Intermittent Aeration in a Hybrid Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor for Carbon and Nutrient Biological Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
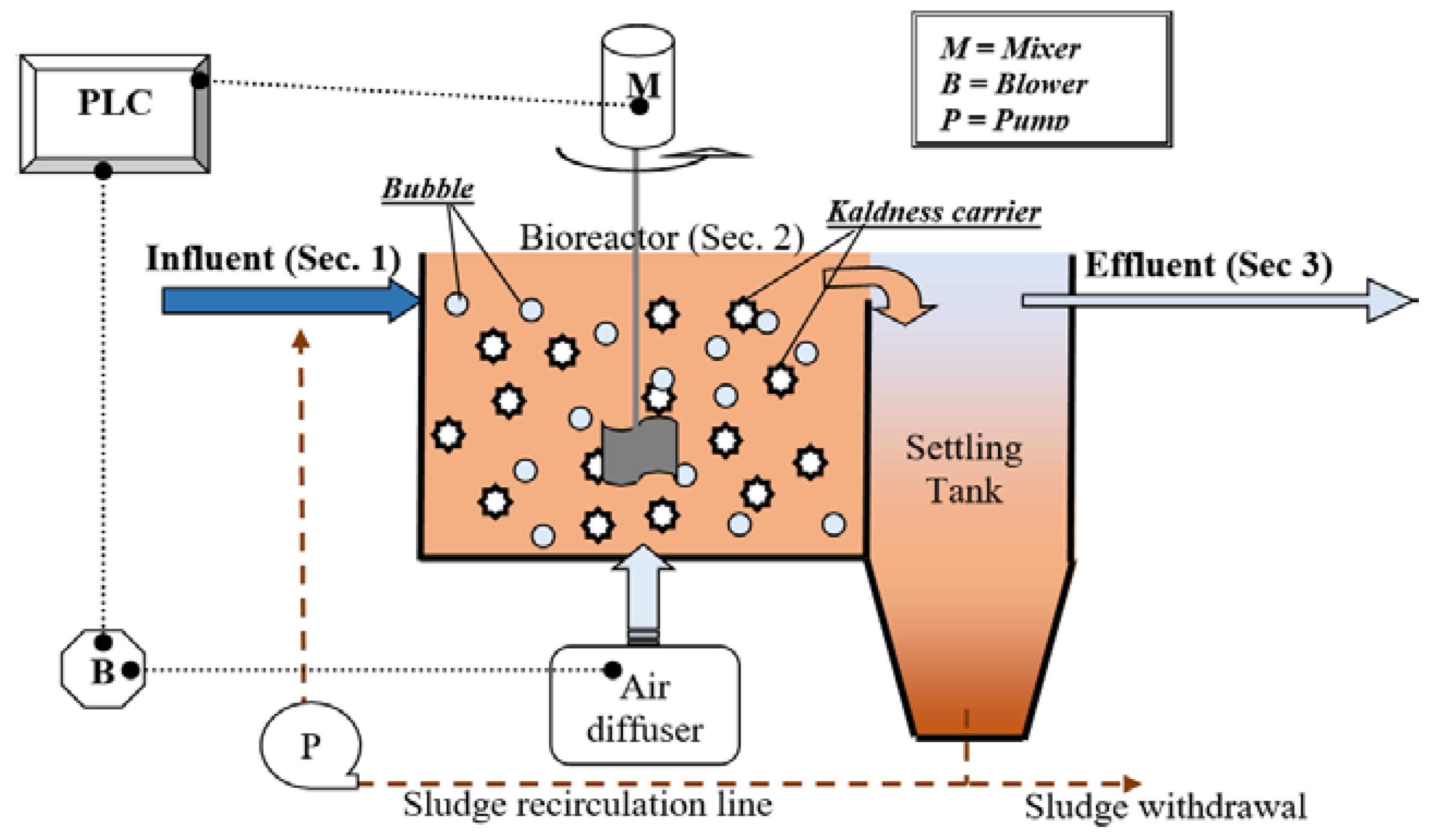
2.1. The Pilot Plant
- In the Phase III, the periods called “Period 2A” and “Period 2B” were characterized by an OLR of 1.4 and 2.2 kgCOD m-3 day−1, respectively;
- In the Phase IV, the periods called “Period 3A” and “Period 3B” were characterized by an OLR of 2.2 and 3.6 kgCOD m-3 day−1, respectively.
2.2. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
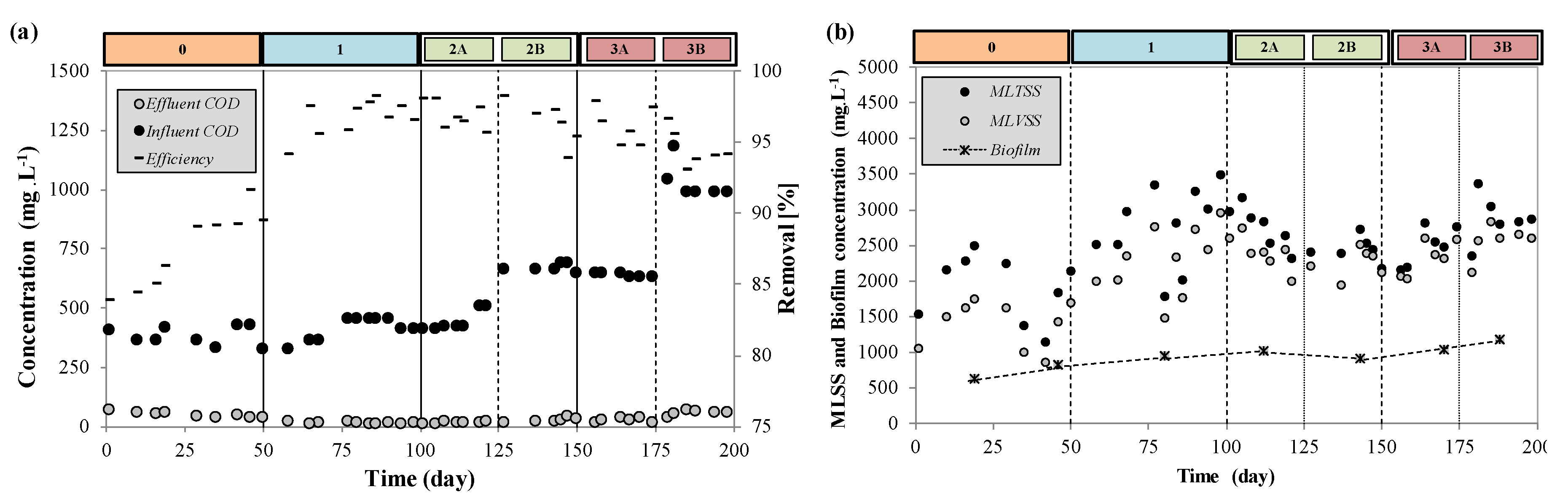
3.1. COD Removal and Biomass Growth
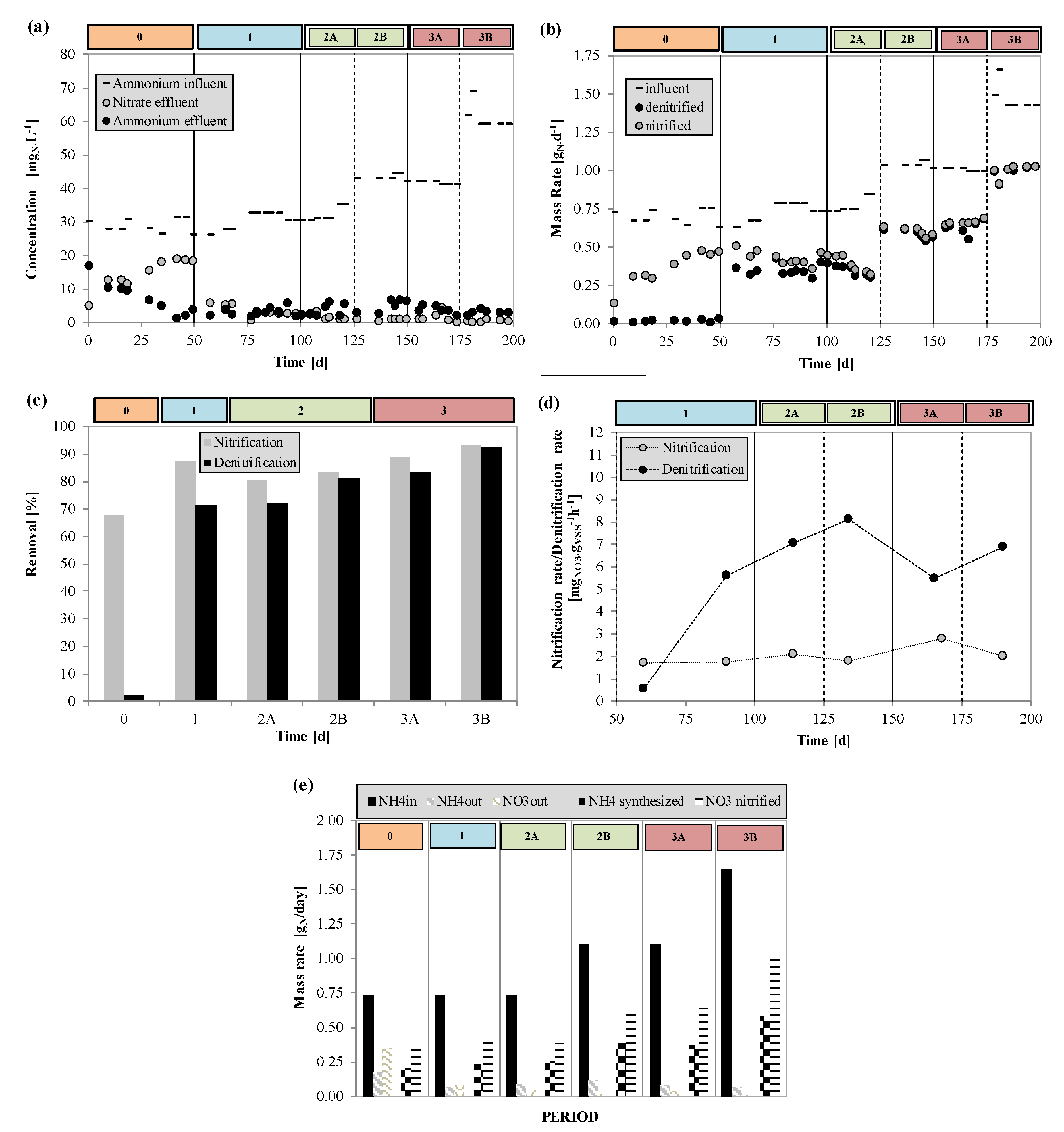
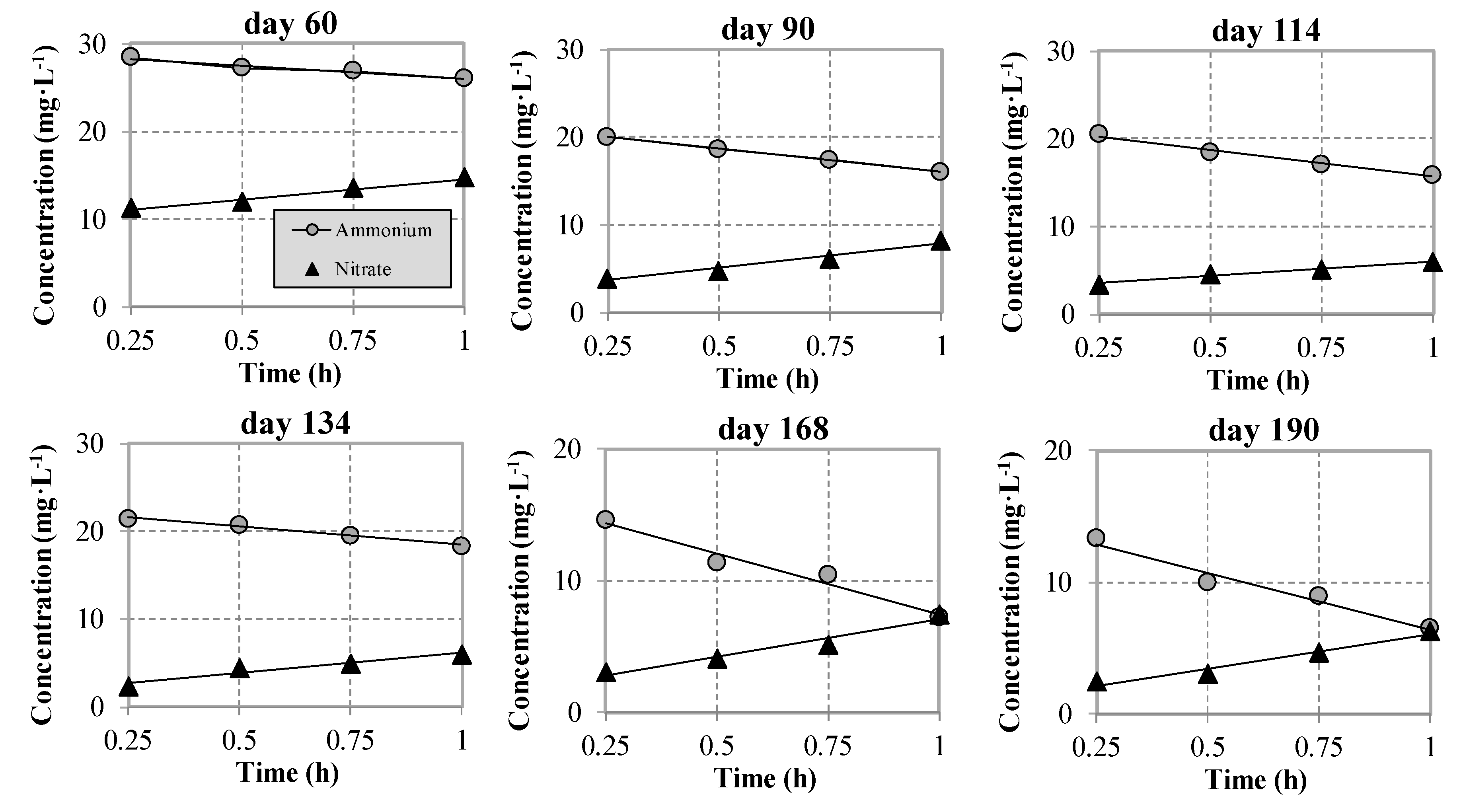
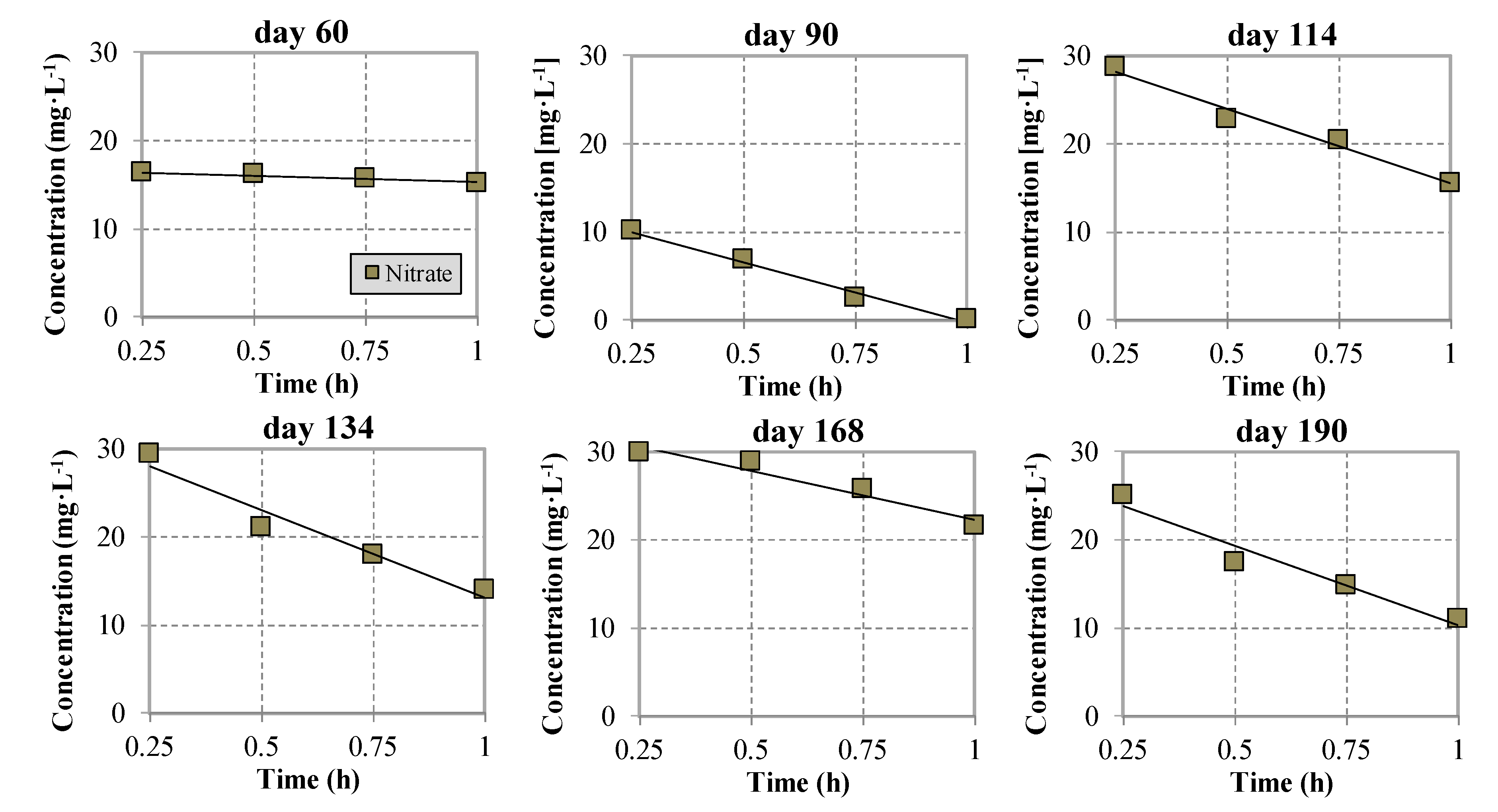
3.2. Nitrification and Denitrification Phenomena
- Nitrified nitrogen increased over time (from Period 0 to Period 3B), depending on the stabilization of the nitrifying bacteria and the optimization of the operating conditions;
- The nitrogen lost by cell synthesis was in the range 33%–38% approximately;
- In almost all experimental periods, the removal of total nitrogen was attributable to a maximum of 65% to the net nitrification of ammonia nitrogen and to 35% of cell assimilation.
- 1.7 ± 0.5 mgNO3-Nnitrified∙gSS−1∙h−1 and 5.58 ± 0.8 mgNO3-Ndenitrified∙gSS−1∙h−1 in Period 1 (at the end of the period),
- 2.09 ± 0.15 mgNO3-Nnitrified∙gSS−1∙h−1 and 7.05 ± 1.4 mgNO3-Ndenitrified∙gSS−1∙h−1 in Period 2A,
- 1.79 ± 0.21 mgNO3-Nnitrified∙gSS−1∙h−1 and 8.11 ± 1.4 mgNO3-Ndenitrified∙gSS−1∙h−1 in Period 2B,
- 2.78 ± 0.4 mgNO3-Nnitrified∙gSS−1∙h−1 and 5.48 ± 0.2 mgNO3-Ndenitrified∙gSS−1∙h−1 in Period 3A,
- 2.01 ± 0.3 mgNO3-Nnitrified∙gSS−1∙h−1 and 6.88 ± 0.4 mgNO3-Ndenitrified∙gSS−1∙h−1 in Period 3B.
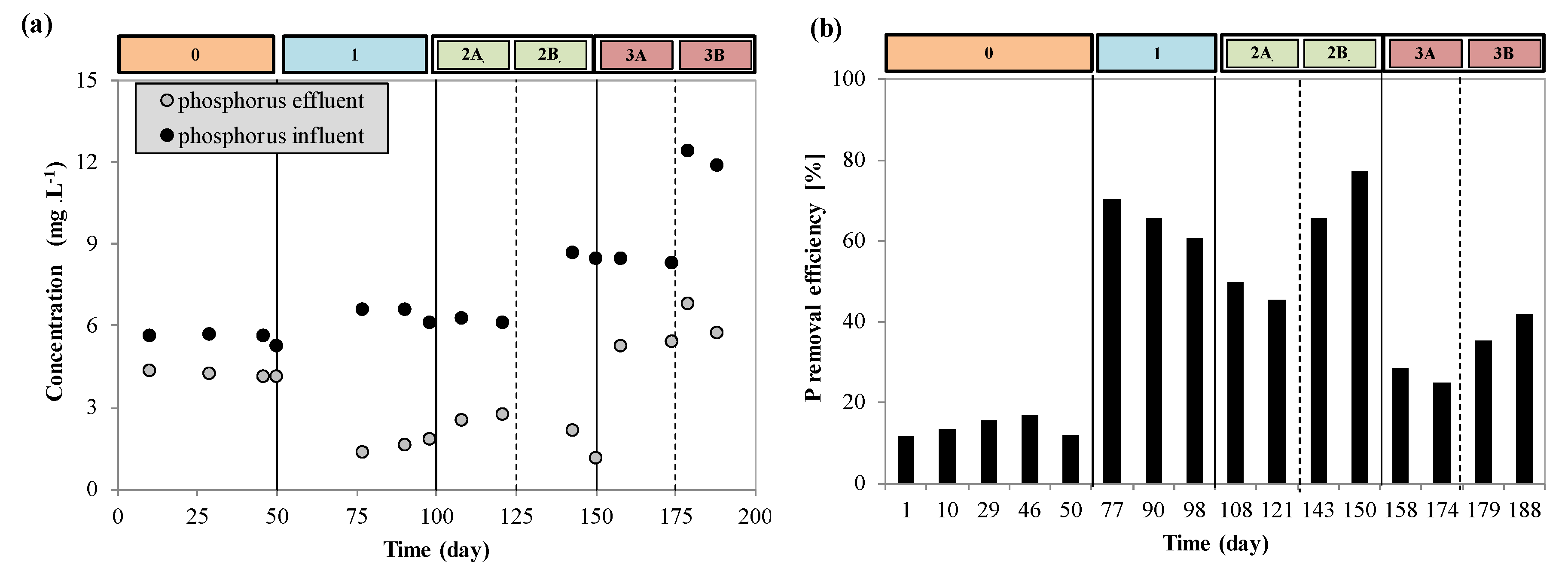
3.3. Phosphorus Removal
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Directive 91/271 of the European Union. EC. Council Directive 91/271/EEC of 21 May 1991 concerning urban waste water treatment. Off. J. 1991, L135, 40–52.
- Wang, J.; Yang, N. Partial nitrification under limited dissolved oxygen conditions. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Di Bella, G.; Torregrossa, M. Simultaneous nitrogen and organic carbon removal in aerobic granular sludge reactors operated with high dissolved oxygen concentration. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carucci, A.; De Mola, M.; Rolle, E.; Smurra, P. A model to control intermittent aeration phases. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanhan, O.; Artan, N.; Orhon, D. Retrofitting activated sludge systems to intermittent aeration for nitrogen removal. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Chang, D.; Son, D.J.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, J.K.; Yeon, H.J.; Yoon, C.Y.; Fan, Y.; Lim, S.Y.; Hong, K.H. Wastewater Treatment in Moving-Bed Biofilm Reactor operated by Flow Reversal Intermittent Aeration System. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 60, 581–584. [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka, T.; Yamada, H.; Kawamura, M.; Tsuno, H. Effect of dissolved oxygen conditions on nitrogen removal in continuously fed intermittent-aeration process with two tanks. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mannina, G.; Di Trapani, D.; Viviani, G.; Ødegaard, H. Modelling and dynamic simulation of hybrid moving bed biofilm reactors: Model concepts and application to a pilot plant. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 56, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Viviani, G. Hybrid moving bed biofilm reactors: An effective solution for upgrading a large wastewater treatment plant. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ødegaard, H.; Rusten, B.; Westrum, T. A new moving bed biofilm reactor-applications and results. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 29, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorelli, G.; Canziani, R.; Pedrazzi, L.; Rozzi, A. Phosphorus and nitrogen removal in Moving-Bed Sequencing Batch Biofilm Reactors. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliekers, A.; Derwort, N.; Gomez, J.L.C.; Strous, M.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M. Completely Autotrophic Nitrogen Removal Over Nitrite in One Single Reactor. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, H.; Koga, K.; Inomae, K.; Kusuda, T.; Awaya, Y. Intermittent aeration for nitrogen removal in small oxidation ditches. Water Sci. Technol. 1990, 22, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodici, M.; Di Bella, G.; Di Trapani, D.; Torregrossa, M. Pilot scale experiment with MBR operated in intermittent aeration condition: Analysis of biological performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, R.; Di Bella, G.; Capodici, M.; Torregrossa, M. The role of EPS in the foaming and fouling for a MBR operated in intermittent aeration conditions. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 118, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luostarinen, S.; Luste, S.; Valentın, L.; Rintala, J. Nitrogen removal from on-site treated anaerobic effluents using intermittently aerated moving bed biofilm reactors at low temperatures. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Di Trapani, D.; Di Bella, G.; Mannina, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Comparison between moving bed-membrane bioreactor (MB-MBR) and membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems: Influence of wastewater salinity variation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 162, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, G.H.; Jørgensen, P.E.; Henze, M. Characterization of Functional Microorganism Groups and Substrate in Activated Sludge and Wastewater by AUR; NUR and OUR. Water Sci. Technol. 1992, 25, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, S.; Shi, W.; Bao, R.; Zhao, Q.; Zuo, X. Comparative performance between intermittently cyclic activated sludge-membrane bioreactor and anoxic/aerobic-membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3877–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrentino, R.; Ferraro, A.; Mattei, M.R.; Esposito, G.; Andreottola, G. Process performance optimization and mathematical modelling of aSBR-MBBR treatment at low oxygen concentration. Process Biochem. 2018, 75, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, B. Nitrification/denitrification in intermittent aeration process for swine wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Eng. 2001, 172, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, A.; Di Bella, G.; Mannina, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Biological Nutrient Removal and Fouling Phenomena in a University of Cape Town Membrane Bioreactor Treating High Nitrogen Loads. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, A.; Di Bella, G.; Mannina, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. The role of EPS in fouling and foaming phenomena for a membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol. 2013, 147, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannina, G.; Capodici, M.; Cosenza, A.; Di Trapani, D.; Ekama, G. The effect of the solids and hydraulic retention time on moving bed membrane bioreactor performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J. Enhanced removal of total nitrogen and total phosphorus by applying intermittent aeration to the Modified Ludzack-Ettinger (MLE) process. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Capodici Cosenza, A.; Di Trapani, D.; Viviani, G. Sequential batch membrane bio-reactor for wastewater treatment: The effect of increased salinity. Bioresour Technol. 2016, 209, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Trapani, D.; Di Bella, G.B.; Mannina, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Effect of C/N shock variation on the performances of a moving bed membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol. 2015, 189, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Phase | Period | Duration | Aeration Condition | Average OLR | Average NLR | Aeration Time (ta) | Anoxic Time (tna) | Cycle Time (tc) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (day) | kgCOD m−3 day−1 | kgN m−3 day−1 | (min) | (min) | (min) | |||
| I | 0 (Day 1–50) | 50 | continuous | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.01 | continuous | - | - |
| II | 1 (Day 51–100) | 50 | intermittent | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.01 | 15 | 15 | 30 |
| III | 2A (Day 101–125) | 25 | intermittent | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.01 | 30 | 30 | 60 |
| 2B (Day 126–150) | 25 | intermittent | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 30 | 30 | 60 | |
| IV | 3A (Day 151–175) | 25 | intermittent | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 40 | 20 | 60 |
| 3B (Day 175–200) | 25 | intermittent | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 40 | 20 | 60 |
| Period | Parameter | Influent | Effluent | Removal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Concentration (mg/L) | Average Concentration (mg/L) | Average (%) | ||
| 0 | COD | 380 ± 26 | 47 ± 12 | 87 ± 4 |
| NH4 | 30 ± 4.5 | 14 ± 4.5 | 67 ± 11 | |
| PTOT | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 4.2 ± 0.1 | 14.3 ± 2 | |
| 1 | COD | 380 ± 35 | 13 ± 5 | 96 ± 2 |
| NH4 | 30 ± 1.5 | 3.5 ± 1.7 | 87 ± 3 | |
| PTOT | 5.5 ± 0.8 | 1.6 ± 0.25 | 65 ± 5 | |
| 2A | COD | 380 ± 54 | 13 ± 4 | 97 ± 1 |
| NH4 | 30 ± 2.5 | 1.7 ± 1.6 | 80 ± 10 | |
| PTOT | 5.5 ± 0.7 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | 47 ± 2 | |
| 2B | COD | 640 ± 31 | 24 ± 18 | 95± 3 |
| NH4 | 45 ± 0.5 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 83 ± 5 | |
| PTOT | 8.5 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 71 ± 6 | |
| 3A | COD | 640 ± 11 | 24 ± 3 | 96± 2 |
| NH4 | 45 ± 3.9 | 1.4 ± 0.6 | 89 ± 1 | |
| PTOT | 8.5 ± 0.1 | 5.3 ± 0.1 | 26 ± 2 | |
| 3B | COD | 1050 ± 70 | 55 ± 13 | 94± 2 |
| NH4 | 61 ± 5 | 0.35 ± 0.15 | 93 ± 2 | |
| PTOT | 12 ± 0.5 | 6.3 ± 0.5 | 38 ± 3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Bella, G.; Mannina, G. Intermittent Aeration in a Hybrid Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor for Carbon and Nutrient Biological Removal. Water 2020, 12, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020492
Di Bella G, Mannina G. Intermittent Aeration in a Hybrid Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor for Carbon and Nutrient Biological Removal. Water. 2020; 12(2):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020492
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Bella, Gaetano, and Giorgio Mannina. 2020. "Intermittent Aeration in a Hybrid Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor for Carbon and Nutrient Biological Removal" Water 12, no. 2: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020492
APA StyleDi Bella, G., & Mannina, G. (2020). Intermittent Aeration in a Hybrid Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor for Carbon and Nutrient Biological Removal. Water, 12(2), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020492






