Comparison of Different Anode Materials to Remove Microcystis aeruginosa Cells Using Electro-Coagulation–Flotation Process at Low Current Inputs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Microcystis aeruginosa Cultures
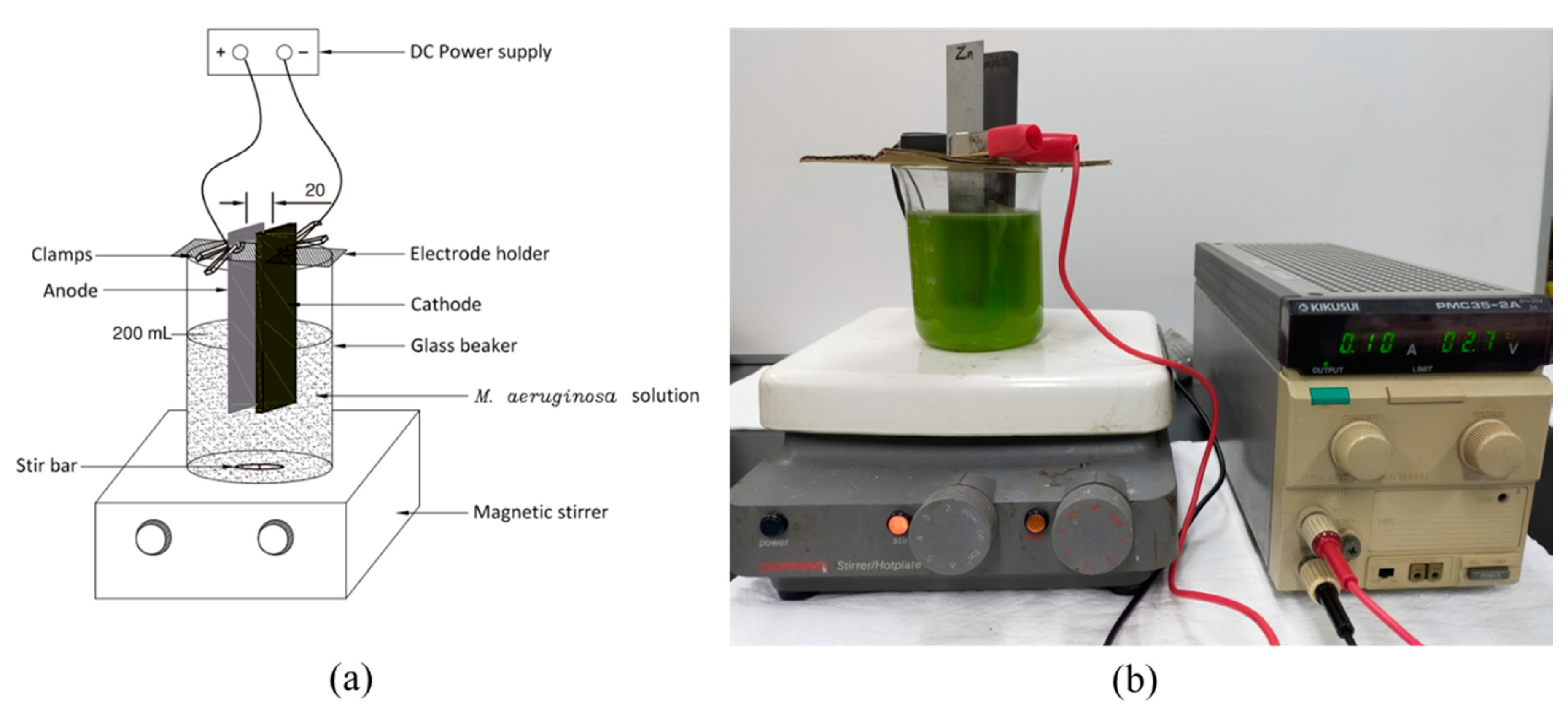
2.2. Experimental Setup and Electrode Materials
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
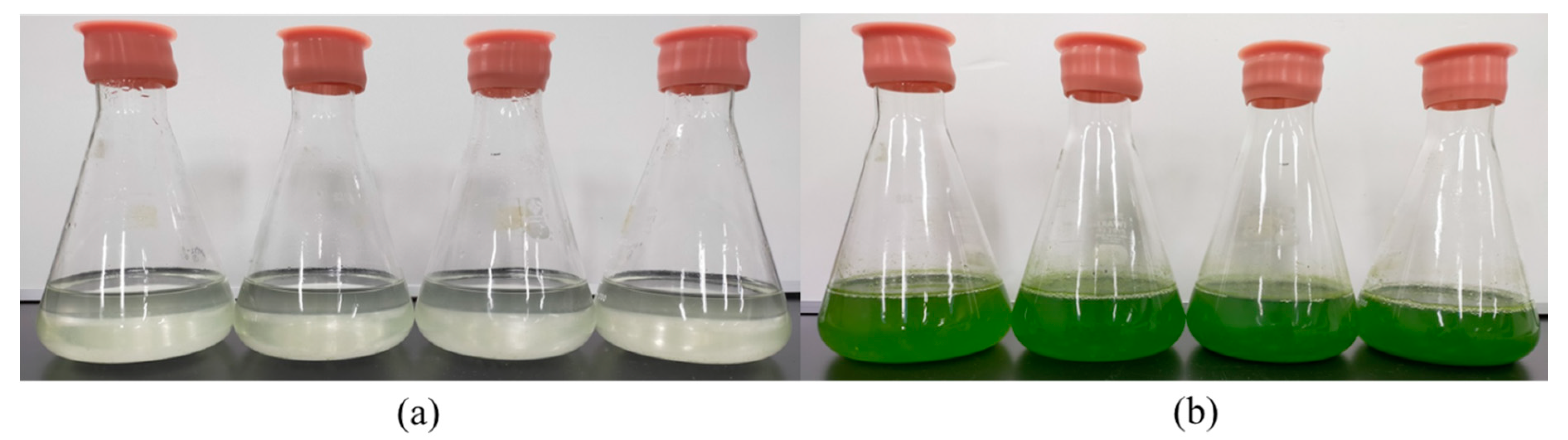
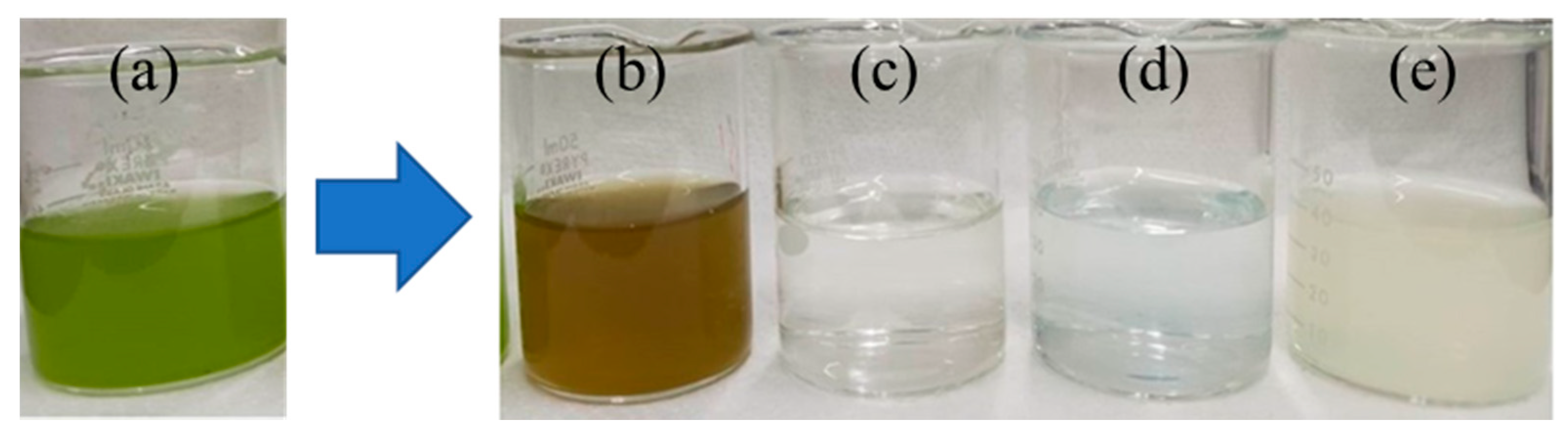
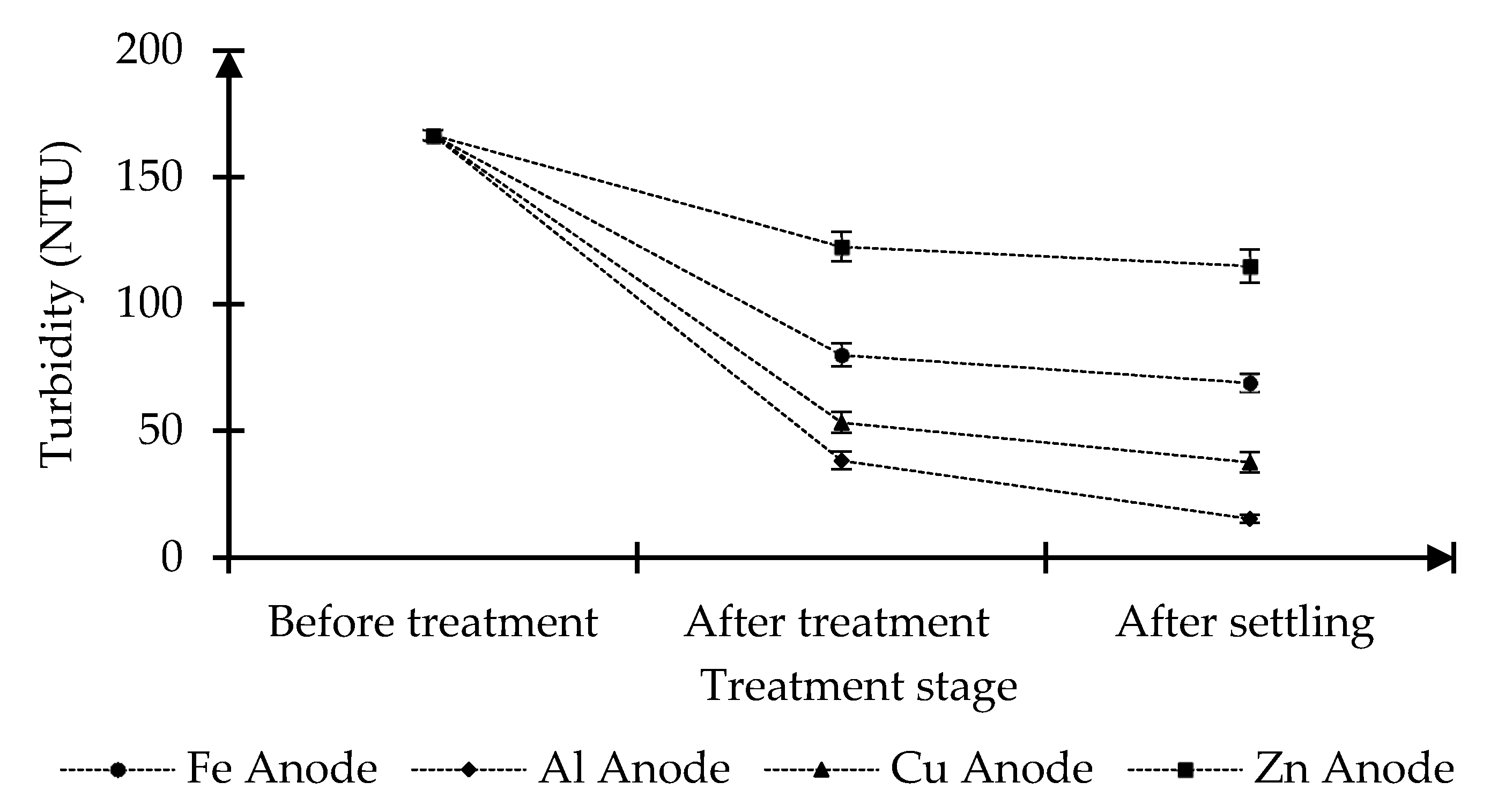
3.1. Comparison of Treated Water Characteristics
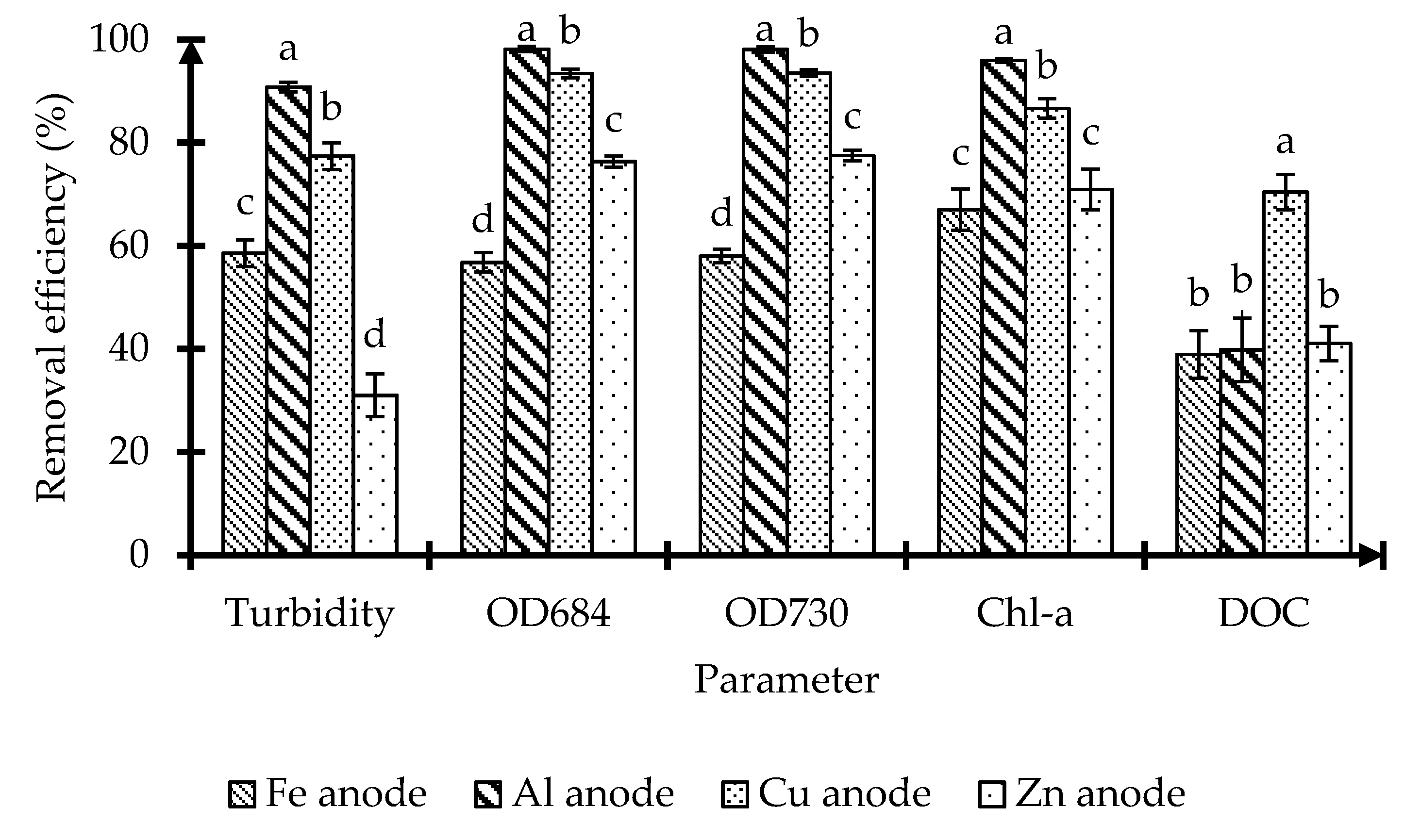
3.2. Comparison of Removal Efficiency with Respect to Turbidity, OD, Chl-a Concentration, and DOC Concentration among Anode Materials
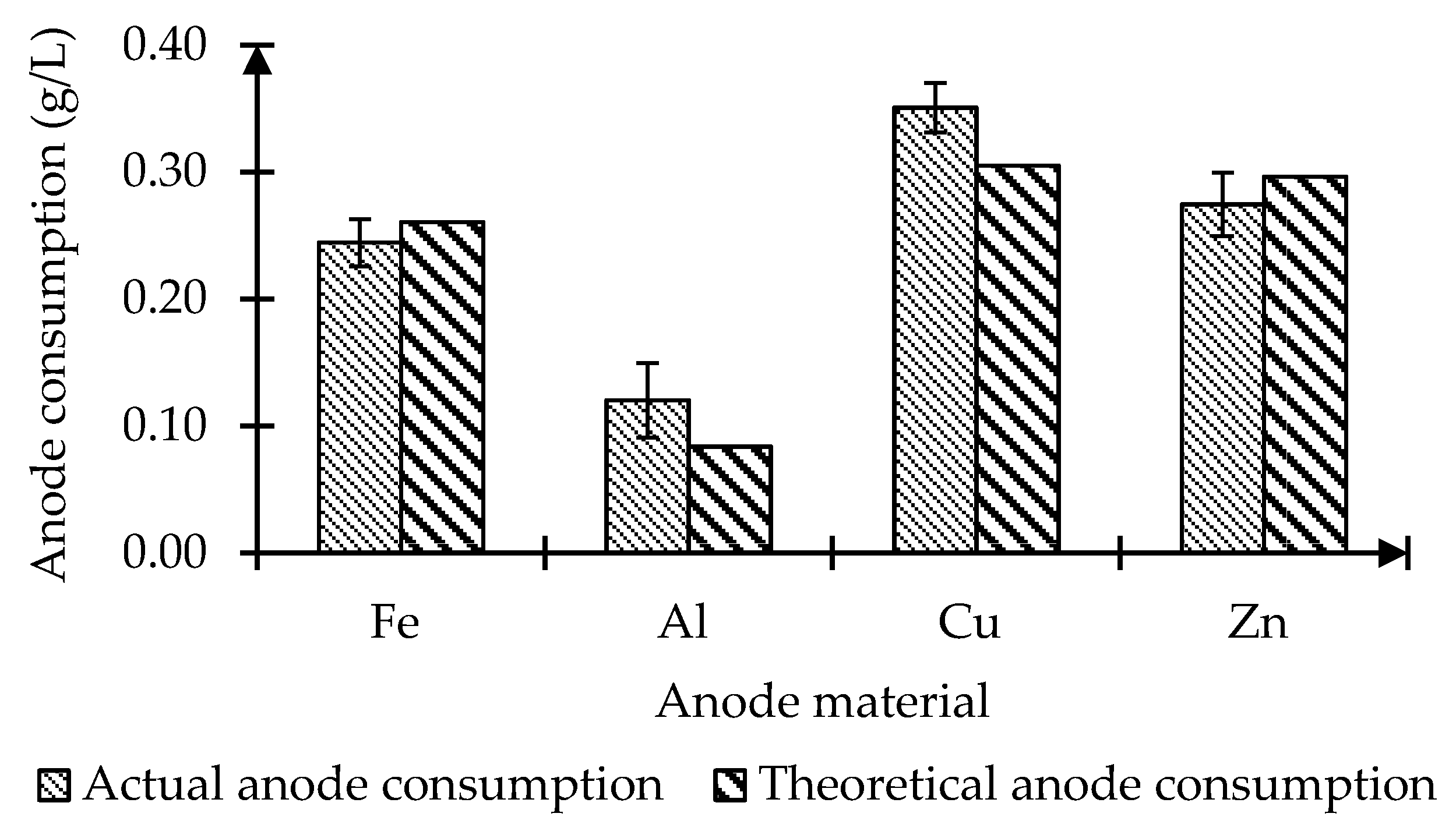
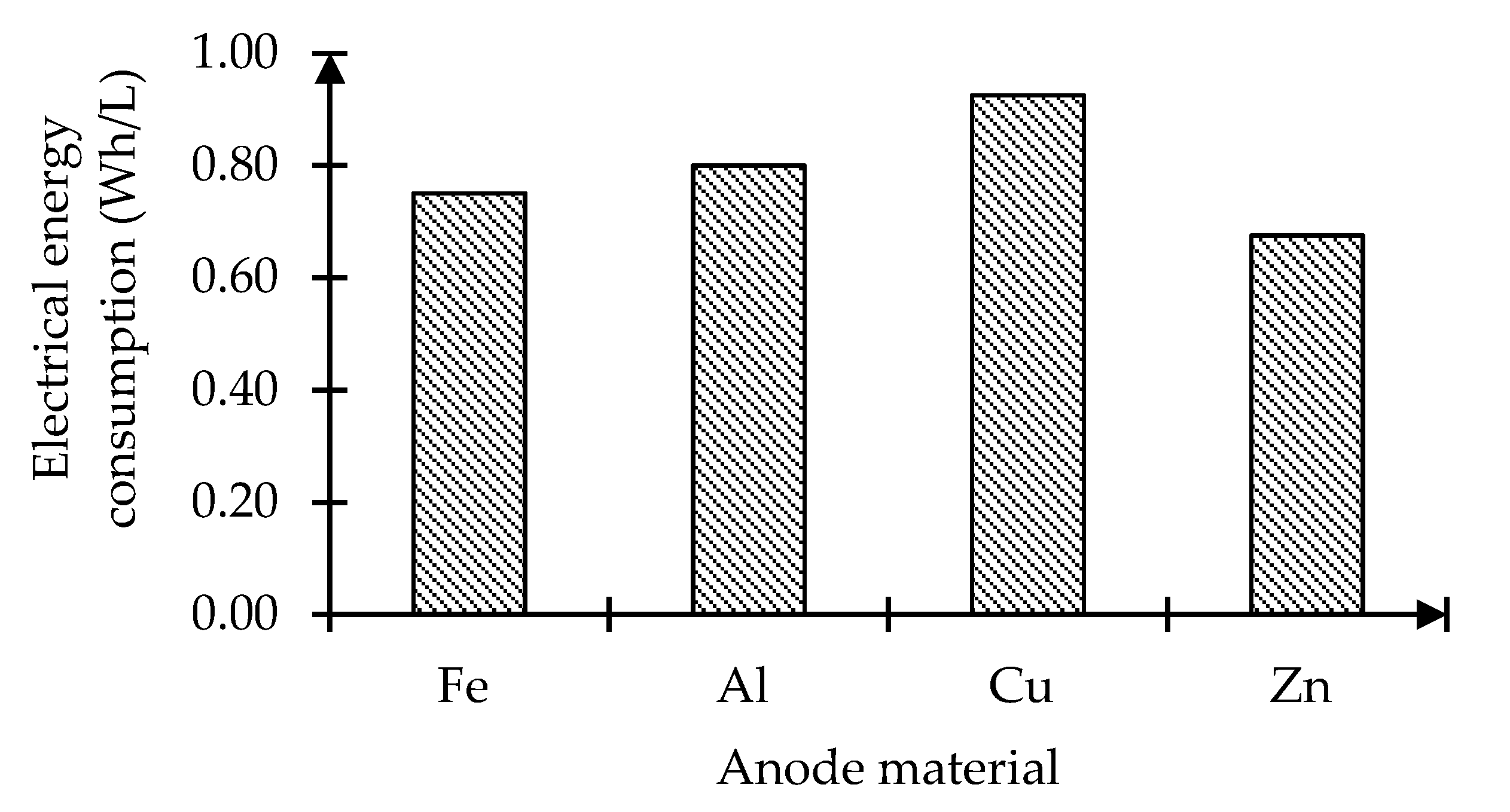
3.3. Comparison of Electrode Consumption and Electrical Energy Consumption among Anode Materials
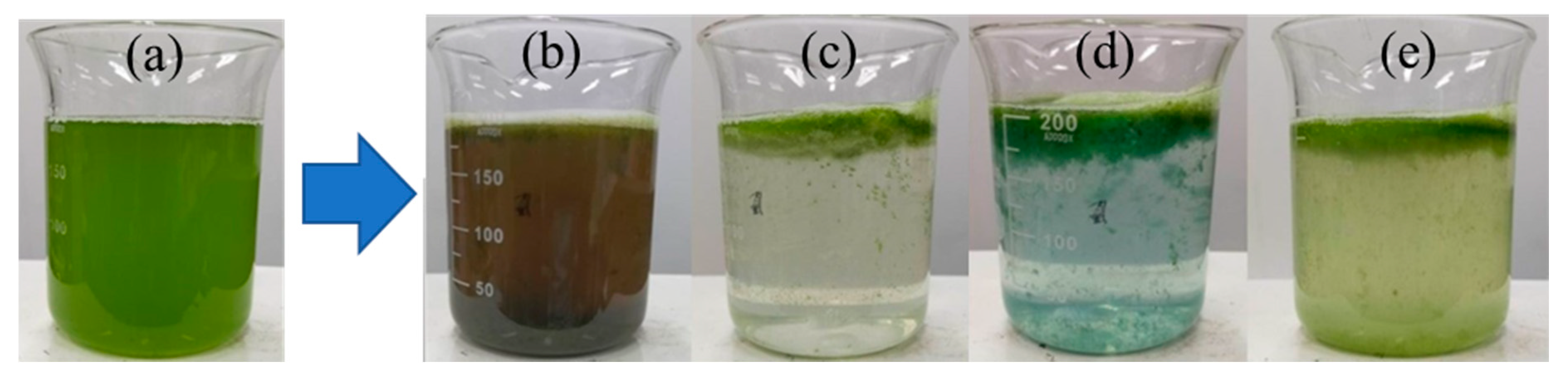
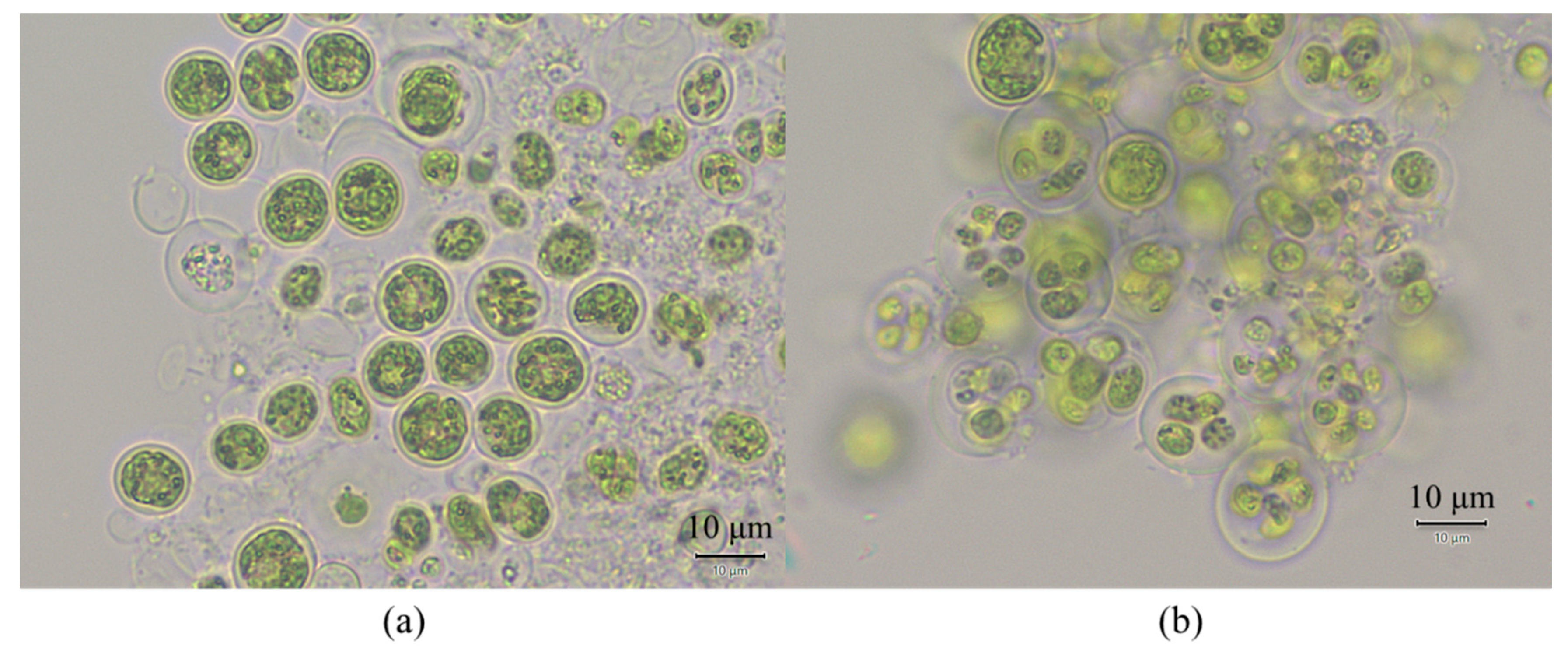
3.4. Appearance of M. aeruginosa Cells before and after ECF Treatment Process
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Environmental Protection Agency. Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins: Information for Drinking Water Systems; United States Environmental Protection Agency EPA-810F11001; Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 1–11.
- Vu, H.P.; Nguyen, L.N.; Zdarta, J.; Nga, T.T.V.; Nghiem, L.D. Blue-Green Algae in Surface Water: Problems and Opportunities. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020, 6, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wert, E.C.; Rosario-Ortiz, F.L. Intracellular Organic Matter from Cyanobacteria as a Precursor for Carbonaceous and Nitrogenous Disinfection Byproducts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6332–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, L.; Roddick, F.A. Influence of the characteristics of soluble algal organic matter released from Microcystis aeruginosa on the fouling of a ceramic microfiltration membrane. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 425–426, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghernaout, D. Electrocoagulation Process for Microalgal Biotechnology—A Review. Djamel Ghernaout Electrocoagul. Process Microalgal Biotechnol. Rev. Appl. Eng. 2019, 3, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coral, L.A.; Zamyadi, A.; Barbeau, B.; Bassetti, F.J.; Lapolli, F.R.; Prévost, M. Oxidation of Microcystis aeruginosa and Anabaena flos-aquae by ozone: Impacts on cell integrity and chlorination by-product formation. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2983–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Yang, X.; Ma, J.; Shang, C.; Zhao, Q. Characterization of algal organic matter and formation of DBPs from chlor(am)ination. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5897–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, R.; Li, J. Current research scenario for microcystins biodegradation—A review on fundamental knowledge, application prospects and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.L.; Utsumi, M. An overview of the accumulation of microcystins in aquatic ecosystems. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Hao, A.; Iseri, Y.; Wang, S.; Kuba, T.; Zhang, Z.; Katayama, H. Occurrence and Distribution of Microcystins in Lake Taihu, China. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Qu, Y.; Li, C.; Han, X.; Ambuchi, J.J.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Feng, Y. Simultaneous algae-polluted water treatment and electricity generation using a biocathode-coupled electrocoagulation cell (bio-ECC). J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 340, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Ou, M.; Wang, Y.; Jia, J. Study of Microcystis aeruginosa inhibition by electrochemical method. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 36, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Li, N.; Wang, S.; Liao, C.; Zhou, L.; Li, T.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y. A novel electro-coagulation-Fenton for energy efficient cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins removal without chemical addition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollah, M.; Morkovsky, P.; Gomes, J.; Kesmez, M.; Parga, J.; Cocke, D. Fundamentals, present and future perspectives of electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 114, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Yang, J.; Tian, J.; Ma, F.; Tu, G.; Du, M. Electro-coagulation-flotation process for algae removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozyonar, F.; Karagozoglu, B. Introduction. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Mouedhen, G.; Feki, M.; Wery, M.D.P.; Ayedi, H.F. Behavior of aluminum electrodes in electrocoagulation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanier, R.Y.; Deruelles, J.; Rippka, R.; Herdman, M.; Waterbury, J.B. Generic Assignments, Strain Histories and Properties of Pure Cultures of Cyanobacteria. Microbiology 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirai, M.; Matumaru, K.; Ohotake, A.; Takamura, Y.; Aida, T.; Nakano, M. Development of a Solid Medium for Growth and Isolation of Axenic Microcystis Strains (Cyanobacteria). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 2569–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.A.; Beardall, J. Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Toxic and Non-Toxic Strains of the Cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and Anabaena circinalis in Relation to Light. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, R.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Ji, S.; Wang, S.; Kong, F. The allelopathic effects of aqueous extracts from Spartina alterniflora on controlling the Microcystis aeruginosa blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakheet, B.; Islam, M.A.; Beardall, J.; Zhang, X.; McCarthy, D. Effective electrochemical inactivation of Microcystis aeruginosa and degradation of microcystins via a novel solid polymer electrolyte sandwich. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AWWA-American Water Works Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rajasekhar, P.; Fan, L.; Nguyen, T.; Roddick, F.A. Impact of sonication at 20kHz on Microcystis aeruginosa, Anabaena circinalis and Chlorella sp. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Wang, B.; Liu, H. Ultrasonic frequency effects on the removal of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2006, 13, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.K.; Sundaram, S.; Patel, A.K.; Kalra, A. Characterization of Seven Species of Cyanobacteria for High-Quality Biomass Production. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavřel, T.; Červený, J.; Sinetova, M.A. Measurement of Chlorophyll. Bio-Protocol 2015, 5, e1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, B.; Clifford, D.A.; Chellam, S. Comparison of electrocoagulation and chemical coagulation pretreatment for enhanced virus removal using microfiltration membranes. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3098–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, P.K.; Barton, G.W.; Wark, M.; Mitchell, C.A. A quantitative comparison between chemical dosing and electrocoagulation. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 211, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleeke, F.; Quante, G.; Winckelmann, D.; Klöck, G. Effect of voltage and electrode material on electroflocculation of Scenedesmus acuminatus. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2015, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tumsri, K.; Chavalparit, O. Optimizing Electrocoagulation-electroflotation Process for Algae Removal. In 2nd International Conference on Environmenta l Science and Technology IPCBEE; IACSIT Press: Singapore, 2011; Volume 6, pp. 452–456. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Torres, A.; Putnam, J.; Jefferson, B.; Stuetz, R.M.; Henderson, R.K. Examination of the physical properties of Microcystis aeruginosa flocs produced on coagulation with metal salts. Water Res. 2014, 60, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guideline for Drinking-Water Quality; Geneva WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 335–336. [Google Scholar]
- Safwat, S.M. Treatment of real printing wastewater using electrocoagulation process with titanium and zinc electrodes. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barışçı, S.; Turkay, O. Domestic greywater treatment by electrocoagulation using hybrid electrode combinations. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 10, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Basri, M.H.; Mohammad Don, N.N.; Kasmuri, N.; Hamzah, N.; Alias, S.; Azizan, F.A. Aluminium recovery from water treatment sludge under different dosage of sulphuric acid. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1349, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Tian, L.-L.; Ren, C.-Y.; Xu, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Li, L. Extracellular polysaccharide synthesis in a bloom-forming strain of Microcystis aeruginosa: Implications for colonization and buoyancy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z. Effects of Drinking Water Treatment Processes on Removal of Algal Matter and Subsequent Water Quality. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, T.; Xie, X. Rationally designed tubular coaxial-electrode copper ionization cells (CECICs) harnessing non-uniform electric field for efficient water disinfection. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, R.; Li, X. Enhanced removal of intracellular organic matters (IOM) from Microcystic aeruginosa by aluminum coagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Sun, W.; Ray, M.B.; Ray, A.K.; Huang, T.; Chen, J. Optimization and modeling of coagulation-flocculation to remove algae and organic matter from surface water by response surface methodology. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredient | NaNO3 | K2HPO4·3H2O | MgSO4·7H2O | CaCl2·2H2O | Citric Acid | Ferric Ammonium Citrate | EDTA | Na2CO3 | Trace Metal Mix * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity in 1 L of deionized water | 1.5 g | 0.04 g | 0.075 g | 0.036 g | 0.006 g | 0.006 g | 0.001 g | 0.02 g | 1 mL |
| Parameter | pH | Temp, °C | EC, µS/cm | TDS, mg/L | Turbidity, NTU | OD684 | OD730 | DOC, mg/L | Chl.-a, µg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (S.D.) | 7.00 (0.01) | 25 (1) | 3893.67 (4.73) | 3002 (2.65) | 166.67 (2.08) | 0.9129 (0.0004) | 0.8520 (0.0002) | 73.85 (1.52) | 0.157 (0.013) |
| Electrode | Oxidation Potential (E0), V | Area (W × L), cm2 | Breadth, mm | Weight, g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 0.44 | 65 (25 × 127) | 0.5 | 14.6 |
| Al | 1.66 | 65 (25 × 127) | 0.5 | 4.3 |
| Cu | −0.52 | 65 (25 × 127) | 0.5 | 13.9 |
| Zn | 0.76 | 65 (25 × 127) | 0.5 | 14.3 |
| Graphite | - | 83.5 (135 × 25) | 5.0 | 25.1 |
| Electrode | pH | EC, µS/cm | TDS, mg/L | Turbidity, NTU | OD684 | OD730 | DOC, mg/L | Chl.-a, µg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 8.88 (0.34) | 4283.34 (0.0058) | 3266.67 (0.0116) | 69.00 (3.61) | 0.3945 (0.0171) | 0.3578 (0.0113) | 45.06 (2.54) | 0.0514 (0.0018) |
| Al | 9.77 (0.32) | 3776.67 (0.0058) | 2890 (0.01) | 15.33 (1.53) | 0.0168 (0.0047) | 0.0164 (0.0047) | 44.39 (3.84) | 0.0063 (0.0001) |
| Cu | 11.46 (0.48) | 3913.34 (0.0153) | 3013.34 (0.0153) | 37.67 (4.04) | 0.0601 (0.0077) | 0.0554 (0.0056) | 21.85 (2.85) | 0.0208 (0.0011) |
| Zn | 10.75 (0.36) | 4250 (0.01) | 3243.34 (0.0153) | 115 (6.56) | 0.2160 (0.0098) | 0.1915 (0.0090) | 43.52 (2.57) | 0.0452 (0.0023) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meetiyagoda, T.A.O.K.; Fujino, T. Comparison of Different Anode Materials to Remove Microcystis aeruginosa Cells Using Electro-Coagulation–Flotation Process at Low Current Inputs. Water 2020, 12, 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123528
Meetiyagoda TAOK, Fujino T. Comparison of Different Anode Materials to Remove Microcystis aeruginosa Cells Using Electro-Coagulation–Flotation Process at Low Current Inputs. Water. 2020; 12(12):3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123528
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeetiyagoda, Thenuwara Arachchige Omila Kasun, and Takeshi Fujino. 2020. "Comparison of Different Anode Materials to Remove Microcystis aeruginosa Cells Using Electro-Coagulation–Flotation Process at Low Current Inputs" Water 12, no. 12: 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123528
APA StyleMeetiyagoda, T. A. O. K., & Fujino, T. (2020). Comparison of Different Anode Materials to Remove Microcystis aeruginosa Cells Using Electro-Coagulation–Flotation Process at Low Current Inputs. Water, 12(12), 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123528






