Abstract
This study provides a conceptual model of the functioning of gravel-bed rivers during the post-regulation period in Poland and forecasts their subsequent evolution. The main difference between fluvial processes during the pre-regulation and post-regulation period is that they are limited to a zone that is currently several times narrower and trapped in a deep-cut channel. During the river post-regulation period, the construction of additional river training works was significantly limited in river channels. Moreover, all forms of economic activity were significantly reduced in the channel free migration zone, particularly bed gravel extraction operations. As a result of these changes, a limited recovery of the functioning and hydromorphology of the river channel occurred via a return to conditions in effect prior to river regulation. In recovering sections of river, the channel gradually broadens, and its sinuosity and number of threads increase. The overall process can be called spontaneous renaturalization, which yields a characteristic post-regulation river channel. The conceptual model was developed on the basis of the evolution of the gravel-bed river, the Raba River, during the post-regulation period in the Polish Carpathian Mountains.
1. Introduction
Since the late 19th century, gravel-bed river channels in mountain areas and their forelands have been subject to strong human impact in the temperate climate zone. This is due to construction of levees, river training works, channel debris extraction, and construction of reservoir dams [1,2,3]. River channels have in effect changed substantially in terms of cross-section and longitudinal profile.
Similar change processes have been observed in the Polish Carpathians and their foreland areas [4,5]. Direct human impact on river channels has been accompanied by changes in land use, which varied from catchment to catchment. Decades of intensive river regulation have led to a simplified morphology and pattern of Carpathian rivers which, consequently, became more narrow and deeper, in addition to following a single thread instead of many, with little ability for the river channel to migrate [4,6,7,8]. Increasing channel depth due to human impact [9,10,11] has led to large changes in connectivity between the river channel and the floodplain. The outcome in terms of ecology has been the loss of the most valuable habitats along the channel including initial gravel bar ecosystems and alluvial forests in mountain areas [12]. The regulation of the Carpathian river channels has also had other negative outcomes including a reduction in their ability to retain water that could be used for commercial or farming purposes, as well as an increase in the erosion risk to bridges, buildings, and other structures found near the river channel [13].
The period of the largest changes in channel morphology and overall functioning of Carpathian river channels caused by river training works and channel debris extraction lasted from 1961 to 1990. Today the drive to change river channels is much less substantial in the studied area. In addition, it is illegal to collect the gravel from river channels and various government agencies have allowed the development of the free migration zone. The period after 1990 is called herein the post-regulation period. Changes in river channels observed during this period of time have been termed spontaneous renaturalization [14]. Such changes occur most often in the Carpathian river channels with a high width to depth ratio (W/D) [8]. Similar evolving patterns are present in the channels of other rivers, for example, the Sacramento River in California, USA [15] and the Magra and Piava rivers in northern Italy [16,17].
Researchers perceive river channel renaturalization either as a hydro-geomorphologic process [5], biological process [18], or ecological process [19,20]. The authors of this paper treat the examined subject matter from a hydro-geomorphologic perspective.
The main purpose of this paper is to discuss the pattern of spontaneous renaturalization in a mountain area gravel-bed river channel. This process is believed to represent an important mechanism that explains the functioning of a channel system during the post-regulation period in Poland. The course of renaturalization is described for the example of the Raba River flowing across southern Poland. The river serves as a good representation of Carpathian gravel-bed rivers. River renaturalization is also discussed in terms of future change directions and rates of change.
The Introduction of this paper focuses on the chronology of river channel change as well as types of human impact in the Raba river channel in the 19th and 20th centuries. This history of human impact led to the creation of a regulated river channel by the 1970s. The paper focuses on the analysis of channel morphology and functioning during the post-regulation period using the 1970s and 1980s as a base period for the purpose of comparison. The changes discussed in this paper occur as a result of fluvial processes that vary in intensity from site to site depending on the local fluvial environment, including type and degree of human impact in the channel. Special attention is given to the role of natural fluvial processes that, in particular, include large floods which are considered to be the most important part of successful spontaneous renaturalization processes in the Raba River.
Large floods occurred along the Raba River every two to four years in the period from 1951 to 1972. These major flooding events affected the morphology and the channel pattern of the Raba River including the years 1951, 1958, 1960, 1962, 1963, 1965, 1970, and 1972. The period from 1973 to 1996 was characterized by a much smaller frequency of large and very large flood events. The only major floods in this period to affect the morphology of the Raba River occurred in 1987 and 1996. The year 1997 initiated a new period of increasingly frequent floods, of which the most critical events in terms of channel morphology change were the floods of 1997, 2001, 2010, and 2014 [8].
The analysis of flood effects on changes of functioning in the Raba river channel in post-regulation period employed the concept of the flood pulse [21,22]. This concept does not focus on the river channel but its relationship with its overall environment including the valley floor [23]. The concept assumes that a river channel follows an oscillating pattern of widening and narrowing. The former occurs most intensively after large flood events, which revitalize lost connectivity between the river channel and its floodplain and allow for a regeneration of hydro-geomorphologic processes [24,25,26]. Looking for proof of the formation of channel widening zones following floods and their narrowing during floodless periods constitutes an important part of this study.
The analysis of morphologic diversity in the longitudinal profile of a post-regulation channel in this paper uses the concept of beads on a string. This concept was proposed by Stanford et al. [27] and Ward et al. [28] and introduces the idea of beads representing zones of the most intensive morphologic, hydrologic, and biological diversity based on the capacity for the formation of a broad floodplain. These zones are characterized by multidimensional interrelationship between the river channel and the floodplain, with one affecting the other. Bead zones alternate with string zones that have a simplified structure and limited ability to affect their surroundings. In this study we identify bead zones along the Raba river channel, analyze conditions for their occurrence, and assess their significance in spontaneous renaturalization. This is another important part of the proposed conceptual model of the evolution of a gravel-bed river in a mountain area during a post-regulation period.
2. Study Area
The Raba River is one of the larger mountain area rivers in the upper Vistula basin. It is 131.7 km long, with an average gradient of 0.25°. The area of the Raba catchment is 1537 km2. It is an elongated catchment, with a larger proportion of right-bank catchment area (Figure 1). The Raba catchment is located in the following two different geomorphologic regions: (1) the Carpathian Mountains and (2) the Carpathian foreland basins (Figure 2). The study area is formed of flysch rocks from the Cretaceous and Paleogene, in its Carpathian part. These are mostly sandstone, claystone, siltstone, and conglomerates [29]. Sub-Carpathian basin, on the other hand, is formed of thick clastic formations from the Miocene that lay atop Mesozoic, Paleozoic, and Precambrian formations to yield an unconformity. The Miocene formation includes mostly siltstone, claystone, and shale with sandstone inserts [29]. The Raba river channel cuts into relatively thin alluvial deposits or flysch parent material [8]. The highest point in the catchment is Mt. Turbacz (1310 m). The lowest point is the river’s point of confluence with the Vistula River at 180 m above sea level. The lowest annual precipitation totals are noted in the northern part of the catchment across the Carpathian foreland and range from about 700 to 800 mm/yr. The highest totals are noted in the middle mountain area of the Gorce Range and equal about 1200 mm/yr. The mean annual discharge of the Raba River at the Proszówki gauging site covering more than 90% of the catchment area equals 17.6 m3/s, while the maximum recorded discharge equals 1470 m3/s [30].
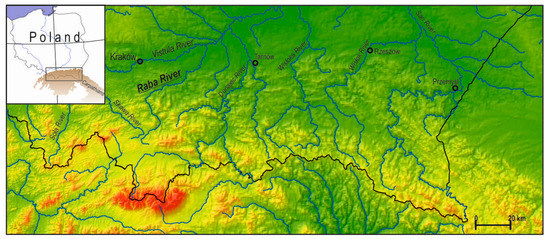
Figure 1.
Study area.
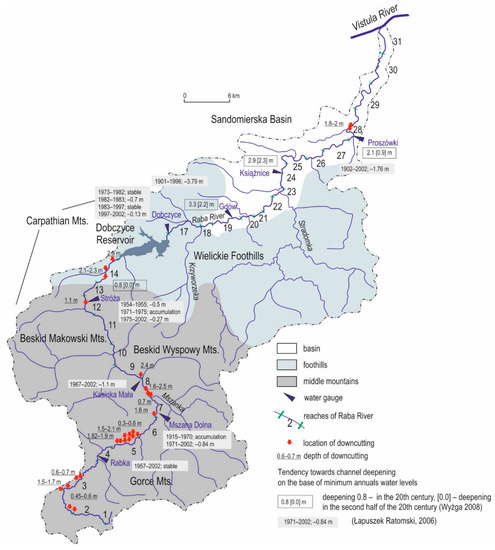
Figure 2.
Location and intensities of downcutting in the Raba river channel.
The Raba catchment is a rural area characterized by the predominance of the agricultural type of land use [31]. Arable land covers 40% of the catchment area, forests cover 35.6%, meadows 12%, and fruit growing areas about 2%. Built-up areas cover the remaining 10.4% of the catchment area [32]. Many municipalities are located in the near vicinity of the Raba River and produce a significant impact on land use and management across the valley floor. This consequently affects the functioning of the channel. The high human impact on the valley floor and river channel is due to the presence of vital transportation links such as roads and railways. One of the most important roads in southern Poland runs through the Raba valley.
The Raba river channel has been gradually regulated since the beginning of the 20th century. Today about 60% of the river channel is lined with longitudinal structures, which were built during every decade since the 1960s. About 600 m of regulated banks are noted, on average, for each one kilometer of the Raba river channel. About two-thirds of the structures were deemed to be well preserved, while the rest as poorly preserved. River training works are found most often along concave banks, and less often along convex banks. The structures are meant to protect against erosion. In areas characterized by a high density of buildings situated close to the riverbanks, both banks are usually regulated in order to provide flood protection.
Transverse training structures such as straight drop structures are much less impactful than longitudinal structures.
The most important hydrotechnical structure found along the Raba River is the dam at Dobczyce. The resulting Dobczyce Reservoir was built in 1986 and is located at the 60th kilometer of the Raba River. The purpose of the reservoir is to help local communities obtain drinking water, protect local communities from flooding, equilibrate river discharge, and generate electricity.
3. Research Methods
Research on channel structure of the Raba River was performed by employing a channel mapping procedure developed at the Institute of Geography and Spatial Management, Jagiellonian University [33,34]. The main assumption employed in this research method is an understanding of the river channel system as a structure consisting of homogenous morphodynamic reaches. The log used to collect data covers the following four groups of data: (1) initial information, (2) channel parameters, (3) hydrodynamic parameters, and (4) hydrometeorologic parameters of the studied period of time. Principal log entries included information on geographic location, geologic structure, channel parameters, cross sections, longitudinal profile, banks, floor type, sediments, buildings along the watercourse, and channel type. The data log included 57 types of quantitative information and 48 types of qualitative information. Quantitative information is used to calculate indices characterizing the studied channel [34]. The entire river channel of the Raba River was surveyed in line with the above guidelines, in 2015. In addition, some reaches were surveyed in 2009, 2010, and 2014. Grain-size distribution of bed material were assessed using a method proposed by Wolman [35].
Information on the degree of river regulation works and their current state was also collected during the field surveys and supplemented with corresponding information from the Regional Water Management Board in Kraków.
The Raba river channel was also examined using a digital elevation model produced from 2010 to 2013. Orthophotos were also examined for the years 2009 and 2012. These are available from the Cartography Collection at Institute of Geography and Spatial Management, Jagiellonian University and were received from the Central Geodesic and Cartographic Documentation Bureau. The analysis in the study was enhanced using orthophotos available from Google Earth for the period 2014 to 2019. Cartographic analysis and morphometric analysis were performed using QGIS software.
Data provided by the Institute of Meteorology and Water Management (Polish, IMGW) were used to examine the hydrodynamic characteristics of the studied watercourses. Six gauging sites were analyzed in total (Figure 1).
This study compares survey data for the Raba river channel from the years 1976 to 2015. A survey of the Raba river channel performed in 2015 utilized the boundaries of homogenous morphodynamic reaches identified during the 1976 survey. Therefore, the zones of spontaneous renaturalization (“beads on a string”) identified in the Raba river channel in 2015 do not overlap with the boundaries of the analyzed channel reaches. The procedure for the survey performed in 2015 was described earlier in this paper. In 1976 the Raba river channel survey was performed as part of a project called “Dynamic river channel typology for the Carpathians and their foreland.” The 1976 project was run by the Institute of Geography of Jagiellonian University, Department of Geomorphology [36]. The survey data on the Raba river channel morphology and pattern from 1976 make it possible to make viable comparisons with analogical survey data collected in 2015. The data logs used in 1976 were somewhat different with respect to selected parameters, i.e., more descriptive and less quantitative. This means that not all information contained in the data logs could be compared. In this study we also looked, in detail, at the morphology and pattern of the Raba river channel, and changes therein, for major flood events in 2010 and 2014. The observed changes make it possible to determine change directions in the evolution of gravel-bed rivers in mountain areas large floods.
4. Human Impact on Carpathian Rivers
Carpathian river channels that were regulated starting in the late 19th century had evolved in earlier periods to high bedload transport conditions resulting from intensive agriculture and the development of a dense network of unpaved roads. In the 19th century the Carpathians were a densely populated region, largely deforested, with arable land found as high as 1000 m above sea level. The region had a very high road density at the time as well. Today, unpaved road density ranges from 4 to 7 km·km−2 in the Carpathians [37]. In the late 19th century, unpaved roads were utilized more intensively and were an important source of both fine and coarse material as they were eroded as deep as bedrock [38]. If we were to consider channel evolution for periods prior to the period of high human impact (regulation works and large scale gravel mining), then we could argue that river channels in the Western Carpathians were multithreaded, wandering, or sinuous with lateral bars, and meandering in basins with a tendency for braiding [10,39,40].
Flood control levees have been built in Carpathian river valleys since the late 19th century. As a result, the channel migration zone has become smaller over time for rivers across the region. Major engineering works began in Carpathian river channels in the late 19th century. The aim was to regulate river channels in order to reduce flood risk and create commercial waterways. River regulation work proceeded in stages starting with reaches at lower elevations, and then shifting upriver [41]. Regulated river channels had gentler bends and longer straight sections [42]. River regulation work in the Carpathians can be divided into several distinct stages which are the following: (1) The period before World War II (described above), (2) the period from 1945 to 1989, and (3) the period after 1990. Each stage varied in terms of the method of regulation, extent of regulation, and intensity of regulation [4,8].
Stage 1 consisted of extensive work on long sections of river and some projects were never fully completed. Regulation work at this stage consisted of watercourse straightening, as well as a narrowing and shortening. Some Carpathian rivers were made shorter by as much as 10% [8,43]. Regulation projects were halted by the outbreak of World War II and resumed only in the late 1950s. In the beginning of Stage 2, since the 1940s to the 1960s, industrial-scale extraction of channel debris was introduced in Carpathian rivers [5]. In later decades, the local population continued to illegally extract debris from the river channels in the Carpathians [6,8]. The most advanced regulation works were performed in the 1960s and 1970s in the later part of Stage 2 [4]. This was a period of the most radical alteration of river channel patterns, longitudinal profiles, and cross-sections. This period produced mainly such river training structures such as groins, flow redirection piers, weirs, and debris dams, but few drop structures or steps.
In the 1970s, in Poland, river regulation works were planned at the local level [44]. The number of regulation projects decreased markedly in the 1980s, with drop structures being the main form of river regulation [6]. Some banks were also reinforced in this period of time. The main reason for this drought in investment was a major economic crisis in Poland, as well as the lack of major flood events. Regulation works became limited in scope when Poland made the transition to a market economy in the 1990s. Then, the river regulation Stage 3 began in the Polish Carpathians. New regulation works were initiated in the late 1990s, especially following a major regional flood in 1997. River engineering projects at the time were limited primarily to repairing damage produced by floods in 1997, 1998, and 2001. Work included the building of drop structures and bank reinforcements. Narrowed and straightened river channels lacked debris, which had been previously supplied by unreinforced banks, leading to an acceleration in downcutting erosion that undercut the base of existing hydrotechnical structures. The next stage would include the destruction of these structures. Given such outcomes, river engineers would reinforce the same banks two or three times [8].
River regulation systems built in the Carpathians turned out to be ineffective and harmful to the natural environment. Regulation works aimed to produce a single, narrow channel with no side channels. The large change in river channel geometry led to a lack of adjustment when paired with a river’s actual hydrologic regime. Downcutting increased in river channels as a result [6,8,11,45,46]. In some cases, downcutting reached solid rock or damaged river engineering structures [4,11,47]. This forced new river regulation work to be performed. This repetition would eventually lead to extensive degradation in river channels, as much as 80% in the Raba river channel [8].
The gradient of regulated rivers would increase along straightened, shortened, and narrowed reaches, as would discharge and the rate of debris transport, which would lead to a deficit of debris in the river channel and, subsequently, a lowering of the channel floor [1,8]. Channel incision by as much as 1.3 to 3.8 m has occurred in the lower and middle reaches of Carpathian rivers since the early 20th century [9,11]. In the second half of the 20th century, channel floor lowering has been observed in upstream reaches of Carpathian rivers, ranging from 0.5 to 3.5 m [8,13,48,49].
In light of the general change in approach to river channel maintenance in the Carpathians, in Poland after 1989, human impact in river channel systems has been severely limited since. In place of extensive intervention, the strategy now is to pursue a minimal intervention focus, i.e., one that is close to what nature itself would pursue. The stoppage of river regulation work in the Carpathian region has led to spontaneous renaturalization of river channels [8].
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Comparison of the Raba River Channel Structure in 1976 and 2015
Changes in the morphology and functioning of the Raba river channel is presented herein on the basis of a comparison between survey results from 1976 and 2016. Both surveys focused on changes in channel morphology and overall river patterns.
The Raba river channel had already been heavily regulated by the time of the survey study in 1976. However, the regulation structures had not been in place for very long and the channel was still alluvial almost in its entirety. Downcutting had not yet occurred. Narrowing had occurred to a substantial extent. In the 1970s, many semi-natural, multi-threaded reaches were still to be found in the middle section of the Raba River.
In the 1980s and early 1990s, these last semi-natural reaches were finally regulated or became submerged due to the construction of the Dobczyce Reservoir. In addition, the Raba channel became much deeper in the late 1970s and 1980s. This was a natural process that had been accelerated by the effects of river regulation in the Raba channel, gravel extraction from the river bed, limitation of the river free migration zone by railway and road infrastructure, and reduction in the arable land area in the Raba river catchment. This process prompted the Raba River to follow the regulated channel more permanently.
Over the next twenty or so years natural fluvial processes, including major floods, have led to major changes in the morphology of the Raba river channel in comparison with the year 1976.
In 1976, more than 90% of the length of the Raba river channel was alluvial type. The largest number of river reaches were shaped by deposition and redeposition processes as well as lateral erosion in some cases. These reaches occupied 49% of the total length of the Raba River and were characterized by the largest area of bars and large area of undercuts in relation to other reaches of the same river. Downcutting and lateral erosion were detected along 28% of the length of the Raba river channel. In the 1970s, as much as 23% of the river channel consisted of sections with transport function and with levees reinforcing banks (Figure 3).
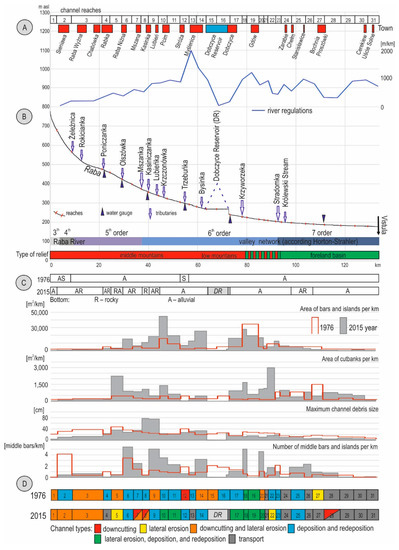
Figure 3.
Raba river channel in 1976 and 2015: (A) Human impact in the Raba River valley, (B) longitudinal profile of the Raba River, (C) morphology of the Raba channel in 1976 and 2015, and (D) channel types of the Raba River in 1976 and 2015.
In 2015, it is difficult to identify one predominant morphodynamic channel type for the Raba river channel in its longitudinal profile. The morphology of the channel is variable and adjusted to local conditions in mountain reaches, and much more homogeneous in basin reaches. The largest number of the river’s reaches remain to be shaped by deposition, redeposition, and lateral erosion. Their number is, however, smaller than that in 1976, and they occupy only 36% of the length of the Raba river channel (Figure 3). It is these reaches that contain more than 70% of the area of bars in the entire Raba river channel system. In comparison with 1976, the share of straight sections of river channel has increased to 35% of the length of the channel. This type is present most often in urbanized areas, as well as in regulated reaches and those with levees. Reaches dominated by downcutting and lateral erosion are concentrated in the upper parts of the Raba river channel. These occupy about 30% of the length of the river channel, which is similar to their share from 1976. This type of river channel along with sinuous channels with lateral undercuts includes river reaches featuring rock formations such as rock steps, rock groins, and rock floor. Generally, a river channel of this type is currently rock alluvial in nature. This makes it different from channel reaches identified in 1976 dominated by downcutting and lateral erosion, as they had an alluvial channel floor. Bars present here are not thick and are often deposited directly atop the rocky channel floor.
This study also examines differences in channel morphologic characteristics for analyzed Raba river channel reaches between 1976 and 2015.
In 2015, the width of the Raba river channel was larger than that in 1976 in more than 75% of the reaches examined. Channel width increased by an average of 14 m, with a maximum increase of 102 m in Channel Reach no. 10 (Figure 4). River bed width increased by 185 m at this site. The width was 45 m after the regulation of the Raba river channel in the 1970s and 1980s and increased to 230 m in 2015 as a result of a few major floods. Spontaneous renaturalization was supported by an artificial supply of gravel to the channel of the Raba River in this river section. This was part of a river restoration project called the ”The Upper Raba River Spawning Grounds” [50]; however, the river bed width is still currently lower than the river bed width at the end of the 19th century, in the period before Raba River regulation. River width was ca. 380 m at the time [51].
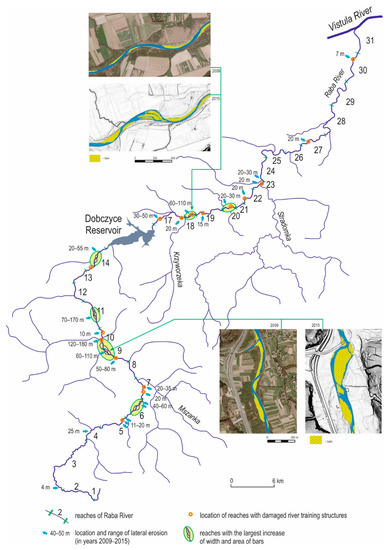
Figure 4.
Location of sections undergoing a spontaneous renaturalization in the Raba river channel from 2009 to 2015.
There are some reaches where the channel is narrower than in 1976. In one case, it is narrower by 18 m (Figure 4).
Increases in channel depth were noted in all the examined reaches of the Raba River. Average increases equaled 1.8 m, with a maximum increase of 3.8 m in a downstream reach of the Raba river channel surrounded by levees (Figure 2). It is important to remember though that an increase in river channel depth in the Raba River is first and foremost caused by intense downcutting erosion occurring in the river following a period of intensive river regulation works.
Minimum annual water levels measured at gauging sites in the middle and lower course of the Raba River were used to assess the tendency towards channel deepening in the 20th century [10,52,53]. According to Wyżga [10,53] the Raba river channel became deeper by 2 or 3 m in its downstream section in the 20th century. Nonetheless, both periods of increased erosion and gradual debris accumulation occurred throughout the 20th century in the Raba river channel (Figure 2). Łapuszek and Ratomski [52] provide similar results. In the years from 1901 to 1996 the downstream reach of the river became deeper by 3.79 m in Gdów and 1.76 m in Proszówka. In the upstream reach of the river, the onset of erosion dates to 1971, and by 2002 the river channeled had become, on average, about 1.4 m deeper (Figure 2).
Additional information on channel deepening in lower reaches comes from an analysis of damage to regulation structures in the Raba river channel. Damage data were collected for 26 river training structures built in the 1960s and 1970s, most of which were located in the upper sections of the Raba River (Figure 2). River training structures damaged by downcutting and lateral erosion serve as unique types of reference sites for the rate of erosional change. River channel deepening at such sites ranged from 0.45 m to 2.5 m. Intensive channel deepening at more than 2 m was also observed upstream of the backwater area of the Dobczyce Reservoir. This reach is currently experiencing significant accumulation. A very high rate of downcutting erosion could have been associated with the construction of the Dobczyce Reservoir.
Accelerated downcutting and lateral erosion in the Raba river channel led to undercuts in the riverbank. Today more than 75% of the Raba River reaches feature a larger area of undercuts in relation to 1976 (Figure 3). The present-day area of undercuts is three times larger than in 1976. The average area of undercuts per reach increased by 515 m2/km. Maximum increases in the area of undercuts per river reach equaled 3011 m2·km−1. An additional outcome of river regulation, although one not associated with downcutting erosion, is a rise in the length of sections of river dominated by water and sediment transport.
The most readily observable present-day change in the Raba river channel in comparison with 1976 is the increase in the area of bars (Table 1). Today the area of Raba bars is twice as large as that in the 1970s. Increases in bar and island areas, in 2015, relative to 1976 were noted in almost 75% of Raba River reaches and equal an average of 2190 m2·km−1. The largest increase in the area of accumulation landforms found in the Raba river channel reached almost 30,000 m2·km−1. It occurred at the point of confluence between the Raba River and one of its major tributaries, the Krzczonówka River (Figure 3 and Figure 4). This reach was also characterized by the largest increase in river channel width. This reach has been viewed as a classic example of a bead of morphologic diversity strung on the string of the studied river channel [27]. Similar accumulation zones occur in most reaches of the mountain section of the Raba river channel. A total of six large accumulation zones and more than 25 rather small channel broadening zones with lateral bars were observed in the present study (Figure 4).

Table 1.
Area of bars and undercuts in the Raba river channel.
The tendency described above is only seemingly inconsistent with the observed decline in the share of Raba river sections characterized by a predominance of deposition and redeposition processes. Deposition occurs along a shorter stretch of the Raba river channel, but it occurs with more intensity. In effect, reaches of channel where bar formation is a predominant morphodynamic process are characterized by channel widening. While the distribution of the area of bars along the Raba River remains uneven, it still differs from that in 1976, when, on the one hand, almost 50% of the area of bars in the studied channel was to be found in a several-kilometer-long stretch on the boundary between mountains and a foreland basin. On the other hand, accelerated deposition of river channel material today occurs at a much larger number of reaches along the Raba River.
In 1976, the gravel fraction of bed material (diameter 2 to 64 mm) dominated in nearly all reaches of the Raba River. In 2015, the most evident change in the surface grain size distribution was an increase in the share of the pebble fraction of bed material (diameter 64 to 256 mm). Today, this is the dominant bed-material fraction in eight Raba river reaches, with most being located upstream of the Dobczyce Reservoir. An increase in the mean grain size of bed material was a general rule in regulated Carpathian rivers in the second half of the 20th century [5,54]. Raba river channelization in the period from the 1960s to the 1980s increased the transport ability of the river. The sediment supply by Raba river tributaries also diminished as they too were regulated resulting in little or no sand and silt being deposited in the river beds, with the material becoming coarser and better sorted, and channel bed armoring developing in some reaches of the river [55]. A surprising discovery was the decline in the maximum bed-material grain size in the Raba river channel between 1976 and 2015, which occurred in more than 50% of the studied reaches (Figure 3). The average decline was 3 cm. The largest decline in the maximum bed-material grain size (24.5 cm) occurred in one of initial reaches of the studied river. A large decline also occurred in several reaches below the Dobczyce Reservoir, i.e., an average of 12 cm. This is likely due to the retention of debris in the area upstream of the Dobczyce Reservoir. On the other hand, marked growth (more than 50 cm) in the maximum bed-material grain size between 1976 and 2015 occurred in two reaches of the Raba River downstream of the point of confluence with the Mszanka, which is the most important tributary of the Raba River in its mountain section.
The river’s braiding ratio [33] also increased to some degree, by an average of 0.43 middle landforms per kilometer of river, over the 40 year period between the first and second survey. An increase in the braiding ratio was noted in more than 50% of the reaches in the study. The largest increase in the braiding ratio (4.4 middle landforms per kilometer) was noted in a reach of the Raba River found downstream of the Dobczyce Reservoir where a tributary flowed into the Raba River (Figure 3).
5.2. Role of High Water Stages in the Evolution of a Post-Regulation River
Floodwaters are an extremely effective channel-shaping factor. Large floods, in particular, are effective in floodplain development [25,56,57,58,59,60,61]. Their significance is examined in this section in terms of how they affect spontaneous renaturalization in a gravel-bed river during the post-regulation period, in this case, the Raba River. The morphological features and functioning of the river channel in 2009 and 2015 are compared for this very purpose.
The state of the Raba river channel in 2009 can be described by hydrodynamic conditions that would be the equivalent of a medium-high water. Such water-stages occurred following an earlier period with large floods from 1996 to 2001. However, the river channel experienced some changes during this earlier period due to the occurrence of major floods. It has adapted to more dynamic flow conditions following a period of low water levels since the early 1980s.
After 2009, the morphology of the Raba river channel was strongly affected by the most recent three large floods, two floods in 2010 and one flood in 2014. The flood in May of 2010 was characterized as a catastrophic flood based on the Punzet classification [62]. The flood occurred along the Raba River both upstream of the Dobczyce Reservoir and downstream of it. A second flood occurred in early June. While it was smaller than the May flood, it occurred at a hydrologically disadvantageous moment when water levels were still high in the river and groundwater levels were still high. The 2014 high-water stage was smaller than the first high-water stage in 2010, especially below the Dobczyce Reservoir (Q10%). However, in the upper reaches of the river it was higher than that in 2010. Water levels and discharge rates during the flood of 2014 were equivalent to a high-water stage that occurs once per 100 years (Q1%).
All the floods discussed above accelerated erosion and accumulation in the Raba river channel. The increase in the intensity of lateral erosion led to a widening of the river channel at about 50% of the studied reaches, although it did not affect the entire length of each reach. In areas where channel widening did occur, its width, in 2015, increased in most cases by several meters or several tens of meters relative to the year 2009. The river channel widened by more than 100 m relative to the year 2009 in several reaches, i.e., in the middle section of the river in the area where the Mszanka and Krzczonówka join the Raba River as well as in the section just below the Dobczyce Reservoir (Figure 4).
The area of bars also increased substantially throughout the Raba river channel after the floods of 2010 and 2014. By 2015 it was about 1.5 times larger than in 2009 (Table 1). The increase in the area of bars in the Raba channel, however, was not distributed evenly along the length of the river after the floods of 2010 and 2014.
In addition, increased channel sinuosity and the formation of multiple threads were observed in some reaches (Figure 4). The effects of the 2010 and 2014 flood events discussed herein are representative of the evolution of a river channel after a series of large floods, as described by the flood pulse model [21]. The widening of the channel and formation of a multithreaded river also suggest that connectivity between the river channel and floodplain has been regained for a period of time and the floodplain has reformed.
Today there are reaches of the Raba River that perform similar morphodynamic functions and repeat along the length of the river, although the morphodynamic functions of reaches also depend on the degree to which a river channel is regulated. Floods damage or destroy hydrotechnical structures, which is usually the first step in the shift from a channel’s morphodynamic function, a transport function, or a downcutting function to a deposition function with lateral erosion.
The most dynamically evolving and morphologically diversified reaches of the Raba River were reaches that, already in 2009, were characterized by substantial sinuosity and large area of bars. These are mountain area reaches of the Raba River that were not “trapped” by road infrastructure and rural settlements.
The largest changes in the river channel were noted upstream of the Dobczyce Reservoir at sites where tributaries would supply large amounts of debris to the Raba River in the course of floods (Figure 4). Lateral erosion and deposition processes are very active at these sites, which has led to a rise in the Raba’s riverbed due to the deposition of a portion of the material transported downstream of each point of confluence, as well as upstream of each point of confluence, due to limited discharge driven by abrupt increases in stream load in the confluence zone of the Raba and its tributaries. This evolution scenario for the Raba River was determined for reaches found downstream of the points of confluence of the following rivers: Olszówka, Kasiniczanka, Krzczonówka, and Bysinka (Figure 3).
Significant, although much smaller, changes in the morphology of the Raba river channel after foods were observed in the foothill section of the Raba channel downstream of the Dobczyce Reservoir. The retention of floodwaters and their sediment load by the Raba River inside the Dobczyce Reservoir limits the morphogenetic potential of flood events below the Dobczyce Dam. However, the floods of 2010 and 2014 have changed the morphodynamic function of these reaches from transport-dominated reaches to reaches with deposition with lateral erosion. A particularly large change in the morphology of the Raba river channel occurred downstream of the point of confluence of the Krzyworzeka River, which is also downstream of the Dobczyce Reservoir. In the flood period from 2010 to 2014 the channel of the Raba River made the transition from single-threaded to multi-threaded along this particular stretch of the river (Figure 4).
Straight and slightly sinuous reaches of the Raba River and reaches characterized by a small post-regulation width became only slightly altered during flood events in 2010 and 2014. As in the period prior to 2009, these reaches perform a mostly transport function, with small changes occurring in the channel due to the concentration of transported material along the main axis of the channel. These are reaches with mostly levees that are located in the lower course of the Raba, as well as two reaches located within the city limits of two largest towns in the Raba Valley, Rabka and Myślenice (Figure 1 and Figure 3).
The last large floods period was followed by a gradual process of adjustment of the river channel to “average” hydrodynamic conditions in line with the flood pulse concept [21]. This period of adjustment could become interrupted by major floods in the future.
6. Conceptual Model of the Evolution of a Gravel-Bed River during the Post-Regulation Period
The fluvial system of a post-regulation river experiences a distorted debris supply pattern in its full longitudinal profile. A shortage of debris generates forces that aim to replenish the channel system with sediments. Erosion damages river training structures and liberates debris material into the channel system from the riverbanks and floodplain. A spatially uneven supply of debris from reaches experiencing less regulation pressure contributes to the formation of a number of wide accumulation zones similar to those discussed in the literature and designated sediment waves or sediment slugs [63,64]. The process of forming these zones is discontinuous. One additional characteristic of these zones in a post-regulation river is their limited mobility resulting from anthropogenic constraints in the river channel and the valley floor. A post-regulation river is characterized by long straight reaches and slightly sinuous reaches playing a primarily transport role where unit stream power values are high. Such reaches do not favor accumulation. Hence, the deposition of transported debris usually occurs in widened zones [65]. These zones can be classified as beads using the beads on a string conceptual model by Stanford and Ward [27].
The following four characteristic reach types were identified for post-regulation river channels based on the Raba River: (A) Regulated reaches, (B) reaches with destroyed regulation works but retained regulation channel, (C) sinuous reaches with bars, and (D) multithreaded reaches, i.e., deposition zones (Table 2 and Figure 5I,II). The first two types (A and B) are single-threaded, compact channels that often feature rock outcrops on the channel floor, characterized by low sinuosity and a W/D ratio implying a narrow, deep channel. The other two types (C and D) are channels at various stages of renaturalization. Type C is a single channel, sinuous, widened, and with bars. Type D is a multithreaded channel characterized by the highest W/D ratio, wide, with a number of threads and multiple mid-channel bars [8].

Table 2.
Characteristics of the reaches of a post-regulation river.
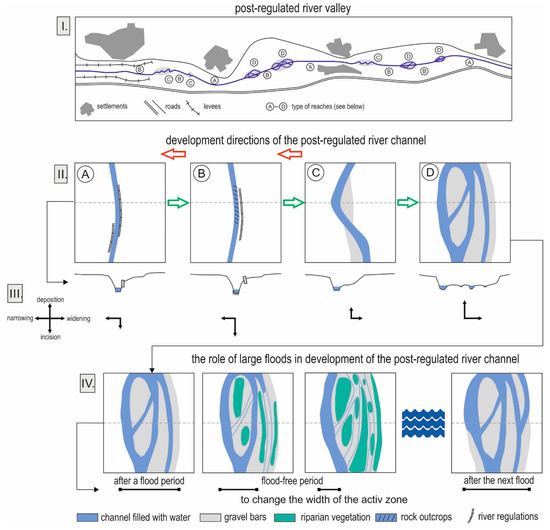
Figure 5.
Conceptual model of the evolution of a gravel-bed river in a mountain area during a post-regulation period.
Types A and B represent a narrow string, which is consistent with the idea of beads on a string. Both small beads (Type C) and large beads (Type D) are scattered along this string at irregular intervals (Figure 5). These four types of reaches alternate along the longitudinal profile of the studied river. However, some river reaches are more homogeneous, where one type will exist over a significant distance, whereas the channel structure in other reaches will be fragmented to a greater extent. Longer homogeneous reaches are found in Type A and B channels. Type C and D reaches occur irregularly along the course of the river and are separated by Type A and B channel reaches. This sort of spatially variable system of channel reaches is found in gravel-bed river valleys in the Carpathians and is accurately described by the beads on a string idea proposed by Stanford and Ward [27].
The location of the above-mentioned reaches, types A through D, in the river system is due to both natural determinants such as geologic structure, relief, and climate, as well as due to human impact associated with river channel regulation, road infrastructure, land use, and human settlement. This is why it is difficult to unequivocally determine the reasons for the occurrence of reaches of type C and D where the pattern of occurrence is the result of a combination of fluvial processes present in a post-regulation river (Figure 5I,II).
Spontaneous renaturalization occurs most intensively in reaches of type C and D, at locations where fluvial processes can proceed freely. Hence, spontaneous renaturalization along a post-regulation river does not occur in a continuous manner, but in a fragmented manner.
Type D reaches constitute initial sites of channel debris restoration in the river system. Debris accumulated in these zones comes primarily from bank erosion and is supplied by tributaries. These wide accumulation zones also serve as sites for the evolution of multithreaded systems and make it possible for the river channel to migrate freely (Figure 5II). The presence of type D reaches, and to a lesser degree type C reaches, is a sign of spontaneous renaturalization in a post-regulation river system. This process begins with the destruction of regulation structures and changes in principal fluvial processes along with a reduction in the share of downcutting and an increase in the share of lateral erosion, where type A and B reaches transition into type C reaches. In the next stage, type C reaches experience accumulation, expansion of the active zone, and expansion of the channel free migration zone or the formation of several channels. This process can occur gradually or abruptly in the course of a single large flood event where type C reaches transition into type D reaches. Type A and B reaches can also develop into type D reaches directly in the event of a catastrophic flood. However, type A and B reaches can suffer further decline as a result of increased downcutting, which makes it impossible for them to transition into type C. In the event of repeated river regulation, type B, C, and D reaches can transition back to type A (Figure 5II).
These wide alluvial reaches (type D) represent a source of channel material, and their evolution follows three different directions as follows: (1) They can become wider, (2) they can become longer, and (3) they can become thicker. The expansion of this zone in a post-regulation river is associated with lateral erosion. This is a necessary precondition for the river renaturalization, as the river is “trapped” in a deep-cut channel and a narrow, regulated flow pathway. Lateral erosion and accumulation are linked processes in this case. Extension of the accumulation reach or its migration along the length of the river is often made difficult by various forms of human impact in the valley. Difficulties include road infrastructure, close proximity to buildings, and river training structures.
The thickness of debris layers increases, as does the width and length of sedimentation zones in the course of flood events. These are zones wherein the river channel can freely migrate and consist of one or more threads and wide bars not covered with perennial vegetation. A period of several years without floods leads to changes in the functioning of the widened channel migration zone, where a river can freely choose its flow pathway (Figure 4III).
In periods without major floods, fluvial processes usually become limited to a narrower zone, i.e., the encroachment of vegetation onto bars, the decline of discharge inside the channels, and the limiting of discharge into the most deeply incised channel narrows down the active zone of the free migration zone. What remains in the active zone is a channel with a low level of water and bars not covered with vegetation [66,67]. However, this remains a zone for accumulation, and it is readily available to fluvial processes during subsequent floods. While this depends on the magnitude of the next flood, this zone can become only refreshed or it can become expanded.
This expansion can occur via the undercutting of floodplain terraces, which incorporates more land into the migration zone. In a post-regulation river, this process is limited in scope. A river that is “trapped” between road embankments, various other structures, or levees has only so much leeway to migrate. This pulse-type pattern of the evolution of accumulation zones with the capability for free migration during flood events and a narrowed down active zone between floods can be conceptually associated with the idea of a flood pulse [21,22] in a geomorphologic sense.
The final research question concerns the direction that mountain river systems are headed during the post-regulation period having been subjected to significant human impact in the last 100 years. Is it possible for river systems to return to their functioning from the 19th century? Or, will completely new channel patterns emerge as a way of adjusting to contemporary factors? A complete answer to these questions is not possible as of today. Currently river systems during the post-regulation period are in their initial stage of spontaneous renaturalization. In order to produce forecasts, it is necessary to conduct more research in such systems over the next few decades or at least over the next decade or so.
7. Conclusions
Compared with the 19th century, present-day river channels in the Carpathians possess more transport capacity, receive a smaller supply of catchment debris due to changes in land use, have a narrower free migration zone, experience less lateral erosion due to reinforced banks, and follow a distorted (i.e., narrowed and straightened) flow path that is not adapted to natural conditions.
Major changes in the morphology of post-regulation river channels occur mostly in the course of flood events. The initial stage of spontaneous renaturalization includes at least two potential channel evolution scenarios. A river channel can evolve in the direction of an accumulation channel with lateral erosion. In the second scenario, a river channel experiences erosion that helps make permanent its regulated structure. Both scenarios can play out in the same river channel, but in adjacent reaches. This indicates great complexity and fragmentation of the structure of a post-regulation river channel. In initial spontaneous renaturalization stages, this process can occur in limited sections and does not need to affect the entire channel system. In the case of river channels situated in urbanized areas, this process could never materialize. The same is true of fully regulated river reaches.
New patterns of channel evolution observed in river channels now affected by spontaneous renaturalization could be indicative of how gravel-bed rivers in mountains areas will evolve in the 21st century if human impact is reduced.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.G. and K.K.; data curation, E.G.; investigation, E.G. and K.K.; methodology, E.G. and K.K.; software, E.G. and K.J.; visualization, E.G.; writing—original draft, E.G., K.J. and K.K.; writing—review and editing, K.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bravard, J.P.; Petts, G.E. Human Impacts on Fluvial Hydrosystems. In The Fluvial Hydrosystems, Chapman and Hall; Petts, G.E., Amoros, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 242–262. [Google Scholar]
- Wohl, E. Human Impacts to Mountain Streams. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 217–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Surian, N.; Comiti, F.; Bussettini, M. A Method for the Assessment and Analysis of the Hydromorphological Condition of Italian Streams: The Morphological Quality Index (MQI). Geomorphology 2013, 180, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpak, J. The Influence of River Training on Mountain Channel Changes (Polish Carpathian Mountains). Geomorphology 2007, 92, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyżga, B.; Zawiejska, J.; Radecki-Pawlik, A.; Hajdukiewicz, H. Environmental Change, Hydromorphological Reference Conditions and the Restoration of Polish Carpathian Rivers. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2012, 37, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpak, J.; Krzemień, K.; Radecki-Pawlik, A. Wpływ czynników antropogenicznych na zmiany koryt cieków karpackich. Infrastruktura I Ekologia Terenów Wiejskich 2008, 4, 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wyżga, B.; Zawiejska, J.; Radecki-Pawlik, A. Impact of Channel Incision on the Hydraulics of Flood Flows: Examples from Polish Carpathian Rivers. Geomorphology 2016, 272, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorczyca, E. Rozwój Górskich Żwirodennych Koryt Rzecznych w Warunkach Antropopresji; Instytut Geografii i Gospodarki Przestrzennej Uniwersytetu Jagiellońskiego: Kraków, Poland, 2016; pp. 1–240. [Google Scholar]
- Wyżga, B. Present-day Downcutting of the Raba River Channel (Western Carpathians, Poland) and its Environmental Effects. Catena 1991, 18, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyżga, B. River Response to Channel Regulation: Case Study of the Raba River, Carpathians, Poland. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1993, 18, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyżga, B. Impact of the Channelization—Induced Incision of the Skawa and Wisłoka Rivers, Southern Poland, on the Conditions of Overbank Deposition. Regulated Rivers. Res. Manag. 2001, 17, 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Perzanowska, J. Pionierska roślinność na kamieńcach górskich potoków. In Monitoring Siedlisk Przyrodniczych. Przewodnik Metodyczny. Część II; Mróz, W., Ed.; Główny Inspektorat Ochrony Środowiska: Warszawa, Poland, 2012; pp. 170–180. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, R.; Wyżga, B.; Surian, N. Sediment Mining in Alluvial Channels: Physical Effects and Management Perspectives. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 805–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorczyca, E.; Krzemień, K.; Sobucki, M.; Jarzyna, K. Can beaver impact promote river renaturalization? The example of the Raba River, southern Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1048–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M. Setting goals in river restoration: When and where can the river “heal itself”. Stream Restor. Dyn. Fluv. Syst. 2011, 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, M.; Simoncini, C.; Piégay, H. Scientific design strategy for promoting sustainable sediment management: The case of the Magra River (Central-Northern Italy). River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiti, F.; Da Canal, M.; Surian, N.; Mao, L.; Picco, L.; Lenzi, M.A. Channel adjustments and vegetation cover dynamics in a large gravel bed river over the last 200 years. Geomorphology 2011, 125, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bańkowska, A.; Sawa, K.; Popek, Z.; Wasilewicz, M.; Żelazo, J. Studia wybranych przykładów renaturyzacji rzek. Infrastruktura i Ekologia Terenów Wiejskich 2010, 9, 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Duszyński, R. Ekologiczne techniki ochrony brzegów i rewitalizacja rzek. Inżynieria Morska i Geotechnika 2007, 6, 341–351. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, M.L.; Andersen, J.M.; Nielsen, K.; Linnemann, M. Restoration of Skjern River and its valley: Project description and general ecological changes in the project area. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 30, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, W.J.; Bayley, P.B.; Sparks, R.E. The flood pulse concept in river-floodplain systems. Can. Spec. Publ. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 106, 110–127. [Google Scholar]
- Tockner, K.; Malard, F.; Ward, J.V. An extension of the flood pulse concept. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 2861–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.V. The four-dimensional nature of lotic ecosystems. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1989, 8, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.V.; Tockner, K. Biodiversity: Towards a unifying theme for river ecology. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjankar, R.; Yager, E.M. The impact of different sediment concentrations and sediment transport formulas on the simulated floodplain processes. J. Hydrol. 2012, 450, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juez, C.; Schärer, C.; Jenny, H.; Schleiss, A.J.; Franca, M.J. Floodplain Land Cover and Flow Hydrodynamic Control of Overbank Sedimentation in Compound Channel Flows. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 9072–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, J.A.; Ward, J.V. An ecosystem perspective of alluvial rivers: Connectivity and the hyporheic corridor. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1993, 12, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.V.; Tockner, K.; Arscott, D.B.; Claret, C. Riverine landscape diversity. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 517–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupnicka, E. Geologia Regionalna Polski; Wydawnictwa Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego: Warszawa, Poland, 1997; pp. 1–332. [Google Scholar]
- Punzet, J. Przepływy charakterystyczne. In Dorzecze Górnej Wisły; cz. I, PWN, Warszawa: Kraków, Poland, 1991; pp. 167–215. [Google Scholar]
- Soja, M.; Zborowski, A. Wybrane zagadnienia zagospodarowania przestrzennego zlewni Raby. Pr. Geogr. IG UJ 2000, 106, 119–140. [Google Scholar]
- Soja, R. Hydrologiczne aspekty antropopresji w polskich Karpatach. Pr. Geogr. IG UJ 2002, 186, 1–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kamykowska, M.; Kaszowski, L.; Krzemień, K. River Channel Mapping Instruction. Key to the River Bed description. Pr. Geogr. IG UJ 1999, 104, 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Krzemień, K. (Ed.) Struktura Koryt Rzek i Potoków (Studium Metodyczne); Instytut Geografii i Gospodarki Przestrzennej Uniwersytetu Jagiellońskiego: Kraków, Poland, 2012; pp. 1–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wolman, M.G. A method of sampling coarse river-bed material. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1954, 35, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszowski, L. Struktura i typy koryt rzecznych w dorzeczu Raby. Sprawozdania z Posiedzeń Komisji Naukowych PAN 1980, 22, 162–163. [Google Scholar]
- Froehlich, W.; Walling, D.E. The role of unmetalled roads as a sediment source in the fluvial systems of the Polish Flysch Carpathians. IAHS Publ. 1997, 245, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Froehlich, W.; Słupik, J. Rola dróg w kształtowaniu spływu i erozji w karpackich zlewniach fliszowych. Przegląd Geogr. 1986, 58, 67–87. [Google Scholar]
- Starkel, L. Rozwój rzeźby Polskich Karpat fliszowych w holocenie. Pr. Geogr. IG PAN 1960, 22, 1–239. [Google Scholar]
- Klimek, K.; Trafas, K. Young-Holocene Changes in the Course of the Dunajec River in the Beskid Sadecki Mts. (Western Carpathians). Studia Geomorphol. Carpatho Balc. 1972, 6, 85–103. [Google Scholar]
- Starkel, L.; Łajczak, A. Kształtowanie rzeźby den dolin w Karpatach (koryt i równin zalewowych). In Współczesne Przemiany Rzeźby Polski; Starkel, L., Kostrzewski, A., Kotarba, A., Krzemień, K., Eds.; Instytut Geografii i Gospodarki Przestrzennej Uniwersytetu Jagiellońskiego: Kraków, Poland, 2008; pp. 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Kościelniak, J. Influence of River Training on Functioning of the Biały Dunajec River Channel System. Geomorphol. Slovaca 2004, 1, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kędzior, A. Roboty wodne i melioracyjne w południowej Małopolsce. cz. III. In Regulacja Rzek Górskich, Zbiorniki Wody I Zabudowanie Potoków Górskich; Ministerstwo Robót Publicznych: Lwów, Poland, 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Łapuszek, M.; Lenar-Matyas, A. Utrzymanie I Zagospodarowanie Rzek Górskich; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Krakowskiej: Kraków, Poland, 2013; pp. 1–283. [Google Scholar]
- Zawiejska, J.; Krzemień, K. Man—Induced Changes in the Structure and Dynamic of the Upper Dunajec River Channel. Geogr. Časopis 2004, 56, 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- Gorczyca, E.; Krzemień, K.; Liro, M.; Sobucki, M. Changes of Mountain River Channels and their Environmental Effects. In Open Channel Hydraulics, River Hydraulics Structures and Fluvial Geomorphology; Radecki-Pawlik, A., Pagliara, S., Hradecký, J., Hendrickson, E., Eds.; Science Publishers, CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 303–321. [Google Scholar]
- Wharton, G. Managing River Environments; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 1–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lach, J.; Wyżga, B. Channel Incision and Flow Increase of the Upper Wisłoka River, Southern Poland, Subsequent to the Reforestation of its Catchment. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2002, 27, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzemień, K. The Czarny Dunajec River, Poland, as an Example of Human-induced Development Tendencies in a Mountain River Channel. Landf. Anal. 2003, 4, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Jeleński, J.; Wyżga, B. The Raba River at Lubień. Erodible river corridor as a restoration measure for mountains rivers. In Proceedings of the International Conference ‘Towards the Best Practice of River Restoration and Maintenance’, Kraków, Poland, 20–23 September 2016; Zawiejska, J., Wyżga, B., Eds.; Ab Ovo Association: Kraków, Poland, 2016; pp. 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Galicia and Bucowina (1861–1864) Second Military Survey of the Habsburg Empire. Available online: https://mapire.eu/en/map/secondsurvey-galicia/?layers=11&bbox=2648791.450423253%2C6410880.850074071%2C2700348.2260016045%2C6426168.255731106 (accessed on 13 December 2019).
- Łapuszek, M.; Ratomski, J. Metodyka określania i charakterystyka przebiegu oraz prognoza erozji dennej rzek górskich dorzecza górnej Wisły. Inżynieria Środowiska Monografia 2006, 332, 1–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wyżga, B. Wcinanie się rzek polskich Karpat w ciągu XX wieku. In Stan Środowiska Rzek Południowej Polski I Możliwość Jego Poprawy—Wybrane Aspekty; Wyżga, B., Ed.; Instytut Ochrony Przyrody PAN: Kraków, Poland, 2008; pp. 7–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zawiejska, J.; Wyżga, B. Twentieth-century channel change on the Dunajec River, southern Poland: patterns, causes and controls. Geomorphology 2010, 117, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyżga, B. A geomorphologist’s criticism of the engineering approach to channelization of gravel-bed rivers: Case study of the Raba River, Polish Carpathians. Environ. Manag. 2001, 28, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erskine, W.D. Downstream Hydrogeomorphic Impacts of Eildon Reservoir on the Mid—Goulburn River. Vic. Proc. Soc. Vic. 1996, 108, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Requena, P.; Weichert, R.B.; Minor, H.E. Self-widening by Lateral Erosion in Gravel Bed Rivers. In River Flow; Ferreira, A., Cardoso, L., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: Lisbon, Portugal, 2006; pp. 1801–1809. [Google Scholar]
- Gorczyca, E.; Krzemień, K.; Wrońska-Wałach, D.; Boniecki, M. Significance of Extreme Hydro-geomorphological Events in the Transformation of Mountain Valleys (Northern Slopes of the Western Tatra Range), Carpathian Mountains, Poland. Catena 2014, 121, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, W.; Radecki-Pawlik, A.; Wyżga, B.; Hajdukiewicz, H. Modelling the Flooding Capacity of a Polish Carpathian River: A Comparison of Constrained and Free Channel Conditions. Geomorphology 2016, 272, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdukiewicz, H.; Wyżga, B.; Mikuś, P.; Zawiejska, J.; Radecki-Pawlik, A. Impact of a Large Flood on Mountain River Habitats, Channel Morphology and Valley Infrastructure. Geomorphology 2016, 272, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehotsky, M.; Rusnak, M.; Kidova, A. Application of Remote Sensing and the GIS in Interpretation of River Geomorphic Response to Floods. In Open Channel Hydraulics, River Hydraulics Structures and Fluvial Geomorphology; Radecki-Pawlik, A., Pagliara, S., Hradecký, J., Hendrickson, E., Eds.; Science Publishers, CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 388–399. [Google Scholar]
- Punzet, J. Zmiany w przebiegu stanów wody w dorzeczu górnej Wisły na przestrzeni 100 lat (1871–1970). Folia Geogr. Ser. Geogr. Phys. 1981, 14, 5–28. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas, A.P.; Ashworth, P.J.; Kirkby, M.J.; Macklin, M.G.; Murray, T. Sediment Slugs: Large-scale Fluctuations in Fluvial Transport Rates and Storage Volumes. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1995, 19, 500–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.L. Secular sediment waves, channel bed waves and legacy sediment. Geogr. Compass 2010, 4, 576–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, M.A.; Jones, D. Channel bars in gravel-bed rivers. In Gravel-Bed Rivers: Fluvial Processes, Engineering and Management; Hey, R.D., Bathurst, J.C., Theme, C.R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1982; pp. 291–338. [Google Scholar]
- Gurnell, A.M.; Petts, G.E.; Harris, N.; Ward, J.V.; Tockner, K.; Edwards, P.J.; Kollmann, J. Large wood retention in river channels: The case of the Fiume Tagliamento, Italy. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2000, 25, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdukiewicz, H.; Wyżga, B.; Amirowicz, A.; Oglęcki, P.; Radecki-Pawlik, A.; Zawiejska, J.; Mikuś, P. Ecological state of a mountain river before and after a large flood: Implications for river status assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).