Available Dissolved Organic Carbon Alters Uptake and Recycling of Phosphorus and Nitrogen from River Sediments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. River Sediment and Column Flow Systems
2.2. Solute Treatments and Column Eluant Sampling
2.3. Analysis of Eluants
2.4. Destructive Analysis of Column Sediment Samples
2.5. Data Handling and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Column and Sediment Conditions
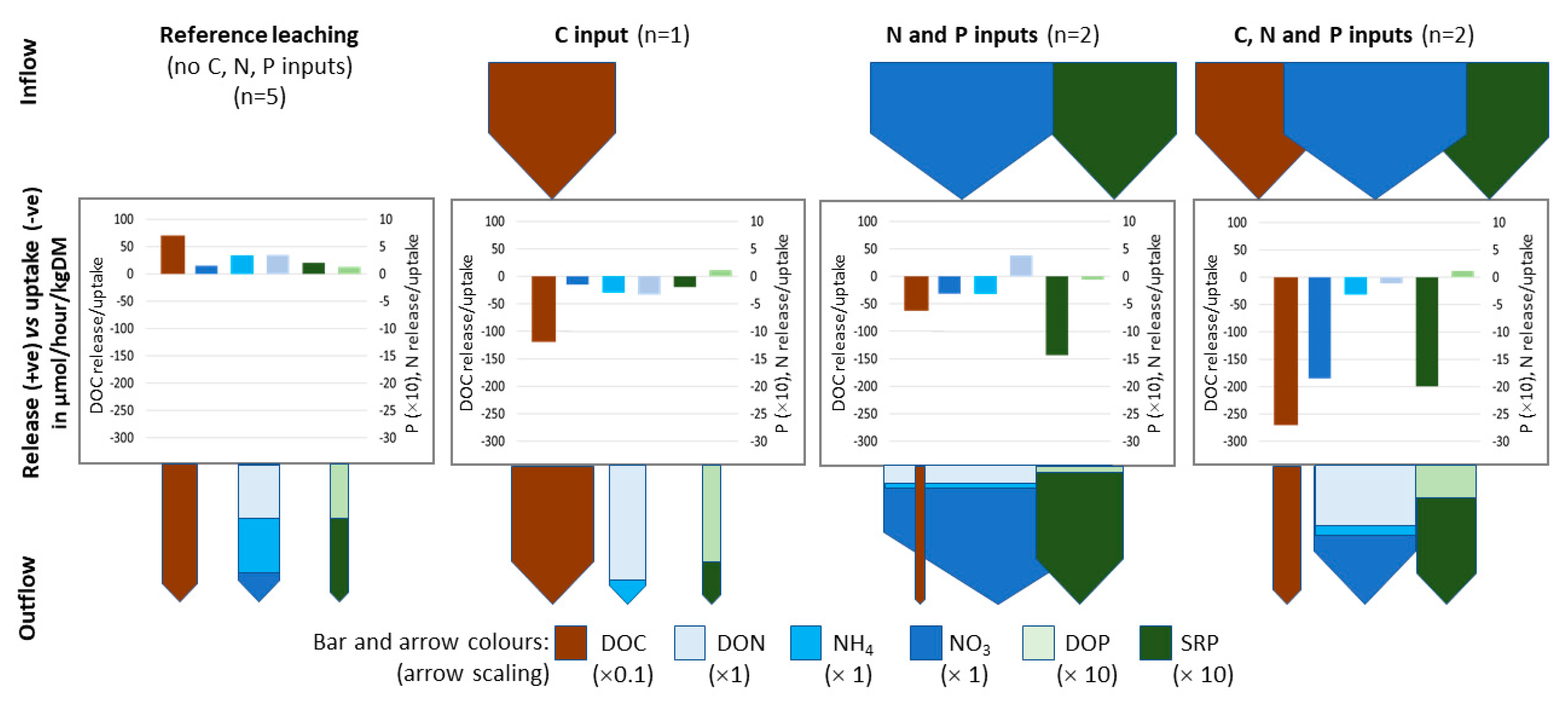
3.2. Column Background Leaching Pre-Treatment Phase
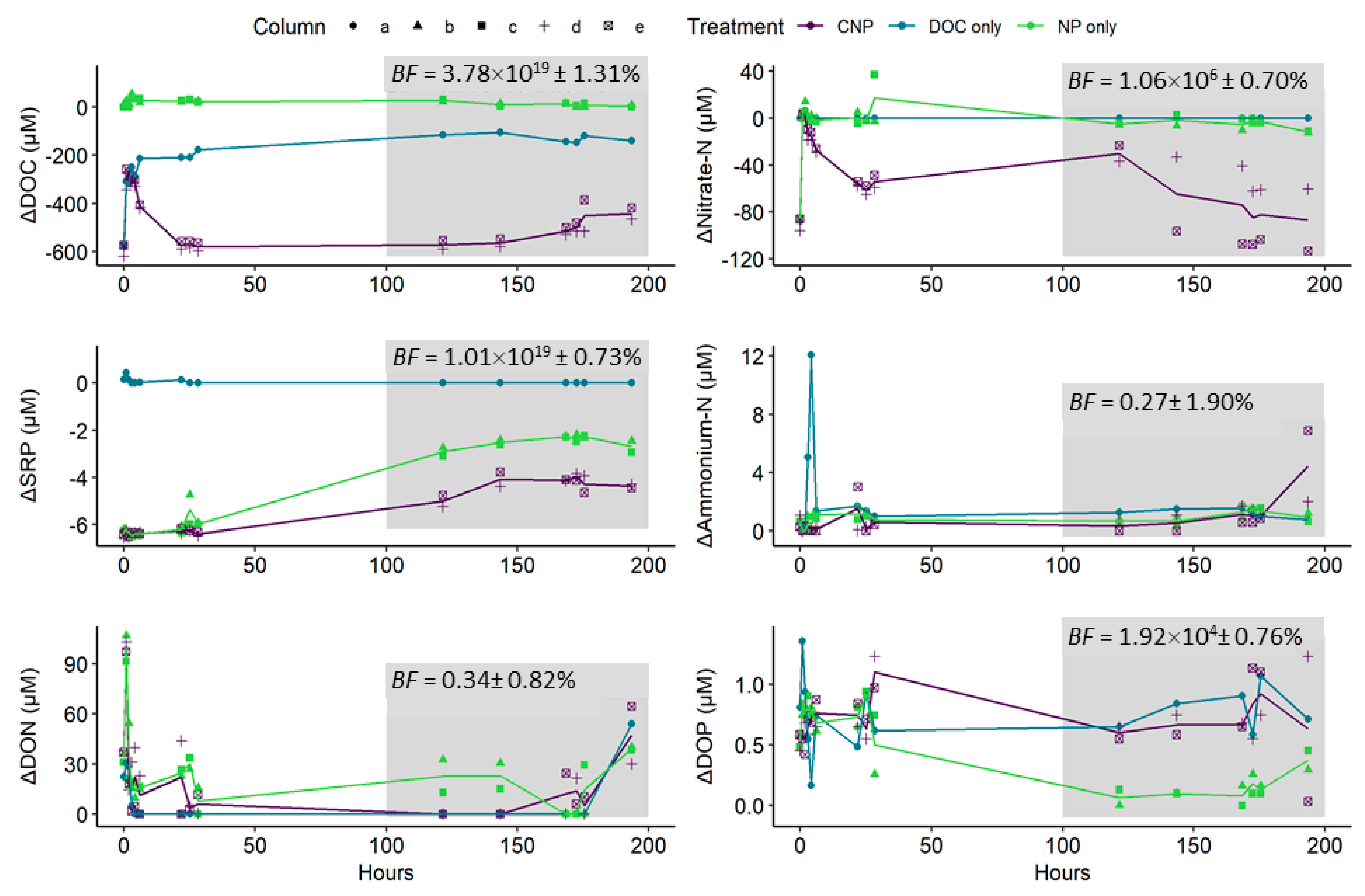
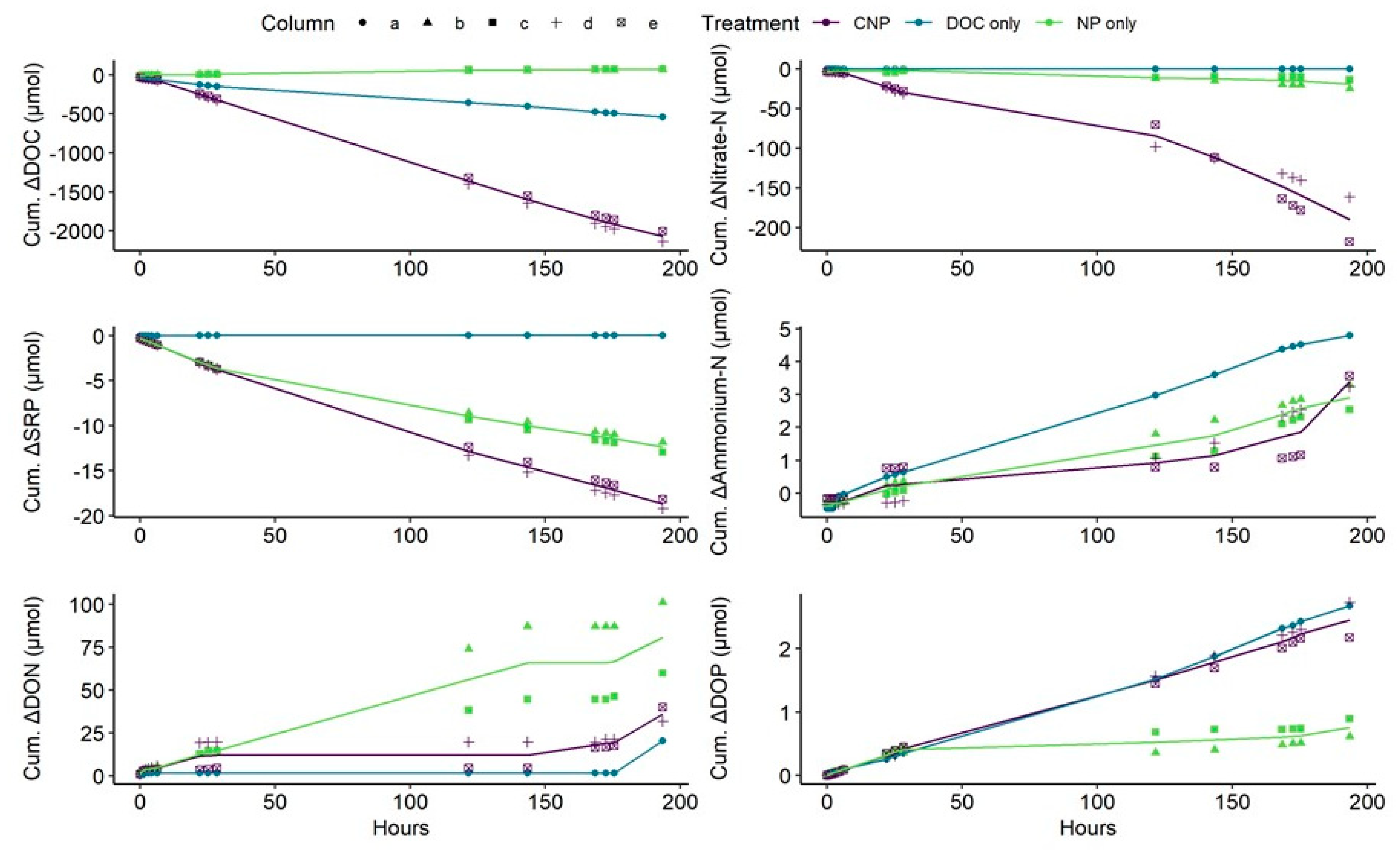
3.3. Column Eluant versus Treatment Inflow Concentrations and Nutrient Uptake Rates
3.4. Destructive Sediment Sampling Post-Column Treatments
4. Discussion
4.1. Antecedent Sediment Conditions and Background Nutrient Leaching
4.2. The Differences Between N and P Retention and Recycling
4.3. Support for Uptake Mechanisms Using Sediment Analyses and Stoichiometric Change
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jarvie, H.P.; Smith, D.R.; Norton, L.R.; Edwards, F.K.; Bowes, M.J.; King, S.M.; Davies, S.S.; Dils, R.M.; Bachiller-Jarenoa, N. Phosphorus and nitrogen limitation and impairment of headwater streams relative to rivers in Great Britain: A national perspective on eutrophication. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Bennet, E.M. Reconsideration of the planetary boundary for phosphorus. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Bouska, W.W.; Eitzmann, J.L.; Pilger, T.J.; Pitts, K.L.; Riley, A.J. Eutrophication of U.S. freshwaters: Analysis of potential economic damages. Envrion. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kronvang, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Conley, D.J.; Sondergaard, M.; Larsen, S.E.; Ovesen, N.B.; Carstensen, J. Nutrient pressures and ecological responses to nutrient loading reductions in Danish streams, lakes and coastal waters. J. Hydrol. 2005, 304, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelhofer, G. The potential of agricultural headwater streams to retain soluble reactive phosphorus. Hydrobiologia 2017, 793, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weigelhofer, G.; Welti, N.; Hein, T. Limitations of stream restoration for nitrogen retention in agricultural headwater streams. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 60, 224–234. [Google Scholar]
- Graeber, D.; Gelbrecht, J.; Pusch, M.T.; Anlanger, C.; von Schiller, D. Agriculture has changed the amount and composition of dissolved organic matter in Central European headwater streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeber, D.; Boëchat, I.G.; Encina-Montoya, F.; Esse, C.; Gellbrecht, J.; Goyenola, G.; Gucker, B.; Heinz, M.; Kronvang, B.; Meerhoff, M.; et al. Global effects of agriculture on fluvial dissolved organic matter. Nature Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinz, M.; Graeber, D.; Zak, D.; Zwirnmann, E.; Gelbrecht, J.; Pusch, M. Comparison of organic matter composition in agricultural versus forest affected headwaters with special emphasis on organic nitrogen. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritzberg, E.; Hasselquist, E.M.; Škerlep, M.; Löfgren, S.; Olsson, O.; Stadmark, J.; Valinia, S.; Hansson, L.-A.; Laudon, H. Browning of freshwaters: Consequences to ecosystem services, underlying drivers, and potential mitigation measures. Ambio 2020, 49, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanley, E.H.; Powers, S.M.; Lottig, N.R.; Buffam, I.; Crawford, J.T. Contemporary changes in dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in human-dominated rivers: Is there a role for DOC management? Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57 (Suppl. S1), 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gücker, B.; Silva, R.C.S.; Graeber, D.; Monteiro, J.A.F.; Boechat, I.G. Urbanization and agriculture increase exports and differentially alter elemental stoichiometry of dissolved organic matter (DOM) from tropical catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to Biosphere; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dodds, W.K.; Marti, E.; Tank, J.L.; Pontius, J.; Hamilton, S.K.; Grimm, N.B. Carbon and nitrogen stoichiometry and nitrogen cycling rates in streams. Ecosyst. Ecol. 2004, 140, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, W.F.; Benstead, J.P.; Frost, P.C.; Thomas, S.A. Ecological stoichiometry in freshwater benthic systems: Recent progress and perspectives. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1895–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.T.; Royer, T.V.; Edgerton, J.M.; Leff, L.G. Manipulation of the dissolved organic carbon pool in an agricultural stream: Responses in microbial community structure, denitrification, and assimilatory nitrogen uptake. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.I.; Graeber, D.; Evans, C.D.; Wade, A.J.; Whiters, P.J.A. Balancing macronutrient stoichiometry to alleviate eutrophication. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Kaplan, L.A.; Findlay, S.; Hopkinson, C.S.; Marti, E.; Packman, A.I.; Newbold, J.D.; Sabater, F. Biophysical controls on organic carbon fluxes in fluvial networks. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.R.; Doyle, M.W. Sediment-water surface area along rivers: Water column versus benthic. Ecosystems 2018, 21, 1505–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.T.; Dolph, C.L.; Finlay, J.C. Do wetlands enhance downstream denitrification in agricultural landscapes? Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.G.; Townsend, A.R. Stoichiometric control of organic carbon-nitrate relationships from soils to the sea. Nature 2010, 464, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Cardona, B.; Wymore, A.S.; McDowell, W.H. DOC:NO3−ratios and NO3− uptake in forested headwater streams. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wymore, A.S.; Coble, A.A.; Rodríguez-Cardona, B.; McDowell, W.H. Nitrate uptake across biomes and the influence of elemental stoichiometry: A new look at LINX II. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2016, 30, 2016GB005468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernhardt, E.S.; Likens, G.E. Dissolved organic carbon enrichment alters nitrogen dynamics in a forest stream. Ecology 2002, 83, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, W.V.; Findlay, S.; Dye, S. Relationships between DOC bioavailability and nitrate removal in an upland stream: An experimental approach. Biogeochemistry 2003, 62, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Leff, L.G. Impacts of labile organic carbon concentration on organic and inorganic nitrogen utilization by a stream biofilm bacterial community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7130–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oviedo-Vargas, D.; Royer, T.V.; Johnson, L.T. Dissolved organic carbon manipulation reveals coupled cycling of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in a nitrogen-rich stream. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, H.A.; Marcarelli, A.M.; Baxter, C.V.; Inouye, R.S. Effects of N, P, and organic carbon on stream biofilm nutrient limitation and uptake in a semi-arid watershed. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.O. Evidence for coupling of the carbon and phosphorus biogeochemical cycles in freshwater microbial communities. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brailsford, F.L.; Glanville, H.C.; Golyshin, P.N.; Marshall, M.R.; Lloyd, C.E.; Johnes, P.J.; Jones, D.L. Nutrient enrichment indices a shift in dissolved organic carbon (DOC) metabolism in oligotrophic freshwater sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stutter, M.; Wyness, A.; Watson, H.; Dodd, N. Coupled macronutrient cycling in stream biofilms: Effects of stoichiometry, light and temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, C.J.; Yeager, A.D.; Cook, S.C.; Doyle, R.D.; Maurer, J.R.; Walker, C.M.; Back, J.A.; Whigham, D.F.; King, R.D. Low-level dissolved organic carbon subsidies drive a tropic upsurge in a boreal stream. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 65, 920–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.I.; Langan, S.J.; Cooper, R.J. Spatial and temporal dynamics of stream water particulate and dissolved N, P and C forms along a catchment transect, NE Scotland. J. Hydrol. 2008, 350, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggerty, R.; Wondzell, S.M.; Johnson, M.A. Power-law residence time distribution in the hyporheic zone of a 2nd-order mountain stream. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 18-1–18-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farmer, V.C.; Russell, J.D.; Smith, B.F.L. Extraction of Inorganic Forms of translocated Al, Fe and Si from a podzol Bs horizon. J. Soil Sci. 1983, 34, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeber, D.; Gelbrecht, J.; Kronvang, B.; Gücker, B.; Pusch, M.T.; Zwirnmann, E. Technical Note: Comparison between a direct and the standard, indirect method for dissolved organic nitrogen determination in freshwater environments with high dissolved inorganic nitrogen concentrations. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 4873–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graeber, D.; Gücker, B.; Zwirnmann, E.; Kronvang, B.; Weih, C.; Gelbrecht, J. Dialysis is superior to anion exchange for removal of dissolved inorganic nitrogen from freshwater samples prior to dissolved organic nitrogen determination. Environ. Chem. 2012, 9, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.R.; Tyler, H.L.; Millar, J.J. Determination of microbial extracellular enzyme activity in waters, soils and sediments using high throughput microplate assays. J. Vis. Exp. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Powlson, D.S.; Jenkinson, D.S. Measurement of soil microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Joergensen, R.G.; Pommerening, B.; Chaussod, R.; Brookes, P.C. Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation-extraction—An automated procedure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Landman, A.; Pruden, G. Chloroform fumigation and release of soil N: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass N in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; He, Z.-L.; Wei, W.-X.; O’Donell, A.G.; Syers, J.K. Quantifying microbial biomass phosphorus in acid soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 32, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouder, J.N.; Speckman, P.L.; Sun, D.; Morey, R.D.; Iverson, G. Bayesian t tests for accepting and rejecting the null hypothesis. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2009, 16, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkenberry, T.J. A simple method for teaching bayesian hypothesis testing in the brain and behavioral sciences. J. Undergrad. Neurosci. Educ. 2018, 16, A126–A130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Morey, R.D.; Rouder, J.N. BayesFactor: Computation of Bayes factors for Common Designs. R package version 0.9.12-4.2. 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/BayesFactor/BayesFactor.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Kass, R.E.; Raftery, A.E. Bayes factors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 773–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdown, K.; Heppell, C.M.; Trimmer, M.; Binley, A.; Heathwaite, A.L.; Bryne, P.; Zhang, H. The interplay between transport and reaction rates as controls on nitrate attenuation in permeable, streambed sediments. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 120, 1093–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hueck, C.; Weig, A.; Spohn, M. Soil microbial biomass C:N:P stoichiometry and microbial use of organic phosphorus. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 85, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutschlechner, A.E.; Guerard, J.J.; Jones, J.B.; Harms, T.K. Phosphorus enhances uptake of dissolved organic matter in boreal streams. Ecosystems 2018, 21, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, C.M.; Cotner, J.B. Stoichiometric flexibility in diverse aquatic heterotrophic bacteria is coupled to differences in cellular phosphorus quotas. Front. Microbiol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLaughlin, C.; Kaplan, L.A. Biological lability of dissolved organic carbon in streamwater and contributing terrestrial sources. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 32, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Torres, Y.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.D.; Elser, J.L.; Islas, A.; Souza, V.; Garcia-Olivia, F.; Oleda-Almerez, G. How to live with phosphorus scarcity in soil and sediment: Lessons from bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2016, 82, 4652–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagul, E. A The molybdenum blue reaction for the determination of orthophosphate revisited: Opening the black box. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pokrovsky, O.S.; Manasypov, R.M.; Loiko, S.V.; Shirikova, L.S. Organic and organo-mineral colloids of discontinuous permafrost zone. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 188, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Reference Leaching | Columns | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctreat | NPtreat1 | NPtreat2 | CNPtreat1 | CNPtreat2 | |||
| (a) | |||||||
| Sediment DM | g | 55 | 53.8 | 52.4 | 52.4 | 53.7 | |
| Column PV | mL | 5.9 | 6.1 | 5 | 6.3 | 5.8 | |
| NO3-N | µmol/L | 0.7 | 1.9 | 2.6 | 5.6 | 9.3 | |
| NH4-N | µmol/L | 13.4 | 9.7 | 8.9 | 10.6 | 4.6 | |
| SRP | µmol/L | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.65 | |
| DOC | µmol/L | 211 | 151 | 172 | 196 | 233 | |
| DON | µmol/L | 14.7 | 10.0 | 5.4 | 10.4 | 7.4 | |
| DOP | µmol/L | 0.35 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.39 | |
| C:N:P of background leaching | Molar ratio | 251:34:1 | 162:23:1 | 190:19:1 | 265:36:1 | 226:21:1 | |
| (b) | |||||||
| NO3-N | µmol h−1 kg−1 DM | 1.5 | 0.0 | −2.2 | −1.2 | −15.7 | −18.3 |
| NH4-N | µmol h−1 kg−1 DM | 3.4 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| SRP | µmol h−1 kg−1 DM | 0.2 | 0.0 | −1.1 | −1.3 | −1.9 | −1.7 |
| DOC | µmol h−1 kg−1 DM | 70.2 | −49.1 | 6.2 | 8.8 | −208.5 | −192.8 |
| DON | µmol h−1 kg−1 DM | 3.5 | 0.2 | 9.1 | 5.5 | 3.0 | 1.8 |
| DOP | µmol h−1 kg−1 DM | 0.13 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| C:N:P of outflow at ~600 PV | Molar ratio | 408:18:1 | 11:24:1 | 12:28:1 | 35:20:1 | 62:11:1 | |
| Eluant DO at ~500 PV | mgO2/L | nd | 6.56 ± 0.03 | 6.95 ± 0.01 | 6.93 ± 0.02 | 4.12 ± 0.36 | 3.98 ± 0.29 |
| O2 uptake | µmol h−1 kg−1 DM | nd | 23.6 | 20.8 | 21.6 | 53.1 | 53.4 |
| Column Treatment | MBC | MBN | MBP | MBC:MBN | MBC:MBP | Phosphatase Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (µmol/kg DM) | (µmol/kg DM) | (µmol/kg DM) | Molar Ratio | Molar Ratio | (µmol h−1 kg−1 DM) | |
| Background | 4170 | 370 | 3.2 | 11.3 | 1322 | 118 |
| Ctreat | 2067 | 320 | 0.3 | 6.5 | 6644 | 384 |
| NPtreat1 | 108 | 102 | 4.8 | 1.1 | 22 | 182 |
| NPtreat2 | 311 | 150 | 6.5 | 2.1 | 48 | 212 |
| CNPtreat1 | 1800 | 146 | 4.2 | 12.3 | 429 | 369 |
| CNPtreat2 | 2202 | 395 | 10.7 | 5.6 | 205 | 362 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stutter, M.; Graeber, D.; Weigelhofer, G. Available Dissolved Organic Carbon Alters Uptake and Recycling of Phosphorus and Nitrogen from River Sediments. Water 2020, 12, 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123321
Stutter M, Graeber D, Weigelhofer G. Available Dissolved Organic Carbon Alters Uptake and Recycling of Phosphorus and Nitrogen from River Sediments. Water. 2020; 12(12):3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123321
Chicago/Turabian StyleStutter, Marc, Daniel Graeber, and Gabriele Weigelhofer. 2020. "Available Dissolved Organic Carbon Alters Uptake and Recycling of Phosphorus and Nitrogen from River Sediments" Water 12, no. 12: 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123321
APA StyleStutter, M., Graeber, D., & Weigelhofer, G. (2020). Available Dissolved Organic Carbon Alters Uptake and Recycling of Phosphorus and Nitrogen from River Sediments. Water, 12(12), 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123321







