Abstract
In order to reveal the pollution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in surface soil of the region around the Qinghai Lake in Tibet Plateau, improve the prevention awareness and measures of local residents and urge the local government to implement necessary prevention and control measures, nine heavy metals (As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn) in the surface soil samples of the region around the Qinghai Lake have been collected and analyzed. The methods such as statistic method, geo-accumulation index method, Nemerow index method, potential ecological risk index method, human health risk evaluation method and positive matrix factor analysis model (PMF) have been used to evaluate pollution characteristics and potential risks and analyze the sources of heavy metals. The results are shown below. First, the average contents of heavy metals (As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn) in soil are 11.73 ± 3.78, 0.62 ± 1.40, 12.38 ± 3.68, 41.35 ± 13.01, 19.33 ± 8.92, 546.96 ± 159.28, 21.18 ± 7.04, 21.86 ± 6.61 and 63.51 ± 19.71 mg·kg−1, respectively. Compared with the background values of the soil environment in Qinghai Province, it can be seen that there is an accumulation of these heavy metals to varying degrees, which is the most serious in Cd, Co and Pb. Second, the analysis of the geo-accumulation index and Nemerow index indicates that the heavy metals in the surface soil of the region around the Qinghai Lake have reached the level of heavy pollution, mainly polluted by Cd, and the accumulation of heavy metal pollution in the north, south, southwest and southeast of the study area is more serious. Third, the results of potential ecological risk evaluation show that the study area as a whole is classified as an area with high ecological risk, and Cd contributes the most to the overall risk. In fact, the heavy metals in the soil of the study area produce no noncarcinogenic and carcinogenic health risks to human health, and children and adults may be exposed to these risks by the mouth. Finally, the PMF results reveal that the sources of heavy metals in the study area include the sources of agricultural production, the nature, coal burning and transportation, with a contribution rate of 43.10%, 25.34%, 19.67% and 11.89%, respectively.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of the urbanization and industrialization process in China, high-intensity development and utilization of mineral resources and improper use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, heavy metals containing pollutants cannot be degraded by microorganisms after entering the soil, water and other environments [1,2,3], and they are also characterized by long action times, wide ranges of pollution, high concealment and difficulty in being reversed, as a result of which, the heavy metal pollution in soil becomes increasingly severe [4,5]. In this study, it is found that the heavy metals accumulated in the soil finally reach the human body through the food chain after being enriched and absorbed by crops, resulting in potential risks to human health [6]. In recent years, domestic and foreign researchers have carried out a large number of studies on the heavy metal pollution of soil in different areas, finding that there are certain differences in heavy metal pollution under the influence of different factors such as natural conditions, industrial and mining development and traffic accessibility [7], etc.
The region around Qinghai Lake enjoys a unique geographical location, where the industrial and agricultural activities are limited, so it is less polluted by human beings. Although the regional differences in the characteristics and sources of heavy metals in the soil of the region around Qinghai Lake make the content of heavy metals lower than that in other areas of China, with the development and utilization of natural resources and the continuous development of tourism, as well as the industrial development and large population of adjacent areas, the soil ecosystem in the region around Qinghai Lake has been polluted by heavy metals to a certain extent [7,8]. Meanwhile, with the development of traffic, transportation has become one of the artificial factors affecting the content of heavy metals in the roadside soil of Qinghai Lake [9,10]. At present, the study of heavy metals in soil is mainly concentrated in farmland and cultivated land, mining areas and areas around power plants, different urban function areas and both sides of roads, while it is less carried out in the region around Qinghai Lake [11,12,13,14]. Due to local sampling, the correlation analysis focuses mainly on several heavy metals, and the coverage is narrow or the data is sampled early. In fact, it is deemed as an effective premise for soil pollution prevention to get the whole picture of the pollution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in the soil of the region around Qinghai Lake. Therefore, nine heavy metals (As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn), which are mainly the items that must be measured for risk screening values for soil contamination, were sampled and analyzed in this study to explore the pollution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in the soil of the region around Qinghai Lake and quantitatively explain the contribution rate of the main influencing factors, hoping to provide a scientific basis for the environmental protection of soil ecosystem and comprehensive control of heavy metal pollution in the region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
As China’s largest inland saltwater lake, Qinghai Lake, is located in the northeast of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Due to the special geographical location, it plays an essential role in maintaining the ecological balance of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau. The lake covers an area of 29,661 km2; the terrain is high in the northwest while low in the southeast. Due to the topography, the annual average temperature is high in the southeast while low in the northwest, ranging from −1.4 to 1.0 °C. The annual precipitation in the lake area is less, generally between 300 and 400 mm, which in the east and south, is slightly higher than that in the north and west. In addition, the rain occurs in the hot season, and the dry and wet seasons are distinct, and the amount of evaporation reaches up to 1502 mm, far beyond the precipitation.
The region around Qinghai Lake discussed in this study refers to the area covering G109, G315, East Lake Road and West Lake Road around Qinghai Lake, where the terrain is flat, soil is fertile and enjoys vast natural pasture. In addition, the lake area enjoys convenient transportation, with a considerable number of highways and various rough roads accessible to each village and town. In view of the large population density and high intensity of human activities in the region around Qinghai Lake, it is also the core area of the Qinghai Lake Natural Reserve (Figure 1). Therefore, it is of particular importance to carry out pollution evaluation and risk assessment on the heavy metals in the surface soil of the region around Qinghai Lake. In the northern part of the study area, the land use types are mainly dry farmland, grassland and a small amount of shrubbery, while those are mainly grassland, desert land and a small amount of dry farmland in the eastern part. However, in the southern and western parts, grassland is dominant.
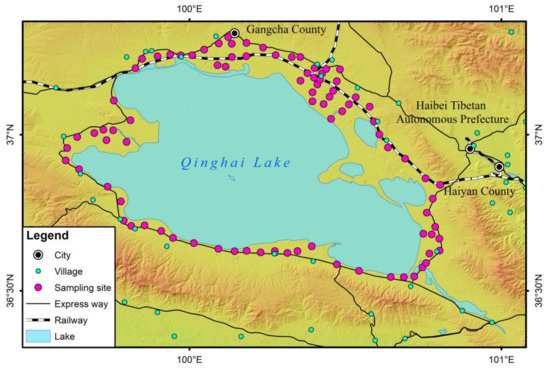
Figure 1.
Distribution of the soil sampling sites around Qinghai Lake.
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
In May 2019, the samples of the surface soil (0–20 cm) were taken, totaling 87 (as shown in Figure 1). The soil samples were collected and pretreated in accordance with the Technical Specification for Soil Environmental Monitoring (HJ/T 166-2004) [15]. In each sampling point, the diagonal multi-point sampling method (scale 100 × 100 m) was used to collect samples of surface soil (0~20 cm) and mix them evenly, and then, the collected soil samples were placed in plastic packaging bags and transported to the laboratory without delay. After the samples were naturally air-dried, it is necessary to remove grass roots, gravels and other sundries; grind the soil samples with a 100-mesh sieve and then save for use. The soil pH values were determined (at the water-soil ratio of 2.5:1) in accordance with the Soil—Determination of pH—Potentiometry (HJ 962–2008) [16]; organic matters were determined by external heating of potassium dichromate; after the heavy metals in soil were fully digested by the combination of microwave digestion and digestion by four acids (hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid and perchloric acid), the concentrations of heavy metals such as As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn were determined with an inductively coupled plasma emitter (ICP-AES) (manufactured by Spectro, Kleve Germany). In addition, the detection limits of the above heavy metals were 0.03, 0.001, 0.01, 0.005, 0.008, 0.002, 0.01, 0.008 and 0.03, respectively.
In order to ensure the accuracy of the analysis, two blank samples were set for every 16 samples in the digestion process of heavy metals in soil, and 10% of the samples were tested and analyzed repeatedly. The details of all the equipment used are as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The main equipment used.
2.3. Pollution and Risk Evaluation Method
2.3.1. Pollution Evaluation Method
Based on the geo-accumulation index and Nemerow index, the accumulation and pollution of heavy metals in the surface soil of the region around Qinghai Lake are evaluated.
The calculation formula of the geo-accumulation index (Igeo) is as follows [17]:
where Ci refers to the measured concentration of heavy metal i, Bi refers to the environmental background value of heavy metal i and the background value of the soil in Qinghai Province is adopted in this study; K refers to the coefficient [18] adopted after taking into account the variation of background values that may be caused by rock differences, which is usually 1.5. The classification standard of the geo-accumulation index is shown in Table 1.
The calculation formula of Nemerow index (Pn) is as follows [19]:
where (Pi)max refers to the maximum value of the single factor pollution index at each sampling point, and (Pi)ave refers to the arithmetic mean value of the single factor pollution index at each sampling point. The classification standard of the Nemerow index is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Criteria of the pollution grade of soil heavy metals.
2.3.2. Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation Method
The calculation formula of the potential ecological risk index is as follows [20,21]:
where refers to the potential ecological risk factor of heavy metal i, refers to the toxic response factor of heavy metal i, Ci refers to the measured concentration of heavy metal i, Coi refers to the evaluation standard of heavy metal i and the soil background values and soil environmental quality standard of Qinghai Province are adopted in this study. In addition, the toxic response factor shall be the standardized toxic response factor of the heavy metals formulated by Hakanson (As = 10, Cd = 30, Co = 5, Cr = 2, Cu = 5, Mn = 1, Ni = 5, Pb = 5 and Zn = 1).
Given the accuracy and universality of the results of Hakanson potential ecological risk evaluation, the classification standard for the ecological risk of heavy metals in the soil is adjusted in this study by the toxicity and types of heavy metals [22]. The specific method is as follows: Er and risk index (RI) grades of the Hakanson method are determined based on the maximum toxic factor of 8 heavy metals and the sum of the toxic factors of 8 heavy metals [23]. Firstly, the grading value of the unit toxic factor is determined as RI = 150/133 = 1.13, where 150 refers to the threshold value of Grade I according to Hakanson, and 133 refers to the total toxic factor of 8 pollutants. In this study, Cd (30) has the maximum toxic factor, and the sum of the toxic factors of 9 heavy metals is 64, so the threshold value of Grade I after adjustment is RIi = 64 × 1.13 ≈ 72, and the threshold value of every remaining grade is twice that of the previous grade [24]. In addition, the values of Er and RI after adjustment are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Comparison of the Hakanson classification standard and this study’s Er and risk index (RI) grading standards.
2.3.3. Human Health Risk Evaluation Method
In this study, the health risk evaluation model [25] proposed by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is used to calculate and evaluate the health risk of heavy metals in the surface soil of the region around Qinghai Lake. However, the human exposure parameters in the model are not in-line with the actual situation of human health in China. Therefore, the exposure parameters selected in this study are sourced from the Technical Guidelines for Risk Assessment of Contaminated Sites (HJ25.3-2014) [26]. In addition, three exposure pathways of heavy metals in the soil, i.e., oral intake, oral and nasal inhalation and skin contact, are selected to evaluate the health risk to adults and children, respectively.
The calculation formulas for the exposure dose of these three exposure pathways are as follows [27]:
where ADIing, ADIinh and ADIdermal refer to the daily exposure dose by oral intake, oral and nasal inhalation and skin contact; c refers to the content of heavy metals in soil; IngR refers to the rate by oral intake; EF refers to the exposure frequency; ED refers to the exposure duration; BW refers to the body weight of children or adults; AT refers to the average time of exposure to heavy metals that are noncarcinogenic or carcinogenic; InhR refers to the inhalation rate through the respiratory system; PEF refers to the dust emission factor; SA refers to the surface area of exposed skin; AF refers to the skin absorption factor and the correlation parameters are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Exposure parameters of the health risk assessment models.
Health risks can be divided into noncarcinogenic or carcinogenic risks, and the noncarcinogenic health risk index is shown below:
where HIi refers to the noncarcinogenic health risk index of a heavy metal in the exposure pathway i, HI refers to the total noncarcinogenic health risk index of the heavy metal in three exposure pathways, ADIi refers to the daily exposure dose of the heavy metal in the exposure pathway i and RfD refers to the reference dose. When HI < 1, it means that the heavy metal has no significant noncarcinogenic health risk; when HI > 1, it means that the heavy metal has a noncarcinogenic risk.
The carcinogenic health risk index is as follows:
where CRi refers to the carcinogenic health risk index of a heavy metal in the exposure pathway i, CR refers to the total carcinogenic health risk index of the heavy metal in three exposure pathways and SF refers to the carcinogenic slope factor. When CR < 1.0 × 10−6, it means that the heavy metal has no carcinogenic risk; when 1.0 × 10−6 < CR < 1.0 × 10−4, it means that the carcinogenic risk is acceptable; when CR > 1.0 × 10−4, it means that the heavy metal has a carcinogenic risk. In addition, the reference dose RfD and carcinogenic risk slope factor SF of the heavy metal in different exposure pathways are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Reference dose and slope factors of heavy metals for different exposure pathways.
2.4. Heavy Metal Source Analysis Method
The positive matrix factorization method (PMF) is a method for analyzing the source of environmental pollutants based on the factor analysis method [28], whose basic formula can be expressed as follows:
where Xij refers to the content of element j in the ith soil sample (mg/kg), gik refers to the content of element j in the source k (mg/kg), fik refers to the contribution of the source k to the ith soil sample and eij refers to the residual matrix.
The minimum objective function Q of the PMF can be described as follows:
where Qi refers to the objective function, and uij refers to the uncertainty of element j in the ith soil sample. The calculation method of the uncertainty is as follows.
When the content of each element is smaller than or equal to the detection limit (MDL) of the corresponding method:
When the content of each element is greater than the detection limit (MDL) of the corresponding method:
where δ refers to the relative deviation, c refers to the content of element (mg/kg) and MDL refers to the detection limit of method.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Analysis of Pollution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Soil
The descriptive statistical analysis for the content of heavy metals in the surface soil samples of the farmland in the region around Poyang Lake is shown in Table 6. It thus can be seen from Table 6 that the average contents of Cd, Co and Pb exceeded the background values of the soil in Qinghai Province and are 4.53, 1.23 and 1.05 times those of the background values, respectively, and there is also a certain degree of accumulation; the average contents of As, Cu, Mn, Ni and Zn do not exceed the background values of the soil in Qinghai Province, but a few samples are found to have excessive heavy metals by 31, 21, 43, 7 and 18 times, respectively; it indicates that these five heavy metals have an accumulation to varying degrees and will have a certain impact on the local farm and pasture products, but excessive Cr is not found in the samples. In addition to Cd, the contents of the other eight heavy metals are far lower than the national soil environmental quality standard Level II.

Table 6.
Statistics of heavy metals in the surface soil in this study.
Wilding divides the coefficient of variation (CV) into three grades [29]. That is, slight variation (CV < 16%), moderate variation (16% < CV < 36%) and strong variation (CV > 36%). The variation coefficients of nine heavy metals are Cd > Cu > 36% > Ni > As > Cr = Zn > Pb = Co > Mn > 16% in descending order. Specifically, the variation coefficients of Cd and Cu are 227% and 46%, respectively, which are classified as strength variations with strong spatial heterogeneity. Therefore, it can be preliminarily judged that Cd and Cu in the soil of the study area may be subject to point source pollution and are obviously affected by some local pollution sources in the area and human interference. In addition, the variation coefficients of the other seven heavy metals are about 30%, indicating that these seven heavy metals in the study area have little difference in contents and are not obviously affected by external activities.
In order to intuitively characterize the spatial distribution law for the content and pollution of heavy metals in the surface soil of the region around Qinghai Lake, combined with the geographic orientation of the sampling point and land use type, 87 sampling points in the study area were divided into five parts for spatial analysis (as shown in Figure 1), i.e., north (34 sampling points to the south of G315), south (18 sampling points to the north of G109), west (13 sampling points to the east of S206 in West Lake Road), southeast (11 sampling points to the west of S301 in East Lake Road) and northeast (11 sampling points near Ganzihe Road).
The spatial distribution law for the contents of heavy metals Cr, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, Ni, Mn and Co in the surface soil of the region around Qinghai Lake is similar (as shown in Figure 2); that is, high-content sampling points are mainly distributed in the north and south, while low-content sampling points are mainly distributed in the northeast of Qinghai Lake. The spatial distribution law of the content of heavy metal Cd is different from that of the other heavy metals, which is manifested as west > north > southeast > southwest > south. In addition to those seven high-content sampling points in a relatively sparse distribution, the contents of the other sampling points are low, with an average of 0.20 ± 0.07 mg/kg, and the south and north are high-content sampling point areas with an average of 0.24 ± 0.06 mg/kg. In addition, the spatial distribution law for the contents of the heavy metals Cr, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, Ni, Mn and Co is similar, indicating that these heavy metals have some certain correlations and may be homologous.
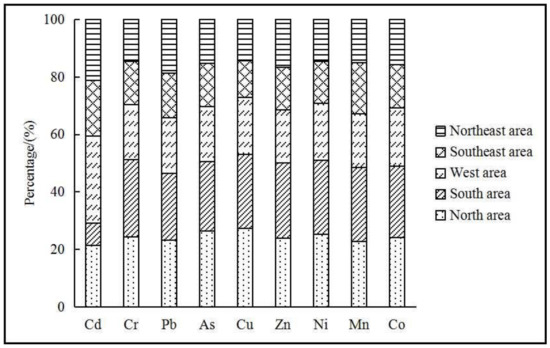
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of the proportions of heavy metals in the surface soil around Qinghai Lake.
3.2. Evaluation of Pollution of Heavy Metals in Soil
3.2.1. Geo-Accumulation Index
The pollution of heavy metals in the surface soil of the region around Qinghai Lake is Cd (0.25) > Co (−0.37) > Pb (−0.60) > Mn (−0.75) > As (−0.96) > Zn (−1.02) > Cu (−1.08) > Ni (−1.18) > Cr (−1.45) (as shown in Figure 3). In the region around Qinghai Lake, the surface soil is mainly polluted by the heavy metal Cd, the overall pollution level is mild and 37.93% and 8.05% of the sampling points are subject to no pollution–moderate pollution and to severe–extreme pollution, respectively. In addition, the other eight heavy metals are not found to have pollution on the whole. However, some sampling points are subject to no pollution–moderation pollution by heavy metals except Cr, and one sampling point is subject to moderate pollution by Cu.
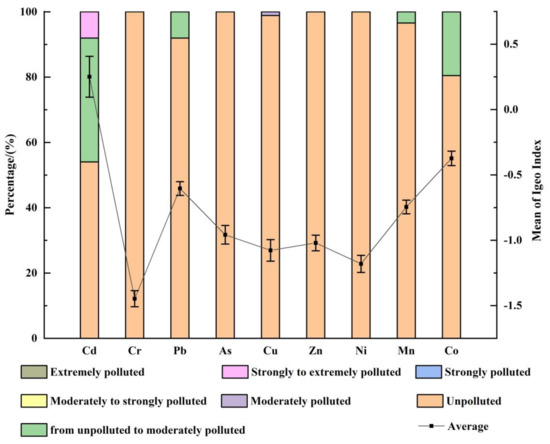
Figure 3.
The results of the geo-accumulation index (Igeo) index of heavy metals in the surface soil around Qinghai Lake.
3.2.2. Nemerow Index
In the region around Qinghai Lake, the Nemerow index of heavy metals in 87 sampling points ranges from 0.46 to 29.00, with an average of 3.43 ± 7.28, indicating that the soil in the study area reaches a severe pollution level (as shown in Figure 4 and Table 1). From the perspective of the proportion of pollution level, 91.80% of the soil sampling points in the study area are polluted, mainly manifested as mild pollution, accounting for 67.82% of the total sampling points; the sampling points subject to moderate and severe pollution account for 3.45% and 8.04% of the total sampling points, respectively; in addition, another 11.59% of the sampling points are around the cordon. In the study area, the pollution level varies in different sampling points, but the pollution is prevailing. Compared with the geo-accumulation index, the Nemerow index is used to evaluate heavier pollution, because the pollution level is upgraded after the maximum value is taken into account, indicating that, in the evaluation and control of heavy metals in the soil, the impact of extremes on the environment may be neglected if the average is taken into account only, thus underestimating the environmental pollution, so it is necessary to take into account the extreme values in the control process.
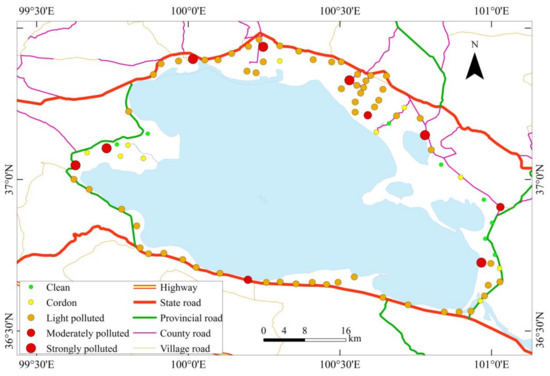
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of the Nemerow index (Pn) of heavy metals in the surface soil around Qinghai Lake.
Based on the above analysis results, it can be seen that there may be some pollution in the north, south, southwest and southeast of the region around Qinghai Lake. The main highways (G315 and G109) in the region around the Qinghai Lake and the Qinghai-Tibet Railway run through the north and south with heavy pollution, indicating that the pollution may be closely correlated with the release of such heavy metals as Pb, Cu, Zn and Cd in the transportation process; in addition, it may also be the result under the joint action of agricultural activities, tourism and other factors. In addition, the pollution of heavy metals in the surface soil of the southwest and southeast is heavier than that in the northwest and northeast, which may be associated with the land utilization type and volume of traffic.
3.3. Risk Evaluation of Heavy Metals in Soil
3.3.1. Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation
The results of the potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the surface soil of the region around Qinghai Lake are shown in Figure 5. The potential ecological risk factor (r) of nine heavy metals in the soil of the study area is Cd > As > Co > Pb > Cu > Ni > Cr > Zn > Mn in descending order (as shown in Figure 5). For Cd, its potential ecological risk factor (r) ranges from 11.01 to 1218.96, with an average of 135.15 ± 308.91, which is classified as a strong ecological risk; specifically, r of 60.92% of the sampling points ranges from 40~80, belonging to a moderate ecological risk, that of 1.15% of the sampling points ranges from 80 to 160, belonging to strong ecological risk and that of 8.05% of the sampling points is greater than 320, belonging to extremely strong ecological risk. The potential ecological risk factor (r) of other elements is less than 40, belonging to negligible ecological risk. In the study area, the potential ecological risk index (RI) of heavy metals in each sampling point ranges from 19.23 to 1259.87, with an average of 165.39 ± 310.95, belonging to a strong ecological risk. Specifically, the RI value of seven sampling points belongs to an extremely strong ecological risk, accounting for 8.05% of the total sampling points, and the other 80 sampling points belong to a mild ecological risk.
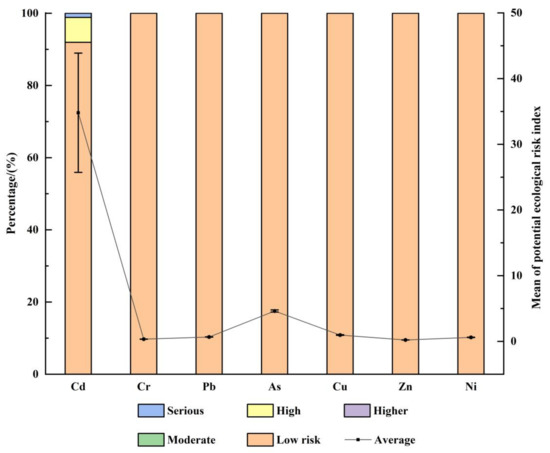
Figure 5.
The results of the potential ecological risk index of heavy metals in the surface soil around Qinghai Lake.
3.3.2. Human Health Risk Evaluation
In the study area, the human health risks of adults and children in different exposure pathways was calculated according to the above-mentioned health risk evaluation model and parameters, and the results are shown in Table 7. The single noncarcinogenic risk index of each heavy metal for children and adults in three exposure pathways is less than 1, indicating that the nine heavy metals in the surface soil of the study area will not produce any significant noncarcinogenic health risks to the population. The noncarcinogenic health risk generated from heavy metals in the soil of the study area in three exposure pathways is As > Cr > Mn > Pb > Ni > Cd > Co > Cu > Zn in descending order. Specifically, the As element has a noncarcinogenic risk much higher than other heavy metals and contributes 49.05% to the noncarcinogenic health risk index, making it a major heavy metal pollutant in the surface soil of the region around Qinghai Lake that produces a noncarcinogenic risk. By comparing the noncarcinogenic comprehensive health risk indexes of adults and children, the latter is 1.68 times that of the former, which is mainly because the weight of children is lighter than that of adults, and the frequency of intake by the hand and mouth is higher. Therefore, children are exposed to higher noncarcinogenic health risks than adults under the same environmental factors. In terms of exposure pathways, an oral intake has the highest noncarcinogenic health risk value, followed by skin contact and the lowest is inhalation through the respiratory system, and oral intake accounts for 92.4%, which indicates that oral intake is the main pathway of exposing the population in the region around Qinghai Lake to heavy metals in the soil, thus producing noncarcinogenic health risks.

Table 7.
Assessment of the health risks for adults and children under different exposure conditions.
Among those carcinogenic risks, the carcinogenic health risk index of Ni and Co in the surface soil of the study area is generally lower than 1.0 × 10−6, belonging to a noncarcinogenic risk. The carcinogenic health risk index of Cd, Cr and As ranges from 1.0 × 10−6 to 1.0 × 10−4, and the carcinogenic risk is acceptable. The pathways of exposing adults and children to different carcinogenic risks are oral intake > skin contact > inhalation through the respiratory system in descending order by exposure dose, and the contribution rate of oral intake to carcinogenic health risks reaches up to 93.68%. It should be noted that, in the carcinogenic health risk evaluation, Cd, Cr and As have a carcinogenic risk slope factor in three exposure pathways, while Ni and Co have a carcinogenic risk slope factor only in the exposure pathway of inhalation through the respiratory system, and their carcinogenic risks may be underestimated.
3.4. Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soil
The PMF model is used to analyze the sources of heavy metals and explore the main sources of pollution. According to the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N), As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn are set as strong, strong, strong, strong, weak, weak, strong, strong and strong, respectively. The number of factors is set to 2, 3, 4 and 5, respectively, and the number of operations is set to 20. After the trial calculation, when the number of factors is four, the difference between the objective function Q and theoretical value Q in the software operation results is the smallest; that is, the heavy metals in the soil of the study area are determined from six main sources. In addition, in order to ensure the accuracy of the model, extreme data samples will be eliminated.
The results of the source component spectrum obtained from the PMF model analysis are shown in Figure 6. It thus can be seen from Figure 6 that Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni and Zn have a higher contribution in Factor 1, with the contribution rates of 45.69%, 44.18%, 50.67%, 63.70%, 43.66%, 56.04% and 49.99%, respectively. Co, Cu, Mn, Ni and Zn are known as the trace elements promoting plant growth, and the use of feed additives containing Cu and Zn may lead to a large amount of heavy metals in the livestock excrement [30]. After the sampling survey in the study area, it is found that the livestock excrement in meadows and farms are directly applied without any treatment, while the livestock excrement or the organic fertilizer and compound fertilizer formed by the fermentation of livestock excrement, animal and plant residues and other raw materials will lead to the pollution of heavy metals in the soil. In addition, Cd is a marker element of agricultural activities such as pesticides and fertilizers [31], so Factor 1 can be explained as an agricultural production.
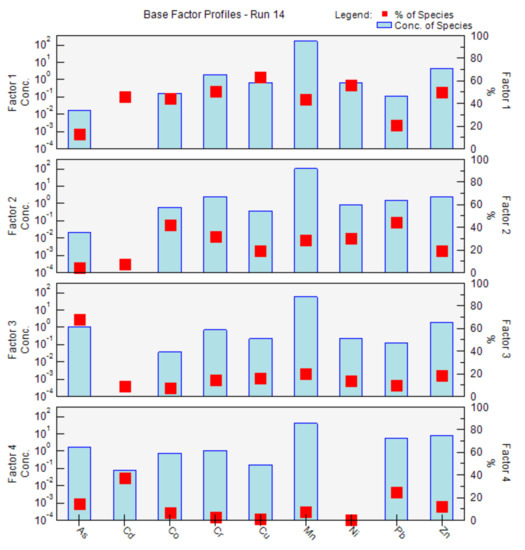
Figure 6.
Factors profiles and source contributions of heavy metals from the positive matrix factor analysis (PMF) model.
Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn have higher contributions in Factor 2, with the contribution rates of 41.84%, 31.75%, 19.61%, 28.59%, 30.23%, 44.49% and 19.53%, respectively. The contribution rates of CO, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn in factor 2 were 41.84%, 31.75%, 19.61%, 28.59%, 30.23%, 44.49% and 19.53%, respectively. The elements Cr and Ni in the soil are usually highly correlated, and they contribute the least to the soil pollution in China [32]; in the study area, the average contents of Cr and Ni are lower than the background values of the soil in Qinghai Province, and the variation coefficients are lower, indicating that Cr and Ni in the soil are subject to little external pollution, and the contents are very likely to be led by the soil formation process due to natural factors such as the natural weathering and erosion of the sedimentary rock. As Mn is rich in the Earth’s crust, it is usually known as a marker element of soil natural sources, which are subject to little external interference and are mainly affected by the soil-forming process and soil loss [33]. In addition, some scholars hold that Cr, Ni and part of Cu are controlled by soil-forming rocks and are related to the diagenetic composition [34]. Therefore, Factor 2 can be explained as a natural source.
As has a higher contribution to Factor 3, with a contribution rate of up to 67.70%. As is mainly affected by coal burning and iron and steel smelting [35], there is no large smelting plant in the study area with scattered peasant households around, and they burn coal for heat, so Factor 3 can be explained as a coal-burning source.
Cd, Pb and Zn have higher contributions in Factor 4, with the contribution rates of 37.50%, 25.08% and 12.18%, respectively. The study shows that transportation (vehicle exhaust, lubricant consumption, tire wear, brake wear and highway wear, etc.) is the key pollution source of heavy metals Pb, Zn and Cd in the soil [36,37]; specifically, Pb and Cd come from brake wear; Pb is known as a key element in gasoline and diesel and that, in vehicle exhaust, can enter the soil after atmospheric sedimentation, so Pb also comes from vehicle exhaust. Zn comes from tire wear and galvanized parts of the fuel tank. Outside the study area, there are main traffic routes such as national and provincial highways, while inside the study area, there are township roads and paths around the lake; in recent years, with the development of tourism, the flow of traffic has increased rapidly. During National Day in 2017 alone, the two-way flow of traffic in Erlangjian Scenic Spot along G109 amounted to 180,000, which undoubtedly aggravated the pollution of heavy metals in the soil, and there are no chemical and mining enterprises in and around the study area, so the accumulation of Pb, Zn and Cd is most likely to be correlated with transportation. Therefore, Factor 4 can be explained as the transportation source.
The results of the PMF source analysis show that agricultural production sources contribute for 43.10%, natural sources contribute for 25.34%, coal-burning sources contribute for 19.67% and transportation sources contribute for 11.89%, respectively (as shown in Figure 7).
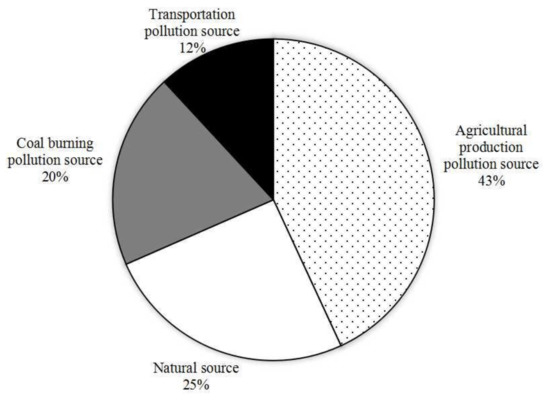
Figure 7.
Contributions rate of different sources by PMF.
4. Conclusions
The content of heavy metals in the surface soil of the region around Qinghai Lake in the Tibet Plateau show that nine heavy metals (As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn) have an accumulation to varying degrees. Among them, the contents of Cd, Co and Pb were higher on the whole. The results of the soil heavy metal harmfulness risk assessment imply that the study area on the whole is deemed to have a strong pollution risk, and individual sampling points are subject to severe–extreme pollution, so that they should be paid special attention to during environmental pollution control. In terms of spatial distribution, there is obvious pollution in the north, south, southwest and southeast of the study area, which may be closely related to transportation and agricultural activities. The PMF analysis showed that the nine heavy metals were mainly affected by four factors, i.e., agricultural production, the nature, coal-burning and transportation sources, with the contribution rates of 43.10%, 25.34%, 19.67% and 11.89%, respectively.
5. Recommendations and Future Research
As the world’s largest developing country and manufacturing power, China provides various producer goods and articles for daily use for almost all countries and regions around the world, and its rate of economic development continues to remain at a higher level. However, meanwhile, the backward environmental protection policy and technology not in harmony with the rapid economic development causes China to face the increasingly serious environmental pollution. As the level of pollution is easily visible by the naked eye, the pollution of the water and atmospheric environment is more prone to attention. Conversely, the pollution of the soil environment is often neglected, because it is not easily noticed by the naked eye. A large number of studies in the past have shown that China also faces stringent soil pollution. As for this study area, although it is located in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau where it is less traveled by, it also faces severe soil pollution.
The research results will be presented to the local government of the study area in order to support the formulation of prevention and control measures. On the basis of systematically determining the content of heavy metals in the surface soil of the region around Qinghai Lake in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, this paper analyzes in detail the risk, distribution and source of the pollution and preliminarily reveals the pollution of heavy metals in the surface soil of the study area. The determination results and analysis conclusions will help the local government and residents raise the awareness of the health risks and take preventive measures and provide scientific data support and references for the optimal selection of control strategies according to the different regions and different levels of pollution in the study area.
According to the human health risk evaluation results, policy measures are essential to control the risk of heavy metal pollution in the study area. For example, prohibit dry farming by laws in the region around Qinghai Lake in the Tibet Plateau to avoid the accumulation of heavy metals in the soil caused by agricultural activities. Compulsorily close, by laws, industrial and mining enterprises producing heavy metal pollutants around the study area, and set up a barrier belt of artificial vegetation or other materials for the highway to weaken the impact of traffic pollution. It has to be said that the application of human health risks to the practice is a complex system with a wide range of concerns. The stakeholders mainly involve surrounding industrial and mining owners, local residents, tourists and so on.
This paper is a phased achievement of the study of heavy metals in the surface soil of the region around Qinghai Lake in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. In the future, the project research group will continue to carry out further research on the mode of occurrence of heavy metals in the soil of the study area, as well as the evaluation, repair and governance and integration demonstration of its pollution risks.
Author Contributions
T.S. conceived and designed the experiments; Z.C., Z.X., Y.Z., D.L., L.F. and F.W. performed the experiments; P.W. and Z.Z. analyzed the data and P.W. and R.W. wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No. GK201803055, the Key Laboratory of Environment and Ecology, Ministry of Education, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: 2018-QHS-K04, Shaanxi province Postdoctoral Science Foundation No: 2016BSHEDZZ27 and the National Natural Science Foundation, Grant No. 41671213.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
References
- Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, S.; Xie, Z. Deposition behavior, risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in reservoir sediments of Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B.; Teng, Y. Soil environmental quality in greenhouse vegetable production systems in eastern China: Current status and management strategies. Chemosphere 2017, 170, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anahi, A.; Francisco, B.; Avto, G.; Felipe, G.O. Health risk of heavy metal in street dust. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 327–345. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.; Hossain, M.B.; Matin, A.; Sarker, S.I. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, distribution and source apportionment in the sediment from Feni River estuary, Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, C.; Fu, X.; Wu, G. Impact of coal power generation on the characteristics and risk of heavy metal pollution in nearby soil. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Dai, M.; Lu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C. Risk assessment and driving factors for artificial topography on element heterogeneity: Case study at Jiangsu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Wang, Y.H.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.l.; Li, J. Evaluation and Source of Heavy Metal Pollution in Surface Soil of Qinghai-Tibet Platean. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 886–894, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Duan, D.; Lu, J.; Luo, Y.; Wen, X.; Guo, X.; Boman, B.J. Inorganic pollution around the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: An overview of the current observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.C.; Cao, X.S.; Li, T.; Lv, M.J. Evolution of accessibility spatial pattern of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in 1976–2016. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1190–1204, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Han, Y.; Chen, L. Past atmospheric Pb deposition in Lake Qinghai, northeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Paleolimnol. 2009, 43, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Shi, Q.Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y. Spatial heterogeneity of heavy metals and influencing factors in the surface cultivated soil of the loess hilly-gully region, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 2465–2475, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, J. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in a tungsten mine soil in south of Jiangxi Province. Environ. Chem. 2017, 36, 1556–1567. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, X.; Renqin, D.; Zhou, X.; Cao, Y.; Guo, B.; Liu, X. Distribution of cadmium among multimedia in Lake Qinghai, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Wei, C.; Bandowe, B.A.M.; Wilcke, W.; Cao, J.; Xu, B.Q.; Gao, S.P.; Tie, X.X.; Li, G.H.; Jin, Z.D.; et al. Elemental Carbon and Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds in a 150-Year Sediment Core from Lake Qinghai, Tibetan Plateau, China: Influence of Regional and Local Sources and Transport Pathways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4176–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State Environmental Protection Administration. The Technical Specification for Soil Environmental Monitoring; China Environmental Protection Industry Standard; HJ/T166-2004; China Environment Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 10–16. (In Chinese)
- State Environmental Protection Administration. Soil-Determination of pH-Potentiometry; China Environmental Protection Industry Standard; HJ 962-2008; China Environment press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 6–11. (In Chinese)
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zahra, A.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Malik, R.N.; Ahmed, Z. Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah—Feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake Reservoir, Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemerow, N.L. Scientific Stream Pollution Analysis; Scripta Book Co.: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; pp. 210–231. [Google Scholar]
- Amouei, A.; Fallah, H.; Asgharnia, H.; Mousapour, A.; Parsian, H.; Hajiahmadi, M.; Khalilpour, A.; Tabarinia, H. Comparison of heavy metals contamination and ecological risk between soils enriched with compost and chemical fertilizers in the North of Iran and ecological risk assessment. Environ. Health Eng. Manag. 2020, 7, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Ma, L.; Sun, R.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Yan, D.; Lin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, Y. Evaluation of potential ecological risk, possible sources and controlling factors of heavy metals in surface sediment of Caohai Wetland, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Jiang, X.S.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, D.F. Assessment of ecological environment and human health of heavy metals in mining area based on GIS. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 1642–1652, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Cui, J.; Liu, J.H.; Gao, J.J.; Bai, Y.X.; Shi, X.F. Extensive study of potential harmful elements (Ag, As, Hg, Sb and Se) in surface sediments of the Bohai Sea, China: Sources and environmental risks. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Fernández, J. Evaluation of Contamination, by Different Elements, in Terrestrial Mosses. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 40, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, E.; Pecorini, I.; Iannelli, R. Methane oxidation of residual landfill gas in a full-scale biofilter: Human health risk assessment of volatile and malodours compound emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State Environmental Protection Administration. Technical Guidelines for Risk Assessment of Contaminated Sites; China Environmental Protection Industry Standard; HJ 25.3-2014; China Environment Press: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 6–10. (In Chinese)
- Wiltse, J.; Dellarco, V.L. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency guidelines for carcinogen risk assessment: Past and future. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. 1996, 365, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, G.; Duvall, R.; Brown, S.; Bai, S. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; EPA/600/R-14/108 (NTIS PB2015-105147); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 1–40.
- Nielsen, D.R.; Bouma, J. Spatial Variability: Its Documentation, Accommodation, and Implication to Soil Surveys. In Soil Spatial Variability; Wageningen University Press: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 166–194. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.M. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Soils and Dusts from the Intensive Human Impact Areas; Zhejaing University Press: Hangzhou, China, 2017; pp. 12–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Q.-S.; Wen, H.-H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.-S.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Zhu, Y.C.; Dai, J.R.; Liu, Y.; Bin, J.S. Identifying dieorigins and spatial distributions of heavy metals in soils of Ju country (Eastern China) using multivariate and geostatistical approach. J. Soils Sediment. 2015, 15, 16–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-A.; Liang, M.-Y.; Nie, Y.; Tang, J.-W.; Siddique, K.H. The conversion of tropical forests to rubber plantations accelerates soil acidification and changes the distribution of soil metal ions in topsoil layers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 134082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.T.; Ara, J.; Muhammad, S.; Khan, S.M.; Tariq, S.M. Health risk assessment via surface water and sub-surface water consumption in the mafic and ultramafic terrain, Mohmand agency, northern Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 118, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Duan, J.; Li, Y.; Jingchun, D.; He, K. Chemical characteristics and source apportionment of PM 2.5 in Lanzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Scott, C.A.; Yan, X. Traffic-related trace elements in soils along six highway segments on the Tibetan Plateau: Influence factors and spatial variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, M.; Li, L. Identification of traffic-related metals and the effects of different environments on their enrichment in roadside soils along the Qinghai–Tibet highway. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521–522, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).