Eco-Efficiency of End-of-Pipe Systems: An Extended Environmental Cost Efficiency Framework for Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. General Scheme of ECE Indicators
2.2. Extended Framework of ECE Indicators
2.2.1. Characterization of Oxygen-Depleting Potential
2.2.2. Integration of BDO Category with Water Quality Models
2.3. Application of the Extended Framework to a WWTP Case
2.3.1. Case Description
2.3.2. Evaluation of Environmental Impact Potential
2.3.3. Economic Analysis
2.3.4. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Environmental and Economic Assessment
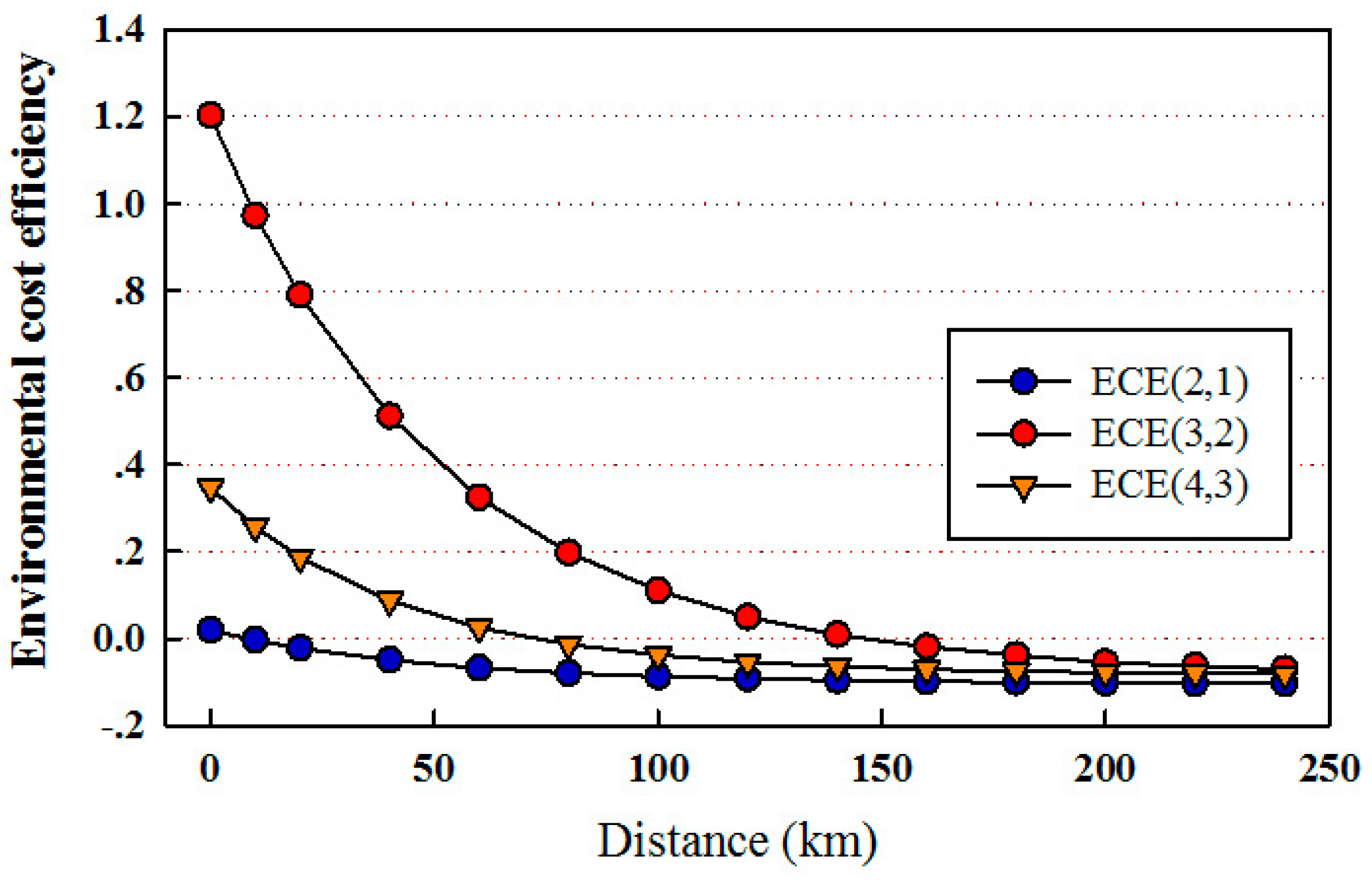
3.2. Eco-Efficiency Analysis Using One-DWQM for the Ashihe River Case
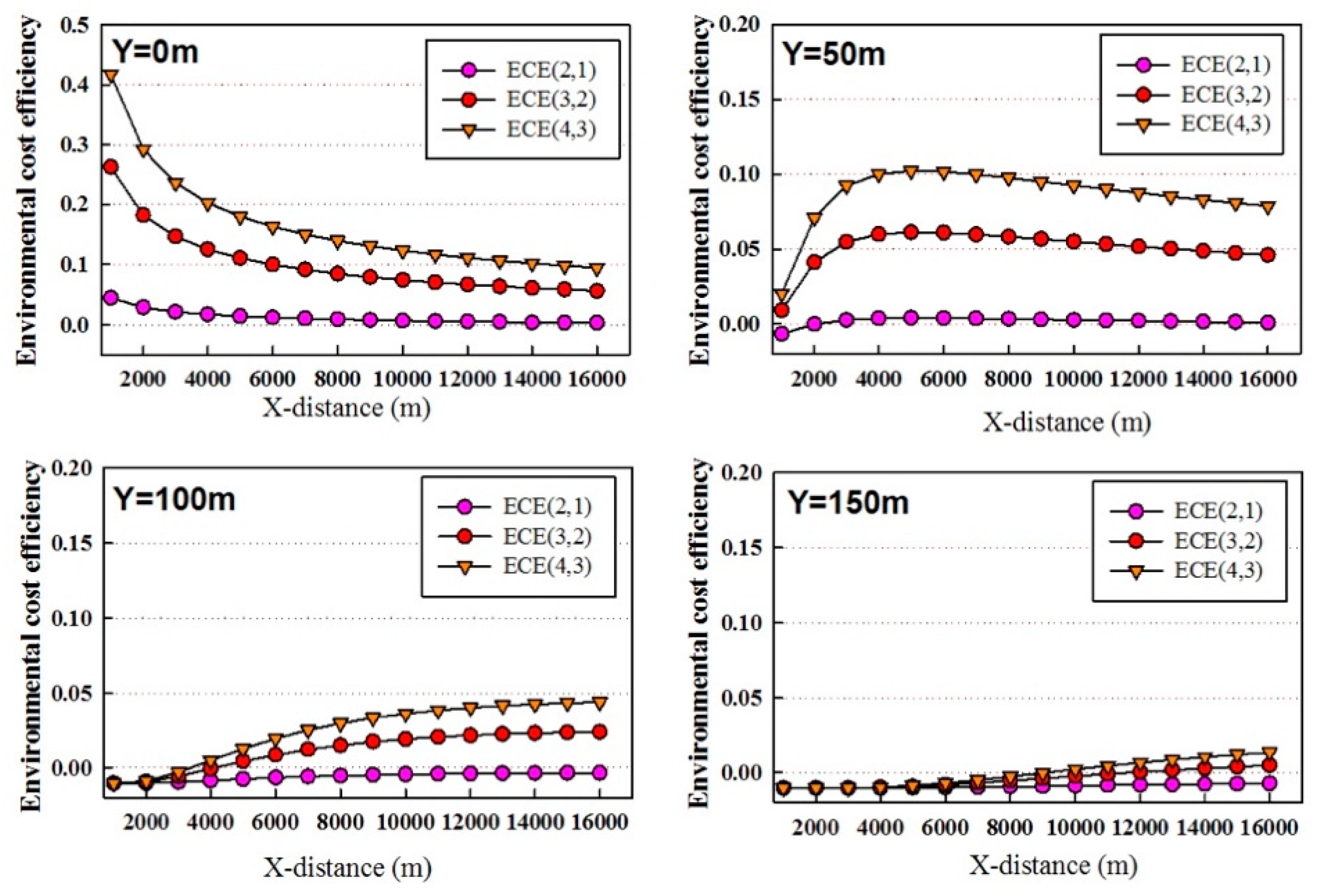
3.3. Eco-Efficiency Analysis Using Two-DWQM for Songhua River Case
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huppes, G.; Ishikawa, M. A framework for quantified eco-Efficiency analysis. J. Ind. Ecol. 2005, 9, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Yu, X.; Feng, C. Evaluating the eco-efficiency of China’s industrial sectors: A two-Stage network data envelopment analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, C.M.; Fujiwara, T.; Ho, C.S. Life cycle assessment and life cycle costing toward eco-Efficiency concrete waste management in Malaysia. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3415–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shonnard, D.R.; Kicherer, A.; Saling, P. Industrial applications using BASF eco-Efficiency analysis: Perspectives on green engineering principles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5340–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohne, R.A.; Brattebø, H.; Bergsdal, H. Dynamic Eco-Efficiency Projections for Construction and Demolition Waste Recycling Strategies at the City Level. J. Ind. Ecol. 2008, 12, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellweg, S.; Doka, G.; Finnveden, G.; Hungerbühler, K. Assessing the Eco-Efficiency of End-of-Pipe Technologies with the Environmental Cost Efficiency Indicator. J. Ind. Ecol. 2005, 9, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingaramo, A.; Heluane, H.; Colombo, M.; Cesca, M. Water and wastewater eco-Efficiency indicators for the sugar cane industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellweg, S.; Mila i Canals, L. Emerging approaches, challenges and opportunities in life cycle assessment. Science 2014, 344, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinee, J.B.; Heijungs, R.; Huppes, G.; Zamagni, A.; Masoni, P.; Buonamici, R.; Ekvall, T.; Rydberg, T. Life cycle assessment: Past, present, and future. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.; Evans, D. Use of life cycle assessment in environmental management. Environ. Manag. 2002, 29, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Ren, N. Engaging multiple weighting approaches and Conjoint Analysis to extend results acceptance of life cycle assessment in biological wastewater treatment technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Bai, S.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Ma, F. Bioaugmentation of atrazine removal in constructed wetland: Performance, microbial dynamics, and environmental impacts. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Bai, S.; Zhang, X. Establishing a decision-support system for eco-Design of biological wastewater treatment: A case study of bioaugmented constructed wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Ren, N. HIT. WATER scheme: An integrated LCA-Based decision-Support platform for evaluation of wastewater discharge limits. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corominas, L.; Foley, J.; Guest, J.; Hospido, A.; Larsen, H.; Morera, S.; Shaw, A. Life cycle assessment applied to wastewater treatment: State of the art. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5480–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, W. Towards more accurate life cycle assessment of biological wastewater treatment plants: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 107, 676–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Wang, X.; Huppes, G.; Zhao, X.; Ren, N. Using site-Specific life cycle assessment methodology to evaluate Chinese wastewater treatment scenarios: A comparative study of site-generic and site-Specific methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 144, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Padilla, F.; Margni, M.; Noyola, A.; Guereca-Hernandez, L.; Bulle, C. Assessing wastewater treatment in Latin America and the Caribbean: Enhancing life cycle assessment interpretation by regionalization and impact assessment sensibility. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2140–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basset-Mens, C.; Anibar, L.; Durand, P.; van der Werf, H.M.G. Spatialised fate factors for nitrate in catchments: Modelling approach and implication for LCA results. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, A.; Rodriguez, L.; Hospido, A.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Development of regional characterization factors for aquatic eutrophication. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, L.B.; Henderson, A.D.; van Zelm, R.; Jolliet, O.; Huijbregts, M.A.J. Assessing the Importance of Spatial Variability versus Model Choices in Life Cycle Impact Assessment: The Case of Freshwater Eutrophication in Europe. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13565–13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmes, R.J.K.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Henderson, A.D.; Jolliet, O. Spatially explicit fate factors of phosphorous emissions to freshwater at the global scale. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2012, 17, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struijs, J.; Beusen, A.; de Zwart, D.; Huijbregts, M. Characterization factors for inland water eutrophication at the damage level in life cycle impact assessment. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2011, 16, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Ren, N. Characterizing water pollution potential in life cycle impact assessment based on bacterial growth and water quality models. Water 2018, 10, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, S.O.; Almeida, C.; Calderón, M.; Mallea, M.; González, P. Assessment of the water self-Purification capacity on a river affected by organic pollution: Application of chemometrics in spatial and temporal variations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2014, 21, 10583–10593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagnetti, R.; Miana, P.; Fabris, M.; Pavoni, B. Self-Purification ability of a resurgence stream. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1781–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnoor, J.L. Environmental Modeling: Fate and Transport of Pollutants in Water, Air, and Soil; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ostroumov, S. On some issues of maintaining water quality and self-Purification. Water Resour. 2005, 32, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinée, J.B. Handbook on life cycle assessment operational guide to the ISO standards. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2001, 7, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmann, B.E.; McCarty, P.L. Environmental Biotechnology: Principles and Applications; Tata McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lap, B.Q.; Mori, K.; Inoue, E. A one-Dimensional model for water quality simulation in medium- and small-Sized rivers. Paddy Water Environ. 2007, 5, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, P.; Marsili-Libelli, S.; Pacini, G. SWAMP: A two-Dimensional hydrodynamic and quality modeling platform for shallow waters. Numer. Methods Part Differ. Equ. 2002, 18, 663–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleeswijk, A.W.; van Oers, L.F.; Guinee, J.B.; Struijs, J.; Huijbregts, M.A. Normalisation in product life cycle assessment: An LCA of the global and European economic systems in the year 2000. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S. Measuring and explaining eco-Efficiencies of wastewater treatment plants in China: An uncertainty analysis perspective. Water Res. 2017, 112, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcilaso, L.; Gaines, W.; Barkdoll, B. Ecoefficiency Analysis of Existing Industrial Wastewater Treatment: How to Include the External Costs to the Environment. World Environmental and Water Resource Congress. 2006, 867–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, J.; Catarino, J. Sustainable value-An energy efficiency indicator in wastewater treatment plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Toja, Y.; Vã, Z.-R.I.; Chenel, S.; Marã-N-Navarro, D.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Eco-Efficiency analysis of Spanish WWTPs using the LCA + DEA method. Water Res. 2015, 68, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Toja, Y.; Vã, Z.-R.I.; Amores, M.J.; Termes-Rifã, M.; Marã-N-Navarro, D.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Benchmarking wastewater treatment plants under an eco-Efficiency perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renou, S.; Thomas, J.S.; Aoustin, E.; Pons, M.N. Influence of impact assessment methods in wastewater treatment LCA. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Ren, N.; You, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Modeling the oxygen-Depleting potential and spatially differentiated effect of sewage organics in life cycle assessment for wastewater management. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Zhang, C.; Bai, S. Eco-Efficiency of End-of-Pipe Systems: An Extended Environmental Cost Efficiency Framework for Wastewater Treatment. Water 2020, 12, 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020454
Zhao X, Zhang C, Bai S. Eco-Efficiency of End-of-Pipe Systems: An Extended Environmental Cost Efficiency Framework for Wastewater Treatment. Water. 2020; 12(2):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020454
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xinyue, Chaofan Zhang, and Shunwen Bai. 2020. "Eco-Efficiency of End-of-Pipe Systems: An Extended Environmental Cost Efficiency Framework for Wastewater Treatment" Water 12, no. 2: 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020454
APA StyleZhao, X., Zhang, C., & Bai, S. (2020). Eco-Efficiency of End-of-Pipe Systems: An Extended Environmental Cost Efficiency Framework for Wastewater Treatment. Water, 12(2), 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020454






