Guidelines for the Use of Unmanned Aerial Systems in Flood Emergency Response
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Flood Emergency Response in England and India and the Potential Use of UAS
2.2. Development of an UAS Deployment Analysis Matrix
| Factor | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Catchment | Catchment size | Size of the catchment where the event has taken place [23,24] |
| Catchment flood response | Catchment response to flooding after the rain event occurs [28,29] | |
| Flood | Flood source type | Source of flooding classified as groundwater, pluvial and fluvial [30] |
| Flood extent | The spatial coverage of the flood event and the associated emergency response coverage (e.g., single scene, regional coverage and national coverage) [31] | |
| Response | Emergency response phases | Pre-event, during-event and post-event [27,32] |
2.3. Technological Needs for the Use of UAS in Flood Emergency Response
3. Results
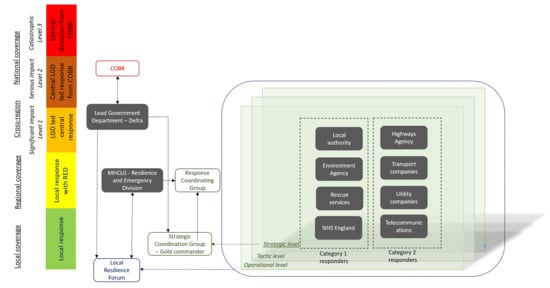
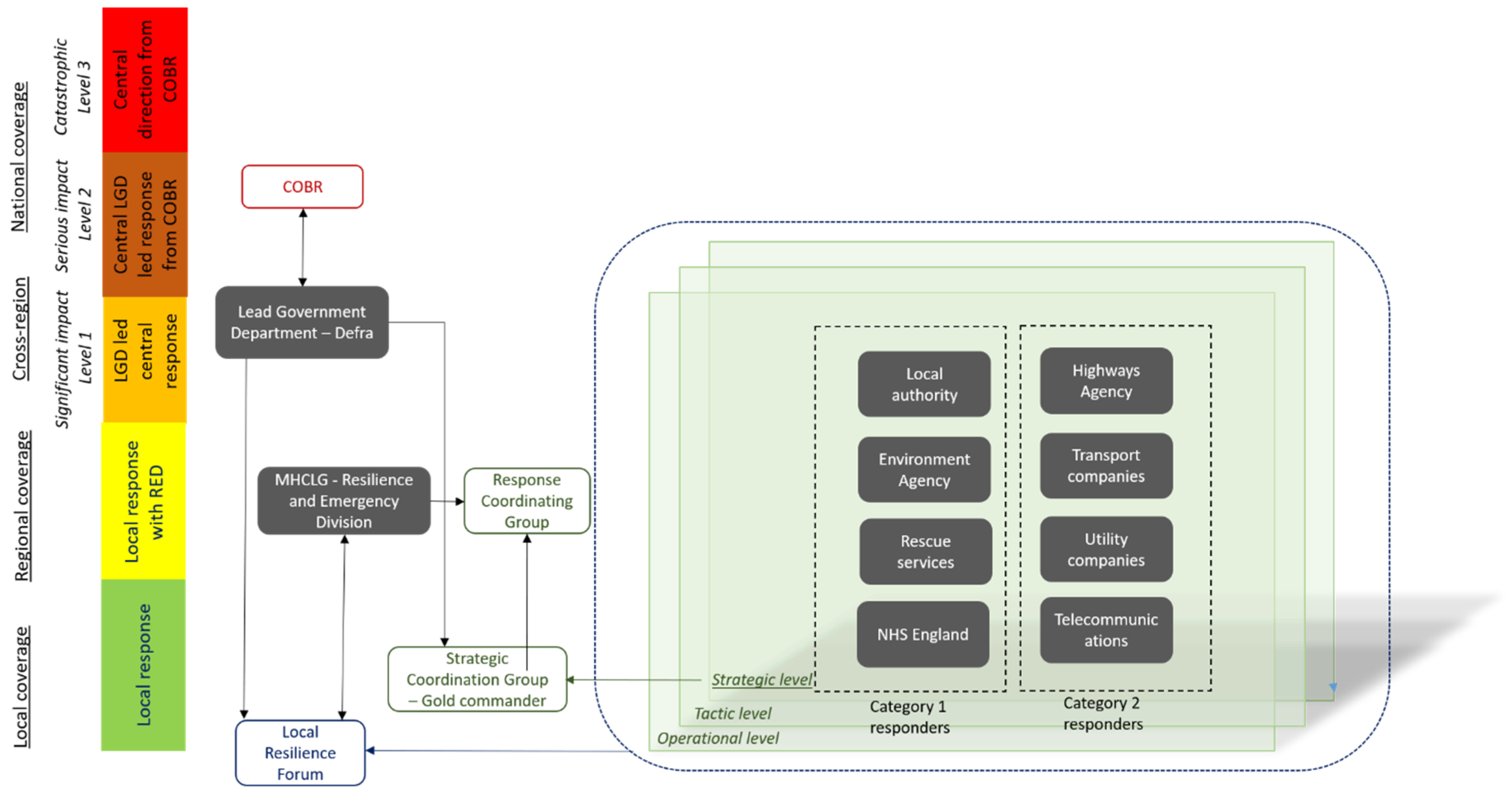
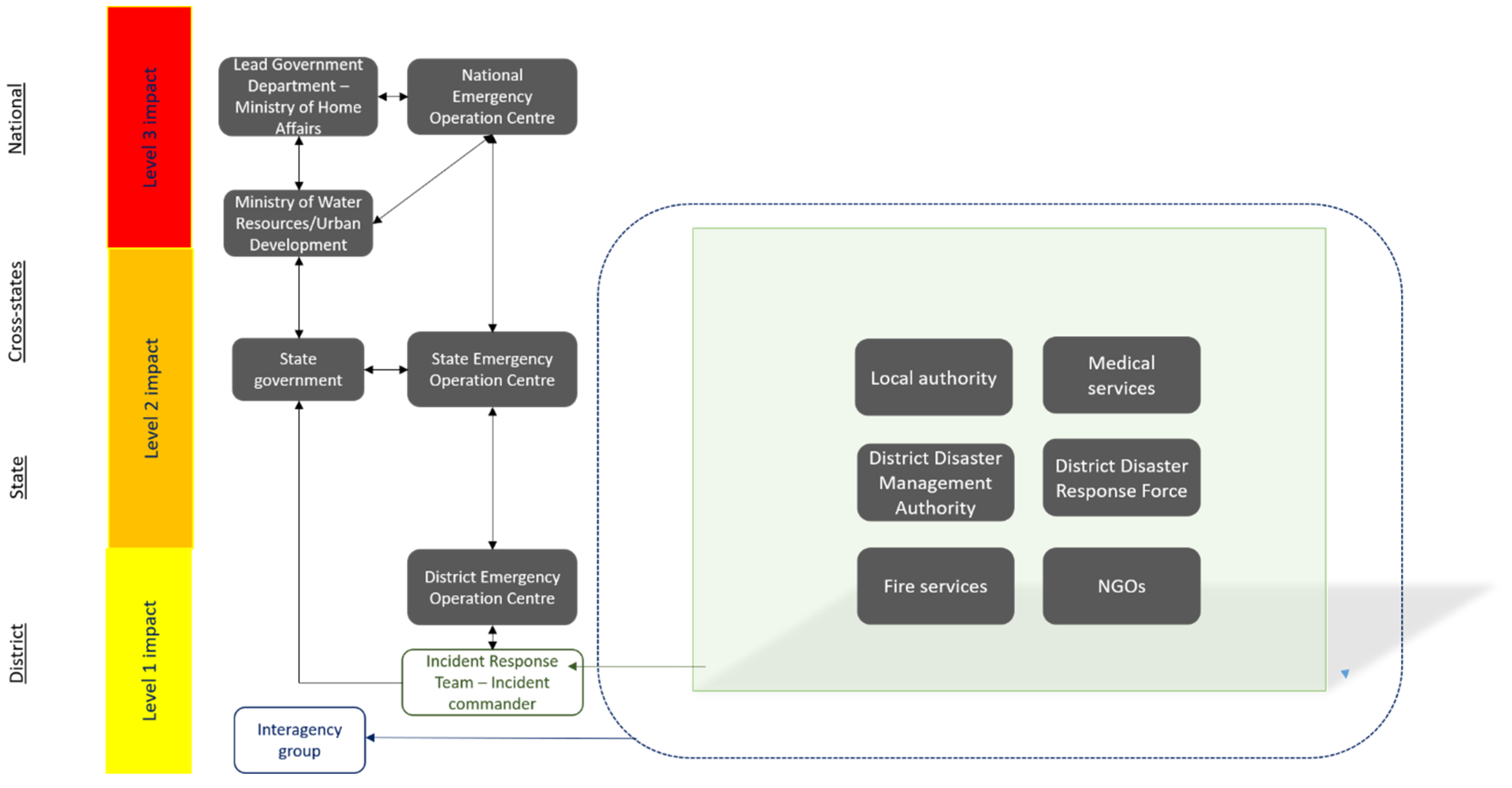
3.1. Organizations Involved in Flood Emergency Response: England and India
3.2. The Potential Use of UAS in Flood Emergency Response
3.3. The UAS Deployment Analysis Matrix for England: Pre-, During- and Post-Event
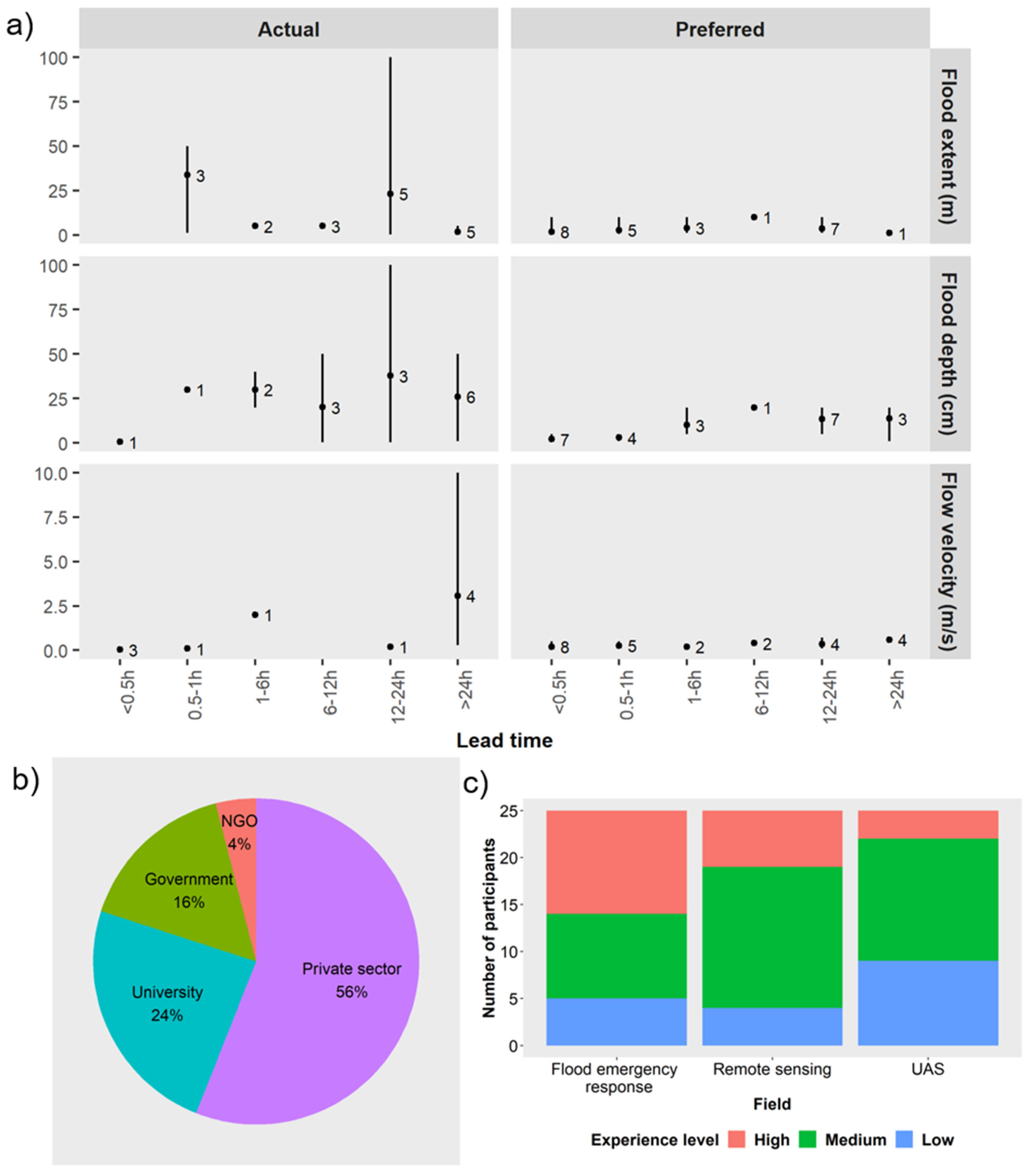
3.4. Preferences in England for UAS Applications in Flood Emergency Response
4. Discussion
4.1. A Purpose-Driven Approach to UAS Deployment in the Context of Flood Emergency Response
4.2. Guidelines for the Deployment of UAS within Flood Risk Management Activities Including Emergency Response
- There is time to produce digital elevation and surface and terrain models which can then be used within flood models to estimate, for a given return period rainfall event, the likely extent, depth and velocity of flooding. The information produced can also be used to identify locations for temporary barriers, shelter points and evacuation routes.
- If flooding has been forecast for a particular area, UAS-based audio systems can be used to provide audible warnings to those at risk.
- High levels of accuracy are often not a priority. The timeliness of the information being available to inform the response activities is paramount.
- Providing information in real-time is key as it enables effective prioritization of emergency response actions including: to identify where to deploy maintenance crews to deal with blockages and low spots in defences which are giving rise to unexpected sources of flooding; to identify whether the flooding is developing in line with modelled predictions in terms of extent and depth; to determine whether flooding is occurring in areas outside of those predicted by the models; to assess whether evacuation routes remain clear of flooding; to identify people and properties impacted by the flooding.
- During an event, typically time is limited to carry out new simulations [14]. During the event responders potentially identify gaps in the existing flood emergency plan (i.e., location of shelter points, evacuation routes, knowledge about resistance and resilience measures). However, in an event that exceeds the planned preparedness plan, it may be necessary to rerun the evacuation routes models.
- UAS can be used to determine the extent, depth and velocity of the flooding and the properties impacted. This information can be extremely valuable after the event to calibrate and refine the models and to determine whether additional flood risk reduction measures are required.
- Many organizations are involved in responding to flood events [81]. The use of UAS should be discussed well in advance of any need to deploy them including what information will be collected, how, by whom and for what purpose.
- UAS of the correct specification, including specified sensors and trained pilots will have to be available for deployment within an agreed standard of service.
- UAS can be used to help determine the impact on people, properties and infrastructure, the flood extents and depths, and in identifying where best to deploy those still involved in rescue activities and in the recovery operations.
- UAS can be used to collect information that enable the calibration and validation of those models used pre-event for flood prediction purposes. Data collected at this stage will also look at features highlighting flood impact (e.g., properties affected).The EA with its strategic overview role for flood risk management in England would be well placed to develop guidelines for the use and deployment of UAS in this context and then to oversee their implementation.
4.3. Selecting the Correct UAS Platform
4.4. The Deployment Decision Approach to an Indian Context
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. House of Representatives. A Failure of Initiative. Final Report of the Selected Bipartisan Committee to Investigate the Preparation for and Response to Hurricane Katrina; U.S. House of Representatives: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Hallegatte, S. An adaptive regional input-output model and its application to the assessment of the economic cost of Katrina. Risk Anal. 2008, 28, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AON Global Catastrophe Recap: October 2018; AON Empower Results: London, UK, 2018; Available online: http://thoughtleadership.aonbenfield.com/Documents/20181107-ab-analytics-if-oct-global-recap.pdf (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Venkataraman, A.; Suhasinini, R.; Abi-Habib, M. After Worst Kerala Floods in a Century, India Rejects Foreign Aid. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2018/08/23/world/asia/india-kerala-floods-aid-united-arab-emirates.html (accessed on 24 November 2019).
- Environment Agency. Managing Flood and Coastal Erosion Risks in England: 1 April 2011 to 31 March 2017; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2018. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/flood-and-coastal-risk-management-national-report (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Paciarotti, C.; Cesaroni, A.; Bevilacqua, M. The management of spontaneous volunteers: A successful model from a flood emergency in Italy. Int. J. Dis. Risk Reduct. 2018, 31, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defra the National Flood Emergency Framework for England. December 2014; Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs: London, UK, 2014.
- NDMA National Disaster Management Plan (NDMP); National Disaster Management Authority Government: New Delhi, India, 2016. Available online: https://ndma.gov.in/images/policyplan/dmplan/National%20Disaster%20Management%20Plan%20May%202016.pdf (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- WMO; US NOAA; US NWS; HRC. Proceedings of the USAID/OFDA First Steering Committee Meeting (SCM 1) of The South Asia Flash Flood Guidance (SAsiaFFG) Project, New Delhi, India, 26–28 April 2016; p. 29.
- CWC Flood Forecast. Central Water Commission. Available online: http://14.143.182.4/ffs/ (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Oleo, M. Developing Data Standards for Flood Models; Cranfield University: Cranfield, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Neelz, S.; Pender, G. Benchmarking the Latest Generation of 2D Hydraulic Modelling Packages; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2013; ISBN 0234-1026. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, E.P.; Simm, J.D.; Thorne, C.R.; Arnell, N.W.; Ashley, R.M.; Hess, T.M.; Lane, S.N.; Morris, J.; Nicholls, R.J.; Penning-Rowsell, E.C.; et al. An Update of the Foresight Future Flooding 2004 Qualitative Risk Analysis; An independent review by Sir Michael Pitt; Cabinet Office: London, UK, 2008.
- Ward, P.J.; Jongman, B.; Salamon, P.; Simpson, A.; Bates, P.; De Groeve, T.; Muis, S.; De Perez, E.C.; Rudari, R.; Trigg, M.A.; et al. Usefulness and limitations of global flood risk models. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas Casado, M.; Irvine, T.; Johnson, S.; Palma, M.; Leinster, P. The use of unmanned aerial vehicles to estimate direct tangible losses to residential properties from flood events: A case study of Cockermouth Following the Desmond Storm. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UN-OCHA Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Humanitarian Response; United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2014.
- Kim, K.; Davidson, J. Unmanned Aircraft Systems Used for Disaster Management. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2015, 2532, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, O.; Murphy, R.; Adams, J.; Merrick, D. Quantitative Data Analysis: CRASAR Small Unmanned Aerial Systems at Hurricane Harvey. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security, and Rescue Robotics (SSRR), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 6–8 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, A.C.; Ambrosia, V.G.; Hinkley, E.A. Unmanned aircraft systems in remote sensing and scientific research: Classification and considerations of use. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reliefweb. Drones Used for Good-Relief Organisation Uses Drones to Map Typhoon Haiyan Recovery Efforts. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/philippines/drones-used-good-relief-organisation-uses-drones-map-typhoon-haiyan-recovery (accessed on 25 April 2019).
- Santos, L.A. In the Philippines, Drones Provide Humanitarian Relief. Available online: https://www.devex.com/news/in-the-philippines-drones-provide-humanitarian-relief-82512 (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- Mathew, A. Up, up and very Far away: Remote Sensing in Flood Response. Available online: https://defradigital.blog.gov.uk/2017/03/30/up-up-and-very-far-away-remote-sensing-in-flood-response/ (accessed on 18 April 2019).
- Schumann, G.J.-P.; Muhlhausen, J.; Andreadis, K.M. Rapid Mapping of Small-Scale River-Floodplain Environments Using UAV SfM Supports Classical Theory. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeBell, L.; Anderson, K.; Brazier, R.E.; King, N.; Jones, L. Water resource management at catchment scales using lightweight UAVs: Current capabilities and future perspectives. J. Unmanned Veh. Syst. 2016, 4, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, M.; Dempsey, P.; Dent, J. Defra/Environment Agency Flood and Coastal Defence R & D Programme; Extreme Rainfall Event Recognition Phase 2 Work Package 5: Establishing a user requirement for a decision-support tool; R & D Technical Report-FD2208; 2005; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen, T.R. Flood Estimation Handbook Supplementary Report No. 1 the Revitalised FSR/FEH Rainfall-Runoff Method; Centre for Ecology and Hydrology: Wallingford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Erdelj, M.; Król, M.; Natalizio, E. Wireless Sensor Networks and Multi-UAV systems for natural disaster management. Comput. Netw. 2017, 124, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Andreadakis, E.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Spyrou, N.I.; Gogou, M.E.; Deligiannakis, G.; Katsetsiadou, N.K.; Antoniadis, Z.; Melaki, M.; Georgakopoulos, A.; et al. An integrated approach of ground and aerial observations in flash flood disaster investigations. The case of the 2017 Mandra flash flood in Greece. Int. J. Dis. Risk Reduct. 2018, 33, 290–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, L.; Borga, M.; Preciso, E.; Gaume, E. Characterisation of selected extreme flash floods in Europe and implications for flood risk management. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment Agency Flooding in England: A National Assessment of Flood Risk. Environ. Agency 2009, 5–32.
- Smith, M.W.; Carrivick, J.L.; Hooke, J.; Kirkby, M.J. Reconstructing flash flood magnitudes using “Structure-from-Motion”: A rapid assessment tool. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1914–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restas, A. Drone Applications for Supporting Disaster Management. World J. Eng. Technol. 2015, 3, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Defra Flood Risks to People-Phase 2-FD2321/TR2 Guidance Document; Department for Environment Food and Rural Affairs: London, UK, 2006.
- Coles, D.; Yu, D.; Wilby, R.L.; Green, D.; Herring, Z. Beyond ‘flood hotspots’: Modelling emergency service accessibility during flooding in York, UK. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Defra Flood and Water Management Act 2010; Department for Environment Food and Rural Affairs: London, UK, 2010.
- Tooth, J.-P. Storms & Emergencies: How A UK Military Response is Decided. Available online: https://www.forces.net/news/storms-emergencies-how-uk-military-response-decided (accessed on 24 November 2019).
- Defra Exercise Tempest Tests the Environment Agency flood Response ahead of Winter. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/exercise-tempest-tests-the-environment-agency-flood-response-ahead-of-winter (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- District Disaster Management Authority Madhubani. District Disaster Management Plan-Madhubani; District Disaster Management Authority Madhubani: Madhubani, Bihar, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, P. Flood Disaster in India: An Analysis of trend and Preparedness. Interdiscip. J. Contemp. Res. 2015, 2, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Gusain, R. Drones Come to NDRF’s Rescue in Locating Stranded People in Kedarnath. Available online: https://www.indiatoday.in/india/north/story/national-disaster-response-force-takes-help-of-drones-to-locate-stranded-people-in-kedarnath-169487-2013-07-08 (accessed on 24 September 2019).
- Sethi, N. Drones Scan Flood-Hit Uttarakhand. Available online: https://www.livemint.com/Politics/ZDib5YWR1G2Mcuth1kbwyO/Drones-scan-floodhit-Uttarakhand.html (accessed on 22 November 2019).
- ENS UAVs Look for Survivors as New Landslides, Rain Hamper Rescue. Available online: http://www.newindianexpress.com/nation/2013/jun/25/UAVs-look-for-survivors-as-new-landslides-rain-hamper-rescue-490250.html (accessed on 24 September 2019).
- Hoyle, C. Pictures: How Netra UAVs Helped Indian Disaster Relief Effort. Available online: https://www.flightglobal.com/news/articles/pictures-how-netra-uavs-helped-indian-disaster-relief-effort-387984/ (accessed on 24 September 2019).
- Popescu, D.; Ichim, L.; Caramihale, T. Flood areas detection based on UAV surveillance system. In Proceedings of the 2015 19th International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), Cheile Gradistei, Romania, 14–16 October 2015; pp. 753–758. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, D.; Ichim, L.; Stoican, F. Unmanned aerial vehicle systems for remote estimation of flooded areas based on complex image processing. Sensors 2017, 17, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Canisius, F.; Guindon, B.; Feng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Canisius, F.; Guindon, B.; Zhen, C.; Feng, B. Effectiveness of RGB imagery from diverse sources for real-time urban flood water mapping. In Proceedings of the SPIE 10793, Remote Sensing Technologies and Applications in Urban Environments III, Berlin, Germany, 9 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gebrehiwot, A.; Hashemi-Beni, L.; Thompson, G.; Kordjamshidi, P.; Langan, T.E. Deep convolutional neural network for flood extent mapping using unmanned aerial vehicles data. Sensors 2019, 19, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şerban, G.; Rus, I.; Vele, D.; Breţcan, P.; Alexe, M.; Petrea, D. Flood-prone area delimitation using UAV technology, in the areas hard-to-reach for classic aircrafts: Case study in the north-east of Apuseni Mountains, Transylvania. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimhuber, V.; Hannemann, J.C.; Rieger, W. Flood risk management in remote and impoverished areas-a case study of Onaville, Haiti. Water 2015, 7, 3832–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, M.; Shaqura, M.; Claudel, C.G.; Gueaieb, W. A UAV based system for real time flash flood monitoring in desert environments using Lagrangian microsensors. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Atlanta, GA, USA, 28–31 May 2013; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Thumser, P.; Haas, C.; Tuhtan, J.A.; Fuentes-Pérez, J.F.; Toming, G. RAPTOR-UAV: Real-time particle tracking in rivers using an unmanned aerial vehicle. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 2439–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauro, F.; Petroselli, A.; Arcangeletti, E. Assessment of drone-based surface flow observations. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1114–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Coz, J.; Patalano, A.; Collins, D.; Guillén, N.F.; García, C.M.; Smart, G.M.; Bind, J.; Chiaverini, A.; Le Boursicaud, R.; Dramais, G.; et al. Crowdsourced data for flood hydrology: Feedback from recent citizen science projects in Argentina, France and New Zealand. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, I.; Notoya, Y.; Tani, K.; Tateguchi, S. Efficient and accurate estimation of water surface velocity in STIV. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2018, 19, 1363–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuji, I.; Tani, K.; Fujita, I.; Notoya, Y. Development of Aerial Space Time Volume Velocimetry for Measuring Surface Velocity Vector Distribution from UAV. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences- River Flow 2018 - Ninth International Conference on Fluvial Hydraulics, Lyon-Villeurbanne, France, 5–8 September 2018; Volume 40, p. 06011. [Google Scholar]
- Srikudkao, B.; Khundate, T.; So-In, C.; Horkaew, P.; Phaudphut, C.; Rujirakul, K. Flood Warning and Management Schemes with Drone Emulator Using Ultrasonic and Image Processing. In Recent Advances Technology 2015; Unger, H., Meesad, P., Boonkrong, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 107–116. ISBN 9783319190235. [Google Scholar]
- Muthusamy, M.; Rivas Casado, M.; Salmoral, G.; Irvine, T.; Leinster, P. A Remote Sensing Based Integrated Approach to Quantify the Impact of Fluvial and Pluvial Flooding in an Urban Catchment. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiabrando, F.; Piras, M.; Aicardi, I.; Vigna, B.; Noardo, F.; Lingua, A.M. A methodology for acquisition and processing of thermal data acquired by UAVs: A test about subfluvial springs’ investigations. Geomatics, Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 8, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, A.; Inoue, M. Generating Evacuation Routes by Using Drone System and Image Analysis To Track Pedestrian and Scan the Area After Disaster Occurrence. In Proceedings of the 10th SEATUC (South East Asian Technical University Consortium) Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 22–24 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lucieer, A.; De Jong, S.M.; Turner, D. Mapping landslide displacements using Structure from Motion (SfM) and image correlation of multi-temporal UAV photography Mapping landslide displacements using Structure from Motion (SfM) and image correlation of multi-temporal UAV photography. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2013, 38, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaioni, M.; Longoni, L.; Melillo, V.; Papini, M. Remote Sensing for Landslide Investigations: An Overview of Recent Achievements and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9600–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohshimo, S.; Sadamori, T.; Shime, N. The western Japan chaotic rainstorm disaster: A brief report from Hiroshima. J. Intensive Care 2018, 6, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, J.; Ramachandran, U. Role of Various Sectors in Demonstrating Resilience during Chennai Flood 2015; Asian Cities Climate Change Network; Taru Leading Edge: Ahmedabad, New Delhi, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Decorah Newspapers. Decorah Fire Department Drone Aids in Allamakee County River Rescue. Available online: https://decorahnewspapers.com/Content/News/Lead-Stories/Article/Decorah-Fire-Department-drone-aids-in-Allamakee-County-river-rescue/2/13/43505 (accessed on 5 June 2019).
- DJI. More Lives Saved: A Year of Drone Rescues Around The World; DJI: Shenzhen, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, F. Drone Used to Help Emergency Crews for the First Time in the Ozarks. Available online: https://www.kspr.com/content/news/Drone-used-to-help-emergency-crews-for-the-first-time-in-the-Ozarks-478245203.html (accessed on 5 July 2019).
- Sharma, S. Flood-Survivors Detection Using IR Imagery on an Autonomous Drone; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gallegos, H.A.; Schubert, J.E.; Sanders, B.F. Structural Damage Prediction in a High-Velocity Urban Dam-Break Flood: Field-Scale Assessment of Predictive Skill. J. Eng. Mech. 2012, 138, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yang, C.; Li, Y. Big Data in Natural Disaster Management: A Review. Geosciences 2018, 5, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCall, I.; Evans, C.; Cockermouth, S. 19 Flood Investigation Report; Environment Agency, Cumbria County Council: Penrith, UK, 2016.
- Deeming, H. Project: Understanding Extreme Events as Catalysts for Flood-Risk Management Policy Change: A Case Study of the Impact of “Storm Desmond” in Cumbria, UK; HD Research: Bentham, UK, 2016; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Krol, C. Storm Desmond: Aerial Footage Shows Extent of Flooding Damage in Cumbria. Available online: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/weather/12036038/Drone-footage-shows-flooding-in-Carlisle.html (accessed on 2 October 2019).
- Pal, I.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Trends in seasonal precipitation extremes-An indicator of “climate change” in Kerala, India. J. Hydrol. 2009, 367, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padma, T.V. Kerala floods made worse by mining and dams. Nature 2018, 561, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnu, C.L.; Sajinkumar, K.S.; Oommen, T.; Coffman, R.A.; Thrivikramji, K.P.; Rani, V.R.; Keerthy, S. Satellite-based assessment of the August 2018 flood in parts of Kerala, India. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- BBC. Kerala Floods: Troops Rush in to Help Rescue Efforts. Available online: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-india-45231222 (accessed on 2 October 2019).
- Putrevu, S. Here’s how these Drone Startups can help in Rescue Operations in Bihar Floods. Available online: https://yourstory.com/2019/09/bihar-floods-drone-startups (accessed on 2 October 2019).
- Manorama. Drones to Deliver Aid to Marooned Tribal Colonies in Idukki. Available online: https://english.manoramaonline.com/news/kerala/2018/08/20/drones-for-idukki-rescue-works.html (accessed on 2 October 2019).
- Parker, D.; Fordham, M. An evaluation of flood forecasting, warning and response systems in the European Union. Water Resour. Manag. 1996, 10, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessis, L. Du A review of effective flood forecasting, warning and response system for application in South Africa. Water SA 2002, 28, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maidment, D.R. Conceptual Framework for the National Flood Interoperability Experiment. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sarda, N.L. Efficient Evacuation Planning for Large Cities. In Database and Expert Systems Applications. 25th International Conference, DEXA 2014 Munich, Germany, September 1–4, 2014 Proceedings, Part I; Decker, H., Lhotská, L., Link, S., Spies, M., Wagner, R.R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 9783319444024. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S. Evaluating climate change adaptation through evacuation decisions: A case study of cyclone management in India. Clim. Chang. 2019, 152, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, G.; Bansod, B.; Mathew, L. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle classification, Applications and challenges: A Review. Preprint 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivas Casado, M.; Ballesteros Gonzalez, R.; Kriechbaumer, T.; Veal, A. Automated identification of river hydromorphological features using UAV high resolution aerial imagery. Sensors 2015, 15, 27969–27989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Kovacs, J.M. The application of small unmanned aerial systems for precision agriculture: A review. Precis. Agric. 2012, 13, 693–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, A. Types of Drones: Multi-Rotor vs. Fixed-Wing vs. Single Rotor vs. Hybrid VTOL. Available online: https://www.auav.com.au/articles/drone-types/ (accessed on 24 November 2019).
- Topcon. Topcon Sirius Unmanned Aerial Solution; Topcon: Tokyo, Japan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wingtra. WingtraOne – Technical specifications; Wingtra AG: Zürich, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://wingtra.com/wp-content/uploads/Wingtra-Technical-Specifications.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Flynt, J. 11 Best Long Flight Time Drones. Available online: https://3dinsider.com/long-flight-time-drones/ (accessed on 5 November 2019).
- Microdrones. Product Line Up: Fully Integrated Systems for Professionals; Microdrones: Ney York, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: https://cdn.microdrones.com/fileadmin/web/_downloads/brochures/english/2020_Brochure_mdSOLUTIONS_LETTER_EN_DL.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Topcon. Sirius Pro Specifications. Available online: https://www.topconpositioning.com/mass-data-collection/aerial-mapping/sirius-pro#panel-product-specifications (accessed on 19 January 2020).
- Fernández-Hernandez, J.; González-Aguilera, D.; Rodríguez-Gonzálvez, P.; Mancera-Taboada, J. Image-Based Modelling from Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Photogrammetry: An Effective, Low-Cost Tool for Archaeological Applications. Archaeometry 2015, 57, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Korzhenevych, A.; Hecht, R. Determinants of commuting patterns in a rural-urban megaregion of India. Transp. Policy 2018, 68, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, G.J.; Shilston, D.T. Terrain geohazards and sustainable engineering in Ladakh, India. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2017, 50, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, G.J.; Shakya, N.M. Engineering challenges for sustainable road access in the Himalayas. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2017, 50, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
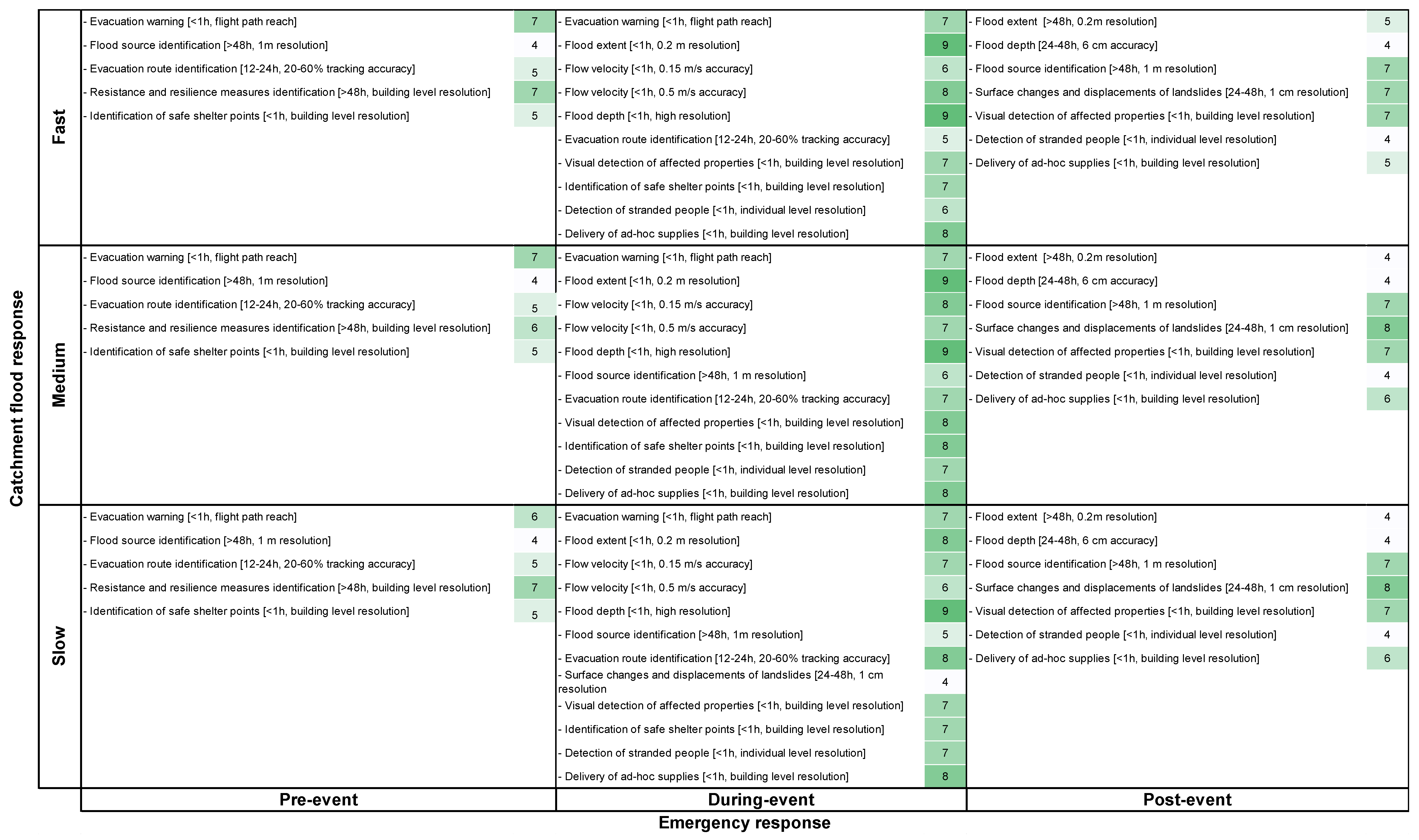
| Flood Management Component | Applications | Examples | UAS Raw Product | Processed Outcome | Time | Details 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flood warning | Evacuation warning | UAS with an embedded audible alarm to provide an alert about an upcoming flood and the need for evacuation (Mozambique). | N/A | N/A | Real-time | Flight path reach |
| Flood monitoring and flood risk assessment | Visualization of flood extent | Delineation of inundated areas by digitizing the boundaries at the contrasting land surface/water boundary [28]. | RGB imagery RGB video | Flood extent, Ponding locations | Real time (<1 h) | 0.2 m high resolution RGB imagery 4 |
| Flood extent detection | Application of an algorithm to detect flood areas automatically [44,45]. | RGB imagery | Orthoimage, flood extent | >48h 1 | 0.2 m high resolution RGB imagery 4 | |
| A spectral difference index is generated from the RGB photos to map flood water extent [46]. | RGB imagery | Orthoimage, flood extent | Real time (<1 h) | 0.2 m high resolution in RGB imagery | ||
| Modelling flood extent | A concept of transfer learning where a Convolutional Neural Network model is trained based on one dataset, transferred and used to classify another dataset to delineate flood extent [47]. | RGB imagery | Orthoimage, DEM, flood extent | <48 h | 1.5 cm ultra-high resolution in RGB imagery with 93% accuracy in flood extent | |
| A high accuracy terrain model combined with hydraulic calculations performed on transverse profiles produce the flood-prone areas at 1% and 5% exceedance probabilities of discharge [48]. | ||||||
| A DEM mapped with UAS is used in hydrologic and hydraulic modelling to provide a flood hazard map [49]. | ||||||
| Point measurement of flow velocity | A set of floating wireless sensors are deployed within the flood extent by multiple UAS to capture water velocity readings at multiple locations [50]. | Water velocity readings. Infrared imaging | Water velocity | Real time (<1 h) | Estimated 0.15 m/s accuracy 5 | |
| A combination of floating, infrared light-emitting particles and a programmable embedded colour vision sensor to simultaneously detect and track objects [51]. | ||||||
| Optical water velocity | Bespoke algorithms are used to track the movement of tracers [52], or texture [53,54,55] in the water surface in consecutive frames obtained from video footage. | RGB imagery RGB video streaming HD video | Orthoimage, water velocity | >48 h 1 | Estimated 0.5 m/s accuracy 5 | |
| Water velocity | Real time (<1 h) | |||||
| Visual flood depth | Flood depth is estimated through the observation of wrack marks (post-event) [28] or via the observation of the water level (during event) against know height points (e.g., cars, bridges, feature buildings). | (Oblique) RGB imagery RGB video | Flood depth | Real time (<1 h) | High resolution RGB imagery | |
| Point measured of flood depth | UAS with ultrasonic sensors used to detect water level [56]. A pre-event DEM is required to estimate flood depth. | Water depth readings | Water level, point cloud, DEM, DTM, DSM | <48 h 2 | 6 cm accuracy | |
| Flood source identification (fluvial, pluvial, groundwater) | Sources of flooding can be identified based on damaged caused within/outside the fluvial flood extent [15,57] or based on differences in water temperature [58]. | RGB frames Thermal frames | Orthoimage, DEM, DTM, DSM | >48 h | 1 m resolution (DEM) | |
| Evacuation routes identification | Modelled evacuation route identification | Modelling of evacuation routes by using UAS as end devices of M2M architecture [59]. The input model needs DEM, DTM and/or DSM as well as hydrological/hydraulic input data. | RGB imagery RGB video | Map of evacuation routes, DSM, DTM, DEM, orthoimage | <24 h | 20–60% tracking accuracy |
| Surface changes and displacements of landslides | Surface changes and displacements of landslides [60,61]. | RGB imagery RGB video | 3D point clouds, DEM, orthoimage | <48 h 2 | 1 cm ultra-high resolution (DEM), accuracy: 7.4 cm (horizontal) × 6.2 cm (vertical) | |
| Damage assessment | Visual detection of affected properties, businesses, hospitals, schools | To collect information on damage to hospitals for patient rescue and for efficient allocation of resources [62]. | RGB imagery | Location of affected properties | Real time (<1 h) | Resolution at building level |
| Resistance and resilience measures identification | Identification of residential properties with resistance measures (i.e., flood aperture guards for doors and windows, flood resistant airbricks, and raised doors or steps leading to a property) [15]. | RGB imagery | Orthoimage, DEM | >48 h | Resolution at building level | |
| Rescue | Identification of safe shelter points | To identify where to best place NGO camps [21] and to identify land that could be safer to relocate families [20]. | RGB imagery RGB video | Map with location of points | Real time (<1 h) | Resolution at building level |
| Detection of stranded people | The use of UAS to locate stranded people [63,64] even at night [65,66] and specifically during floods [67]. | RGB imagery RGB video Infrared imaging | N/A | Real time (<1 h) | Resolution at individual level | |
| Delivery of ad-hoc supplies | The use of UAS to deliver equipment or resources that guarantee the survival of stranded people e.g. to carry a radio to communicate [64], floating devices [65]. | RGB imagery RGB video | N/A | Real time (<1 h) | Resolution at individual level |
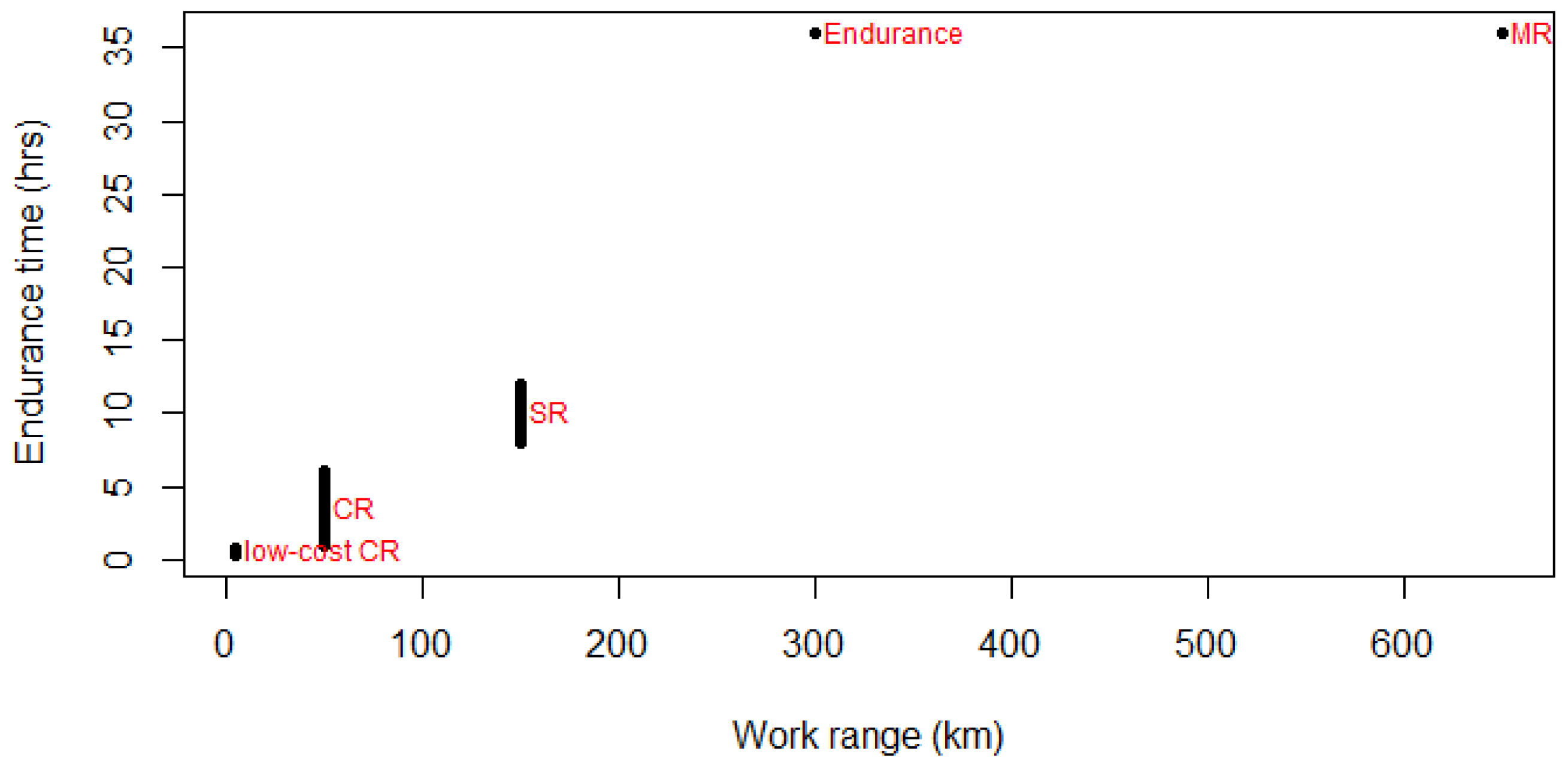
| UAS Type | Range (km) | Endurance Time (h) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low cost close range | 5 | 1/3—3/4 | This type includes Micro and Nano air vehicles, low altitude flying with a maximum altitude of ca. 1000 m, no need for runways. |
| Close range | 50 | 1—6 | Need runways, altitude up to ca. 1500 m. |
| Short range | 150 | 8—12 | Need runways, altitude of a few thousand meters. |
| Mid-range | 650 | - | Need runways, altitude up to 9000 m. |
| Endurance | 300 | 36 | Need runways, altitude of 20,000 m or more. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salmoral, G.; Rivas Casado, M.; Muthusamy, M.; Butler, D.; Menon, P.P.; Leinster, P. Guidelines for the Use of Unmanned Aerial Systems in Flood Emergency Response. Water 2020, 12, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020521
Salmoral G, Rivas Casado M, Muthusamy M, Butler D, Menon PP, Leinster P. Guidelines for the Use of Unmanned Aerial Systems in Flood Emergency Response. Water. 2020; 12(2):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020521
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalmoral, Gloria, Monica Rivas Casado, Manoranjan Muthusamy, David Butler, Prathyush P. Menon, and Paul Leinster. 2020. "Guidelines for the Use of Unmanned Aerial Systems in Flood Emergency Response" Water 12, no. 2: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020521
APA StyleSalmoral, G., Rivas Casado, M., Muthusamy, M., Butler, D., Menon, P. P., & Leinster, P. (2020). Guidelines for the Use of Unmanned Aerial Systems in Flood Emergency Response. Water, 12(2), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020521