Antimicrobials and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: A Risk to the Environment and to Public Health
Abstract
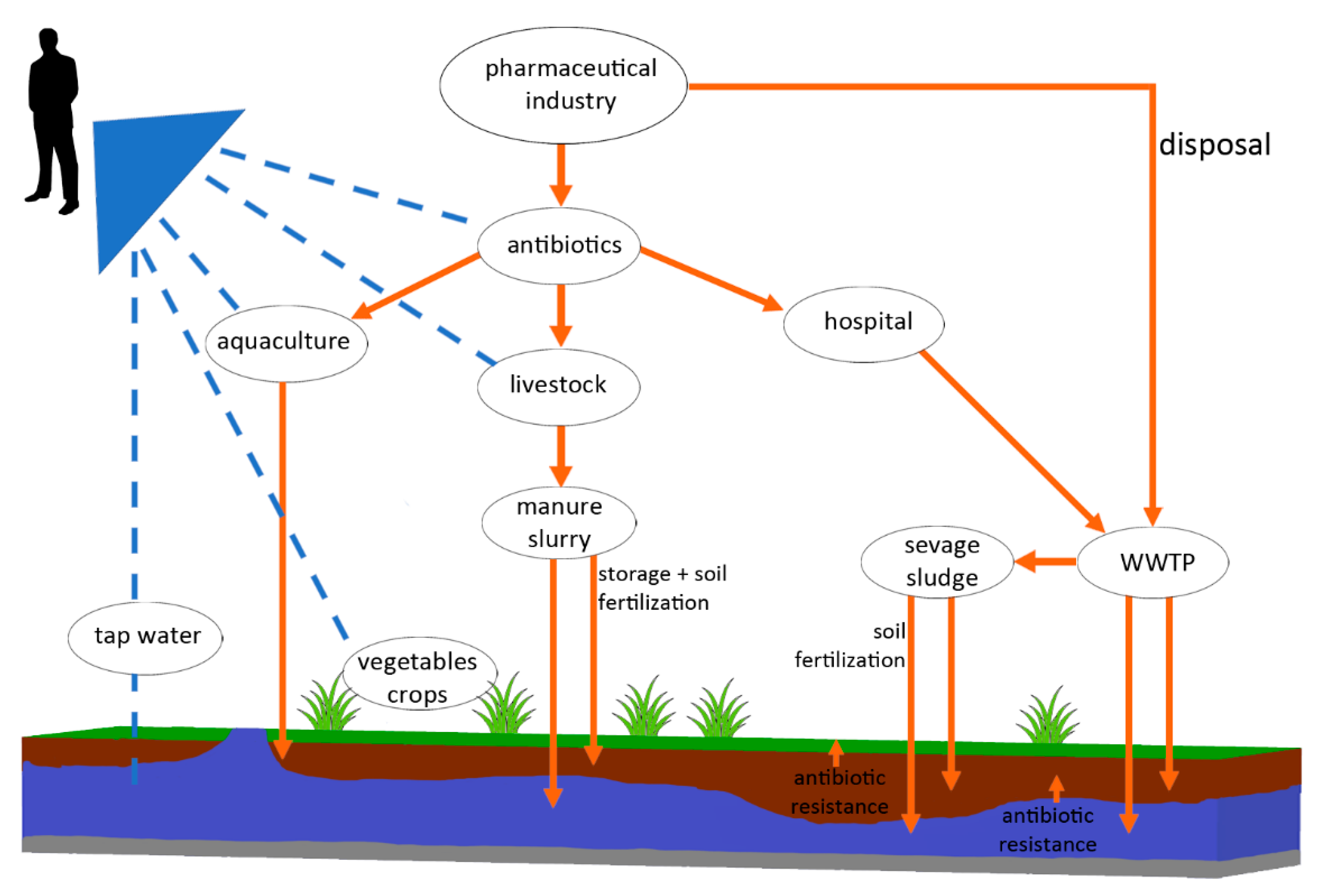
:1. Introduction
2. The Fate of Antibiotics in the Environment and their Biological Effects
3. Sub-Inhibitory Concentrations of Antibiotics in the Environment and their Biological Effects
4. Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria (ARB)
5. Antibiotics, ARB, and ARG in Water, Wastewater, and Sewage Sludge
6. Antibiotic Residues and Antimicrobial Resistance in Agriculture
7. Antimicrobials in Aquaculture
8. Government Policy Interventions to Protect Antimicrobials
9. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.; Tang, J.C. Research of antibiotics pollution in soil environments and its ecological toxicity. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Czekalski, N.; Gascon Díez, E.; Bürgmann, H. Wastewater as a point source of antibiotic-resistance genes in the sediment of a freshwater lake. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe 2015; Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net); ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017; Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/media/en/publications/Publications/antimicrobial-resistance-europe-2015.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2020).
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manaia, C.M. Assessing the Risk of Antibiotic Resistance Transmission from the Environment to Humans: Non-Direct Proportionality between Abundance and Risk. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grare, M.; Mourer, M.; Fontanay, S.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.B.; Finance, C.; Duval, R.E. In Vitro activity of paraguanidinoethylcalixarene against susceptible and antibiotic resistant Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Kraker, M.E.A.; Davey, P.G.; Grundmann, H. Mortality and hospital stay associated with resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli bacteremia: Estimating the burden of antibiotic resistance in Europe. PLoS Med. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlet, J.; Collignon, P.; Goldmann, D.; Goossens, H.; Gyssens, I.C.; Harbarth, S.; Jarlier, V.; Levy, S.B.; N’Doye, B.; Pittet, D.; et al. Society’s failure to protect a precious resource: Antibiotics. Lancet 2011, 378, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruden, A.; Pei, R.; Storteboom, H.; Carlson, K.H. Antibiotic resistance genes as emerging contaminants: Studies in northern Colorado. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7445–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2014. Available online: http://www.jpiamr.eu/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/AMR-Review-Paper-Tackling-a-crisis-for-the-health-and-wealth-of-nations_1-2.pdf (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2016. Available online: https://amrreview.org/sites/default/files/160525_Final%20paper_with%20cover.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2020).
- Katz, S.E. The effects of human health. In Subtherapeutic Use of Antimicrobials in Animal Feeds; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Dong, Y.H.; Wang, H. Residues of veterinary antibiotics in manures from feedlot livestock in eight provinces of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbel, A.; McArdell, C.S.; Suter, M.J.F.; Giger, W. Trace determination of macrolide and sulfonamide antimicrobials a human sulfonamide metabolite and trimetoprim in wastewater using liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4756–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, N. Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.F.; Ying, G.G.; Zhao, J.L.; Tao, R.; Su, H.C.; Chen, F. Simultaneous determination of four classes of antibiotics in sediments of the Pearl Rivers using RRLC–MS/MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3424–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review: Part I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, G.; Sommer, M.O.; Oluwasegun, R.D.; Church, G.M. Bacteria subsisting on antibiotics. Science 2008, 320, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turiel, E.; Bordin, G.; Rodríguez, A.R. Study of the evolution and degradation products of ciprofloxacin and oxolinic acid in river water samples by HPLC-UV/MS/MS-MS. J. Environ. Monit. 2005, 7, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.L. Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by an-tibiotic resistance determinants. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, M.; Spielmeyer, A.; Zom, H.; Hamscher, G. Degradation and transformation of fluoroquinolones by microorganisms with special emphasis on ciprofloxacin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 6933–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; de Pedro, C.; Paxeus, N. Effluent from drug manufactures contains extremely high levels of pharmaceuticals. J. Hazard Mater. 2007, 148, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jechalke, S.; Heuer, H.; Siemens, J.; Amelung, W.; Smalla, K. Fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics in soil. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 22, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee-Sanford, J.; Krapac, I.J.; Yannarell, A.C.; Mackie, R.I. Environmental Impacts of Antibiotic Use in the Animal Production Industry. Ecol. Anim. Health Ecosyst. Health Sustain. Agric. 2012, 2, 228–368. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ryu, D.; Houtkooper, R.H.; Auwerx, J. Antibiotic use and abuse: A threat to mitochondria and chloroplasts with impact on research, health, and environment. Bioessays 2015, 37, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minden, V.; Deloy, A.; Volkert, A.M.; Leonhardt, S.D.; Pufal, G. Antibiotics impact plant traits, even at small concentrations. AoB Plants 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darwish, W.S.; Eldaly, E.A.; El-Abbasy, M.T.; Ikenaka, Y.; Nakayama, S.; Ishizuka, M. Antibiotic residues in food: The African scenario. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 2013, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, R.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Pasier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, M.; Batto, J.-M. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Academies of Sciences Medicine. Environmental Chemicals, the Human Microbiome, and Health Risk: A Research Strategy. 2018. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK481563/ (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Damman, C.J.; Miller, S.; Surawicz, C.; Zisman, T. The Microbiome and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Is There a Therapeutic Role for Fecal Microbiota Transplantation? Am. J. Gastroentero. 2012, 107, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, L.M.; Yamanishi, S.; Sohn, J.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Leung, J.M.; Cho, I.; Mahana, D. Altering the Intestinal Microbiota during a Critical Developmental Window Has Lasting Metabolic Consequences. Cell 2014, 158, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, I.; Yamanishi, S.; Cox, L.; Methé, B.A.; Zavadil, J.; Li, K.; Li, H. Antibiotics in early life alter the murine colonic microbiome and adiposity. Nature 2012, 488, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Larsson, D.G. Concentrations of antibiotics predicted to select for resistant bacteria: Proposed limits for environmental regulation. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gullberg, E.; Cao, S.; Berg, O.G.; Ilbäck, C.; Sandegren, L.; Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Selection of resistant bacteria at very low antibiotic concentrations. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Evolution of antibiotic resistance at non-lethal drug concentrations. Drug Resist. Update 2012, 15, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, E.B.; Yim, G.; Tsui, W.; McClure, J.; Surette, M.G.; Davies, J. Transcriptional modulation of bacterial gene expression by subin-hibitory concentrations of antibiotics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 17025–17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaw, K.J.; Miller, N.; Liu, X.; Lerner, D.; Wan, J.; Bittner, A.; Morrow, B.J. Comparison of the changes in global gene expression of Escherichia coli induced by four bactericidal agents. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 5, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.; Ryan, K.S. Introducing the parvome: Bioactive com-pounds in the microbial word. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laureti, L.; Matic, I.; Gutierrez, A. Bacterial responses and genome instability induced by subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics. Antibiotics 2013, 2, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Couce, A.; Blazquez, J. Side effects of antibiotics on genetic variability. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blázquez, J.; Couce, A.; Rodríguez-Beltrán, J.; Rodríguez-Rojas, A. Antimicrobials as promoters of genetic variation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchmann, J.; Kirchen, S.; Schwartz, T. Sub-inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics and wastewater influencing biofilm formation and gene expression of multi-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa wa-stewater isolates. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 3539–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Renzoni, A.; Estoppey, T.; Bisognano, C.; Francois, P.; Kelley, W.L.; Lew, D.P.; Schrenzel, J.; Vaudaux, P. Induction of fibronectin adhesins in quinolone-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by subinhibitory levels of ciprofloxacin or by sigma B transcription factor activity is mediated by two separate pathways. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joo, H.S.; Chan, J.L.; Cheung, G.Y.; Otto, M. Subinhibitory con-centrations of protein synthesis-inhibiting antibiotics promote in-creased expression of the agr virulence regulator and production of phenol-soluble modulin cytolysins in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4942–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, L.K.M.; Ghaly, T.M.; Gillings, M.R. A survey of sub-inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics in the environment. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, D.A.; Pry, T. Limit of blank, limit of detection and limit of quantitation. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2008, 29, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, Data from the EU—CAST MIC Distribution Website. Available online: https://eucast.org/ (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Yu, L.F. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, R.L.; Monnet, D.L. Plasmid-mediated colistin resistance (mcr-1 gene): Three months later, the story unfolds. Eurosurveillance 2016, 21, 30155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Zhao, Y.I.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; Zhang, S.Y.; Yu, S.; Su, J.Q. Continental-scale pollution of estuaries with antibiotic resistance genes. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 16270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengge-Aronis, R. Signal transduction and regulatory mechanisms involved in control of the δS (RpoS) subunit of RNA poly-merase. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, S.M.; Schellhorn, H.E. Evolution of the RpoS regulon: Origin of RpoS and the conservation of RpoS-dependent regulation in bacteria. J. Mol. Evol. 2010, 70, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, A.; Laureti, L.; Crussard, S.; Abida, H.; Rodriguez-Rojas, A.; Blazquez, J.; Baharoglu, Z.; Mazel, D.; Darfeuille, F.; Vogel, J.; et al. β-lactam antibiotics promote bacterial mutagenesis via an RpoS-me-diated reduction in replication fidelity. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tenover, F.C. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lopez, R.; de Toro, M.; Moncalian, G.; Garcillan-Barcia, M.P.; de la Cruz, F. Comparative genomics of the conjugation region of F-like plasmids: Five shades of F. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2016, 3, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De la Cruz, F.; Davies, J. Horizontal gene transfer and the origin of species: Lessons from bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbolt, N.J.; Amézquita, A.; Backhaus, T.; Borriello, P.; Brandt, K.K.; Collignon, P.; Lawrence, J.R. Human Health Risk Assessment (HHRA) for environmental development and transfer of antibiotic resistance. Environ. Health. Perspect. 2013, 121, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, J.L. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Science 2008, 321, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perron, G.G.; Whyte, L.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Goordial, J.; Hanage, W.P.; Dantas, G.; Desai, M.M. Functional characterization of bacteria isolated from ancient arctic soil exposes diverse resistance mechanisms to modern antibiotics. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0069533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Rodriguez, T.M.; Fornaciari, G.; Luciani, S.; Dowd, S.E.; Toranzos, G.A.; Marota, I.; Cano, R.J. Gut microbiome of an 11th century A.D. pre-columbian andean mummy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rascovan, N.; Telke, A.; Raoult, D.; Rolain, J.M.; Desnues, C. Exploring divergent antibiotic resistance genes in ancient metagenomes and discovery of a novel beta-lactamase family. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 8, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaitan, A.O.; Rolain, J.M. Ancient resistome. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugli, G.A.; Milani, C.; Mancabelli, L.; Turroni, F.; Ferrario, C.; Duranti, S.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Ancient bacteria of the Otzi’s microbiome: A genomic tale from the copper age. Microbiome 2017, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweney, M.T.; Lubbers, B.V.; Schwarz, S.; Watts, J.L. Applying definitions for multidrug resistance, extensive drug resistance and pandrug resistance to clinically significant livestock and companion animal bacterial pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1460–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, L.; Sharp, H.; Hille, K.; Seibt, U.; Fischer, J.; Pfeifer, Y.; Michael, G.B.; Nickel, S.; Friese, A.; Bauerfeind, R.; et al. Subgrouping of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli from animal and human sources: An approach to quantify the distribution of ESBL types between different reservoirs. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Stephan, R. Epidemiology of extendedspectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in the humanlivestock environment. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep 2016, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tîrziu, E.; Lazăr, R.; Sala, C.; Nichita, I.; Morar, A.; Şereş, M.; Imre, K. Salmonella in raw chicken meat from the Romanian seaside: Frequency of isolation and antibiotic resistance. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppé, É.; Woerther, P.L.; Barbier, F. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative bacilli. Ann. Intensive Care 2015, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bush, K.; Jacoby, G.A. Updated functional classification of -lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyagi, K.; Hirai, I. A survey of extended-spectrum b-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in environmental water in Okinawa Prefecture of Japan and relationship with indicator organisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7697–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.G.; Litake, G.M. Acinetobacter baumannii: An emerging pathogenic threat to public health. World J. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 3, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, H.G.; Moghim, S.; Isfahani, B.N.; Fazeli, H.; Poursina, F.; Yadegari, S.; Nasirmoghadas, P.; Hosseininassab Nodoushan, S.A. Distribution of the strains of multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant, and pandrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from burn patients. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2017, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Xu, X.; Yao, J.; Deng, K.; Chen, S.; Shen, Z.; Yang, L.; Feng, G. Predictors of mortality in patients infected with carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Infect. Control 2019, 47, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arora, S.; Gautam, V.; Rana, S.; Ray, P. Novel chromogenic medium for detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae, methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin resistant Enterococcus. J. Med. Investig. Pract. 2014, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djenadi, K. Antibiotic resistance bacteria from rivers water in Algeria. J. Bacteriol. Parasitol. 2017, 8, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations, World Organisation for Animal Health. In Monitoring Global Progress on Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance: Analysis Report of the Second Round of Results of AMR Country Self-Assessment Survey; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Czekalski, N.; Sigdel, R.; Birtel, J.; Matthews, B.; Bürgmann, H. Does human activity impact the natural antibiotic resistance background? Abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in 21 Swiss lakes. Environ. Int. 2015, 81, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hao, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, N.; Ye, B. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes of wastewater and surface water in livestock farms of Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 13950–13959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, D.; He, S.; Ye, H.; Zhang, L.; Wen, Y.; Chen, S. Prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in drinking water sources in Hangzhou city. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieliński, W.; Korzeniewska, E.; Harnisz, M.; Hubeny, J.; Buta, M.; Rolbiecki, D. The prevalence of drug-resistant and virulent Staphylococcus spp. in a municipal wastewater treatment plant and their spread in the environment. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Z.; Zhang, X. blaNDM-1-carrying Acinetobacter johnsonii detected in hospital sewage. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maravić, A.; Skočibusić, M.; Cvjetan, S.; Šamanić, I.; Puizina, J.; Fredotović, Ž. Prevalence and diversity of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae from marine beach waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Sun, D. Detection of, NDM-1 carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and Acinetobacter junii in environmental samples from livestock farms. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serwecińska, L.; Kiedrzyńska, E.; Kiedrzyński, M. A catchment-scale assessment of the sanitary condition of treated wastewater and river water based on fecal indicators and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter spp. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 142266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, E.; McClellan, K.; Halden, R.U. Occurrence and loss over three years of 72 pharmaceuticals and personal care products from biosolids-soil mixtures in outdoor mesocosms. Water Res. 2010, 44, 6011–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reis, A.; Kolvenbach, B.A.; Nunes, O.C.; Corvini, P.F.X. Biodegradation of antibiotics: The new resistance determinants—Part I. New Biotechnol. 2016, 54, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.M.; Ullman, J.L.; Teel, A.L.; Watts, R.J. Hydrolysis of amphenicol and macrolide antibiotics: Chloramphenicol, florfenicol, spiramycin, and tylosin. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Peters, D. Photodegradation of pharmaceutical antibiotics on slurry and soil surfaces. Landbauforsch. Volkenrode 2007, 57, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kümmerer, K. Drugs in the environment: Emission of drugs, diagnostic aids and disinfectants into wastewater by hospitals in relation to other sources—A review. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, E.; Bonetta, S.; Bertino, C.; Lorenzi, E.; Bonetta, S.; Gilli, G. Hospital effluents management: Chemical, physical, microbiological risks and legislation in different countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 168, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak, M.; Wyrwicka, A.; Tołoczko, W.; Serwecińska, L.; Zieliński, M. The effect of sewage sludge application on soil properties and willow (Salix sp.) cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero-Caceres, W.; Colomer-Lluch, M.; Stoll, C.; Lucena, F.; Jofre, J.; Muniesa, M. Sludge as potential important source of antibiotic resistance genes in both the bacterial and bacteriophage fractions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7602–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.; Wong, K.; Xagoraraki, I. Release of antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes in the effluent and biosolids of five wastewater utilities in Michigan. Water Res. 2011, 45, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potron, A.; Poiller, L.; Nordmann, P. Emerging Broad-spectrum resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii: Mechanisms and epidemiology. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2015, 45, 568–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tello, A.; Austin, B.; Telfer, T.C. Selective pressure of antibiotic pollution on bacteria of importance to public health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, C.W.; Dolfing, J.; Ehlert, P.A.I.; Graham, D.W. Evidence of increasing antibiotic resistance gene abundances in archived soils since 1940. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zelong, Z.; Jngwen, C.; Lu, L.; Liu, L.; Zhou, J.; Guan, X. PAHs accelerate the propoagation of antibiotic resistance genes in coastal water microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, N.; Sun, P.; Sun, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Ji, X.; Dyar, O.J. Presence of antibiotic residues in various environmental compartments of Shandong province in eastern China: Its potential for resistance development and ecological and human risk. Environ. Int. 2018, 114, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, A.M.; Ciorba, P.; Döhla, M.; Exner, M.; Felder, C.; Lenz-Plet, F.; Sib, E.; Skutlarek, D.; Schmithausen, R.M.; Faerbe, H.A. The investigation of antibiotic residues, antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotic-resistant organisms in a drinking water reservoir system in Germany. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 224, 113449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, A.R.; Al-Haideri, H.H.; Hassan, F.M. Detection of Antibiotics in Drinking Water Treatment Plants in Baghdad City, Iraq. Adv. Public Health 2019, 7851354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, D.I. Persistence of antibiotic resistant bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnisz, M. Total resistance of native bacteria as an indicator of changes in the water environment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 174, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittinger, C.; Kirschner, A.; Lipp, M.; Baumert, R.; Mascher, F.; Farnleitner, A.H.; Zarfel, G.E. Antibiotic Resistance of Acinetobacter spp. Isolates from the River Danube: Susceptibility Stays High. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harmon, D.E.; Miranda, O.A.; McCarley, A.; Eshaghian, M.; Carlson, N.; Ruiz, C. Prevalence and characterization of carbapenem-resistant bacteria in water bodies in the Los Angeles–Southern California area. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marti, E.; Jofre, J.; Balcazar, J.L. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community composition in a river influenced by a wastewater treatment plant. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, N.A.; Schmitt, H.; Van der Zaan, B.; Gerritsen, H.W.; Zuidema, T.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Langenhoff, A.A.M. Prevalence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in a wastewater effluent-receiving river in The Netherlands. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.L.; Boehm, A.B.; Davies-Colley, R.J.; Dodd, M.C.; Kohn, T.; Linden, K.G.; Nguyen, T.H. Sunlight-mediated inactivation of health-relevant microorganisms in water: A review of mechanisms and modeling approaches Environmental Science Processes & Impacts. Critical review. Anim. Physiol. 2018, 20, 1089–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Dodd, M.C.; Lee, Y. Elimination of transforming activity and gene degradation during UV and UV/H2 O2 treatment of plasmid-encoded antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control); EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); EMA (European Medicines Agency). ECDC/EFSA/EMA second joint report on the integrated analysis of the consumption of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from humans and food-producing animals—Joint Interagency Antimicrobial Consumption and Resistance Analysis (JIACRA) Report. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, B. MRSA: Farming up trouble. Nature 2013, 499, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA/AMEG (European Medicines Agency—Antimicrobial Advice Ad Hoc Expert Group). Answers to the Requests for Scientific Advice on the Impact on Public Health and Animal Health of the Use of Antibiotics in Animals. 2014. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/ Other/2014/07/WC500170253 (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- WHO. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/255027/1/9789241512220-eng.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobials in Agriculture and the Environment: Reducing Unnecessary Use and Waste. The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; HM Government: London, UK, 2015; p. 40. Available online: https://amr-review. org/sites/default/files/Antimicrobials%20in%20agriculture%20and%20the% 20environment%20-%20Reducing%20unnecessary%20use%20and%20waste.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Kümmerer, K. Resistance in the environment. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McManus, P.S.; Stockwell, V.O.; Sundin, G.W.; Jones, A.L. Antibiotic use in plant agriculture. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2002, 40, 443–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymann, K.; Shaffer, Z.; Nancy, A.; Moran, N.A. Antibiotic exposure perturbs the gut microbiota and elevates mortality in honeybees. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.M.; Levy, S.B. Food animals and antimicrobials: Impacts on human health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, P.Y.; Yannarell, A.; Mackie, R.I. The Contribution of Antibiotic Residues and Antibiotic Resistance Genes from Livestock Operations to Antibiotic Resistance in the Environment and Food Chain; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kariuki, S.; Onsare, R.; Mwituria, J.; Ng’etich, R.; Nafula, C.; Karimi, K.; Karimi, P.; Njeruh, F.; Irungu, P.; Mitema, E. FAO/WHO Project Report. Improving Food Safety in Meat Value Chains in Kenya. Food Protec. Trends 2013, 33, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Marti, R.; Scott, A.; Tien, Y.C.; Murray, R.; Sabourin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Topp, E. Impact ofmanure fertilization on the abundance of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and frequency of detection ofantibiotic resistance genes in soil and on vegetables at harvest. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5701–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria: A challenge for the food industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessler, A.T.; Olde, R.G.; Riekerink, G.; Rothkamp, A.; Kadlec, K.; Sampimon, O.C.; Lam, T.J.; Schwarz, S. Characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC398 obtained from humans and animals on dairy farms. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 160, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreausukon, K.; Fetsch, A.; Kraushaar, B.; Alt, K.; Müller, K.; Krömker, V.; Zessin, K.H.; Käsbohrer, A.; Tenhagen, B.A. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from bulk tank milk of dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 4382–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morar, A.; Sala, C.; Imre, K. Occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella isolates recovered from the pig slaughter process in Romania. J. Infect. Dev. Countr. 2015, 9, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skočková, A.; Bogdanovičová, K.; Koláčková, I.; Karpíšková, R. Antimicrobial resistant and extended Spectrum β-lactamase producing Escherichia coli in raw cow’s milk. J. Food Protect. 2015, 78, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.S.; Benomar, N.; Abriouel, H.; Cañamero, M.M.; Gálvez, A. Isolation and identification of Enterococcus faecium from seafoods: Antimicrobial resistance and production of bacteriocin-like substances. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. In Contributing to Food Security and Nutrition for All; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i5555e.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2020).
- FAO. Fisheries and Aquaculture Department Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. 2010. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/i1820e/i1820e00.htm (accessed on 2 September 2020).
- Cabello, F.C. Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: A growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1137–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Gloria Feijoo, C.; Navarrete, P. Antibiotics in Aquaculture—Use, Abuse and Alternatives. In Health and Environment in Aquaculture; Carvalho, E.D., David, G.D., Silva, R.J., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 159–198. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/health-and-environment-in-aquaculture/ antibiotics-in-aquaculture-use-abuse-and-alternatives (accessed on 2 September 2020). [CrossRef]
- Burridge, L.; Weis, J.S.; Cabello, F.; Pizarro, J.; Bostick, K. Chemical use in salmon aquaculture: A review of current practices and possible environmental effects. Aquaculture 2010, 306, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, F.C.; Godfrey, H.P.; Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Dölz, H.; Millanao, A.; Buschmann, A.H. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: Its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1917–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.H.; Park, S.G.; Choi, S.M.; Hwang, Y.O.; Ham, H.J.; Kim, S.U.; Chae, Y.Z. Antimicrobial resistance and resistance genes in Escherichia coli strains isolated from commercial fish and seafood. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 152, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Done, H.Y.; Venkatesan, A.K.; Halden, R.U. Does the recent growth of aquaculture create antibiotic resistance threats different from those associated with land animal production in agriculture? AAPS J. 2015, 17, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.D.; Chen, D.H.; Huang, M.H. The source of antibiotics in the environment and progress of its ecological impact research. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2010, 35, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maron, D.F.; Smith, T.J.S.; Nachman, K.E. Restrictions on antimicrobial use in food animal production: An international regulatory and economic survey. Glob. Health 2013, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ECDPC. 33000 People Die Every Year Due to Infections with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. 2018. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/33000-people-die-every-year-due-infections-antibiotic-resistant-bacteria (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- CDC. Antibiotic/Antimicrobial Resistance (AR/AMR). 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/index.html (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Hoffman, S.J.; Caleo, G.M.; Daulaire, N.; Elbe, S.; Matsoso, P.; Mossialos, E.; Rizvi, Z.; Røttingen, J.A. Strategies for achieving global collective action on antimicrobial resistance. Bull. World Health Organ. 2015, 93, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Drug Resistant Infections: A Threat to Our Economic Future; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, S.J.; Outterson, K.; Røttingen, J.A.; Cars, O.; Clift, C.; Rizvi, Z.; Zorzet, A. An international legal framework to address antimicrobial resistance. Bull. World Health Organ. 2015, 9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, S.J.; Outterson, K. What will it take to address the global threat of antibiotic resistance? J. Law Med. Ethics 2015, 43, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United Nations General Assembly. Political Declaration of the High-Level Meeting of the General Assembly on Antimicrobial Resistance; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- G20 Health Ministers. Berlin Declaration of the G20 Health Ministers: Together Today for a Healthy Tomorrow. Berlin, Germany. 2017. Available online: http://www.g20.utoronto.ca/2017/170520-health-en.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2020).
- European Parliament Draft Report. On a European One Health Action Plan against Antimicrobial Resistance; AMR: Greenwood Village, CO, USA, 2018; Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/doceo/document/ENVI-PR-613613_EN.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Davey, P.; Marwick, C.A.; Scott, C.L.; Charani, E.; McNeil, K.; Brown, E.; Gould, I.M.; Ramsay, C.R.; Michie, S. Interventions to improve antibiotic prescribing practices for hospital inpatients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2, 1465–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers Van Katwyk, S.; Grimshaw, J.M.; Nkangu, M.; Nagi, R.; Mendelson, M.; Taljaard, M.; Hoffman, S.J. Government policy interventions to reduce human antimicrobial use: A systematic review and evidence map. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, T.; Östergren, P.O. The correlation between regulatory conditions and antibiotic consumption within the WHO European Region. Health Policy 2016, 120, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serwecińska, L. Antimicrobials and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: A Risk to the Environment and to Public Health. Water 2020, 12, 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123313
Serwecińska L. Antimicrobials and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: A Risk to the Environment and to Public Health. Water. 2020; 12(12):3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123313
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerwecińska, Liliana. 2020. "Antimicrobials and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: A Risk to the Environment and to Public Health" Water 12, no. 12: 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123313
APA StyleSerwecińska, L. (2020). Antimicrobials and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: A Risk to the Environment and to Public Health. Water, 12(12), 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123313



