Water Residence Time in a Typical Tributary Bay of the Three Gorges Reservoir
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Setup
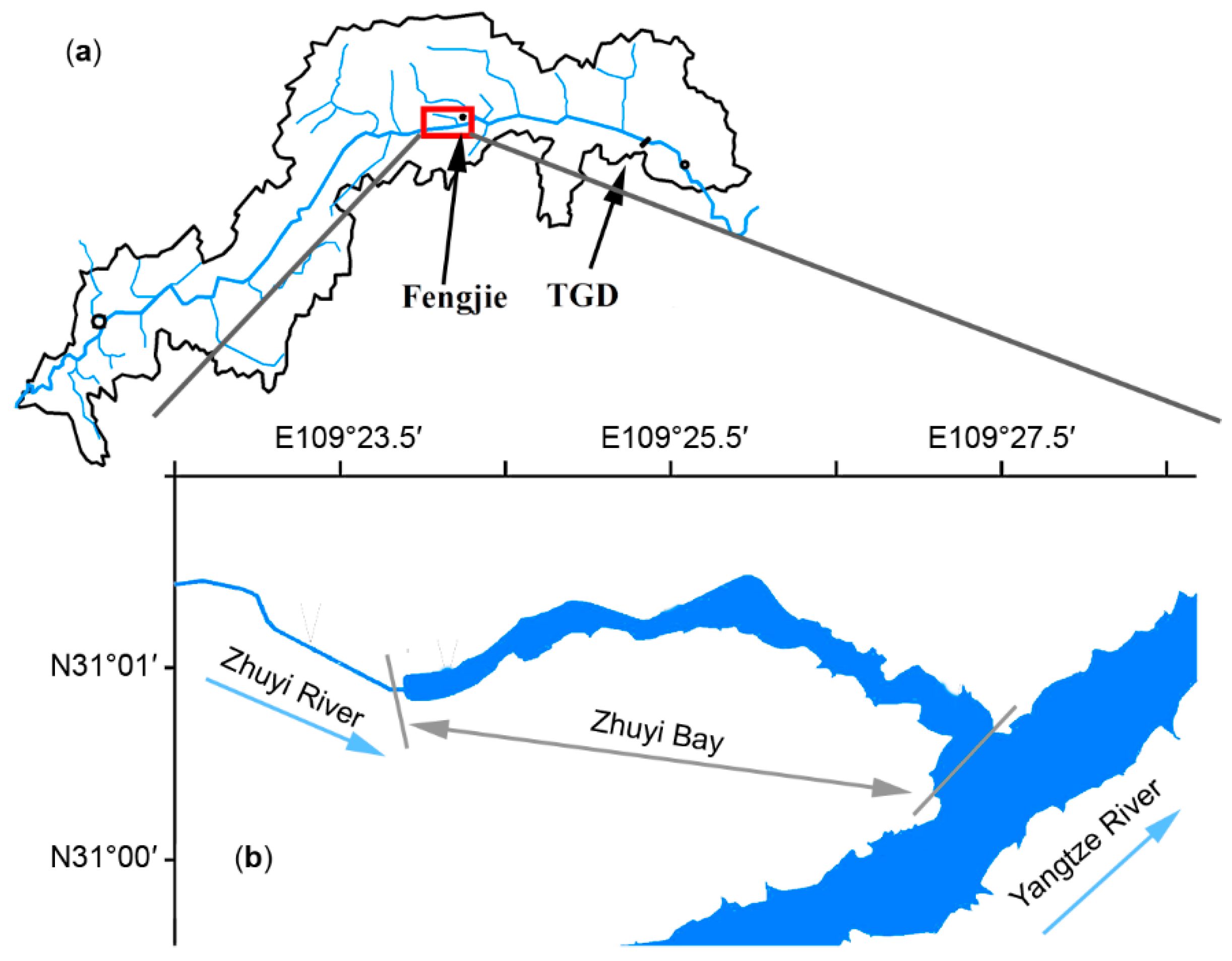
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Hydrodynamic Model
2.3. Diagnosing RT by the Adjoint Method
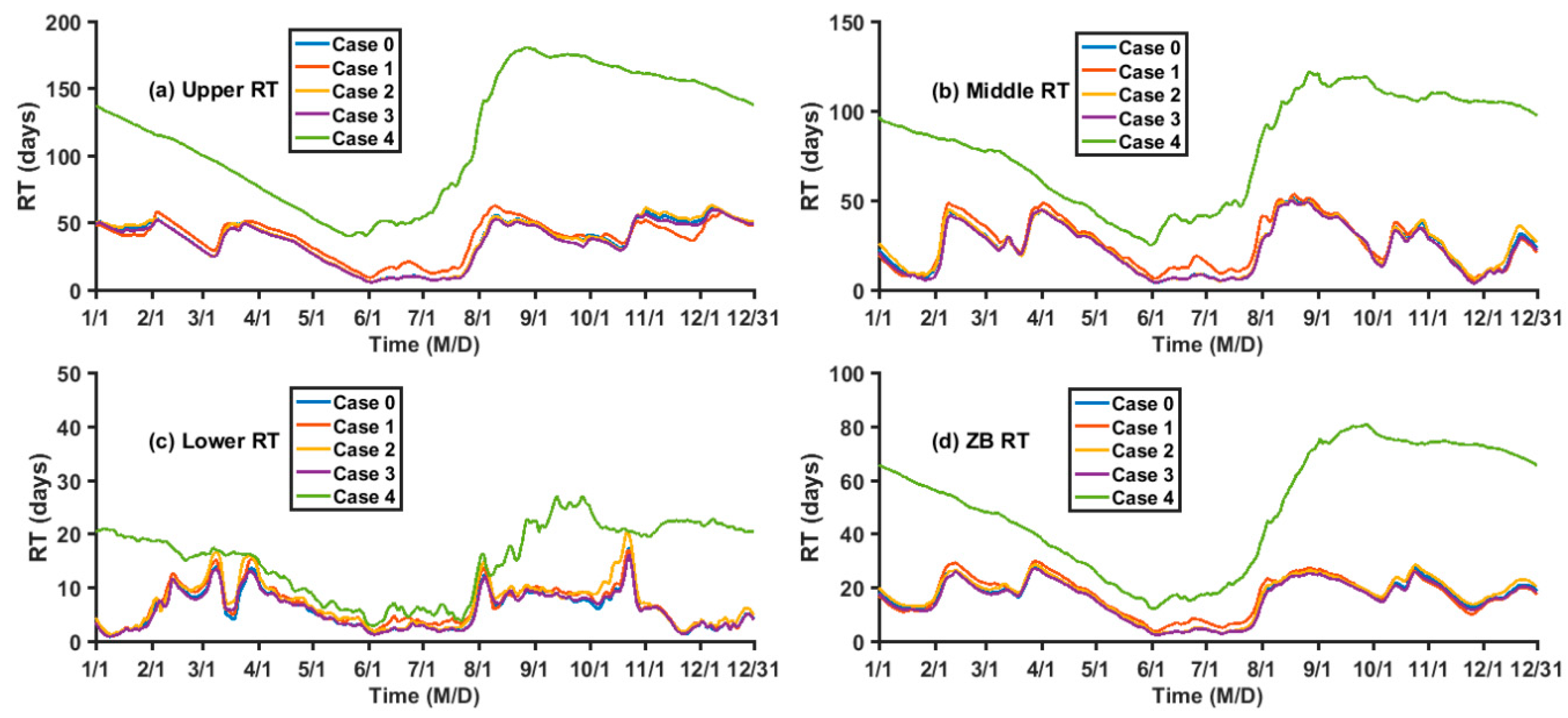
3. Results
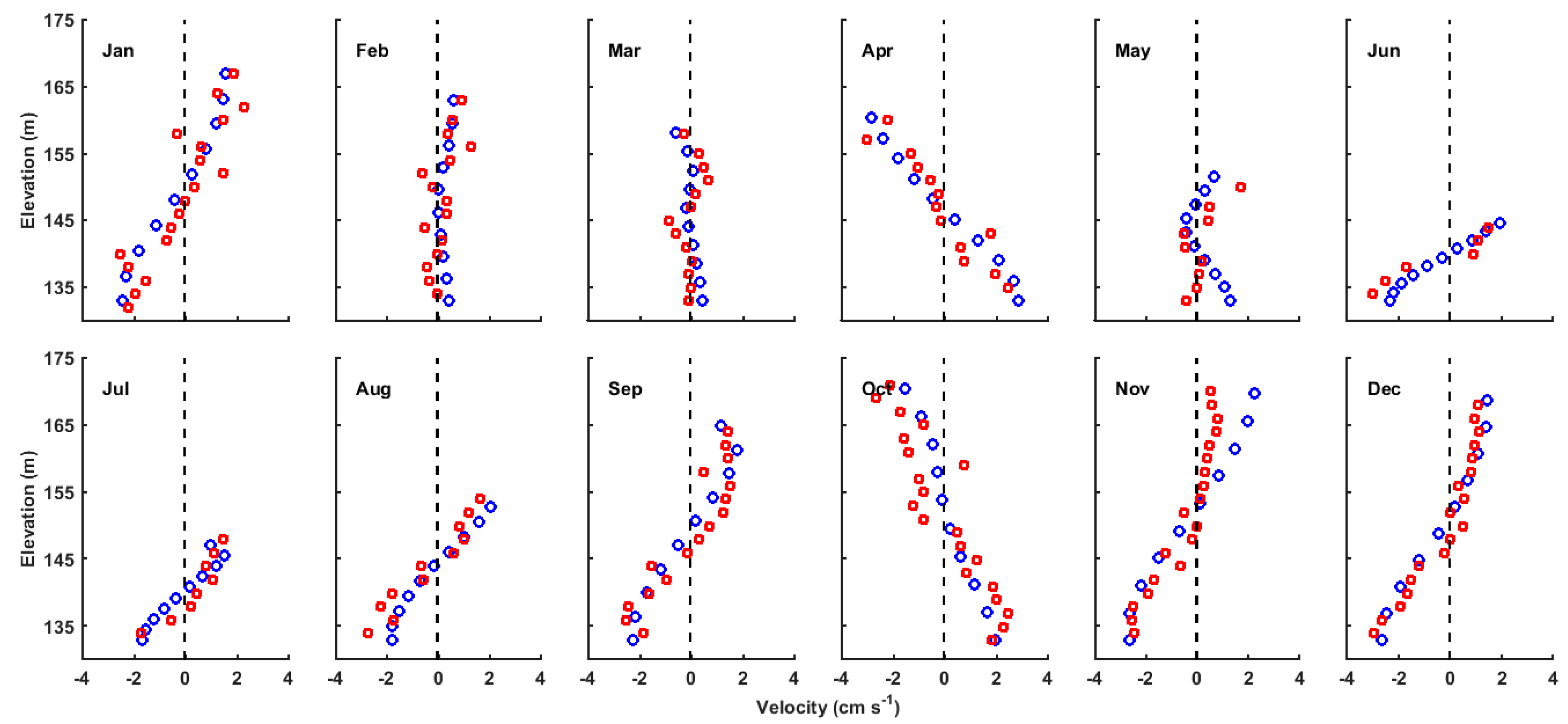
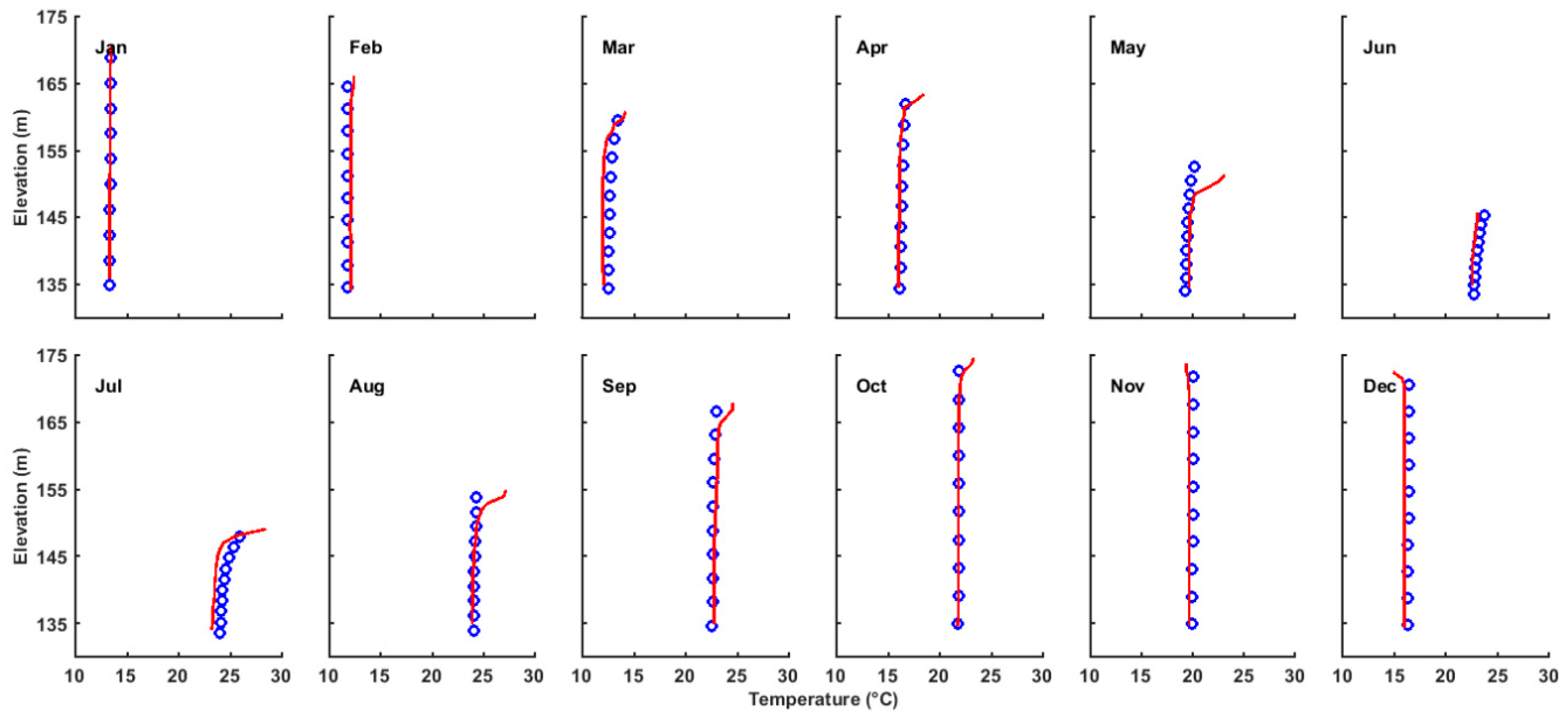
3.1. Validation of the Hydrodynamic Model
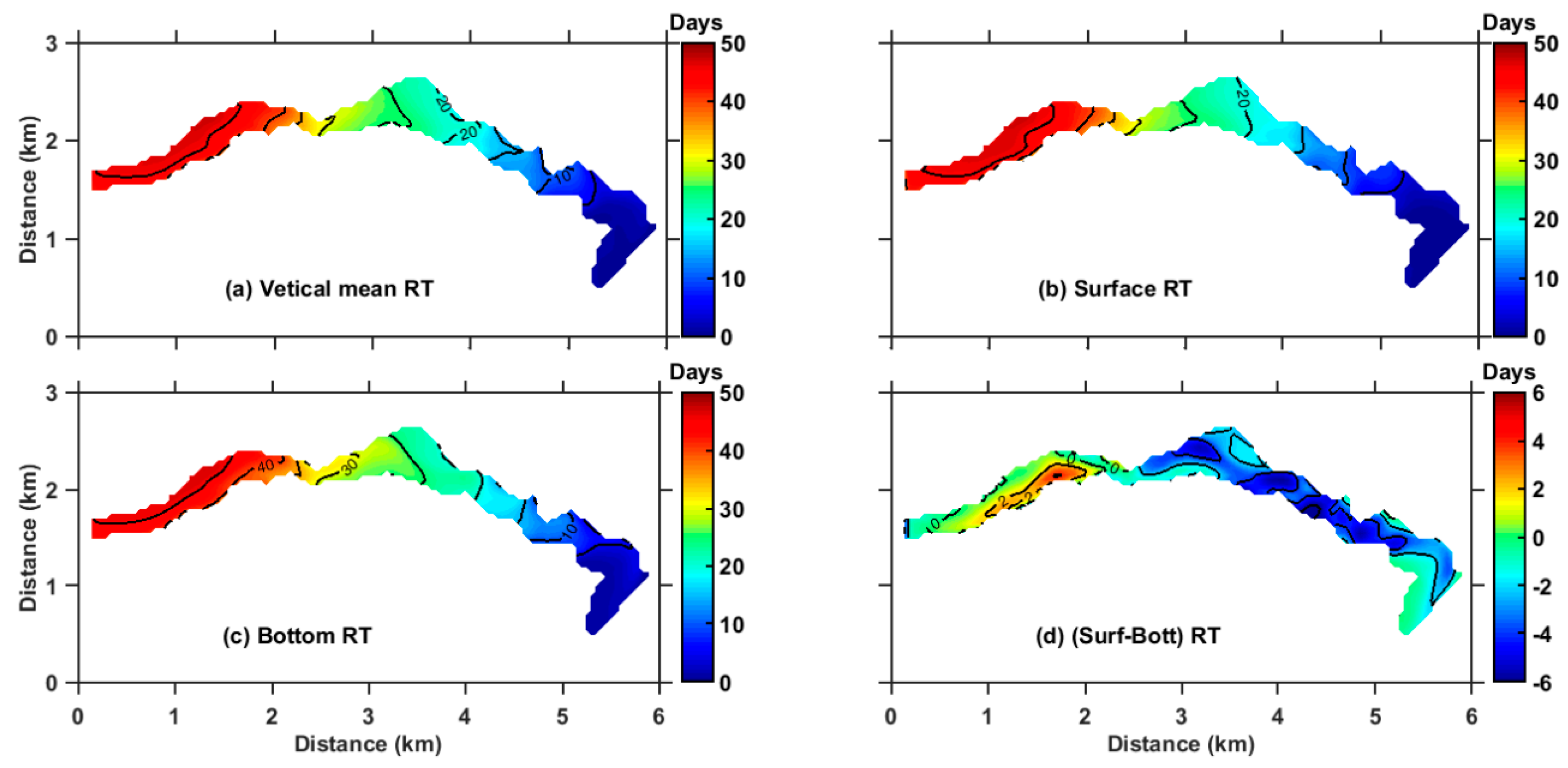
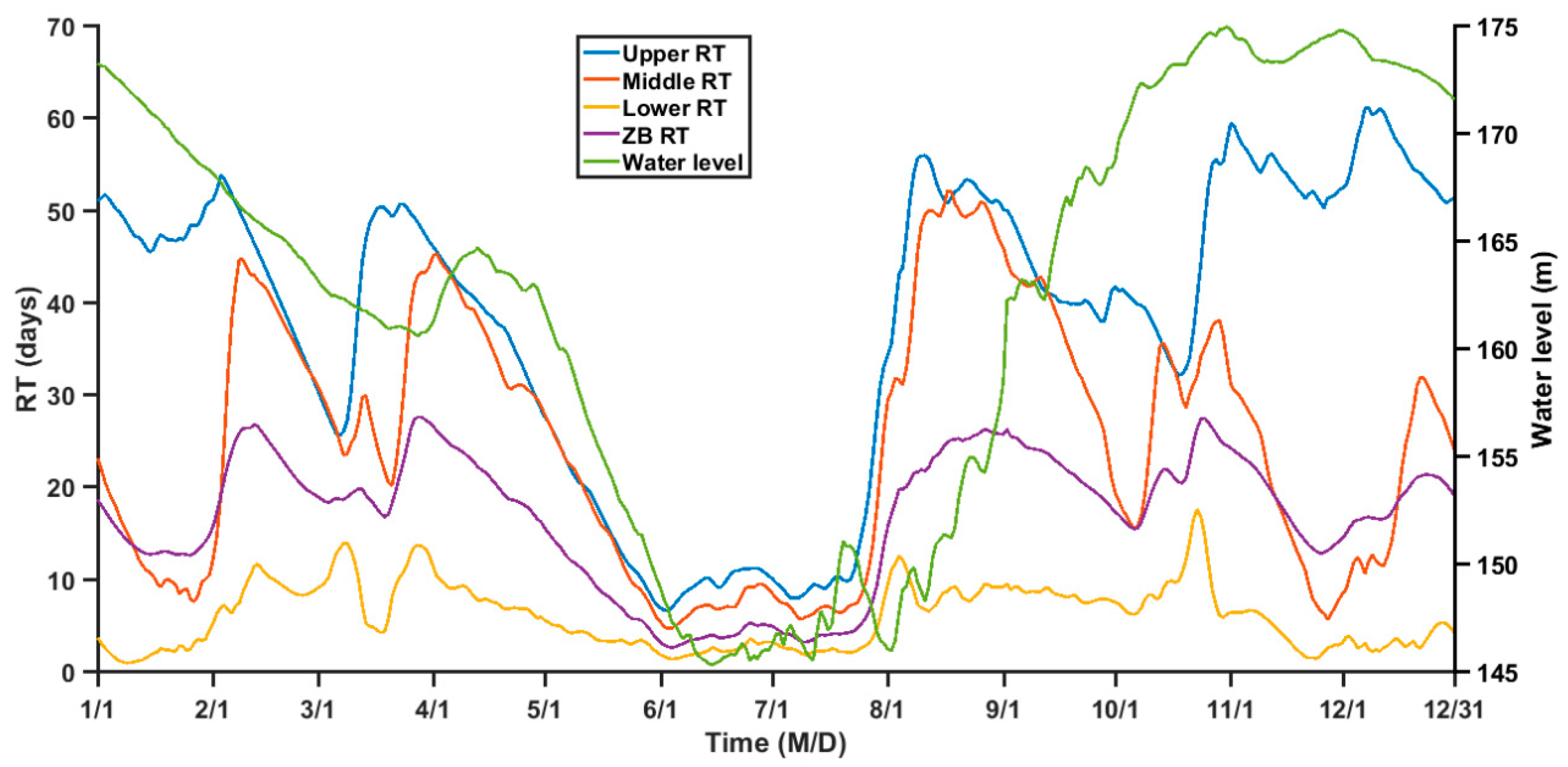
3.2. Annual Mean RT of ZB
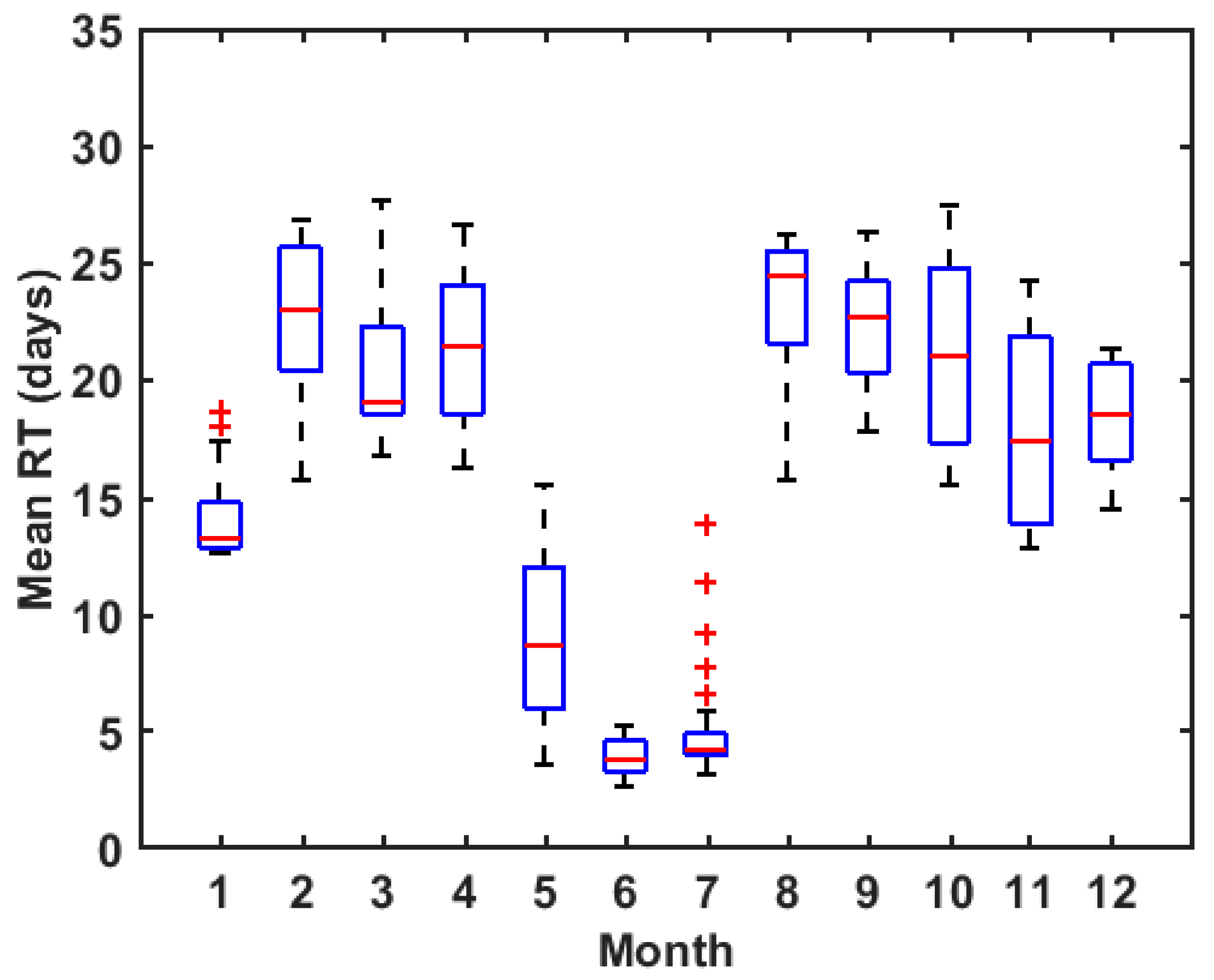
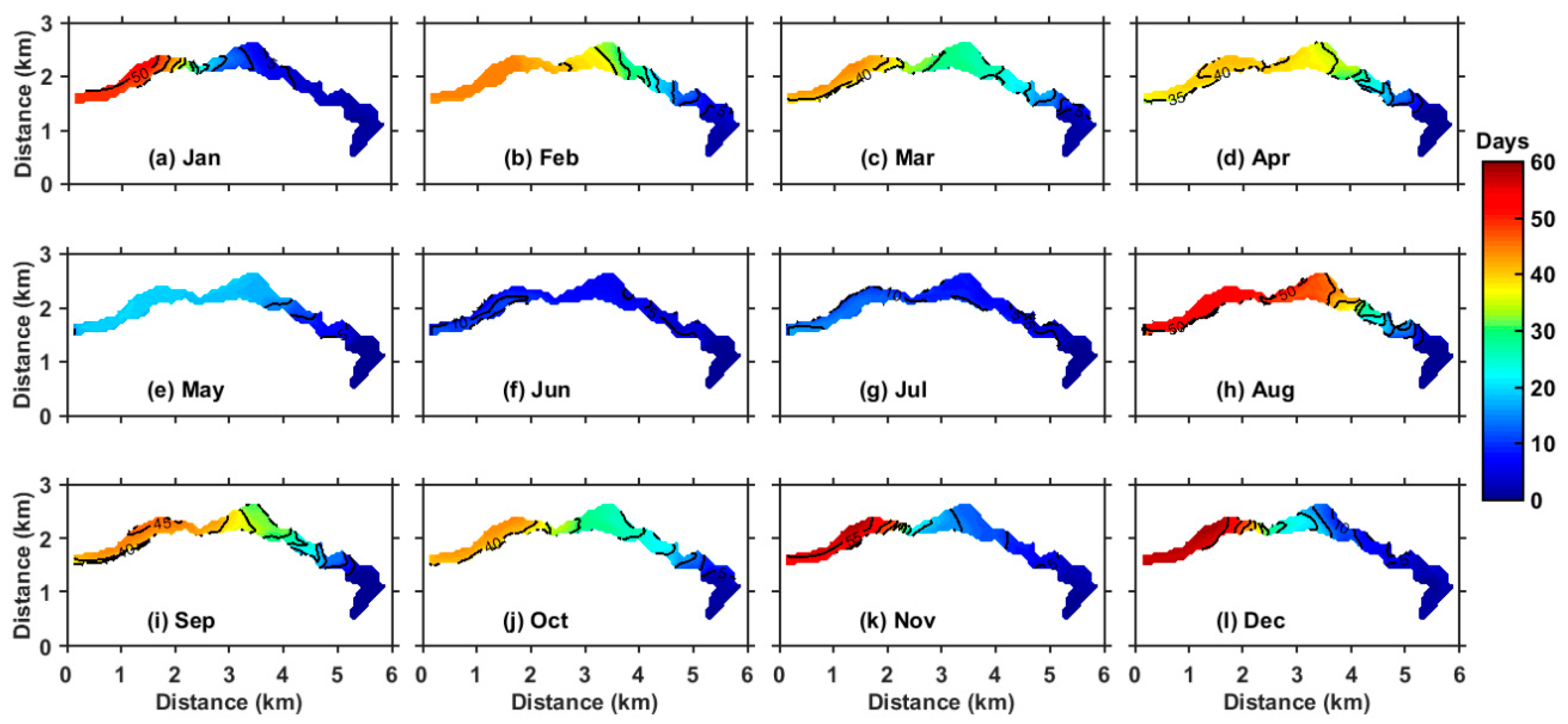
3.3. Seasonal Variation of RT
4. Discussion
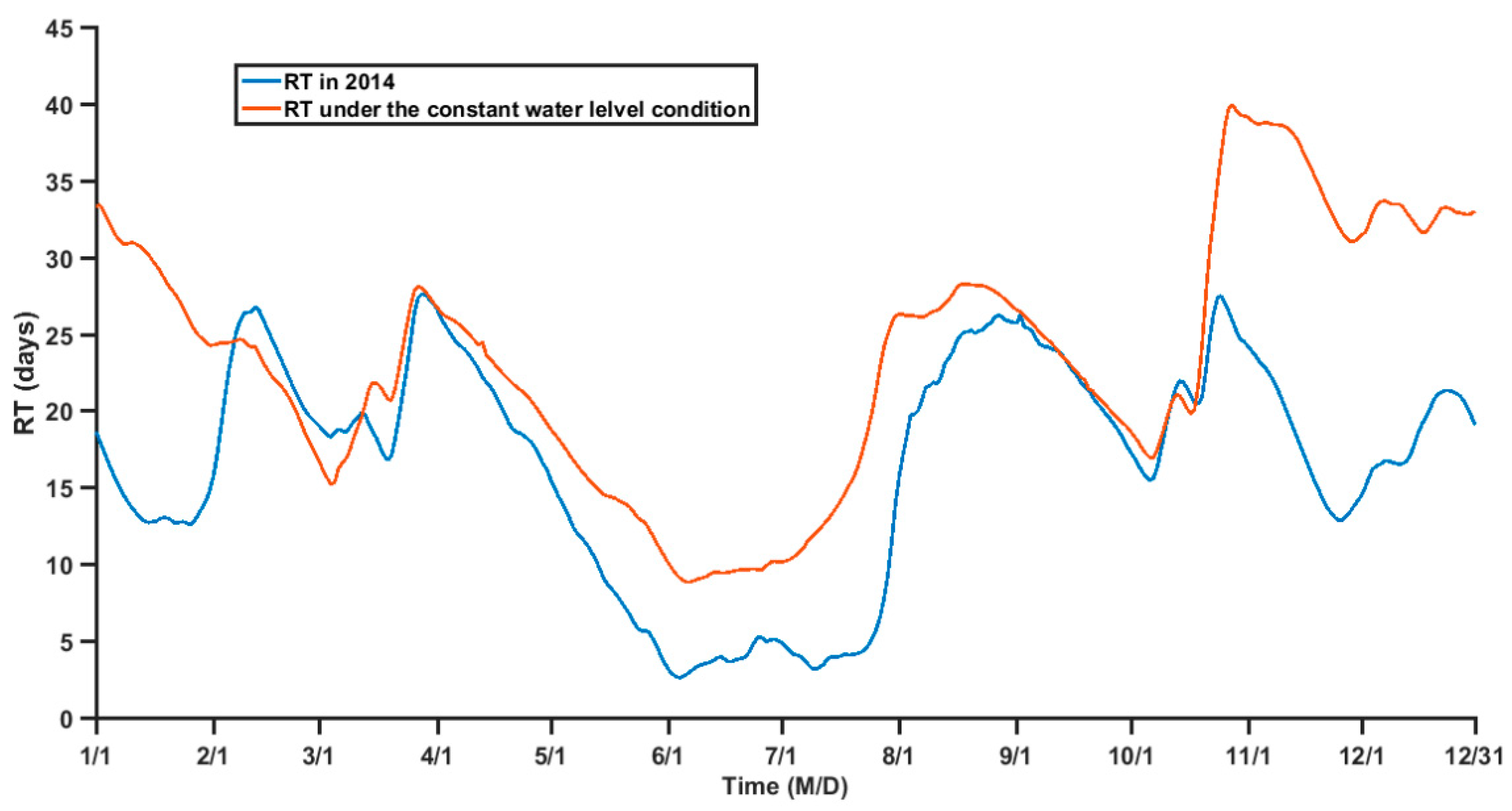
4.1. Relationship between RT and TGR Regulation
4.2. Influences of Dynamic Processes on the RT
4.3. The Potential Relationship between RT and Algal Blooms in the Tributary
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acronym | Full Name |
| TGR | Three Gorges Reservoir |
| TGD | Three Gorges Dam |
| ZB | Zhuyi Bay |
| RT | Residence time |
References
- De Brauwere, A.; de Brye, B.; Blaise, S.; Deleersnijder, E. Residence time, exposure time and connectivity in the Scheldt Estuary. J. Mar. Syst. 2011, 84, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.V.; Thompson, J.K.; Brown, L.R. Why are diverse relationships observed between phytoplankton biomass and transport time? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLusky, D.S.; Elliott, M.; Elliott, M. The Estuarine Ecosystem: Ecology, Threats and Management; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wolanski, E.; Elliott, M. Estuarine Ecohydrology: An Introduction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Delhez, É.J.M.; Wolk, F. Diagnosis of the transport of adsorbed material in the Scheldt Estuary: A proof of concept. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 128, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andutta, F.P.; Ridd, P.V.; Deleersnijder, E.; Prandle, D. Contaminant exchange rates in estuaries—New formulae accounting for advection and dispersion. Prog. Oceanogr. 2014, 120, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolin, B.; Rodhe, H. A note on the concepts of age distribution and transit time in natural reservoirs. Tellus 1973, 25, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, J.T.F. Mixing and flushing of tidal embayments in the western dutch wadden sea part I: Distribution of salinity and calculation of mixing time scales. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1976, 10, 149–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeoka, H. Fundamental concepts of exchange and transport time scales in a coastal sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 1984, 3, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhez, E.J.M.; Campin, J.-M.; Hirst, A.C.; Deleersnijder, E. Toward a general theory of the age in ocean modelling. Ocean Model. 1999, 1, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhez, É.J.M. On the concept of exposure time. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 71, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S.W.; Ammerman, J.W.; Atkinson, L.P.; Berounsky, V.M.; Billen, G.; Boicourt, W.C.; Boynton, W.R.; Church, T.M.; Ditoro, D.M.; Elmgren, R.; et al. The fate of nitrogen and phosphorus at the land-sea margin of the north atlantic ocean. Biogeochemistry 1996, 35, 141–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmann, E.H. Effect of water residence time on annual export and denitrification of nitrogen in estuaries: A model analysis. Estuaries 2001, 24, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, B.C.; Hopkinson, C.S.; Sogin, M.L.; Hobbie, J.E. Microbial biogeography along an estuarine salinity gradient: Combined influences of bacterial growth and residence time. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delesalle, B.; Sournia, A. Residence time of water and phytoplankton biomass in coral reef lagoons. Cont. Shelf Res. 1992, 12, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.V.; Koseff, J.R.; Cloern, J.E.; Monismith, S.G.; Thompson, J.K. Processes governing phytoplankton blooms in estuaries. I: The local production-loss balance. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 187, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.V.; Koseff, J.R.; Monismith, S.G.; Cloern, J.E.; Thompson, J.K. Processes governing phytoplankton blooms in estuaries. II: The role of horizontal transport. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 187, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiela, I.; McClelland, J.; Hauxwell, J.; Behr, P.J.; Hersh, D.; Foreman, K. Macroalgal blooms in shallow estuaries: Controls and ecophysiological and ecosystem consequences. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, J.; Shen, H.; Wang, Z. Yangtze river of China: Historical analysis of discharge variability and sediment flux. Geomorphology 2001, 41, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, C.; Reidy, C.A.; Dynesius, M.; Revenga, C. Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river systems. Science 2005, 308, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Dai, S.B.; Li, M.; Xu, X.J. Effect of deposition and erosion within the main river channel and large lakes on sediment delivery to the estuary of the yangtze river. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Han, X.; Xie, Z.; Gao, X. Three-gorges dam—Experiment in habitat fragmentation? Science 2003, 300, 1239–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Xie, Z. Three Gorges Project: Chance and challenge. Science 2004, 304, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R. Three Gorges Dam: Into the unknown. Science 2008, 321, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.-J.; Wu, B.-F.; Lü, Y.-H.; Xu, Z.-H.; Cao, J.-H.; Niu, D.; Yang, G.-S.; Zhou, Y.-M. Three Gorges Project: Efforts and challenges for the environment. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 34, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, Y.; Yang, G. Environmental impact assessments of the Three Gorges Project in China: Issues and interventions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2013, 124, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbach, A.; Norra, S.; Wang, L.; Yijun, Y.; Hu, W.; Zheng, B.; Bi, Y. Three Gorges Reservoir: Density pump amplification of pollutant transport into tributaries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7798–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zheng, B.; Wang, L.; Qin, Y.; Li, H.; Cao, W. Characterization of mixing processes in the confluence zone between the Three Gorges Reservoir mainstream and the daning river using stable isotope analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9907–9914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Dang, C. The influence of the Three Gorges Reservoir regulation on a typical tributary heat budget. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Hu, M.; Jiang, R.; Bao, Y.; Dang, C. Heat budget contribute rate in the Three Gorges Reservoir tributary bay between mainstream and tributary using stable isotope analysis. Water Supply 2019, 19, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cai, Q.; Tan, L.; Kong, L. Phytoplankton development and ecological status during a cyanobacterial bloom in a tributary bay of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3820–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, D.; Johnson, D.M.; Yi, Z.; Huang, Y. Effects of vertical mixing on phytoplankton blooms in xiangxi bay of Three Gorges Reservoir: Implications for management. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cheng, B.; Xu, Y.; Liu, D.; Ma, J.; Ji, D. Stable isotopes in water indicate sources of nutrients that drive algal blooms in the tributary bay of a subtropical reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, F.; Wang, Y. Global sensitivity analysis of a water quality model in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water 2018, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Li, B.; Liu, T.; Ai, B.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Chen, Q. Macrobenthic assemblage characteristics under stressed waters and ecological health assessment using ambi and m-ambi: A case study at the xin’an river estuary, yantai, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Yu, J.; Liu, B. Evaluation of ecosystem services: A case study in the middle reach of the heihe river basin, northwest China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2015, 89–90, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, L.; Xie, L.; Gao, H. Partially implicit finite difference scheme for calculating dynamic pressure in a terrain-following coordinate non-hydrostatic ocean model. Ocean Model. 2016, 106, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.H. Note on the theory of the thermocline. J. Mar. Res. 1948, 7, 276–295. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Liu, Z. Tvdal: Total variation diminishing scheme with alternating limiters to balance numerical compression and diffusion. Ocean Model. 2019, 134, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.W.; Bradley, E.F.; Rogers, D.P.; Edson, J.B.; Young, G.S. Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes for tropical ocean-global atmosphere coupled-ocean atmosphere response experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1996, 101, 3747–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhez, É.J.M.; Heemink, A.W.; Deleersnijder, É. Residence time in a semi-enclosed domain from the solution of an adjoint problem. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhez, E.J.M. Transient residence and exposure times. Ocean Sci. 2006, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhez, É.J.M.; Deleersnijder, É. The boundary layer of the residence time field. Ocean Dyn. 2006, 56, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brye, B.; de Brauwere, A.; Gourgue, O.; Delhez, E.J.M.; Deleersnijder, E. Water renewal timescales in the Scheldt Estuary. J. Mar. Syst. 2012, 94, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Song, L.; Yu, Z.; Chen, H. Distribution of phytoplankton in the Three-Gorge Reservoir during rainy and dry seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Bi, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, L.; Hu, Z. Algal growth potential and nutrient limitation in spring in Three-Gorges Reservoir, China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2009, 18, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Kang, L.; Sun, X.; Jia, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, H.; Ai, H. Spatiotemporal distribution and potential risk assessment of microcystins in the Yulin River, a tributary of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 347, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Mao, J.; Jiang, D.; Wang, L. Longitudinal hydrodynamic characteristics in reservoir tributary embayments and effects on algal blooms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagy, J.D.; Boynton, W.R.; Sanford, L.P. Estimation of net physical transport and hydraulic residence times for a coastal plain estuary using box models. Estuaries 2000, 23, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Haas, L. Calculating age and residence time in the tidal york river using three-dimensional model experiments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.E. Wind modulation of dissolved oxygen in Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries Coasts 2010, 33, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M. Wind-driven lateral circulation in a stratified estuary and its effects on the along-channel flow. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Shen, J. Water residence time in Chesapeake Bay for 1980–2012. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 164, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Lin, J. Modeling study of the influences of tide and stratification on age of water in the tidal James River. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, H. The age of Yellow River water in the Bohai Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Liu, Z. The age of Yodo River water in the Seto Inland Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2019, 191, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, W.; Li, W.; Mu, L.; Jin, Z. Coupled hydrodynamic and water quality simulation of algal bloom in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 119, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.; Cai, Q. Spatial analysis for spring bloom and nutrient limitation in xiangxi bay of Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 127, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Case | Tributary Discharge | Yangtze River Discharge | Local Winds | Baroclinic Forcing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 1 | 0.5 times | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2 | Yes | 0.5 times | Yes | Yes |
| 3 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| 4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Mu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, F.; Li, Y.; Lin, L. Water Residence Time in a Typical Tributary Bay of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water 2019, 11, 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081585
Cheng Y, Mu Z, Wang H, Zhao F, Li Y, Lin L. Water Residence Time in a Typical Tributary Bay of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water. 2019; 11(8):1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081585
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yao, Zheng Mu, Haiyan Wang, Fengxia Zhao, Yu Li, and Lei Lin. 2019. "Water Residence Time in a Typical Tributary Bay of the Three Gorges Reservoir" Water 11, no. 8: 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081585
APA StyleCheng, Y., Mu, Z., Wang, H., Zhao, F., Li, Y., & Lin, L. (2019). Water Residence Time in a Typical Tributary Bay of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water, 11(8), 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081585






