Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Precipitation and Temperature in Punjab, Pakistan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Time Serial Autocorrelation
2.4.2. Mann–Whitney Test (MW)
2.4.3. Mann–Kendall Test (MK)
2.4.4. Theil and Sen’s Slope (TSS)
2.4.5. Spatial Interpolation
3. Results and Discussion
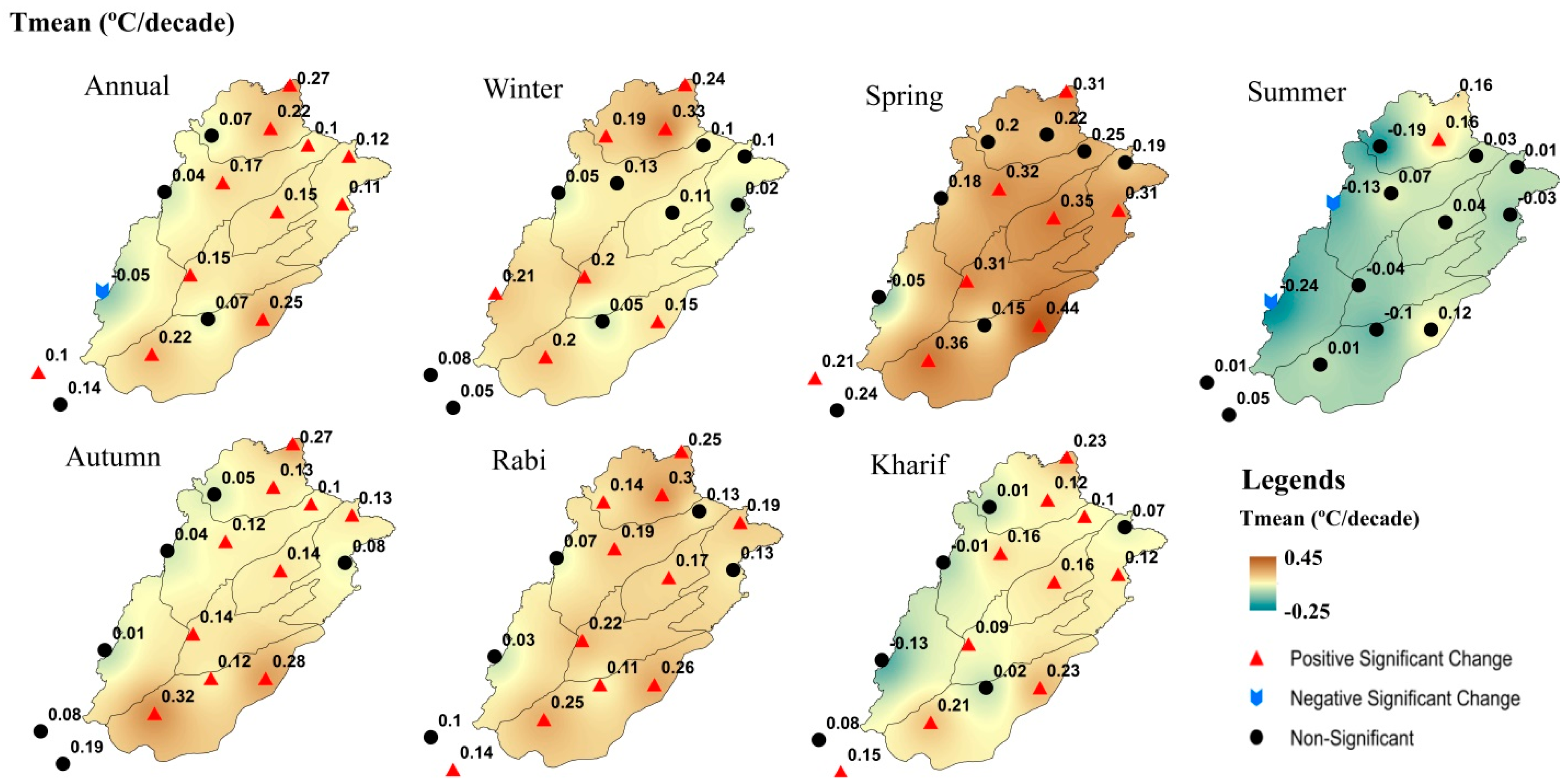
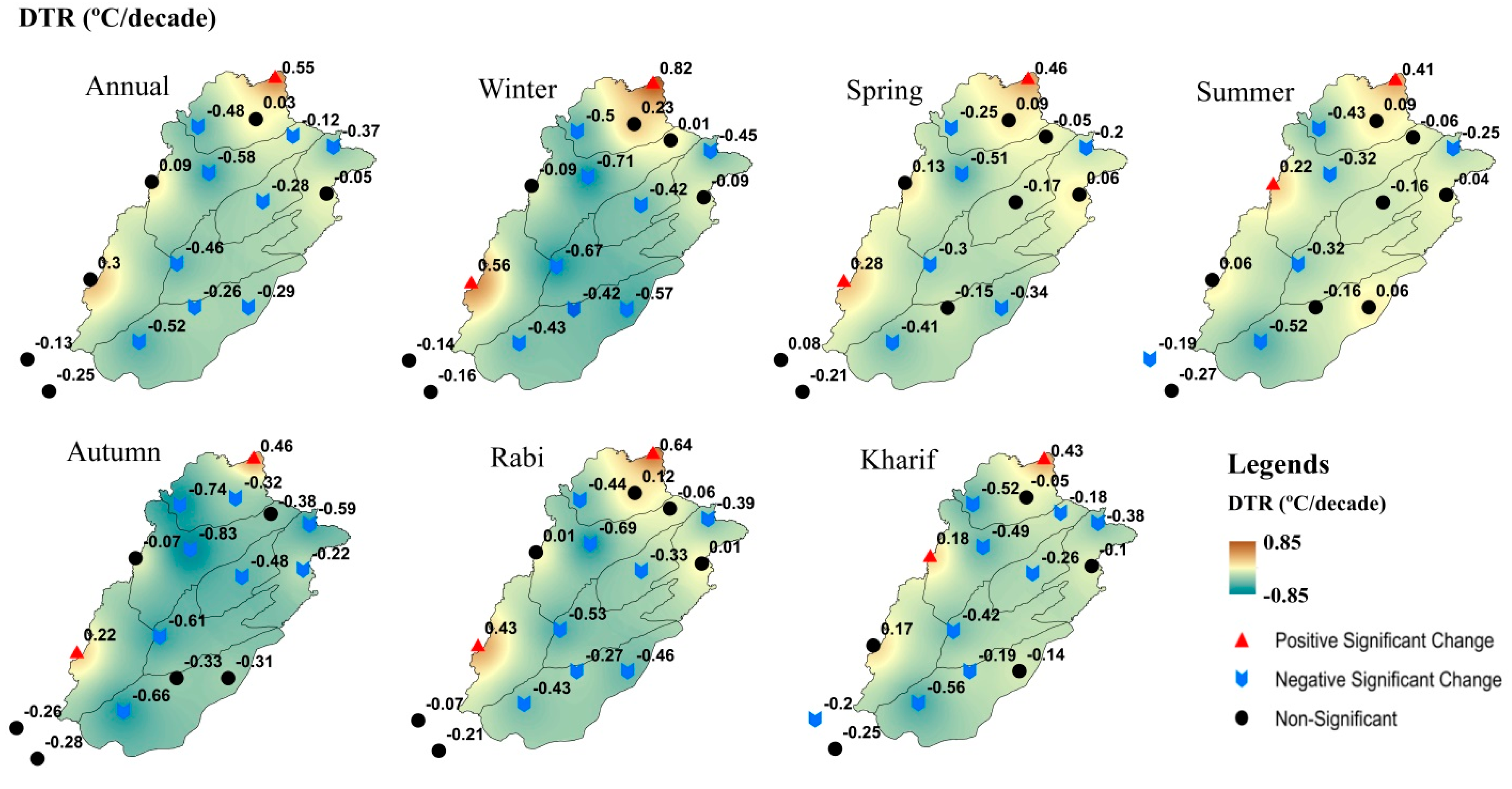
3.1. Absolute Changes and Trends of Temperature Indices
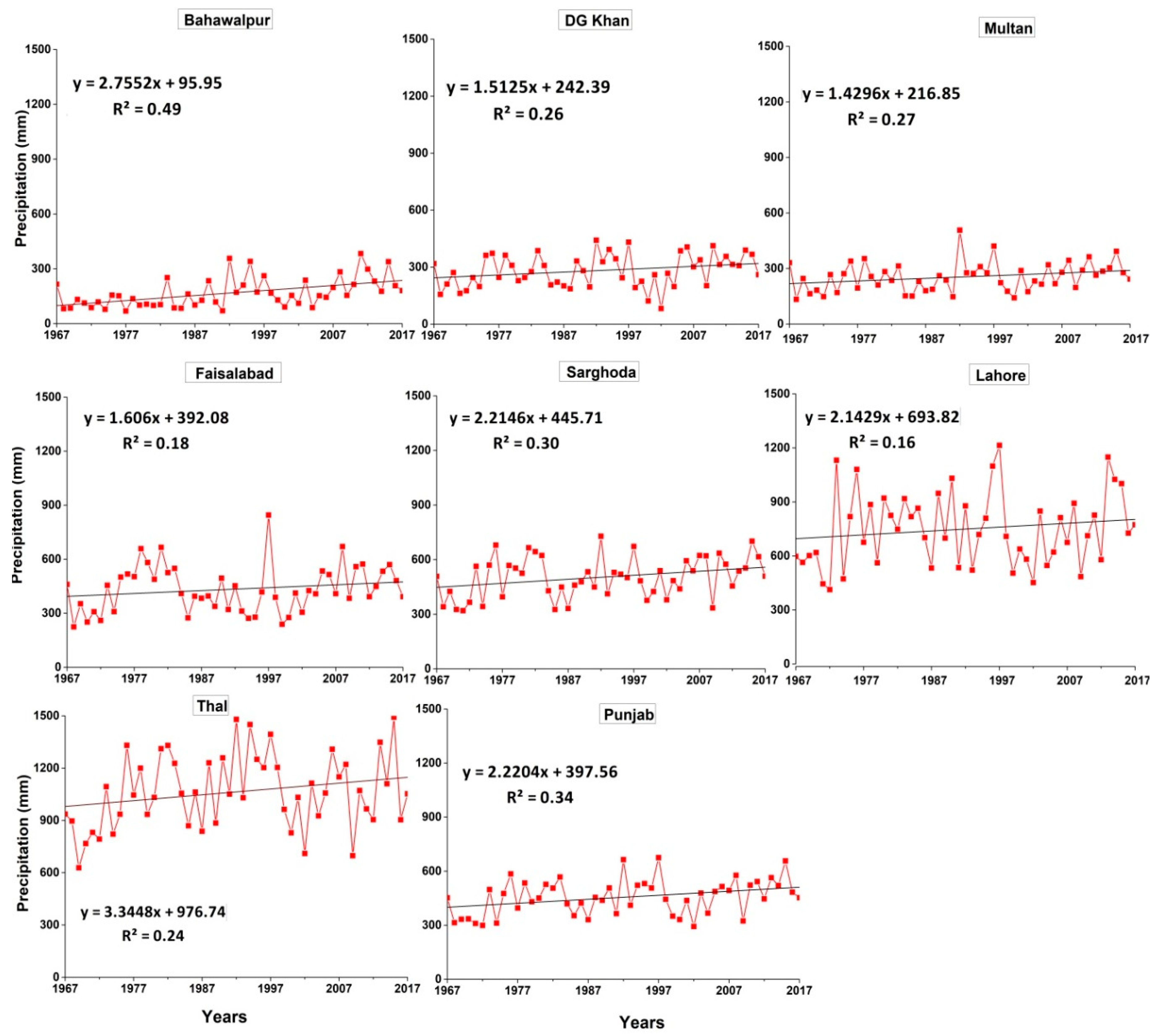
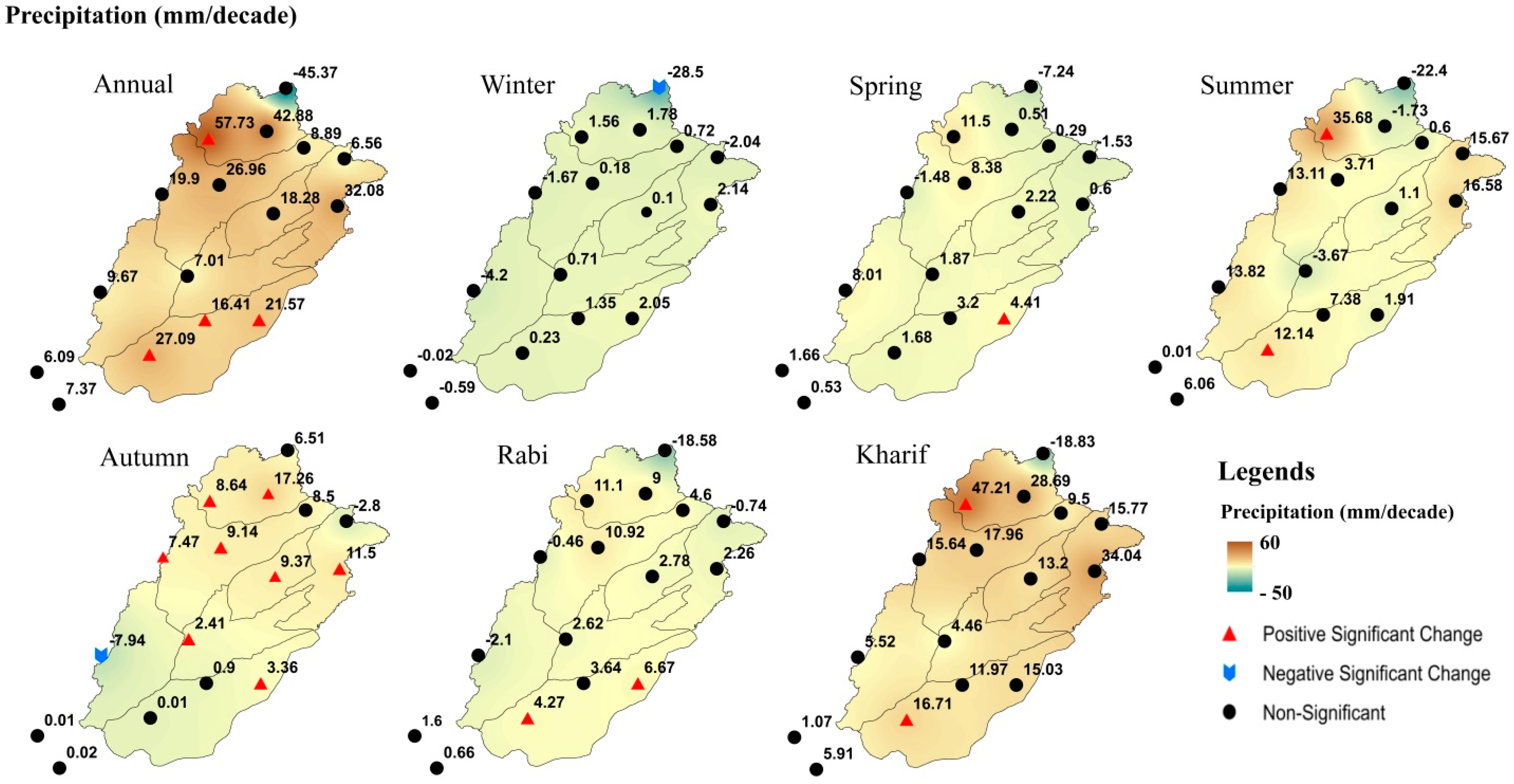
3.2. Annual and Seasonal Trends of Precipitation
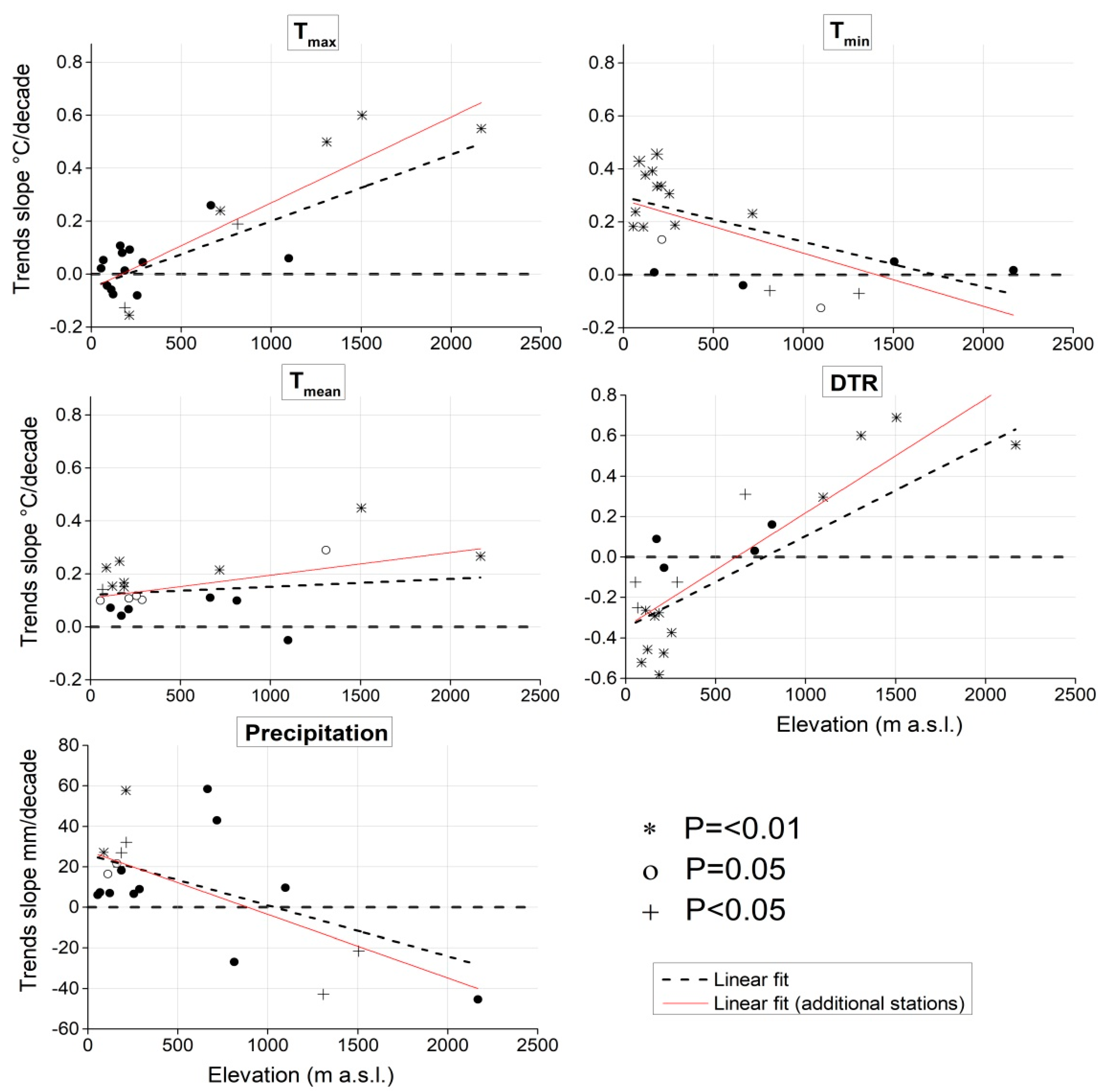
3.3. Annual and Seasonal Elevation-Dependent Trends (EDTs)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tabari, H.; Somee, B.S.; Zadeh, M.R. Testing for long-term trends in climatic variables in Iran. Atmos. Res. 2011, 100, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Tignor, M.M.B.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P.M. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis, Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of IPCC the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- New, M.; Todd, M.; Hulme, M.; Jones, P. Precipitation measurements and trends in the twentieth century. Int. J. Climatol. A J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 21, 1889–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Saharia, M. Analysis of rainfall and temperature trends in northeast India. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Chiang, J.C.H.; Lan, C.-W.; Chung, C.-H.; Liao, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-J. Increase in the range between wet and dry season precipitation. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Knight, R.W.; Easterling, D.R.; Quayle, R.G. Indices of climate change for the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Dickinson, R.E. New observational evidence for global warming from satellite. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Harun, S.B.; Katimon, A. Changes in diurnal temperature range in Bangladesh during the time period 1961–2008. Atmos. Res. 2012, 118, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Río, S.; Iqbal, M.A.; Cano-Ortiz, A.; Herrero, L.; Hassan, A.; Penas, A. Recent mean temperature trends in Pakistan and links with teleconnection patterns. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.-F. Spatial and temporal variability of daily temperature in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 112, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D. Maximum and minimum temperature trends in Ireland, Italy, Thailand, Turkey and Bangladesh. Atmos. Res. 1995, 37, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, N.; Bradley, R.S.; Diaz, H.F.; Baraër, M.; Caceres, E.B.; Forsythe, N.; Fowler, H.; Greenwood, G.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Liu, X.D.; et al. Elevation-dependent warming in mountain regions of the world. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 424. [Google Scholar]
- Gleick, P.H. Climate change, hydrology, and water resources. Rev. Geophys. 1989, 27, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.B.; Chowdary, P.S.; Sandeep, V.M.; Rao, V.U.M.; Venkateswarlu, B. Rising minimum temperature trends over India in recent decades: Implications for agricultural production. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 117, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; You, Q.; Ullah, W.; Ali, A. Observed changes in precipitation in China-Pakistan economic corridor during 1980–2016. Atmos. Res. 2018, 210, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.B.; Wang, X.J. Spatial distribution of unidirectional trends in temperature and temperature extremes in Pakistan. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 136, 899–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Khlaid, S.; Shams, D.F. Spatiotemporal variations and trends in minimum and maximum temperatures of Pakistan. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci. 2014, 4, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Khattak, M.S.; Babel, M.S.; Sharif, M. Hydro-meteorological trends in the upper Indus River basin in Pakistan. Clim. Res. 2011, 46, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, G.; Dawood, M. Spatial and temporal variation of rainfall and drought in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province of Pakistan during 1971–2015. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Tang, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Wagan, B. Precipitation trends over time using Mann-Kendall and spearman’s rho tests in swat river basin, Pakistan. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 431860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Chung, E.-S.; Ismail, T.; Wang, X.-J. Spatial distribution of secular trends in annual and seasonal precipitation over Pakistan. Clim. Res. 2017, 74, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggiani, P.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Rientjes, T.H.M.; Khan, A. A joint analysis of river runoff and meteorological forcing in the Karakoram, Upper Indus Basin. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 31, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.; Khan, A.H.; Adnan, S. Latitudinal precipitation characteristics and trends in Pakistan. J. Hydrol. 2013, 492, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.S.; Lee, S. Long-term variability and changes of the precipitation regime in Pakistan. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 50, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattak, M.S.; Reman, N.U.; Sharif, M.; Khan, M.A. Analysis of streamflow data for trend detection on major rivers of the Indus Basin. J. Himal. Earth Sci. 2015, 48, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Ashiq, M.W.; Zhao, C.; Ni, J.; Akhtar, M. GIS-based high-resolution spatial interpolation of precipitation in mountain–plain areas of Upper Pakistan for regional climate change impact studies. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, F. Analysis of a historical (1981–2010) temperature record of the Punjab province of Pakistan. Earth Interact. 2013, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Hasan, M.U.; Khan, F.K.; Bari, A. Climate classification of Pakistan. In Proceedings of the 2010 Balwois Conference, Ohrid, Republic of Macedonia, 25–29 May 2010; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Asmat, U.; Athar, H.; Nabeel, A.; Latif, M. An AOGCM based assessment of interseasonal variability in Pakistan. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, H.J.; Archer, D.R. Conflicting signals of climatic change in the Upper Indus Basin. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4276–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Wen, J.; Wang, X.; Lan, Y.; Tian, H.; Anjum, M.N.; Adnan, M. Assessment of air temperature trends in the Source Region of Yellow River and its sub-basins, China. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 54, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.M.; Dzerdzeevskii, B.; Flohn, H.; Hofmeyr, W.L.; Lamb, H.H.; Rao, K.N.; Wallén, C.C. Climatic Change; Technical Note, No. 79; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1966; p. 99. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, T.C.; Easterling, D.R.; Karl, T.R.; Groisman, P.; Nicholls, N.; Plummer, N.; Torok, S.; Auer, I.; Boehm, R.; Gullett, D. Homogeneity adjustments of in situ atmospheric climate data: A review. Int. J. Climatol. A J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 18, 1493–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, M.A. On the use of double-mass analysis for testing the consistency of meteorological records and for making required adjustments. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1949, 30, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buishand, T.A. Some methods for testing the homogeneity of rainfall records. J. Hydrol. 1982, 58, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiessen, A.H. Precipitation averages for large areas. Mon. Weather Rev. 1911, 39, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Li, T.; Wei, J.; Fu, W.; Wang, G. Spatial and temporal characteristics of precipitation over the Three-River Headwaters region during 1961–2014. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 6, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Berndtsson, R.; Zhang, L.; Uvo, C.B.; Hao, Z.; Wang, X.; Yasuda, H. Hydro climatic trend and periodicity for the source region of the Yellow River. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 5015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Engel, B.; Zhang, W.; Peng, H.; Chen, X.; Xia, H. Performance assessment of spatial interpolation of precipitation for hydrological process simulation in the Three Gorges Basin. Water 2017, 9, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partal, T. Wavelet transform-based analysis of periodicities and trends of Sakarya basin (Turkey) streamflow data. River Res. Appl. 2010, 26, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonali, P.; Kumar, D.N. Review of trend detection methods and their application to detect temperature changes in India. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayemuzzaman, M.; Jha, M.K. Seasonal and annual precipitation time series trend analysis in North Carolina, United States. Atmos. Res. 2014, 137, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachar, N. The Mann-Whitney U: A test for assessing whether two independent samples come from the same distribution. Tutor. Quant. Methods Psychol. 2008, 4, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, S. Temporal and spatial variations of precipitation in Northwest China during 1960–2013. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guan, Y.; Shao, G.; Zhang, D. Investigating trends in streamflow and precipitation in Huangfuchuan Basin with wavelet analysis and the Mann-Kendall test. Water 2016, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, R.; Mirabbasi, R.; Abdollahi, S.; Jhajharia, D. Streamflow trend analysis by considering autocorrelation structure, long-term persistence, and Hurst coefficient in a semi-arid region of Iran. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 129, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.A.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Chung, E.-S.; Al-Abadi, A.M. Long-term trends in daily temperature extremes in Iraq. Atmos. Res. 2017, 198, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Measures; Charles Griffin Book Series; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1975; Volume 202, p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Maskey, S.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Zhao, H. Streamflow trends and climate linkages in the source region of the Yellow River, China. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3399–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, K.E.; Andsager, K.; Easterling, D.R. Long-term trends in extreme precipitation events over the conterminous United States and Canada. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2515–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zwiers, F.W.; Li, G. Monte Carlo experiments on the detection of trends in extreme values. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, K.; Ver Hoef, J.M.; Krivoruchko, K.; Lucas, N. Using ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst; ESRI Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 380. [Google Scholar]
- Price, C.; Michaelides, S.; Pashiardis, S.; Alpert, P. Long term changes in diurnal temperature range in Cyprus. Atmos. Res. 1999, 51, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isaaks, E.H.; Srivastava, R.M. An Introduction to Applied Geostatistics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Penas, A.; Cano-Ortiz, A.; Kersebaum, K.C.; Herrero, L.; del Río, S. Analysis of recent changes in maximum and minimum temperatures in Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2016, 168, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Jain, S.K.; Gupta, R.D. Trend in observed and projected maximum and minimum temperature over NW Himalayan basin. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 12, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; You, Q.; Ali, A.; Ullah, W.; Jan, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W.; Xie, X. Observed changes in maximum and minimum temperatures over China-Pakistan economic corridor during 1980–2016. Atmos. Res. 2019, 216, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.S.; Mudasser, M.; Sheikh, M.M.; Manzoor, N. Climate change and variability in mountain regions of Pakistan implications for water and agriculture. Pakistan J. Meteorol. 2005, 2, 75–90. [Google Scholar]
- Gadiwala, M.S.; Burke, F. Climate change and precipitation in Pakistan-a meteorological Prospect. Int. J. Econ. Environ. Geol. 2019, 4, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dimri, A.P.; Niyogi, D.; Barros, A.P.; Ridley, J.; Mohanty, U.C.; Yasunari, T.; Sikka, D.R. Western disturbances: A review. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, C.; New, M.; Lizcano, G. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles—Kenya; University of Oxford School of Geography and the Environment: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.; Fatima, A.; Awan, U.K.; Anwar, A. Analysis of long term meteorological trends in the middle and lower Indus Basin of Pakistan—A non-parametric statistical approach. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 122, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alward, R.D.; Detling, J.K.; Milchunas, D.G. Grassland vegetation changes and nocturnal global warming. Science 1999, 283, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.-Z.; Zhou, G.-S. Effects of water stress and high nocturnal temperature on photosynthesis and nitrogen level of a perennial grass Leymus chinensis. Plant Soil 2005, 269, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Sheehy, J.E.; Laza, R.C.; Visperas, R.M.; Zhong, X.; Centeno, G.S.; Khush, G.S.; Cassman, K.G. Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9971–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhry, Q.-Z.; Mahmood, A.; Rasul, G.; Afzaal, M. Climate Change Indicators of Pakistan; Pakistan Meterological Department: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Smadi, M.M. Observed abrupt changes in minimum and maximum temperatures in Jordan in the 20th century. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 2, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.S.; Kiany, K.; Sadegh, M.; Balling, R.C. A significant population signal in Iranian temperature records. Int. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dai, A.; Dai, Y.; Vose, R.S.; Zou, C.-Z.; Tian, Y.; Chen, H. Spatial dependence of diurnal temperature range trends on precipitation from 1950 to 2004. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 32, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, A.; Ahmad, A.; Safeeq, M.; Ali, S.; Saleem, F.; Hammad, H.M.; Farhad, W. Changes in precipitation extremes over arid to semiarid and subhumid Punjab. Pak. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2013, 116, 671–680. [Google Scholar]
- Salma, S.; Shah, M.A.; Rehman, S. Rainfall trends in different climate zones of Pakistan. Pak. J. Meteorol. 2012, 9, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Thakuri, S.; Dahal, S.; Shrestha, D.; Guyennon, N.; Romano, E.; Colombo, N.; Salerno, F. Elevation-dependent warming of maximum air temperature in Nepal during 1976–2015. Atmos. Res. 2019, 228, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggiani, P.; Boyko, O.; Rientjes, T.H. In the Central Indus River Basin; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128127827. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, A.B.; Wake, C.P.; Mayewski, P.A.; Dibb, J.E. Maximum temperature trends in the Himalaya and its vicinity: An analysis based on temperature records from Nepal for the period 1971–94. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2775–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Yu, R.; Zheng, H.; Gan, M. Spatial and temporal variations in extreme temperature in Central Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, e388–e400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutiyani, M.R.; Kale, V.S.; Pawar, N.J. Long-term trends in maximum, minimum and mean annual air temperatures across the Northwestern Himalaya during the twentieth century. Clim. Chang. 2007, 85, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R.; Horton, B.; Jones, P.D.; Peterson, T.C.; Karl, T.R.; Parker, D.E.; Salinger, M.J.; Razuvayev, V.; Plummer, N.; Jamason, P. Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe. Science 1997, 277, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talchabhadel, R.; Karki, R.; Thapa, B.R.; Maharjan, M.; Parajuli, B. Spatio-temporal variability of extreme precipitation in Nepal. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 4296–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Trenberth, K.E.; Karl, T.R. Effects of clouds, soil moisture, precipitation, and water vapor on diurnal temperature range. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2451–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, F.; Guyennon, N.; Thakuri, S.; Viviano, G.; Romano, E.; Vuillermoz, E.; Cristofanelli, P.; Stocchi, P.; Agrillo, G.; Ma, Y. Weak precipitation, warm winters and springs impact glaciers of south slopes of Mt. Everest (central Himalaya) in the last 2 decades (1994–2013). Cryosphere 2015, 9, 1229–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
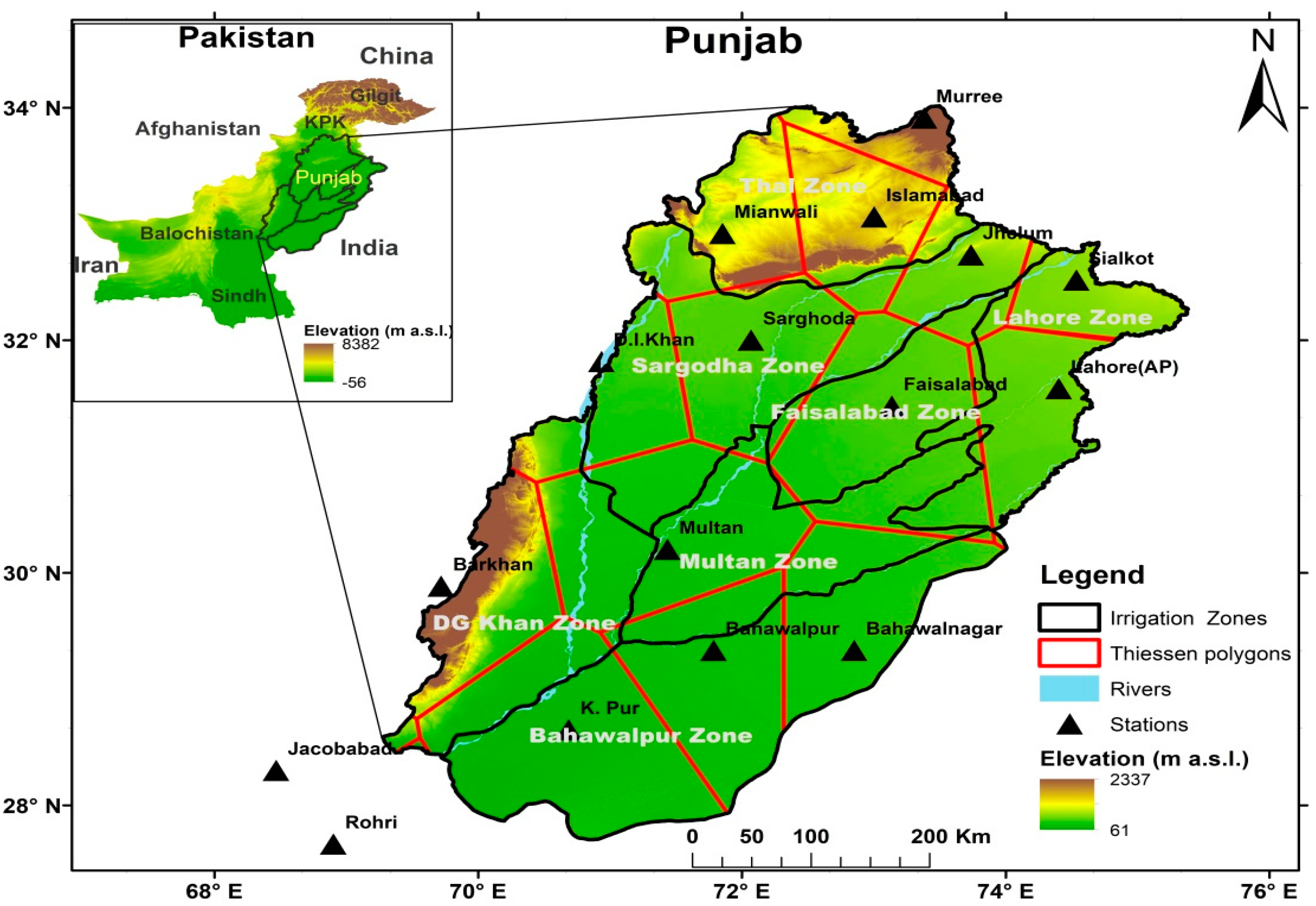
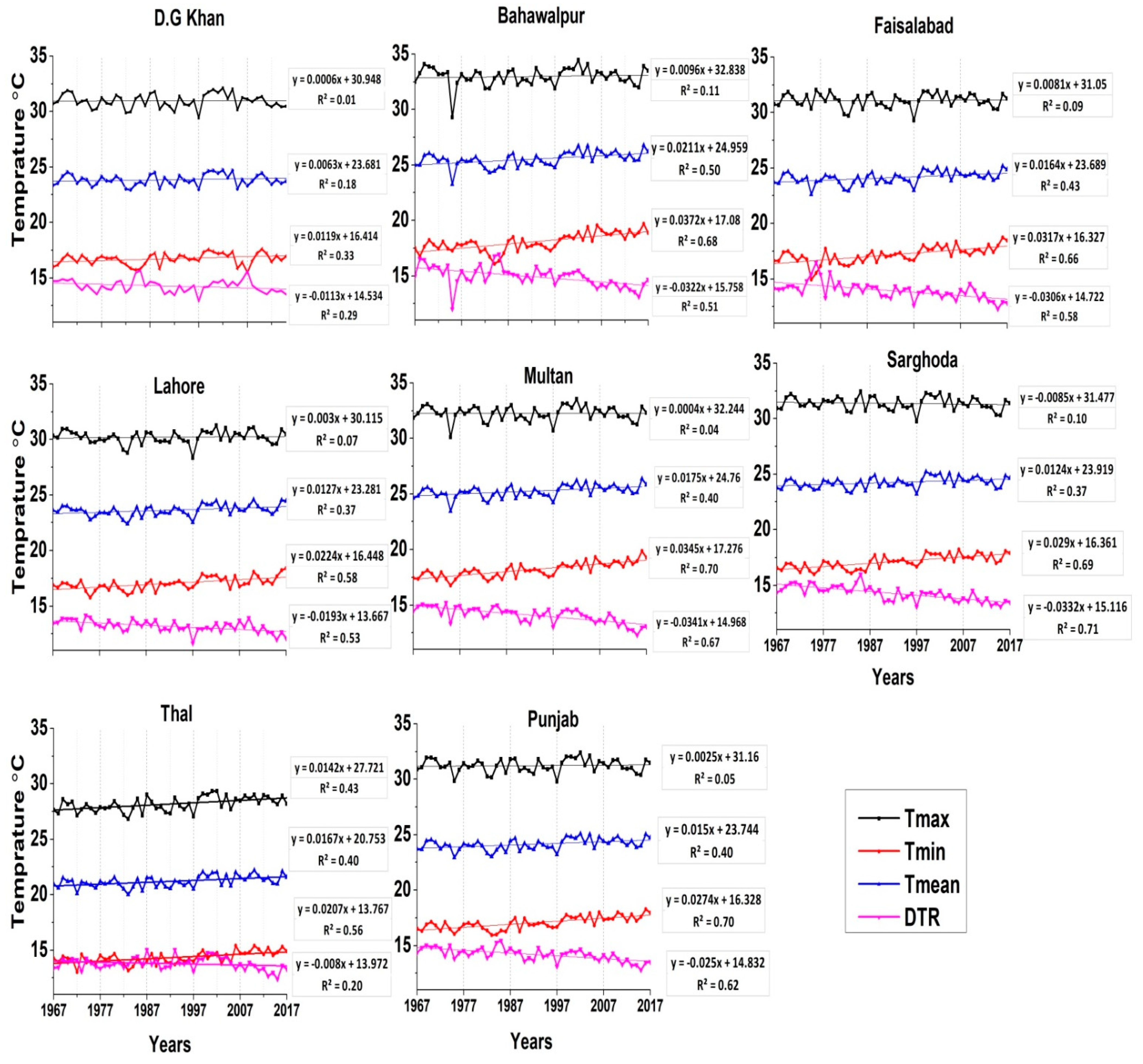
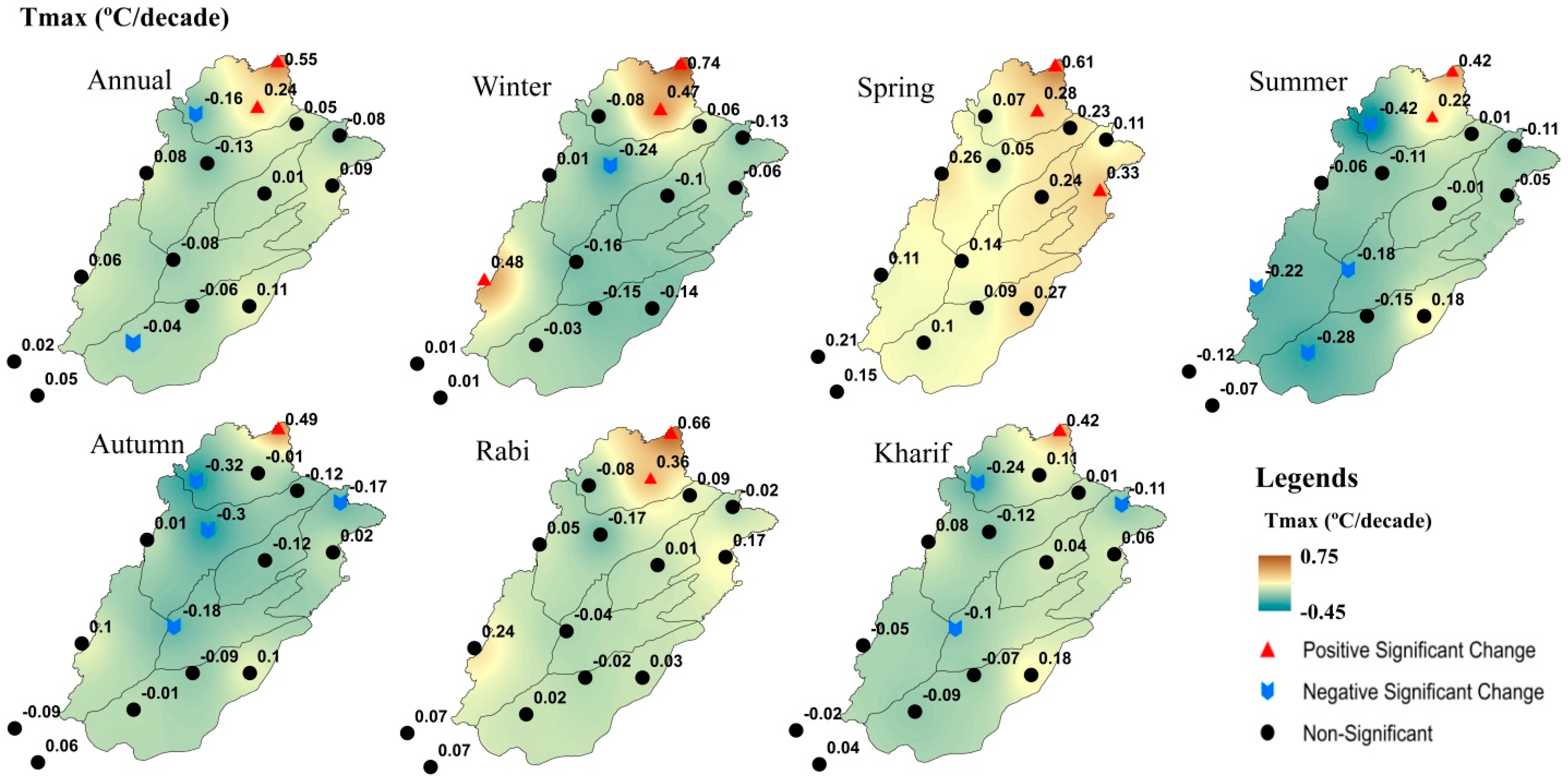
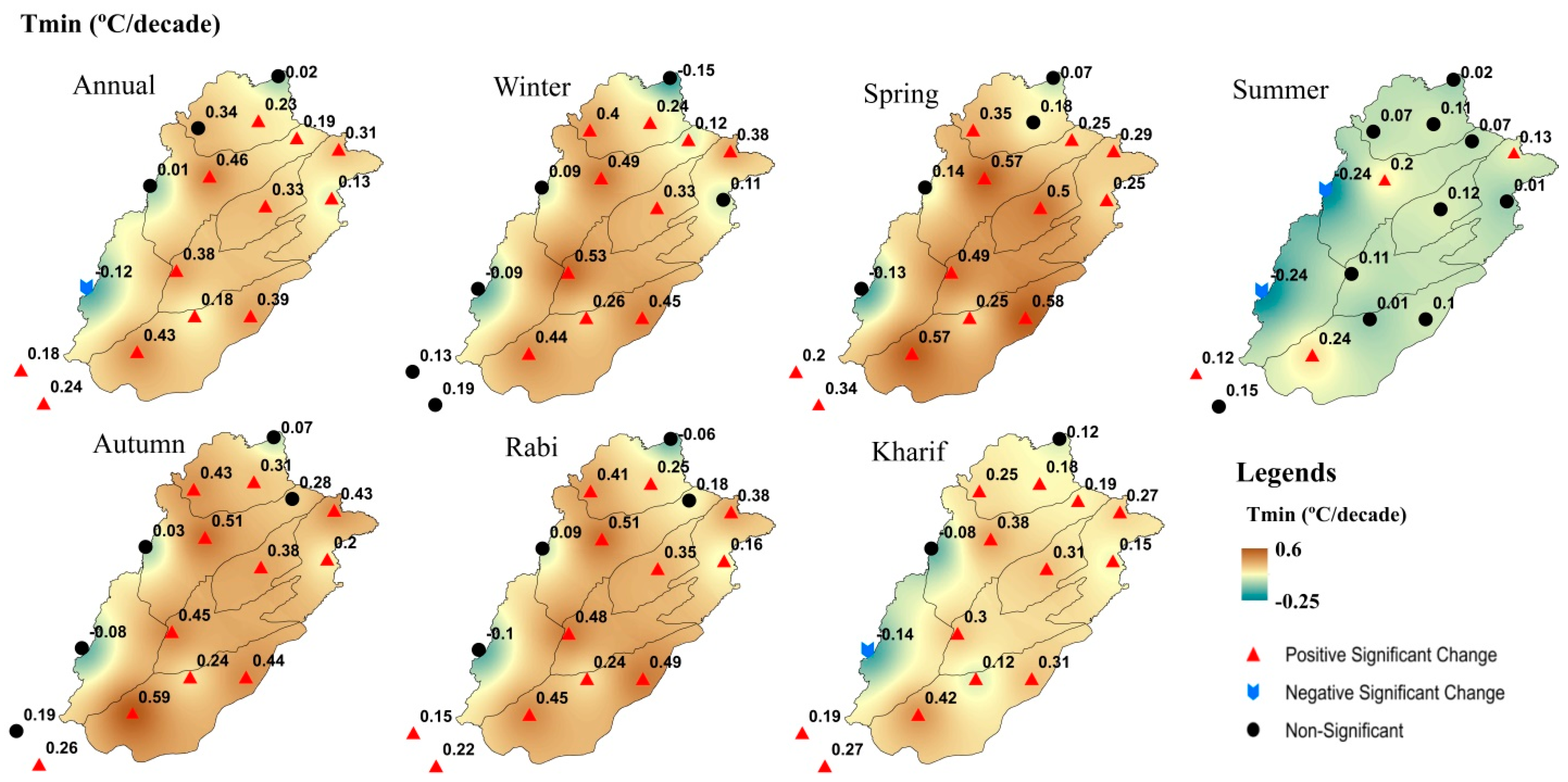
| Stations | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bahawalnagar | 72.85 | 29.33 | 161 |
| Bahawalpur | 71.78 | 29.33 | 110 |
| Lahore | 74.40 | 31.58 | 214 |
| Multan | 71.43 | 30.20 | 122 |
| Sialkot | 74.53 | 32.52 | 255 |
| K. Pur | 70.68 | 28.65 | 88 |
| Jhelum | 73.73 | 32.73 | 287 |
| Faisalabad | 73.13 | 31.43 | 186 |
| Murree | 73.38 | 33.91 | 2167 |
| Islamabad | 73.00 | 33.06 | 718 |
| D.I. Khan | 70.93 | 31.82 | 171 |
| Rohri | 68.90 | 27.67 | 66 |
| Jacobabad | 68.47 | 28.30 | 55 |
| Barkhan | 69.72 | 29.88 | 1097 |
| Mianwali | 71.85 | 32.92 | 212 |
| Sarghoda | 72.07 | 32.00 | 187 |
| Time Scale | Tmax | Tmin | Tmean | DTR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | 0.14 | 0.75 | 0.44 | −0.61 |
| Winter | 0.07 | 0.84 | 0.45 | −0.61 |
| Spring | 0.70 | 1.00 | 0.85 | −0.3 |
| Summer | −0.22 | 0.23 | −0.08 | −0.45 |
| Autumn | 0.02 | 0.93 | 0.48 | −0.91 |
| Rabi | 0.32 | 0.87 | 0.60 | −0.55 |
| Kharif | 0.01 | 0.62 | 0.30 | −0.65 |
| Time Scale | Tmax | Tmin | Tmean | DTR | Precipitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.14 | −0.25 | 22.24 |
| Winter | −0.03 | 0.32 | 0.18 | −0.31 | −0.03 |
| Spring | 0.17 | 0.37 | 0.27 | −0.17 | 3.40 |
| Summer | −0.13 | 0.08 | −0.04 | −0.19 | 10.78 |
| Autumn | −0.08 | 0.36 | 0.15 | −0.39 | 5.23 |
| Rabi | 0.06 | 0.32 | 0.20 | −0.24 | 3.61 |
| Kharif | −0.02 | 0.23 | 0.11 | −0.25 | 20.14 |
| Stations | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zhob | 69.28 | 31.21 | 1505 |
| Kotli | 73.54 | 33.31 | 814 |
| Kohat | 71.53 | 33.45 | 664 |
| Kakul | 73.15 | 34.18 | 1308 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawaz, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Nawaz, N. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Precipitation and Temperature in Punjab, Pakistan. Water 2019, 11, 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091916
Nawaz Z, Li X, Chen Y, Guo Y, Wang X, Nawaz N. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Precipitation and Temperature in Punjab, Pakistan. Water. 2019; 11(9):1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091916
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawaz, Zain, Xin Li, Yingying Chen, Yanlong Guo, Xufeng Wang, and Naima Nawaz. 2019. "Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Precipitation and Temperature in Punjab, Pakistan" Water 11, no. 9: 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091916
APA StyleNawaz, Z., Li, X., Chen, Y., Guo, Y., Wang, X., & Nawaz, N. (2019). Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Precipitation and Temperature in Punjab, Pakistan. Water, 11(9), 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091916






