Spatiotemporal Distribution and Species Composition of Fish Assemblages in the Transitional Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Environmental Data Collection
2.3. Hydroacoustics Surveys
2.4. Biological Samplings
2.5. Acoustic Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Factors
3.2. Species Composition and Assemblage Structure
3.3. Biological and Acoustic Fish Lengths
3.4. Longitudinal and Vertical Distributions of Fish
4. Discussion
4.1. Fish Distribution and Relevant Environmental Factors
4.2. Species Compositions and Fish Sizes
4.3. Future Fish Monitoring and Conservation Suggestions for the Upper Yangtze River
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooke, S.J.; Martins, E.G.; Struthers, D.P.; Gutowsky, L.F.G.; Power, M.; Doka, S.E.; Dettmers, J.M.; Crook, D.A.; Lucas, M.C.; Holbrook, C.M.; et al. A moving target—Incorporating knowledge of the spatial ecology of fish into the assessment and management of freshwater fish populations. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esselman, P.C.; Allan, J.D. Relative influences of catchment- and reach-scale abiotic factors on freshwater fish communities in rivers of northeastern Mesoamerica. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2010, 19, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimov, Y.V.; Borisenko, E.S.; Bazarov, M.I.; Stolbunov, I.A. Density and distribution of fish in a river with a pronounced heterogeneity of the environment: Hydroacoustic Survey. Inland Water Biol. 2019, 12, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Midway, S.R.; Whittier, J.B.; Deweber, J.T.; Paukert, C.P. Annual changes in seasonal river water temperatures in the eastern and western United States. Water 2017, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-S.; Chang, J.; Lek, S.; Cao, W.; Brosse, S. Conservation strategies for endemic fish species threatened by the Three Gorges Dam. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 1748–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, E.F.; Goulart, E.; Minte-Vera, C.V. Fish diversity along spatial gradients in the Itaipu Reservoir, Paraná, Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2004, 64, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gao, X.; Li, M.; Ma, B.; Liu, H.Z. Interannual variations of the fish assemblage in the transitional zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir: Persistence and stability. Environ. Boil. Fishes 2011, 93, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muška, M.; Tušer, M.; Frouzová, J.; Mrkvička, T.; Ricard, D.; Sed’a, J.; Morelli, F.; Kubečka, J. Real-time distribution of pelagic fish: Combining hydroacoustics, GIS and spatial modelling at a fine spatial scale. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, J.E.; Maclennan, D.N. Fisheries Acoustics: Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; Blackwell: London, UK, 2005; p. 437. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M. Overview of the applications of hydroacoustic methods in South Korea and fish abundance estimation methods. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 17, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pollom, R.A.; Rose, G.A. A global review of the spatial, taxonomic, and temporal scope of freshwater fisheries hydroacoustics research. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Tang, X.; Brosse, S.; Chang, J. Chinese Sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) in the Yangtze River: A hydroacoustic assessment of fish location and abundance on the last spawning ground. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2006, 22, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Ye, S.; Godlewska, M.; Huang, G.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Du, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Diurnal, seasonal and inter-annual variability of fish density and distribution in the Three Gorges Reservoir (China) assessed with hydroacoustics. Limnologica 2017, 63, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Lin, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Xie, X.; Wei, Q. Spatiotemporal distribution and assemblages of fishes below the lowermost dam in protected reach in the Yangtze River main stream: Implications for river management. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Yuan, J.; Chu, T.; Lian, Q. Hydroacoustic assessment of fish resources in three reservoirs: The effects of different management strategies on fish density, biomass and size. Fish. Res. 2019, 215, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Gao, X.; Liu, F.; Li, M.; Liu, H. Long-term monitoring revealed fish assemblage zonation in the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 37, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Qin, J.; Xu, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Biodiversity decline of fish assemblages after the impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2019, 29, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qu, X.; Xiong, F.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hughes, R.M. Challenges to saving China’s freshwater biodiversity: Fishery exploitation and landscape pressures. Ambio 2019, 49, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Fujiwara, M.; Winemiller, K.O.; Lin, P.; Li, M.; Liu, H.Z. Regime shift in fish assemblage structure in the Yangtze River following construction of the Three Gorges Dam. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.L.; Yu, Z.T.; Liang, Z.X. Gezhouba Water Control Project and Four Famous Chinese Carps in the Yangtze River; Hubei Science & Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 1988; p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.H.; Wu, G.X.; Wang, Z.L. Reproduction ecology of Coreius Heterodon (Bleeker) and Coreius Guichenoti (Sauvage et Dabry) in the mainstream of the Changjiang River after the construction of Gezhouba Dam. Acta Hydrobiologia Sinica 1990, 14, 205–215. [Google Scholar]
- The Website of National Hydrological and Rainfall Information. Available online: http://xxfb.mwr.cn/sq_djdh.html (accessed on 31 December 2017).
- Foote, K.G.; Knudsen, H.P.; Vestnes, G.; MacLennan, D.N.; Simmonds, E.J. Calibration of Acoustic Instruments for Fish Density Estimation: A Practical Guide; ICES Cooperative Research Report; ICES Cooperative Research: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1987; p. 144. [Google Scholar]
- Aglen, A. Random Errors of Acoustic Fish Abundance Estimates in Relation to the Survey Grid Density Applied; FAO Fisheries Report; FAO Fisheries: Rome, Italy, 1983; pp. 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Godlewska, M.; Długoszewski, B.; Doroszczyk, L.; Jóźwik, A. The relationship between sampling intensity and sampling error—Empirical results from acoustic surveys in Polish vendace lakes. Fish. Res. 2009, 96, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, J.; Vergès, C. The repeatability of fish biomass and size distribution estimates obtained by hydroacoustic surveys using various survey designs and statistical analyses. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2007, 92, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gao, X.; Ma, B.; Kong, Y.; Liu, H. Seasonal dynamics of fish community in Mudong section of the Three Gorges Reservoir of the Yangtze River, China. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2010, 16, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, R.H. The fishes of Sichuan, China; Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology: Chengdu, China, 1994; p. 641. [Google Scholar]
- Balk, H.; Lindem, T. Sonar4 and Sonar5 Post Processing Systems, Operator Manual v5.9.4; University of Oslo: Oslo, Norway, 2004; p. 405. [Google Scholar]
- Parker-Stetter, S.L.; Rudstam, L.G.; Sullivan, P.J.; Warner, D.M. Standard Operating Procedures for Fisheries Acoustic Surveys in the Great Lakes; Great Lakes Fisheries Commission Special Publication, 09–01; Great Lakes Fisheries Commission: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tušer, M.; Kubečka, J.; Frouzová, J.; Jarolím, O. Fish orientation along the longitudinal profile of the Římov reservoir during daytime: Consequences for horizontal acoustic surveys. Fish. Res. 2009, 96, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frouzova, J.; Kubecka, J.; Balk, H.; Frouz, J. Target strength of some European fish species and its dependence on fish body parameters. Fish. Res. 2005, 75, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, V.; Encina-Encina, L.; Ruiz, A.R.; Sánchez-Carmona, R. Horizontal target strength of Luciobarbus sp. in ex situ experiments: Testing differences by aspect angle, pulse length and beam position. Fish. Res. 2015, 164, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Robertis, A.; McKelvey, D.R.; Ressler, P.H. Development and application of an empirical multifrequency method for backscatter classification. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 67, 1459–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Furusawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Effective and accurate use of difference in mean volume backscattering strength to identify fish and plankton. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 59, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneliussen, R.J.; Ona, E. Synthetic echograms generated from the relative frequency response. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2003, 60, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abes, S.D.S.; Agostinho, A.A. Spatial patterns in fish distributions and structure of the ichthyocenosis in the Água Nanci stream, upper Paraná River basin, Brazil. Hydrobiologia 2001, 445, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, C.; Macnaughton, C.J.; Lanthier, G.; Harvey-Lavoie, S.; Lapointe, M.; Boisclair, D. Identifying key environmental variables shaping within-river fish distribution patterns. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 77, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, S.; Nakamura, F. The significance of meandering channel to habitat diversity and fish assemblage: A case study in the Shibetsu River, northern Japan. Limnology 2017, 19, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Yang, Z.; An, R.; Cai, L.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Zou, X. Water flow and substrate preferences of Schizothorax wangchiachii (Fang, 1936). Ecol. Eng. 2019, 138, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, X.-F.; Schnauder, I.; Pusch, M.T. Complex hydromorphology of meanders can support benthic invertebrate diversity in rivers. Hydrobiology 2012, 685, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, I.G. Strength in diversity: Fish sanctuaries and deep-water pools in Lao PDR. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2006, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.C.; Gao, X.; Zhu, Q.G.; Wang, T.; Liu, H.Z. Hydroacoustic survey on the spatial distribution pattern and day-night rhythmic behaviour of fishes in the Xiaonanhai reach of the upper Yangtze River. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2013, 29, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vašek, M.; Prchalová, M.; Říha, M.; Blabolil, P.; Čech, M.; Draštík, V.; Frouzová, J.; Jůza, T.; Kratochvíl, M.; Muška, M.; et al. Fish community response to the longitudinal environmental gradient in Czech deep-valley reservoirs: Implications for ecological monitoring and management. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 63, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, B.C.; Stewart, A.J. Fish size and habitat depth relationships in headwater streams. Oecologia 1991, 87, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, A.P. Habitat partitioning in a patchy environment: Considering the role of intraspecific competition. Environ. Boil. Fishes 2000, 57, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beldade, R.; Borges, R.; Gonçalves, E.J. Depth distribution of nearshore temperate fish larval assemblages near rocky substrates. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.S.; Hubert, W.A.; Daly, S.F. A primer on winter, ice, and fish: What fisheries biologists should know about winter ice processes and stream-dwelling fish. Fisheries 2011, 36, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, C. Temperature influence on the fish assemblage structure in a large lowland river, the lower Oder River, Germany. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2007, 16, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, H.-Z.; Duan, Z.-H.; Cao, W.-X. Seasonal variation in drifting eggs and larvae in the upper Yangtze, China. Zool. Sci. 2010, 27, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.L. Studies on early fish resources in Jiangjin cross-section in the Upstream of Yangtze River. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Gorfine, H.; Shan, X.; Shen, L.; Yang, H.; Du, H.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Inland fisheries development versus aquatic biodiversity conservation in China and its global implications. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2020, 30, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Fajaryanti, R.; Son, W.; Kim, J.H.; La, H.S. Acoustic setection of krill scattering layer in the Terra Nova Bay Polynya, Antarctica. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 584550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Li, W.; Castello, L.; Murphy, B.R.; Xie, S. Potential effects of dam cascade on fish: Lessons from the Yangtze River. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.-Z. Seasonal variations in food resource partitioning among four sympatric gudgeon species in the upper Yangtze River. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 7227–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, B.D.F.; Dos Santos, A.B.I.; Araújo, F.G. Fish assemblage in a dammed tropical river: An analysis along the longitudinal and temporal gradients from river to reservoir. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2010, 8, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckmeier, D.L.; Smith, N.G.; Fleming, B.P.; Bodine, K.A. Intra-annual variation in river-reservoir interface fish assemblages: Implications for fish conservation and management in regulated rivers. River Res. Appl. 2013, 30, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, H.A.C.C.; Rypel, A.L.; Murphy, B.R.; Li, Z.; Xia, Y.; Liu, J. Population characteristics of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) along the longitudinal profile of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2013, 29, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xiong, F.; Wang, K.; Chang, Y. Status of research on Yangtze fish biology and fisheries. Environ. Boil. Fishes 2009, 85, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, J. Status of freshwater fish biodiversity in the Yangtze River Basin, China. In Aquatic Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem Services; Nakano, S., Yahara, T., Nakashizuka, T., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 13–30. [Google Scholar]

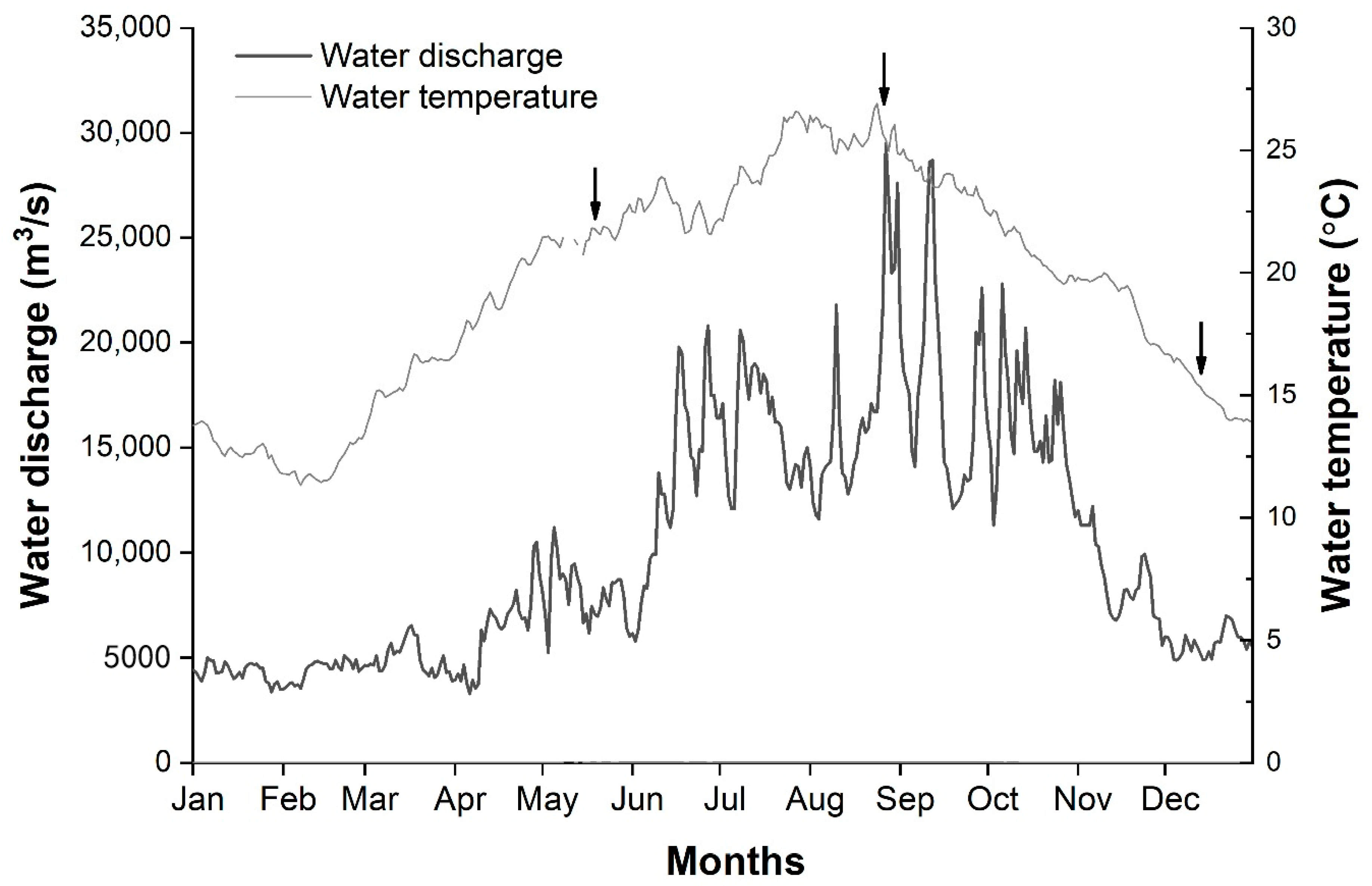
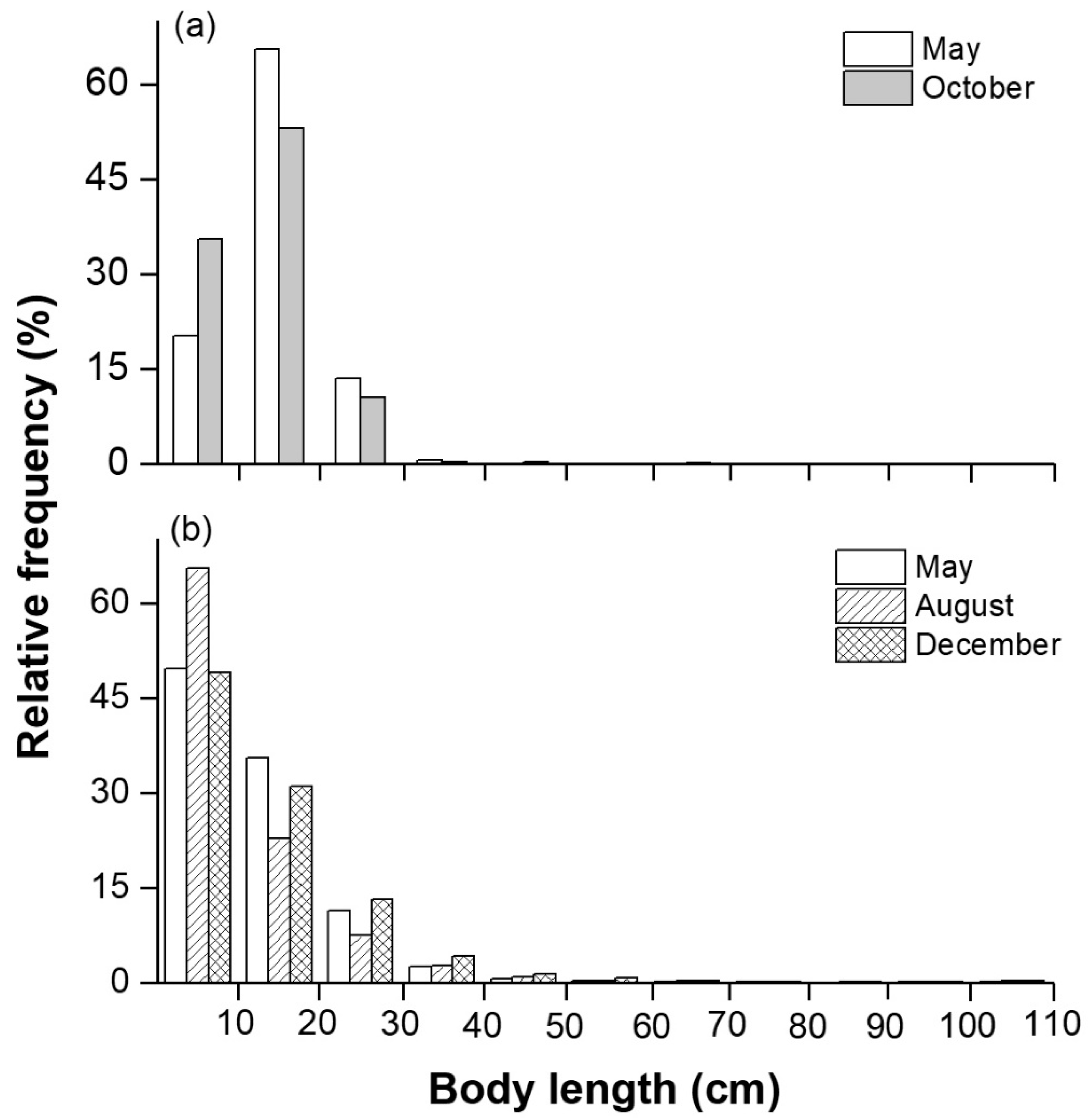
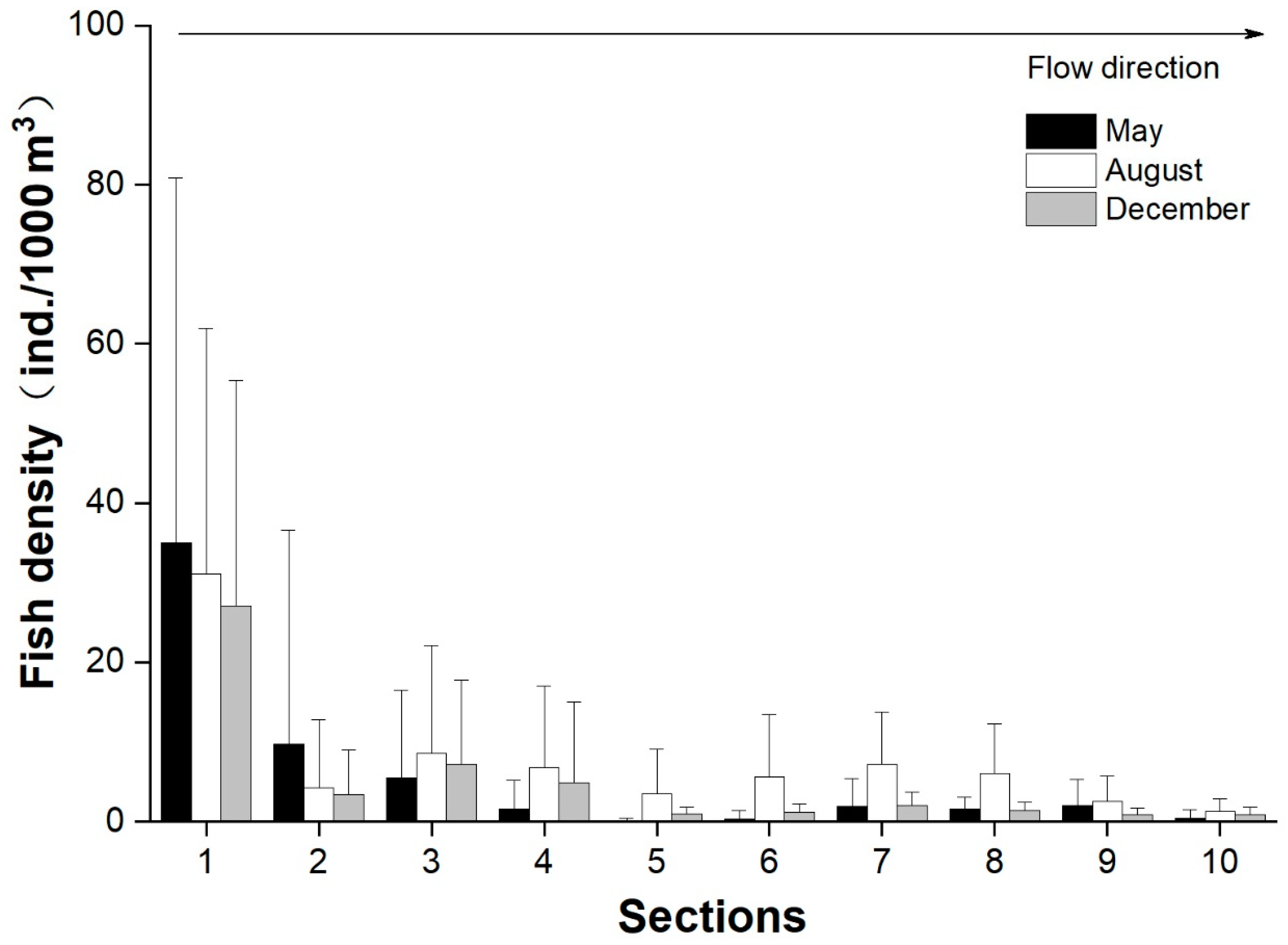
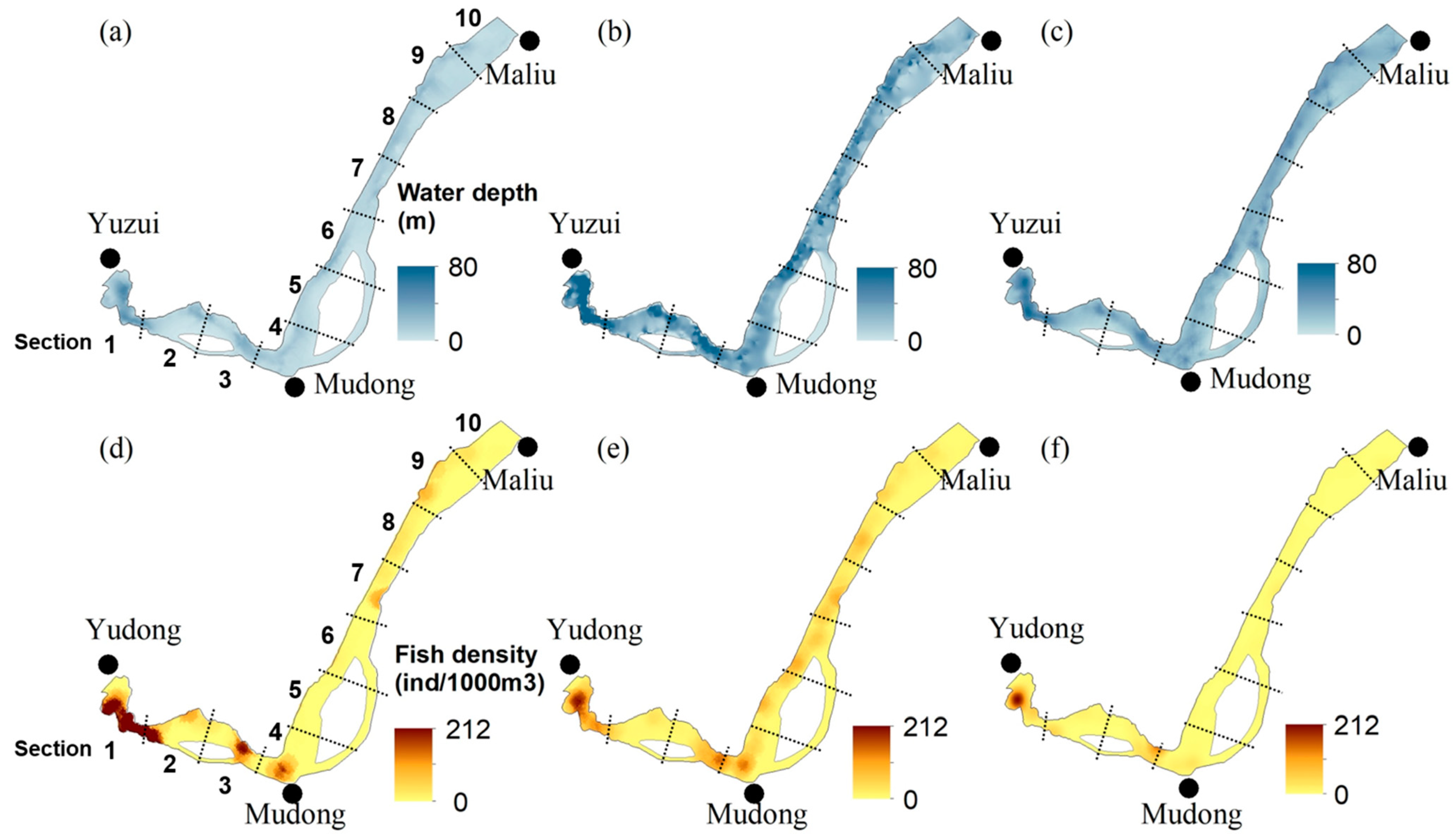
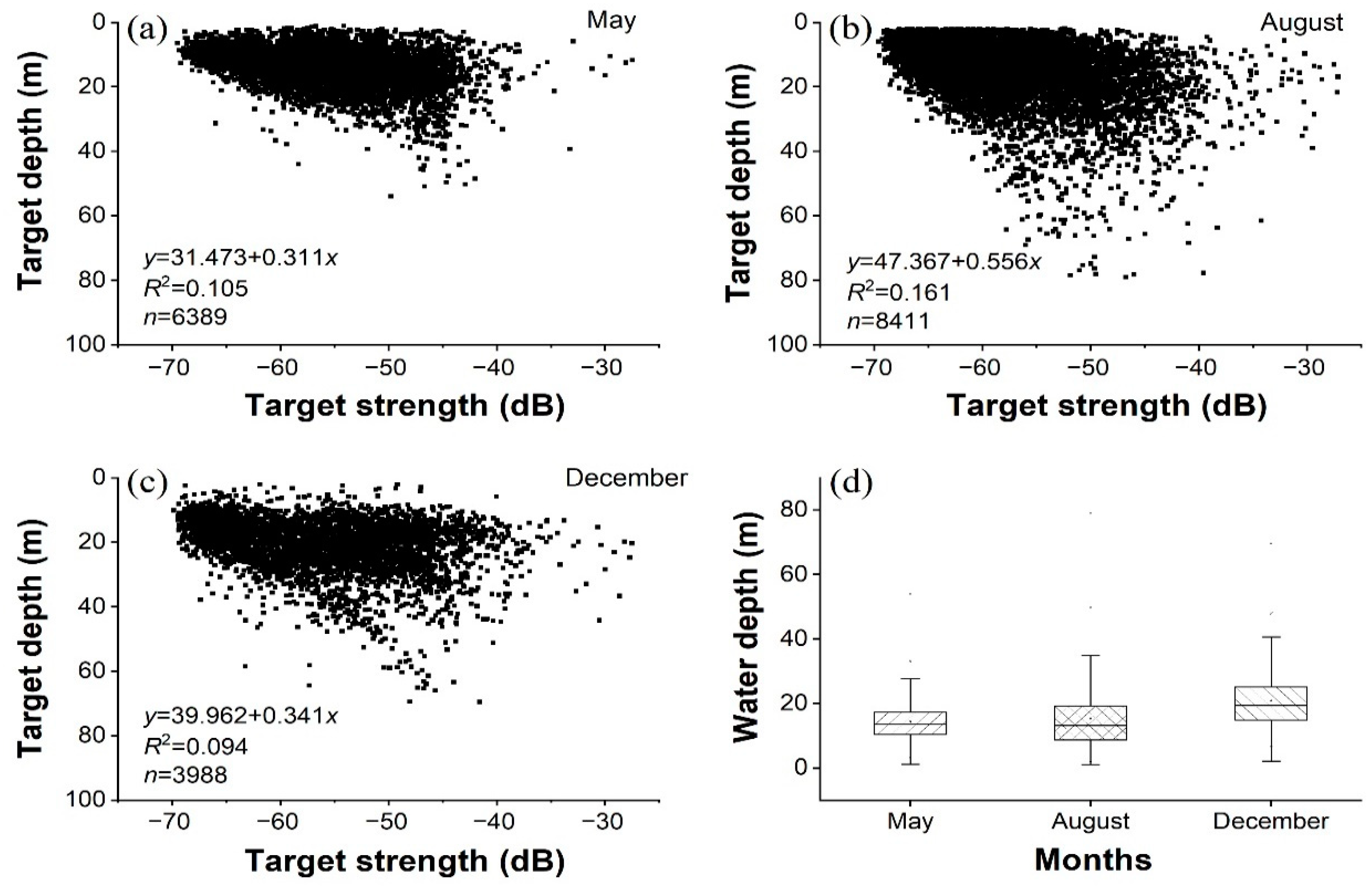
| Sampling Period | Average Water Depth (m) | Maximum Water Depth (m) | Water Temperature (°C) | Total Sailing Distance (km) | Degree of Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22–23 May | 13.1 | 60.0 | 21.6 | 70.9 | 14.5 |
| 30–31 August | 20.4 | 81.0 | 25.7 | 70.2 | 14.4 |
| 9–10 December | 23.9 | 73.0 | 15.1 | 93.5 | 19.2 |
| Sampling Period | Total Mass (kg) | Number of Boat Days |
|---|---|---|
| 13–29 May | 199.2 | 31 |
| 26 September–9 October | 193.1 | 24 |
| Species | May | October | Mean TL (mm) | Mean W (g) | Ecological Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W% | N% | W% | N% | ||||
| Rhinogobio cylindricus (Günther) * | 43.5 | 29.9 | 43.6 | 42.6 | 158 | 64 | Rheophilic |
| Coreius heterodon (Bleeker) | 18.9 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 1.7 | 219 | 165 | Rheophilic |
| Hemiculter bleekeri (Warpachowski) | 9.1 | 30.7 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 104 | 18 | Limnophilic |
| Leiocassis crassilabris (Günther) | 5.2 | 4.2 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 134 | 56 | Eurytopic |
| Squalidus argentatus (Sauvage and Dabry) | 3.5 | 11.4 | -- | -- | 91 | 16 | Eurytopic |
| Hemiculter leucisculus (Basilewsky) | 3.0 | 7.9 | -- | -- | 107 | 21 | Limnophilic |
| Leiocassis longirostris (Günther) | 2.8 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 266 | 310 | Rheophilic |
| Cyprinus carpio (Linnaeus) | 2.7 | 0.2 | 11.3 | 0.3 | 359 | 1429 | Limnophilic |
| Siniperca chuatsi (Basilewsky) | 1.8 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 215 | 269 | Limnophilic |
| Culter mongolicus (Basilewsky) | 1.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 291 | 606 | Limnophilic |
| Pseudolaubuca sinensis (Bleeker) | 1.1 | 0.4 | -- | -- | 211 | 118 | Limnophilic |
| Pelteobagrus vachelli (Richardson) | 1.0 | 0.7 | 3.1 | 3.7 | 141 | 52 | Eurytopic |
| Myxocyprinus asiaticus (Bleeker) | 0.8 | 0.0 | -- | -- | 370 | 1550 | Rheophilic |
| Rhinogobio typus (Bleeker) | 0.7 | 0.5 | 3.4 | 7.2 | 126 | 30 | Rheophilic |
| Parabramis pekinensis (Basilewsky) | 0.5 | 0.0 | -- | -- | 382 | 1094 | Eurytopic |
| Culter alburnus (Basilewsky) | 0.5 | 0.1 | -- | -- | 303 | 360 | Limnophilic |
| Megalobrama skolkovii (Dybowski) ** | 0.5 | 0.0 | -- | -- | 287 | 528 | Limnophilic |
| Squaliobarbus curriculus (Richardson) | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 228 | 244 | Eurytopic |
| Silurus asotus (Linnaeus) | 0.4 | 0.0 | 6.6 | 0.6 | 300 | 581 | Limnophilic |
| Pseudobrama simoni (Bleeker) | 0.3 | 1.1 | -- | -- | 93 | 16 | Limnophilic |
| Pelteobagrus nitidus (Sauvage and Dabry) | 0.3 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 1.5 | 107 | 20 | Eurytopic |
| Mystus macropterus (Bleeker) | 0.3 | 0.1 | 2.9 | 10.7 | 116 | 23 | Rheophilic |
| Coreius guichenoti (Sauvage and Dabry) * | 0.3 | 0.1 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 215 | 193 | Rheophilic |
| Gobiobotia filifer (Garman) | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 2.5 | 76 | 8 | Rheophilic |
| Ctenopharyngodon idella (Cuvier and Valenciennes) | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 178 | 131 | Eurytopic |
| Saurogobio gymnocheilus (Lo, Yao and Chen) | 0.2 | 1.0 | -- | -- | 87 | 9 | Eurytopic |
| Leptobotia elongata (Bleeker) * | 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 8.8 | 97 | 23 | Rheophilic |
| Saurogobio dabryi (Bleeker) | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 69 | 9 | Eurytopic |
| Mylopharyngodon piceus (Richardson) | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 193 | 330 | Eurytopic |
| Coilia brachygnathus (Kreyenberg and Pappenheim) ** | 0.0 | 0.0 | -- | -- | 230 | 46 | Limnophilic |
| Hemiculter tchangi (Fang) * | 0.0 | 0.1 | -- | -- | 104 | 11 | Rheophilic |
| Pseudobagrus truncatus (Regan) | 0.0 | 0.1 | -- | -- | 65 | 10 | Eurytopic |
| Rhinogobius giurinus (Rutter) | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 41 | 2 | Limnophilic |
| Pseudolaubuca engraulis (Nichols) | 0.0 | 0.0 | -- | -- | 119 | 19 | Limnophilic |
| Misgurnus anguillicaudatus (Cantor) | 0.0 | 0.0 | -- | -- | 134 | 30 | Limnophilic |
| Pelteobagrus fulvidraco (Richardson) | 0.0 | 0.0 | -- | -- | 116 | 28 | Limnophilic |
| Glyptothorax fokiensis (Rendahl) | 0.0 | 0.1 | -- | -- | 59 | 3 | Rheophilic |
| Parabotia fasciata (Dabry) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 93 | 12 | Rheophilic |
| Glyptothorax sinensis (Regan) | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 59 | 4 | Rheophilic |
| Sinogastromyzon szechuanensis (Fang) * | 0.0 | 0.0 | -- | -- | 78 | 13 | Rheophilic |
| Carassius potanini * | 0.0 | 0.0 | -- | -- | 85 | 8 | Rheophilic |
| Xenophysogobio boulengeri (Tchang) * | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 9.1 | 66 | 6 | Rheophilic |
| Liobagrus marginatoides (Wu) * | 0.0 | 0.0 | -- | -- | 47 | 2 | Rheophilic |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix (Cuvier and Valenciennes) | 4.4 | 0.1 | 558 | 2146 | Eurytopic | ||
| Silurus meridionalis (Chen) | 4.1 | 0.0 | 866 | 7850 | Limnophilic | ||
| Carassius auratus (Linnaeus) | 3.4 | 1.5 | 145 | 125 | Limnophilic | ||
| Leptobotia taeniops (Sauvage) | 0.8 | 4.6 | 84 | 11 | Eurytopic | ||
| Procypris rabaudi (Tchang) * | 0.2 | 0.1 | 204 | 235 | Rheophilic | ||
| Megalobrama pellegrini (Tchang) * | 0.1 | 0.0 | 195 | 143 | Rheophilic | ||
| Pseudobagrus emarginatus (Regan) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 112 | 31 | Eurytopic | ||
| Leptobotia microphthalma (Fu and Ye) * | 0.1 | 0.8 | 64 | 4 | Rheophilic | ||
| Rhinogobio ventralis (Sauvage and Dabry) * | 0.0 | 0.1 | 91 | 16 | Rheophilic | ||
| Siniperca kneri (Garman) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 158 | 78 | Limnophilic | ||
| Leptobotia rubrilabris (Dabry) * | 0.0 | 0.1 | 77 | 7 | Rheophilic | ||
| Saurogobio gracilicaudatus | 0.0 | 0.1 | 60 | 12 | Eurytopic | ||
| Paramisgurnus dabryanus | 0.0 | 0.0 | 108 | 19 | Limnophilic | ||
| Hybrid Sturgeon ** | 0.0 | 0.0 | 137 | 16 | Limnophilic | ||
| Botia superciliaris (Günther) | 0.0 | 0.1 | 69 | 5 | Rheophilic | ||
| Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton) ** | 0.0 | 0.0 | 81 | 10 | Limnophilic | ||
| Rhinogobius brunneus (Temminck and Schlegel) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 46 | 3 | Limnophilic | ||
| Lepturichthys fimbriata (Günther) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 58 | 1 | Rheophilic | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, P.; Chen, L.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Kang, M. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Species Composition of Fish Assemblages in the Transitional Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water 2020, 12, 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123514
Lin P, Chen L, Gao X, Wang C, Gao X, Kang M. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Species Composition of Fish Assemblages in the Transitional Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water. 2020; 12(12):3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123514
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Pengcheng, Lin Chen, Xingchen Gao, Chunling Wang, Xin Gao, and Myounghee Kang. 2020. "Spatiotemporal Distribution and Species Composition of Fish Assemblages in the Transitional Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China" Water 12, no. 12: 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123514
APA StyleLin, P., Chen, L., Gao, X., Wang, C., Gao, X., & Kang, M. (2020). Spatiotemporal Distribution and Species Composition of Fish Assemblages in the Transitional Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water, 12(12), 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123514





