Drinking Water Quality Mapping Using Water Quality Index and Geospatial Analysis in Primary Schools of Pakistan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
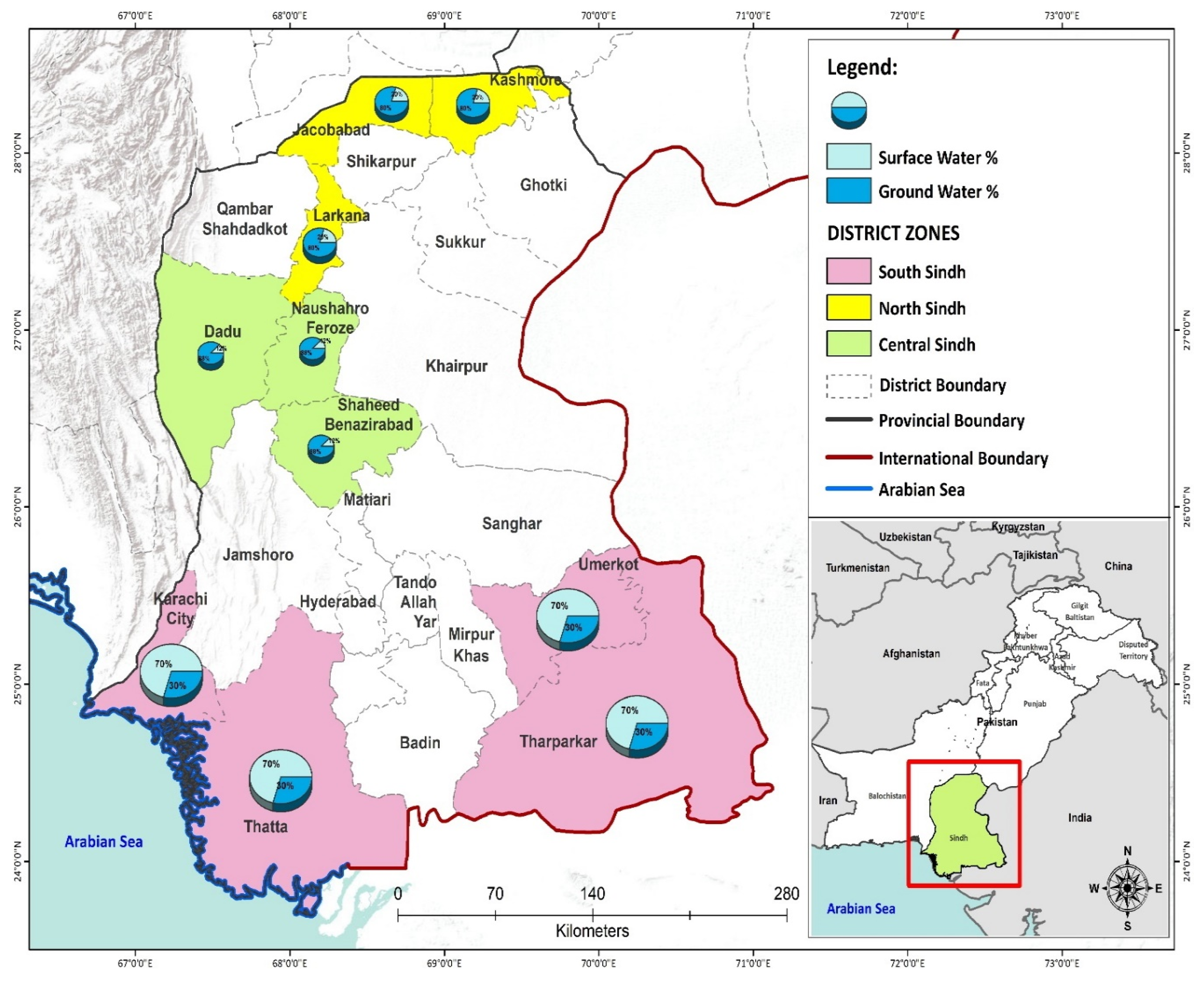
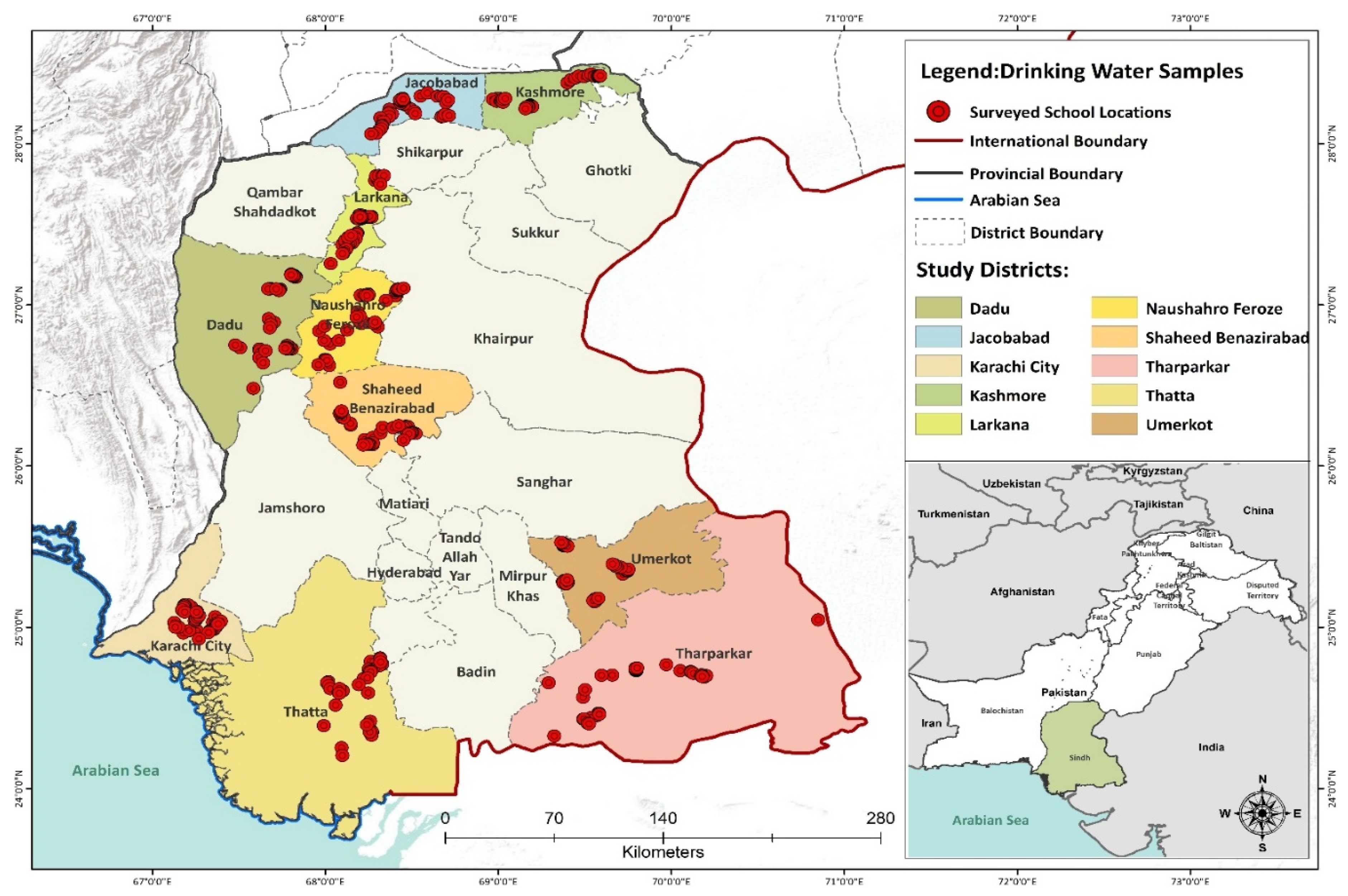
2.1. Study Setting and Sampling
2.2. Water Sample Collection
2.3. Water Sample Analysis
2.4. Water Quality Index (WQI) Calculations
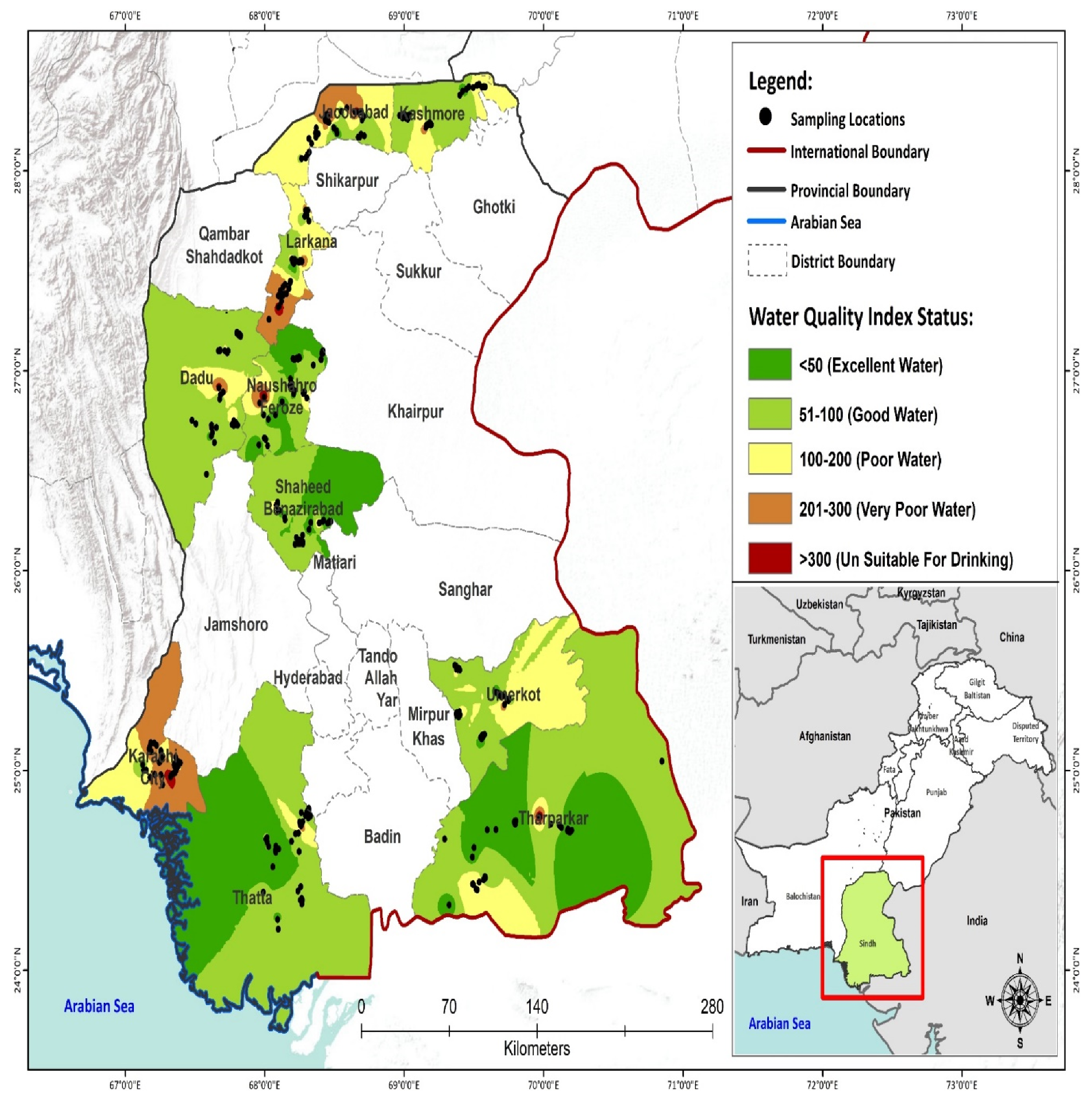
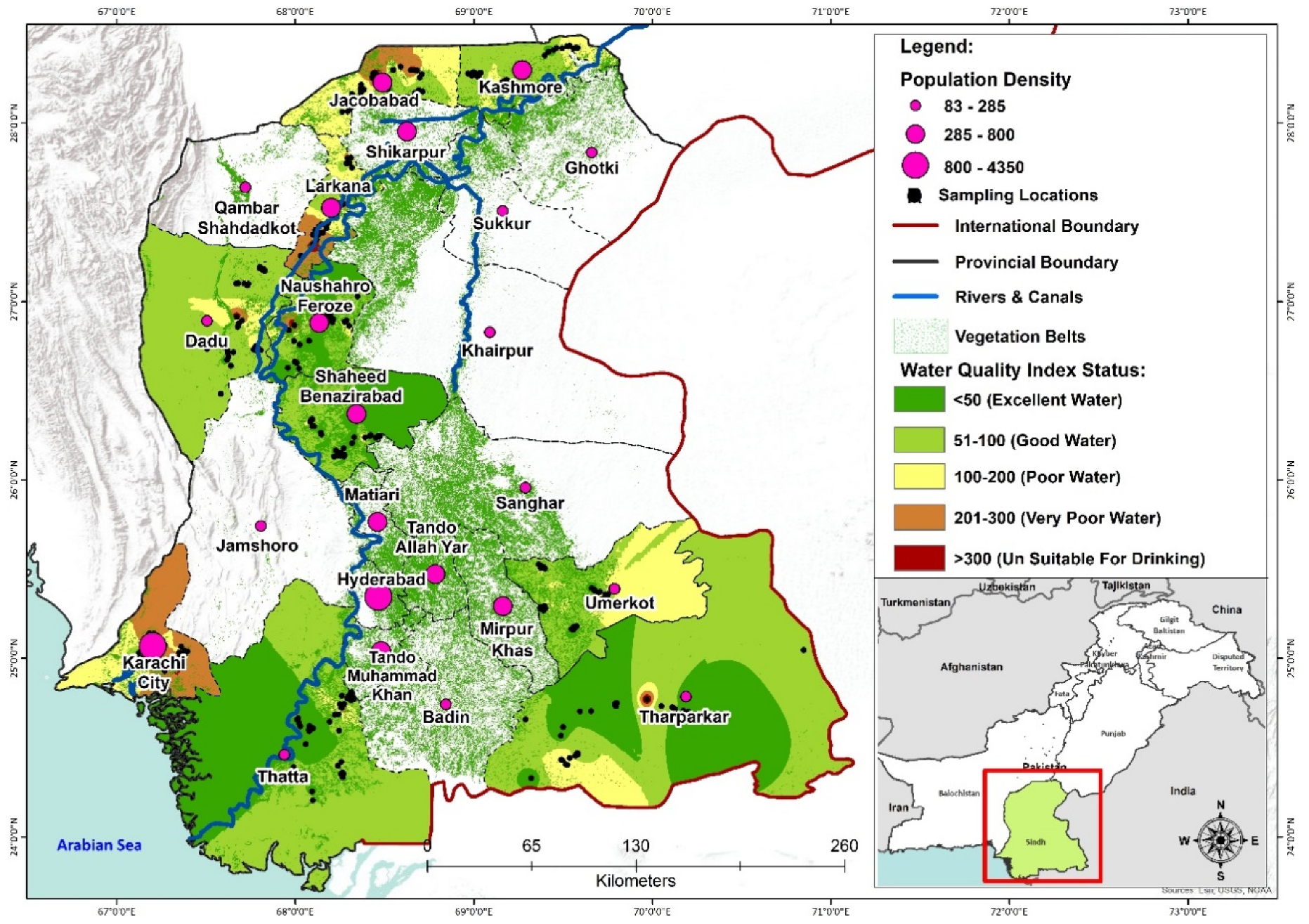
3. Results and Discussion
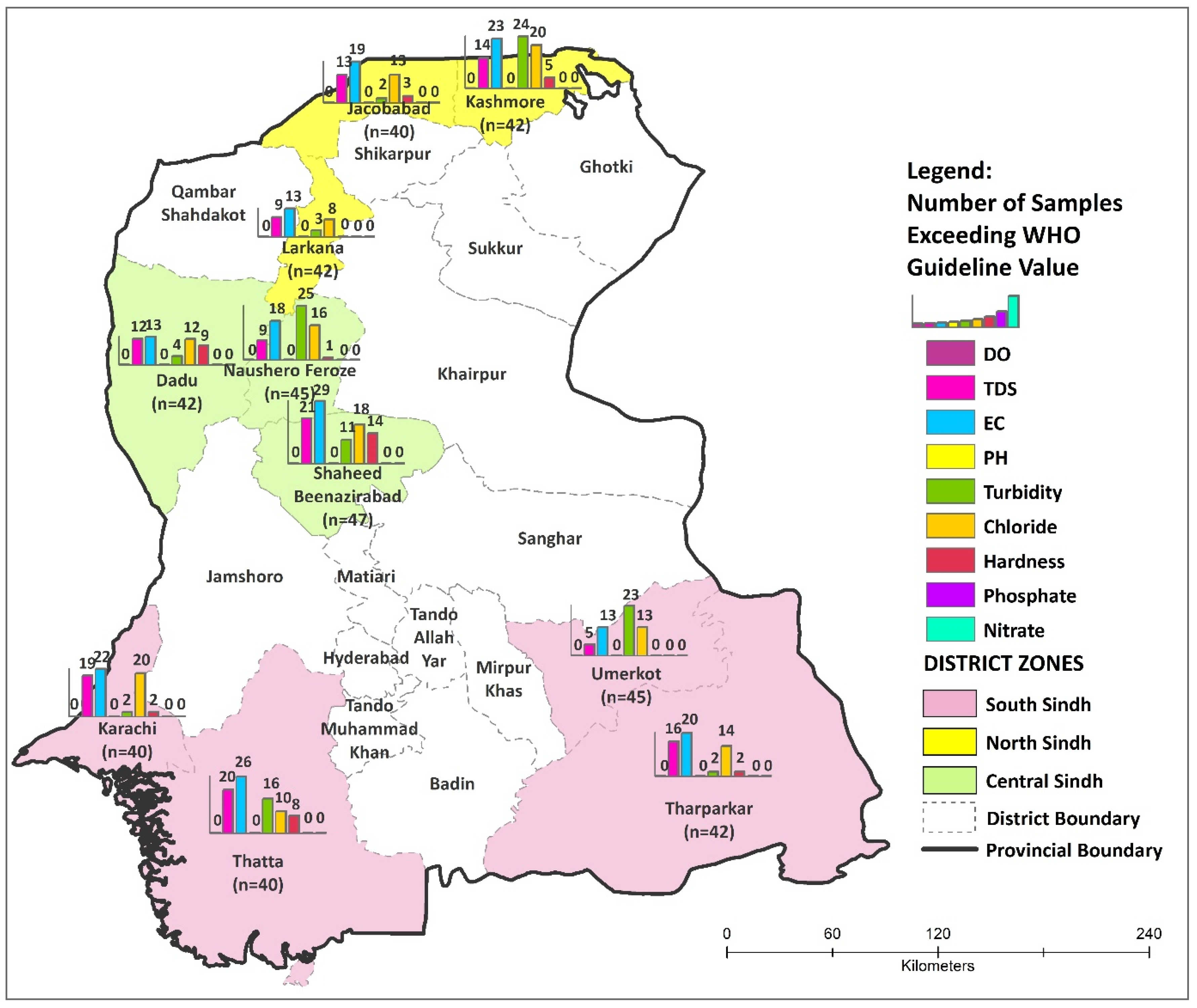
3.1. Characteristics of Drinking Water
3.1.1. Electric Conductivity
3.1.2. Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
3.1.3. pH
3.1.4. Turbidity
3.1.5. Chloride
3.1.6. Hardness
3.1.7. Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Nitrate and Phosphate
3.2. Correlation Analysis
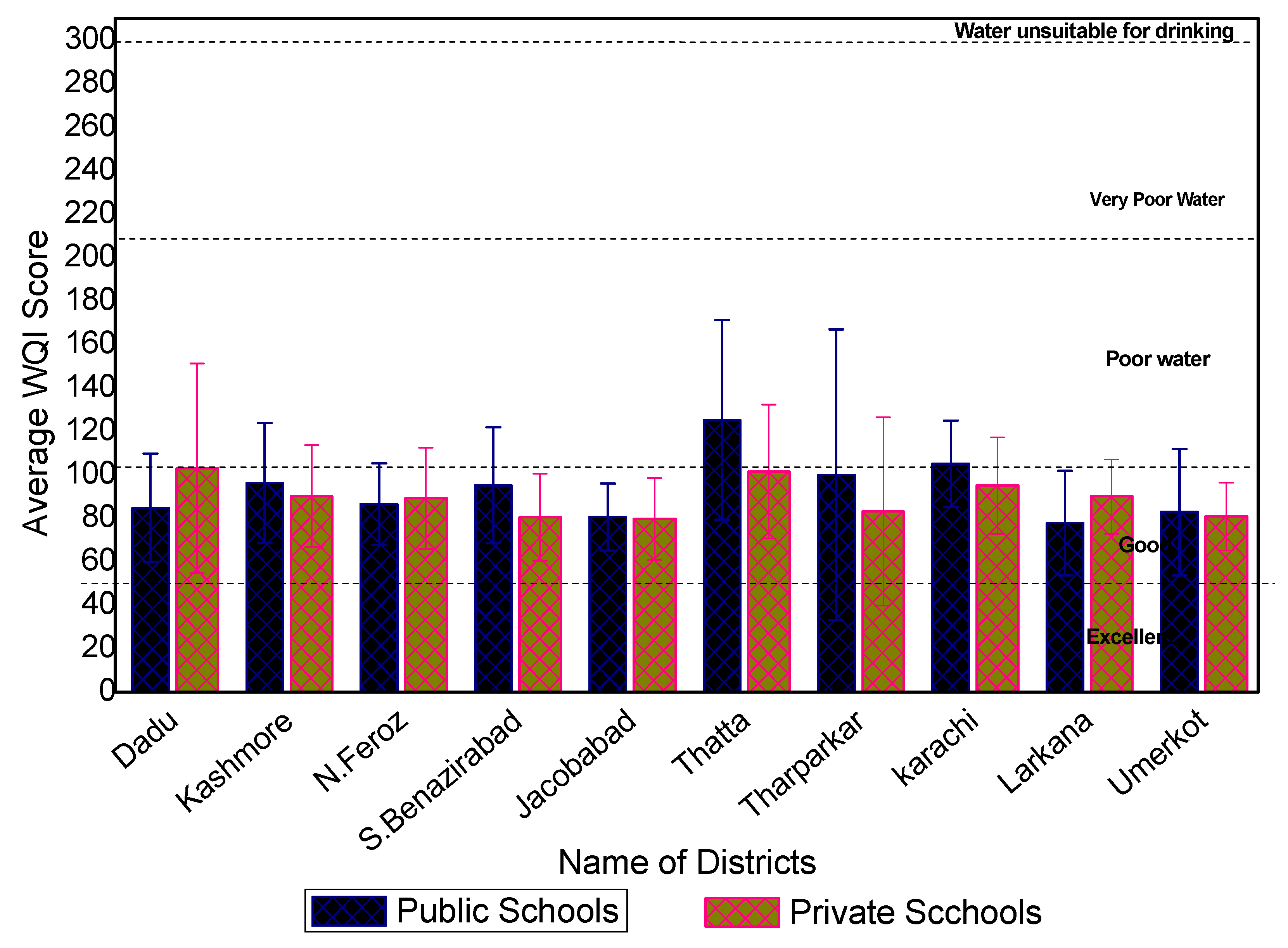
3.3. Water Quality Index
3.3.1. Water Quality Results
3.3.2. Discussion on Water Quality Index
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| District Name | District Population | Number of Primary Schools | Children Enrollment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dadu | 1,555,266 | 1935 | 234,346 |
| Thatta | 781,967 | 1639 | 75,632 |
| Karachi | 14,910,352 | 2917 | 458,846 |
| Jacobabad | 1,006,297 | 1443 | 145,931 |
| Larkana | 1,524,391 | 1166 | 222,226 |
| Kashmore | 1,089,169 | 1497 | 123,940 |
| Tharparkar | 1,649,661 | 4010 | 154,679 |
| Umerkot | 1,073,146 | 2234 | 112,957 |
| Naushero Feroze | 1,612,373 | 2334 | 246,403 |
| Shaheed Benazirabad | 2,012,847 | 2532 | 236,341 |
| DO | TDS | EC | pH | Turbidity | Chloride | Hardness | Phosphate | Nitrate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO | 1 | ||||||||
| TDS | −0.255 | 1 | |||||||
| EC | −0.236 | 0.997 ** | 1 | ||||||
| pH | −0.458 | −0.117 | −0.088 | 1 | |||||
| Turbidity | 0.156 | 0.361 | 0.379 | 0.028 | 1 | ||||
| Chloride | −0.144 | 0.915 ** | 0.934 ** | 0.099 | 0.399 | 1 | |||
| hardness | 0.651 * | 0.398 | 0.413 | −0.582 | 0.228 | 0.345 | 1 | ||
| Phosphate | −0.404 | 0.291 | 0.281 | 0.241 | 0.166 | 0.307 | −0.083 | 1 | |
| Nitrate | −0.327 | 0.006 | 0.045 | 0.568 | −0.196 | 0.193 | −0.184 | 0.117 | 1 |
References
- UNICEF. Child Survival Fact Sheet: Water and Sanitation; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- WHO/UNICEF. Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: Update and SDG Baselines; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Trinies, V.; Chang, H.H.; Garn, J.V.; Freeman, M.C. The Impact of a School-Based Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene Program on Absenteeism, Diarrhea, and Respiratory Infection: A Matched–Control Trial in Mali. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garn, J.V.; Brumback, B.A.; Drews-Botsch, C.D.; Lash, T.L.; Kramer, M.R.; Freeman, M.C. Estimating the Effect of School Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene Improvements on Pupil Health Outcomes. Epidemiology 2016, 27, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garn, J.V.; Trinies, V.; Toubkiss, J.; Freeman, M.C. The Role of Adherence on the Impact of a School-Based Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene Intervention in Mali. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, G.; Ali, M.; Khan, S.; Kumar, S. The crisis of water shortage and pollution in Pakistan: Risk to public health, biodiversity, and ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 10443–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, M.K.; Nafees, M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Bajwa, R.A.; Shakoor, M.B.; Arshad, M.U.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Deeba, F.; Murad, W.; et al. Drinking Water Quality Status and Contamination in Pakistan. BioMed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7908183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, R.; Zaidi, M.B.; Bashir, S.; Khanani, R.; Nawaz, R.; Ali, S.; Khan, S. Microbial contamination levels in the drinking water and associated health risks in Karachi, Pakistan. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2019, 9, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, S.; Ali, Y. Factors Affecting the Performance of Water Treatment Plants in Pakistan. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2018, 3, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Li, P.; Venkatayogi, S. Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes and Integrated Interpretation with Water Quality Index Studies. Environ. Process. 2018, 5, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, M.; Khokhar, M.; Hussain, W.; Hussain, M. Drinking Water Quality Challenges in Pakistan; Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources: Lahore, Pakistan, 2011; pp. 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zahid, J. Impact of Clean Drinking Water and Sanitation on Water Borne Diseases in Pakistan; Sustainable Development Policy Institute: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2018; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- NIPS. Pakistan Demographic and Health Survey, 2017–2018; National Institute of Population Studies (NIPS) Pakistan: Islamabad, Pakistan; ICF: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019; p. 573. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, W.; Nafees, M.; Turab, S.A.; Khan, M.Y.; Rehman, K. Drinking water quality assessment using water quality index and geostatistical techniques, Mardan District, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J. Him. Earth Sci. 2019, 52, 56–85. [Google Scholar]
- Hamlat, A.; Guidoum, A. Assessment of groundwater quality in a semiarid region of Northwestern Algeria using water quality index (WQI). Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsadailakshmi, S.; Sankari, S.G.; Prasanna, S.M.; Madhurambal, G. Evaluation of water quality suitability for drinking using drinking water quality index in Nagapattinam district, Tamil Nadu in Southern India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 6, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, H.; Nasri, O.; Ojaghi, B.; Pasalari, H.; Hosseini, M.; Hashemzadeh, B.; Kavosi, A.; Masoumi, S.; Radfard, M.; Adibzadeh, A.; et al. Data on drinking water quality using water quality index (WQI) and assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes in Qorveh & Dehgolan, Kurdistan, Iran. Data Brief 2018, 20, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, Ş.; Şener, E.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, B.; Reddy, Y.S.; Sunitha, V.; Reddy, B.M.; Prasad, M.; Reddy, M.R. Data on application of water quality index method for appraisal of water quality in around cement industrial corridor, Yerraguntla Mandal, Y.S.R. District, A.P South India. Data Brief 2020, 28, 104872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketata, M.; Gueddari, M.; Bouhlila, R. Use of geographical information system and water quality index to assess groundwater quality in El Khairat deep aquifer (Enfidha, Central East Tunisia). Arab. J. Geosci. 2011, 5, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat-Noori, M.; Ebrahimi, K.; Liaghat, A. Groundwater quality assessment using the Water Quality Index and GIS in Saveh-Nobaran aquifer, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 3827–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental protection agency, Government of Pakistan. National standard for drinking water quality. Gaz. Pak. 2010, 1062, 3207–3208. [Google Scholar]
- Sayato, Y. WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. Eisei Kagaku 1989, 35, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- School Education Department. G.o.S. Water, Sanitation & Hygiene (WASH) in Public Sector Schools Strategic Plan for Sindh. Available online: http://www.sindheducation.gov.pk/Contents/Menu/WASH%20in%20Public%20Sector.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- School Education and Literacy Department, Government of Sindh. 2019. Available online: http://www.sindheducation.gov.pk/ (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Malik, S.M.; Awan, H.; Khan, N. Mapping vulnerability to climate change and its repercussions on human health in Pakistan. Glob. Health 2012, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakistan Demographics Profile. Mundi Index. 2019. Available online: https://www.indexmundi.com/pakistan/demographics_profile.html (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Maskooni, E.K.; Naseri-Rad, M.; Berndtsson, R.; Nakagawa, K. Use of Heavy Metal Content and Modified Water Quality Index to Assess Groundwater Quality in a Semiarid Area. Water 2020, 12, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iticescu, C.; Georgescu, L.P.; Murariu, G.; Topa, C.; Timofti, M.; Pintilie, V.; Arseni, M. Lower Danube Water Quality Quantified through WQI and Multivariate Analysis. Water 2019, 11, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Basnet, N. An evaluation of physicochemical analysis and water quality index of Ratuwa River of Damak, Jhapa, Nepal. Int. J. Rec. Res. Rev. 2018, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-Toscano, C.A.; Alfaro-Cuevas-Villanueva, R.; Cortés-Martínez, R.; Morton-Bermea, O.; Hernández-Álvarez, E.; Buenrostro-Delgado, O.; Ávila-Olivera, J.A. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Assessment of Drinking Water Quality in the Urban Area of Zamora, Mexico. Water 2020, 12, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. World Report on Disability 2011; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kachroud, M.; Trolard, F.; Kefi, M.; Jebari, S.; Bourrié, G. Water Quality Indices: Challenges and Application Limits in the Literature. Water 2019, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Meher, P.K.; Kumar, A.; Gautam, Y.P.; Mishra, K.P. Changes in water quality index of Ganges river at different locations in Allahabad. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2014, 3, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, A.; Arshad, J.; Iqbal, F.; Sajjad, A.; Mehmood, Z.; Murtaza, G. Pollution Status of Pakistan: A Retrospective Review on Heavy Metal Contamination of Water, Soil, and Vegetables. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 813206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Parveen, Z.; Iqbal, M.; Riazuddin, M.; Iqbal, S.; Ahmed, M.; Bhutto, R. Monitoring of toxic metals (cadmium, lead, arsenic and mercury) in vegetables of Sindh, Pakistan. Kathmandu Univ. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 6, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, S.K.; Azizullah, A.; Murad, W.; Daud, M.K.; Nabeela, F.; Rahman, H.; Rehman, S.U.; Häder, D.-P. Toxic Metal Pollution in Pakistan and Its Possible Risks to Public Health. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindha, K.; Vaman, K.V.N.; Srinivasan, K.; Babu, M.S.; Elango, L. Identification of surface water-groundwater interaction by hydrogeochemical indicators and assessing its suitability for drinking and irrigational purposes in Chennai, Southern India. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 4, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshkumar, B.; Jaideep, C. Groundwater quality assessment using Water Quality Index (WQI) approach–Case study in a coastal region of Tamil Nadu, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Res. 2011, 1, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, N.; Siyal, A.; Qureshi, A. Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index: A Case study of Nagarparkar, Sindh, Pakistan. Sindh Univ. Res. J. 2018, 50, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Solangi, G.S.; Siyal, A.A.; Babar, M.M.; Siyal, P. Evaluation of drinking water quality using the water quality index (WQI), the synthetic pollution index (SPI) and geospatial tools in Thatta district, Pakistan. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 160, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjwani, S.K. Drinking Water Quality and Environmental Monitoring in Rural Areas of District Malir, Karachi. Master’s Thesis, University of Oulu Faculty of Technology, Oulu, Finland, March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shahab, A.; Shihua, Q.; Rashid, A.; Hasan, F.; Sohail, M. Evaluation of Water Quality for Drinking and Agricultural Suitability in the Lower Indus Plain in Sindh Province, Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 2563–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, M.B.; Ullah, I.; Niaz, A.; Shah, N.; Shah, A.; Hussain, Z.; Tariq, M.; Afridi, H.I.; Baig, J.A.; Kazi, T.G. Evaluation of water quality parameters in drinking water of district Bannu, Pakistan: Multivariate study. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2014, 3, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanian, N.; Ali, S.H.B.; Homayoonfard, M.; Ali, N.J.; Rehan, M.; Sadef, Y.; Nizami, A.-S. Analysis of Physiochemical Parameters to Evaluate the Drinking Water Quality in the State of Perak, Malaysia. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 716125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, G.S.; Siyal, A.A.; Babar, M.M.; Siyal, P. Groundwater quality mapping using geographic information system: A case study of District Thatta, Sindh. Mehran Univ. Res. J. Eng. Tech. 2017, 36, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Aziz, T.; Noor-Ul-Ain, A.K.; Ahmed, I. Drinking Water Quality in 13 Different Districts of Sindh, Pakistan. Health Care Curr. Rev. 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.L.; Mahessar, A.A.; Leghari, M.E.-U.-H.; Lashari, B.K.; Mari, F.M. Impact of Releasing Wastewater of Sugar Industries into Drainage System of LBOD, Sindh, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2015, 6, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Qureshi, F.R. Groundwater Quality Assessment through Water Quality Index (WQI) in New Karachi Town, Karachi, Pakistan. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2018, 15, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Wong, L.P.; Piaw, C.Y.; Channa, N.; Mahar, R.B.; Yasmin, A.; Vanderslice, J.; Garn, J. Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment of Drinking Water Quality to Predict the Risk of Waterborne Diseases in Primary-School Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Wong, L.P.; Chua, Y.P.; Yasmin, A.; Channa, N.; Van Derslice, J.A. Estimation of Hepatitis A Virus Infection Prevalence Through Drinking Water Supply of Primary Schools of Sindh, Pakistan. Zahedan J. Res. Med Sci. 2020, 20, 98412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Butt, A.R.; Uzma, F.; Ahmed, R.; Irshad, S.; Rehman, A.; Yousaf, B. A comprehensive review of climate change impacts, adaptation, and mitigation on environmental and natural calamities in Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 192, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Mumtaz, S. Climate change and managing water crisis: Pakistan’s perspective. Rev. Environ. Health 2014, 29, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.J.; Koch, M.; Tahir, A.A. Impacts of Climate Change on the Water Availability, Seasonality and Extremes in the Upper Indus Basin (UIB). Sustainablity 2020, 12, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawadi, S.; Ahmad, S. Evaluating the impact of demand-side management on water resources under changing climatic conditions and increasing population. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 114, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, M.T. Sugarcane and Punjab, Pakistan: Production, Processing and Challenges. Available online: https://ethicalsugar.files.wordpress.com/2014/02/ethical-sugar-sugarcane-in-punjab-pakistan.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).

| Parameter | Instrument | Model/Method |
|---|---|---|
| DO | DO meter | Hanna Model H19146-04 |
| pH | pH Meter | Hanna H18424 |
| EC/TDS | EC/TDS Meter | Hanna Hi99301 |
| Turbidity | Turbidity Meter | Hanna 9844 |
| Chloride | Titration Method | 4500-Cl-B |
| Total Hardness | Titration Method | 2340 C |
| Nitrate | Spectrophotometer | 4500-NO3 |
| Phosphate | Spectrophotometer | 4500-P |
| Parameter | WHO Standard [23] | Pakistan EPA Standard [15] | Weight (wi) | Relative Weights (Wi) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO mg/L | 5 | * | 5 | 0.16 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 1000 | 1000 | 5 | 0.16 |
| EC (uS/cm) | 1500 | * | 4 | 0.12 |
| pH | 6.5–8.5 | 6.5–8.5 | 4 | 0.12 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 5 | 5 | 2 | 0.06 |
| Chloride (mg/L) | 250 | 250 | 3 | 0.09 |
| Hardness (mg/L) | 500 | 500 | 2 | 0.06 |
| Phosphate (mg/L) | 5 | * | 1 | 0.03 |
| Nitrate (mg/L) | 50 | 50 | 5 | 0.16 |
| Σ wi = 31 | Σ Wi = 1.00 | |||
| Class | WQI Value | Water Quality Status |
|---|---|---|
| A | <50 | Excellent |
| B | 51–100 | Good |
| C | 101–200 | Poor water |
| D | 201–300 | Very Poor Water |
| E | >300 | Water unsuitable for drinking |
| District | Tharparkar | Thatta | Karachi | Umerkot | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 42 | n = 40 | n = 40 | n = 45 | |||||||||
| Statistics | Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min |
| DO mg/L | 7.1 | 8.0 | 6.0 | 7.3 | 8.0 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 6.4 | 7.6 | 8.4 | 7.0 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 1083.1 | 3440.0 | 130.0 | 1192.7 | 3730.0 | 390.0 | 930.0 | 2360.0 | 260.0 | 667.2 | 2220.0 | 240.0 |
| EC (uS/cm) | 2098.5 | 6600.0 | 250.0 | 2292.1 | 7190.0 | 760.0 | 1805.6 | 4550.0 | 510.0 | 1330.6 | 4380.0 | 470.0 |
| PH | 7.8 | 8.4 | 6.9 | 7.6 | 8.3 | 6.8 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 7.2 | 7.9 | 8.6 | 7.0 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 2.3 | 8.2 | 0.3 | 15.8 | 44.7 | 0.4 | 2.1 | 8.4 | 0.0 | 7.8 | 46.0 | 0.3 |
| Chloride (mg/L) | 350.9 | 2161.8 | 25.0 | 349.5 | 937.2 | 87.5 | 249.2 | 487.3 | 37.5 | 202.3 | 371.3 | 67.0 |
| Hardness (mg/L) | 199.9 | 650.0 | 31.0 | 346.9 | 775.0 | 103.0 | 258.3 | 600.0 | 58.0 | 217.7 | 400.0 | 70.0 |
| Phosphate (mg/L) | 0.5 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 0.0 |
| Nitrate (mg/L) | 5.7 | 27.0 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 20.9 | 0.0 | 7.0 | 20.7 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 9.8 | 0.0 |
| District. | Larkana | Jacobabad | Kashmore | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 42 | n = 40 | n = 42 | |||||||
| Statistics | Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min |
| DO mg/L | 7.2 | 8.1 | 6.3 | 7.3 | 8.0 | 6.3 | 7.5 | 8.2 | 6.8 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 741.2 | 2510.0 | 240.0 | 835.2 | 1910.0 | 180.0 | 931.7 | 2500.0 | 130.0 |
| EC (uS/cm) | 1395.7 | 4860.0 | 480.0 | 1628.2 | 3670.0 | 360.0 | 1818.2 | 4830.0 | 250.0 |
| PH | 7.5 | 8.2 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.3 | 7.0 | 7.8 | 8.4 | 7.1 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 2.5 | 9.4 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 8.3 | 0.0 | 8.7 | 46.0 | 0.9 |
| Chloride (mg/L) | 166.5 | 937.2 | 25.0 | 206.2 | 649.0 | 12.5 | 250.6 | 691.0 | 29.0 |
| Hardness (mg/L) | 154.7 | 425.0 | 30.0 | 261.5 | 775.0 | 25.0 | 309.4 | 622.0 | 20.0 |
| Phosphate (mg/L) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.0 |
| Nitrate (mg/L) | 1.5 | 5.9 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 8.1 | 0.0 |
| District | S.Benazirabad | Dadu | N.Feroz | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 47 | n = 42 | n = 45 | |||||||
| Statistics | Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min | Average | Max | Min |
| DO mg/L | 7.7 | 8.2 | 7.0 | 7.72 | 8.10 | 7.30 | 7.4 | 8.3 | 7 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 937.7 | 2090.0 | 310.0 | 893.19 | 2730.0 | 280 | 757.6 | 1450.0 | 389.0 |
| EC (uS/cm) | 1822.4 | 4070.0 | 620.0 | 1738.29 | 5260.0 | 550 | 1520.2 | 2990.0 | 778.0 |
| PH | 7.4 | 8.45 | 6.77 | 7.45 | 8.30 | 6.92 | 7.7 | 8.4 | 7.0 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 3.9 | 38.6 | 0 | 3.38 | 29.26 | 0.10 | 7.2 | 32.0 | 0.5 |
| Chloride (mg/L) | 253.8 | 1040 | 20 | 252.06 | 1130.0 | 24.9 | 232.5 | 691.0 | 71 |
| Hardness (mg/L) | 421.6 | 850 | 78 | 399.48 | 1200.0 | 72 | 255.2 | 510.0 | 88.0 |
| Phosphate (mg/L) | 0.0 | 0.73 | 0 | 0.58 | 2.02 | 0.02 | 0.6 | 2.7 | 0.0 |
| Nitrate (mg/L) | 3.5 | 19 | 0 | 2.41 | 11.43 | 0 | 7.5 | 22.4 | 0.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, J.; Wong, L.P.; Chua, Y.P.; Channa, N. Drinking Water Quality Mapping Using Water Quality Index and Geospatial Analysis in Primary Schools of Pakistan. Water 2020, 12, 3382. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123382
Ahmed J, Wong LP, Chua YP, Channa N. Drinking Water Quality Mapping Using Water Quality Index and Geospatial Analysis in Primary Schools of Pakistan. Water. 2020; 12(12):3382. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123382
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Jamil, Li Ping Wong, Yan Piaw Chua, and Najeebullah Channa. 2020. "Drinking Water Quality Mapping Using Water Quality Index and Geospatial Analysis in Primary Schools of Pakistan" Water 12, no. 12: 3382. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123382
APA StyleAhmed, J., Wong, L. P., Chua, Y. P., & Channa, N. (2020). Drinking Water Quality Mapping Using Water Quality Index and Geospatial Analysis in Primary Schools of Pakistan. Water, 12(12), 3382. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123382