Levantine Intermediate and Levantine Deep Water Formation: An Argo Float Study from 2001 to 2017
Abstract
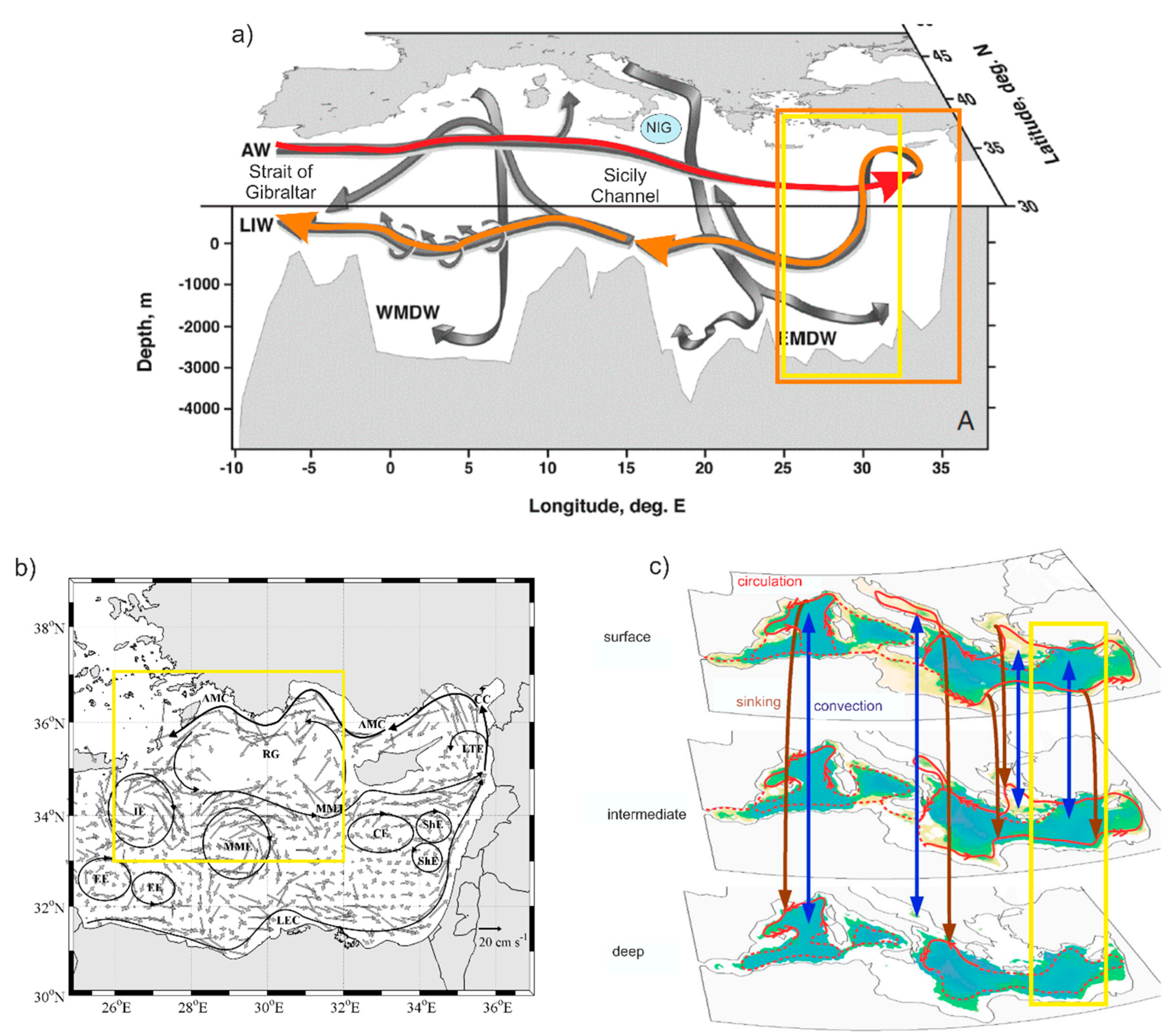
1. Introduction
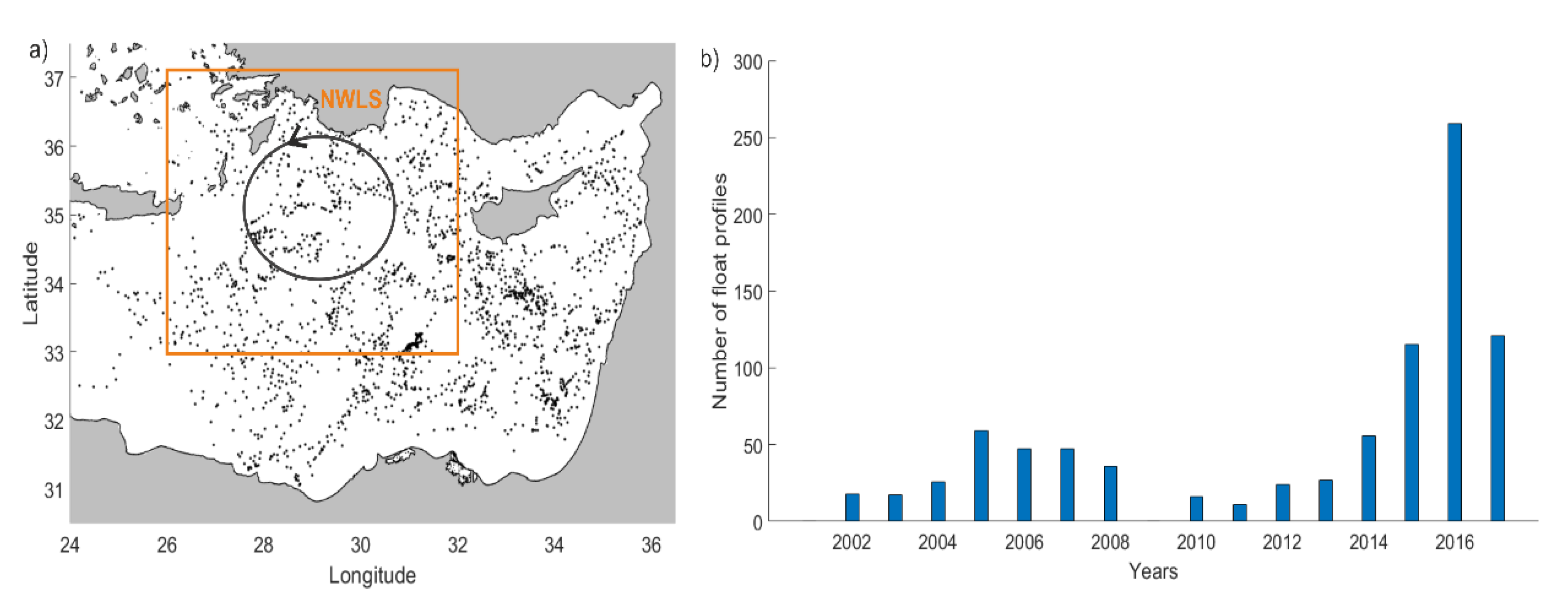
2. Datasets and Methods
3. Results
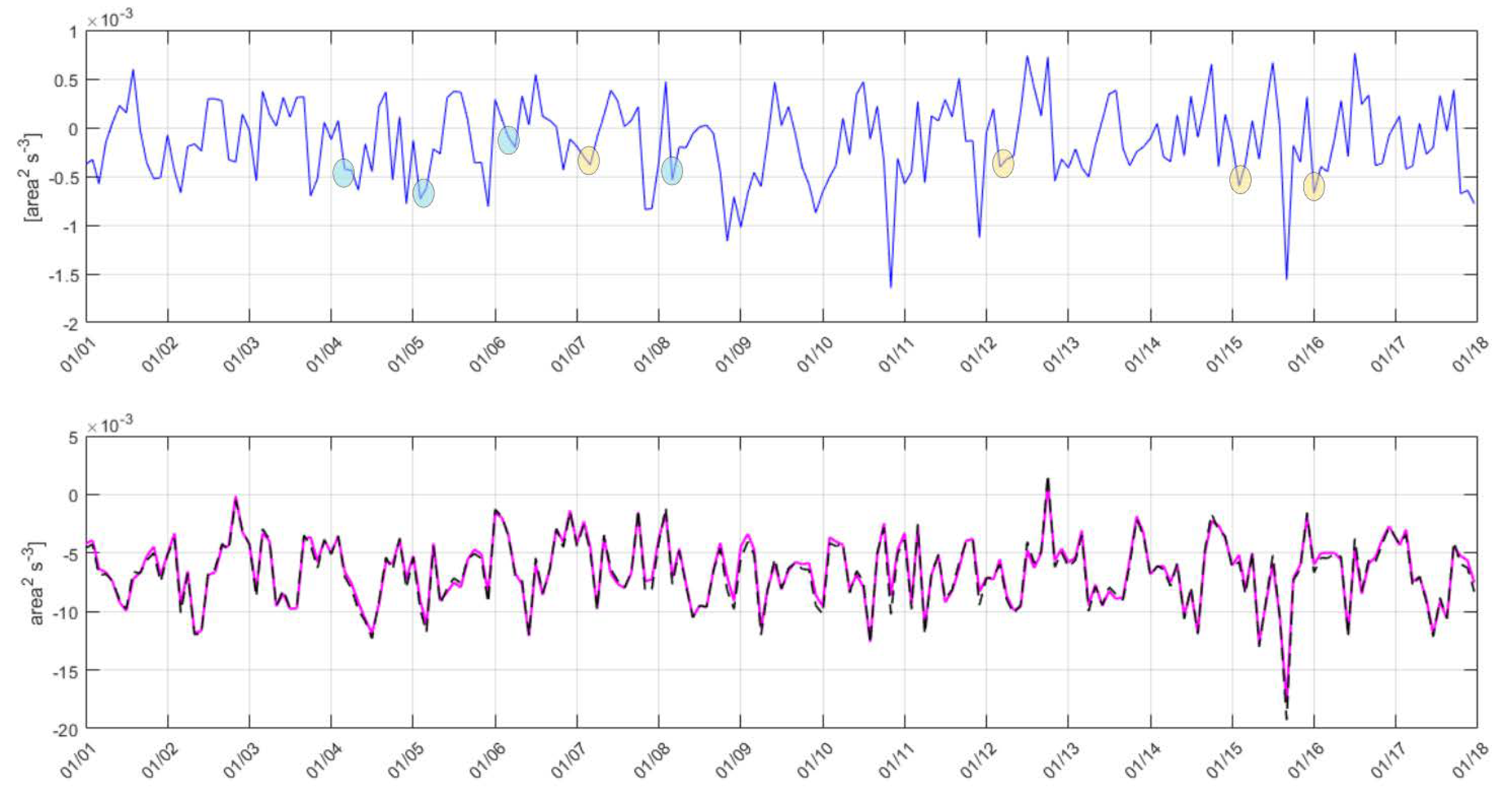
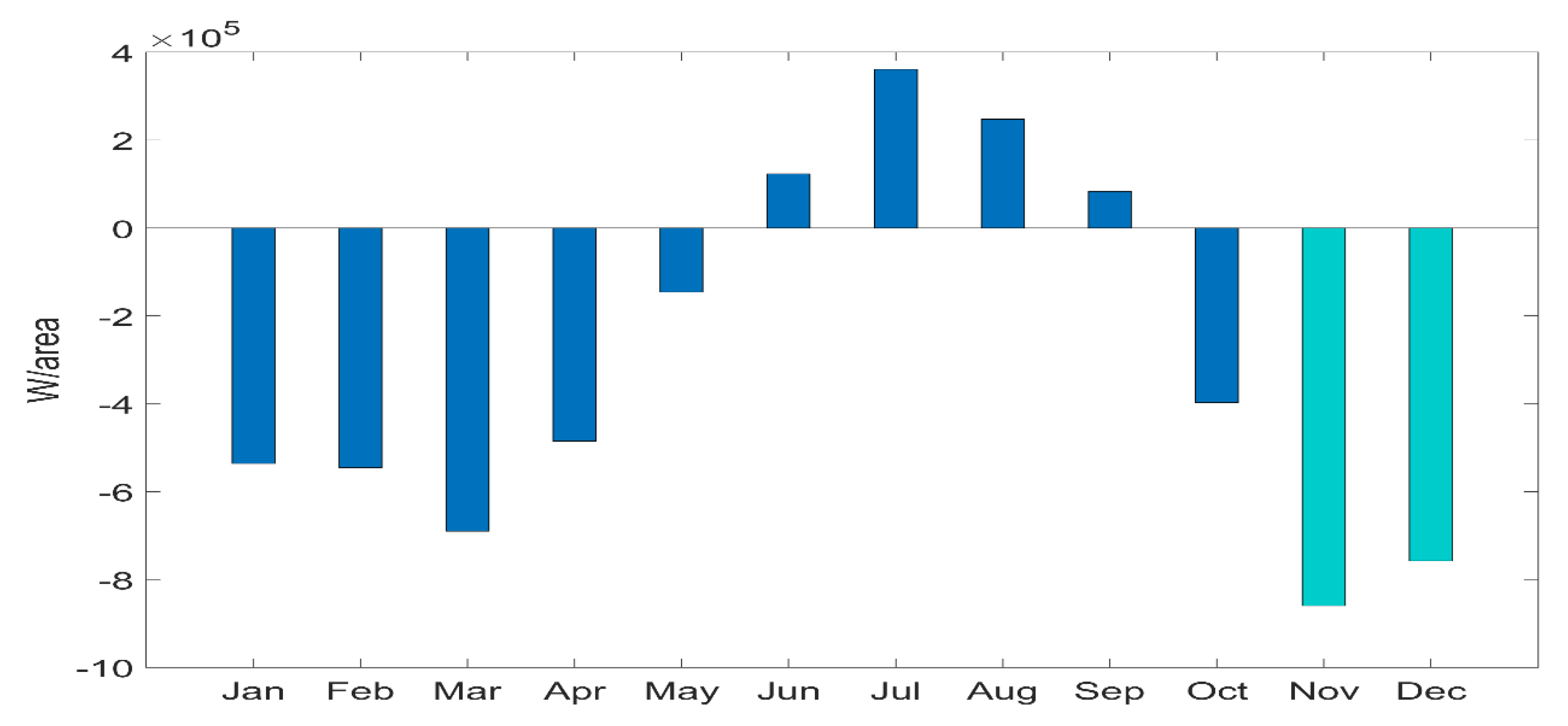
3.1. Heat and Freshwater Fluxes within the Northwestern Levantine Sea
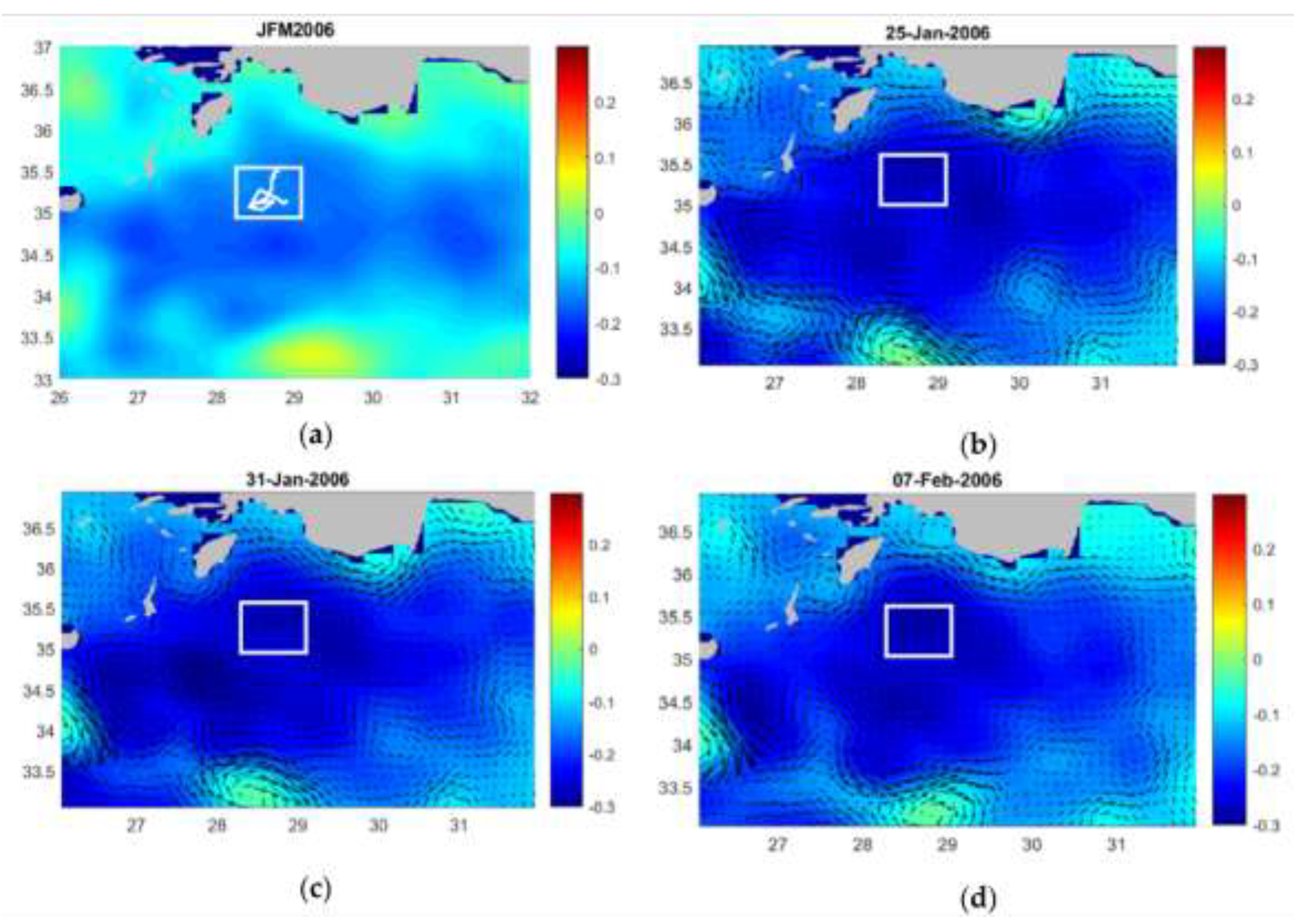
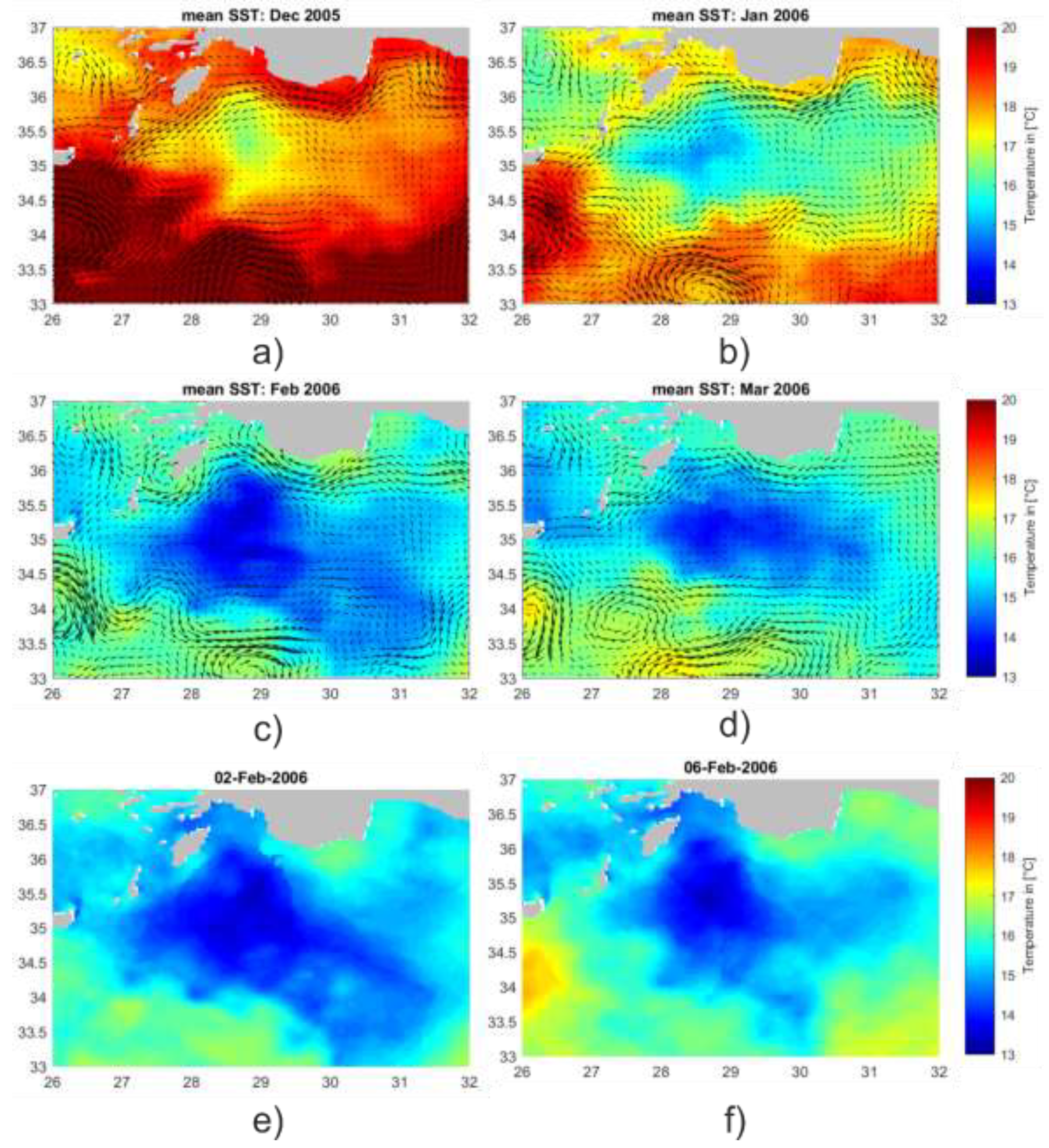
3.2. LIW and LDW Formation within the Northwestern Levantine Sea
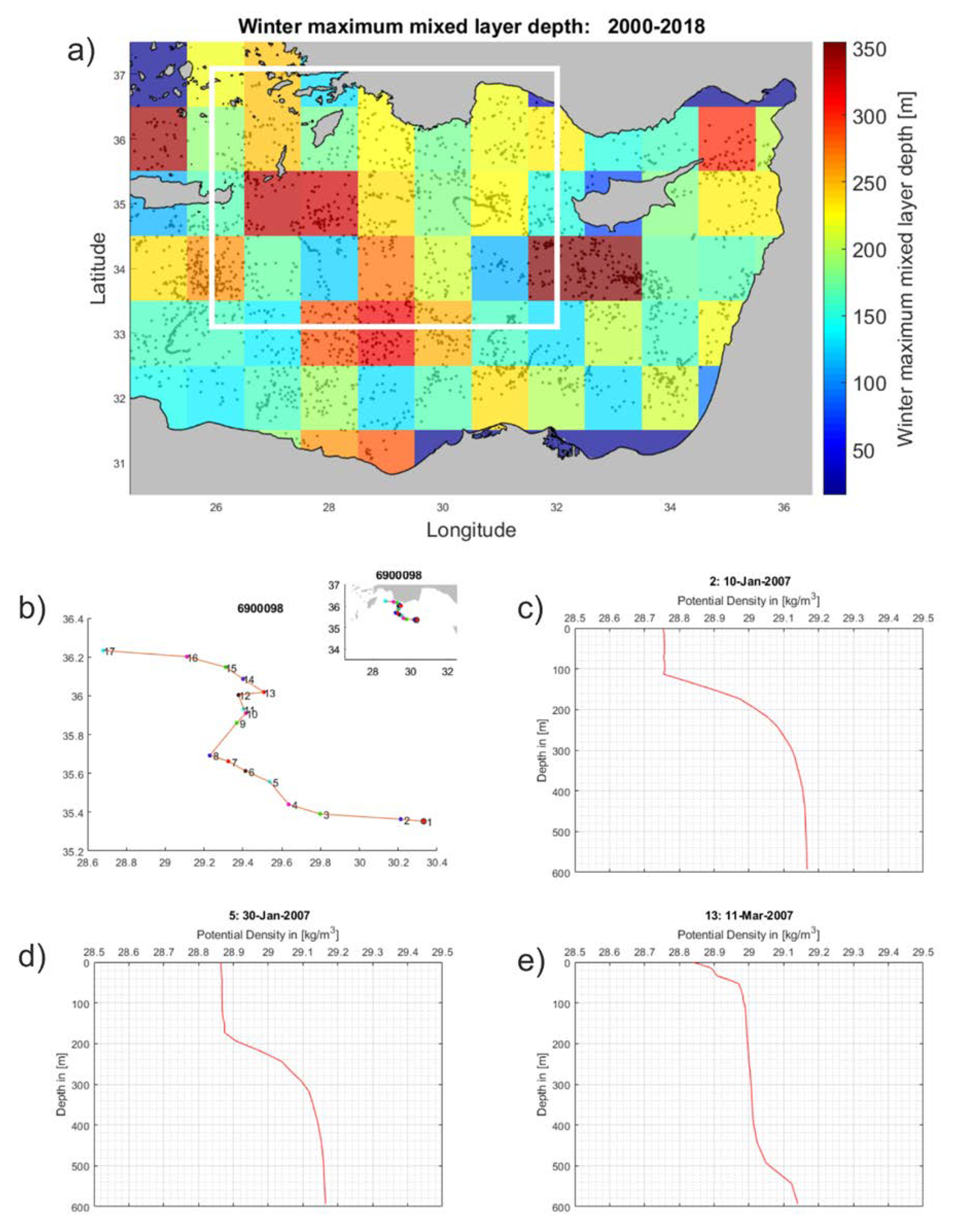
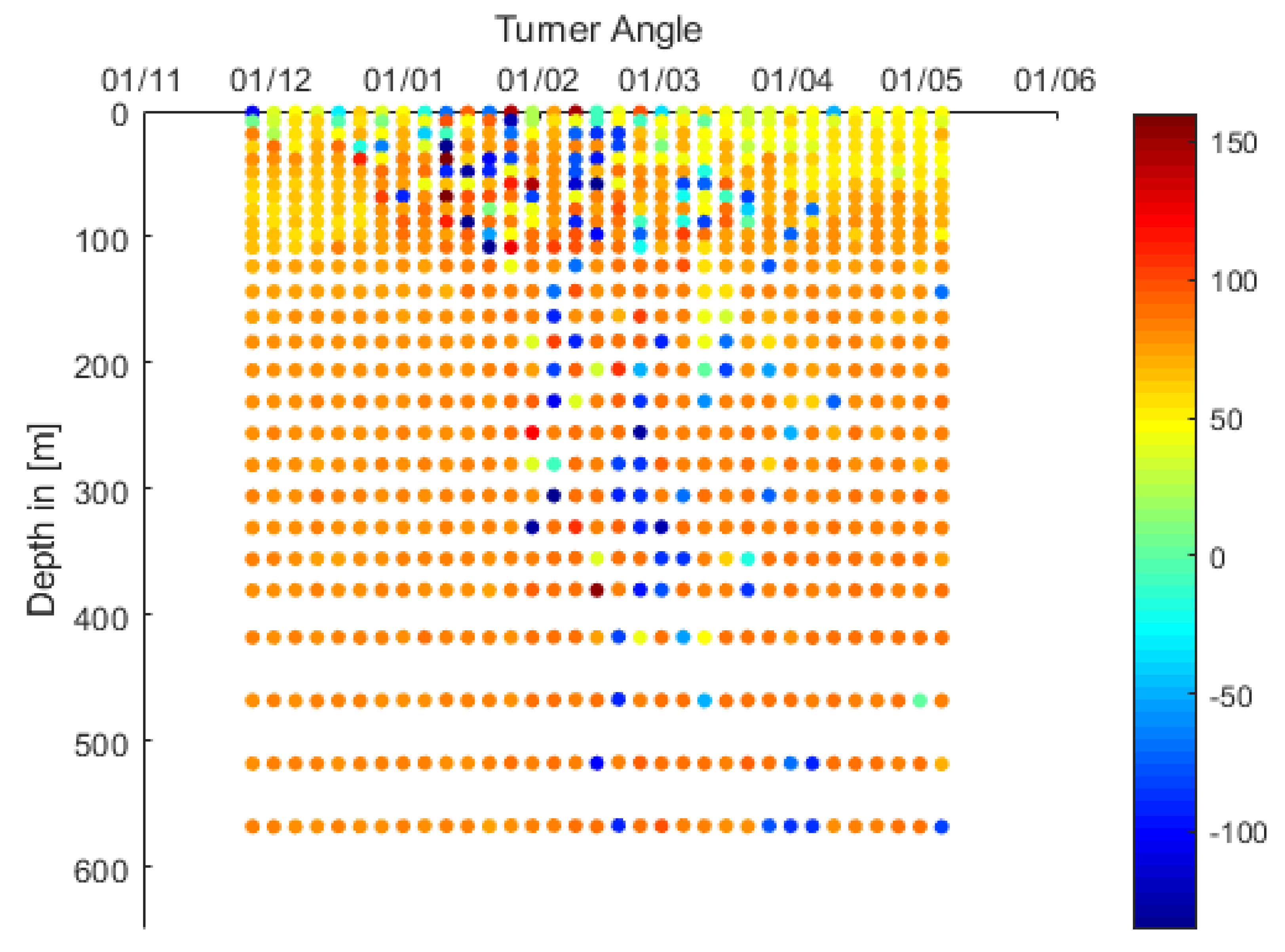
3.2.1. LDW formation within the Rhodes Gyre
3.2.2. LIW Formation along the Coastline
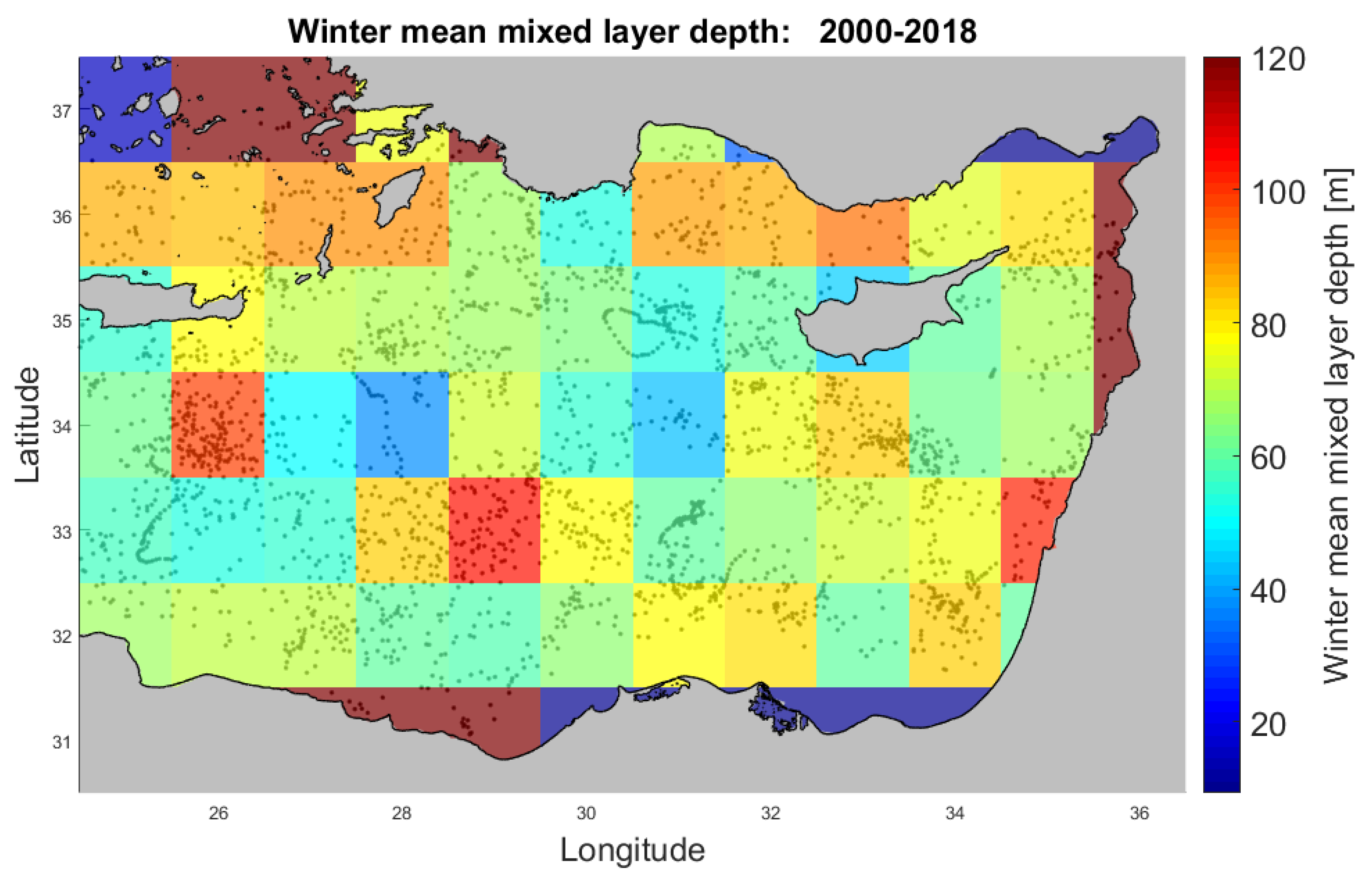
3.3. Climatology of Winter Mean MLD from 2000 to 2018
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsimplis, M.N.; Zervakis, V.; Josey, S.A.; Peneva, E.L.; Struglia, M.V.; Stanev, E.V.; Theocharis, A.; Lionello, P.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Artale, V.; et al. Changes in the Oceanography of the Mediterranean Sea and their Link to Climate Variability, in Mediterranean Climate Variability. In Developments in Earth & Environmental Sciences; Lionello, P., Malanotte-Rizzoli, P., Boscolo, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 4, pp. 227–282. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamasco, A.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P. The circulation of the Mediterranean Sea: A historical review of experimental investigations. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2010, 1, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacic, M.; Civitarese, G.; Eusebi Borzelli, G.L.; Kovacevic, V.; Poulain, P.-M.; Theocharis, A.; Menna, M.; Catucci, A.; Zarokanellos, N. On the relationship between the decadal oscillations of the Northern Ionian Sea and the salinity distributions in the Eastern Mediterranean. J. Geophys. Res. (Ocean.) 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacic, M.; Schroeder, K.; Civitarese, G.; Vetrano, A.; Eusebi Borzelli, G.L. On the relationship among the Adriatic-Ionian Bimodal Oscillating System (BiOS), the Eastern Mediterranean salinity variations and the Western Mediterranean thermohaline cell. Ocean Sci. Discuss. 2012, 9, 2561–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, M.; Suarez, C.; Civitarese, G.; Gacic, M.; Poulain, P.-M.; Rubino, A. Decadal variations of circulation in the Central Mediterranean and its interactions with mesoscale gyres. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Manca, B.; Marullo, S.; Ribera d’Alcala, M.; Roether, W.; Theocharis, A.; Bergamasco, A.; Budillon, G.; Sansone, E.; Civitarese, G.; et al. The Levantine Intermediate Water Experiment (LIWEX) Group: Levantine basin—A laboratory for multiple water mass formation processes. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, A.; Krokos, G.; Velaoras, D.; Korres, G. An Internal Mechanism Driving the Alternation of the Eastern Mediterranean Dense/DeepWater Sources. The Mediterranean Sea: Temporal Variability and Spatial Patterns. In The Mediterranean Sea: Temporal Variability and Spatial Patterns, 1st ed.; Eusebi Borzelli, G.L., Gagic, M., Lionello, P., Malanotte-Rizzoli, P., American Geophysical Union, Eds.; Geophysical Monograph 202; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 10, pp. 113–137. [Google Scholar]
- Lionello, P.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Boscolo, R.; Alpert, P.; Artale, V.; Li, L.; Luterbacher, J.; May, W.; Trigo, R.; Tsimplis, M.; et al. The Mediterranean Climate: An Overview of the Main Characteristics and Issues. Dev. Earth Environ. Sci. 2006, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sur, H.I.; Özsoy, E.; Unluata, U. Simultaneous deep and intermediate depth convection in the Northern Levantine Sea, winter 1992. Oceanol. Acta 1993, 16, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Gertman, I.F.; Ovchinnikov, I.M.; Popov, Y.I. Deep convection in the eastern basin of the Medi-terranean Sea. Oceanology 1994, 34, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Spall, M.A.; Pickart, R.S. Where does dense water sink? A subpolar gyre example. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 810–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spall, M.A. Boundary currents and water mass transformation in marginal seas. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 1197–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spall, M.A. Buoyancy-forced downwelling in boundary currents. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2008, 38, 2704–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spall, M.A. Dynamics of downwelling in an eddy-resolving convective basin. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 2341–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, R.; Brüggemann, N.; Bosse, A.; Spall, M.; Somot, S.; Sevault, F. Overturning the Mediterranean Thermohaline Circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinardi, N.; Cessi, P.; Borile, F.; Wolfe, C. The Mediterranean Sea Overturning Circulation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, M.; Poulain, P.-M.; Zodiatis, G.; Gertman, I. On the surface circulation of the Levantine sub-basin derived from Lagrangian drifters and satellite altimetry data. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2012, 65, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, P.-M.; Barbanti, R.; Font, J.; Cruzado, A.; Millot, C.; Gertman, I.; Griffa, A.; Molcard, A.; Rupolo, V.; Le Bras, S.; et al. MedArgo: A drifting profiler program in the Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Sci. 2007, 3, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holte, J.; Talley, L.D.; Gilson, J.; Roemmich, D. An Argo mixed layer climatology and database. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5618–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahariev, K.; Garrett, C. An Apparent Surface Buoyancy Flux Associated with the Nonlinearity of the Equation of State. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1997, 27, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, B.R. A practical indicator of the stability of the water column to double-diffusivity activity. Deep Sea Res. Part A 1983, 30, 1105–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOC; SCOR; IAPSO. The International Thermodynamic Equation of Seawater—2010: Calculation and Use of Thermodynamic Properties; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, UNESCO (English): Paris, France, 2010; p. 196. [Google Scholar]
- Roether, W.; Klein, B.; Manca, B.B.; Theocharis, A.; Kioroglou, S. Transient Eastern Mediterranean deep waters in response to the massive dense-water output of the Aegean Sea in the 1990’s. Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 74, 540–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliks, Y. Downwelling along the Northeastern Coasts of the Eastern Mediterranean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1991, 21, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliks, Y.; Ghil, M. Downwelling-front instability and eddy formation in the Eastern Mediterranean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1993, 23, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karstensen, J.; Lorbacher, K. A practical indicator for surface ocean heat and freshwater buoyancy fluxes and its application to the NCEP reanalysis data. Tellus 2011, 63, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWF Mediterranean Marine Initiative Report. Stop the Flood of Plastic: How Mediterranean Countries Can Save Their Sea. 2019. Available online: http://awsassets.panda.org/downloads/a4_plastics_reg_low.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2019).



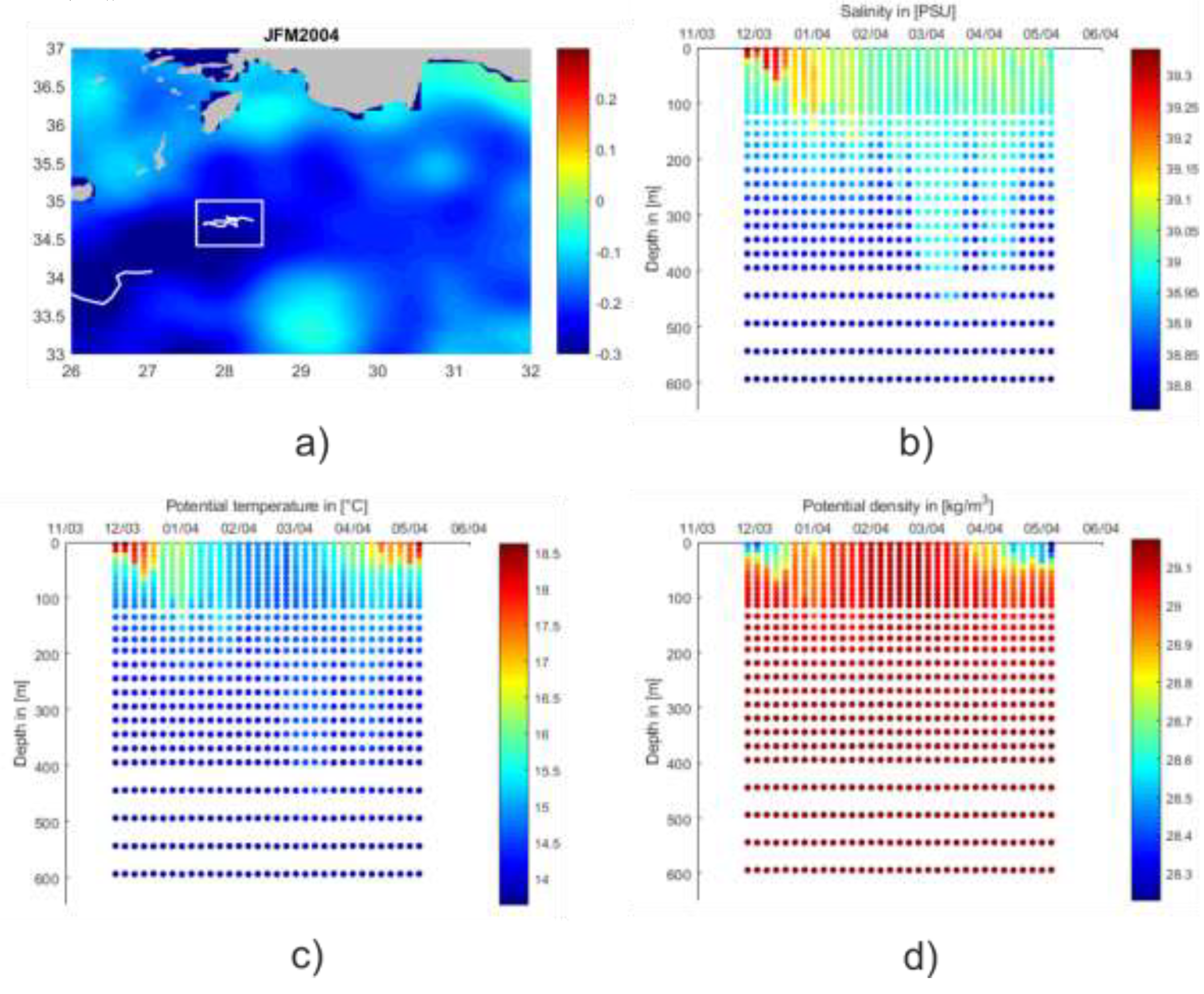
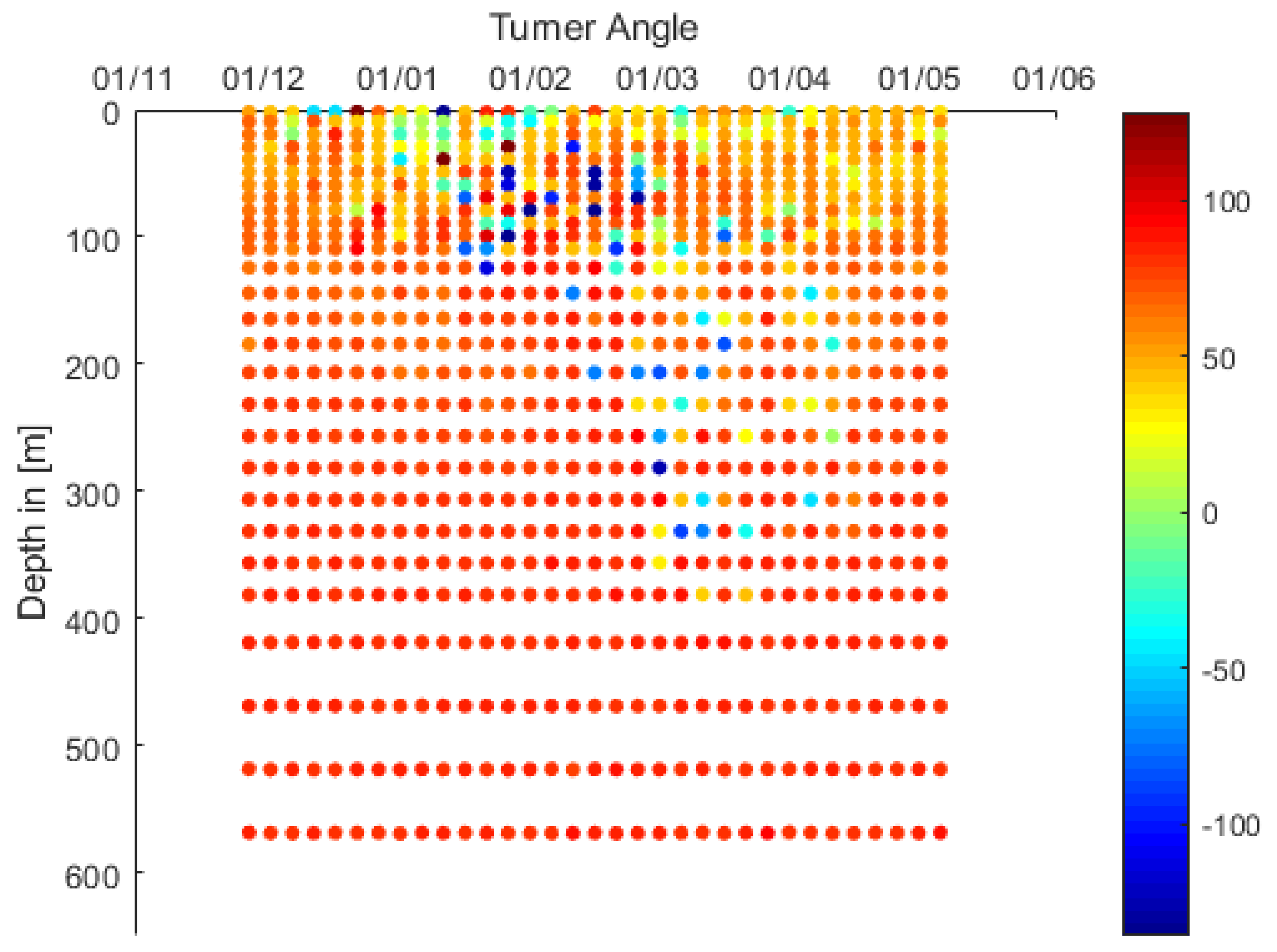
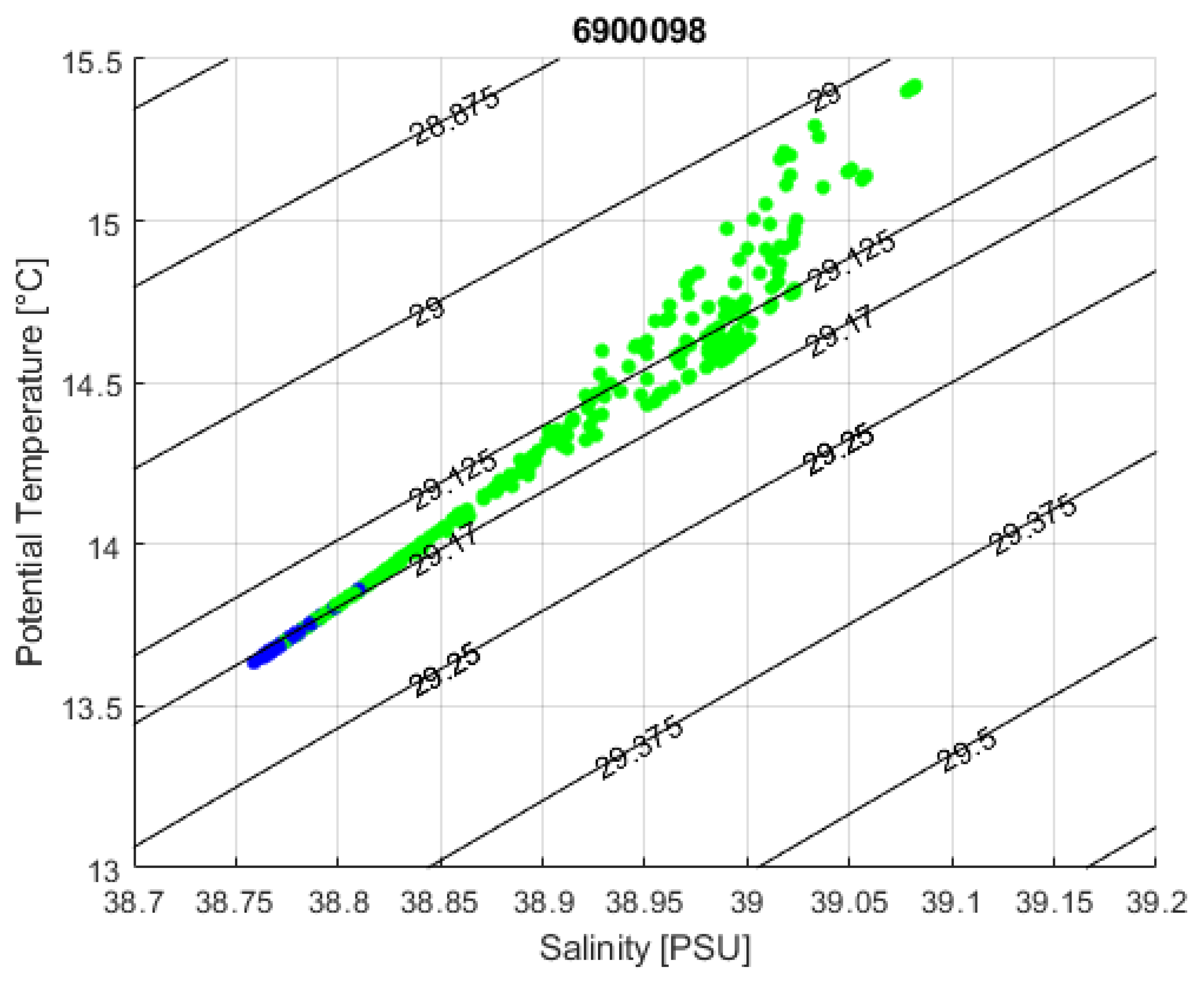

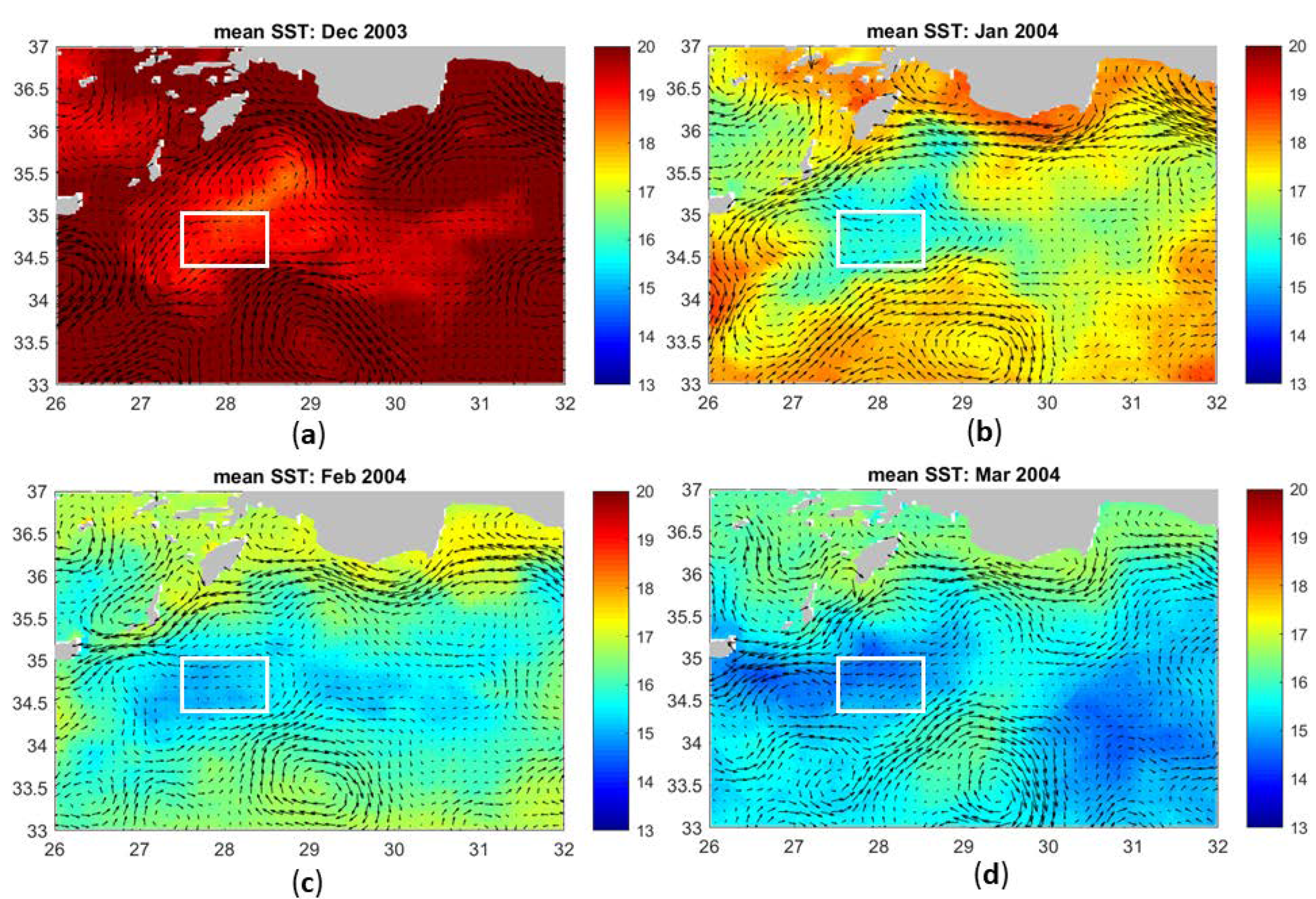
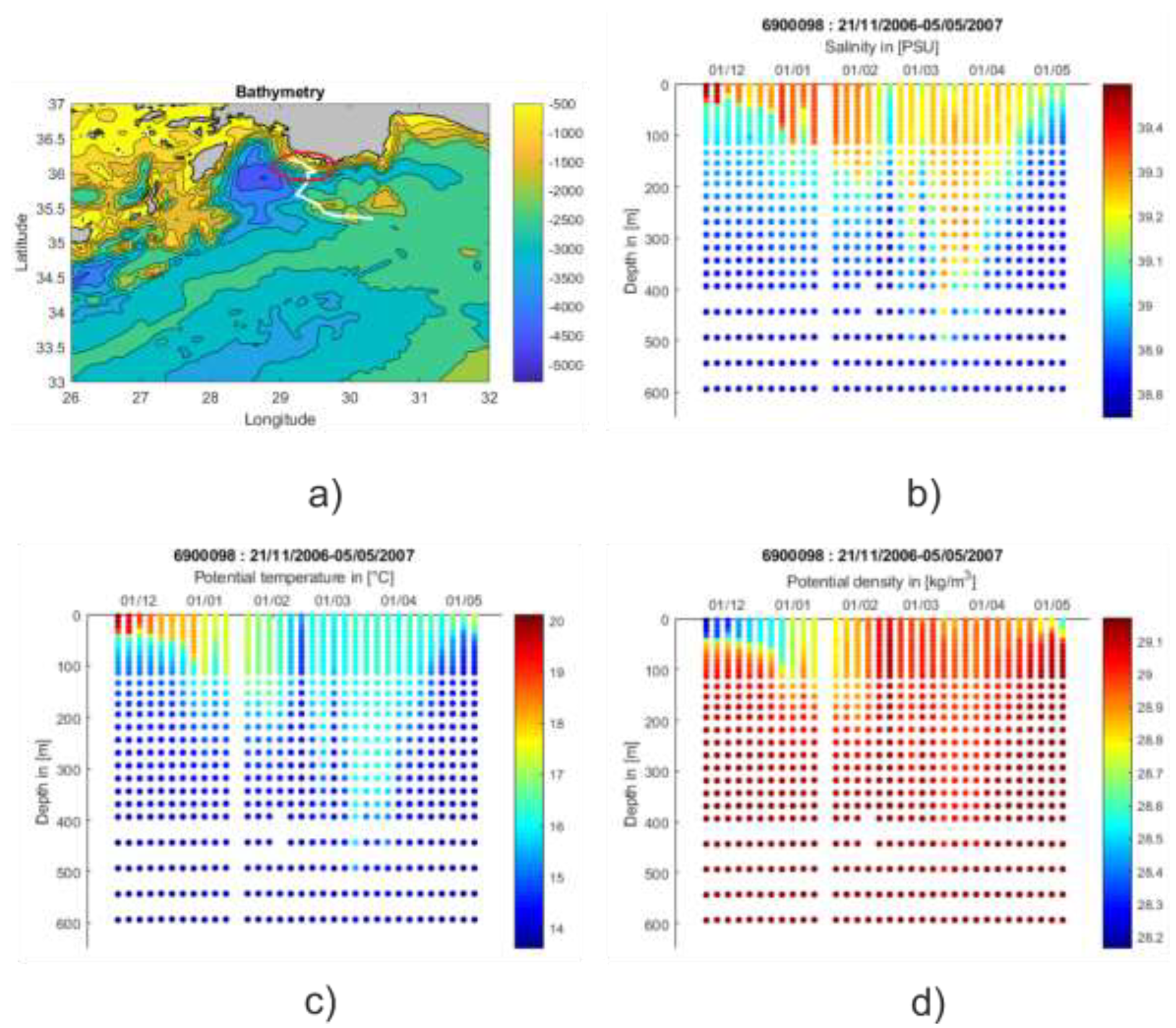
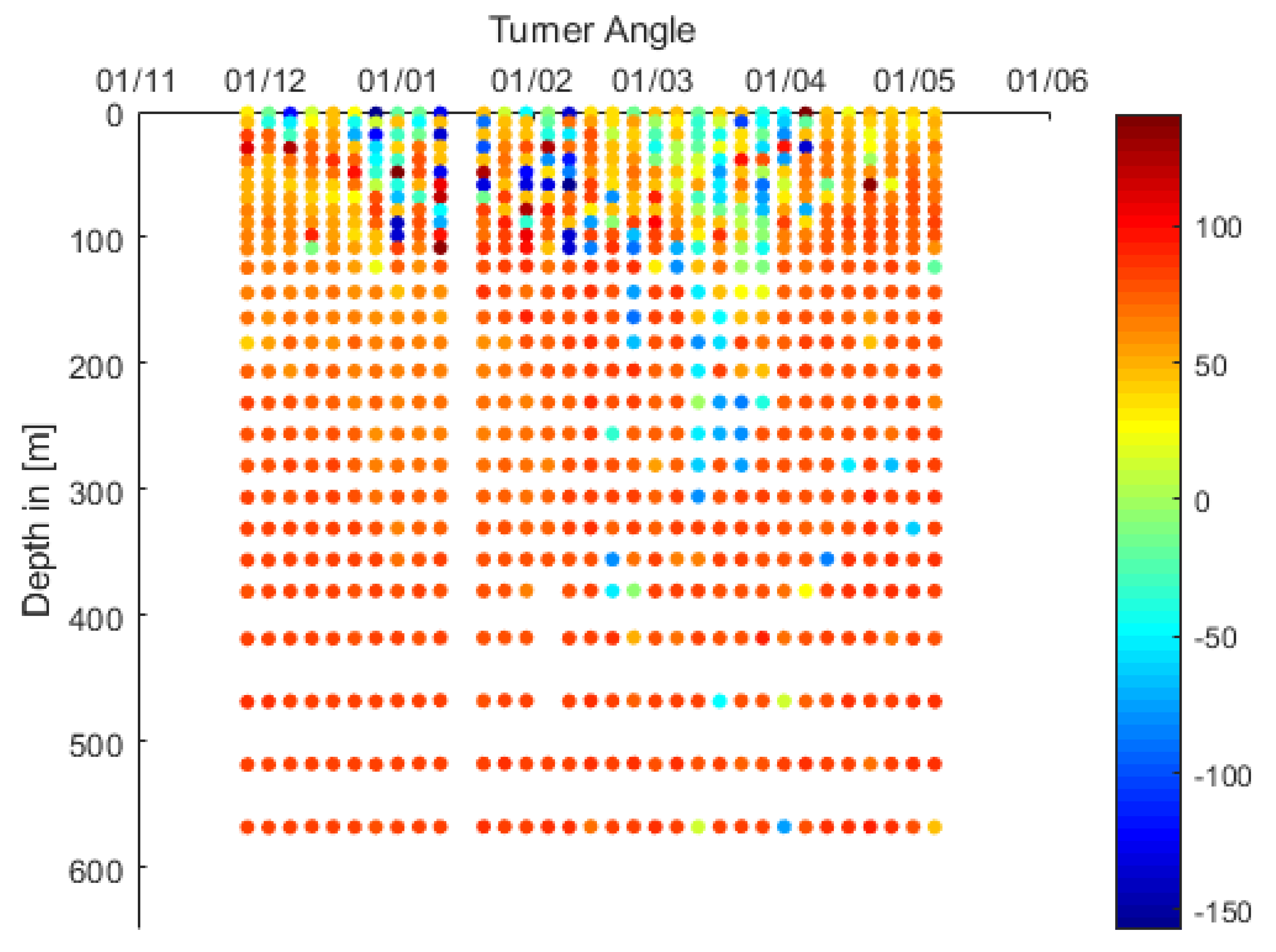
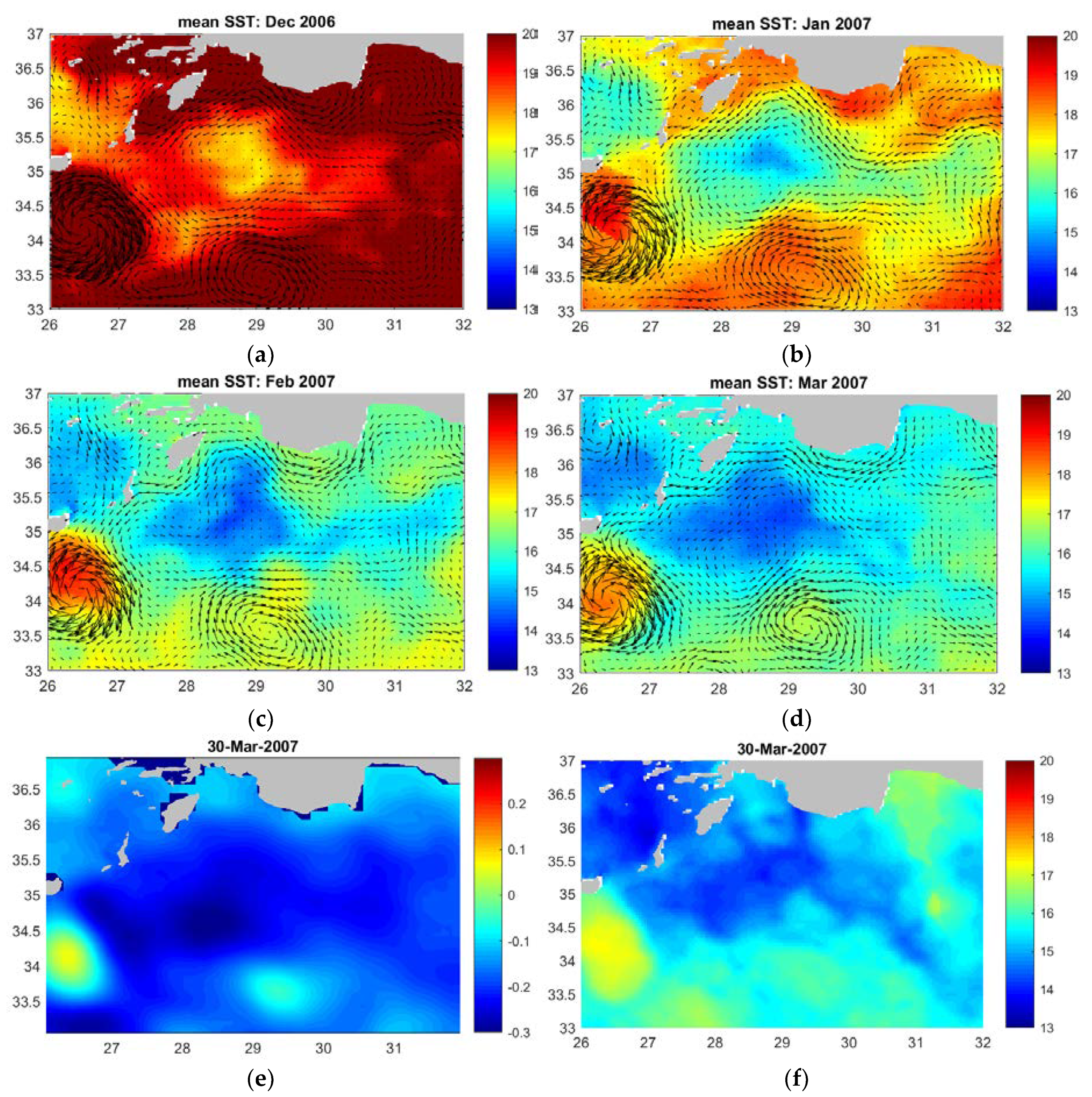
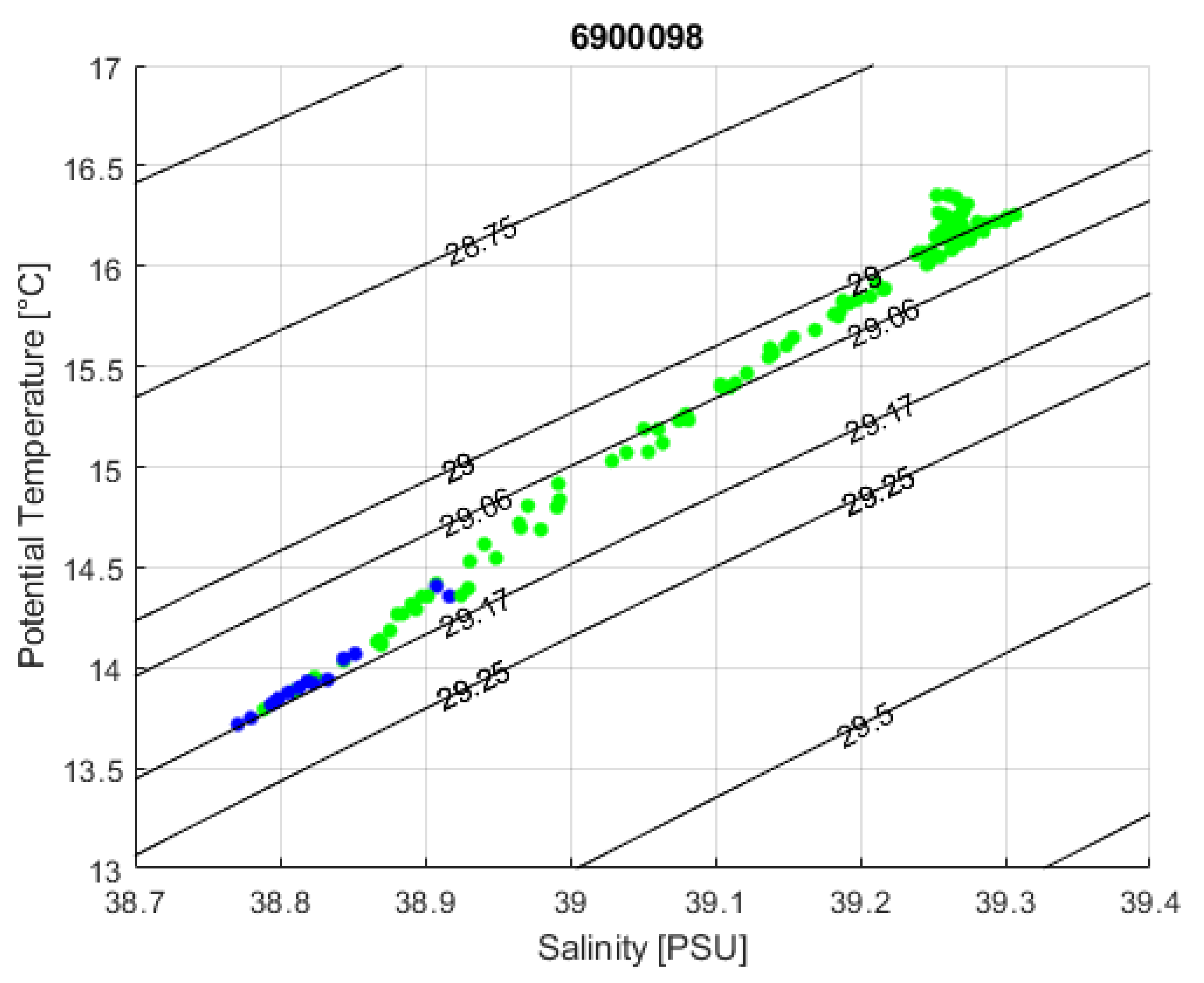

| Area of Formation | Float WMO | Time Period | Water Mass Characteristics | Maximum Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RG | 6900098 | FM 2004 | LDW | At least 600 m, probably 1000 m 1 |
| RG | 6900098 | FM 2005 | LDW | At least 600 m, probably 1000 m 1 |
| RG | 6900098 | JF 2006 | LDW | At least 600 m, probably 1000 m 1 |
| RG | 6900098 | FM 2008 | LDW | At least 600 m, probably 1000 m 1 |
| COAST | 6900098 | M 2007 | LIW | About 550 m |
| COAST | 6900843 | FM 2012 | LIW | About 350 m |
| COAST | 6901824 | FM 2015 | LIW | About 350 m |
| COAST | 6901868 | FM 2016 | LIW | About 300 m |
| Float Number | Float Description |
|---|---|
| WMO 6900098 | Apex Profiling Float, Naval Oceanographic Office (NAVO) Alive from 20.07.2003 to 19.04.2009, lifetime approximately 5 years Parking depth (PD)=1000 m; 5 day cycle; |
| WMO 6900843 | Apex Profiling Float, Argomed, Euro-Argo Alive from 03.10.2011 to 31.5.2014, PD=350 m; 5 day cycle; |
| WMO 6901824 | Arvor Profiling Float, Argo Italy, Argomed, Euro-Argo Alive from 04.11.2013 to 03.02.2018, PD=350 m; 5 day cycle; |
| WMO 6901868 | Apex Profiling Float, Argo Italy, Euro-Argo Alive from 01.12.2014 to 29.07.2017. PD=350 m; 5 day cycle; |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubin, E.; Poulain, P.-M.; Mauri, E.; Menna, M.; Notarstefano, G. Levantine Intermediate and Levantine Deep Water Formation: An Argo Float Study from 2001 to 2017. Water 2019, 11, 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091781
Kubin E, Poulain P-M, Mauri E, Menna M, Notarstefano G. Levantine Intermediate and Levantine Deep Water Formation: An Argo Float Study from 2001 to 2017. Water. 2019; 11(9):1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091781
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubin, Elisabeth, Pierre-Marie Poulain, Elena Mauri, Milena Menna, and Giulio Notarstefano. 2019. "Levantine Intermediate and Levantine Deep Water Formation: An Argo Float Study from 2001 to 2017" Water 11, no. 9: 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091781
APA StyleKubin, E., Poulain, P.-M., Mauri, E., Menna, M., & Notarstefano, G. (2019). Levantine Intermediate and Levantine Deep Water Formation: An Argo Float Study from 2001 to 2017. Water, 11(9), 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091781







