Allocation of Groundwater Recharge Zones in a Rural and Semi-Arid Region for Sustainable Water Management: Case Study in Guadalupe Valley, Mexico
Abstract
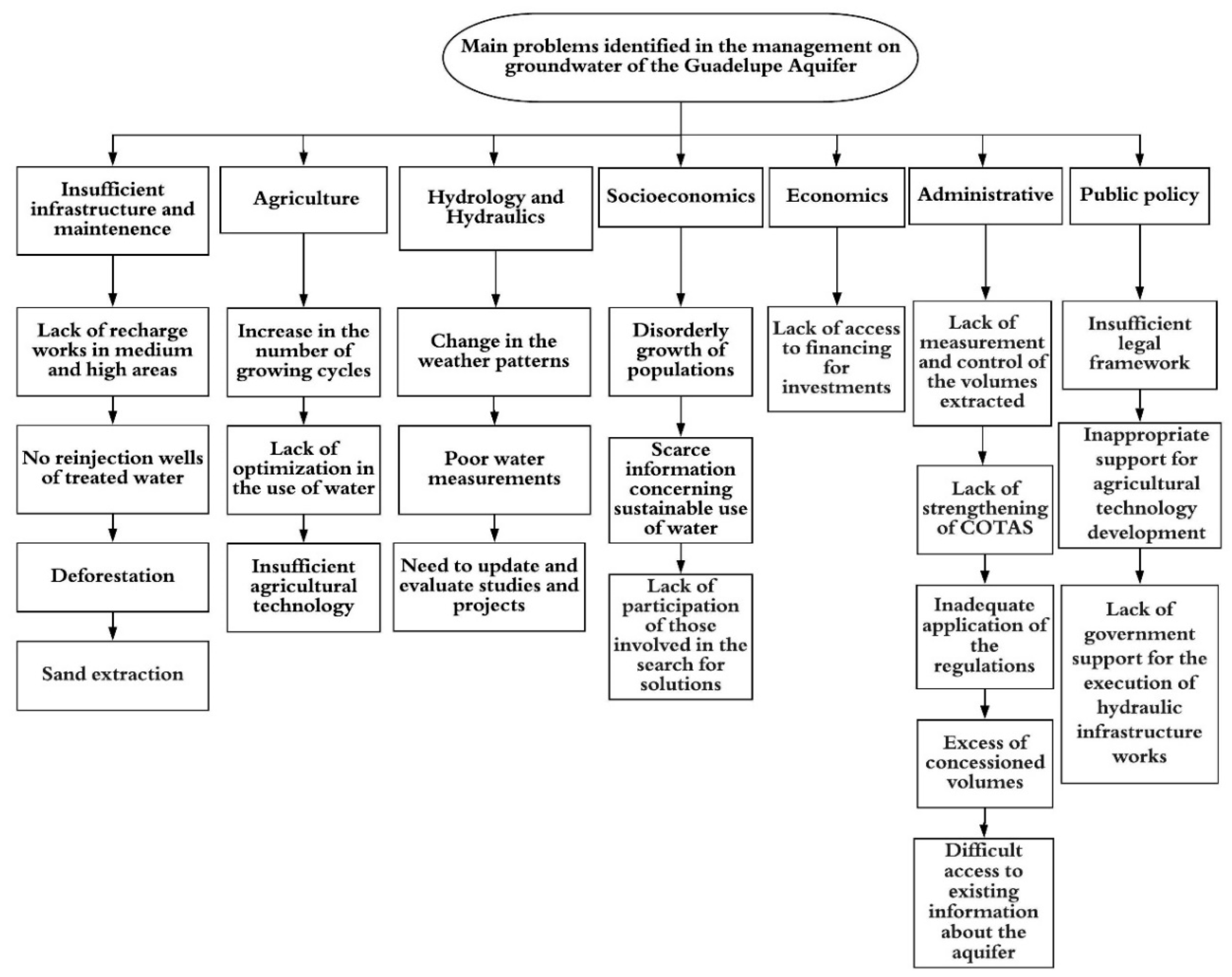
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
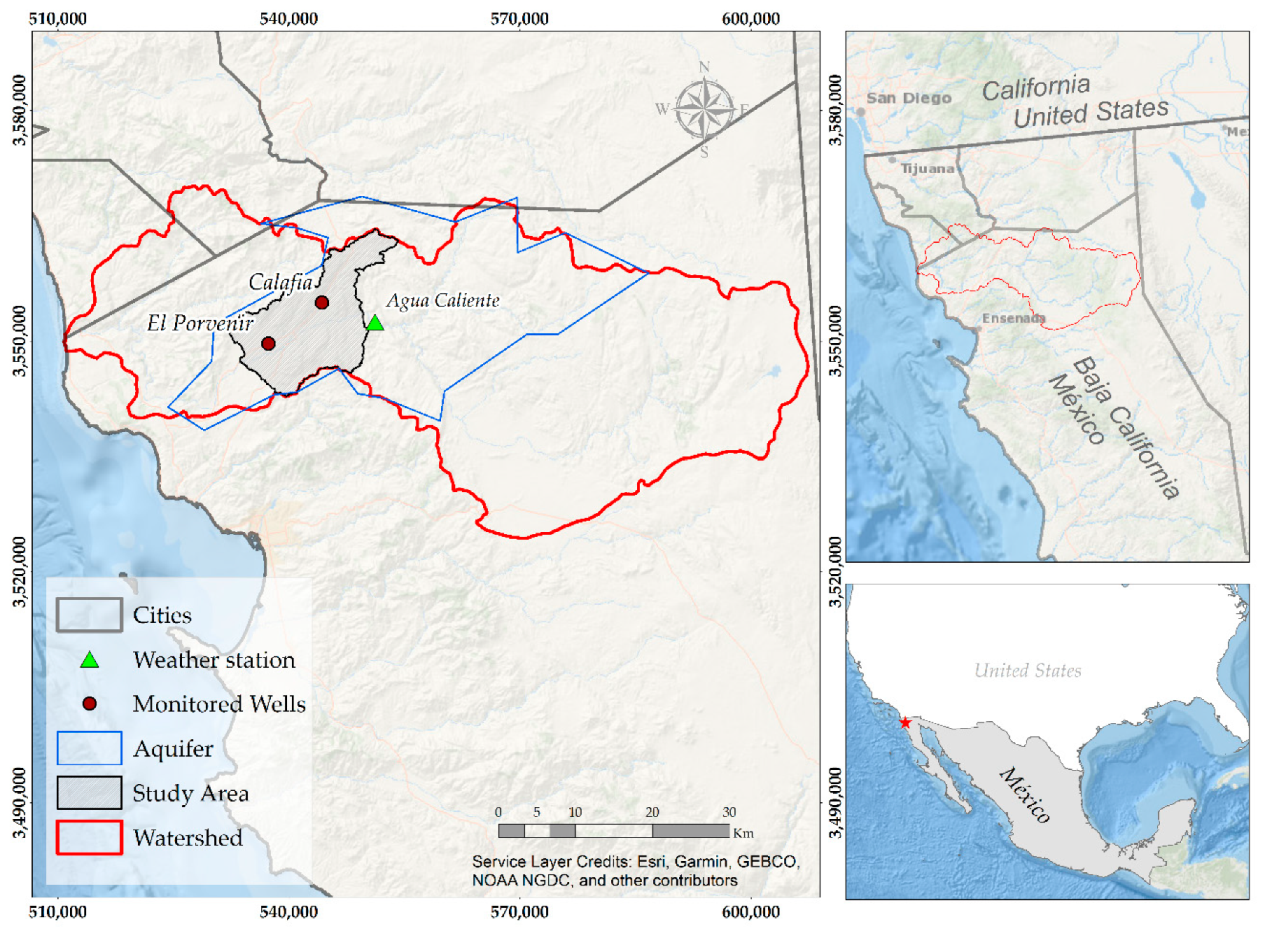
2.1. Study Area
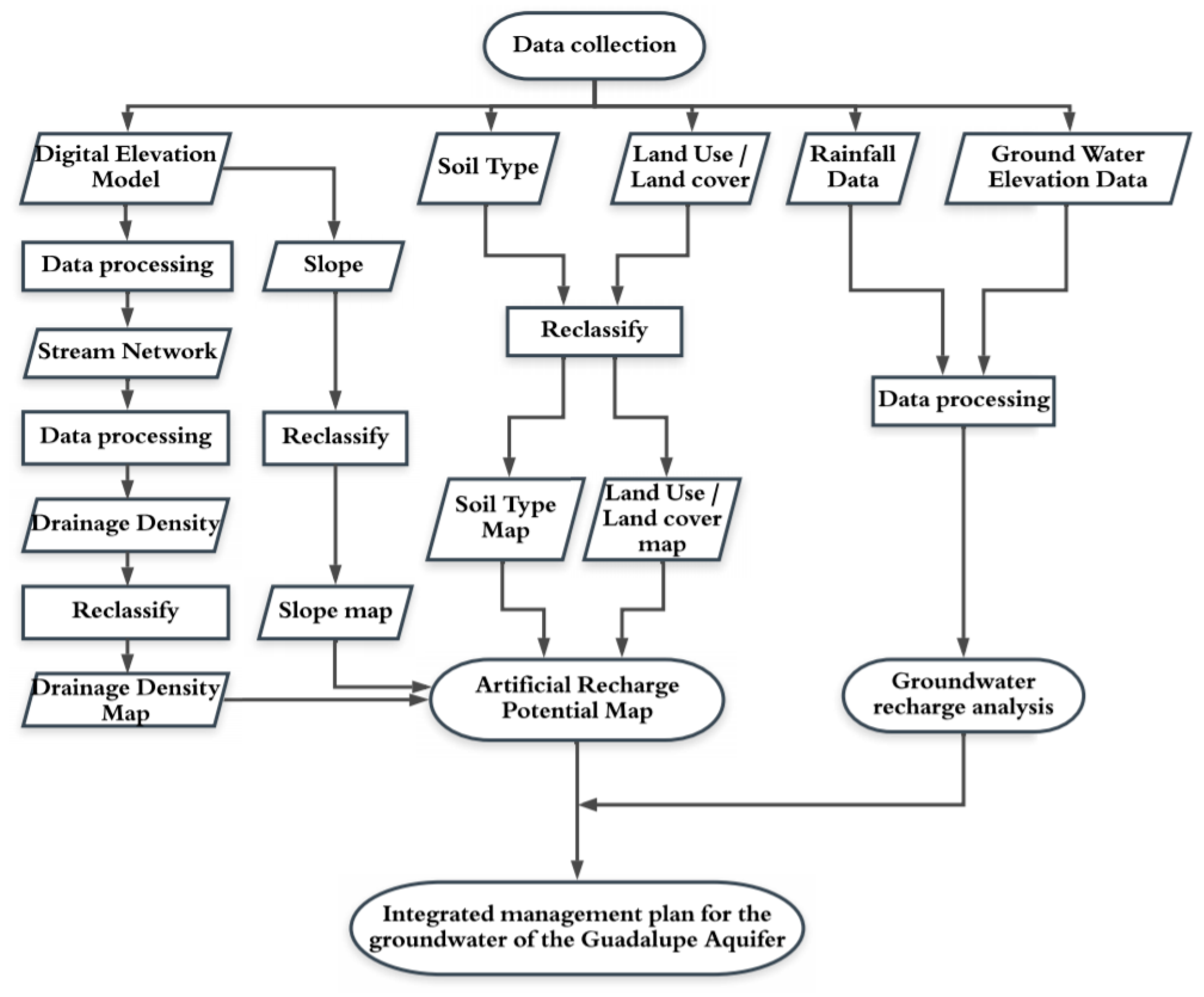
2.2. Recharge Model
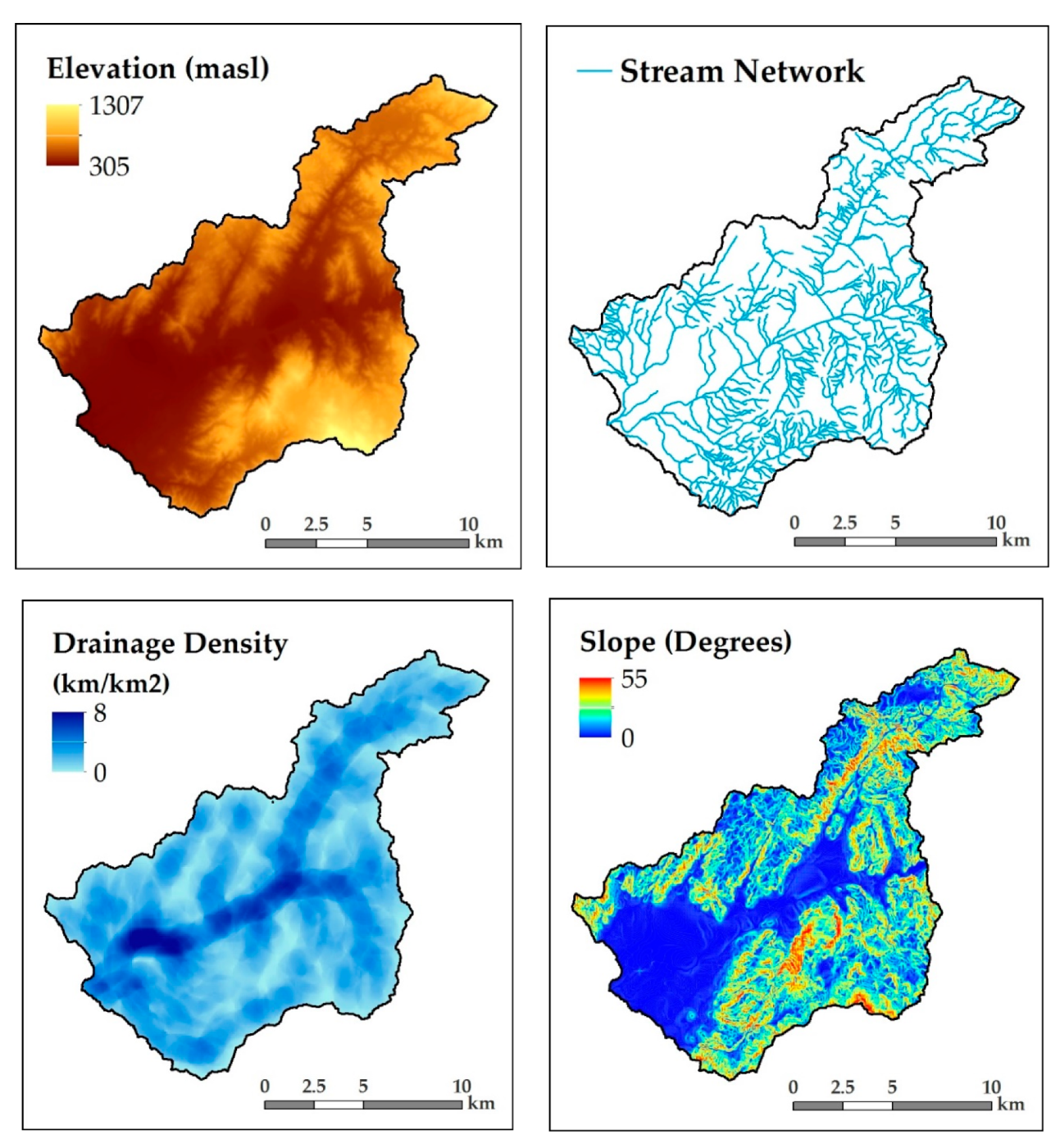
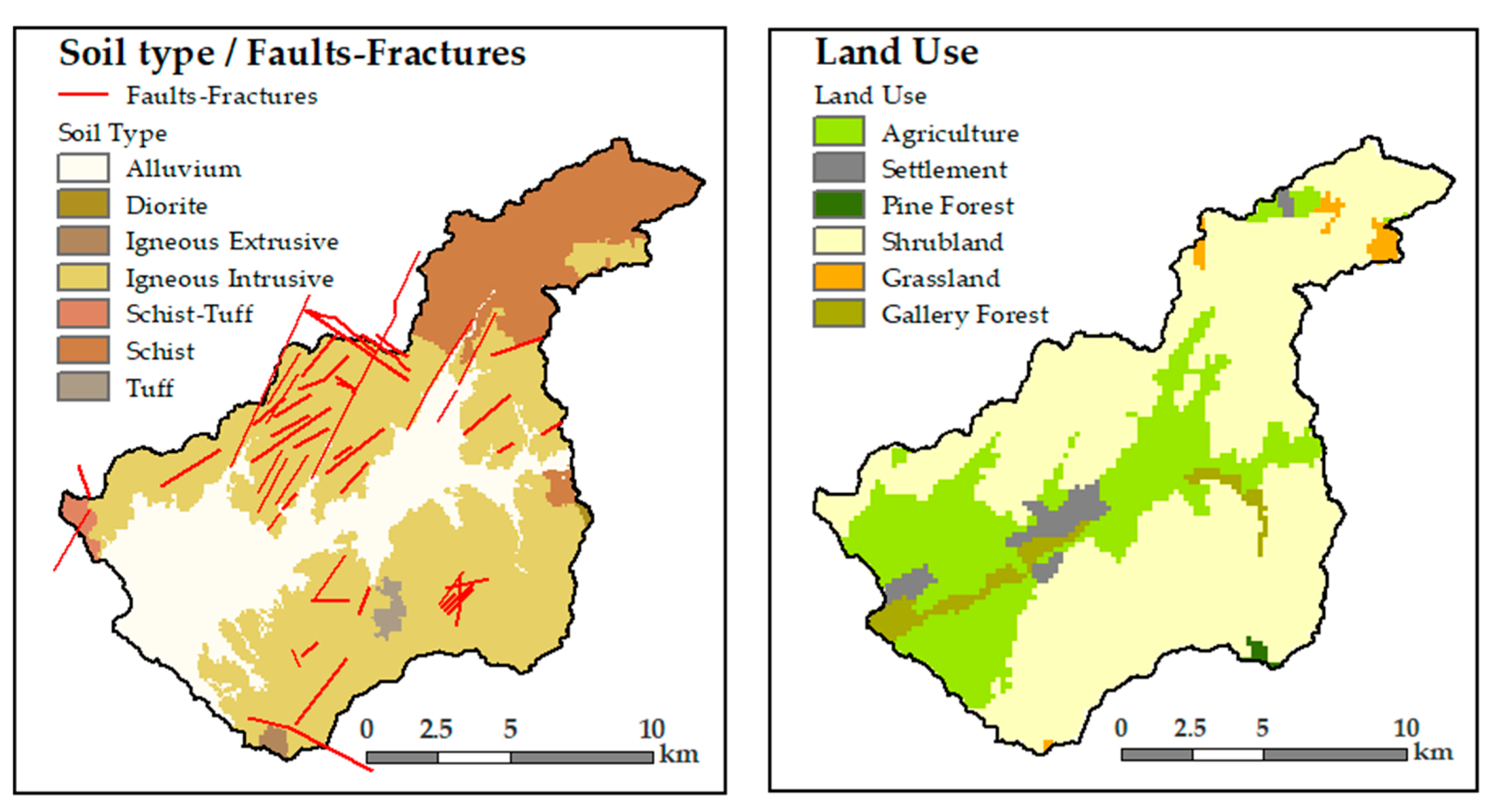
2.2.1. Input Data
2.2.2. Reclassification
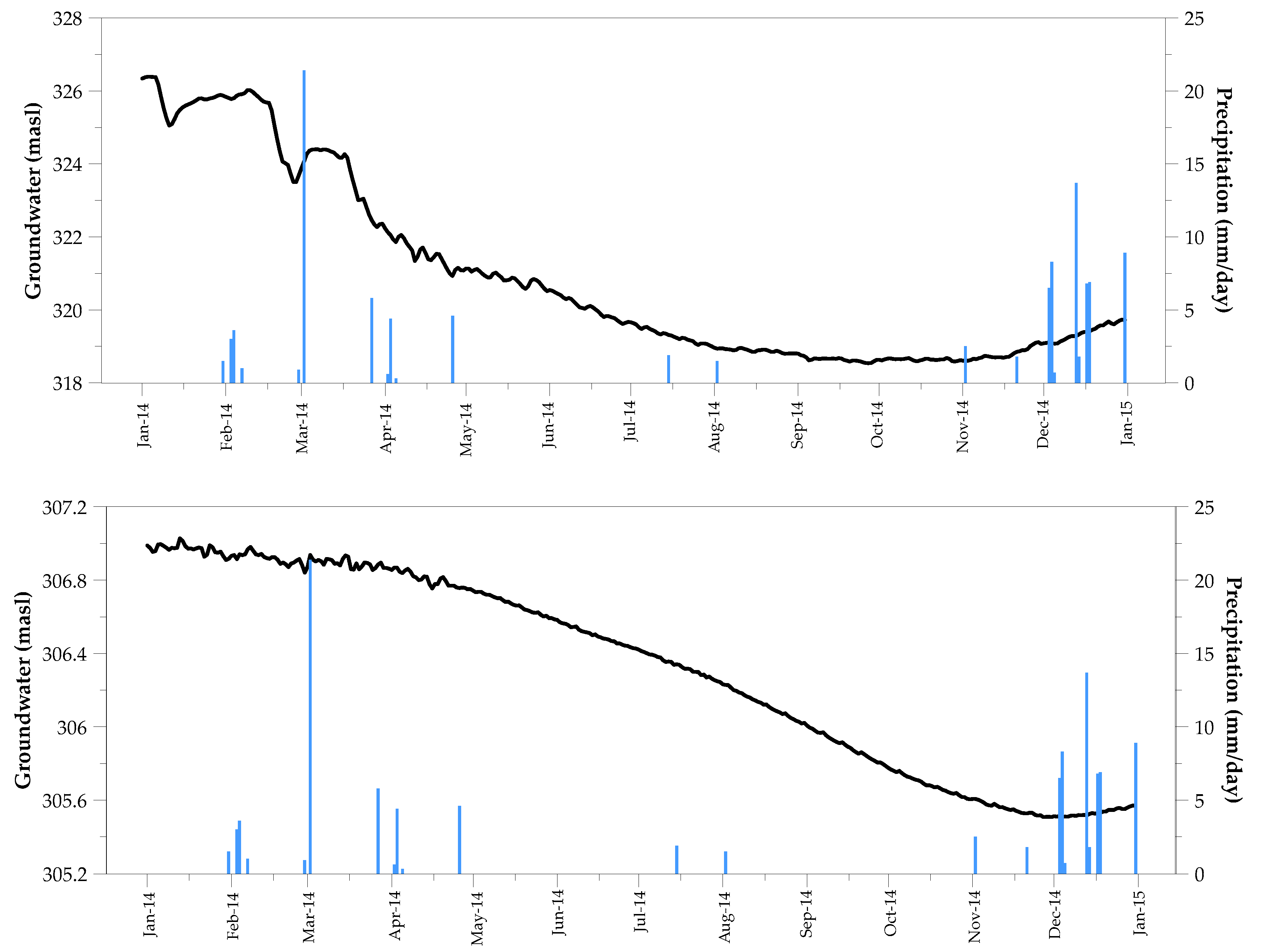
2.3. Analysis of Precipitation and Recharge
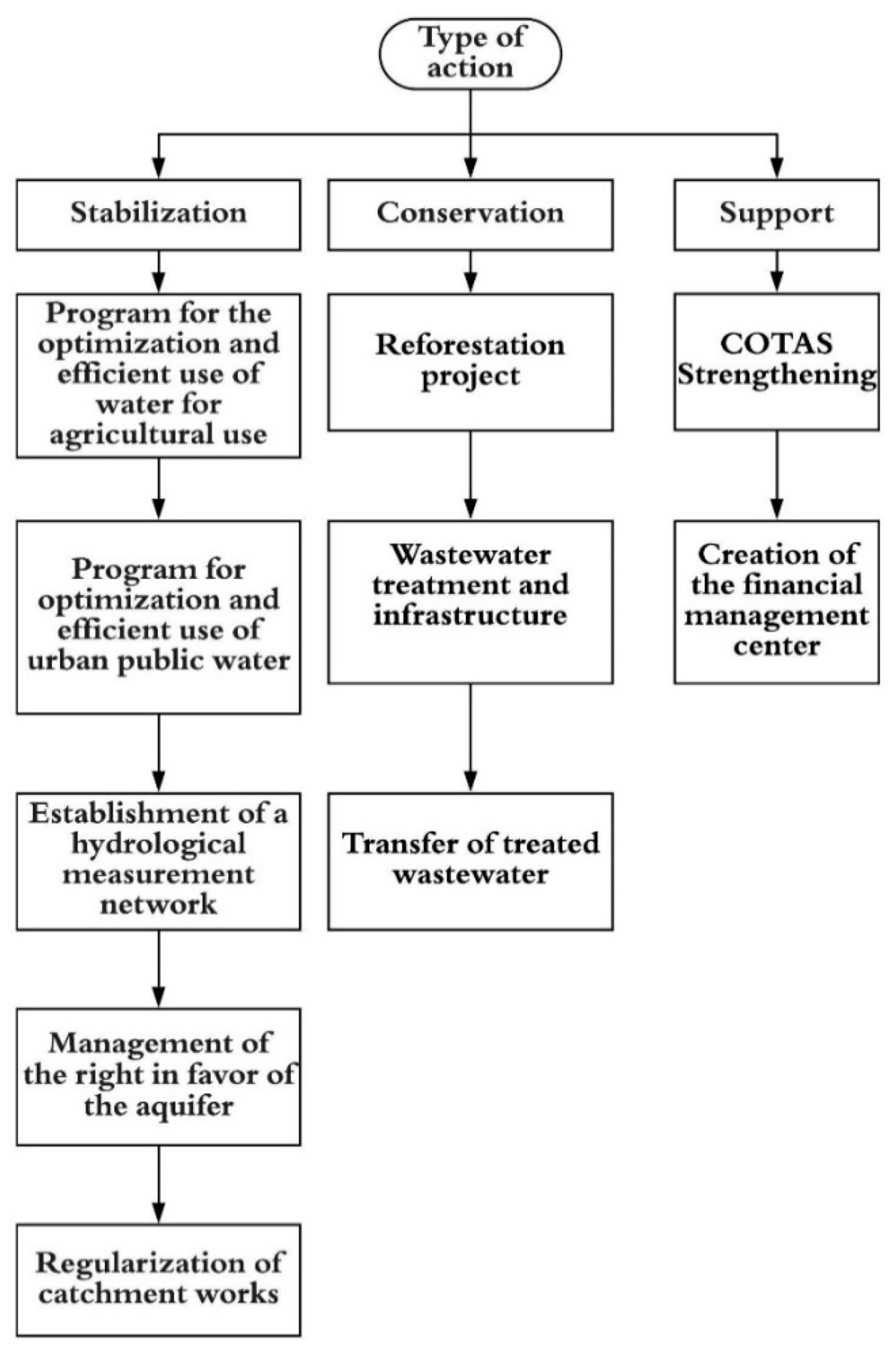
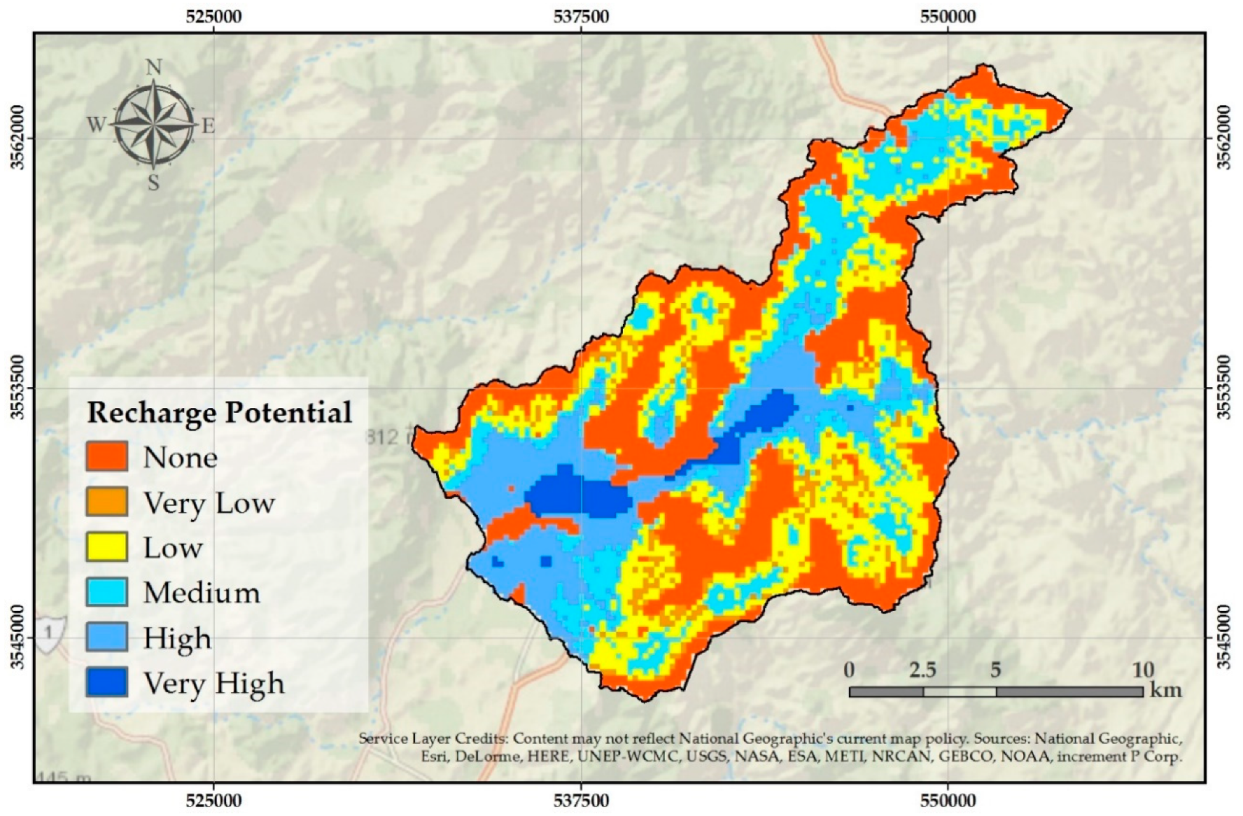
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, M.; Ward, R. Principles of Hydrology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Magesh, N.; Chandrasekar, N.; Soundranayagam, J.P. Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Theni district, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. Geosci. Front. 2012, 3, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.; Dissanayake, D.; Mayadunna, B.; Weerasekera, W. An approach to delineate groundwater recharge potential sites in Ambalantota, Sri Lanka using GIS techniques. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture (SOLAW) Managing Systems at Risk; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, L.; Bosch, P.; Canziani, O.; Chen, Z.; Christ, R.; Riahi, K. IPCC, 2007: Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Şen, Z. Applied Drought Modeling, Prediction, and Mitigation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S. Targeting saline aquifer by remote sensing and geophysical methods in a part of Hamirpur-Kanpur, India. Hydrogeol. J. 1996, 19, e64. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Krishnamurthy, J.; Saxena, R. Role of remote sensing and GIS techniques for generation of groundwater prospect zones towards rural development—An approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangdamrongsub, N.; Han, S.-C.; Tian, S.; Müller Schmied, H.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; Ran, J.; Feng, W. Evaluation of groundwater storage variations estimated from GRACE data assimilation and state-of-the-art land surface models in Australia and the North China Plain. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzelbach, W.; Bauer, P.; Siegfried, T.; Brunner, P. Sustainable groundwater management—Problems and scientific tool. Epis. Newsmag. Int. Union Geol. Sci. 2003, 26, 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, T. Groundwater Markets and Agricultural Development: A South Asian Overview; Pakistan Water Partnership: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chenini, I.; Mammou, A.B.; El May, M. Groundwater recharge zone mapping using GIS-based multi-criteria analysis: A case study in Central Tunisia (Maknassy Basin). Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 921–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, K. Ground water potential in a semi-arid region of Andhra Pradesh-a geographical information system approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweed, S.O.; Leblanc, M.; Webb, J.A.; Lubczynski, M.W. Remote sensing and GIS for mapping groundwater recharge and discharge areas in salinity prone catchments, southeastern Australia. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresha, K.J. Delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones in the Mudugunduru Sub Watershed, Mandya District, Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2016, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machiwal, D.; Jha, M.K.; Mal, B.C. Assessment of groundwater potential in a semi-arid region of India using remote sensing, GIS and MCDM techniques. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 1359–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.F.; Cheng, Y.S.; Lin, H.I.; Lee, C.H. Mapping groundwater recharge potential zone using a GIS approach in Hualian River, Taiwan. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, A.; Khawlie, M.; Abdallah, C. Use of remote sensing and GIS to determine recharge potential zones: The case of Occidental Lebanon. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, M. Identificación y Caracterización de las zonas de Recarga Hídrica Mediante Herramientas SIG de los acuíferos La Carbonería, Guaraczapas, Yuyucocha Y Santa Clara para la Protección de las Fuentes de Aprovisionamiento de agua en la zona Urbana de Ibarra; Univ. Técnica Norte Ibarra: Ibarra, Ecuador, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera Jiménez, K.F. Identificación hidrológica de zonas de recarga de las fuentes de abastecimiento de agua en la comuna la Esperanza, provincia del Carchi. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Técnica del Norte, Ibarra, Ecuador, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sáenz-López, Á.A.; Bravo-Peña, L.C.; Torres-Olave, M.E.; Alatorre-Cejudo, L.C. Localización de zonas con Potencial Natural de Recarga Hídrica: Ensayo de Enfoque Multiescalar en el Acuífero Cuauhtémoc. 2015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/302511670_Localizacion_de_zonas_con_potencial_natural_de_recarga_hidrica_ensayo_de_enfoque_multiescalar_en_el_acuifero_Cuauhtemoc (accessed on 26 February 2019).
- Cruz-Falcón, A.; Vázquez-González, R.; Ramírez-Hernández, J.; Nava-Sánchez, E.H.; Troyo-Diéguez, E.; Rivera-Rosas, J.; Vega-Mayagoitia, J. Precipitación y recarga en la cuenca de La Paz, BCS, México. Univ. Cienc. 2011, 27, 251–263. [Google Scholar]
- Emami, F.; Koch, M. Agricultural water productivity-based hydro-economic modeling for optimal crop pattern and water resources planning in the Zarrine River Basin, Iran, in the wake of climate change. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaeta Lara, A. Productividad de la vid en Función del Aprovechamiento de agua Subterránea en el Valle de Guadalupe 1994–2004. MPA Thesis, Centro de Investigación Cientıfica y de Educación Superior de Ensenada (CICESE), Ensenada, Mexico, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kurczyn-Robledo, J.A.; Kretzschmar, T.; Hinojosa-Corona, A. Evaluación del escurrimiento superficial en el noreste del Valle de Guadalupe, BC, México, usando el método de curvas numeradas y datos de satélite. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geológicas 2007, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, L.M.; Martínez, J.A.V.; Radillo, S.E.M. La Ruta del Vino en el Valle de Guadalupe, Baja California, México. Perspectiva frente al Cambio climático: Una Primera Aproximación. 2012. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sonia_Maldonado-Radillo/publication/262449906_La_Ruta_del_Vino_en_el_Valle_de_Guadalupe_Baja_California_Mexico_Perspectiva_frente_al_cambio_climatico_Una_primera_aproximacion/links/00b49537bae3bc732b000000/La-Ruta-del-Vino-en-el-Valle-de-Guadalupe-Baja-California-Mexico-Perspectiva-frente-al-cambio-climatico-Una-primera-aproximacion.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2019).
- Badán, A.; Kretzschmar, T.; Espejel, I.; Cavazos, T.; D’Acosta, H.; Vargas, P.; Mendoza, L.; Leyva, C.; Aramburo, G.; Daessle, W.; et al. Hacia un plan de manejo del agua en Valle de Guadalupe, Baja California. Memorias del II Seminario Internacional de Vitivinicultura: Ensenada, Baja California, México. INIFAP 2006, 45–64. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Gaytan, J.R.; Kretzschmar, T.; Herrera-Oliva, C.S. Future groundwater extraction scenarios for an aquifer in a semi-arid environment: Case study of Guadalupe Valley Aquifer, Baja California, Northwest Mexico. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 7961–7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comisión Nacional del Agua (CONAGUA). Actualización de la disponibilidad media anual de agua en el acuífero de Guadalupe (204), Estado de Baja California. In Diario Oficial de la Feración; Secretariat of the Interior: Mexico City, Mexico, 2018; Available online: https://sigagis.conagua.gob.mx/gas1/Edos_Acuiferos_18/BajaCalifornia/DR_0207.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2019).
- Comité Técnico de Aguas Subterraneas del Valle de Guadalupe (COTAS del Valle de Guadalupe) Actualización de la red de Monitoreo Piezométrica del Acuífero de Guadalupe. 2012. Available online: http://cotas.comtitec.com/uploads/docs/actualizacion_piezometria_noviembre_2012.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2019).
- Bodenstendt Engel, A. Art Boden Mexican Wine Guide; Grupo Editorial M&M, SA de CV: México City, Mexico, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Meraz, L. Diseño de una Estrategia de Mercadotecnia Para una Pequeña Empresa Vitivinícola en Ensenada, Baja California. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Baja California, México City, Mexico, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaría de Protección al Ambiente. 2016 Programa Ambiental Estratégico de la región vitivinícola de Valle de Guadalupe, Municipio de Ensenada, Baja California, México city, Mexico. Gobierno del Estado de Baja California, 2016. Available online: http://www.spabc.gob.mx/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/PROGRAMA-AMBIENTAL-ESTRATEGICO-DE-LA-REGION-VITIVINICOLA-DEL-VALLE-DE-GUADALUPE-MUNICIPIO-ENSENADA-B.C.-2016-1.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Celaya, D. El Desarrollo del Sector Vitivinícola en Baja California (2000–2013): Un Análisis Desde la Perspectiva del Desarrollo Endógeno. Colegio de la Frontera Norte, 2014. Available online: https://www.colef.mx/posgrado/wp-content/uploads/2014/11/TESIS-Celaya-Tentori-Diana-DCSER.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Espejel, I.; Fischer, D.W.; Hinojosa, A.; García, C.; Leyva, C. Land-use planning for the Guadalupe Valley, Baja California, Mexico. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1999, 45, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amey, R. Wines of Baja California: Touring and Tasting Mexico’s Undiscovered Treasures; Board and Bench Publishing: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hallack-Alegria, M.; Ramirez-Hernandez, J.; Watkins, D. ENSO-conditioned rainfall drought frequency analysis in northwest Baja California, Mexico. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, V.M.; Pandey, R.P.; Kumar, S. Groundwater recharge by channel infiltration in El Barbon basin, Baja California, Mexico. J. Hydrol. 1999, 214, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresic, N. Quantitative Solutions in Hydrogeology and Groundwater Modeling; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; 461p. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade Borbolla, M. Actualización geohidrológica del Valle de Guadalupe, Municipio de Ensenada, Baja California; Grupo Agroindustrial del Valle de Guadalupe: Ensenada, Baja California, México, 1997; 60p. [Google Scholar]
- González Ramírez, J. Monitoreo y Modelado de la Respuesta del nivel Freático ante Eventos de Precipitación en el Acuífero de Valle de Guadalupe, B.C. MPA Thesis, Centro de Investigación Cientıfica y de Educación Superior de Ensenada (CICESE), Ensenada, Mexico, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado, T. El uso de Tecnologías de la Información en el Desarrollo de un plan de Manejo Sustentable del Acuífero del Valle de Guadalupe, BC. Ph.D. Thesis, Colegio de Postgraduados, Montecillo, Mexico, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez Zepeda, L. Localización Territorial y Organización Productiva de la Industria Vinícola del Valle de Guadalupe. Aproximación a la Incidencia de la Industria Vinícola en el Desarrollo Económico del Valle de Guadalupe (México) y La Manchuela (España). Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Castilla–La Mancha, Ciudad Real, España, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Greenbaum, D. Review of Remote Sensing Applications to Groundwater Exploration in Basement and Regolith. 1985. Available online: http://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/505150/1/WC_OG_85_1.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2019).
- Al Saud, M. Mapping potential areas for groundwater storage in Wadi Aurnah Basin, western Arabian Peninsula, using remote sensing and geographic information system techniques. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 1481–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, V.; Sotelo, C. Los vinos del Valle de Guadalupe: Análisis de su comercialización. Eur. Sci. J. 2014, 10, 90–106. [Google Scholar]
- Leduc, C.; Favreau, G.; Schroeter, P. Long-term rise in a Sahelian water-table: The Continental Terminal in south-west Niger. J. Hydrol. 2001, 243, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.F.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, K.C.; Chang, P.H. GIS for the assessment of the groundwater recharge potential zone. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva Aguilera, J.A.; Espejel Carbajal, M.I. El valle de Guadalupe. Conjugando Tiempos. Universidad Autonoma de Baja California. 2013. Available online: https://ciencias.ens.uabc.mx/documentos/libros/LibroValleGuadalupe.pdf. (accessed on 20 February 2019).
| Factor | Value | Reclassification | Recharge Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | >20 | 0 | Very low |
| 15–20 | 3 | Low | |
| 10–15 | 6 | Medium | |
| 5–10 | 8 | High | |
| <5 | 10 | Very high | |
| Land Use | Settlement | 0 | Very low |
| Pine forest | 2 | Low | |
| Grassland | 3 | Medium | |
| Shrubland and Bush | 4 | High | |
| Agriculture | 7 | Very high | |
| Lithology | Igneous rocks | 0 | Very low |
| Sedimentary rocks | 2 | Low | |
| Metamorphic rocks | 3 | Medium | |
| Lineaments | 8 | High | |
| Alluvium | 10 | Very high | |
| Drainage density (km/km2) | 3–8 | 0 | Very low |
| 2–3 | 2 | Low | |
| 1–2 | 3 | Medium | |
| 0.5–1 | 5 | High | |
| 0–0.5 | 7 | Very high |
| Factor/Influence | Slope (Sl) | Land Use (Lu) | Soil Type (St), Faults | Drainage Density (Dd) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | |
| Land use | 1 | 0.5, 0.5 | 1 | |
| Soil type | 1 | 1 | ||
| Drainage density | 1 | 0.5 |
| Factor | A | B | A + B | Proposed Influencing Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | 1 + 1 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 0.28 |
| Land use | 1 + 1 | 0.5 + 0.5 | 3 | 0.33 |
| Soil type | 1 + 1 | 2 | 0.22 | |
| Drainage density | 1 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0.17 |
| ∑9 | ∑1 |
| Recharge Potential | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| None | 68.99 | 32.50 |
| Very Low | 11.45 | 5.40 |
| Low | 49.37 | 23.26 |
| Medium | 40.10 | 18.89 |
| High | 34.63 | 16.31 |
| Very High | 7.72 | 3.64 |
| ∑212.26 | ∑100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saiz-Rodríguez, J.A.; Lomeli Banda, M.A.; Salazar-Briones, C.; Ruiz-Gibert, J.M.; Mungaray-Moctezuma, A. Allocation of Groundwater Recharge Zones in a Rural and Semi-Arid Region for Sustainable Water Management: Case Study in Guadalupe Valley, Mexico. Water 2019, 11, 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081586
Saiz-Rodríguez JA, Lomeli Banda MA, Salazar-Briones C, Ruiz-Gibert JM, Mungaray-Moctezuma A. Allocation of Groundwater Recharge Zones in a Rural and Semi-Arid Region for Sustainable Water Management: Case Study in Guadalupe Valley, Mexico. Water. 2019; 11(8):1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081586
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaiz-Rodríguez, Juan Alejandro, Marcelo A. Lomeli Banda, Carlos Salazar-Briones, José Mizael Ruiz-Gibert, and Alejandro Mungaray-Moctezuma. 2019. "Allocation of Groundwater Recharge Zones in a Rural and Semi-Arid Region for Sustainable Water Management: Case Study in Guadalupe Valley, Mexico" Water 11, no. 8: 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081586
APA StyleSaiz-Rodríguez, J. A., Lomeli Banda, M. A., Salazar-Briones, C., Ruiz-Gibert, J. M., & Mungaray-Moctezuma, A. (2019). Allocation of Groundwater Recharge Zones in a Rural and Semi-Arid Region for Sustainable Water Management: Case Study in Guadalupe Valley, Mexico. Water, 11(8), 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081586




