Effects of Tropical Cyclones on Sea Surface Salinity in the Bay of Bengal Based on SMAP and Argo Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Tropical Cyclones and Satellite Data
2.2. Argo Data
3. Results and Discussion
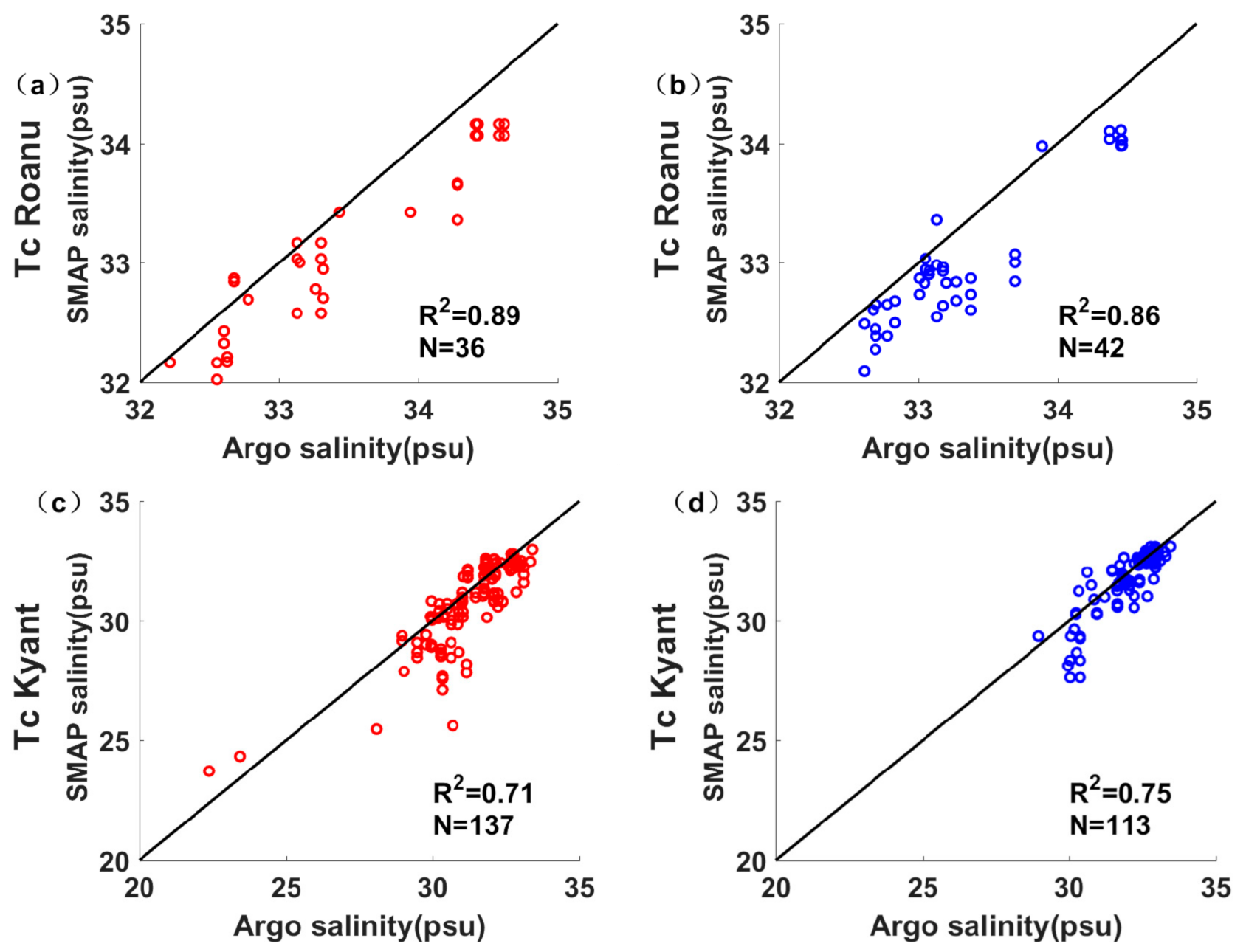
3.1. SMAP Data Validation with Individual Argo
3.2. The Seasonal SMAP SSS during 2015–2019
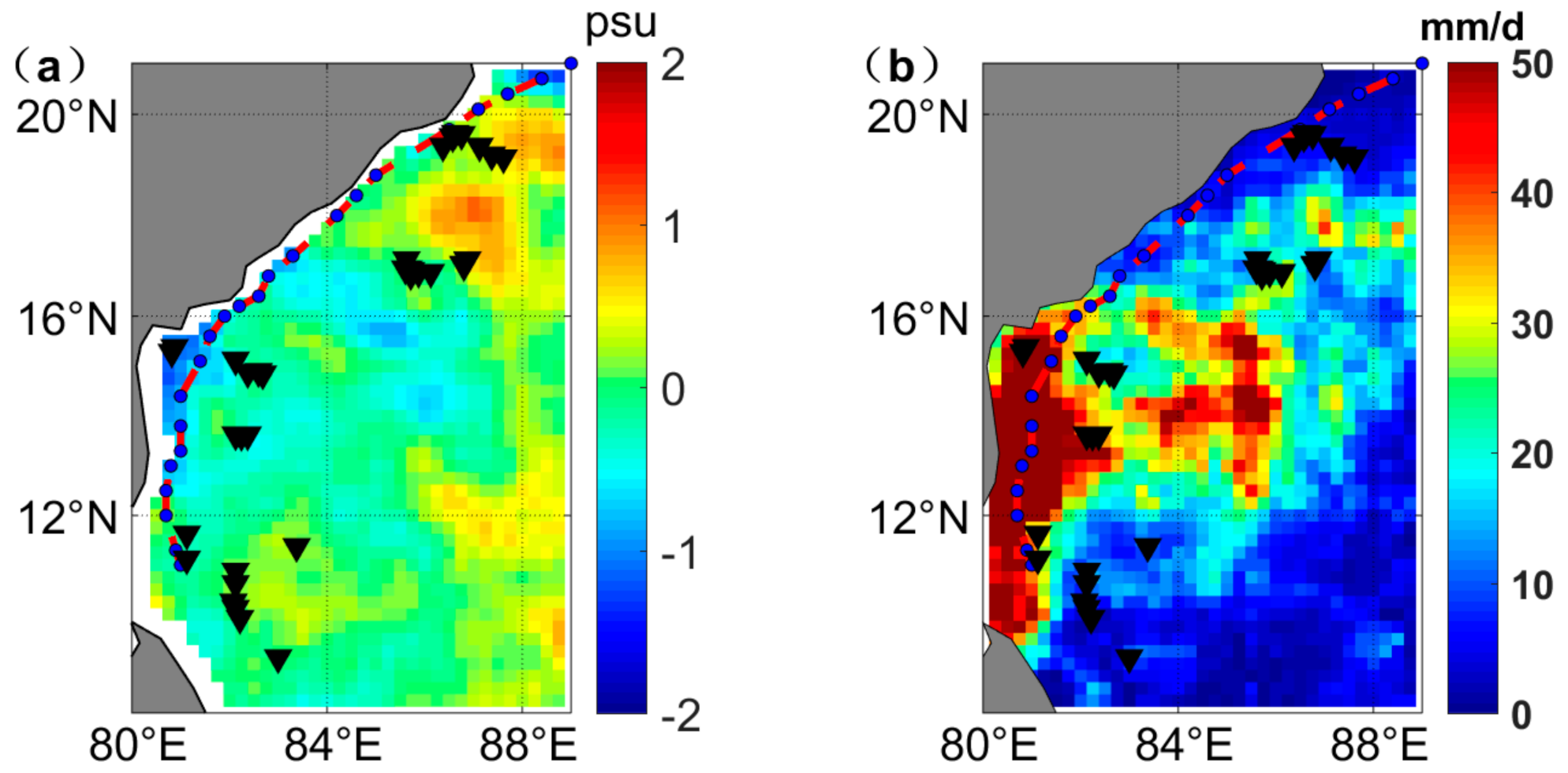
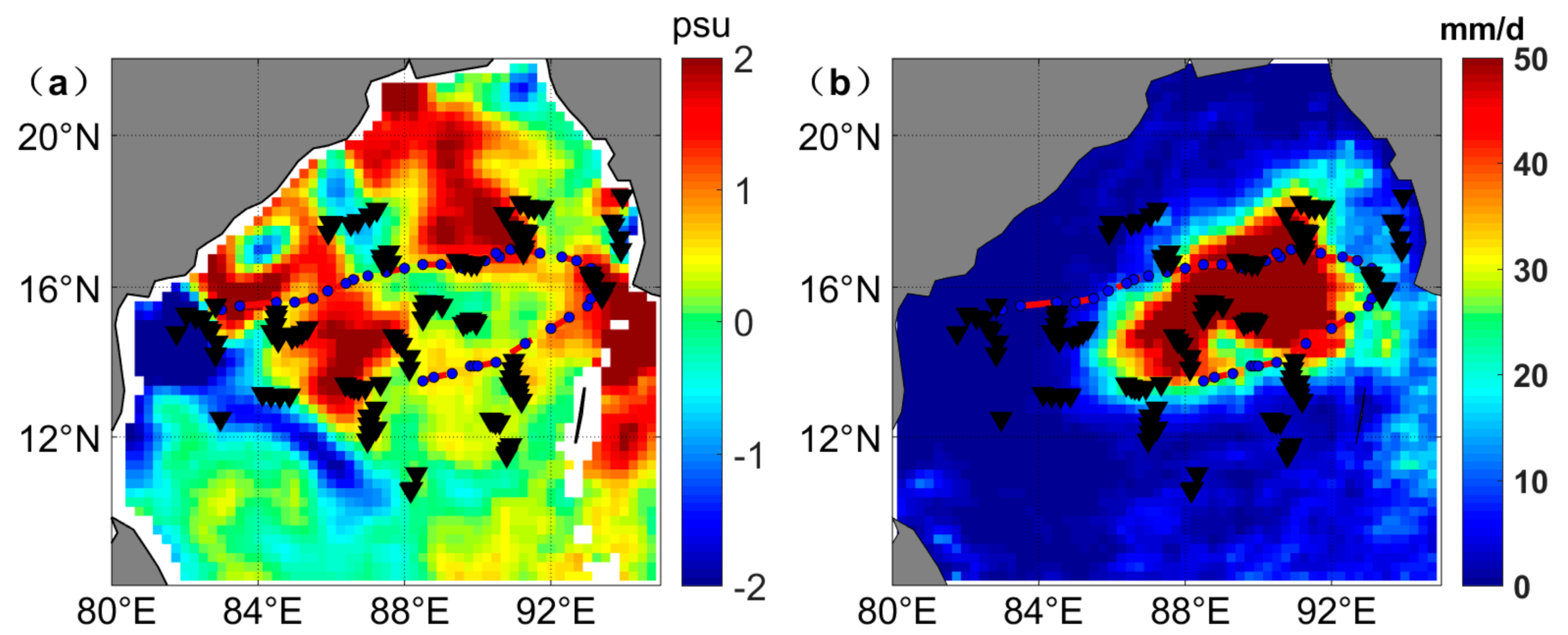
3.3. Two Specific TCs to Study the TC Impact on the SSS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaitanya, A.V.S.; Durand, F.; Mathew, S.; Gopalakrishna, V.V.; Papa, F.; Lengaigne, M.; Vialard, J.; Kranthikumar, C.; Venkatesan, R. Observed year-to-year sea surface salinity variability in the Bay of Bengal during the 2009–2014 period. Ocean Dyn. 2015, 65, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Qiu, Y.; Cha, J.; Guo, X. Assessment of Aquarius sea surface salinity with Argo in the Bay of Bengal. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 8547–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdary, J.S.; Srinivas, G.; Fousiya, T.S.; Parekh, A.; Gnanaseelan, C.; Seo, H.; MacKinnon, J.A. Representation of Bay of Bengal Upper-Ocean Salinity in General Circulation Models. Oceanography 2016, 29, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Tang, D.; Sheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Sui, Y. Study of dissolved oxygen responses to tropical cyclones in the Bay of Bengal based on Argo and satellite observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neetu, S.; Lengaigne, M.; Vincent, E.M.; Vialard, J.; Madec, G.; Samson, G.; Kumar, M.R.R.; Durand, F. Influence of upper-ocean stratification on tropical cyclone-induced surface cooling in the Bay of Bengal. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117, C12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girishkumar, M.S.; Ravichandran, M. The influences of ENSO on tropical cyclone activity in the Bay of Bengal during October-December. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117, C02033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.F. Upper Ocean Response to a Hurricane. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1981, 11, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, I.I. Typhoon-induced phytoplankton blooms and primary productivity increase in the western North Pacific subtropical ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117, C03039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, N. Chlorophyll bloom in response to tropical cyclone Hudhud in the Bay of Bengal: Bio-Argo subsurface observations. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2017, 124, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tang, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Dissolved oxygen responses to tropical cyclones “Wind Pump” on pre-existing cyclonic and anticyclonic eddies in the Bay of Bengal. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Sheng, J.; Tang, D.; Siswanto, E.; Kalhoro, M.A.; Sui, Y. Storm-induced changes in pCO2 at the sea surface over the northern South China Sea during Typhoon Wutip. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 4761–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Kalhoro, M.A.; Sun, J.; Tang, D. Chlorophyll blooms induced by tropical cyclone Vardah in the Bay of Bengal. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2018, 47, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Xie, L.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Zheng, M.; Shen, Y. Impacts of Typhoon Mujigea on Sea Surface Temperature and Chlorophyll-a Concentration in the Coastal Ocean of Western Guangdong. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2017, 37, 49–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky, S.A.; Reul, N.; Lagerloef, G.; Reverdin, G.; Carton, J.A.; Chapron, B.; Quilfen, Y.; Kudryavtsev, V.N.; Kao, H.-Y. Haline hurricane wake in the Amazon/Orinoco plume: AQUARIUS/SACD and SMOS observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L20603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reul, N.; Quilfen, Y.; Chapron, B.; Fournier, S.; Kudryavtsev, V.; Sabia, R. Multisensor observations of the Amazon-Orinoco river plume interactions with hurricanes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 8271–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhil, V.P.; Vialard, J.; Lengaigne, M.; Keerthi, M.G.; Boutin, J.; Vergely, J.L.; Papa, F. Bay of Bengal Sea surface salinity variability using a decade of improved SMOS re-processing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, V.V. Statistical Assessment of Sea-Surface Salinity from SMAP: Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal and a Promising Red Sea Application. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chacko, N. Insights into the haline variability induced by cyclone Vardah in the Bay of Bengal using SMAP salinity observations. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Ming, J.; Zheng, J.; Tian, D.; Chen, D. Importance of Precipitation on the Upper Ocean Salinity Response to Typhoon Kalmaegi (2014). Water 2020, 12, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, H.; Sheng, J.; Tang, D.; Morozov, E.; Kalhoro, M.A.; Wang, S.; Xu, H. Examining the Impact of Tropical Cyclones on Air-Sea CO2 Exchanges in the Bay of Bengal Based on Satellite Data and In Situ Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.B.; Boutin, J.; Martin, N.; Spurgeon, P. Optimization of L-Band Sea Surface Emissivity Models Deduced from SMOS Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1414–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jiang, H.; Kang, X. Rainfall asymmetries of tropical cyclones prior to, during, and after making landfall in South China and Southeast United States. Atmos. Res. 2014, 139, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, D.; Tang, S.; Morozov, E.; Liang, W.; Sui, Y. A case study of Chlorophyll a response to tropical cyclone Wind Pump considering Kuroshio invasion and air-sea heat exchange. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
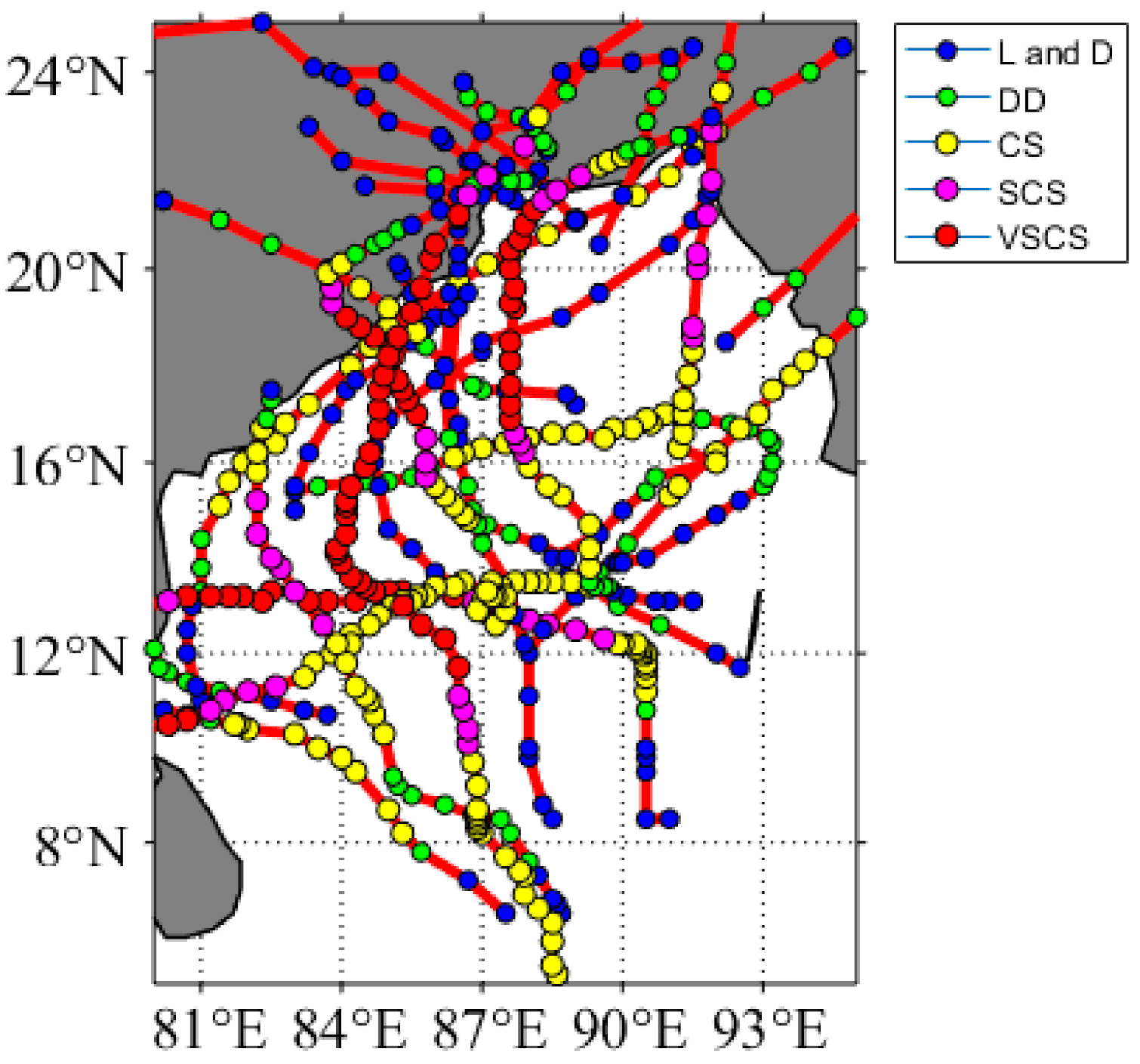
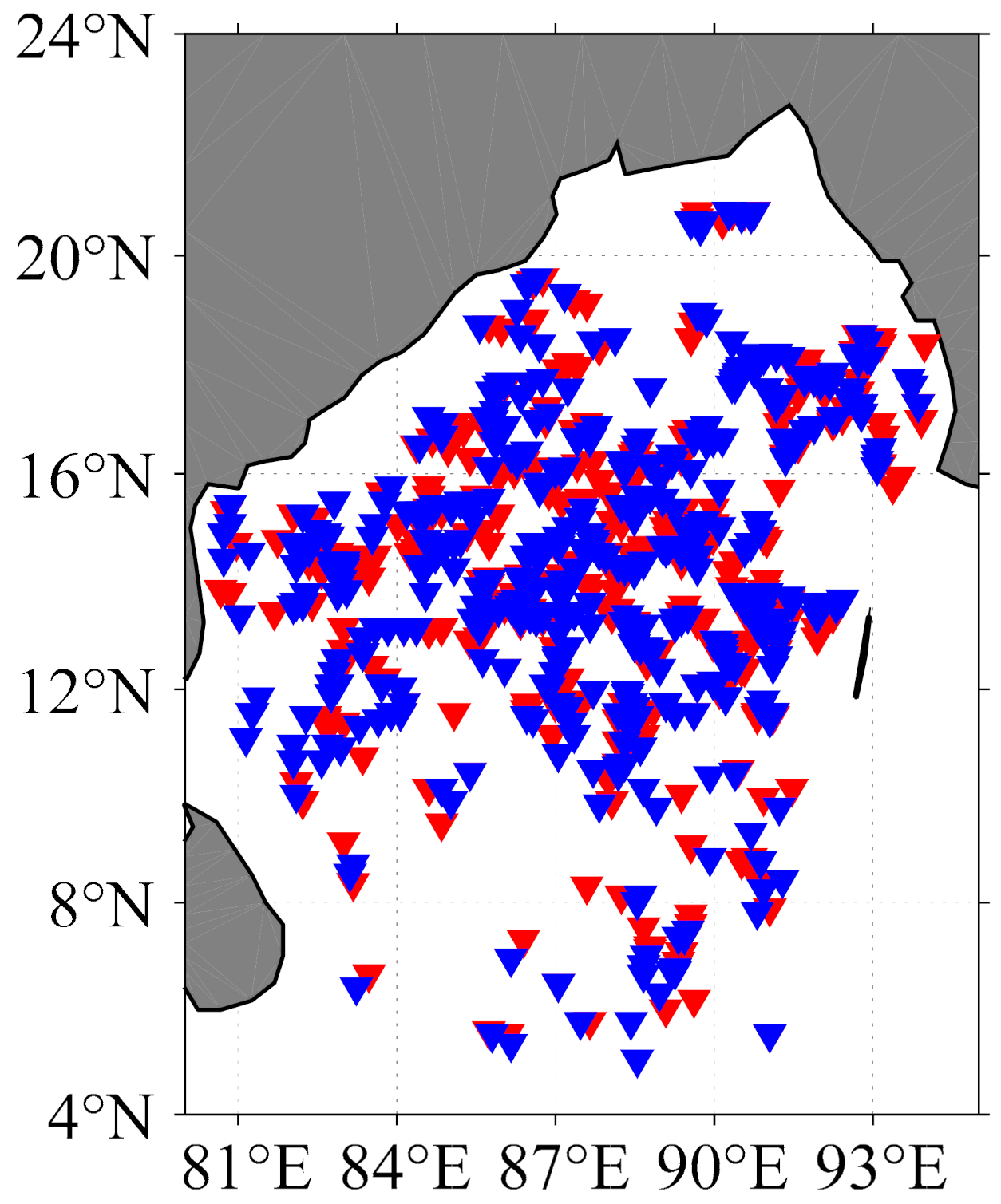
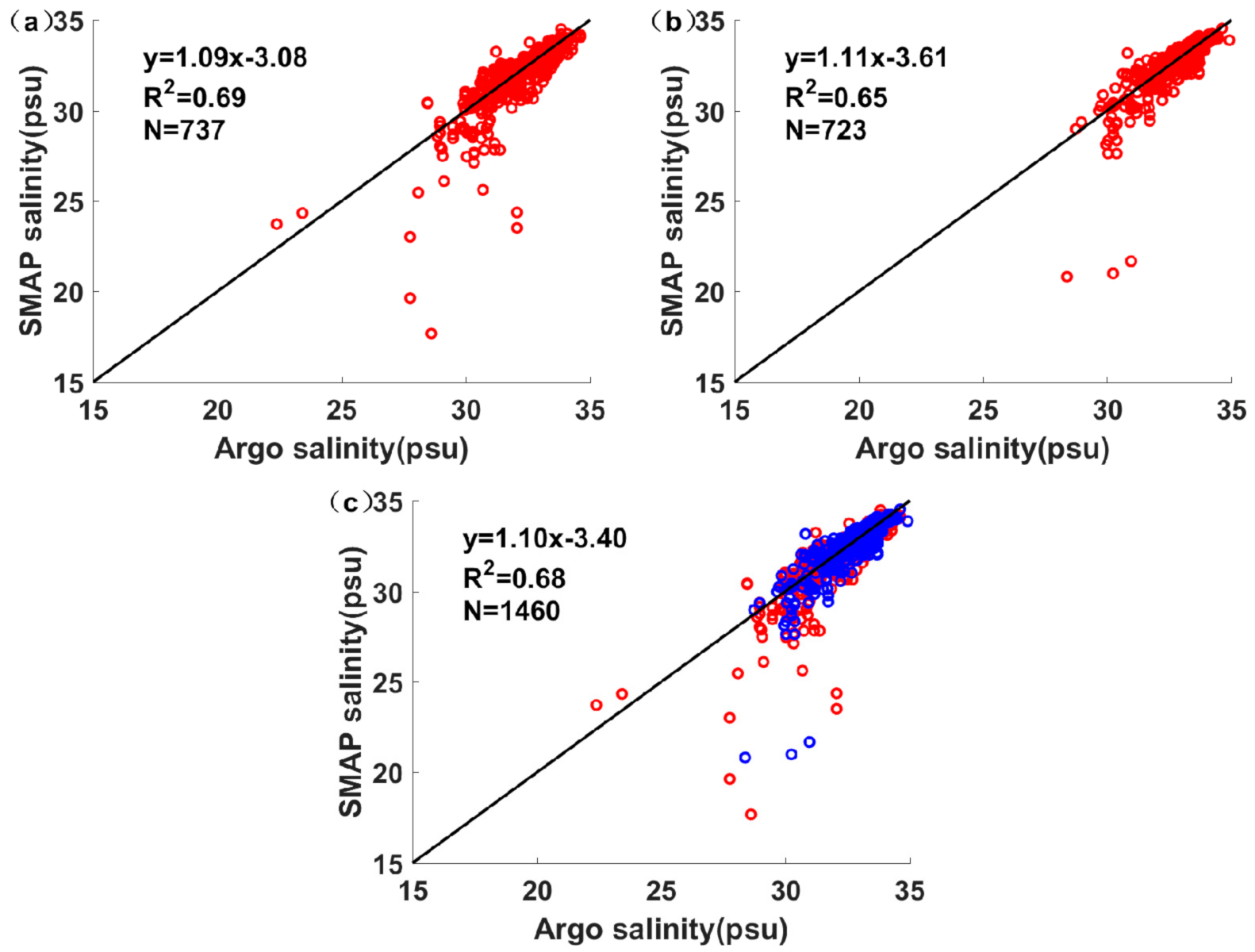
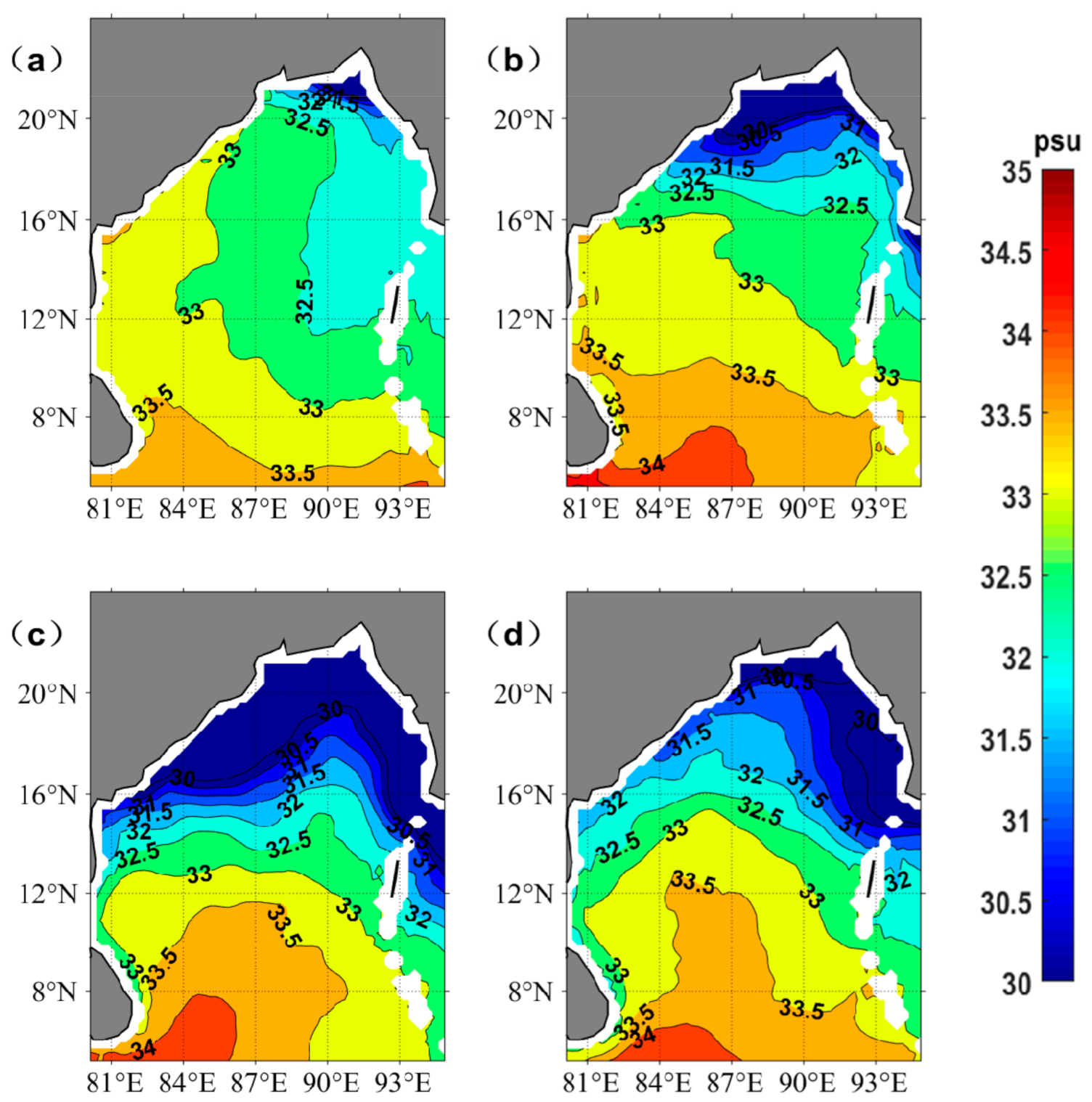

| Date | Name | The Minimum Pressure (hpa) |
|---|---|---|
| 8–10 November 2015 | Deep Depression | 996 |
| 17–22 May 2016 | Cyclonic Storm Roanu | 983 |
| 21–28 October 2016 | Cyclonic Storm Kyant | 996 |
| 2–6 November 2016 | Depression | 1000 |
| 29 November–2 December 2016 | Cyclonic Storm Nada | 1000 |
| 6–13 December 2016 | VSCS Vardah | 975 |
| 15–17 April 2017 | Cyclonic Storm Maarutha | 996 |
| 28–31 May 2017 | SCS Mora | 978 |
| 11–13 June 2017 | Deep Depression | 988 |
| 18–19 July 2017 | Depression | 992 |
| 9–10 October 2017 | Land Depression | 996 |
| 19–22 October 2017 | Depression | 997 |
| 15–17 November 2017 | Depression | 1001 |
| 6–9 December 2017 | Deep Depression | 1002 |
| 29–30 May 2018 | Deep Depression | 992 |
| 10–11 June 2018 | Depression | 988 |
| 21–23 July 2018 | Depression | 989 |
| 7–8 August 2018 | Depression | 992 |
| 6–7 September 2018 | Deep Depression | - |
| 19–22 September 2018 | Cyclonic Storm Daye | 992 |
| 8–13 October 2018 | VSCS Titli | 972 |
| 10–19 November 2018 | VSCS Gaja | 976 |
| 13–18 December 2018 | SCS Phethai | 992 |
| 26 April–4 May 2019 | ESCS Fani | 932 |
| 5–11 November 2019 | VSCS Bulbul | 976 |
| Date | Name | R2 before TCs | R2 after TCs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8–10 November 2015 | Deep Depression | NaN (3) | NaN (5) |
| 17–22 May 2016 | Cyclonic Storm Roanu | 0.89 (36) | 0.86 (42) |
| 21–28 October 2016 | Cyclonic Storm Kyant | 0.71 (137) | 0.75 (113) |
| 2–6 November 2016 | Depression | 0.77 (63) | 0.76 (74) |
| 29 November–2 December 2016 | Cyclonic Storm Nada | 0.88 (16) | 0.87 (18) |
| 6–13 December 2016 | VSCS Vardah | 0.71 (128) | 0.51 (121) |
| 15–17 April 2017 | Cyclonic Storm Maarutha | 0.68 (54) | 0.71 (49) |
| 28–31 May 2017 | SCS Mora | 0.4 (46) | 0.22 (53) |
| 11–13 June 2017 | Deep Depression | NaN (0) | 0.76 (15) |
| 18–19 July 2017 | Depression | NaN (2) | NaN (2) |
| 9–10 October 2017 | Land Depression | NaN (2) | NaN (2) |
| 19–22 October 2017 | Depression | 0.07 (9) | 0.72 (8) |
| 15–17 November 2017 | Depression | 0.55 (20) | 0.74 (14) |
| 6–9 December 2017 | Deep Depression | 0.71 (49) | 0.78 (37) |
| 29–30 May 2018 | Deep Depression | NaN (4) | NaN (4) |
| 10–11 June 2018 | Depression | NaN (2) | NaN (1) |
| 21–23 July 2018 | Depression | NaN (3) | NaN (4) |
| 7–8 August 2018 | Depression | NaN (3) | NaN (3) |
| 6–7 September 2018 | Deep Depression | NaN (2) | NaN (2) |
| 19–22 September 2018 | Cyclonic Storm Daye | 0.98 (9) | 0.03 (12) |
| 8–13 October 2018 | VSCS Titli | 0.51 (31) | 0.03 (28) |
| 10–19 November 2018 | VSCS Gaja | 0.6 (38) | 0.76 (38) |
| 13–18 December 2018 | SCS Phethai | 0.42 (14) | 0.02 (12) |
| 26 April–4 May 2019 | ESCS Fani | 0.61 (35) | 0.43 (38) |
| 5–11 November 2019 | VSCS Bulbul | 0.73 (31) | 0.71 (28) |
| SSSArgo before TCs | SSSSMAP before TCs | SSSArgo after TCs | SSSSMAP after TCs | All SSSArgo | All SSSSMAP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 32.36 | 32.14 | 32.71 | 32.58 | 32.54 | 32.36 |
| STD | 1.25 | 1.64 | 0.90 | 1.23 | 1.10 | 1.47 |
| Bias | −0.23 | −0.13 | −0.18 | |||
| RMSE | 0.95 | 0.75 | 0.86 | |||
| p-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Yu, R.; Tang, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Fu, D. Effects of Tropical Cyclones on Sea Surface Salinity in the Bay of Bengal Based on SMAP and Argo Data. Water 2020, 12, 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12112975
Xu H, Yu R, Tang D, Liu Y, Wang S, Fu D. Effects of Tropical Cyclones on Sea Surface Salinity in the Bay of Bengal Based on SMAP and Argo Data. Water. 2020; 12(11):2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12112975
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Huabing, Rongzhen Yu, Danling Tang, Yupeng Liu, Sufen Wang, and Dongyang Fu. 2020. "Effects of Tropical Cyclones on Sea Surface Salinity in the Bay of Bengal Based on SMAP and Argo Data" Water 12, no. 11: 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12112975
APA StyleXu, H., Yu, R., Tang, D., Liu, Y., Wang, S., & Fu, D. (2020). Effects of Tropical Cyclones on Sea Surface Salinity in the Bay of Bengal Based on SMAP and Argo Data. Water, 12(11), 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12112975





