Nutrient Removal from Chinese Coastal Waters by Large-Scale Seaweed Aquaculture Using Artificial Upwelling
Abstract
1. Introduction
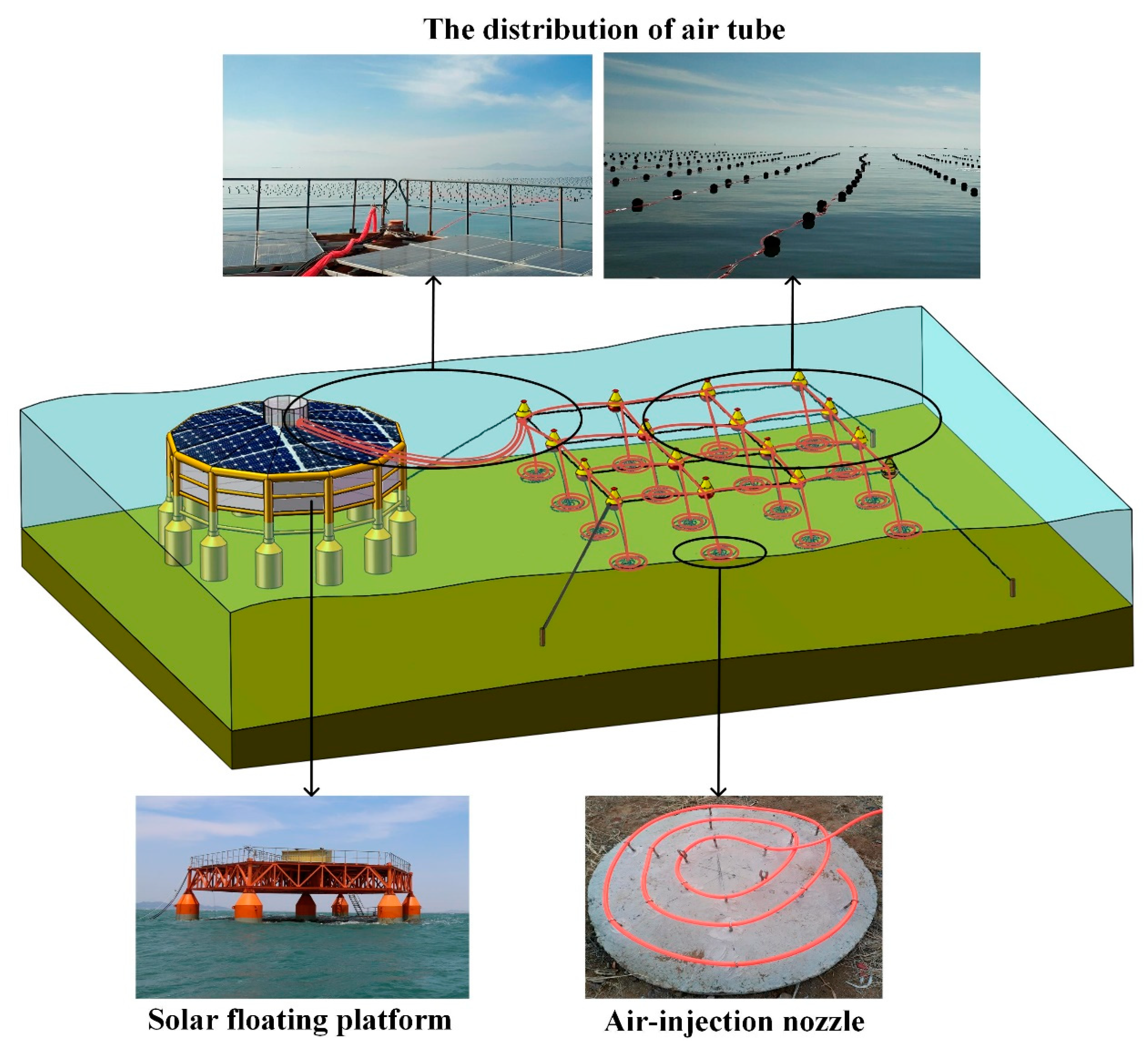
2. Ecological Engineering by Artificial Upwelling
3. Material and Method
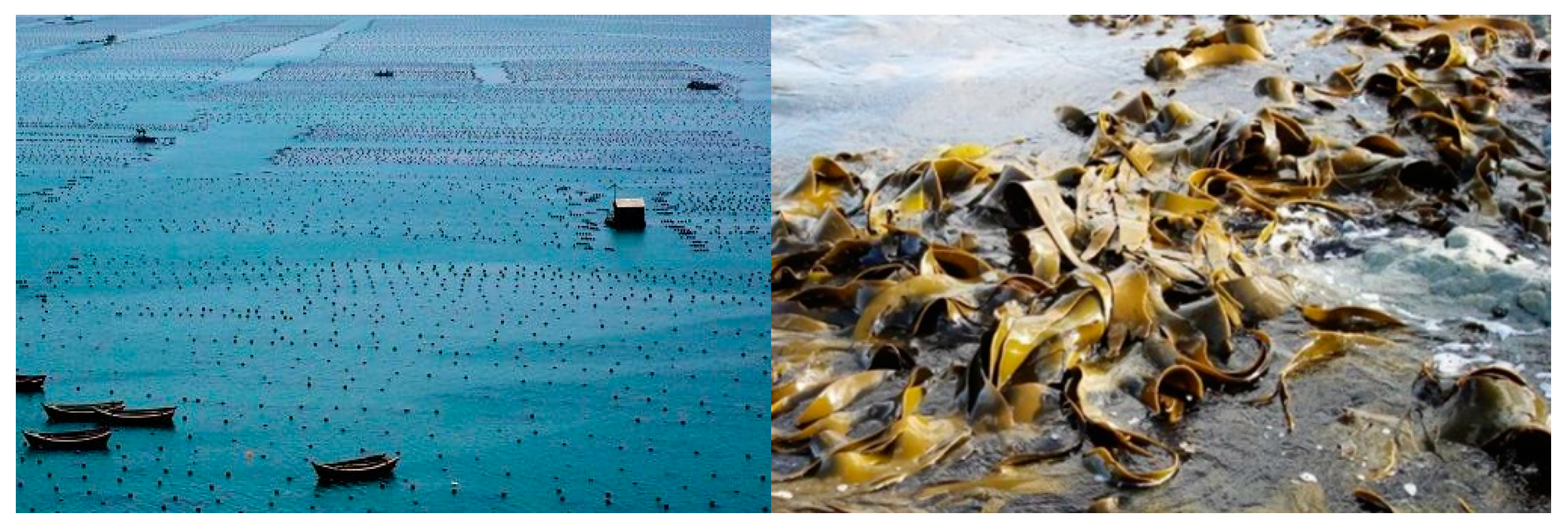
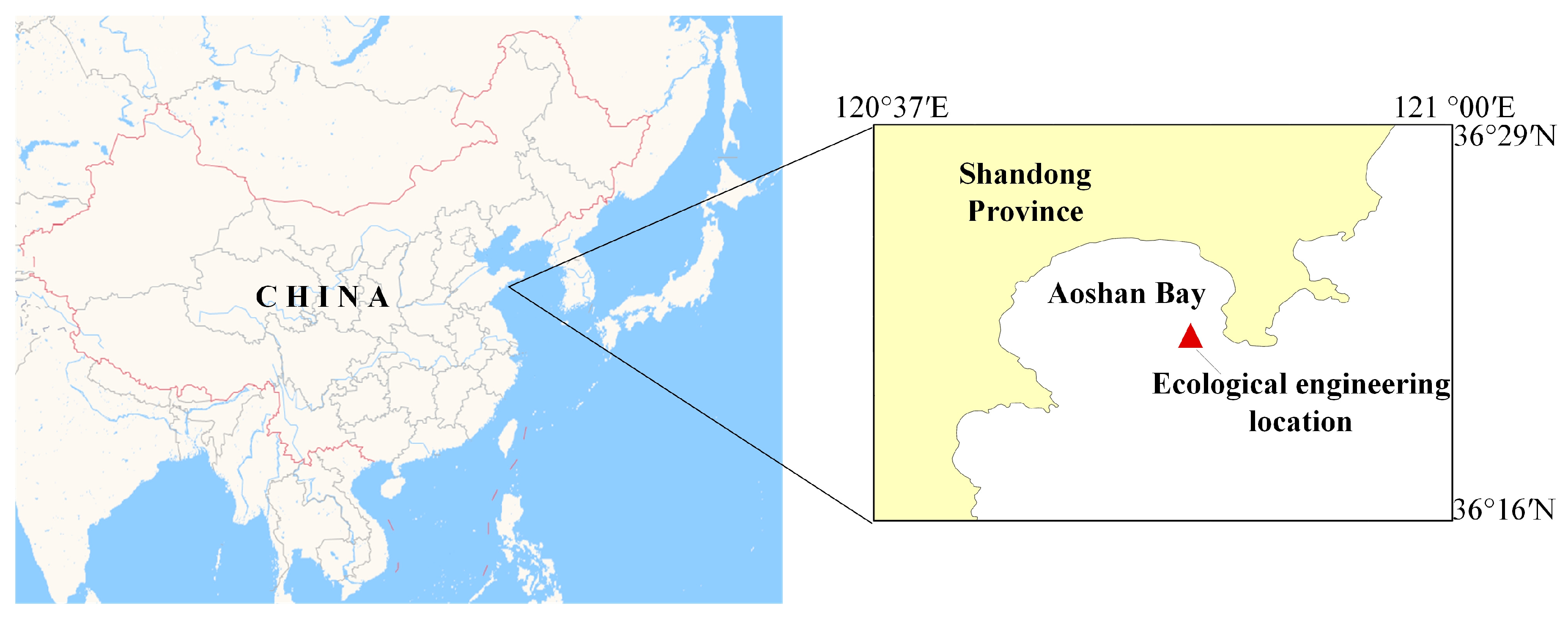
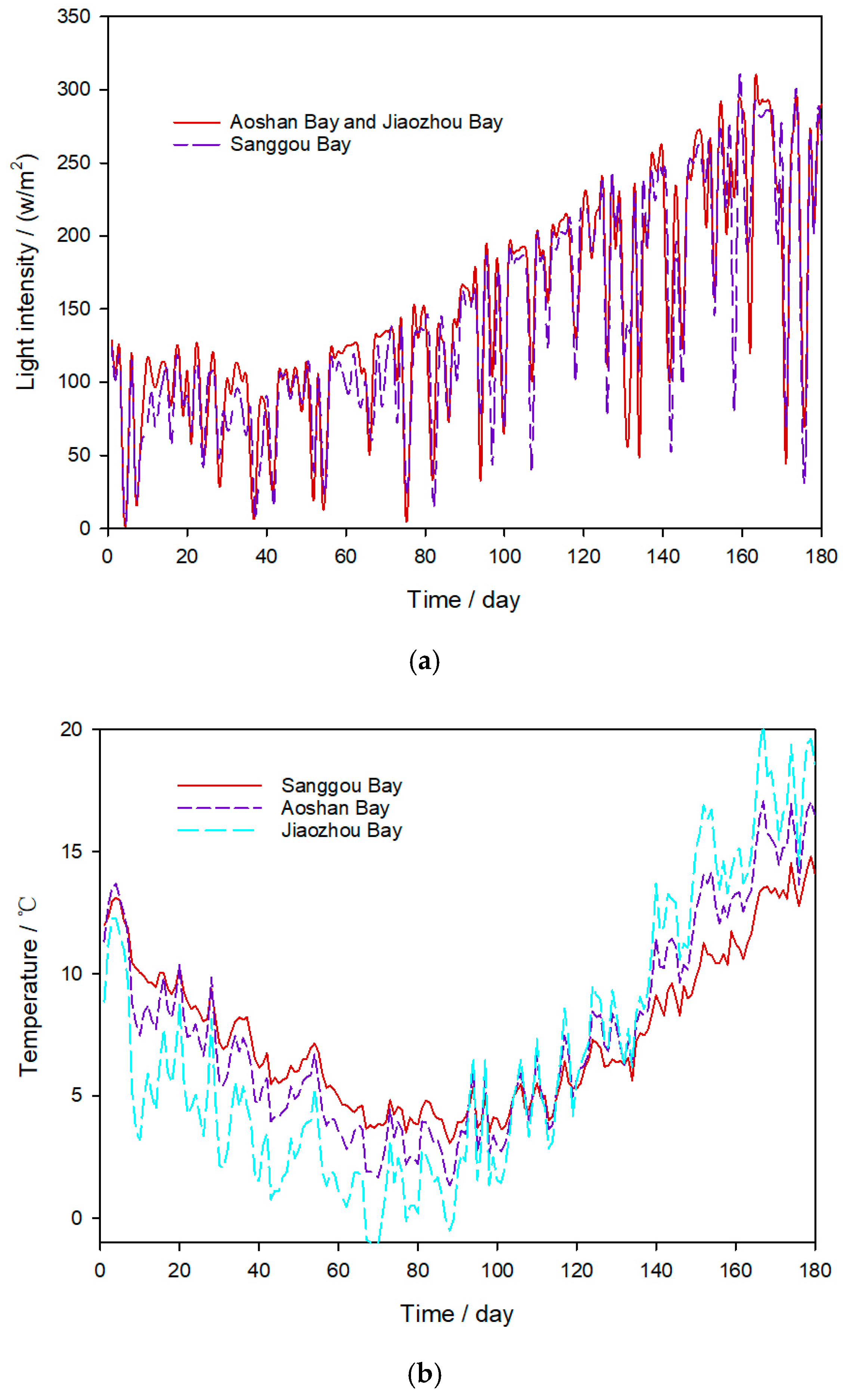
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Dynamic Individual Growth Model of Mariculture Kelp
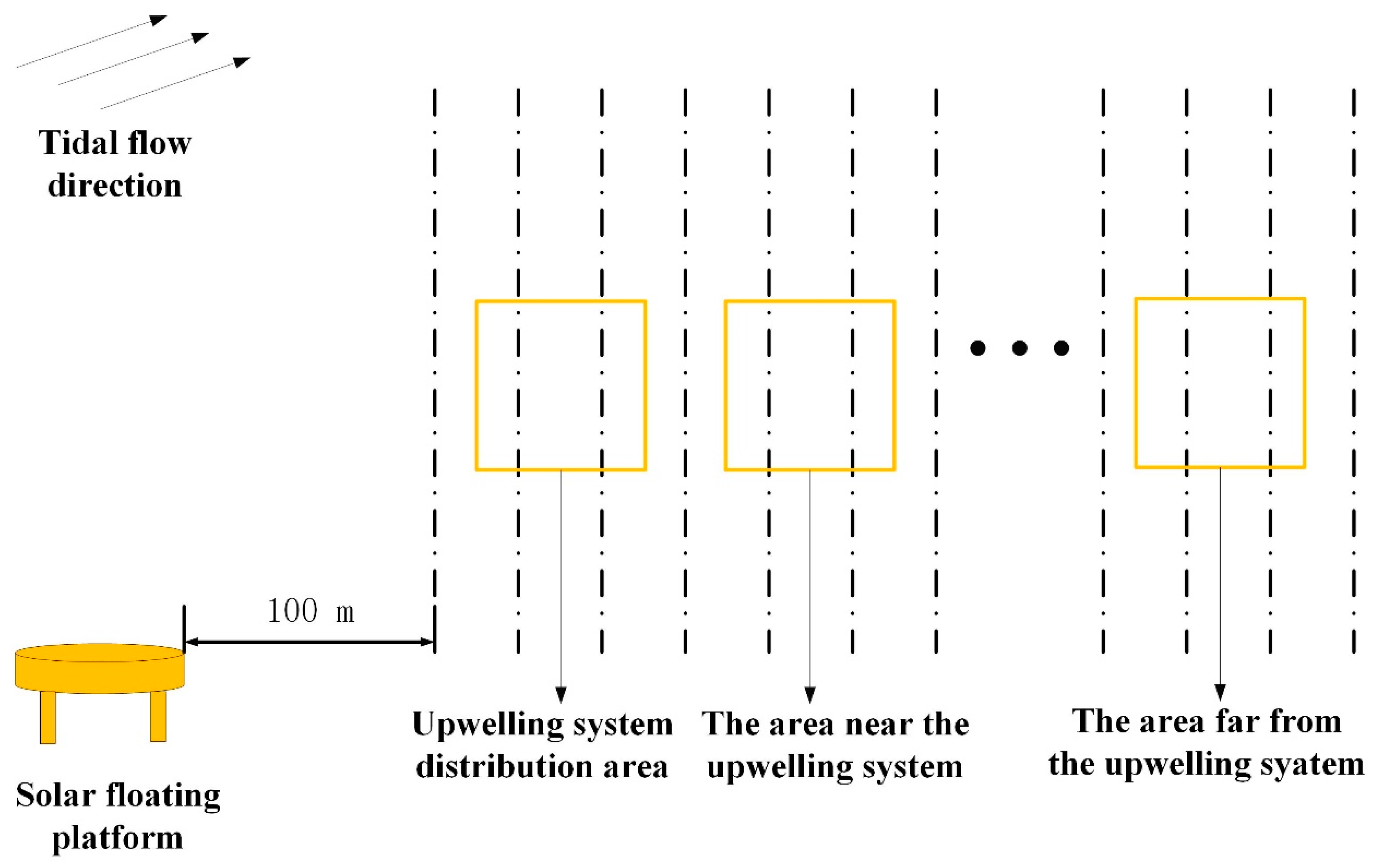
3.3. Data Acquisition
4. Results
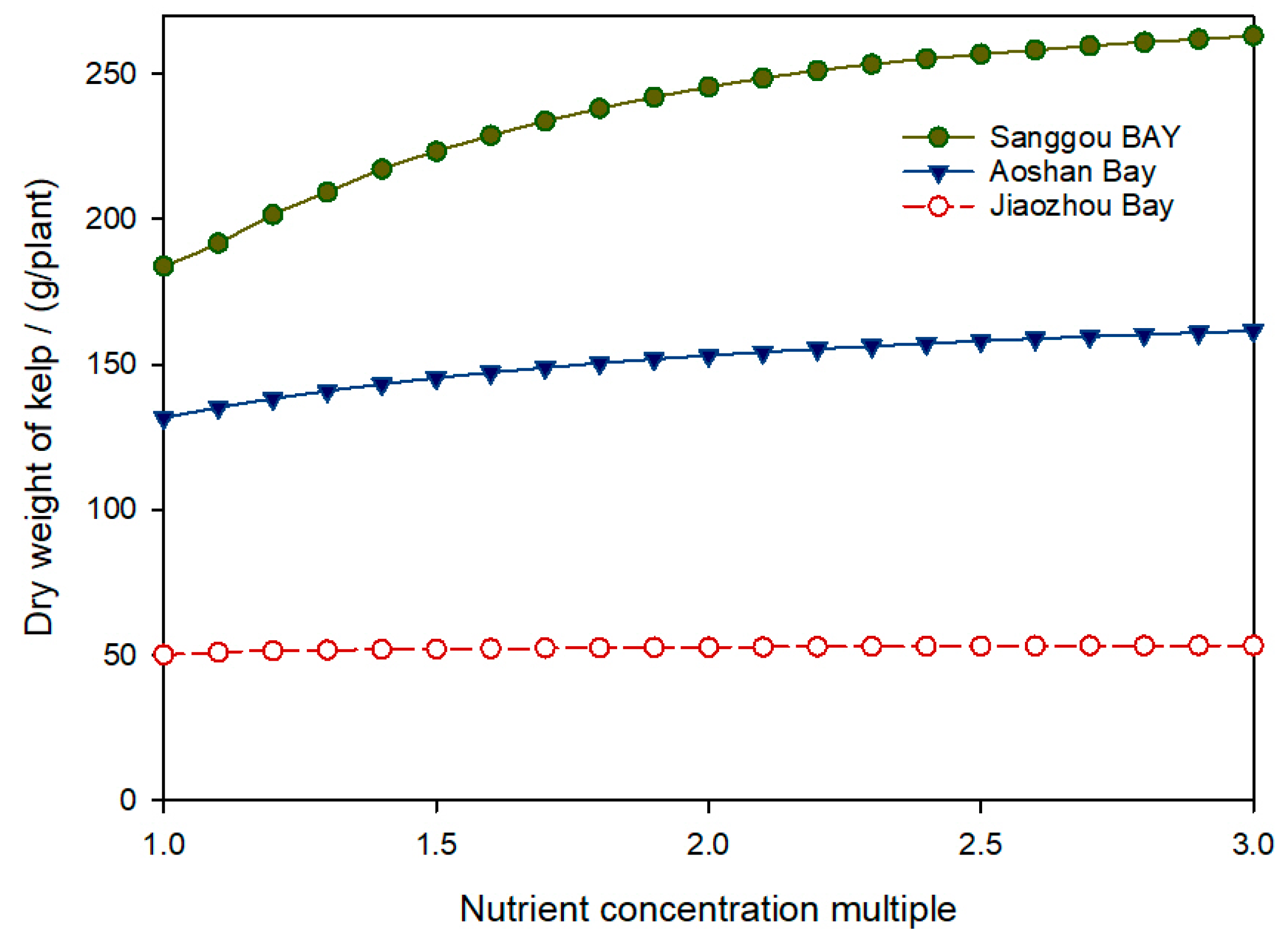
4.1. Simulated Results of the Kelp Growth Model
4.2. The Effect of Kelp Growth and Nutrient Removal in the Natural Aquaculture Area
5. Discussion and Conclusion
5.1. Engineering Feasibility
5.2. Four Suggestions on Engineering Implementation
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hai-Sheng, L.U.; Chen, B. Effects of the development of marine industry on offshore environment in Guangxi. J. South. Agric. 2014, 45, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.Q. Nutrient export by rivers to the coastal waters of China: Management strategies and future trends. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2012, 12, 153–167. [Google Scholar]
- China Marine Environment Quality Bulletin 2017. Available online: http://www.nmdis.org.cn/gongbao/huanjing/201806/t20180625_37513.html (accessed on 2 March 2019).
- Cardinale, B.J. Biodiversity improves water quality through niche partitioning. Nature 2011, 472, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krausejensen, D.; Duarte, C.M. Substantial role of macroalgae in marine carbon sequestration. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Agusti, S.; Lin, F.; Li, K.; Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Duarte, C.M. Nutrient removal from Chinese coastal waters by large-scale seaweed aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inés, M.; Olsen, Y.S.; Eva, M.; Núria, M.; Duarte, C.M. Rapid growth of seaweed biotechnology provides opportunities for developing nations. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 591–592. [Google Scholar]
- Mcclimans, T.A.; Handå, A.; Fredheim, A.; Lien, E.; Reitan, K.I. Controlled artificial upwelling in a fjord to stimulate non-toxic algae. Aquac. Eng. 2010, 42, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forchino, A.; Borja, A.; Brambilla, F.; Rodríguez, J.G.; Muxika, I.; Terova, G.; Saroglia, M. Evaluating the influence of off-shore cage aquaculture on the benthic ecosystem in Alghero Bay (Sardinia, Italy) using AMBI and M-AMBI. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, S.; Zhou, C.; Huang, X. The porewater nutrient and heavy metal characteristics in sediment cores and their benthic fluxes in Daya Bay, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Li, D.J.; Zhou, J.L.; Gao, L. Nutrient dynamics in pore water of tidal marshes near the Yangtze Estuary and Hangzhou Bay, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.; Björkman, K.; Grabowski, E.; Letelier, R.; Poulos, S.; Watkins, B.; Karl, D. An Open Ocean Trial of Controlled Upwelling Using Wave Pump Technology. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, A.; Mcclimans, T.A.; Reitan, K.I.; Knutsen, Ø.; Tangen, K.; Olsen, Y. Artificial upwelling to stimulate growth of non-toxic algae in a habitat for mussel farming. Aquac. Res. 2015, 45, 1798–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, K.; Otsuka, K.; Omura, H. Recent advances of ocean nutrient enhancer” TAKUMI” project. In Proceedings of the Sixth ISOPE Ocean Mining Symposium, Changsha, China, 9–13 October 2005; International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Fan, W.; Xiao, C.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, R.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Y. Energy Management and Operational Planning of an Ecological Engineering for Carbon Sequestration in Coastal Mariculture Environments in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. Research on hydro-environment of Aoshan Bay. Mar. Fish. Res. 2001, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Liu, B.H.; Xi-Shuang, L.I.; Jing-Long, W.U.; Tian-Yun, S.U. Topography Feature and Migration of Submarine Sand Waves in Jiaozhoy Bay Mouth. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2006, 37, 464–471. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, Q. Research on the relationship between the coastal current and lam1nar1a japon1ca raising I. Exp. Comp. Curr. Speed Laminaria Jpn. Growth 1986, 6, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Liu, S.M.; Ren, J.L.; Zhang, J.H.; Jiang, Z.J. Distribution features of nutrients and flux across the sediment-water interface in the Sanggou Bay. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2010, 32, 108–117. [Google Scholar]
- Rongjun, W.U.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, Y. A Model for the Growth of Haidai (Laminaria Japonica) in Aquaculture. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2009, 28, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kirihara, S.; Fujikawa, Y.; Notoya, M. Effect of temperature and day length on the zoosporangial sorus formation and growth of sporophytes Laminaria japonica Areschoug (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae) in tank culture. Aquac. Sci. 2003, 51, 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, I.; Marques, J.C. A Model for the Growth of Opportunistic Macroalgae (Enteromorpha sp.) in Tidal Estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 55, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, P. A mechanistic model of the effects of light and temperature on algal primary productivity. Ecol. Model. 1995, 82, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Prediction of Worldwide Energy Resources. Available online: https://power.larc.nasa.gov (accessed on 16 May 2019).
- Zhang, J.H.; Wang, W.; Han, T.T.; Liu, D.H.; Fang, J.G.; Jiang, Z.J.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, X.J.; Lian, Y. The distributions of dissolved nutrients in spring of Sungo Bay and potential reason of outbreak of red tide. J. Fish. China 2012, 36, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, M.M.; Liu, Y.L. Assessment on the Change of Nutrient Structure and Eutrophication in the Jiaozhou Bay in 2014. J. Ocean Technol. 2016, 10, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Petrell, R.J.; Tabrizi, K.M.; Harrison, P.J.; Druehl, L.D. Mathematical model of Laminaria production near a British Columbian salmon sea cage farm. J. Appl. Phycol. 1993, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.S.; Liu, S.L.; Yi zhao, H.E.; Zhang, F.S. Chemical composition and net organic production of cultivated and fouling organisms in Sishili Bay and their ecological effects. J. Fish. China 2002, 26, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, N.K.; Peng, H.K. A study of air-lift artificial upwelling. Ocean Eng. 2005, 32, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, M.T. Influences of wave fetch, tidal flow and ocean colour on subtidal rocky communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 445, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norderhaug, K.M.; Christie, H.; Rinde, E.; Gundersen, H.; Bekkby, T. Importance of wave and current exposure to fauna communities in Laminaria hyperborea kelp forests. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 502, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tuya, F.; Haroun, R.J. Spatial patterns and response to wave exposure of shallow water algal assemblages across the Canarian Archipelago: A multi-scaled approach. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 311, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


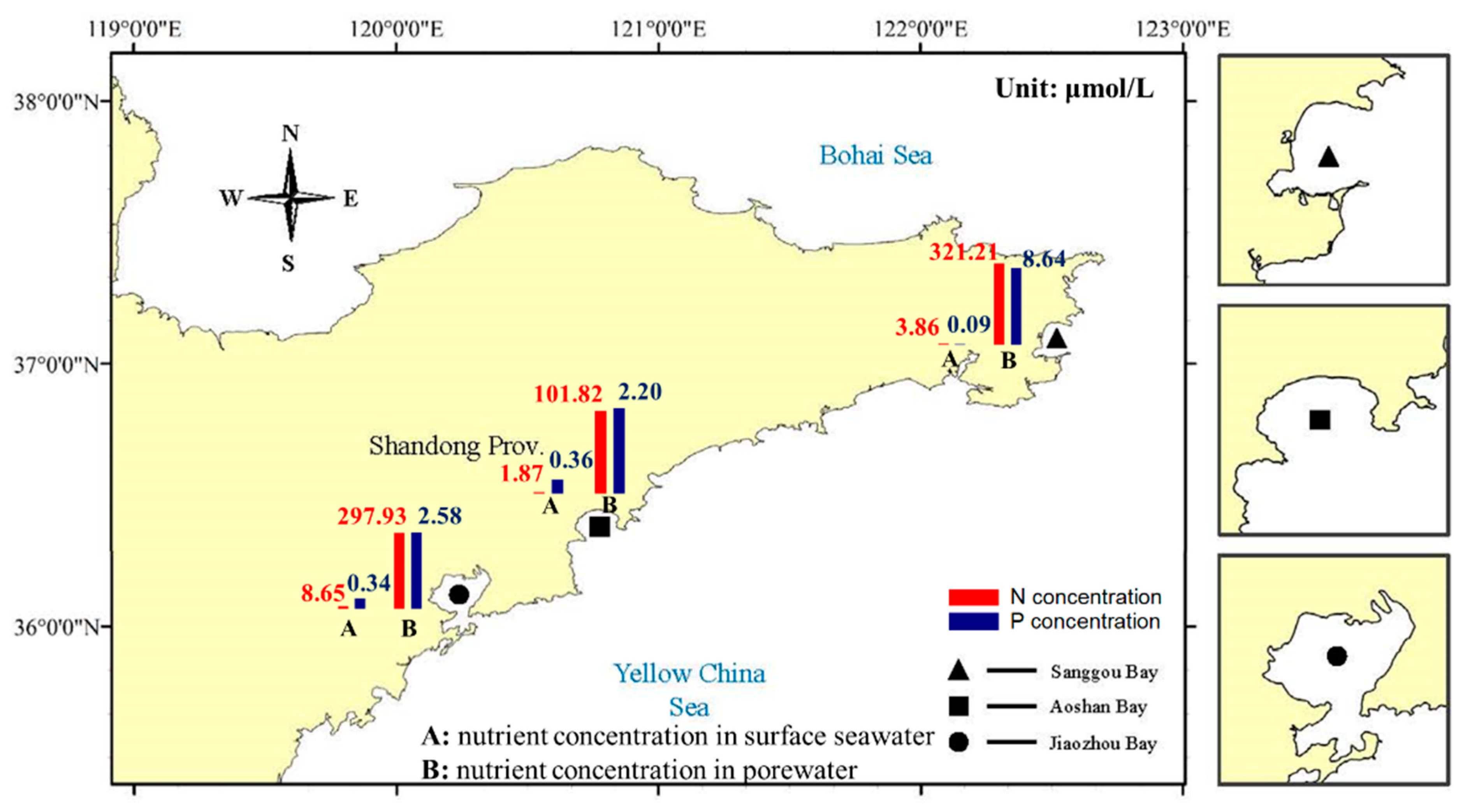

| Surface water (μmol/L) | 1.87 | 0.36 |
| Sediment (μmol/L) | 101.82 | 2.20 |
| Kelp Weight (g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Upwelling Area | Near the Upwelling Area | Away from Upwelling Area | |||
| 1 | 11.3 | 28.7 | 44 | 27.8 | 10.3 | 8.6 |
| 15.8 | 12.6 | 37.6 | 66.3 | 12.5 | 8 | |
| 13.4 | 23.1 | 62.1 | 40.9 | 11 | 6.2 | |
| 13.1 | 22.4 | 44.1 | 46.8 | 8.2 | 6.1 | |
| 18.8 | 10.8 | 62.9 | 40.5 | 9.9 | 5.2 | |
| 2 | 16.9 | 56.8 | 63.2 | 71.7 | 17.7 | 12 |
| 24.8 | 28.7 | 32 | 53.1 | 15.1 | 6.9 | |
| 29.5 | 23 | 72 | 87.5 | 10 | 9 | |
| 19.5 | 14.8 | 79.8 | 36.8 | 13.8 | 7.4 | |
| 25 | 78.8 | 44.9 | 50.7 | 14.8 | 4.7 | |
| 3 | 25.6 | 14.6 | 34.6 | 32.3 | 7.7 | 6 |
| 15.9 | 18.1 | 38.4 | 36.9 | 12.2 | 11 | |
| 8 | 10.3 | 37.6 | 42.9 | 14.3 | 10.2 | |
| 9.1 | 13.8 | 19.1 | 23.7 | 13.2 | 10 | |
| 21 | 11.1 | 24 | 32.5 | 12.6 | 9 | |
| Average weight of per plant | 21.2 | 46.2 | 10.1 | |||
| Sea Area (km2) | Average Water Depth (m) | Tidal Current Type | Average Velocity (cm/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aoshan Bay | 164 | 4 | Regular semi-diurnal tides | 25 |
| Sanggou Bay | 150.3 | 7.5 | Regular semi-diurnal tides | 35 |
| Jiaozhou Bay | 500 | 7 | Regular semi-diurnal tides | 45 |
| Bay | Nutrient Concentration (μmol/L) | Year | Reference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter | Spring | Summer | ||||||
| DIN | DIN | DIN | ||||||
| Aoshan Bay | 11.86 | 0.82 | 8.96 | 0.29 | 3.16 | 0.26 | 2018–2019 | This study |
| Sanggou Bay | 9.28 | 0.30 | 13.03 | 0.13 | 10.12 | 0.08 | 2010 | Zhang et al. [25] |
| Jiaozhou Bay | 26.42 | 0.35 | 25.00 | 0.19 | 20.00 | 0.19 | 2014 | Gao et al. [26] |
| Items | Data | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Increased dry weight | 55 | g/plant |
| Aquaculture area in Shandong | 18,397 | Hectares in 2017 |
| Aquaculture area in China | 44,236 | Hectares in 2017 |
| Culture density | 12 | Plant/ |
| Increased dry weight in Shandong | 121,419 | t/year |
| Increased dry weight in China | 291,956 | t/year |
| N concentration | 1.67–2.2 | % Dry weight |
| P concentration | 0.25–0.37 | % Dry weight |
| Increased N removal in Shandong | 2028–2671 | t/year |
| Increased N removal in China | 4875–6422 | t/year |
| Increased P removal in Shandong | 303–449 | t/year |
| Increased P removal in China | 730–1080 | t/year |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, W.; Zhao, R.; Yao, Z.; Xiao, C.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, Y. Nutrient Removal from Chinese Coastal Waters by Large-Scale Seaweed Aquaculture Using Artificial Upwelling. Water 2019, 11, 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091754
Fan W, Zhao R, Yao Z, Xiao C, Pan Y, Chen Y, Jiao N, Zhang Y. Nutrient Removal from Chinese Coastal Waters by Large-Scale Seaweed Aquaculture Using Artificial Upwelling. Water. 2019; 11(9):1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091754
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Wei, Ruolan Zhao, Zhongzhi Yao, Canbo Xiao, Yiwen Pan, Ying Chen, Nianzhi Jiao, and Yao Zhang. 2019. "Nutrient Removal from Chinese Coastal Waters by Large-Scale Seaweed Aquaculture Using Artificial Upwelling" Water 11, no. 9: 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091754
APA StyleFan, W., Zhao, R., Yao, Z., Xiao, C., Pan, Y., Chen, Y., Jiao, N., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Nutrient Removal from Chinese Coastal Waters by Large-Scale Seaweed Aquaculture Using Artificial Upwelling. Water, 11(9), 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091754







