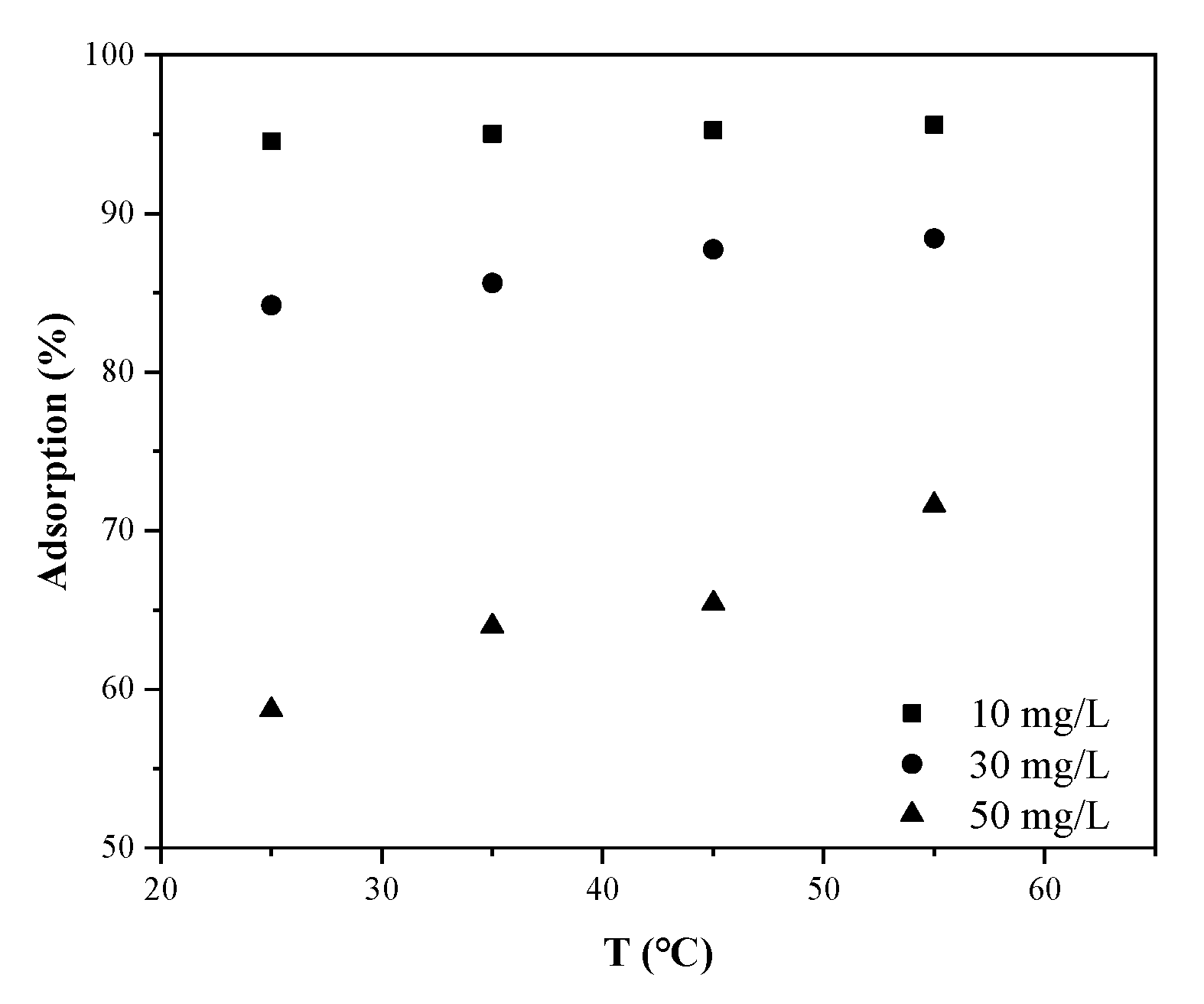
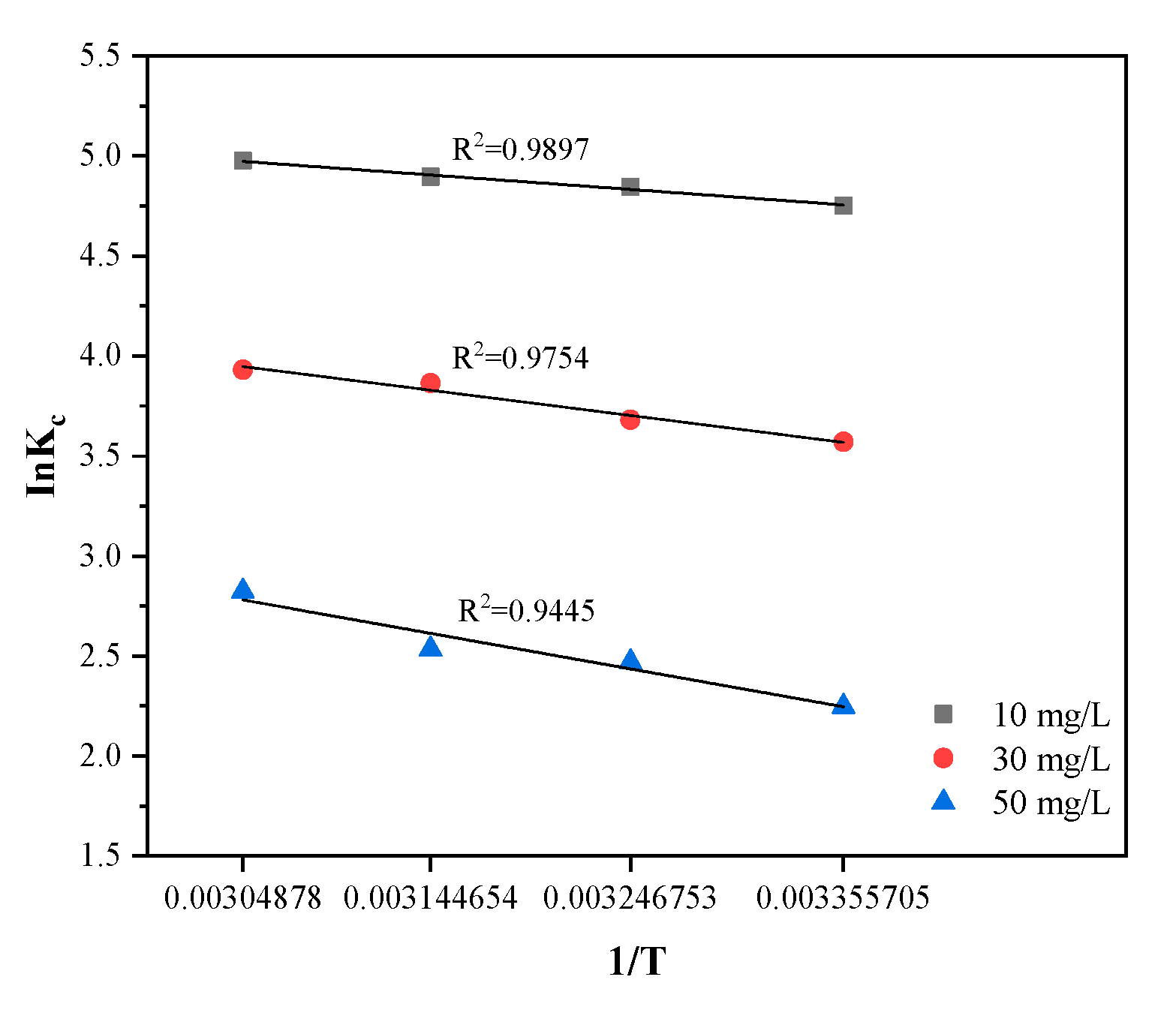
3.8. Temperature Effect and Thermodynamic Parameters
3.9. Effect of Additive Salts
3.10. Decolorization of MB in Real Water Samples by SLS-C
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, Y.C.; Szeto, Y.S.; Cheung, W.H.; McKay, G. Adsorption of acid dyes on chitosan—equilibrium isotherm analyses. Process. Biochem. 2004, 39, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.A.W.; Ahmad, A.L.; Hameed, B.H. Adsorption of basic dye on high-surface area activated carbon prepared from coconut husk: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, K.G.; Kumar, P.S.; Jaikumar, V.; Rajan, P.S. Removal of colorants from wastewater: A review on sources and treatment strategies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 75, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Dash, R.R.; Bhunia, P. A review on chemical coagulation/flocculation technologies for removal of colour from textile wastewaters. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 93, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Liu, M.; Ma, M.; Qi, M.; Lü, Z.; Gao, C. Impacts of membrane properties on reactive dye removal from dye/salt mixtures by asymmetric cellulose acetate and composite polyamide nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 350, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alventosa-deLara, E.; Barredo-Damas, S.; Alcaina-Miranda, M.I.; Iborra-Clar, M.I. Ultrafiltration technology with a ceramic membrane for reactive dye removal: Optimization of membrane performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar, A.; Abdul Raman, A.A.; Wan Daud, W.M.A. Advanced oxidation processes for in-situ production of hydrogen peroxide/hydroxyl radical for textile wastewater treatment: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kordouli, E.; Bourikas, K.; Lycourghiotis, A.; Kordulis, C. The mechanism of azo-dyes adsorption on the titanium dioxide surface and their photocatalytic degradation over samples with various anatase/rutile ratios. Catal. Today 2015, 252, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X. Adsorption of anionic dyes from aqueous solution on fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, S.; Gürses, A.; Açıkyıldız, M.; Ejder, M.K. Adsorption of cationic dye from aqueous solutions by activated carbon. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 115, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Gao, M.; Shen, T.; Cao, G.; Zhao, B.; Guo, S. Comparative study of three novel organo-clays modified with imidazolium-based gemini surfactant on adsorption for bromophenol blue. J. Mol. liquids 2019, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Li, X. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by sewage sludge-derived biochar: Adsorption kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, S.; Xi, Y. Structures of nonionic surfactant modified montmorillonites and their enhanced adsorption capacities towards a cationic organic dye. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 148, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, G.; An, C.; Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P. Adsorption of anionic azo dyes from aqueous solution on cationic gemini surfactant-modified flax shives: Synchrotron infrared, optimization and modeling studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1986–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, S.L.; Nair, B.U.; Mesfin, R.A.; Diaz, I.; Tessema, M. Preparation and characterization of cationic surfactant modified zeolite adsorbent material for adsorption of organic and inorganic industrial pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3319–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Castañeda, M.; Medina, D. Use of Surfactant-Modified Zeolites and Clays for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Water. Water 2017, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, L.; Yuan, X.; Zeng, G.; Shao, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Peng, X. Surface characterization of rice husk bio-char produced by liquefaction and application for cationic dye (Malachite green) adsorption. Fuel 2015, 155, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.M. Acid dye removal: Comparison of surfactant-modified mesoporous FSM-16 with activated carbon derived from rice husk. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 272, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, T.M.; Mohamed, T.M.; Mahmoud, E.; Somia, B.; Matthew, A.; Huff, D.; James, W.L.; Sandeep, K. Biochar from woody biomass for removing metal contaminants and carbon sequestration. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 22, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarik, S.; Saeeda, A.; Athar, M.M.; Iqbal, M. Characterization and mechanism of the adsorptive removal of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by biochar prepared from sugarcane baggase. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Nabil, G.M.; El-Mallah, N.M.; Bassiouny, H.I.; Kumar, S.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of reactive red 195 A dye from water by modified Switchgrass Biochar adsorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 37, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathania, D.; Sharma, S.; Singh, P. Removal of methylene blue by adsorption onto activated carbon developed from Ficus carica bast. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1445–S1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R. Adsorption of Dye by Modified Activated Carbon and Heavy and Heavy Metals by Rice Husk-Based Activated Carbon. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2011. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.D.; Jung, W.S.; Cho, J.M.; Ryu, B.G.; Yang, J.S.; Baek, K. Adsorption of Cr(VI) onto cationic surfactant-modified activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Yoon, S.; Choe, J.K.; Lee, M.; Choi, Y. Anionic surfactant modification of activated carbon for enhancing adsorption of ammonium ion from aqueous solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Chen, W.f.; Cheng, M.T.; Li, Q. Investigation of factors that affect cationic surfactant loading on activated carbon and perchlorate adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 434, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.D.; Shin, M.C.; Kim, D.H.; Jeon, C.S.; Baek, K. Removal characteristics of reactive black 5 using surfactant-modified activated carbon. Desalination 2008, 223, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Suresh Kumar, M.V. Removal of chromium (VI) from water and wastewater using surfactant modified coconut coir pith as a biosorbent. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2218–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Andrew, H.; Ren, B. Gemini Surfactant-Modified Activated Carbon for Remediation of Hexavalent Chromium from Water. Water 2018, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhter, M.S. Effect of acetamide on the critical micelle concentration of aqueous solutions of some surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1997, 121, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, R.; Xu, Q. Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Pendleton, P. Adsorption of anionic surfactant by activated carbon: Effect of surface chemistry, ionic strength, and hydrophobicity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 243, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. Fabrication of Polyacrylonitrile-Based Activated Carbon Fibers Functionalized Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate for the Adsorptive Removal of Organic Dye from Aqueous Solution. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2017. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Ang, H.M. Equilibrium, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics of Methylene Blue Adsorption by Pine Tree Leaves. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 5267–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, N.; Sundaram, M.M. Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption on various carbons—a comparative study. Dye Pigment 2001, 51, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.K. Removal of reactive dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto activated carbons prepared from sugarcane bagasse pith. Desalination 2008, 223, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, Z.; Acar, F.N. Adsorption of Reactive Black 5 from an aqueous solution: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Desalination 2006, 194, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazinski, W.; Rudzinski, W.; Plazinska, A. Theoretical models of sorption kinetics including a surface reaction mechanism: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 152, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; You, W.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhan, H. Mildly alkaline preparation and methylene blue adsorption capacity of hierarchical flower-like sodium titanate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 12654–12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Bu, H.; Jiang, G.; Zeng, M. Cross-linked succinyl chitosan as an adsorbent for the removal of Methylene Blue from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mall, I.D.; Srivastava, V.C.; Agarwal, N.K. Removal of Orange-G and Methyl Violet dyes by adsorption onto bagasse fly ash—kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Dyes Pigment 2006, 69, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, F.; Chen, M.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, Z. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue on carbon nanotubes. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3040–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouni, L.; Belkhiri, L.; Bollinger, J.C.; Bouzaza, A.; Assadi, A.; Tirri, A.; Dahmoune, F.; Madani, K.; Reminie, H. Removal of Methylene Blue from aqueous solutions by adsorption on Kaolin: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 153, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobi, K.; Mashitah, M.D.; Vadivelu, V.M. Adsorptive removal of methylene blue using novel adsorbent from palm oil mill effluent waste activated sludge: Equilibrium, thermodynamics and kinetic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, M.B.H. Hameed, Chitosan–clay composite as highly effective and low cost adsorbent for batch and fixed-bed adsorption of methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, Y.; Aydın, H. A kinetics and thermodynamics study of methylene blue adsorption on wheat shells. Desalination 2006, 194, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, W.; Jiang, L.H.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.G.; Zeng, Z.W.; Wang, X.H.; Ning, Q.M.; Liu, S.H.; Zhang, P.; Liu, S.B. Influence of sodium dodecyl sulfate coating on adsorption of methylene blue by biochar from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 70, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
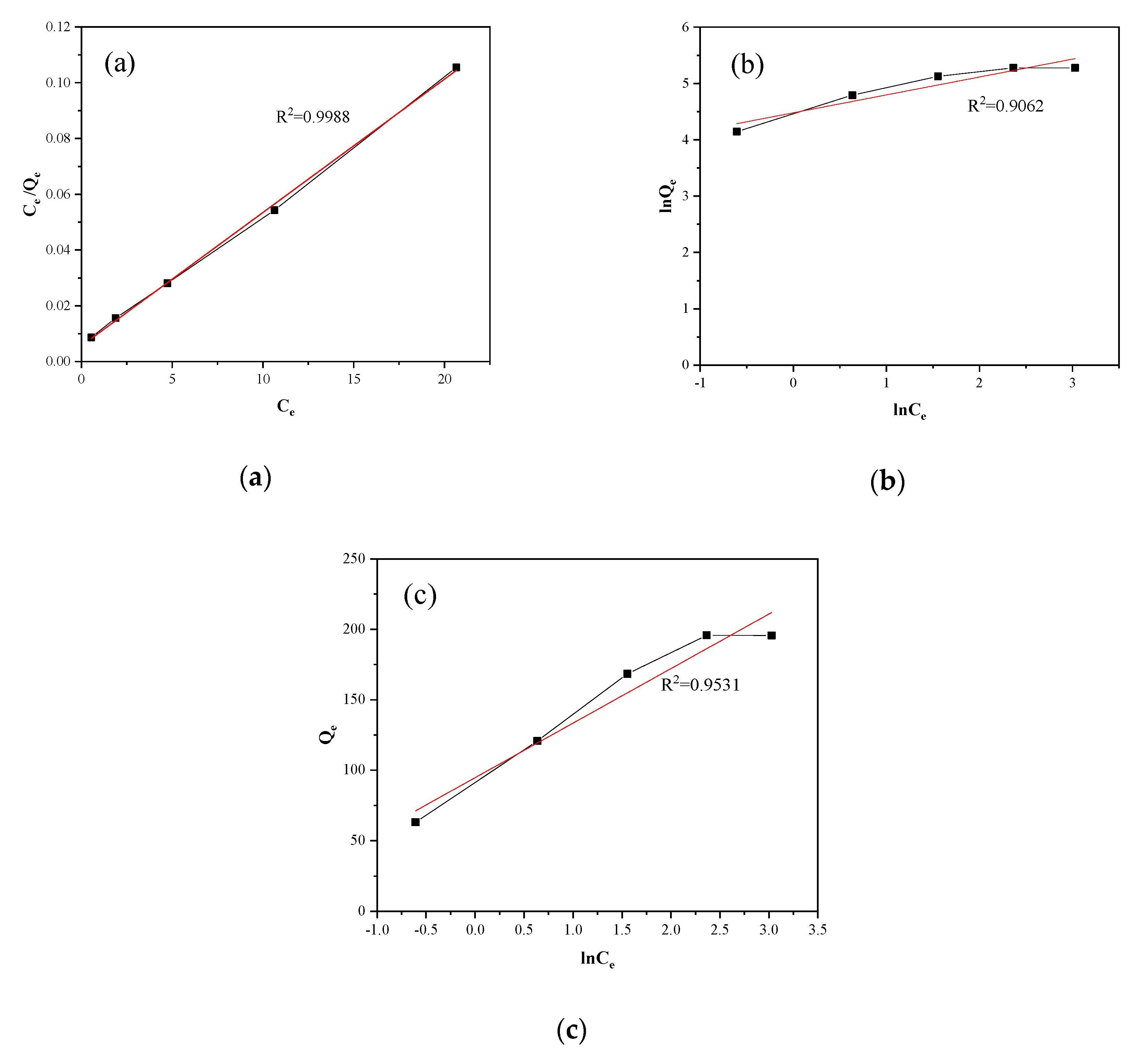
| MB Concentration (mg·L−1) | SLS-C | Virgin-C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent Adsorption (%) | Adsorption Capacity (mg·g−1) | Percent Adsorption (%) | Adsorption Capacity (mg·g−1) | |
| 10 | 96.6 | 64.4 | 80.9 | 53.9 |
| 20 | 90.6 | 120.8 | 72.7 | 96.0 |
| 30 | 86.7 | 173.4 | 66.3 | 132.6 |
| 40 | 73.4 | 195.8 | 51.9 | 138.4 |
| 50 | 58.7 | 195.7 | 41.3 | 137.6 |
| C0 (mg.L−1) | Qe,cal (mg.g−1) | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | Qe (mg.g−1) (exp.) | R2 | k2 (g.mg−1. min−1) | Qe (mg.g−1) (exp.) | R2 | ||
| 10 | 64.4 | 0.0090 | 4.4 | 0.644 | 0.00195 | 64.1 | 1 |
| 30 | 173.4 | 0.0107 | 40.9 | 0.966 | 0.00188 | 171.1 | 0.999 |
| 50 | 195.7 | 0.0069 | 42.1 | 0.974 | 0.00157 | 190.9 | 0.998 |
| C0 (mg·L−1) | Intra-Particle Diffusion Model | Elovich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kip (mg·g−1·min−1/2) | Ci | R2 | R2 | |||
| 10 | Kip1 = 3.800 Kip2 = 0.303 | 57.64 | 0.985 0.974 | 2.395 | 0.436 | 0.816 |
| 30 | 4.426 | 127.73 | 0.957 | 14.373 | 0.078 | 0.997 |
| 50 | 4.542 | 144.74 | 0.974 | 14.197 | 0.078 | 0.970 |
| Adsorption Model | Isotherm Parameters | |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | = 232.5 mg·g−1 | 0.999 |
| = 0.842 L·m-1·g−1 | ||
| = 0.106 | ||
| Freundlich | = 88.235 mg·g−1 | 0.906 |
| = 0.318 | ||
| Temkin | = 38.73 J·mol−1 | 0.953 |
| = 11.53 L·g−1 | ||
| = 63.98 L·g−1 |
| Thermodynamics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c/mg·L−1 | T/K | |||
| 10 | 298 | −11.78 | 0.059 | 5.90 |
| 308 | −12.38 | |||
| 318 | −12.97 | |||
| 328 | −13.56 | |||
| 30 | 298 | −8.84 | 0.064 | 10.28 |
| 308 | −9.48 | |||
| 318 | −10.12 | |||
| 328 | −10.77 | |||
| 50 | 298 | −5.57 | 0.067 | 14.46 |
| 308 | −6.24 | |||
| 318 | −6.91 | |||
| 328 | −7.58 | |||
| MB Concentration (mg·L−1) | Removal Efficiency (%) in Presence of Salt Species | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | NaCl | KCl | CaCl2 | NH4Cl | MgSO4 | NaNO2 | FeSO4 | |
| 10 | 94.3 | 94.6 | 94.6 | 94.6 | 94.6 | 94.6 | 94.6 | 90.4 |
| 30 | 78.1 | 79.7 | 77.0 | 78.3 | 78.3 | 73.7 | 85.3 | 60.5 |
| 50 | 53.2 | 55.5 | 52.7 | 53.9 | 53.9 | 52.0 | 56.9 | 44.2 |
| Water Sample | MB Concentration (mg·L−1) | Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Distilled water | 10 | 94.3 |
| 30 | 78.1 | |
| 50 | 53.4 | |
| Tap water | 10 | 94.3 |
| 30 | 80.1 | |
| 50 | 54.1 | |
| Raw water | 10 | 94.3 |
| 30 | 81.0 | |
| 50 | 55.3 | |
| waste water | 10 | 94.3 |
| 30 | 81.1 | |
| 50 | 55.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Water onto Activated Carbon by Surfactant Modification. Water 2020, 12, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020587
Kuang Y, Zhang X, Zhou S. Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Water onto Activated Carbon by Surfactant Modification. Water. 2020; 12(2):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020587
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuang, Yu, Xiaoping Zhang, and Shaoqi Zhou. 2020. "Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Water onto Activated Carbon by Surfactant Modification" Water 12, no. 2: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020587
APA StyleKuang, Y., Zhang, X., & Zhou, S. (2020). Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Water onto Activated Carbon by Surfactant Modification. Water, 12(2), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020587





