Abstract
Traces of Molybdenum (Mo) in drinking water pose potent dangers owing to its harmful effects on the health of humans. This study used nanoscale zero-valent iron (Fe0) supported by activated carbon (NZVI/AC) for removing Mo(VI) from raw water. In an attempt to gain an understanding of the various factors that affect the process, we designed the study to look into the impact of various experimental parameters including pH, adsorption kinetics, and coexisting ions on the Mo(VI) removal using fixed-bed column runs and a batch-adsorption method and for Mo(VI) removal using NZVI/AC. The optimum conditions were found to be pH 4.5 and an equilibrium time of 9 h and 72 h for simulation water (SW) and raw water (RW), respectively. The removal of Mo(VI) was remarkably inhibited by the presence of silicate () and phosphate (), while the impact of humic acid and some other anions was insignificant. Metal cations such as Fe3+, Al3+, Zn2+, and Ni2+ enhanced the adsorption of Mo(VI). The influent contaminant concentration Mo(VI) in raw water was found to be 0.1603 mg/L, the empty-bed contact time (EBCT) was 3 and 6 min, whereas the breakthrough empty-bed volumes were 800 and 1100 and at the value of 70 μg/L provided by WHO provisional guidelines, respectively.
1. Introduction
Plants and animals need Molybdenum (Mo) as an essential trace element, which has a relatively low level of toxicity at <5 μg/L. However, due to the massive amounts of Mo effluents generated from mining tailings, several tens of μg/L to mg/L Mo have been detected in water systems. Moreover, incidents of Mo pollution have been reported at a few places around the world including the San Joaquin Valley, USA, Brenda Mines in British Columbia, Canada, and Wujintang and other Reservoirs, China. The quest for a feasible method for Mo removal from aqueous solutions has become a growing concern since the maximal Mo contaminant level in drinking water has reached 0.07 mg/L according to the Chinese drinking water standard (GB 5794-2006).
Ion exchange [1], solvent extraction [2], coagulation (coprecipitation) [3], bioremediation [4], and adsorption [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13] are some techniques contemporarily employed for removing Mo from water. Owing to the simplicity of technique and economy of cost, adsorption is a frequently employed practice for removing Mo from water. Elemental iron is extensively employed as an adsorbent for Mo elimination [5,13] due to its high affinity for Mo. In fact, recent reports suggest the use of nanoscale zero-valent iron (NZVI) as an excellent material for remediation of Mo-polluted water in situ [14]. As for the removal of Mo from drinking water, it also has a promising potential due to its large active surface area as well as an increased capacity to adsorb Mo.
However, due to the appearance of NZVI as fine powders, it is not possible to apply it in fixed-bed columns unless they come in the shape of granules. NZVI particles tend to agglomerate into larger particles, a tendency manifested by other nanomaterials, particularly due to its intrinsic magnetic interactions and high surface energies, resulting in the decline in reactivity performance as well as a reduction of surface area. NZVI immobilization in supports like activated carbon [15,16], sand [13], resin [6], and multiwalled carbon nanotubes is an approach with the potential to solve the aforementioned problem. In addition, as an environmentally friendly material, iron will not cause harm to human health. However, there has been no study on the kinetics of Mo(VI) elimination from raw water by nano zero-valent iron supported on activated carbon (NZVI/AC). Furthermore, an in-depth understanding of its dynamics and fixed-bed column experiments would help in accelerating the application of nanomaterials in engineering.
In our previous work, activated carbon supports were used for nanoscale zero-valent iron to achieve arsenic removal from drinking water. The current study was based on our attempt to test its performance for Mo removal from water using nano zero-valent iron supported on activated carbon (NZVI/AC). The impact of different parameters such as adsorption kinetics, common ions, pH, and fixed-bed column runs on Mo removal were ascertained.
2. Experimental
2.1. NZVI/AC; Synthesis and Characterization
The synthesis and characterization of NZVI/AC were carried out as follows. The carbon was washed by soaking in HNO3 followed by repeated rinsing with distilled water. AC was equilibrated with ferrous sulfate solution. The solution was diluted using a mixture of ethanol and deionized water. NaBH4 was then added in a dropwise manner into the solution with magnetic stirring and N2 bubbling. Ferrous iron (Fe2+) was reduced. After agitation, the AC-supported NZVI was separated from the mixture and washed with acetone, vacuum-dried and stored in a N2-purged desiccator [15]. Its main features are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Main features of nano zero-valent iron supported by activated carbon (NZVI/AC).
2.2. The Simulation Water and Raw Water Quality Parameters of a Reservoir
Specific ions were dissolved in de-ionized water in mentioned concentrations to make simulation water of certain chemical composition.
In order to investigate how the synthesized NZVI/AC perform to remove Mo(VI) from raw water, we took water from a reservoir in Songxian county, Henan Province, China, which has molybdenum mines in the upper streams of its river. Its water quality parameters are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
The water quality parameters of a reservoir/μg·L−1.
Due to the large daily consumption of drinking water, it is impossible to adjust its pH value in industrial production, and it can only be quantified at its natural pH around 8.1. Therefore, this study fixed the pH value at around 8.1.
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
In the previous experiments, we screened the activated carbon with the weakest molybdenum adsorption from the common activated carbons. In this experiment, the adsorption of molybdenum by activated carbon was only 1.1%, so we ignored its ability to adsorb molybdenum in batches and fixed-bed.
0.5 g/L NZVI/AC absorbent was added to each of the three conical flasks having 0.1603 mg/L Mo(VI) in 500 mL volume. The pH of the solution was maintained at 8.1 using 0.1mol/L HCl or NaOH. An air-bath shaker was used to shake the mixtures at 25 °C for 72 h. An aliquot of the supernatant was drawn at intervals and a 0.22 µm membrane filter (Millipore) was employed to filter it for analysis of aqueous Mo. The mean value was reported after running each experiment in triplicate.
The following expression was used to calculate residual concentration in the adsorbent (qt, mg/g):
where V represents the volume of solution (in L), C0 and Ct are the respective Mo(VI) concentrations initially and at a time t (in mg/L), and Ws stands for the adsorbent weight (g). The following equation was used to calculate the percentage of removed Mo(VI) (R%):
2.4. Models
Mo(VI) adsorption kinetics were computed using an intraparticle diffusion model [16] in the current investigation by employing the expression given below.
qt = kid t0.5
qt (mg/g) represents the quantity of Mo(VI) adsorbed at time t, and kid describes the original intraparticular diffusion rate (mg·g−1·h−0.5).
2.5. The Influence of pH on the Adsorption Behavior of NZVI/AC
The mineral suspensions containing Mo(VI) were adjusted to an initial pH range of 3.5–9.5 using 1 M NaOH or 1 M HCl while keeping the total volume change under <2%.
A 1000 mL conical flask was taken, and a 500 mL portion of Mo(VI) solution along with 0.25 mg of NZVI/AC. Mo(VI) concentration initially was 0.1603 mg/L in simulation water (SW) or raw water (RW), and the pH was in the range of 3.5–9.5. A to-and-fro shaker maintained at 25 ± 1 °C and 150 rpm was used to mix the samples. Multiple adjustments of the samples resulted in the attainment of a stable desired pH. Following 9 or 72 h, sample aliquots were drawn for analyzing Mo(VI) using an atomic absorption spectrophotometer with graphite furnace (AAS-GF, ZA3700, Hitachi High-Tech Instruments Co., Ltd. Kumagaya-shi, Japan).
Specific ions dissolved in deionized water define the chemical makeup of the simulation water.
2.6. Effect of Humic Acid and Coexisting Ions
We investigated the impact of commonly present anions (carbonate, oxalate, sulfate, phosphate, silicate, chromate, arsenate), cations (iron, aluminum, zinc, nickel), and humic acid (HA) on Mo(VI) adsorption onto NZVI/AC. The concentration of humic acid was maintained at 5 mg/L, and the mole ratio of the ions added to Mo(VI) was 10:1. A Mo(VI) solution (500 mL volume of 0.1603 mg/L) having coexisting ions added to it was adjusted to pH 8.1 and added with 0.5 g/L of the NZVI/AC. The mixtures were allowed to equilibrate at 25 ± 1 °C and a fixed pH for 9 h or 72 h with 150 rpm.
2.7. Column Experiments and Regeneration
A fixed-bed column system was installed to examine the dynamic behavior of removal of Mo(VI) by NZVI/AC. The polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) columns having an internal diameter of 1 cm and a height of 40 cm were set up for conducting column experiments. A small piece of glass wool was used to plug the column at both ends. The experimental design of the column and the components associated with it is illustrated in Figure 1. The tests were carried out at 25 ± 1 °C. A peristaltic pump (HL-1S, Shanghai Huxi Analytical Instrument Co., China) was used to attain an affixed flow rate. In order to ensure that the bed was perfectly saturated, an upward transfer of the Mo(VI) ions solution was made through the NZVI/AC beds. The tests were carried out as a function of empty-bed contact time (EBCT). Effluent samples were withdrawn at intervals to estimate the breakthrough points and for drawing breakthrough curves (BTCs). The tests were carried out until the complete saturation of adsorbents, followed by the analysis of column data.
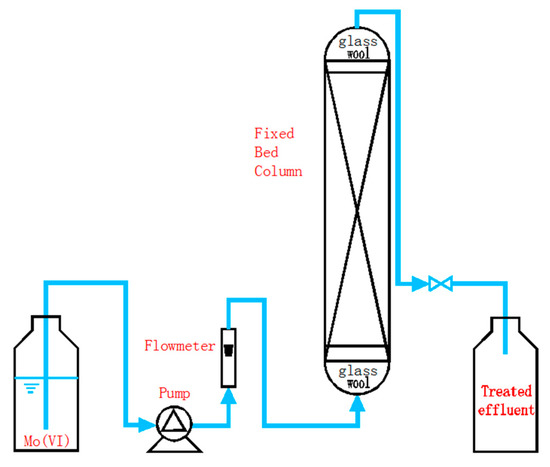
Figure 1.
Experimental setup for column tests.
At an effluent Mo(VI) concentration above 70 μg/L, NZVI/AC was taken out of the column for regeneration and stored in a 250 mL flask. A 0.5 mol/L NaOH solution equivalent to 5 times the volume of NZVI/AC was added, followed by the shaking of the suspension for 5 h at 150 rpm at 25 ± 1 °C, after which the alkaline solution was discarded. Four repetitions of the desorption process were performed, and deionized water was used to elute the NZVI/AC treated with alkaline solutions.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption Kinetics
The kinetics of adsorption of Mo(VI) by NZVI/AC, as illustrated in Figure 2, comprises two steps: initial fast sorption followed later by a relatively slower adsorption event. Roughly 89.5% of Mo(VI) was eliminated from simulation water during the first 1.5 h, whereas 74.0% was removed from raw water during the first 14 h; meanwhile adsorption equilibrium was attained in ~9 h and 72 h, respectively. Thus 9 h and 72 h equilibration times were applied in further investigations carried out with SW and RW. Quite a similar phenomenon was manifested in the case of the adsorption of metal cations (e.g.,) on NZVI/AC and the fast initial adsorption was ascribed to the metal ions transferring initially at a fast rate to adsorbent particles’ surface, whereas the slow adsorption following later was due to metal ions slowly diffusing into the pores of the intra-particle adsorbent [15].
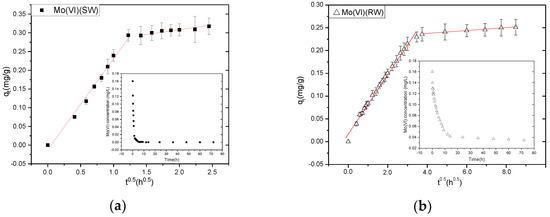
Figure 2.
Adsorption kinetics of Mo(VI) on NZVI/AC. (a) Intraparticle diffusion model of the kinetics of Mo adsorption onto NZVI/AC in SW. Right inset shows original data of Mo(VI) adsorption with respect to time in SW. (b) Intraparticle diffusion model of the kinetics of Mo adsorption onto NZVI/AC in RW. Right inset shows original data of Mo(VI) adsorption with respect to time in RW. Conditions: pH = 8.1, 20 × 40 mesh particle size, 150 rpm, adsorbent dosage in simulation water = 0.5 g/L, t = 72 h, T = 298 K, C0 SW = 0.1603 mg/L, C0 RW = 0.1603 mg/L.
We have used many models to analyze the adsorption kinetic data, but only the intraparticle diffusion model fitted well (R2 > 0.9) in this study. In an attempt to devise the adsorption-based treatment systems, the adsorption kinetic data of liquid-phase adsorption was analyzed using many models; however, in this study, the best explanation of the experimental data is given by the intraparticle diffusion model (R2 > 0.99) (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Rate constants for the adsorption kinetic model of Mo(VI) in simulation water (SW) and raw water (RW) on NZVI/AC.
It has been illustrated by Weber and Morris that the rate-determining step in an adsorption system is intraparticle diffusion, and the amount of the substrate adsorbed (qt) varies as a function of the square root of time (t0.5) in a linear fashion. The speeds of adsorption are then calculated using these data [9]. A linear relationship was observed in a plot of qt versus t0.5 in two separate stages (Figure 2b). Therefore, to both these stages, Equation (1) was applied individually. The adsorption on the NZVI situated in the macropores corresponds to the first linear section of the graph, while the diffusion of Mo(VI) corresponds to diffusion into meso- and/or micropores. The adsorption was quick on the NZVI particles in the AC channels or macropores; however, their diffusion was rather slow into micro- and mesopores due to the blockage of most pores. Additionally, there was the involvement of the corrosion of the NZVI surface, diffusion, and adsorption in the corrosion layers. For the 1st stage, the kid values were higher than the 2nd stage, in fact, 11.99 and 22.40 times higher, respectively, in SW and RW, suggesting a higher velocity of the stage 1 reaction compared to the stage 2, thus corroborating with Figure 2.
A similar phenomenon was manifested during adsorption of acidic dye [16], and [15], and Cu(II) and Cd(II), on activated palm ash and rice/modified rice husk [17], on NZVI/AC. However, when using clay-impregnated nanoscale zero-valent iron for the degradation and adsorption of Cu2+ and Zn2+ from wastewaters, the calculated qe values and the rate constants were observed to lie close to the experimental qe values for the pseudo-second-order (PSO) model as compared to when the pseudo-first-order (PFO) expression was taken into consideration.
The mechanism of removal of Mo(VI) by NZVI is immature. However, it was suggested by Jingge Shang that, for Cr(VI) elimination by nanoscale zerovalent iron particles supported on herb-residue biochar, the PSO model provides a better fit with the kinetic data. Hence, the kinetic parameters are regulated by a chemical process, which implies that the processes occurring during Cr(VI) removal are reduction and adsorption/coprecipitation [18]. Considering that and are both anions (−2 valence) and have the same structure. The radius of and are 0.240 nm and 0.246 nm, respectively. We therefore speculate the similarity in the adsorption/coprecipitation mechanism of Cr(VI) and Mo(VI) in solution by nanoscale zero-valent iron.
3.2. Effect of pH
The adsorption envelopes of Mo(VI) from solutions on NZVI/AC in a pH range of 3.5–9.5 are shown in Figure 3. Apparently, media pH strongly impacts Mo(VI) removal efficiency, and increased removal of Mo(VI) from Mo(VI) solution was observed from pH 3.5 to pH 4.5, whereas a decrease was observed from pH 4.5 to pH 9.5. The previous work also reports a decrease in Mo(VI) adsorption on nanosized zero-valent iron after pH 5, while adsorption of Mo(VI) exhibited an increase in acidic solution but a decrease in alkaline media [5]. At pH ~5, the adsorption profiles of arsenate and arsenate onto iron oxyhydroxide supported by bead cellulose were observed to intersect [19].
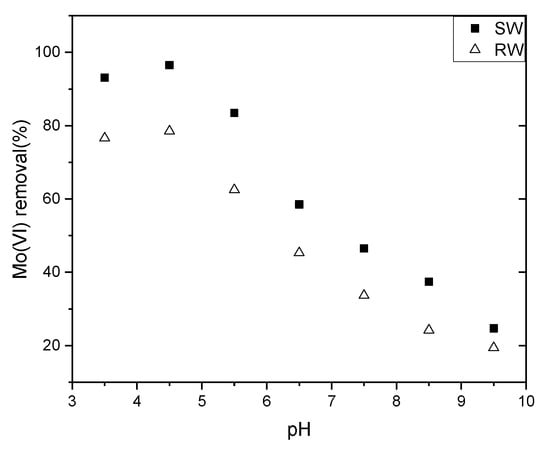
Figure 3.
Effects of varying equilibrium pH values on Mo(VI) adsorption. Conditions: solid/liquid = 0.5 g/L, T = 298 K, initial Mo concentration in simulation water = 0.1603 mg/L; initial Mo concentration in raw water = 0.1603 mg/L.
A strong acid will dissolve and lose iron from NZVI/AC, so we investigated the pH of the simulation and raw water from 3.5 to 9.5, while J.J. Lian studied the pH 2–10 using nano zero-valent iron supported on biochar [5].
The pH dependency in the adsorption of Mo(VI) onto NZVI/AC is the impact of numerous factors that compete with one another in regulating adsorption. We suggest that there are three steps in the adsorption of Mo(VI) onto the NZVI surface: (1) migration onto the surface; (2) deprotonation or dissociation of an aqueous complex of Mo(VI); and (3) surface complexation [15]. As a prerequisite to the adsorption reaction, Step 1 is largely controlled by electrostatic interaction (attractive or repulsive) among the surfaces of the adsorbent and aqueous Mo(VI) species. Hence, the speciation of aqueous Mo(VI) and the pH of zero-point charge (pHZPC) of the adsorbent are the governing factors. As is already known, there exists a negative charge on solid surfaces at pH above pHZPC, whereas a positive charge exists at pH below pHZPC, leading to a rise in electrostatic repulsion or attraction with anionic Mo(VI) species, thereby resulting in an increased or decreased efficiency of adsorption. When the pH increased to 9.0, the percentage of adsorption decreased rapidly toward a negligible efficiency of removal by the end of the test (<30%). Other studies reported similar observations [5].
3.3. Effect of Coexisting Ions
Various anions and cations are commonly present in drinking water which may positively or negatively impact the adsorption of Mo(VI). The influence of some common anions ( , ), cations (Fe3+, Al3+, Zn2+, Ni2+), and HA on Mo(IV) adsorption by NZVI/AC were examined in the current study (see Figure 4). The presence of humic acid and anions adversely affected the removal of Mo(VI). Silicate, arsenate, and phosphate caused a more adverse effect; however, the HA caused a less-adverse effect on Mo(VI) removal amongst all the oxyanions investigated in this work.
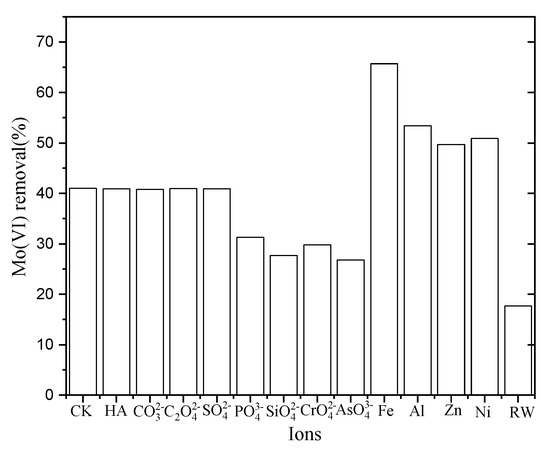
Figure 4.
Impact of coexisting ions on Mo(VI) removal by NZVI/AC at 8.1. Initial Mo(VI) concentration was 0.1603 mg/L and 0.1603 mg/L; the molar ratio of Mo to coexisting anions was 1:10; humic acid (HA) added was 5 mg/L.
Arsenate, molybdenum, phosphate, and silicate can form inner-sphere complexes with an iron oxide surface. Due to their competition for capturing the similar binding sites, they would decrease the sorption of molybdenum. Both non-specific and specific sorption is observed for sulfate ions. However, they have a much weaker strength of bonding with iron (hydr)oxide than molybdate [20]. While earlier reports suggest that arsenic removal by zero-valent iron improved at an increased concentration of sulphate [21], the presence of sulfate at a level relevant to the environment manifested a very little negative effect.
Divalent/multivalent metallic cations of the Fe3+, Zn2+, Ni2+, and Al3+ notably enhanced Mo(VI) adsorption on NZVI/AC. The positive impact remarkably increased upon the increase in pH, particularly for ferrous iron Fe3+. This is particularly useful for the treating reservoir water contaminated with Mo(VI), contamination which normally contains copious amounts of Al3+ dissolved in it. The augmenting impact of metal cationic species on Mo(IV) adsorption has been mentioned in earlier reports for iron (hydr)oxides [22]. Presumably, this is because the metal cations present in the solution transformed the adsorbent surface to a positively charged nature, which in turn led to the adsorbent showing a higher affinity for Mo(VI) anions.
According to the discussion above, the adsorption of Mo(VI) is majorly regulated by H2MoO4 deprotonating at pH < 9. Fe3+ ions presumably form complexes with Mo(VI) in aqueous media. Consequently, the extent of deprotonation/dissociation suppresses and the net adsorption reduces. The adsorption of metal cations (e.g., and ) on NZVI/AC also manifested a similar phenomenon in our previous research [15].
3.4. Fixed-Bed Column Runs
In view of the treatment efficiency, further investigation was based on examining the operational parameters like EBCT. EBCT is undoubtedly a crucial attribute to be taken into account in adsorption studies, because the efficiency of removal efficiency is strongly dependent on the duration of contact between the adsorbate (Mo(VI)) and the adsorbent (NZVI/AC). The empty-bed contact time of the influent was kept generally at 1.5–12 min when adsorption was employed as a potential technique to eliminate the pollutants from aqueous systems [23]. Figure 5 shows breakthrough behavior during the fixed-bed column runs from deionized water supplemented with Mo(VI).
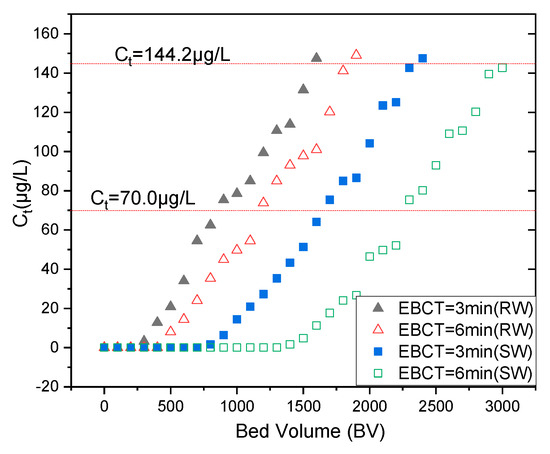
Figure 5.
Mo(VI) breakthrough behavior of the column test from deionized water (temperature 25 ± 1 °C, influent pH 8.1 ± 0.1, initial SW and RW [Mo(VI)] 0.1603 mg/L, SW Mo(VI) and RW Mo(VI) empty-bed contact time (EBCT) = 3.0 and 6.0 min.
As anticipated, EBCT essentially impacted the breakthrough behavior, and the increasing EBCT resulted in an increase in adsorptive efficiency due to the increase in contact time. At 6.0 min, even when the effluent volume was as high as 1100 BV, the RW [Mo(VI)] concentration in the remaining solution remained well below 70 μg/L, whereas at an EBCT of 3.0 min breakthrough (MCL, 70 μg/L) was found to be 800 BV.
In accordance with WHO’s Mo(VI) maximum contaminant level (MCL, 70 μg/L), at a 3.0 min EBCT (empty-bed contact time), the SW and RW Mo(VI) effluent concentrations were under 70 μg/L till the empty-bed volume reached 1600 and 800 BV, respectively. The SW [Mo(VI)] and RW [Mo(VI)] concentration in the effluent solution was above 70 μg/L, at an EBCT of 6.0 min when the effluent volume reached 2300 BV and 1300 BV. The RW’s EBCTs of neither 3.0 nor 6.0 min are less than the SWs attributed to its complicated water quality composition
As the solute concentration in the effluent reaches up to 95% of the influent value, the point of column exhaustion is attained, where the solid-phase concentration reaches a maximum value. It is noteworthy that in comparison to the obtained maximum adsorption capacities, the maximal retention capacities were much lower in batch experiments, which can be attributed to the comparatively high flow rate in the column experiments, which might result in insufficient contact time between Mo(IV) and NZVI/AC. Breakthrough empty-bed volume depends primarily on NZVI/AC and influent Mo(VI) concentration. It should hence have a bigger value at longer EBCTs and lower initial Mo(VI) concentrations.
The batch experiments described above exhibit that the adsorption capacity for Mo(VI) by NZVI/AC was about 3 times compared to that of Mo(VI) at neutral pH. This shows that in batch experiments, NZVI/AC manifested a higher removal performance for Mo(VI) (neither SW nor RW) than in fixed-bed column; however, the fixed-bed column is more suitable for continuous industrial production than batch experiments.
The exhausted NZVI/AC was regenerated in 0.5 mol/L NaOH solution 5 times, and then it was eluted by deionized water a few times. The alkaline solutions have been analyzed prior to handing over to the special laboratory hazardous waste treatment center according to Chinese policy. The results displayed that more than 90% of adsorbed Mo(IV) was recovered and iron showed almost no shedding when Mo(IV)-saturated NZVI/AC was regenerated with 0.5 mol/L NaOH. The regeneration process could be interpreted as follows:
Fe-Mo(IV) + OH−⇄Fe-OH + Mo(IV) (Kdes)
3.5. Mechanism of Removing Mo(VI) from Water by NZVI/AC
The mechanism regulating the removal of molybdenum from water through the use of zero-valent iron is mainly adsorption, surface complexation, Mo(OH)3 precipitation, and Mo-Fe mineral (FeMoO4) formation.
In the current work, the removal rate of molybdenum is faster in the initial stage of the reaction, indicating that adsorption is the major process during the initial stages of reaction. The adsorptive removal of molybdenum can take place through complexation or electrostatic interaction.
The main mechanism enabling zero-valent iron to remove molybdenum from water is the combined action of adsorption and chemical precipitation.
Once zero-valent nano-iron enters the solution, it will be oxidized by water to form Fe2+. Fe2+ is affected by the pH of the solution, oxidation-reduction potential, and other factors to further form iron (hydrated) oxide and various iron (hydrated) oxides in solution. The molybdenum in the liquid tends to form compounds such as FeMoO4·xH2O, thus molybdenum in the liquid phase is transferred to the adsorbent and removed.
In this experiment, the loaded iron was found to play a major role in Mo(VI) elimination. The nano-iron will react with water and trace oxygen dissolved in water and corrode [7,9,19,20]. According to the results obtained by Bruce et al. [24] using EXAFS research, nano-iron first generates intermediate products like ferrous iron (Hydrate) oxides, and later produces iron (hydrated) oxides. The final product may include maghemite (γ-Fe2O3), magnetite (Fe3O4), lepidocrocite (γ-FeOOH), etc. Following the series of multiphase complex reactions on the iron surface as mentioned above, a variety of hydrated oxides having a strong adsorption capacity for Mo(IV) are finally formed (see Figure 6).
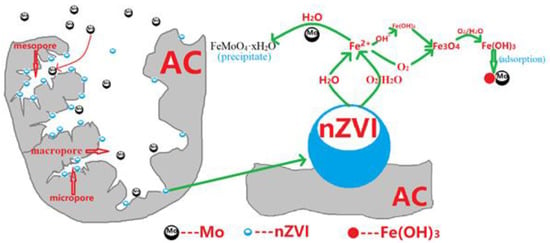
Figure 6.
Proposed mechanism of removal of Mo(VI) from water by NZVI/AC.
The above reactions can be expressed as follows [20]:
- (1)
- Fe0 reacts with water or dissolved oxygen to form Fe2+:
Fe0 + 2H2O→Fe2+ + H2 + 2OH−
Fe0 + O2 + 2H2O→Fe2+ + 4OH−
- (2)
- Fe2+ is further transformed into iron (hydrated) oxides by the pH of the solution and the oxidation-reduction potential and other factors:
6Fe2+ + O2 + 6H2O→2Fe3O4(s) + 12H+
Fe2+ + 2OH−→2Fe(OH)2 (s)
6Fe(OH)2(s) + O2→2Fe3O4(s) + 6H2O
Fe3O4(s) + O2(aq) + 18H2O⇌12Fe(OH)3(s)
Fe2− + MoO42− + xH2O→FeMoO4·xH2O
Fe2+ + 2OH−→2Fe(OH)2 (s)
6Fe(OH)2(s) + O2→2Fe3O4(s) + 6H2O
Fe3O4(s) + O2(aq) + 18H2O⇌12Fe(OH)3(s)
Fe2− + MoO42− + xH2O→FeMoO4·xH2O
Hydrated iron oxide has a large number of active sites (-OH) on the surface, so it has a strong adsorption capacity for Mo(VI).
It is generally believed that the adsorption of Mo(VI) on the surface of hydrated iron oxide takes place as a bidentate binuclear chelate [9,16,19]. Recent studies have shown that in neutral to weakly alkaline media, this form is adsorbed on the surface of hydrated iron oxide; however, it forms an amorphous iron molybdate surface precipitate (FeMoO4·xH2O) in a weakly acidic medium [25]. Yong H. Huang et al. found a conventional ZVI-only system or a ZVI/Fe(II) system could not be efficiently removed molybdate from water. The hybridized ZVI/Fe3O4/Fe(II) system can achieve rapid and sustainable reduction and immobilization of molybdate from water. Molybdate can be rapid and sustainable reduction and immobilization from water by the hybridized ZVI/Fe3O4/Fe(II) system [26].
4. Conclusions
The supported nano-iron, NZVI/AC, prepared in this study manifests a good potential for the removal of Mo(IV) in a neutral media among the common anions and cations in natural water environments. Phosphate and silicate have been found to affect the adsorption and removal of Mo(IV) with different degrees of inhibition. However, other common ions have little effect on it. The application of the loaded nano-iron adsorbent to the removal of Mo(IV) in drinking water has potentially valuable application prospects.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z.; investigation, Q.H. and M.S.; methodology X.Z. and S.F.; resources X.Z. and S.F.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Z. and M.S.; writing—review and editing, B.L.; supervision, B.L.; funding acquisition, X.Z. and M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China, grant number 51709141&400773076.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Orrego, P.; Hernández, J.; Reyes, A. Uranium and molybdenum recovery from copper leaching solutions using ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 184, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Kim, D.J.; Sukla, L.B.; Pattanaik, A.; Lee, S.W. Evaluation of molybdenum recovery from sulfur removed spent catalyst using leaching and solvent extraction. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, J. Study on the efficient removal of molybdenum ions from water by polyferric chloride. Water Supply Wastewater 2016, 42, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sabullah, M.K.; Rahman, M.F.; Ahmad, S.A.; Sulaiman, M.S.; Shukor, M.S.; Shamaan, N.A.; Shukor, M.Y. Assessing Resistance and Bioremediation Ability of Enterobacter sp. Strain Saw-1 on Molybdenum in Various Heavy Metals and Pesticides. J. Math. Fundam. Sci. 2017, 49, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.J.; Huang, Y.G.; Chen, B.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, P.; Niu, S.P.; Liu, Z.L. Removal of molybdenum(VI) from aqueous solutions using nano zero-valent iron supported on biochar enhanced by cetyl-trimethyl ammonium bromide: Adsorption kinetic, isotherm and mechanism studies. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 2017, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toli, A.; Mystrioti, C.; Xenidis, A.; Papassiopi, N. Continuous Flow Process for Cr(VI) Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Resin Supported Zero-Valent Iron. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Kim, S.Y. Adsorption and separation behaviors of molybdenum from high-level liquid waste using a silica-based hydroxyoxime impregnated adsorbent. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 316, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumihiko, O.; Takehiro, N.; Naohito, K. Adsorption capability of virgin and calcined wheat bran for molybdenum present in aqueous solution and elucidating the adsorption mechanism by adsorption isotherms, kinetics, and regeneration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4459–4466. [Google Scholar]
- Denkova, A.G.; Terpstra, B.E.; Steinbach, O.M.; Dam, J.; Wolterbeek, H.T. Adsorption of Molybdenum on Mesoporous Aluminum Oxides for Potential Application in Nuclear Medicine. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Lu, C. Kinetics, thermodynamics and regeneration of molybdenum adsorption in aqueous solutions with NaOCl-oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2521–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Yang, J.; Pang, M.; He, J.; Yang, W.; Qin, H.; Zhan, Y. Adsorption and migration behavior of molybdenum atom on graphite (0001) surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 470, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Zhou, F.; Chen, B.; Yang, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Niu, S. Enhanced adsorption of molybdenum(VI) onto drinking water treatment residues modified by thermal treatment and acid activation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Selim, M. Kinetic Modeling of pH-Dependent Molybdenum (VI) Adsorption and Desorption on Iron Oxide-Coated Sand. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.; Mushovic, P.; Niesen, P. Early breakthrough of molybdenum and uranium in a permeable reactive barrier. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jia, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, H. Removal of arsenic from water by supported nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Ahmad, A.A.; Aziz, N. Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of acid dye adsorption on activated palm ash. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 133, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.A.; Seng, C.E.; Lim, P. Kinetics of adsorption of Cu (II) and Cd (II) from aqueous solution on rice husk and modified rice husk. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 6, 1764–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z. Simultaneous adsorption and degradation of Zn2+ and Cu2+ from wastewaters using nanoscale zero-valent iron impregnated with clays. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 3639–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, F. Removal of arsenic by bead cellulose loaded with iron oxyhydroxide from groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6808–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Demopoulos, G.P. Adsorption of arsenate onto ferrihydrite from aqueous solution: Influence of media (sulfate vs nitrate), added gypsum, and pH alteration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9523–9527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasuddin, A.B.M.; Kanel, S.R.; Choi, H. Adsorption of humic acid onto nanoscale zerovalent iron and its effect on arsenic removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkie, J.A.; Hering, J.G. Adsorption of arsenic onto hydrous ferric oxide: Effects of adsorbate/adsorbent ratios and co-occurring solutes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1996, 107, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.X.; Zhan, J.Q.; Song, Z.X. Ion Exchanger Engineering; Tianjin University Press: Tianjin, China, 1992; p. 206. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, B.A.; Hunt, M.L.; Amrhein, C.; Yarmoff, J.A. Arsenic (III) and arsenic (V) reactions with zerovalent iron corrosion products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 5455–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Research on the Removal of Molybdenum from Water by Zero-Valent Iron; Dalian University of Technology: Dalian, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.H.; Tang, C.; Zeng, H. Removing molybdate from water using a hybridized zero-valent iron/magnetite/Fe(II) treatment system. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200–202, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).