Abstract
Riparian vegetation represents a protective barrier between human activities installed in catchments and capable of generating and exporting large amounts of contaminants, and stream water that is expected to keep quality overtime. This study explored the combined effect of landscape composition and buffer strip width (L) on stream water quality. The landscape composition was assessed by the forest (F) to agriculture (A) ratio (F/A), and the water quality by an index (IWQ) expressed as a function of physico-chemical parameters. The combined effect (F/A × L) was quantified by a multiple regression model with an interaction term. The study was carried out in eight catchments of Uberaba River Basin Environmental Protection Area, located in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil, and characterized by very different F/A and L values. The results related to improved water quality (larger IWQ values) with increasing values of F/A and L, which were not surprising given the abundant similar reports widespread in the scientific literature. But the effect of F/A × L on IWQ was enlightening. The interaction between F/A and L reduced the range of L values required to sustain IWQ at a fair level by some 40%, which is remarkable. The interaction was related to the spatial distribution of infiltration capacity within the studied catchments. The high F/A catchments should comprise a larger number of infiltration patches, allowing a dominance of subsurface flow widespread within the soil layer, a condition that improves the probability of soil water to cross and interact with a buffer strip before reaching the stream. Conversely, the low F/A catchments are prone to the generation of an overland flow network, because the absence of permanent vegetation substantially reduces the number of infiltration patches. The overland flow network channelizes runoff and conveys the surface water into specific confluence points within the stream, reducing or even hampering an interaction with a buffer strip. Notwithstanding the interaction, the calculated L ranges (45–175 m) are much larger than the maximum width imposed by the Brazilian Forest Code (30 m), a result that deserves reflection.
1. Introduction
Riparian buffers represent undeniable benefits to stream water quality in catchments affected by agricultural nonpoint source pollution [1,2,3,4]. The benefits occur because riparian buffer strips favor physical processes, such as infiltration, sediment deposition or adsorption, as well as biochemical mechanisms, such as nutrient uptake or denitrification [5,6,7]. The role of riparian vegetation in the retention of nutrients and sediments has been reviewed in various studies [8,9,10,11,12]. A key parameter of riparian buffers is the width. Several studies refer minimum thresholds for riparian buffer width [13], while in some countries, such as Brazil or the United States, this width has been legally imposed or recommended [14,15]. However, other studies consider fixed-width recommendations problematic because riparian ecological responses are highly variable [8], and hence, optimal buffer widths are expected to vary from site to site [13]. On the other hand, width is just one among other major factors influencing stream water quality. Other key factors are landscape composition and patterns.
Following an early work by Kuehne, dated from the 1960s [16], numerous studies investigated the impacts of landscape composition and patterns on stream and lake water quality [17], even reporting that landscape characteristics are critical to water quality [18,19]. The reports evolved from cases where the relationship between the composition of landscape and the variation in water quality indicators was explored [20], to cases where the focus was moved to the spatial arrangement of the landscape (patterns) [21,22]. In the earlier studies, good water quality was generally associated with undeveloped watersheds dominated by forest land use, while poor water quality was linked to human development activities, such as agriculture [23]. In the more recent studies, a variety of landscape metrics was used to explain the correlation between landscape patterns and stream water quality, including patch density, largest patch index, landscape shape index or contagion [24,25,26,27].
The assessment of stream water quality based on the correlation with buffer strip widths or on the relationship with landscape composition usually leads to distinct results, and sometimes the standpoints are antagonistic. Various studies have shown that landscape composition within the river basin are decisive to identify the impacts of human activities on water quality [28,29], while other studies stated that patterns at the riparian buffer zones are more powerful to explain those impacts [30,31]. Eventually, the observed discrepancies were related to the dataset structure. Riparian variables are expected to become better explanatory variables when the land use is fairly homogenous and/or one land use category is widely dominant, as occurred in the [30,31] studies. In other cases, the landscape composition is almost always the first explanatory variable. However, discrepancies can also be interpreted as a scale problem [32]. The combined roles of the whole basin and buffer strip scales have been discussed in recent studies [33,34,35,36]. It has been reported that water quality varies along the direction of flow, due to human activities and the changing size of the buffer zone, and the self-purification ability of the water is influenced by the landscape composition in the river basin [37].
Despite the abundance of scientific literature on the relationship between stream water quality, buffer strip widths and landscape composition, a specific issue has not been tackled so far: The potential interaction among buffer strip widths and landscape composition. The studies mentioned in the previous paragraph link stream water quality variations to changes in buffer strip width and(or) landscape composition, acting independently as main effects, but fail to address potential joint effects. However, interactions among main effects are widely discussed in the scientific literature about regression models [38,39,40], and can play a role in the context of water quality assessments and their correlation with multi-scale factors. For example, stream water quality could be improved with narrower buffer strips if an enhanced self-purification of runoff was accomplished within a rural catchment by a large proportion of forest areas relative to agricultural areas. The negative consequences of overlooking interaction effects have been discussed in some forums (https://statisticsbyjim.com/regression/interaction-effects/). When interaction effects are statistically significant, the main effects cannot be interpreted without considering the interactions, under the sentence of severe misinterpretation of results and prognosis.
The general purpose of this study was to explore the relationship between water quality variation, landscape composition, buffer strip widths, and potential interactions between composition and widths. This general goal comprised the following specific objectives: (1) Investigate potential interactions between landscape composition and buffer strip widths using a linear regression model with and without an interaction term; (2) determine the range of buffer strip widths that ensure a regular water quality, as a function of a landscape composition index (ratio native forest/agriculture), with and without considering the interaction effects; (3) interpret the results from a management standpoint. The research was carried out in the Uberaba River Basin (state of Minas Gerais, Brazil), namely within the Municipal Environmental Protection Area (EPA-MURB) located at the headwaters. The study area comprises eight sub-basins of EPA-MURB. Watercourses in these catchments may be affected by a diversity of non-point (diffuse) pollutants, including nitrogen and phosphorus from fertilizers or fine sediments from soil erosion, mostly derived from sugar cane plantations. In this study, water quality was assessed by an index that involves the measurement of dissolved oxygen, turbidity, total dissolved solids, which means parameters that can be interpreted as proxies to those pollutants. The index is called IWQ—Index for Water Quality and was proposed by the Environmental Company of São Paulo State—CETESB (https://cetesb.sp.gov.br) to be used in water quality assessments. The regression models were first applied to the IWQ and then to its formation variables, with the purpose to identify the most influencing ones. The studied watercourses are characterized by approximately 15, 30 and 50 m wide riparian forests. The reason for selecting these buffer widths relates to the rules imposed in the Brazilian Forest Code (Law No. 12651/12). There are two rules: The transition rule takes into account the size of land property calculated as fiscal modules and creates a distance from the stream margin that goes from a minimum of 5 m to a maximum of 20 m, considering the regular river bank; the permanent rule defines 30 m as unique distance. The rationale was, therefore, to span buffer widths that enclose these limits, considering the real buffer widths observed in the field.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area encompasses the Municipal Environmental Protection Area of Uberaba River Basin (EPA-MURB), which covers 528.1 km2 of Triângulo Mineiro Region, State of Minas Gerais, Brazil (Figure 1). The EPA-MURB is located in the Brazilian Central Plateau, and the Northeast portion of Paraná River Basin, between the altitudes 710–1040 m and within the planimetric coordinates 188–220 km East and 7815–7840 km North expressed in the Universal Transverse Mercator system, zone 23K. The topography is characterized by undulated landscapes, sometimes incised by steep valleys.
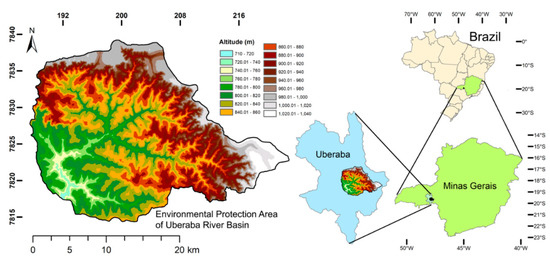
Figure 1.
Location of the Environmental Protection Area of Uberaba River Basin in the Uberaba Municipality, State of Minas Gerais, and Brazil. Adapted from Valera et al. [15].
Geology is dominated by two groups and associated formations (Figure 2a). The São Bento Group and associated Serra Geral Formation is composed of Lower Cretaceous grey to black basaltic lava flows (15–70 m thick), cropping out at lower altitudes. The Bauru Group, which overlays the São Bento Group along with an erosive contact, comprises the Uberaba Formation overlaid by the Marília Formation, being both composed of Cretaceous sandstones and conglomerates. The contact between the two sequences is abrupt, being marked by a silexite level and a conglomerate rich in quartz grains cemented with calcite [41]. The latosols dominate the landscape while the argisols occupy just small areas (Figure 2b) (https://www.embrapa.br/solos/sibcs). The latosols are characterized by clayey texture, whereas the argisols are characterized by sandy texture. Soil erosion may be intense because the land is prepared for seeding in the Autumn season, a period characterized by erosive rainfall events [42].
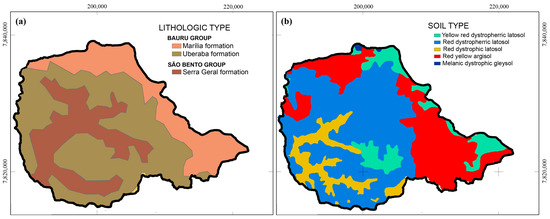
Figure 2.
Geology (a) and soils (b) in the Environmental Protection Area of Uberaba River Basin. The soil map was adapted from Siqueira et al. [44].
Climate is tropical (Aw in the Köppen’s classification scheme) and the climatic domain is semi-humid with 4 to 5 dry months and relative humidity of 70–75%. The temperature ranges between 20 and 24 °C, on the annual average. The period from October to February observes the warmest temperatures that vary between 21 and 25 °C. The coldest month arrives in July, when temperatures drop to 16 to 18 °C. Based on a sixty-two years record, mean annual precipitation of 1584.2 mm is estimated for Uberaba municipality. The amount of rainfall varies considerably during the year, with average values ranging between 42.8 and 541 mm (www.inmet.gov.br/).
Agriculture and livestock production are important economic activities in the EPA-MURB. These areas form a mosaic where they alternate with spots of native vegetation (Cerrado), as illustrated in Figure 3. The landscape has changed significantly in the past half-century. In the 1960s, the Cerrado was the dominating land cover, reaching 40% of the EPA-MURB. In the following decades, expansion of managed pastures and (to a smaller extent) areas used for short-cycle agriculture (mostly corn and rice) caused a significant reduction in the share of native vegetation in the region. More recently, large areas have been converted to sugar cane plantations related to the production of energy from ethanol [43].
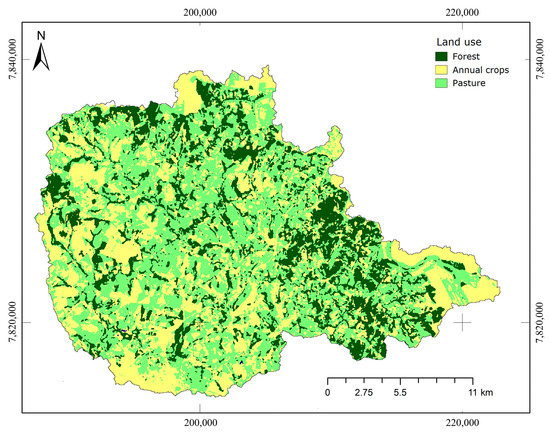
Figure 3.
Land cover in the Environmental Protection Area of Uberaba River Basin. Adapted from Siqueira et al. [44].
On 20 January 1999, the EPA-MURB was legally protected through the State Law No. 13183, for an area of 463 km2, being recognized as Sustainable Land Use Conservation Unit because of its important groundwater resources and remnants of Cerrado Biome. On 28 December 2005, the protection has been considered at Municipal level by the Law No. 9892 for an area of 528.1 km2. The management plan for the EPA-MURB was published by the Municipal Secretary of the Environment (http://www.uberaba.mg.gov.br/), which divided the area into five zones: (1) Urban consolidation zone; (2) tourism and/or leisure development zone; (3) agricultural area; (4) conservation area of natural resources and (5) recovery zone. Recently (2017), Complementary Law No. 561 has regulated the urban perimeter within the EPA-MURB.
2.2. Studied Sub-Basins
The studied sites comprised eight small to medium sub-basins selected within the EPA-MURB (Figure 4), with areas ranging from 136.3 hectares (Borá 1 sub-basin) and 3764 hectares (Lajeado sub-basin). The distribution of main land uses or covers is summarized in Table 1. In all cases the catchments were mostly used for agriculture, namely sugar cane plantations, as well as natural or managed (used for the grazing of domestic livestock) pastures. The use for agriculture (“A” column in Table 1) represents 56.7% (Borá 2 sub-basin) to 88.8% (Borá 2 sub-basin) of the catchment areas, and therefore, they can be considered basins with significant anthropogenic influence. Besides the use for agriculture, the eight catchments are substantially covered with native (Cerrado) and managed (eucalyptus) forests (“F” column), with proportions to the agriculture use (“F/A” column) ranging from 0.1 to 0.7. The other uses or covers (“Other” column) comprise the rural dwellings, water bodies (lakes and reservoirs), roads, orchards and areas used for rainfed or irrigated corps. The riparian buffers marginal to the watercourses (“L” column) were characterized by quite different widths: On average and approximately, 15 m in the Alegria, Lageado and Mangabeira 1 sub-basins; 30 m in the Borá 1, Mangabeira 2 and Uberaba sub-basins; and 50 m in the Borá 2 and Lanhoso sub-basins. The water samples were collected at the sub-basins’ outlets.
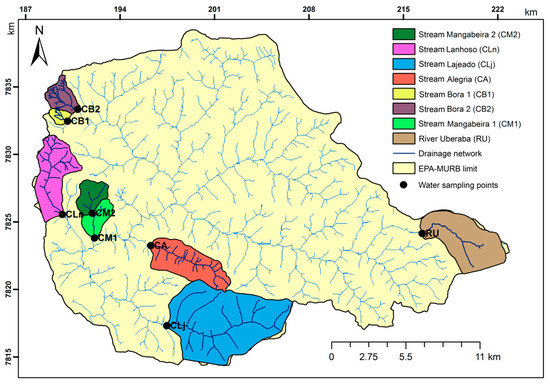
Figure 4.
Distribution of studied sub-basins within the Environmental Protection Area of Uberaba River Basin.

Table 1.
Land use and cover within the studied sub-basins. Symbols: L—approximate average width of riparian buffer marginal to the water course, observed in satellite images; F—forest cover (native or managed); A—use for agriculture (sugar cane plantations; natural and managed pastures); Other—other uses or covers.
2.3. Water Sampling and Physico-Chemical Analyses
The stream water samples were collected in the streams, 60 cm far from the stream margin, in sectors that were adjacent to the riparian buffer. The sampling campaigns were conducted on a monthly basis, from January 2016 to January 2017 (13 months). The sampling took place from calendar days 15 and 20, every month. The year of 2016 was dry because the annual rainfall (1214.4 mm) was smaller than the local long-term average precipitation (1584.2 mm). Table 2 reviews the prevailing weather conditions in the sampling days, as well as during the three antecedent days. The sampling days were characterized by low rainfall (<5 mm), with the exception of February 2016 and January 2017 campaigns. In these two campaigns, rainfall during the sampling day has reached 5.9 and 10.9 mm, respectively. Average rainfall in the three antecedent days was also small (3.5–5.8 mm), with the few exceptions represented in Table 2 in boldface. The exceptional days were 13 November 2016, and 16 January 2017, with precipitation >25 mm. Taken altogether, the average analytical results should be related to long-term effects of landscape composition and buffer strip width on the quality of stream water, rather than short term effects associated with storm events.

Table 2.
Weather conditions (rainfall) in the water sampling day and the three antecedent days (day-1 until day-3). Values larger than 10 mm day-1 are represented in boldface. Source: Valera et al. [15].
The measurement of water quality parameters in every campaign involved 10 repetitions, as recommended in the CONAMA’s Resolution No. 357/2005. The parameters were measured using a Horiba U-50 Series multi-parameter probe, and comprised: T—water temperature (°C), pH, ORP—Oxidation Reduction Potential (mV), Ec—Electrical conductivity (μS cm−1), Turbidity, measured in Nephelometric Turbidity Units (NTU), DO—Dissolved oxygen (mg L−1), PDO—Percentage of Dissolved Oxygen (%), and TDS—total dissolved solids (mg L−1). The analytical results are provided as Supplementary Material.
A subset of parameters was used to calculate the Index for Water Quality (IWQ) proposed by the Environmental Company of São Paulo State—CETESB (https://cetesb.sp.gov.br):
where 0 ≤ IWQ ≤ 100, qi is the quality of ith parameter obtained from standardization of the measured values into a 0–100 range, wi is the weight of ith parameter, which varies in the 0 ≤ wi ≤ 1 interval as a function of its importance to the overall quality, and n is the total number of parameters. This IWQ evaluates water quality on the basis of nine parameters (n = 9), including water temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, total dissolved solids, biochemical oxygen demand, fecal coliforms, total nitrogen and total phosphorus. Data may be lacking for some parameters, but the index can still be calculated using the available data and adjusting the weights to different values. In the present study, the calculus of IWQ was based on five parameters (n = 5), namely the first five from the CETESB list, while the weights were set to—0.10 (water temperature); 0.21 (pH); 0.17 (turbidity); 0.2 (dissolved oxygen); 0.17 (total dissolved solids), as proposed in [45]. The transformation of measured parameters into q scores (Equation (1)) is based on standardization curves, which are portrayed in Figure 5 for the selected parameters. The average of each parameter in the studied catchments, as well as the corresponding IWQ values, are depicted in Table 3.
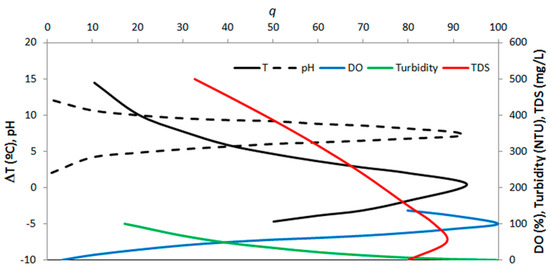
Figure 5.
Standardization curves used to transform the water quality parameters into q scores (Equation (1)). Source: https://cetesb.sp.gov.br.

Table 3.
Average water quality based on the five parameters used to calculate the IWQ (Index for Water Quality) index (Equation (1)). The full inventory of values, obtained within the monitoring period (January 2016–January 2017), is provided as Supplementary Material.
According to https://cetesb.sp.gov.br, the quality of stream water is graded as follows: Extremely poor (IWQ ≤ 19), poor (19 < IWQ ≤ 36), regular (36 < IWQ ≤ 51), good (51 < IWQ ≤ 79), excellent (79 < IWQ ≤ 100). It is worth to note that the IWQ index is rather sensitive to small changes in the bearing parameters, given the multiplicative formulation of Equation (1). As corollary of this conception, a good water quality (IWQ > 51) requires that all q values are high, while an excellent quality (IWQ > 79) implies that all q scores are very high.
2.4. Multiple Linear Regression with Interactions
A typical multiple linear regression model involving a dependent variable (Y) and two independent variables (X1 and X2) is written as:
where β1 and β2 are regression coefficients representing the main effects of X1 and X2 on the predicted values of Y. Sometimes, besides the main effects, the dependence of Y on X1 and X2 is further constrained by interaction effects. An interaction exists when the effect of one independent variable changes, depending on the value of the other independent variable. In those cases, Equation (2) is recast as [46]:
where is the joint effect of X1 and X2 on Y and the product X1X2 is the interaction between X1 and X2 producing that effect. This product is also called a two-way interaction term, because it is the interaction between two independent variables.
The presence of interactions in multiple regression can be identified through statistical tests, namely through assessing the statistical significance of the interaction term, and comparing the coefficient of determination with and without the interaction term. If the interaction term is statistically significant, the interaction term is probably important. And if the coefficient of determination is also much bigger with the interaction term, it is definitely important. If neither of these outcomes is observed, the interaction term can be removed from the regression equation. As alerted in various forums (e.g., https://statisticsbyjim.com/regression/interaction-effects/), when interaction effects are present, it means that interpretation of main effects without considering joint effects may be incomplete or misleading.
In the present study, the independent variables used to model water quality with multiple regression were the riparian buffer strip width and the ratio between forest and agriculture, represented by the variables L and F/A in Table 1. In the first run, the dependent variable was the water quality index represented as IWQ in Table 3. In a second run, the regression analysis was replicated for water temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, turbidity and total dissolved solids, which are the formation parameters of IWQ, to evaluate their specific roles in the studied area. The dataset comprehended the values of all these variables in the eight catchments. These data were processed for estimation of main effects and joint effects in the STATISTICA computer program (http://www.statsoft.com).
2.5. Thematic Maps
The thematic maps (e.g., Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3) were prepared in ArcMap software of ESRI [47], a common tool in spatial analysis of hydrologic and environmental data widely used in many studies [42,44,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66]. The base information was compiled from various spatial databases, namely the maps published by the Brazilian Institute for Geography and Statistics (https://ww2.ibge.gov.br) on the 1: 100,000 scale, and the digital terrain model obtained from the ASTER GDEN V2 satellite image with a spatial resolution of 30 m.
3. Results
The scatter plots representing the IWQ index as a function of variables L (buffer strip width) and F/A (ratio forest over agriculture), as well as of interaction term L× F/A, are displayed in Figure 6a, 6b and 6c, respectively. The corresponding coefficients of determination are R2 = 0.61, R2 = 0.72 and R2 = 0.93, meaning that the variance explained by the models raises from the main effects (L, F/A) to the interaction effect (L × F/A). The scatter plot of Figure 6a may be influenced by the small number of buffer strip widths (just three different values). This may limit the use of buffer strip width as a continuous variable in a regression model. The results of multiple regression support the conclusions taken from observation of Figure 6. In Table 4, it is evidenced that all multiple regression terms are significant at p ≤ 0.05 and that the adjusted coefficient of determination is slightly higher (R2 = 0.99) when the interaction term is incorporated in the model, relative to the no interaction case (R2 = 0.97).
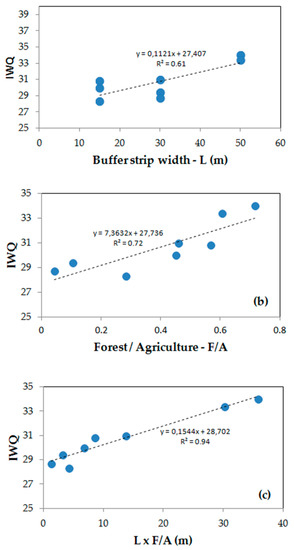
Figure 6.
IWQ scatter plots. (a) This variable is projected as a function of buffer strip width (L), (b,c) as a function of ratio forest over agriculture (F/A) and interaction term L × F/A, respectively. The data used to draw the plots are depicted in Table 1 (L, F/A and L × F/A) and 3 (IWQ).

Table 4.
Results of multiple regression model. In this run, the IWQ was used as a dependent variable.
In keeping with the results of multiple regression (Table 4), the relationship between water quality (IWQ), buffer strip width (L) and landscape composition (F/A) can be expressed by the following Equations:
where Equation (4a) represents the relationship without considering the interaction between L and F/A and Equation (4b) the case where this interaction is accounted for. The graphical representation of Equation (4a,b) are illustrated in Figure 7a,b. Figure 7a portrays a couple of parallel lines describing the evolution of IWQ as a function of L, for the extreme values of F/A (0 and 1). The lines are parallel because the model predicts no interaction [67]. The buffer strip widths required to ensure a regular water quality in the studied sub-basins (36 < IWQ ≤ 51) range from L = 130 m to L = 310 m, when F/A = 0, and from L = 60 m to L = 250 m when F/A = 1. These results change considerably when the interaction term is incorporated in the regression analysis, as demonstrated in Figure 7b. Now, the non-parallel lines indicate much smaller L ranges to attain the regular water quality, namely L = 75–175 m for F/A = 0, and L = 45–155 m for F/A = 1. The consequences for planning of adopting one or the other model are evident, either for the planning of landscape composition or buffer strip widths. The interaction model may be more realistic because of its larger R2 and interaction term significance.
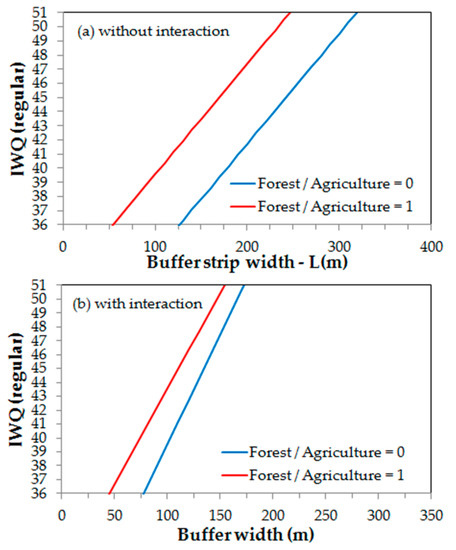
Figure 7.
Interaction multiple regression plots: (a) No interaction model; (b) interaction model.
The results of multiple regression applied to the IWQ parameters are depicted in Table 5. Only the regressions with interaction term were considered in this second run. The results suggest a dominance of turbidity in the control of IWQ in the studied sub-basins. For this parameter, the coefficient of determination (R2 = 0.6) is satisfactory, and all regression coefficients are significant at p-level ≤ 0.05. The results for total dissolved solids are characterized by a moderate R2 = 0.5, but the regression coefficients are not significant. The results for the other parameters are characterized by a low R2 = 0.1 and non-significant regression coefficients.

Table 5.
Results of multiple regression model. In this run, the formation parameters of IWQ were used as dependent variables, namely water temperature, pH, turbidity, dissolved oxygen and total dissolved solids. The significant values (p-level ≤ 0.05) are represented in boldface.
4. Discussion
The results of multiple regression, with and without interaction effects (Equation (4a,b)), indicate the improvement of water quality as a function of increasing forest to agriculture ratios (landscape composition) and buffer strip widths. The non-scaled regression coefficients (β; Table 4) point to a 45% contribution of L and 55% of F/A to IWQ values in the studied catchments, when the non-interaction model is used, and an equal contribution (50%) from both variables when the interaction model is adopted. These results are not surprising because many studies so far reported the benefits of forest cover and buffer strip widths to stream water quality, as quoted in the Introduction section [8,9,10,11,12].
The striking result refers to the interaction between F/A and L (Equation (4b)), because it describes a substantial reduction of L values required to sustain a regular water quality (36 < IWQ ≤ 51) in the streams, relative to the non-interaction model. The reductions related to the interaction reach 44% when the lines representing F/A = 0 are compared for L values across Figure 7a,b, and 38% in the case of F/A = 1. This is remarkable and requires a thorough interpretation. It seems that the positive effects on water quality resulting from the independent actions of F/A and L are amplified by a combined action (F/A × L) that ought to identify and justify.
The runoff that reaches a riparian buffer is mostly generated upstream within the catchment. It is, therefore, acceptable to link the combined action to hydrologic processes taken place away from the buffer strips, and hence, related to F/A. These processes must, however, describe a hydrologic connection between forested areas (high F/A) and buffer strips, because a combined action inherently assumes an interplay between the two land cover parameters. A potential strong candidate is the infiltration capacity of soils, and, more importantly, its spatial distribution [68]. This is a crucial control on hydrological processes at the interface between the ground surface and soil, including the distribution of flowing water by overland flow and shallow underground flow. The continuity of overland flow or alternation with subsurface flow depends on the intensity of rainfall and the locations of relatively high infiltration patches isolated on hillslopes [69,70,71]. In this context, it is expected that high F/A catchments comprise a larger number of infiltration patches, and that subsurface flow dominates in these catchments. It is also expected that subsurface flow is widespread within the soil layer, a condition that improves the probability of soil water to cross a buffer strip before reaching the stream. The higher the F/A ratios, the larger will be the chance of soil water to interact with the buffer strip. This scenario could explain a combined action of F/A and L on IWQ. Contrarily to high F/A catchments, low F/A catchments (e.g., dominated by agriculture) are prone to the generation of an overland flow network, because the absence of permanent vegetation substantially reduces the number of infiltration patches. The overland flow network channelizes runoff and conveys the surface water into specific confluence points within the stream, reducing or even hampering an interaction with a buffer strip [72]. Taken altogether, the F/A and L parameters represent the buffering capacity of vegetated areas distributed away and along the stream banks, respectively, while the F/A × L parameter represents the additional capacity promoted by a hydraulic connection between the two areas.
Besides the infiltration capacity issue, it is worth to explore the potential influence of rainfall intensity in the interaction effect, considered relevant in areas where annual climate fluctuations are stronger, including the tropical regions [73,74]. Turbidity is extremely sensitive to rainfall intensity and played a dominant role in the regression analyses of individual parameters (Table 5). The turbidity records of all studied catchments (see Supplementary Materials) are represented graphically in Figure 8, along with the corresponding daily precipitation record. It is evident the response of turbidity to larger values of daily precipitation, namely in the Borá 1 (January 2016), Lageado (April 2016) and Alegria (January 2017) catchments. A close inspection of Table 1 reveals that these catchments are among those with a lower L × F/A value. There are, however, striking exceptions: The Uberaba River catchment has the lowest L × F/A value (1.3 m), but barely responds to precipitation events; the Borá 2 catchment turbidity peak in September 2016 is not justified by a precipitation event. It is worth recalling, however, that the control of turbidity in streams is not only determined by the studied parameters, namely F/A, L, infiltration capacity and flow convergence related to L × F/A, and rainfall intensity. Topography is also a key parameter [75], which was not addressed in this study because the focus here was put on the interaction between landscape composition and buffer strip widths. We believe topography would help to explain the Uberaba River exception. This is a headwater catchment located in a relatively flat area (compare Figure 4 with Figure 1). These areas are well acquainted with retain sediments because they generate lower overland flow velocity while maximizing infiltration and particle deposition, in opposition to steep slope areas [76].
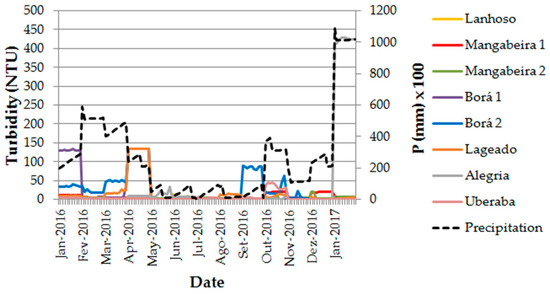
Figure 8.
Values of daily precipitation and stream water turbidity observed in the studied catchments during the sampling campaigns. The discrete values are provided as Supplementary Material.
The regression results based on individual parameters (Table 5) exposed a significant relationship between catchment variables (landscape composition, buffer strip width), including their interactions, and water turbidity, but did not reveal identical influences of those variables or their interactions on other parameters measured in water. It should be remembered, however, that water quality parameters may respond differently to catchment variables depending on the spatial scale or antecedent rainfall conditions, as noted in Uriarte [31]. We, therefore, clarify that our results are valid at the studied spatial scales (Figure 4) and antecedent rainfall conditions (Table 2). Transposition to other settings needs verification.
The recognition of an interaction effect between landscape composition and buffer strip widths capable of amplifying stream water quality improvements is certainly beneficial for water resources planning and management. The dominant role of turbidity in the regression analyses of individual terms suggests that water quality deterioration in the studied sub-basins is mostly related to soil erosion and sediment transport rather than with leaching of dissolved fertilizers from the arable land into the stream. Therefore, conservation measures related to the control of soil erosion should be prioritized in this protected area. Eventually, the most cost-effective measure is the reinforcement of manuring and composting of soil to raise the levels of organic matter [77] and produce stable aggregates that are resistant to detachment by rain drop action. The level plantation is another measure of soil erosion control, frequently used to reduce laminar erosion and increase soil water uptake. The level plantation can be successfully coupled with strip cropping [78] that involves the alternation of forages with strips of row crops, such as sugar cane. The control of soil erosion also comprises implementation of techniques that prevent soil compaction, such as no-tillage treatments [79], maintenance of crop residue to keep organic matter and nutrients in the topsoil, or more costly measures, such as terraces in level or gradient, since they reduce the ramp length reducing the surface drag of particles and nutrients [80]. To become effective, implementation of conservation measures should be monitored within spatial decision support systems focused on water resources planning and management [81], and integrate public policies and environmental management plans.
The regression results showed that, even considering the interaction effect regular water quality in the studied catchments is only attained when buffer strip widths are within the ranges 75 ≤ L ≤ 175 m (F/A = 0) or 45 ≤ L ≤ 155 m (F/A = 1) (Figure 7). These values are much larger than legal values in force in Brazil. So far, the Brazilian law has defined the buffer width limits based on two scenarios: The Old Forest Code (Federal Law No. 4771/1965) and the New Forest Code (Federal Law No. 12651/2012). In the first case, for watercourses up to 10 m wide the permanent preservation areas needed to extend at least 30 m upwards from the stream margin considering the widest seasonal riverbank. In the second case, there are two rules: The transition rule takes into account the size of land property calculated as fiscal modules and creates a distance from the stream margin that goes from a minimum of 5 m to a maximum of 20 m, considering the regular river bank; the permanent rule defines 30 m as unique distance. This study reinforces the suggestion of Valera et al. [15], who alerted that a 30 m buffer strip width, as proposed in the New Forest Code, is barely capable of protecting water quality in the EPA-MURB. The discussion on buffer strips, their geometry and composition, optimal widths, cost-benefit analysis for implementation [82,83,84,85], among other topics, is still a matter of debate. The discussion on interaction effects is expected to become another topic on this so challenging analysis.
5. Conclusions
The results of a multiple regression model involving an interaction term revealed the combined positive influence of landscape composition and buffer strip widths (L) on stream water quality, in eight catchments of Uberaba River Basin Environmental Protection Area (Minas Gerais State, Brazil). The landscape composition was characterized by the forest to agriculture ratio (F/A), and high F/A catchments were viewed as basins where forested areas located away from the stream are in hydraulic connection with riparian vegetation distributed along the stream banks. This hydraulic connection presumably amplifies the buffering capacity of forested areas and riparian buffers acting independently. To our best knowledge, this is a new finding in the study of buffer strips and their relationship with stream water quality. In practice, the combined effect reduced the width of buffer strips required to keep water quality at a fair level. Without the interaction, the calculated L range was 60–310 m. It decreased to 45–175 m when the interaction term was accounted for in the regression model. The reduction was expressive, but not enough to drop below the maximum legal value imposed by the Brazilian Forest Code (30 m). Eventually, this legal framework could be adapted to our scientific findings. The problem of setting thresholds to buffer strip widths is not exclusive from Brazil, and therefore, our results could serve as alert to other national realities.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/11/9/1757/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.A.V. and T.C.T.P.; methodology, C.A.V. and T.C.T.P.; software, R.F.V.J. and H.E.S.; validation, C.V., T.C.T.P., L.F.S.F. and F.A.L.P.; formal analysis, C.A.V., F.A.L.P., T.C.T.P. and M.V.M.F.; investigation, T.C.T.P. and C.A.V.; resources, T.C.T.P.; data curation, C.A.V. and T.C.T.P.; writing—original draft preparation, T.C.T.P.; writing—review and editing, F.A.L.P.; visualization, R.C.A.C.; supervision, T.C.T.P. and M.V.M.F.; project administration, T.C.T.P. and M.V.M.F.; funding acquisition, T.C.T.P., M.V.M.F. and R.F.V.J.
Funding
The present study was carried out within the framework of the Post Graduation Research Programme of Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES); Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq); Agência do Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia, Inovações e Comunicações (MCTIC); and Land Use Policy Brazilian Group (POLUS). The author affiliated to IFTM Renato Farias do Valle Júnior wishes to acknowledge the funding through the CNPq research scholarship Proc. 307921/2018-2. For the author integrated into the CITAB research center, it was further financed by the FEDER/COMPETE/POCI—Operational Competitiveness and Internationalization Program, under Project POCI-01-0145-FEDER-006958, and by National Funds of FCT—Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, under the project UID/AGR/04033/2019. For the author integrated into the CQVR, the research was additionally supported by National Funds of FCT–Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, under the project UID/QUI/00616/2019.
Acknowledgments
Mauro Ferreira Machado is acknowledged for fruitful discussions and sharing of information.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Cooper, J.R.; Gilliam, J.W. Phosphorus Redistribution from Cultivated Fields into Riparian Areas1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1987, 51, 1600–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowrance, R.; Todd, R.; Fail, J.; Hendrickson, O.; Leonard, R.; Asmussen, L. Riparian Forests as Nutrient Filters in Agricultural Watersheds. BioScience 1984, 34, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterjohn, W.T.; Correll, D.L. Nutrient Dynamics in an Agricultural Watershed: Observations on the Role of a Riparian Forest. Ecology 1984, 65, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowrance, R.; Sheridan, J.M. Surface Runoff Water Quality in a Managed Three Zone Riparian Buffer. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoonover, J.E.; Williard, K.W.J.; Zaczek, J.J.; Mangun, J.C.; Carver, A.D. Agricultural Sediment Reduction by Giant Cane and Forest Riparian Buffers. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2006, 169, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, R.B.; Gilliam, J.W. Sediment and Chemical Load Reduction by Grass and Riparian Filters. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowrance, R. Groundwater Nitrate and Denitrification in a Coastal Plain Riparian Forest. J. Environ. Qual. 1992, 21, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.D.; Reich, P.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Lake, P.S. Challenges in applying scientific evidence to width recommendations for riparian management in agricultural Australia. Ecol. Manag. Restor. 2015, 16, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.R. Nitrate Removal in Stream Riparian Zones. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.C.; Kjaergaard, C.; Uusi-Kämppä, J.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Kronvang, B. Phosphorus Retention in Riparian Buffers: Review of Their Efficiency. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1942–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M. Major Factors Influencing the Efficacy of Vegetated Buffers on Sediment Trapping: A Review and Analysis. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.M.; Stutter, M.I.; Haygarth, P.M. Phosphorus Retention and Remobilization in Vegetated Buffer Strips: A Review. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, B.W.; Newbold, J.D. Streamside Forest Buffer Width Needed to Protect Stream Water Quality, Habitat, and Organisms: A Literature Review. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 560–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, P.M.; Reynolds, S.K.; Canfiel, T.J. Riparian Buffer Width, Vegetative Cover, and Nitrogen Removal Effectiveness: A Review of Current Science and Regulations; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Valera, C.; Pissarra, T.; Filho, M.; Valle Júnior, R.; Oliveira, C.; Moura, J.; Sanches Fernandes, L.; Pacheco, F. The Buffer Capacity of Riparian Vegetation to Control Water Quality in Anthropogenic Catchments from a Legally Protected Area: A Critical View over the Brazilian New Forest Code. Water 2019, 11, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehne, R.A. A Classification of Streams, Illustrated by Fish Distribution in an Eastern Kentucky Creek. Ecology 1962, 43, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, M.; Yackulic, C.B.; Lim, Y.; Arce-Nazario, J.A. Influence of land use on water quality in a tropical landscape: A multi-scale analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckert, K.A.; Fisher, T.R.; O’Neil, J.M.; Jesien, R.V. Characterization and Comparison of Stream Nutrients, Land Use, and Loading Patterns in Maryland Coastal Bay Watersheds. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 221, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G. Landscape Ecology: The Effect of Pattern on Process. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1989, 20, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, C.R.; Doledec, S.; Norris, R.; Peacock, K.; Arbuckle, C. The influence of scale and geography on relationships between stream community composition and landscape variables: Description and prediction. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 768–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryjecki, R.; Zawal, A.; Stępień, E.; Buczyńska, E.; Buczyński, P.; Czachorowski, S.; Szenejko, M.; Śmietana, P. Water mites (Acari, Hydrachnidia) of water bodies of the Krąpiel River valley: Interactions in the spatial arrangement of a river valley. Limnology 2016, 17, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wu, J.; Peng, S. Assessing the effects of landscape pattern on river water quality at multiple scales: A case study of the Dongjiang River watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J. Spatially varying relationships between land use and water quality across an urbanization gradient explored by geographically weighted regression. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaei, F.; Sari, A.E.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Delavar, M.; Bavani, A.R.M.; Srinivasan, R. Surface drainage nitrate loading estimate from agriculture fields and its relationship with landscape metrics in Tajan watershed. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, Z.; Marques, J.C. Relating landscape to stream nitrate-N levels in a coastal eastern-Atlantic watershed (Portugal). Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awoke, A.; Beyene, A.; Kloos, H.; Goethals, P.L.M.; Triest, L. River Water Pollution Status and Water Policy Scenario in Ethiopia: Raising Awareness for Better Implementation in Developing Countries. Environ. Manag. 2016, 58, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnaro, T.; Frate, L.; Carranza, M.L.; Sitzia, T. Multi-scale analysis of alpine landscapes with different intensities of abandonment reveals similar spatial pattern changes: Implications for habitat conservation. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q. Influences of the land use pattern on water quality in low-order streams of the Dongjiang River basin, China: A multi-scale analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, B.M.; Reis, R.; Vale, M.J.; Saraiva, R. Land use and land cover changes in Zêzere watershed (Portugal)—Water quality implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, S.K.; Tuttle, A.K.; Jennings, G.D.; Gardner, A. Influence of Restoration Age and Riparian Vegetation on Reach-Scale Nutrient Retention in Restored Urban Streams. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Carlisle, D.M.; Meador, M.R.; Short, T.M. Can Basin Land Use Effects on Physical Characteristics of Streams Be Determined at Broad Geographic Scales? Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 130, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, C.K. Response of three lotic assemblages to riparian and catchment-scale land use: Implications for designing catchment monitoring programmes. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Hou, X.; Li, W.; Aini, G. Relating landscape characteristics to non-point source pollution in a typical urbanized watershed in the municipality of Beijing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 123, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikman, A.; Sarkkola, S.; Koivusalo, H.; Sallantaus, T.; Laine, J.; Silvan, N.; Nousiainen, H.; Nieminen, M. Nitrogen retention by peatland buffer areas at six forested catchments in southern and central Finland. Hydrobiologia 2010, 641, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chi, G.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Fan, Z. Identifying the critical riparian buffer zone with the strongest linkage between landscape characteristics and surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Hou, X.; Li, W.; Aini, G.; Chen, L.; Gong, Y. Impact of landscape pattern at multiple spatial scales on water quality: A case study in a typical urbanised watershed in China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toothaker, L.E.; Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1994, 45, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Burks, J.J.; Randolph, D.W.; Seida, J.A. Modeling and interpreting regressions with interactions. J. Account. Lit. 2019, 42, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, C.D.; Franzese, R.J. Modeling and interpreting interactive hypotheses in regression analysis. Choice Rev. Online 2008, 45, 45–3841. [Google Scholar]
- Quintão, D.A.; Caxito, F.D.A.; Karfunkel, J.; Vieira, F.R.; Seer, H.J.; Moraes, L.C.; Ribeiro, L.C.B.; Pedrosa-Soares, A.C. Geochemistry and sedimentary provenance of the Upper Cretaceous Uberaba Formation (Southeastern Triângulo Mineiro, MG, Brazil). Braz. J. Geol. 2017, 47, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, C.A.; Pissarra, T.C.T.; Martins Filho, M.V.; Valle Junior, R.F.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Pacheco, F.A.L. A legal framework with scientific basis for applying the ‘polluter pays principle’ to soil conservation in rural watersheds in Brazil. Land Use Policy 2017, 66, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, C.A.; Valle Junior, R.F.; Varandas, S.G.P.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Pacheco, F.A.L. The role of environmental land use conflicts in soil fertility: A study on the Uberaba River basin, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, H.E.; Pissarra, T.C.T.; do Valle Junior, R.F.; Fernandes, L.F.S.; Pacheco, F.A.L. A multi criteria analog model for assessing the vulnerability of rural catchments to road spills of hazardous substances. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 64, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ribeiro, I.V.A.S.; Bouchonneau, N.; Da Silva, A.C.; Fernandes, R.M.C.; De Pinheiro, L.S. Cálculo do índice de qualidade de água (IQA), com estudo de caso nos rios Cocó e Maranguapinho, Ceará. In Proceedings of the Simpósio Brasileiro de Recursos Hídricos, Associação Brasileira de Recursos Hídricos, Campo Grande, Brazil, 22–26 November 2009; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- ESRI ArcGIS Professional GIS for the Desktop. 2010. Versão 10. Available online: http://desktop.arcgis.com (accessed on 23 August 2019).
- Fonseca, A.R.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Fontainhas-Fernandes, A.; Monteiro, S.M.; Pacheco, F.A.L. The impact of freshwater metal concentrations on the severity of histopathological changes in fish gills: A statistical perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, A.R.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Fontainhas-Fernandes, A.; Monteiro, S.M.; Pacheco, F.A.L. From catchment to fish: Impact of anthropogenic pressures on gill histopathology. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 972–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle Junior, R.F.; Varandas, S.G.P.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Multi Criteria Analysis for the monitoring of aquifer vulnerability: A scientific tool in environmental policy. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 48, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.R.L.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Assessing anthropogenic impacts on riverine ecosystems using nested partial least squares regression. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.M.B.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Varandas, S.G.P.; Jesus, J.J.B.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Integrative assessment of river damming impacts on aquatic fauna in a Portuguese reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Fernandes, A.C.P.; Ferreira, A.R.L.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Pacheco, F.A.L. A partial least squares—Path modeling analysis for the understanding of biodiversity loss in rural and urban watersheds in Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1069–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, X.; Valero, E.; Santos, R.M.B.; Varandas, S.G.P.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Anthropogenic nutrients and eutrophication in multiple land use watersheds: Best management practices and policies for the protection of water resources. Land Use Policy 2017, 69, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.A.L. Regional groundwater flow in hard rocks. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.F.S.; Marques, M.J.; Oliveira, P.C.; Moura, J.P. Decision support systems in water resources in the demarcated region of Douro-case study in Pinhão river basin, Portugal. Water Environ. J. 2014, 28, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.F.S.; dos Santos, C.M.M.; Pereira, A.P.; Moura, J.P. Model of management and decision support systems in the distribution of water for consumption. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2011, 15, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.A.L.; Van der Weijden, C.H. Weathering of plagioclase across variable flow and solute transport regimes. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420–421, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Valle Júnior, R.F.; Siqueira, H.E.; Valera, C.A.; Oliveira, C.F.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Moura, J.P.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Diagnosis of degraded pastures using an improved NDVI-based remote sensing approach: An application to the Environmental Protection Area of Uberaba River Basin (Minas Gerais, Brazil). Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 14, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.A.L.; Szocs, T. “Dedolomitization reactions” driven by anthropogenic activity on loessy sediments, SW Hungary. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 614–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.A.L. Application of Correspondence Analysis in the Assessment of Groundwater Chemistry. Math. Geol. 1998, 30, 129–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.A.L.; Landim, P.M.B. Two-Way Regionalized Classification of Multivariate Datasets and its Application to the Assessment of Hydrodynamic Dispersion. Math. Geol. 2005, 37, 393–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.A.L.; Sousa Oliveira, A.; Van Der Weijden, A.J.; Van Der Weijden, C.H. Weathering, biomass production and groundwater chemistry in an area of dominant anthropogenic influence, the Chaves-Vila Pouca de Aguiar region, north of Portugal. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1999, 115, 481–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.A.L. Finding the number of natural clusters in groundwater data sets using the concept of equivalence class. Comput. Geosci. 1998, 24, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.J.; Cabecinha, E.; Andrade dos Santos, J.C.; Mendes Andrade, C.M.; Mendes Lopes, D.M.; da Fonseca Trindade, H.M.; dos Santos Cabral, J.A.F.A.; dos Santos, M.G.S.; Lourenço, J.M.M.; Marques Aranha, J.T.; et al. A predictive modelling tool for assessing climate, land use and hydrological change on reservoir physicochemical and biological properties. Area 2012, 44, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesto Gonzalez Pereira, M.J.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Barros Macário, E.M.; Gaspar, S.M.; Pinto, J.G. Climate Change Impacts in the Design of Drainage Systems: Case Study of Portugal. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2015, 141, 05014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S.; Gomi, T.; Sidle, R.C.; Hiraoka, M.; Onda, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Nonoda, T. Assessing spatially distributed infiltration capacity to evaluate storm runoff in forested catchments: Implications for hydrological connectivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomi, T.; Sidle, R.C.; Miyata, S.; Kosugi, K.; Onda, Y. Dynamic runoff connectivity of overland flow on steep forested hillslopes: Scale effects and runoff transfer. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, T.; Sidle, R.C.; Ueno, M.; Miyata, S.; Kosugi, K. Characteristics of overland flow generation on steep forested hillslopes of central Japan. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, T.; Asano, Y.; Uchida, T.; Onda, Y.; Sidle, R.C.; Miyata, S.; Kosugi, K.; Mizugaki, S.; Fukuyama, T.; Fukushima, T. Evaluation of storm runoff pathways in steep nested catchments draining a Japanese cypress forest in central Japan: A geochemical approach. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 550–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosskey, M.G.; Helmers, M.J.; Eisenhauer, D.E.; Franti, T.G.; Hoagland, K.D. Assessment of concentrated flow through riparian buffers. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 57, 336–343. [Google Scholar]
- Hénault-Ethier, L.; Larocque, M.; Perron, R.; Wiseman, N.; Labrecque, M. Hydrological heterogeneity in agricultural riparian buffer strips. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.; Estrany, J.; Ranzini, M.; de Cicco, V.; Martín-Benito, J.M.T.; Hedo, J.; Lucas-Borja, M.E. Effects of land use and seasonality on stream water quality in a small tropical catchment: The headwater of Córrego Água Limpa, São Paulo (Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhou, L. Influence of spatial variation in land-use patterns and topography on water quality of the rivers inflowing to Fuxian Lake, a large deep lake in the plateau of southwestern China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, V.; Fares, A.; Ryder, M.H. Precision riparian buffers for the control of nonpoint source pollutant loading into surface water: A review. Environ. Rev. 2005, 13, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodar Reddy, D.; Subba Rao, A.; Rupa, T.R. Effects of continuous use of cattle manure and fertilizer phosphorus on crop yields and soil organic phosphorus in a Vertisol. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 75, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, N.K.; Satapathy, K.K.; Lal, R.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, N.A.K.; Agrawal, P.K.; Choudhury, P.; Rathore, A. Weed strip management for minimizing soil erosion and enhancing productivity in the sloping lands of north-eastern India. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 170, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogunovic, I.; Pereira, P.; Kisic, I.; Sajko, K.; Sraka, M. Tillage management impacts on soil compaction, erosion and crop yield in Stagnosols (Croatia). Catena 2018, 160, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.A.L.; Varandas, S.G.P.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Valle Junior, R.F. Soil losses in rural watersheds with environmental land use conflicts. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485–486, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, N.; Ruan, X.-H.; Xu, J.; Pan, Z.-R. Estimating the optimal width of buffer strip for nonpoint source pollution control in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Ecol. Modell. 2014, 276, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bren, L.J. Aspects of the geometry of riparian buffer strips and its significance to forestry operations. For. Ecol. Manag. 1995, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-L.; Hsu, Y.-S.; Lee, B.-J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Weng, L.-J. A cost-benefit analysis for the implementation of riparian buffer strips in the Shihmen reservoir watershed. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 26, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigel, R.; Chokmani, K.; Novoa, J.; Rousseau, A.N.; El Alem, A. An extended riparian buffer strip concept for soil conservation and stream protection in an agricultural riverine area of the La Chevrotière River watershed, Québec, Canada, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Can. Water Resour. J. 2014, 39, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richit, L.A.; Bonatto, C.; Carlotto, T.; da Silva, R.V.; Grzybowski, J.M.V. Modelling forest regeneration for performance-oriented riparian buffer strips. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigel, R.; Chokmani, K.; Novoa, J.; Rousseau, A.N.; Dufour, P. Recommendations for riparian buffer widths based on field surveys of erosion processes on steep cultivated slopes. Can. Water Resour. J. 2013, 38, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-F.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chou, W.-C.; Lin, W.-T.; Tsai, J.-S.; Wu, C.-F. Modeling of riparian vegetated buffer strip width and placement. Ecol. Eng. 2004, 23, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanowski, J.M.; Walter, P.T.; Niemi, G.J. Effects of prescriptive riparian buffers on landscape characteristics in Northern Minnesota, USA. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2002, 38, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).