Unravelling Climate and Anthropogenic Forcings on the Evolution of Surface Water Resources in Southern France
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
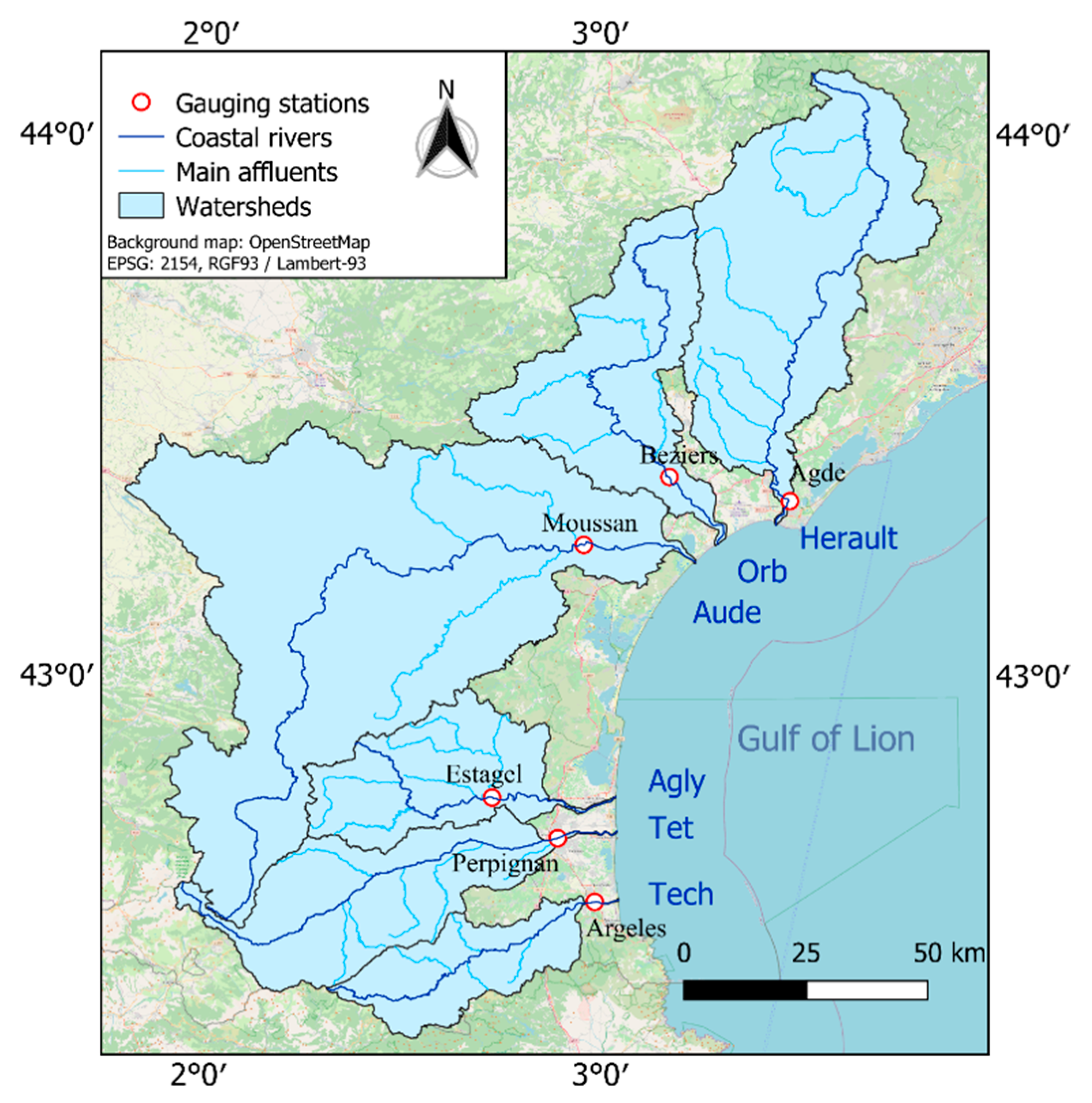
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Climate Data
2.3. Hydrological Data
2.4. Land Use Data and Anthropogenic Water Extractions
2.5. Statistics and Data Treatment
3. Results
3.1. Average Basin Characteristics
3.1.1. Hydro-Climatic Parameters
3.1.2. Water and Land Use
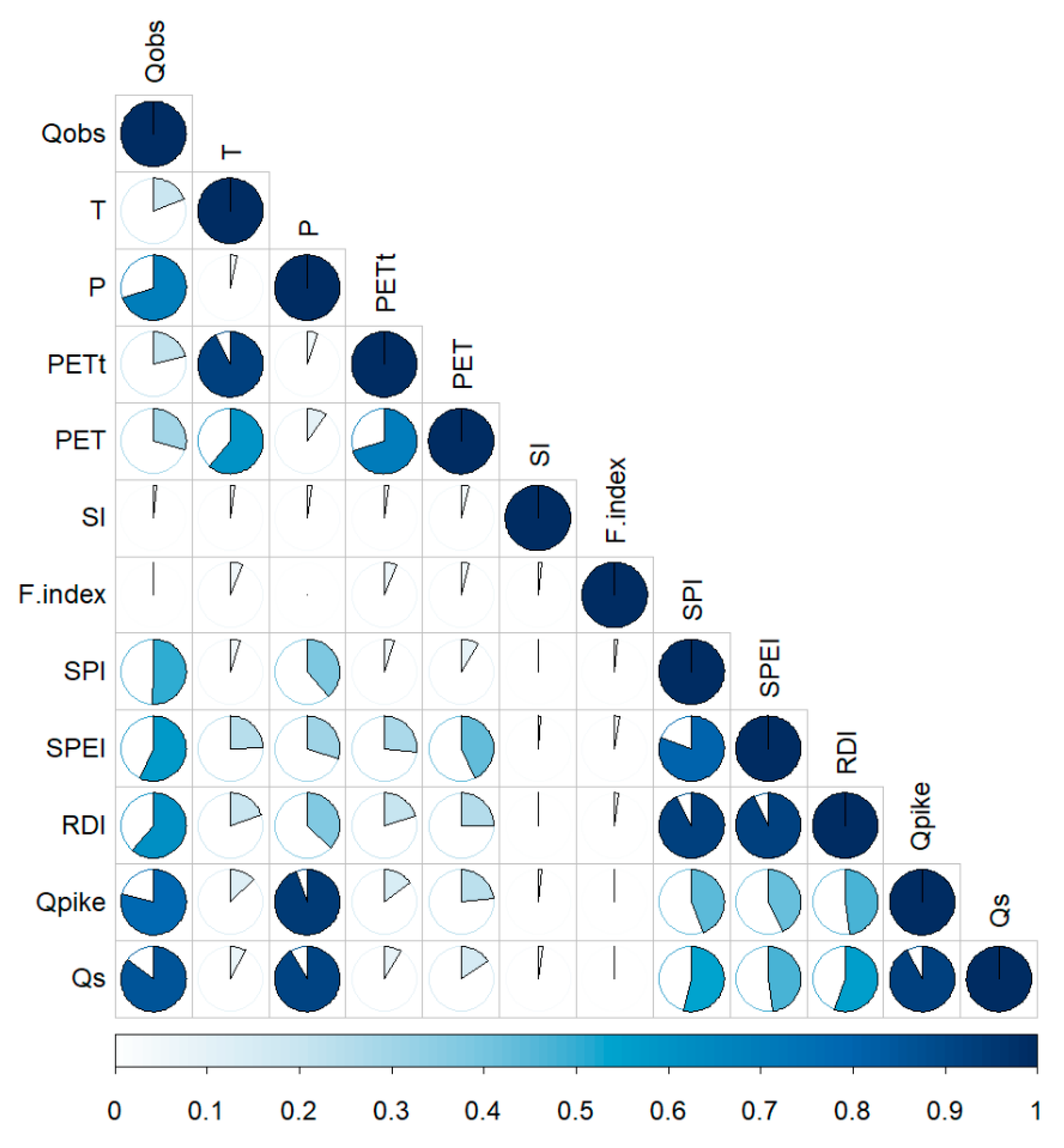
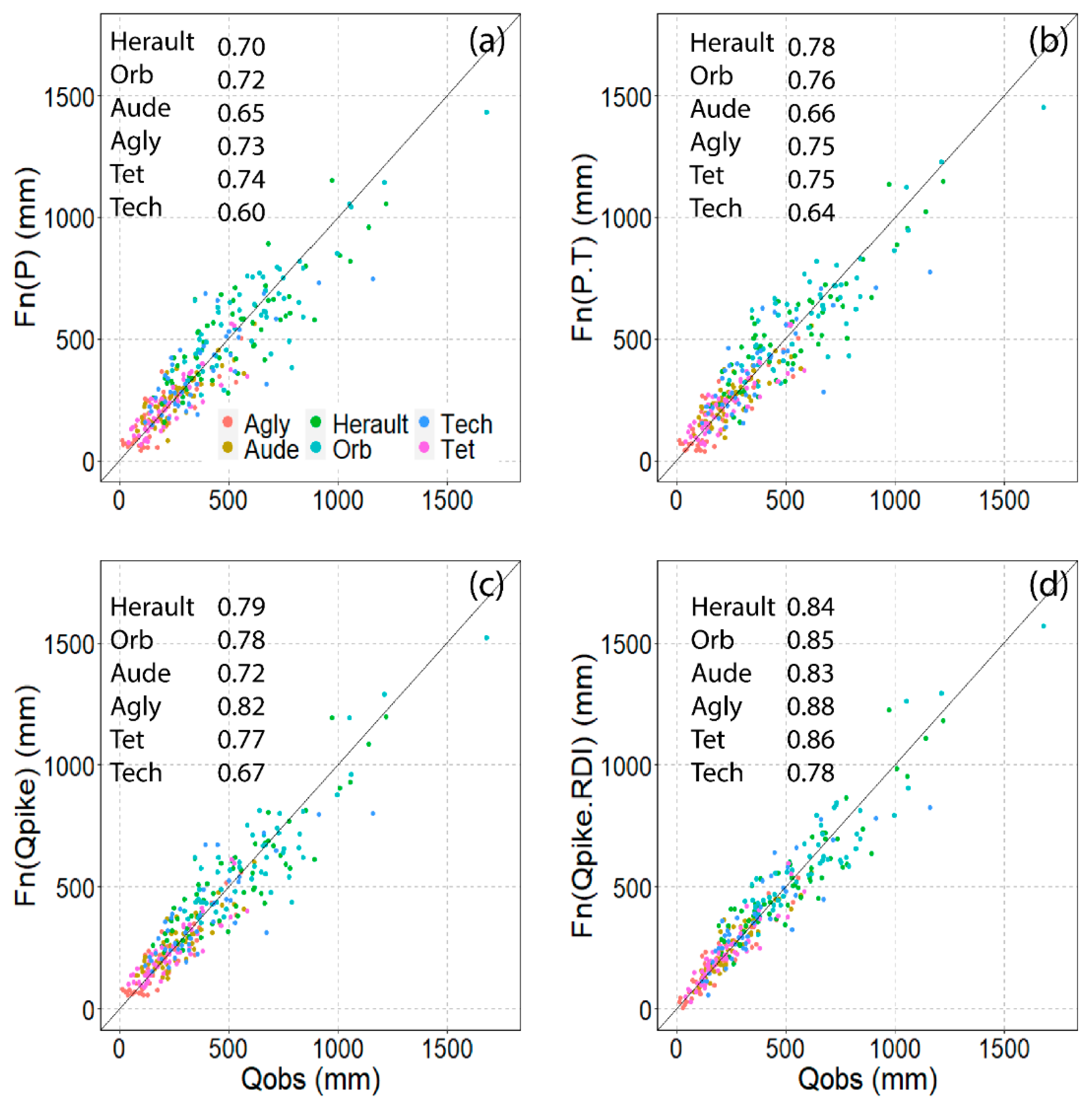
3.1.3. Parameter Relationships and Models
3.1.4. Multiple Parameter Relationships
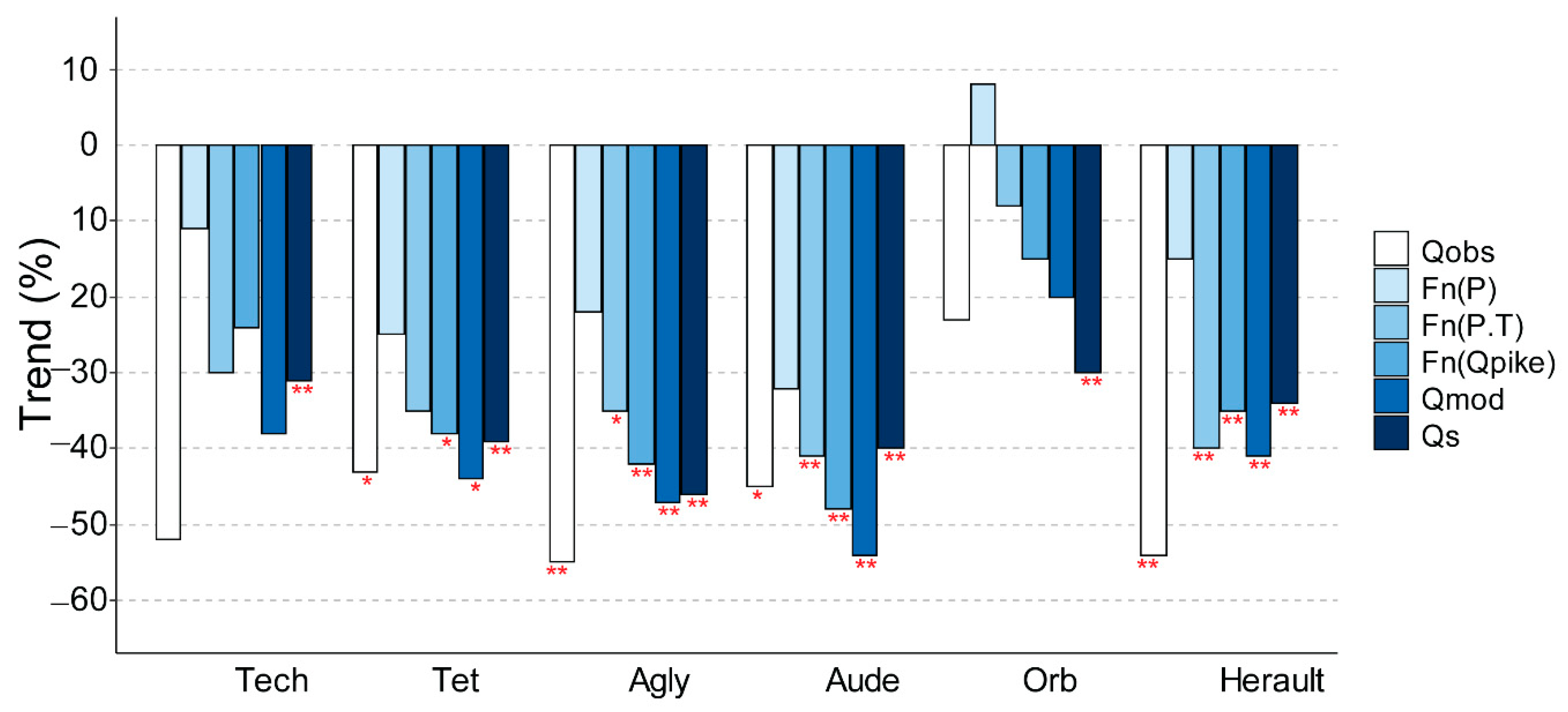
3.2. Trends
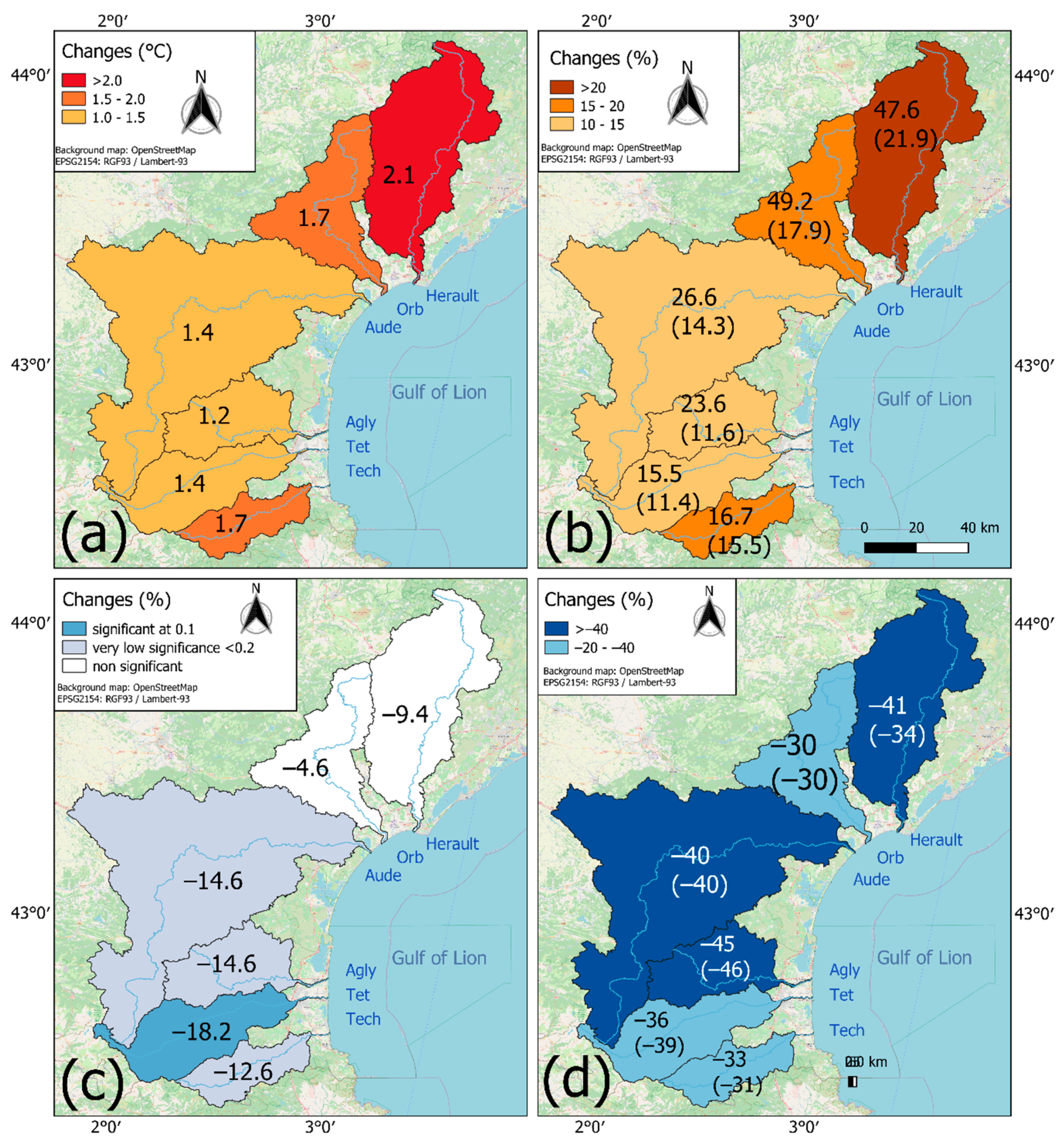
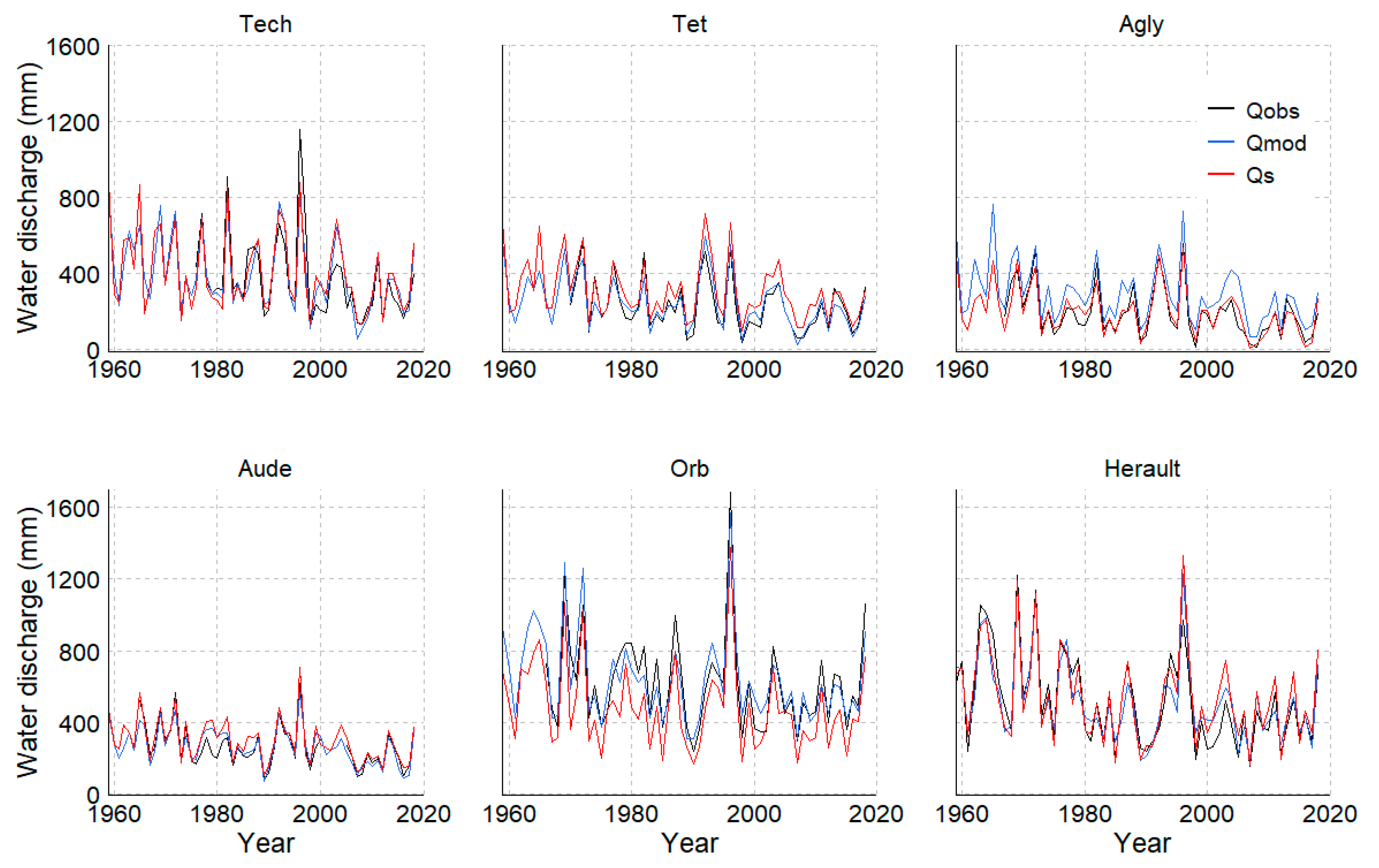
3.2.1. Hydro-Climatic Parameters
3.2.2. Water and Land Use
4. Discussion
4.1. Hydro-Climatic Trends
4.2. Drivers of Water Discharge
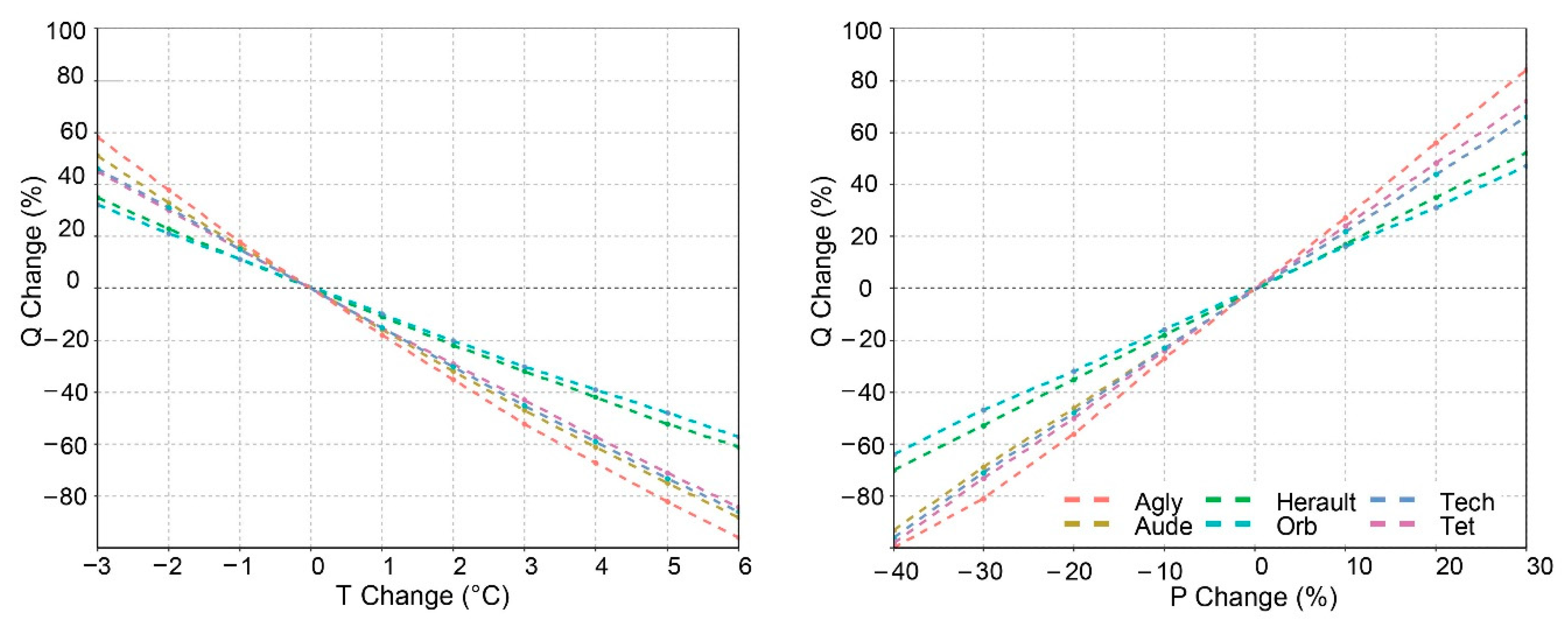
4.3. Model Applications
4.4. Model Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giorgi, F.; Lionello, P. Climate change projections for the Mediterranean region. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 63, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F. Climate change hot-spots. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionello, P.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Boscolo, R. Mediterranean Climate Variability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lionello, P. The Climate of the Mediterranean Region: From the Past to the Future; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lionello, P.; Scarascia, L. The relation between climate change in the Mediterranean region and global warming. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 18, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luterbacher, J.; Xoplaki, E.; Casty, C.; Wanner, H.; Pauling, A.; Küttel, M.; Rutishauser, T.; Brönnimann, S.; Fischer, E.; Fleitmann, D.; et al. Chapter 1 Mediterranean climate variability over the last centuries: A review. Dev. Earth Environ. Sci. 2006, 4, 27–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudennec, C.; LeDuc, C.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Dryland hydrology in Mediterranean regions—A review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2007, 52, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Lasanta–Martínez, T.; Beguería, S. Mediterranean water resources in a global change scenario. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 105, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merheb, M.; Moussa, R.; Abdallah, C.; Colin, F.; Perrin, C.; Baghdadi, N. Hydrological response characteristics of Mediterranean catchments at different time scales: A meta-analysis. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 2520–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masseroni, D.; Camici, S.; Cislaghi, A.; Vacchiano, G.; Massari, C.; Brocca, L. 65-year changes of annual streamflow volumes across Europe with a focus on the Mediterranean basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, W.; Serrat, P.; Cesmat, L.; Garcia-Esteves, J. Evaluating the impact of the recent temperature increase on the hydrology of the Têt River (Southern France). J. Hydrol. 2004, 289, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lespinas, F.; Ludwig, W.; Heussner, S. Impact of recent climate change on the hydrology of coastal Mediterranean rivers in Southern France. Clim. Chang. 2010, 99, 425–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Tejeda, E.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Barbancho, A.C.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M. River regimes and recent hydrological changes in the Duero basin (Spain). J. Hydrol. 2011, 404, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Hall, J.; Viglione, A.; Perdigão, R.A.P.; Parajka, J.; Merz, B.; Lun, D.; Arheimer, B.; Aronica, G.T.; Bilibashi, A.; et al. Changing climate both increases and decreases European river floods. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 573, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lespinas, F.; Ludwig, W.; Heussner, S. Hydrological and climatic uncertainties associated with modeling the impact of climate change on water resources of small Mediterranean coastal rivers. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 403–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirel, G.; Andréassian, V.; Perrin, C. On the need to test hydrological models under changing conditions. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insee—Statistiques Locales—Indicateurs: Cartes, Données et Graphiques. Available online: https://statistiques-locales.insee.fr/#c=indicator&i=pop_legales.popmun_&s=2017&view=map2 (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Durand, Y.; Giraud, G.; Brun, E.; Mérindol, L.; Martin, E. A computer-based system simulating snowpack structures as a tool for regional avalanche forecasting. J. Glaciol. 1999, 45, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durand, Y.; Brun, E.; Merindol, L.; Guyomarc’h, G.; Lesaffre, B.; Martin, E. A meteorological estimation of relevant parameters for snow models. Ann. Glaciol. 1993, 18, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintana-Seguí, P.; Le Moigne, P.; Durand, Y.; Martin, E.; Habets, F.; Baillon, M.; Canellas, C.; Franchistéguy, L.; Morel, S. Analysis of Near-Surface Atmospheric Variables: Validation of the SAFRAN Analysis over France. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2008, 47, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartridge Database. Vinyl Engine. Available online: https://www.vinylengine.com/cartridge_database.php (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Vidal, J.; Martin, E.; Franchistéguy, L.; Baillon, M.; Soubeyroux, J.M. A 50-year high-resolution atmospheric reanalysis over France with the Safran system. Int. J. Clim. 2010, 30, 1627–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fournier, F. Climat et Érosion; Presses Universitaires de France: Paris, France, 1960; p. 201. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, R.P.D.; Lawler, D.M. Rainfall seasonality: Description, spatial patterns and change through time. Weather 1981, 36, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the Eighth Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsakiris, G.; Pangalou, D.; Vangelis, H. Regional Drought Assessment Based on the Reconnaissance Drought Index (RDI). Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapter 2—FAO Penman-Monteith Equation. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/X0490E/x0490e06.htm (accessed on 30 July 2020).
- Venkataraman, K.; Nelson, M.; Frandsen, C. Comparison of Two Temperature-Based Methods of Estimating Potential Evapotranspiration (PET) in Texas. World Environ. Water Resour. Congr. 2016 2016, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudin, L.; Hervieu, F.; Michel, C.; Perrin, C.; Andréassian, V.; Anctil, F.; Loumagne, C. Which potential evapotranspiration input for a lumped rainfall–runoff model?: Part 2—Towards a simple and efficient potential evapotranspiration model for rainfall–runoff modelling. J. Hydrol. 2005, 303, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folton, N.; Lavabre, J. Approche par modélisation PLUIE-DEBIT pour la connaissance régionale de la ressource en eau: Application à la moitié du territoire français. Houille Blanche 2007, 3, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydroweb. Available online: http://www.hydro.eaufrance.fr/ (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Quintana-Seguí, P.; Ribes, A.; Martin, E.; Habets, F.; Boé, J. Comparison of three downscaling methods in simulating the impact of climate change on the hydrology of Mediterranean basins. J. Hydrol. 2010, 383, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintana Seguí, P.; Martin, E.; Habets, F.; Noilhan, J. Improvement, calibration and validation of a distributed hydrological model over France. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaoui, M.; Ludwig, W.; Bourrin, F.; Romero, E. The impact of reservoir construction on riverine sediment and carbon fluxes to the Mediterranean Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 163, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, W.; Dumont, E.; Meybeck, M.; Heussner, S. River discharges of water and nutrients to the Mediterranean and Black Sea: Major drivers for ecosystem changes during past and future decades? Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 80, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Land Monitoring Service. Corine Land Cover (CLC). Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover (accessed on 31 July 2020).
- Acces-Donnees|BNPE. Available online: https://bnpe.eaufrance.fr/acces-donnees (accessed on 21 October 2020).
- Chiffres et Analyses|Agreste, la Statistique Agricole. Available online: https://agreste.agriculture.gouv.fr/agreste-web/disaron/irrigation/5b74baf2-991c-41ae-a920-02217b25d182/search/ (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- The Climate Data Guide. NDVI: Normalized Difference Vegetation Index-3rd Generation: NASA/GFSC GIMMS; National Center for Atmospheric Research Staff, 2018; Available online: https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/ndvi-normalized-difference-vegetation-index-3rd-generation-nasagfsc-gimms (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank correlation methods. Econometrica 1948, 25, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z. Detecting Trend and Other Changes in Hydrological Data; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fathian, F.; Dehghan, Z.; Bazrkar, M.H.; Eslamian, S. Trends in hydrological and climatic variables affected by four variations of the Mann-Kendall approach in Urmia Lake basin, Iran. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 892–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, R.; Kuriqi, A.; Abubaker, S.; Kisi, O. Long-Term Trends and Seasonality Detection of the Observed Flow in Yangtze River Using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s Innovative Trend Method. Water 2019, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, E.S. The Test of Significance for the Correlation Coefficient. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1931, 26, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Esteves, J.; Ludwig, W.; Kerhervé, P.; Probst, J.-L.; Lespinas, F. Predicting the impact of land use on the major element and nutrient fluxes in coastal Mediterranean rivers: The case of the Têt River (Southern France). Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 230–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruf, T. Droits d’eau et institutions communautaires dans les Pyrénées-Orientales. Hist. Soc. Rural. 2001, 16, 11–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AR5 Synthesis Report: Climate Change 2014—IPCC. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/syr/ (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- Occitanie, D. DONNÉES. Available online: https://draaf.occitanie.agriculture.gouv.fr/DONNEES (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Spadoni, G.L.; Cavalli, A.; Congedo, L.; Munafò, M. Analysis of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) multi-temporal series for the production of forest cartography. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 20, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townshend, J.R.G.; Justice, C. Analysis of the dynamics of African vegetation using the normalized difference vegetation index. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorchani, M.; Nadal-Romero, E.; Tague, C.; Lasanta, T.; Zabalza, J.; Lana-Renault, N.; Domínguez-Castro, F.; Choate, J. Effects of active and passive land use management after cropland abandonment on water and vegetation dynamics in the Central Spanish Pyrenees. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juez, C.; Peña-Angulo, D.; Khorchani, M.; Regüés, D.; Nadal-Romero, E. 20-years of hindsight into hydrological dynamics of a mountain forest catchment in the Central Spanish Pyrenees. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 142610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susskind, J.; Schmidt, G.A.; Lee, J.N.; Iredell, L. Recent global warming as confirmed by AIRS. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 044030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piervitali, E.; Colacino, M.; Conte, M. Rainfall over the Central-Western Mediterranean basin in the period 1951-1995. Part I: Precipitation trends. Nuovo Cim. 1998, 21, 331–344. Available online: http://www.sif.it/riviste/ncc/econtents/1998/021/03/article/1 (accessed on 18 October 2020).
- Valdes-Abellan, J.; Pardo, M.; Tenza-Abril, A.J. Observed precipitation trend changes in the western Mediterranean region. Int. J. Clim. 2017, 37, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, E.; Petrangeli, A.B.; Preziosi, E. Spatial and Time Analysis of Rainfall in the Tiber River Basin (Central Italy) in relation to Discharge Measurements (1920–2010). Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Serrano, S.M.V.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Morán-Tejeda, E.; Zabalza, J. Recent trends in Iberian streamflows (1945–2005). J. Hydrol. 2012, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Moreno, J.I.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M. Atmospheric circulation influence on the interannual variability of snow pack in the Spanish Pyrenees during the second half of the 20th century. Hydrol. Res. 2007, 38, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Fernández, J.; Sánchez, N.; Herrero-Jiménez, C.M. Recent trends in rivers with near-natural flow regime. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2013, 37, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lespinas, F. Impacts du Changement Climatique sur L’hydrologie des Fleuves Côtiers en Region Languedoc-Roussillon. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Perpignan, Perpignan, France, 2008. Available online: https://www.theses.fr/2008PERP1261 (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Creed, I.F.; Hwang, T.; Lutz, B.; Way, D. Climate warming causes intensification of the hydrological cycle, resulting in changes to the vernal and autumnal windows in a northern temperate forest. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3519–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, W.; Bouwman, A.F.; Dumont, E.; Lespinas, F. Water and nutrient fluxes from major Mediterranean and Black Sea rivers: Past and future trends and their implications for the basin-scale budgets. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Ragab, R. Assessment of the potential impacts of climate change on the hydrology at catchment scale: Modelling approach including prediction of future drought events using drought indices. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; Darehshouri, S.; Hassanzadeh, E.; Tajrishy, M.; Schüth, C. Climate change or irrigated agriculture—What drives the water level decline of Lake Urmia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Stahl, K.; Clark, D.B.; Dumont, E.; Hagemann, S.; Bertrand, N.; Gerten, D.; Heinke, J.; Hanasaki, N.; et al. Comparing Large-Scale Hydrological Model Simulations to Observed Runoff Percentiles in Europe. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 604–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Gavin, H.; Refsgaard, A.; Sørenson, H.R.; Gowing, D.J.G. Modelling the hydrological impacts of climate change on UK lowland wet grassland. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 17, 503–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petelet-Giraud, E.; Luck, J.-M.; Ben Othman, D.; Negrel, P. Dynamic scheme of water circulation in karstic aquifers as constrained by Sr and Pb isotopes. Application to the Hérault watershed, Southern France. Hydrogeol. J. 2003, 11, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Basin | Number of Years | Area Basin (km2) | Mean Elevation (m) | Annual Temperature (°C) | Annual Rainfall (mm) | Snowfall (%) | PET (mm) | Qobs (mm) | Qs (mm) | Qpike (mm) | Agriculture (mm) * | Drinking Water (mm) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herault | 59 | 2550 | 367 | 12.6 | 1103 | 2.4 | 1023 | 518 | 537 | 381 | 23 | 0 |
| Orb | 53 | 1330 | 444 | 12.6 | 1013 | 2.4 | 1003 | 615 | 462 | 324 | 29 | 9 |
| Aude | 50 | 4838 | 462 | 12.2 | 838 | 7.2 | 978 | 263 | 296 | 215 | 29 | 2 |
| Agly | 52 | 903 | 508 | 12.6 | 802 | 5.5 | 1045 | 191 | 277 | 183 | 60 | 1 |
| Tet | 49 | 1300 | 1061 | 10.1 | 802 | 20.7 | 1017 | 228 | 293 | 187 | 186 | 11 |
| Tech | 43 | 729 | 778 | 11.7 | 998 | 9.4 | 1046 | 370 | 386 | 295 | 76 | 2 |
| Basin | Artificial Area | Forest | Agricultural Lands | Herbaceous Vegetation | Other |
| Tech | 3.25 | 60 | 18.5 | 15.8 | 2.5 |
| Tet | 3.05 | 37 | 20 | 33.7 | 6.3 |
| Agly | 1.7 | 34.35 | 27 | 35.4 | 1.6 |
| Aude | 2.75 | 32.5 | 48.5 | 15.4 | 0.9 |
| Orb | 4 | 48.8 | 30.5 | 14.85 | 1.85 |
| Herault | 2.8 | 30.8 | 31.5 | 33.4 | 1.5 |
| (a) | |||||
| Basin | Arable Land | Vineyards | Fruit and Olive Trees | Pastures | Heterogeneous Areas |
| Tech | 1.1 | 37.3 | 8.3 | 6.5 | 46.9 |
| Tet | 0.4 | 31.8 | 24.5 | 6.1 | 37.3 |
| Agly | 0 | 71.2 | 0.1 | 3.9 | 24.8 |
| Aude | 16.2 | 53.4 | 0.2 | 6.2 | 23.5 |
| Orb | 1.2 | 58.9 | 0.4 | 4.4 | 35.1 |
| Herault | 2.5 | 64.8 | 0.3 | 6.3 | 26.2 |
| (b) | |||||
| Basin | Qpike | RDI | Intercept | r2 | n |
| Herault | 0.7183 | 96.9 | 244 | 0.85 | 59 |
| Orb | 0.8531 | 95.5 | 346 | 0.84 | 53 |
| Aude | 0.6041 | 55.1 | 135 | 0.81 | 50 |
| Agly | 0.7829 | 50.4 | 51 | 0.88 | 52 |
| Tet | 0.6930 | 66.1 | 104 | 0.85 | 49 |
| Tech | 0.6847 | 104.0 | 179 | 0.76 | 43 |
| (a) | |||||
| Basin | Qpike | RDI | Intercept | r2 | n |
| Herault | 0.7173 | 95.6 | 243 | 0.84 | 59 |
| Orb | 0.8184 | 109.9 | 356 | 0.85 | 53 |
| Aude | 0.5613 | 63.6 | 143 | 0.83 | 50 |
| Agly | 0.7723 | 54.0 | 53 | 0.88 | 52 |
| Tet | 0.6644 | 72.1 | 111 | 0.86 | 49 |
| Tech | 0.6354 | 121.4 | 198 | 0.78 | 43 |
| (b) | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Labrousse, C.; Ludwig, W.; Pinel, S.; Sadaoui, M.; Lacquement, G. Unravelling Climate and Anthropogenic Forcings on the Evolution of Surface Water Resources in Southern France. Water 2020, 12, 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123581
Labrousse C, Ludwig W, Pinel S, Sadaoui M, Lacquement G. Unravelling Climate and Anthropogenic Forcings on the Evolution of Surface Water Resources in Southern France. Water. 2020; 12(12):3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123581
Chicago/Turabian StyleLabrousse, Camille, Wolfgang Ludwig, Sébastien Pinel, Mahrez Sadaoui, and Guillaume Lacquement. 2020. "Unravelling Climate and Anthropogenic Forcings on the Evolution of Surface Water Resources in Southern France" Water 12, no. 12: 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123581
APA StyleLabrousse, C., Ludwig, W., Pinel, S., Sadaoui, M., & Lacquement, G. (2020). Unravelling Climate and Anthropogenic Forcings on the Evolution of Surface Water Resources in Southern France. Water, 12(12), 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123581





