Estimation of Water-Use Rates Based on Hydro-Meteorological Variables Using Deep Belief Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
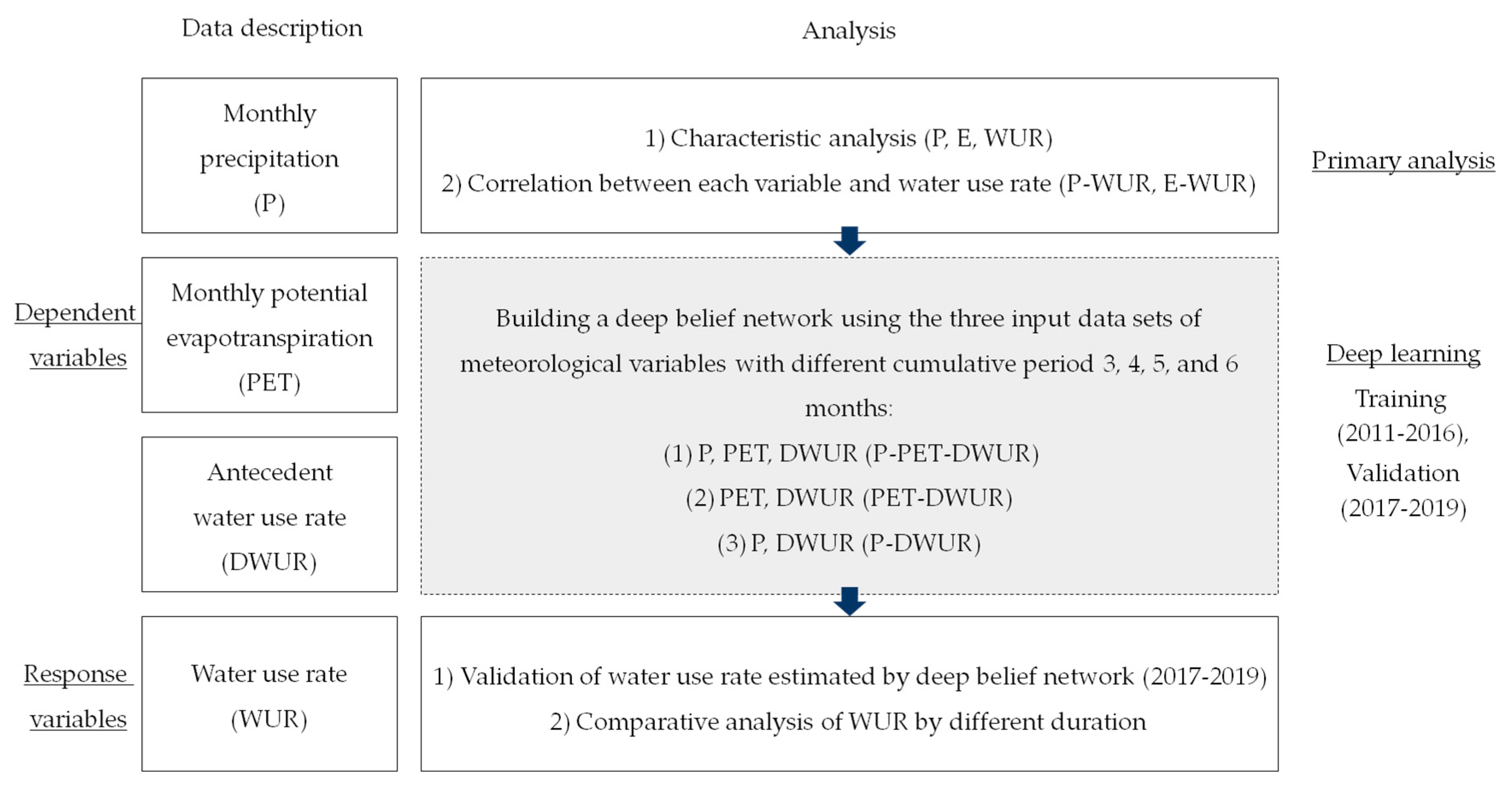
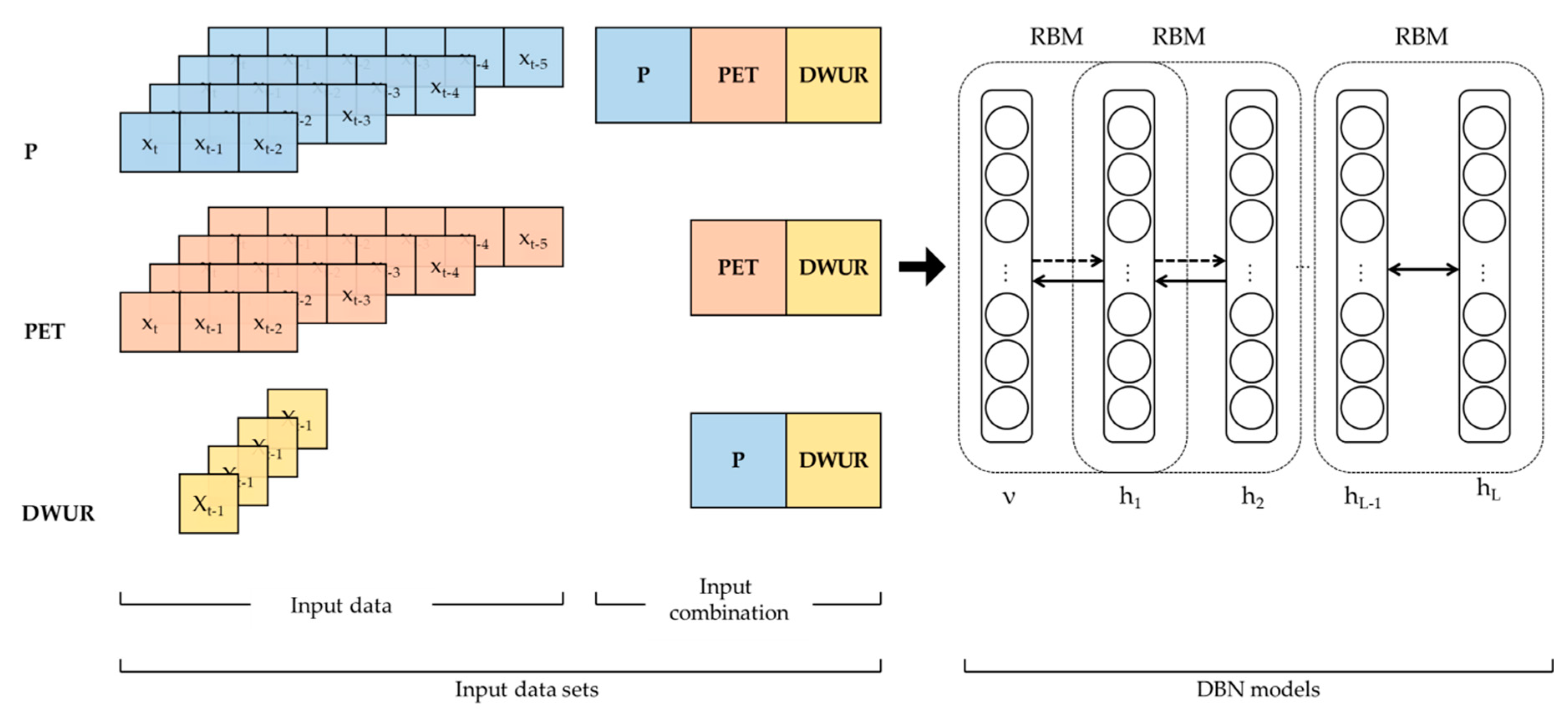
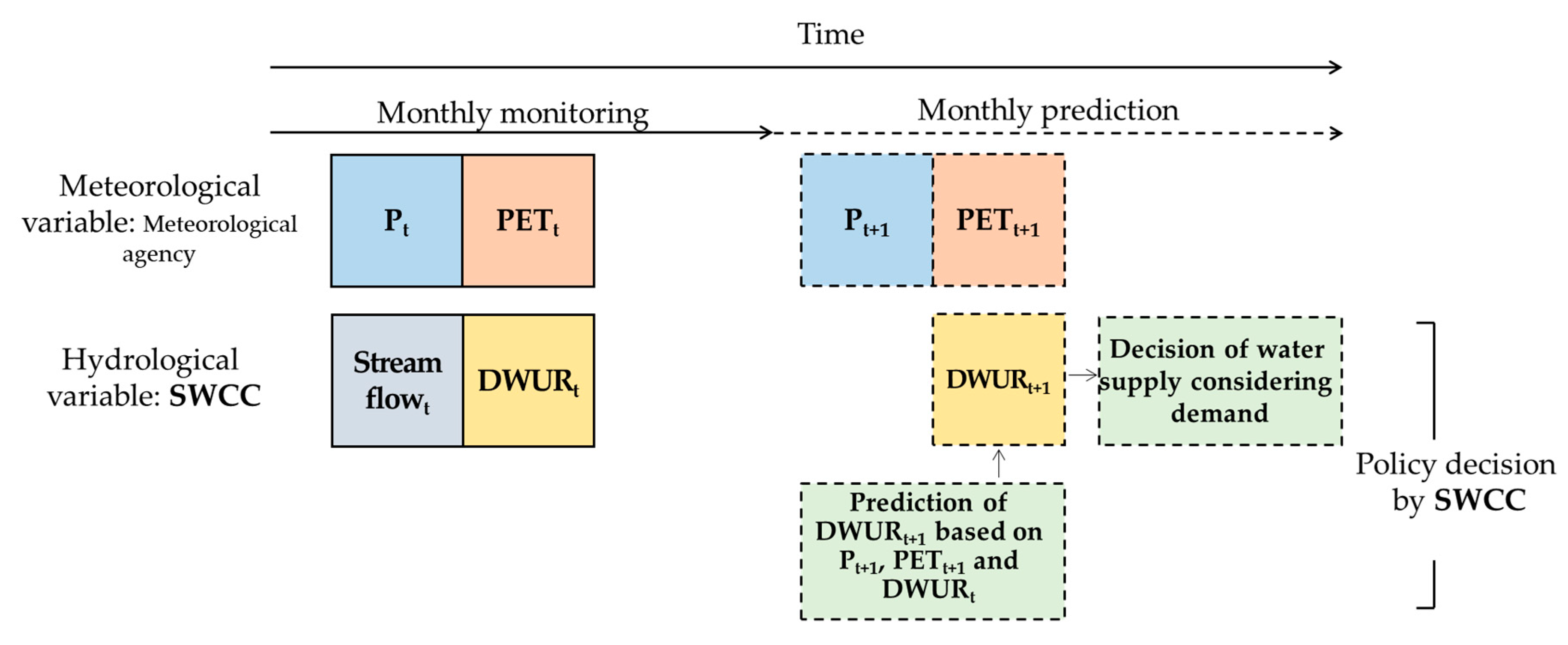
2.1. Experimental Design
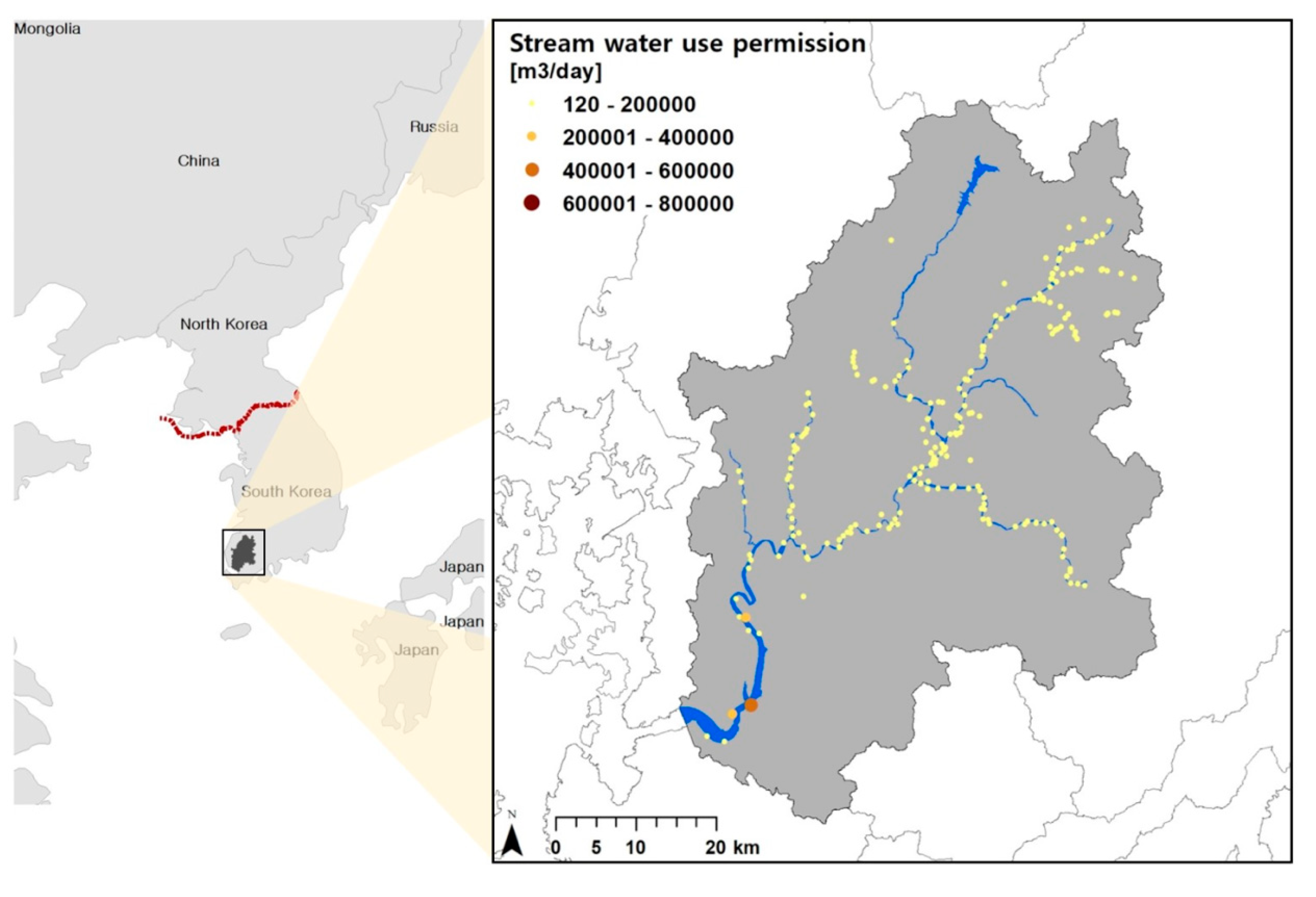
2.2. Study Area and Data
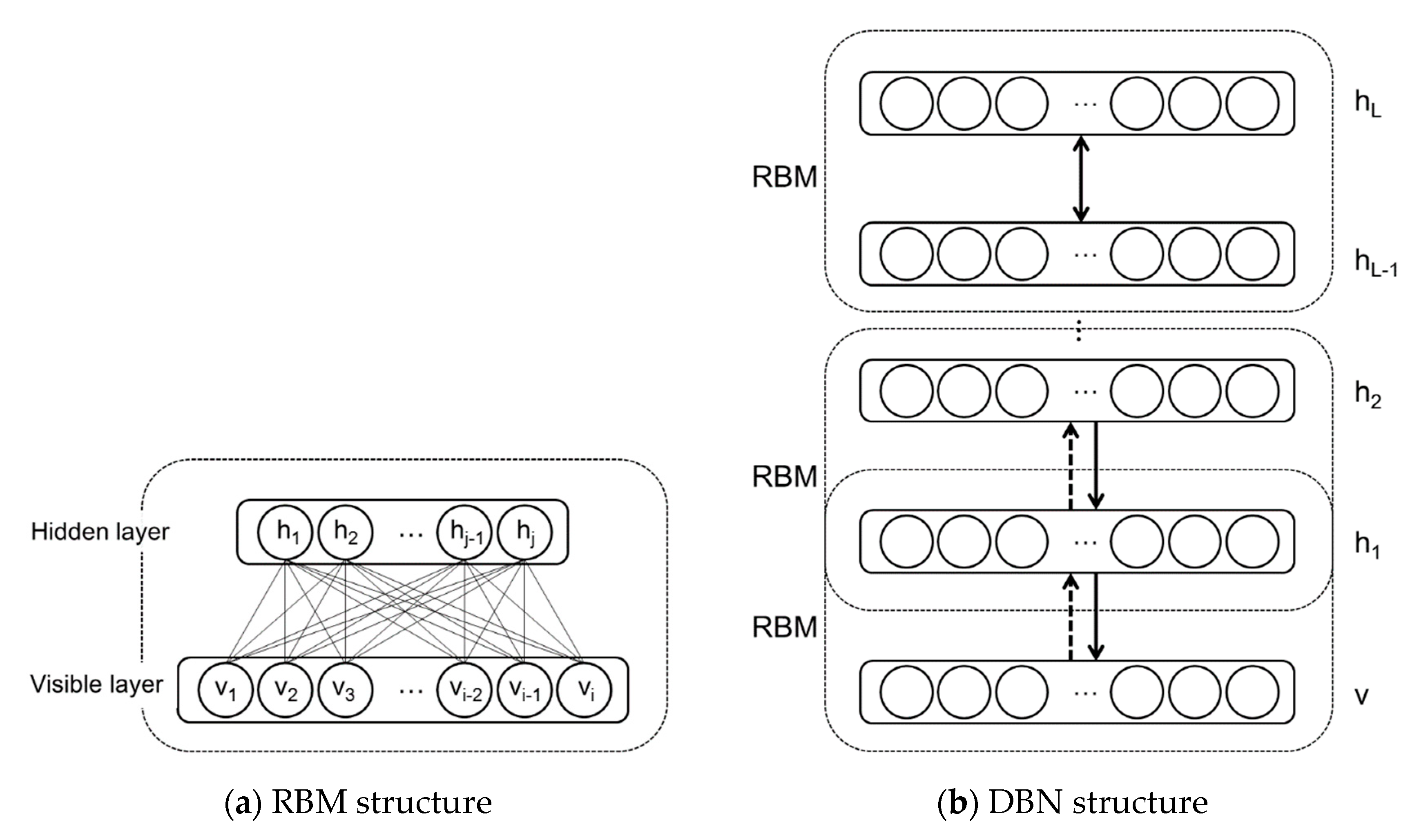
2.3. Deep Belief Network (DBN)
3. Results
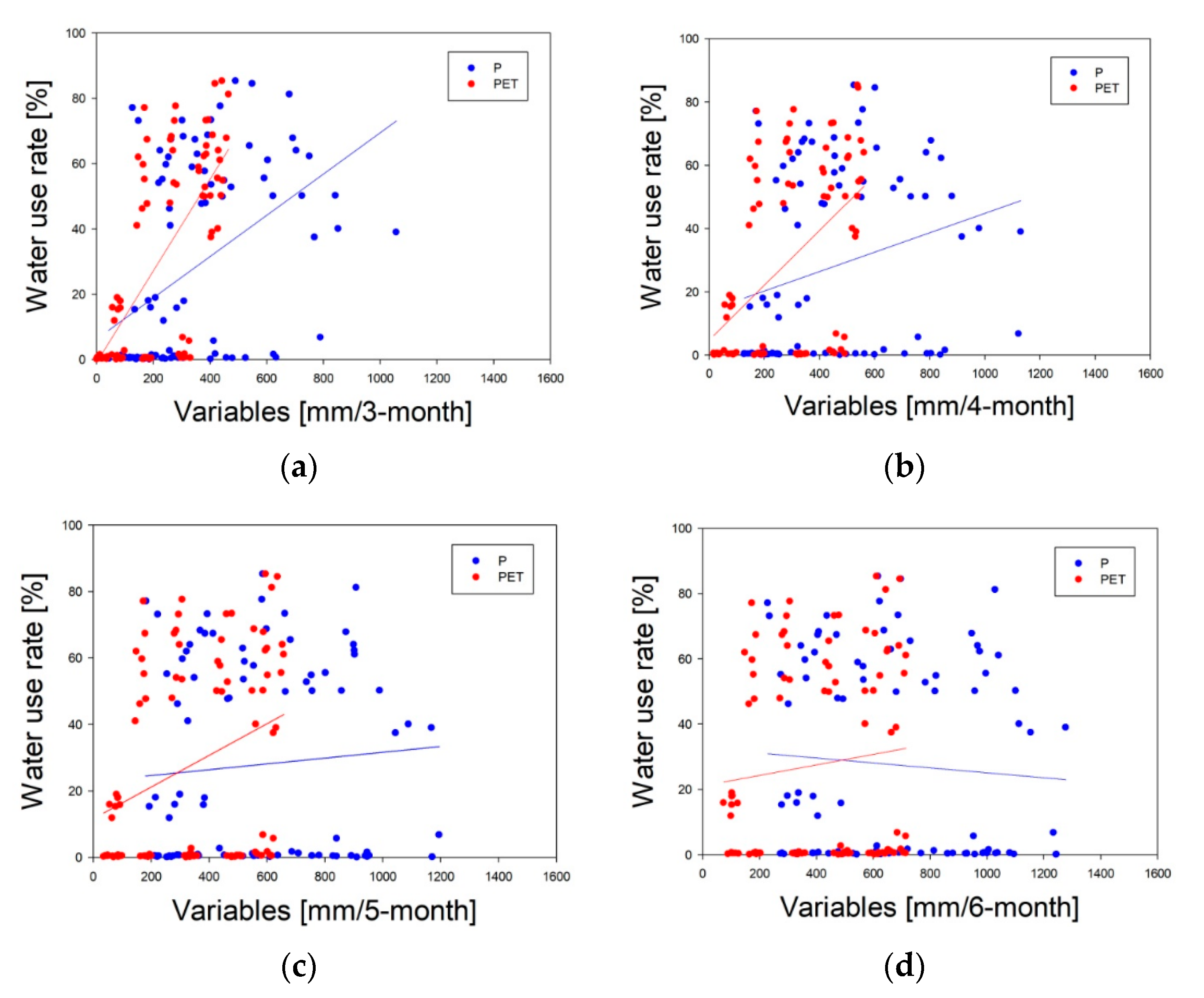
3.1. Relationship between Meteorological Variables and Stream Water-Use Rate
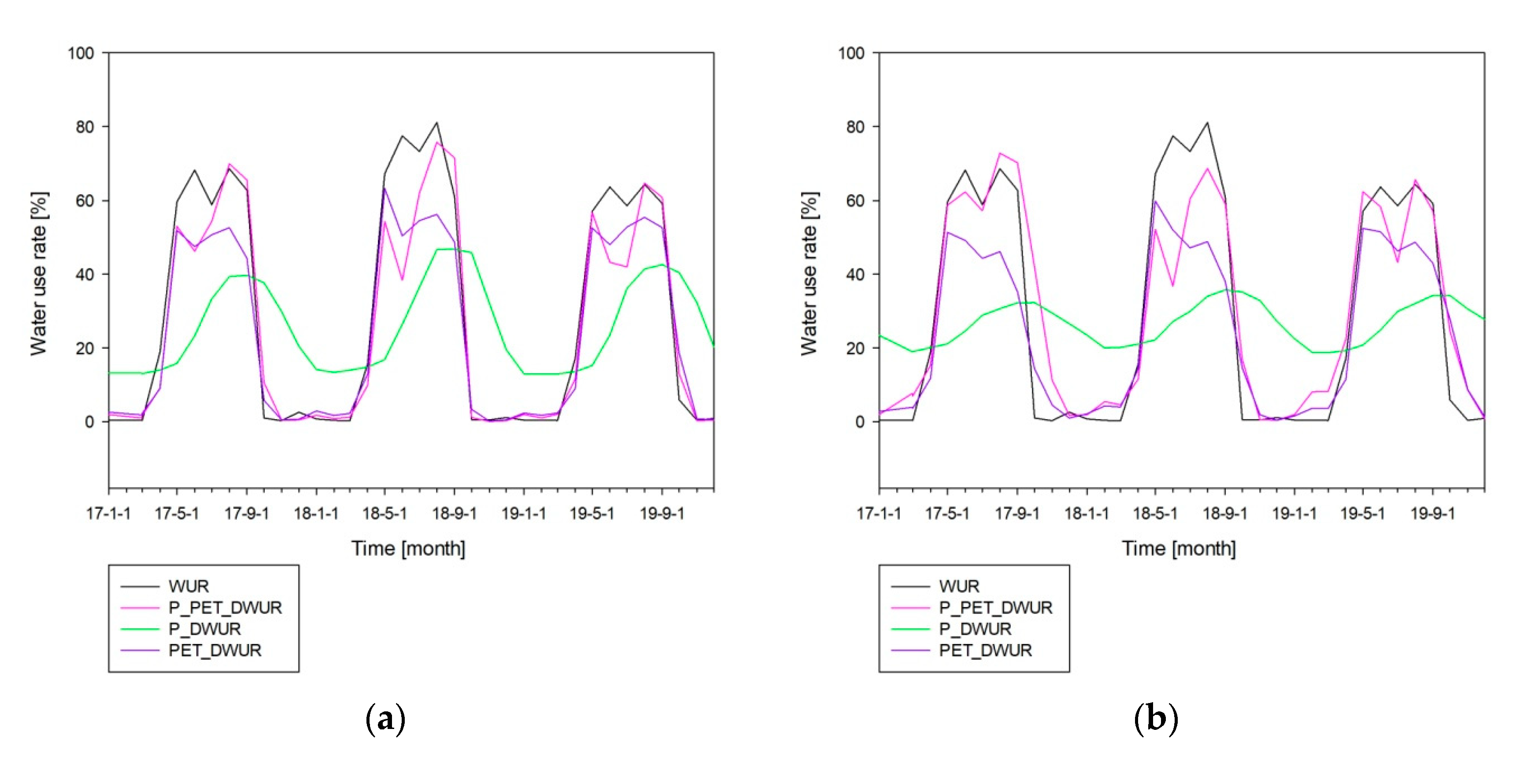
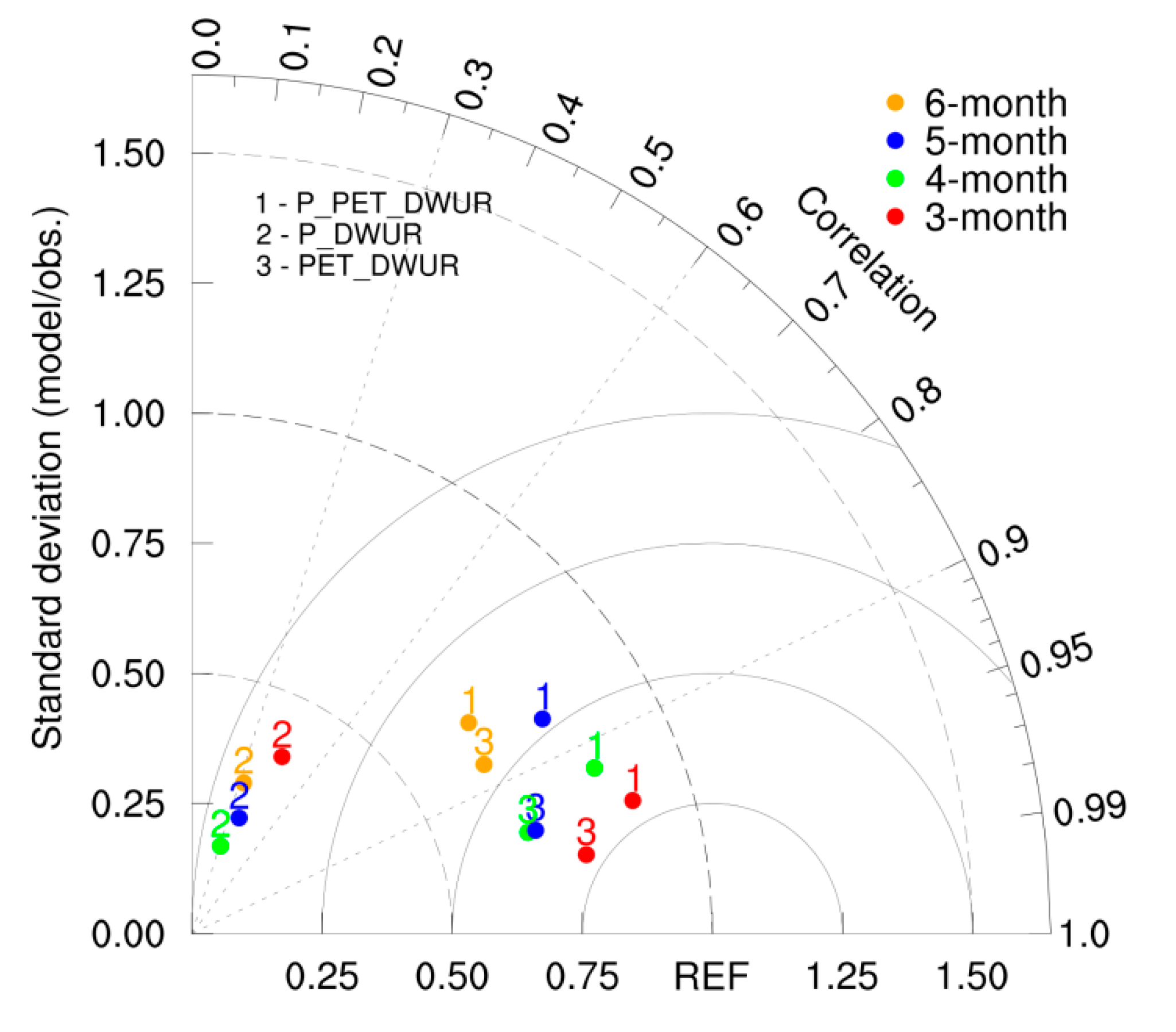
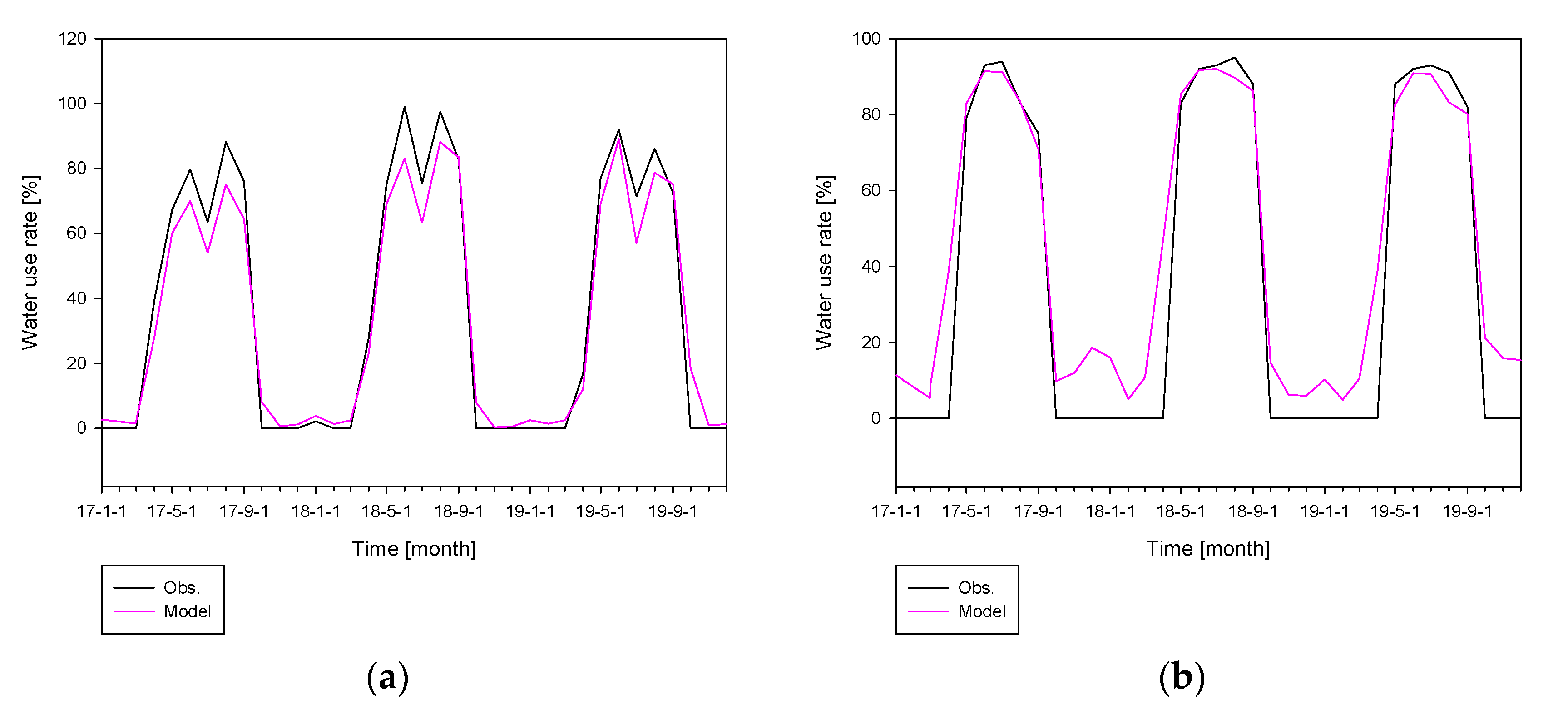
3.2. Estimation of Stream Water-Use Rate
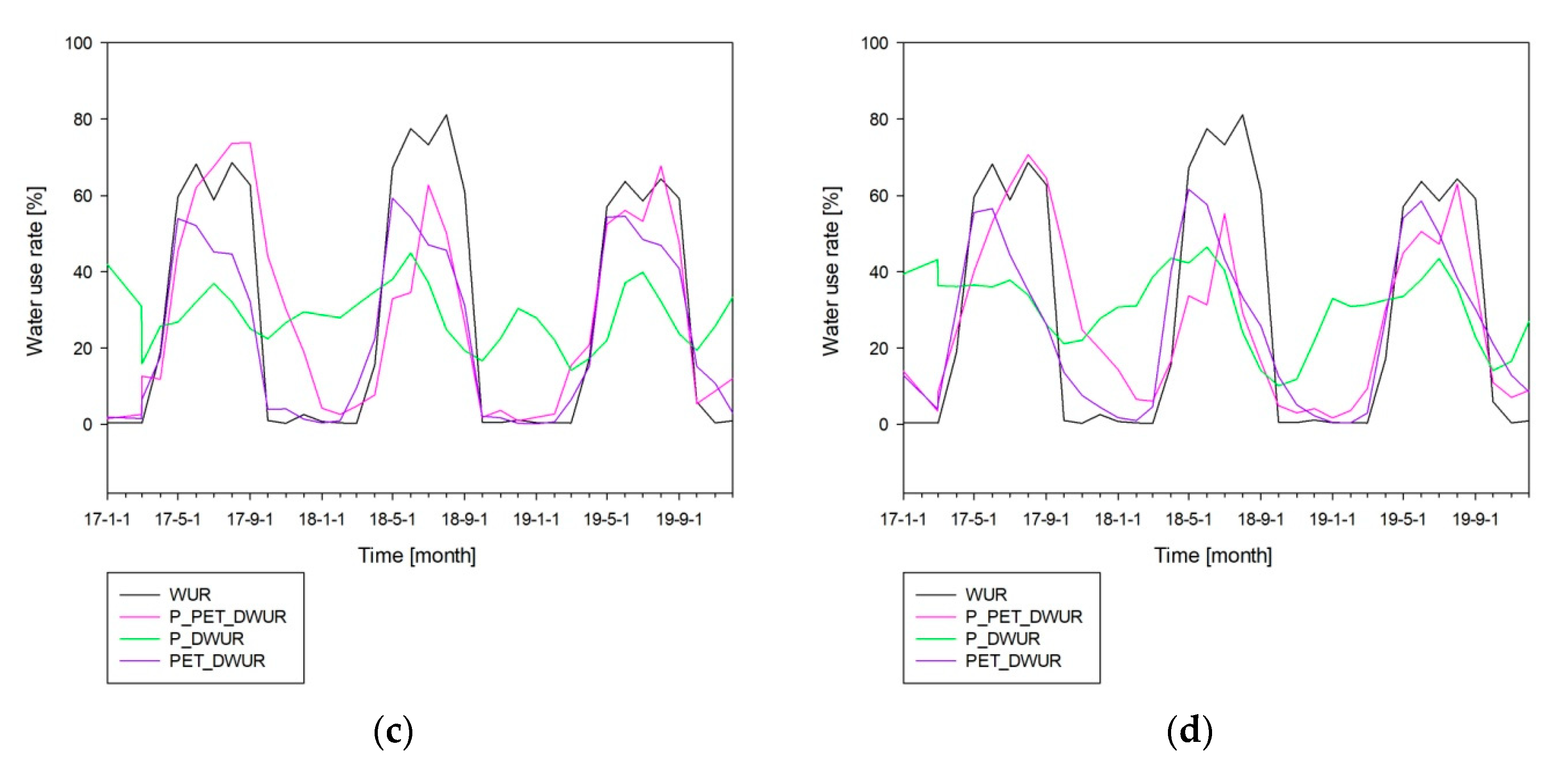
3.3. Estimation of Stream Water-Use Rate on Stream Water-Use Facilities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milly, P.C.D.; Betancourt, J.; Falkenmark, M.; Hirsch, R.M.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Stouffer, R.J. Stationarity is dead: Whither water management? Science 2008, 319, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.H.; Chung, E.S.; Lee, B.; Kim, Y. Meteorological hazard risk assessment based on the detection of trends and abrupt changes in the precipitation characteristics of the Korea peninsula. Theoret. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 127, 305–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulai, P.J.; Chung, E.S. Uncertainty assessment in drought severities for the Cheongmicheon watershed using multiple GCMs and the reliability ensemble averaging method. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.-H.; Lall, U.; Kim, S.-J. The unusual 2013–2015 drought in South Korea in the context of a multicentury precipitation record: Inferences from a nonstationary, multivariate, Bayesian copula model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 8534–8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.H.; Chung, E.S. Development of streamflow drought severity-duration-frequency curves using the threshold level method. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.H.; Chung, E.S.; Shahid, S. Reliability–resiliency–vulnerability approach for drought analysis in South Korea using 28 GCMs. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleick, P.H.; Burns, W.C.G.; Chalecki, E.L.; Cohen, M.; Cushing, K.K.; Mann, A.S.; Reyes, R.; Wolff, G.H.; Wong, A.K. The World’s Water 2002–2003: The Biennial Report on Freshwater Resources; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-1-55963-949-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cooley, H.; Fulton, J.; Gleick, P.H. Water for Energy: Future Water Needs for Electricity in the Intermountain West; The Pacific Institute: Oakland, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wutich, A.; White, A.C.; White, D.D.; Larson, K.L.; Brewis, A.; Roberts, C. Hard paths, soft paths or no paths? Cross-cultural perceptions of water solutions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, D.B.; Holtz, S. Water soft path analysis: From principles to practice. Water Int. 2009, 34, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.-Y.; Chang, H.; Chung, E.-S. Resident perceptions of urban stream restoration and water quality in South Korea. River Res. Appl. 2018, 34, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyantash, J.; Dracup, J.A. The quantification of drought: An evaluation of drought indices. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliades, L.; Loukas, A. Hydrological response to meteorological drought using the Palmer drought indices in Thessaly, Greece. Desalination 2009, 237, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Camarero, J.J.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Revuelto, J.; Morán-Tejeda, E.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A. Performance of drought indices for ecological, agricultural, and hydrological applications. Earth Interact. 2012, 16, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengio, Y.; Lamblin, P.; Popovici, D.; Larochelle, H. Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 December 2006; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Ranzato, M.; Poultney, C.; Chopra, S.; LeCun, Y. Efficient Learning of Sparse Representations with an Energy-Based Model. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 December 2006; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 1137–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Partal, T.; Cigizoglu, H.K. Estimation and forecasting of daily suspended sediment data using wavelet–neural networks. J. Hydrol. 2008, 358, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Perera, B.J.C.; Ng, A.W.M.; Tran, D. Drought forecasting using an aggregated drought index and artificial neural network. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2010, 1, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, M.K.; Chatterjee, C. Development of an accurate and reliable hourly flood forecasting model using wavelet–bootstrap–ANN (WBANN) hybrid approach. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamowski, J.; Chan, H.F. A wavelet neural network conjunction model for groundwater level forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2011, 407, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaee, T.; Nourani, V.; Zounemat-Kermani, M.; Kisi, O. River suspended sediment load prediction: Application of ann and wavelet conjunction model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 16, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothiprakash, V.; Magar, R.B. Multi-time-step ahead daily and hourly intermittent reservoir inflow prediction by artificial intelligent techniques using lumped and distributed data. J. Hydrol. 2012, 450–451, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Seo, Y.; Singh, V.P. Assessment of pan evaporation modeling using bootstrap resampling and soft computing methods. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2015, 29, 04014063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Kim, S.; Kisi, O.; Singh, V.P.; Parasuraman, K. River stage forecasting using wavelet packet decomposition and machine learning models. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4011–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.-H.; Ho, H.V.; Lee, G.; Jung, S. Application of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network for flood forecasting. Water 2019, 11, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Chung, E.-S.; Shiru, M.S. Uncertainty Analysis of Monthly Precipitation in GCMs Using Multiple Bias Correction Methods under Different RCPs. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.-W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Jin, Q.; Chao, J. Design of deep belief networks for short-term prediction of drought index using data in the huaihe river basin. Math. Probl. Eng. 2012, 2012, 235929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agana, N.A.; Homaifar, A. EMD-based predictive deep belief network for time series prediction: An application to drought forecasting. Hydrology 2018, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Long, Z.; Chen, Y. A novel dual-scale deep belief network method for daily urban water demand forecasting. Energies 2018, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gers, F.A.; Eck, D.; Schmidhuber, J. Applying LSTM to time series predictable through time-window approaches. In Proceedings of the Neural Nets WIRN Vietri-01, Vienna, Austria, 21–25 August 2001; Tagliaferri, R., Marinaro, M., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2002; pp. 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, J.H.; Seo, S.B. Estimation of river management flow considering stream water deficit characteristics. Water 2018, 10, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornthwaite, C.W. An approach toward a rational classification of climate. Geogr. Rev. 1948, 38, 55–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolensky, P. Information processing in dynamical systems: Foundations of harmony theory. In Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition, Volume 1: Foundations; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 194–281. ISBN 978-0-262-68053-0. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Items | Detail |
|---|---|
| Prediction variable | Stream water-use rate (WUR) |
| Input variable | 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6-month cumulative precipitations (P) 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6-month cumulative PETs (PET) Antecedent stream water-use rate (DWUR) |
| Training parameters | Number of hidden units: 10, 20, 30 Learning rate: 0.1, 0.5, 0.9 Number of epochs: 100, 500, 1000 Batch size: 6, 12, 24 |
| Parameters | Duration | P_PET_DWUR | P_DWUR | PET_DWUR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hidden layer | 3 months | 20 | 10 | 20 |
| 4 months | 20 | 10 | 30 | |
| 5 months | 30 | 30 | 10 | |
| 6 months | 10 | 20 | 20 | |
| Learning rate | 3 months | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 4 months | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.5 | |
| 5 months | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.9 | |
| 6 months | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.9 | |
| Epochs | 3 months | 1000 | 100 | 1000 |
| 4 months | 1000 | 100 | 1000 | |
| 5 months | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | |
| 6 months | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | |
| Batch size | 3 months | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 4 months | 12 | 24 | 6 | |
| 5 months | 12 | 6 | 6 | |
| 6 months | 12 | 6 | 6 |
| Duration | Performance Index | P_PET_DWUR | P_DWUR | PET_DWUR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 months | RMSE | 0.12 | 0.33 | 0.12 |
| NSE | 0.90 | 0.18 | 0.89 | |
| R2 | 0.92 | 0.21 | 0.96 | |
| 4 months | RMSE | 0.14 | 0.35 | 0.16 |
| NSE | 0.85 | 0.07 | 0.81 | |
| R2 | 0.85 | 0.10 | 0.92 | |
| 5 months | RMSE | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.16 |
| NSE | 0.72 | 0.12 | 0.81 | |
| R2 | 0.73 | 0.14 | 0.92 | |
| 6 months | RMSE | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.21 |
| NSE | 0.61 | 0.10 | 0.68 | |
| R2 | 0.63 | 0.11 | 0.75 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sung, J.H.; Ryu, Y.; Chung, E.-S. Estimation of Water-Use Rates Based on Hydro-Meteorological Variables Using Deep Belief Network. Water 2020, 12, 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102700
Sung JH, Ryu Y, Chung E-S. Estimation of Water-Use Rates Based on Hydro-Meteorological Variables Using Deep Belief Network. Water. 2020; 12(10):2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102700
Chicago/Turabian StyleSung, Jang Hyun, Young Ryu, and Eun-Sung Chung. 2020. "Estimation of Water-Use Rates Based on Hydro-Meteorological Variables Using Deep Belief Network" Water 12, no. 10: 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102700
APA StyleSung, J. H., Ryu, Y., & Chung, E.-S. (2020). Estimation of Water-Use Rates Based on Hydro-Meteorological Variables Using Deep Belief Network. Water, 12(10), 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102700






