Wastewater Treatment and Water Reuse in Spain. Current Situation and Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methods
3. Situation of Wastewater Treatment and Water Reuse in Spain
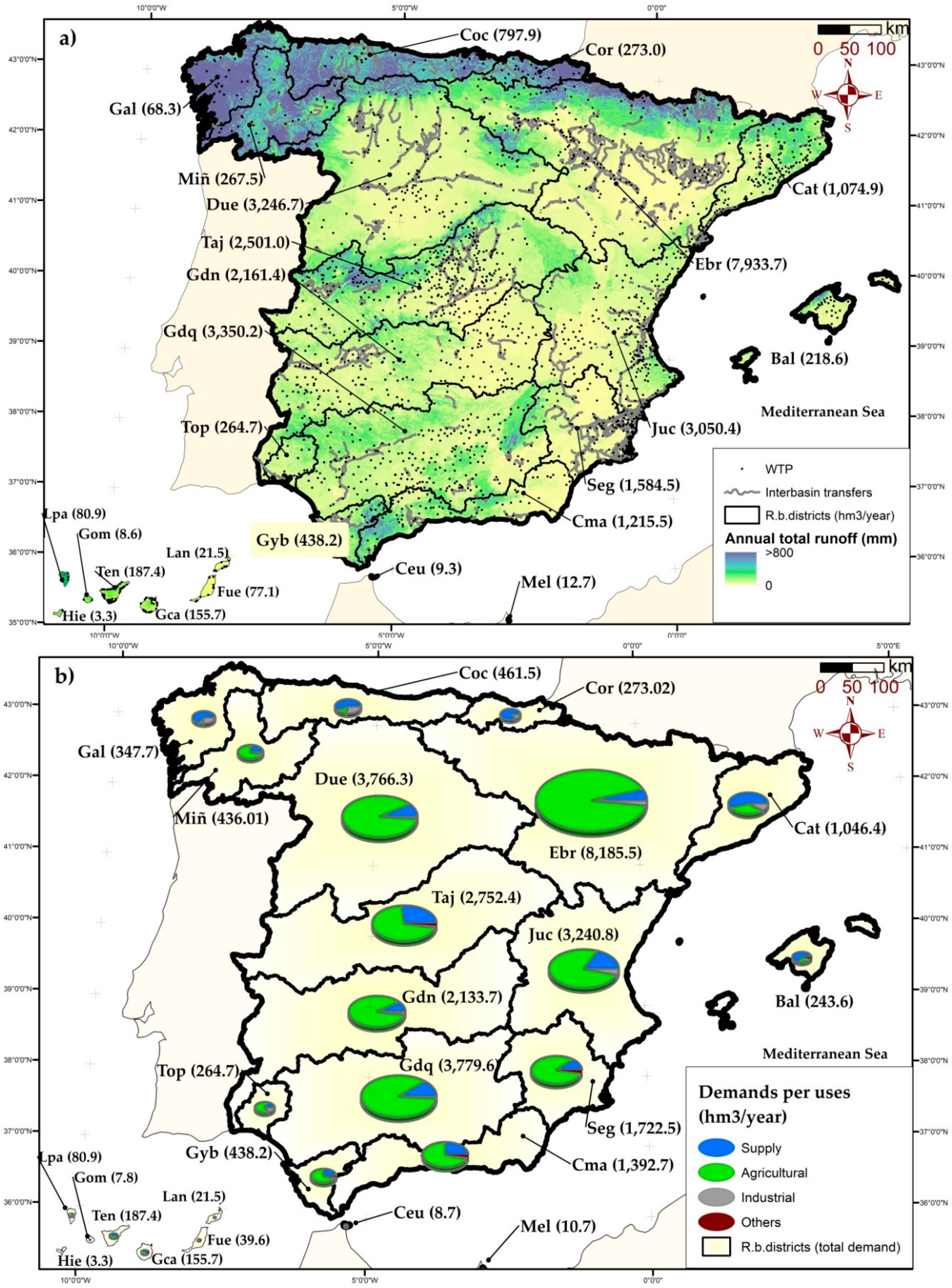
3.1. General Overview
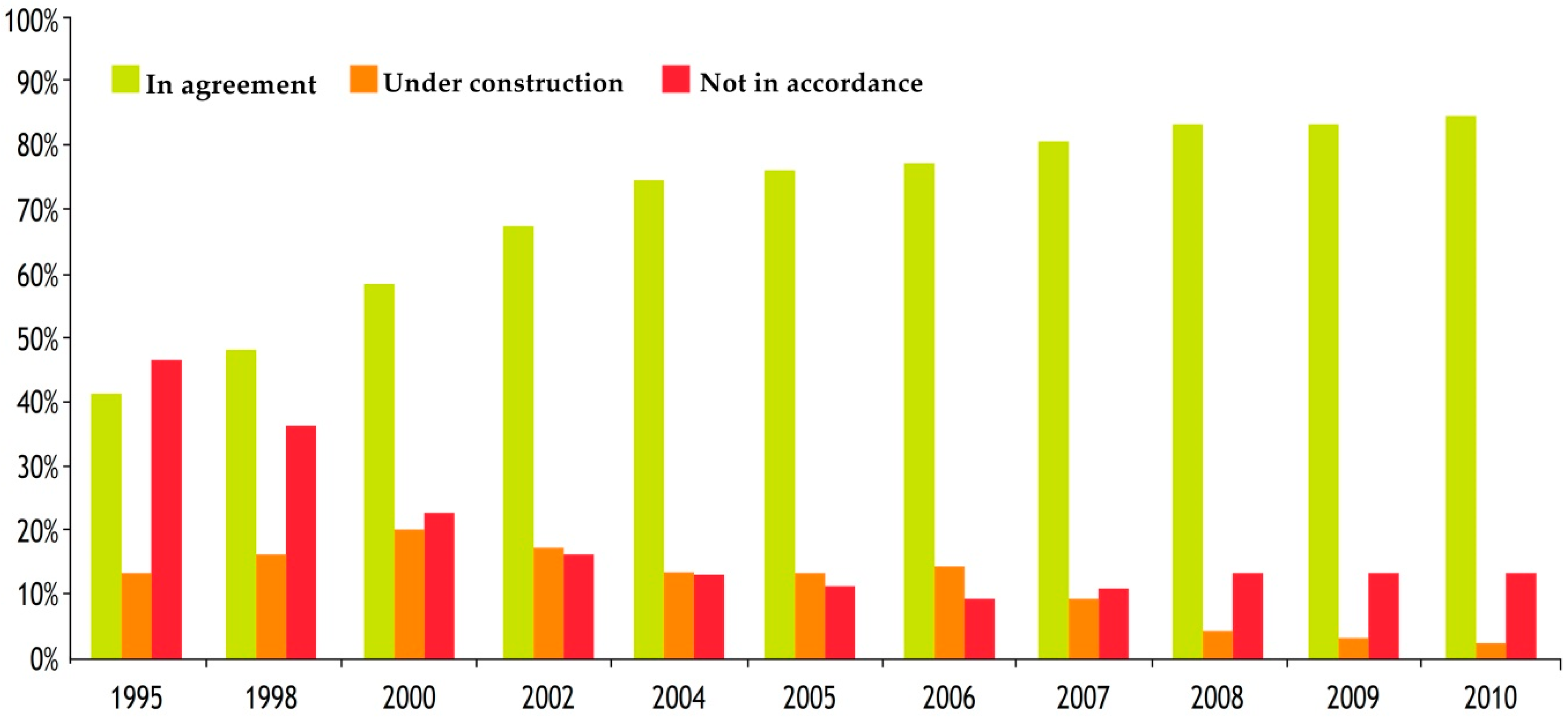
3.2. The National Plan of Sanitation and Water Treatment
3.3. The National Water Quality Plan: Sanitation and Water Treatment
3.4. The Plan of Measures for Growth, Competitiveness and Efficiency
- In 2016, 64% of surface water bodies had to reach the good status.
- In 2021, 74% of surface water bodies will have to achieve the good status.
4. Evolution of the Planned Reuse in Spain
4.1. The Origins of the Planned Wastewater Reuse
4.2. The Programme of Actions for Water Management and Water Use
4.3. The National Water Reuse Plan
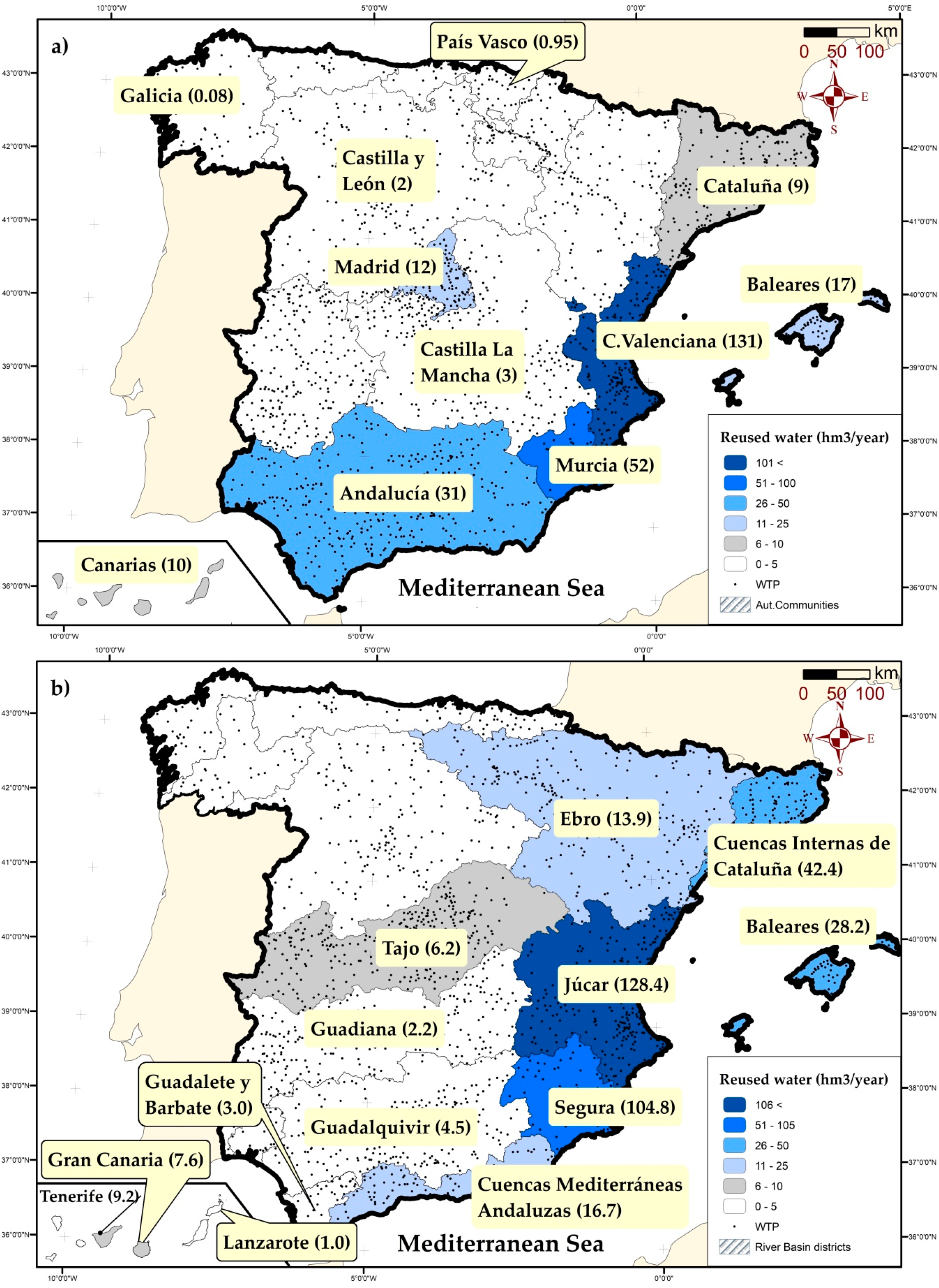
4.4. Total Volume of Wastewater Reused in Spain
- In 2014, the CEDEX organism fixed the reused volume “with concessions” at 796.8 hm3/year [23,55]. In the same year, the Spanish Statistical Office (INE) quantified the reused water at 531 hm3/year, while the Spanish Association of water supply and sanitation (AEAS) indicated 373 hm3/year of reclaimed waters in Spain and 4097 hm3/year as the total volume of wastewaters treated in Spain [41,42,71,72].
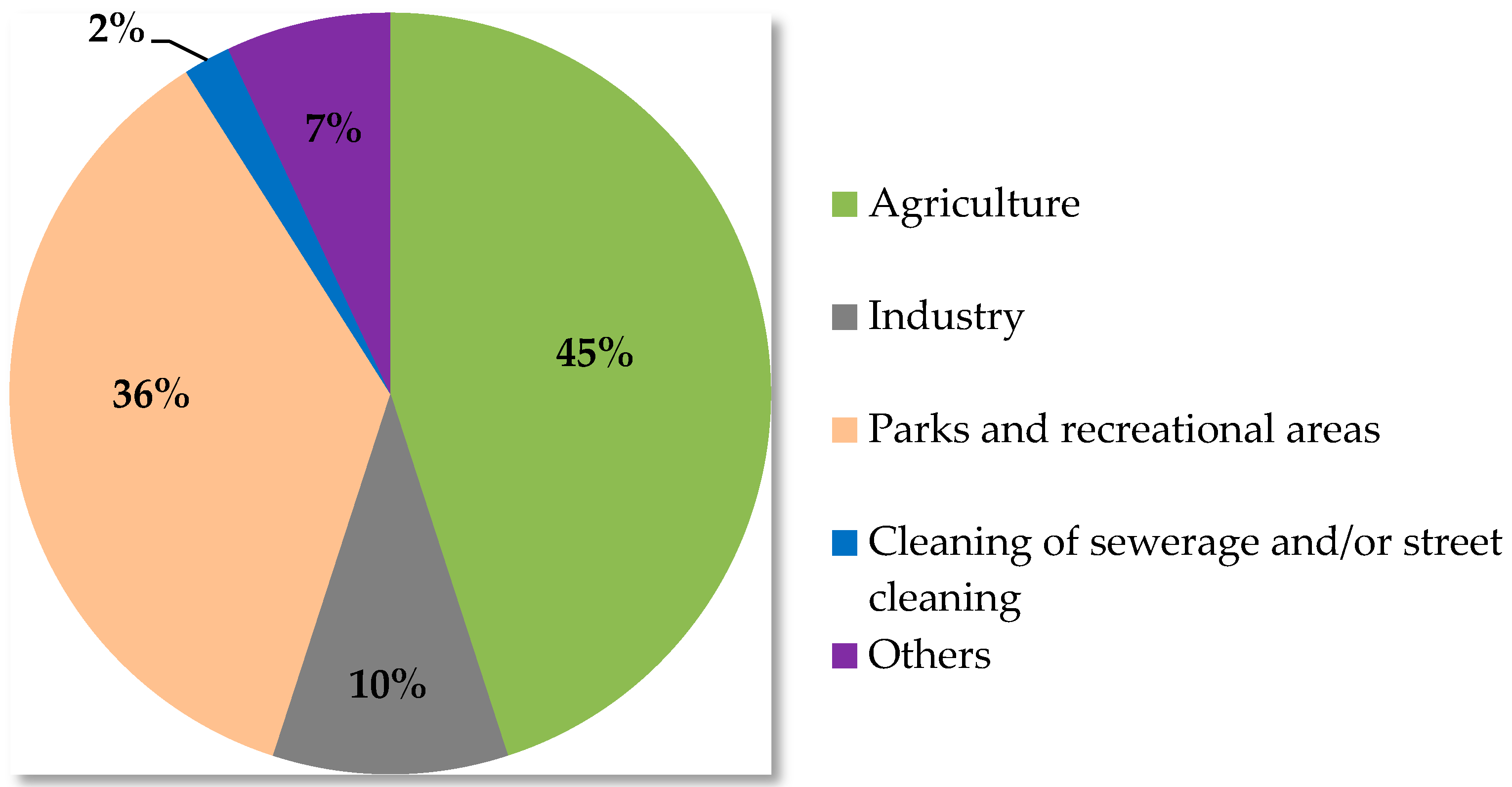
5. Uses of Reclaimed Waters in Spain
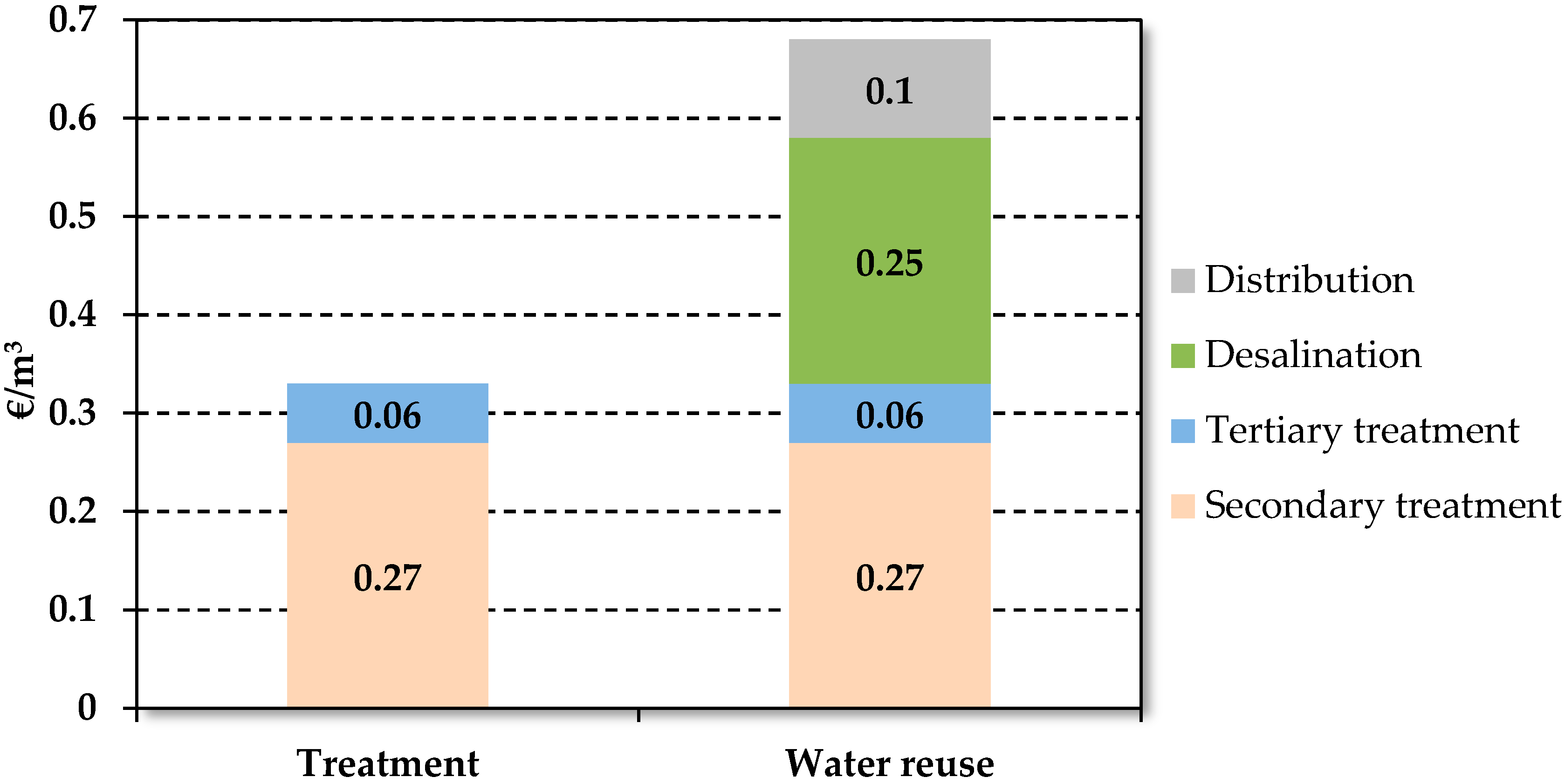
6. Costs of Wastewater Treatment and Reuse
The Case of the Valencia Community
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aldaya, M.M.; Custodio, E.; Llamas, R.; Fernández, M.F.; García, J.; Ródenas, M.A. An academic analysis with recommendations for water management and planning at the basin scale: A review of water planning in the Segura River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custodio, E.; Andreu-Rodes, J.M.; Aragón, R.; Estrela, T.; Ferrer, J.; García-Aróstegui, J.L.; Manzano, M.; Rodríguez-Hernández, L.; Sahuquillo, A.; del Villar, A. Groundwater intensive use and mining in south-eastern peninsular Spain: Hydrogeological, economic and social aspects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, A.D.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, L.; Smerdon, B.D.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Yu, L.; Li, L. An Initial Inventory and Indexation of Groundwater Mega-Depletion Cases. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 507–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Guzmán, C.A.; Melgarejo, J.; Prats, D.; Torres, A.; Martínez, S. Urban Water Cycle Simulation/Management Models: A Review. Water 2017, 9, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgarejo-Moreno, J.; López-Ortiz, M.I.; Fernández-Aracil, P. Water distribution management in South-East Spain: A guaranteed system in a context of scarce resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNESCO. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2019: Leaving No One Behind. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000367306 (accessed on 19 May 2019).
- Gleick, P.H. Water use. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 275–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Muñoz, J.F.; Aznar-Sánchez, J.A.; Batlles-delaFuente, A.; Fidelibus, M.D. Rainwater Harvesting for Agricultural Irrigation: An Analysis of Global Research. Water 2019, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, R.; Pinilla, V.; Serrano, A. Looking backward to look forward: Water use and economic growth from a long-term perspective. Appl. Econ. 2014, 46, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Giménez, A.; Melgarejo-Moreno, J. Water policy in Spain: Seeking a balance between transfers, desalination and wastewater reuse. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2015, 32, 781–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgarejo, J.; Prats, D.; Molina, A.; Trapote, A. A case study of urban wastewater reclamation in Spain: Comparison of water quality produced by using alternative processes and related costs. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2016, 6, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Llamas, M.J.; Trapote, A.; Prats, D. Removal of micropollutants from urban wastewater using a UASB reactor coupled to a MBR at different organic loading rates. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morote, Á.-F.; Olcina, J.; Hernández, M. The Use of Non-Conventional Water Resources as a Means of Adaptation to Drought and Climate Change in Semi-Arid Regions: South-Eastern Spain. Water 2019, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalavrouziotis, I.K.; Arambatzis, C.; Kalfountzos, D.; Varnavas, S.P. Wastewater Reuse Planning in Agriculture: The Case of Aitoloakarnania, Western Greece. Water 2011, 3, 988–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats-Rico, D. Reuse of Purified Regenerated Water Worldwide: Analyzes and Projections. Water Landsc. 2016, 8, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barkey, B.L.; Bailey, R.T. Estimating the Impact of Drought on Groundwater Resources of the Marshall Islands. Water 2017, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodar-Abellan, A.; Fernández-Aracil, P.; Melgarejo-Moreno, J. Assessing Water Shortage through a Balance Model among Transfers, Groundwater, Desalination, Wastewater Reuse, and Water Demands (SE Spain). Water 2019, 11, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, T. Modernization and Urban Water Governance: Organizational Change and Sustainability in Europe; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2018; p. 446. ISBN 978-1-137-59254-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, B.C.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Brown, R.R. A strategic program for transitioning to a Water Sensitive City. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 117, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Buurman, J.; van Ginkel, K.C.H. Urban water security: A review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 053002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.C.; da Cruz, N.F.; Pires, J. Measuring the sustainability of urban water services. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noiva, K.; Fernández, J.E.; Wescoat, J.L. Cluster analysis of urban water supply and demand: Toward large-scale comparative sustainability planning. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 27, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Esteban, R. La reutilización de efluentes depurados en España: Retrospectiva, desarrollo del marco normativo, estudio de las tecnologías de regeneración frente a los biorreactores de membrana y sus costes en función del uso. Tesis Doctoral, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid, España, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Melgarejo-Moreno, J.; López-Ortiz, M.I. Depuración y reutilización de aguas en España (Wastewater Treatment and Water Reuse in Spain). Agua y Territ. 2016, 8, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, A.; Andreu, J.M.; Solá, F.; Pulido-Bosch, A. The anthropogenic impact on Mediterranean karst aquifers: Cases of some Spanish aquifers. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats-Rico, D.; Melgarejo-Moreno, J. Desalación y reutilización de aguas. Situación en la provincia de Alicante. Ed: Confederación empresarial de la provincia de Alicante (COEPA). Available online: https://iuaca.ua.es/en/documentos/documents/ebooks/ebook-desalacion-y-reutilizacion-de-aguas-en-la-provincia-de-alicante.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2006).
- WFD. Directive 2000/60/EC of The European Parliament and of The Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy; DOUE: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sales, J.; Tamoh, K.; Lopez-Gonzalez, J.L.; Gaaloul, N.; Candela, L. Controlling seawater intrusion by treated wastewater recharge. Numerical modelling and cost-benefit analysis (CBA) at Korba case study (Cap Bon, Tunisia). Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 76, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgarejo-Moreno, J. Efectos ambientales y económicos de la reutilización del agua en España. CLM Econ. 2009, 15, 245–270. [Google Scholar]
- PWC. La gestión del agua en España, análisis de la situación actual del sector y retos futuros. Available online: https://commonmedia.blob.core.windows.net/legacymedia/1226705/informe_gestion_agua.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2014).
- Hochstrat, R.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T. Development of integrated water reuse strategies. Desalination 2008, 218, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart, S.; Rico, A.M. Assessing technical and social driving factors of water reuse in agriculture: A review on risks, regulation and the yuck factor. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellis, M.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K.; Gikas, P. Review of wastewater reuse in the Mediterranean countries, focusing on regulations and policies for municipal and industrial applications. Glob. Nest J. 2013, 15, 333–350. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Caballero, M.T. Water reuse and desalination in Spain-challenges and opportunities. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2018, 8, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Giménez, A. Delineating the Legal Framework for the Reuse of Reclaimed Water in Spain. Water Landsc. 2016, 8, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bastian, R.; Murray, D. Guidelines for Water Reuse; EPA/600/R-12/618; US EPA Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 643. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/region1/npdes/merrimackstation/pdfs/ar/AR-1530.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2018).
- CEDEX. Evaluación del Impacto del Cambio Climático en los Recursos Hídricos y Sequías en España; Clave CEDEX: 42-415-0-001; Informe Final; Centro de Estudios y Experimentación de Obras Públicas (CEDEX): Madrid, Spain, 2017; p. 346. Available online: http://www.cedex.es/CEDEX/LANG_CASTELLANO/ORGANISMO/CENTYLAB/CEH/Documentos_Descargas/EvaluacionimpactoCCsequiasEspana2017.htm (accessed on 14 March 2017).
- Valdes-Abellan, J.; Pardo, M.A.; Tenza-Abril, A.J. Observed precipitation trend changes in the western Mediterranean region. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAPAMA. Informe de Seguimiento de los Planes Hidrológicos de Cuenca y de los Recursos Hídricos en España. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/agua/temas/planificacion-hidrologica/memoria_infoseg2017_web_tcm30-482594.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2017).
- Gomariz-Castillo, F.; Alonso-Sarria, F.; Cabezas-Calvo-Rubio, F. Calibration and spatial modelling of daily ET0 in semiarid areas using Hargreaves equation. Earth Sci. Inform. 2018, 11, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgarejo-Moreno, J. Agua y Economía Circular. Ponencia Marco. In Proceedings of the Congreso Nacional del Agua 2019: Innovación y Sostenibilidad, Alicante, Spain, 7–9 May 2019; pp. 27–52, ISBN 978-984-1302-1034-1301. [Google Scholar]
- AEAS-AGA. XV Estudio Nacional. Suministro de Agua Potable y Saneamiento en España; Asociación Española de Abastecimientos de Agua y Saneamiento (AEAS) & Asociación Española de Empresas Gestoras de los Servicios de Agua Urbana (AGA): Madrid, Spain, 2018; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Zarzo, D.; Prats, D. Desalination and energy consumption. What can we expect in the near future? Desalination 2018, 427, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAPAMA. Ministerio de Agricultura, Medio Ambiente. Descargas del Área de actividad del Agua. Available online: http://www.mapama.gob.es/es/cartografia-y-sig/ide/descargas/agua/default.aspx (accessed on 4 April 2018).
- SIA. Series de Datos. Sistema Integrado de Información del Agua. Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica (MITECO). Available online: https://servicio.mapama.gob.es/sia/visualizacion/descargas/series.jsp (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- R-CRAN. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 22 November 2018).
- ArcGIS. ArcGIS 10.5 (Geographic Information System). Available online: https://support.esri.com/es/downloads (accessed on 16 November 2018).
- Kaika, M. The Water Framework Directive: A New Directive for a Changing Social, Political and Economic European Framework. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2003, 11, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B. The Water Framework Directive: Total environment or political compromise? Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajigas-Delgado, A. La evolución de la depuración de las aguas residuales urbanas en España. Ing. Civ. 2012, 168, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Directive91/271/EEC. Directive of 21 May 1991 Concerning Urban Waste Water Treatment (91/271/EEC). 1991. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:31991L0271&from=EN (accessed on 12 September 2018).
- BOE. Resolución de 28 de abril de 1995, de la Secretaría de Estado de Medio Ambiente y Vivienda, por la que se dispone la publicación del Acuerdo del Consejo de Ministros de 17 de febrero de 1995, por el que se aprueba el Plan Nacional de Saneamiento y Depuración de Aguas Residuales; B.O.E. núm. 113, de 12 de mayo de 1995; Ministerio de Obras Públicas, Transporte y Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 1995. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/doc.php?id=BOE-A-1995-11343 (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- MAGRAMA. Informe de Sostenibilidad en España. 2014; p. 175. Available online: http://www.upv.es/contenidos/CAMUNISO/info/U0679775.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2018).
- ESAMUR. Entidad de Saneamiento y Depuración de Aguas Residuales de la Región de Murcia (ESAMUR). Available online: http://www.esamur.com/ (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- CEDEX. Centro de Estudios y Experimentación de Obras Públicas (CEDEX). Available online: http://www.cedex.es/CEDEX/lang_castellano/ (accessed on 14 April 2019).
- MAGRAMA. Informe de Sostenibilidad en España; Observatorio de la Sostenibilidad en España (OSE): Madrid, Spain, 2012; p. 316. Available online: http://www.upv.es/contenidos/CAMUNISO/info/U0637061.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2018).
- CEDEX. Realización de Una Base de Datos Sobre los Sistemas de Reutilización de Aguas Depuradas en España; Centro de Estudios y Experimentación de Obras Públicas. Ministerio de Agricultura, Alimentación y Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 2008.
- Torres-Sánchez, G. Situación de la Depuración de Las Aguas Urbanas en España; MAGRAMA: Madrid, Spain, 2014; p. 28. Available online: http://www.conama.org/conama/download/files/conama2014/GTs%202014/1996711165_ppt_GTorres.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2016).
- MAGRAMA. Plan Nacional de Calidad de las Aguas: Saneamiento y Depuración (2007–2015); PNCA: Madrid, Spain, 2007; p. 117. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/images/es/PlanNacionalCalidadAguas_tcm30-279844.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2009).
- Asociación Española de Abastecimientos de Agua y Saneamiento (AEAS). Hacia un funcionamiento económicamente competitivo, sostenible y alternativo en la gestión de las aguas residuales en España. GT-14. In Proceedings of the Congreso Nacional del Medio Ambiente (CONAMA 2014), Madrid, Spain, 4 November 2014; p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, F. L’application du Droit Communautaire de L’environnement: De la Prise de Conscience à la Mobilisation des Acteurs; Information Report to the French Senate; French Senate: Paris, French, 12 October 2011; Available online: https://www.senat.fr/notice-rapport/2011/r11-020-notice.html (accessed on 7 June 2018).
- Bolognesi, T. The paradox of the modernisation of urban water systems in Europe: Intrinsic institutional limits for sustainability. Nat. Resour. Forum 2014, 38, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BOE. Ley 11/2005, de 22 de Junio, por la que se Modifica la Ley 10/2001, de 5 de Julio, del Plan Hidrológico Nacional; N° 149; Agencia Estatal Boletín Oficial del Estado: Madrid, Spain, 2005. Available online: https://www.boe.es/boe/dias/2005/06/23/pdfs/A21846-21856.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- BOE. Real Decreto 1620/2007, de 7 de diciembre, por el que se establece el régimen jurídico de la reutilización de las aguas depuradas; N° 294; Agencia Estatal Boletín Oficial del Estado: Madrid, Spain, 2007. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/pdf/2007/BOE-A-2007-21092-consolidado.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- BOE. Ley 10/2001, de 5 de julio, del Plan Hidrológico Nacional; N° 161; Agencia Estatal Boletín Oficial del Estado: Madrid, Spain, 2001. Available online: https://www.boe.es/boe/dias/2001/07/06/pdfs/A24228-24250.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2009).
- PNRA. Plan Nacional de Reutilización de Aguas. Ministerio de Medio Ambiente Medio Rural y Marino. Web page. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/agua/participacion-publica/pnra.aspx (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- PNRA. Plan Nacional de Reutilización de Aguas; Versión Preliminar del Plan; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente Medio Rural y Marino: Madrid, Spain, 2010; p. 131. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/agua/participacion-publica/version_preliminar_pnra231210_tcm30-136850.pdf (accessed on 7 October 2015).
- PNRA. Plan Nacional de Reutilización de Aguas. In Informe de Sostenibilidad Ambiental; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente Medio Rural y Marino: Madrid, Spain, 2010; p. 222. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/agua/participacion-publica/isa_pnra_231210_tcm30-136851.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2017).
- PNRA. Evaluación Ambiental Estratégica del Plan Nacional de Reutilización de Aguas Regeneradas; Documento Inicial; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente Medio Rural y Marino: Madrid, Spain, 2009; p. 187. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/images/es/2009_p_006_documentoinicio_tcm30-97960.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2018).
- Corrochano-Codorniu, A. Nuevo Real Decreto sobre Reutilización de Aguas Depuradas. Ambienta 2008, 76, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- INE. Suministro y Saneamiento del agua en España; Instituto Nacional de Estadística (Spanish Statistical Office): Madrid, Spain, 2018; Available online: https://www.ine.es/infografias/infografia_suministro_agua.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2019).
- AEAS. Informe Sobre Aguas Residuales en España; Día Mundial del Agua (2017); Asociación Española de Abastecimientos de Agua y Saneamiento (AEAS): Madrid, Spain, 2017; p. 24. Available online: https://www.asoaeas.com/sites/default/files/Documentos/Informe%20sobre%20aguas%20residuales%20AEAS.pdf (accessed on 8 November 2018).
- Jodar-Abellan, A.; Ruiz, M.; Melgarejo, J. Evaluación del impacto del cambio climático sobre una cuenca hidrológica en régimen natural (SE, España) usando un modelo SWAT. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geol. 2018, 35, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MITECO. Depuradoras de aguas residuales (Q2015. Dir 91/271/CEE). Cartographic information. Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica (MITECO). Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/cartografia-y-sig/ide/descargas/agua/situacion-q2015.aspx (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- EEA. Waterbase-UWWTD: Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive-reported data. European Environmental Agency (EEA). Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/waterbase-uwwtd-urban-waste-water-treatment-directive-5#tab-additional-information (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- Fernanda-Jaramillo, M.; Restrepo, I. Wastewater Reuse in Agriculture: A Review about Its Limitations and Benefits. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BOE. Ley 9/2006, de 5 de diciembre, reguladora de Campos de Golf en la Comunitat Valenciana; Agencia Estatal Boletín Oficial del Estado: Valencia, Spain, 2007; p. 21. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/pdf/2007/BOE-A-2007-1300-consolidado.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2011).
- BOE. Ley 5/2014, de 25 de julio, de la Generalitat, de Ordenación del Territorio, Urbanismo y Paisaje, de la Comunitat Valenciana; Agencia Estatal Boletín Oficial del Estado: Valencia, Spain, 2014; p. 214. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/pdf/2014/BOE-A-2014-9625-consolidado.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2018).
- Ortuño, A.; Civera, S. El Riego en los Campos de Golf. El caso de la Provincia de Alicante (España) bajo una Comparativa Internacional; Publ. Univ. Alicante: Alicante, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jodar-Abellan, A.; Melgarejo, J.; Lopez-Ortiz, M.I. The Floodable Park “La Marjal” (Alicante, South East Spain) as a Paradigmatic Example of Water Reuse and Circular Economy. In WIT Transactions on The Built Environment; Syngellakis, S., Melgarejo, J., Eds.; WIT Press: London, UK, 2018; Volume 179, pp. 315–321. ISBN 978-1-78466-259-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, F.; De Las Fuentes, L.; Urkiaga, A. Guía para la realización de estudios de viabilidad en proyectos de reutilización de aguas depuradas; AQUAREC, MIMAM y Ministerio de Fomento: Madrid, Spain, 2006.
- INE. Encuesta sobre el Suministro y Saneamiento del Agua. 2015. Available online: http://www.ine.es/dyngs/INEbase/es/operacion.htm?c=Estadistica_C&cid=1254736176834&menu=ultiDatos&idp=1254735976602 (accessed on 4 July 2018).
- EPSAR. Entidad Pública de Saneamiento de Aguas residuales (EPSAR). Available online: http://www.epsar.gva.es/ (accessed on 10 May 2018).
- STJ. Sentencia del Tribunal de Justicia (Sala Octava) de 25 de julio de 2018. Comisión Europea contra Reino de España. Incumplimiento de Estado-Recogida y tratamiento de las aguas residuales urbanas-Directiva 91/271/CEE-Artículos 3 y 4-Sentencia del Tribunal de Justicia por la que se declara un incumplimiento-No ejecución-Artículo 260 TFUE, apartado 2-Sanciones pecuniarias-Multa coercitiva y suma a tanto alzado. Asunto C-205/17. ECLI identifier: ECLI:EU:C:2018:606. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/ES/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A62017CJ0205 (accessed on 24 may 2018).
| A. Communities 1 | Compliance Percentage (%) | A. Communities 1 | Compliance Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Andalucía | 73 | Comunidad Foral de Navarra | 100 |
| Aragón | 88 | Comunidad Valenciana | 90 |
| Canarias | 52 | Extremadura | 63 |
| Cantabria | 98 | Galicia | 64 |
| Castilla y León | 86 | Islas Baleares | 92 |
| Castilla La Mancha | 78 | La Rioja | 100 |
| Cataluña | 86 | País Vasco | 75 |
| Ciudad Autónoma de Ceuta | 100 | Principado de Asturias | 93 |
| Ciudad Autónoma de Melilla | 100 | Región de Murcia | 100 |
| Madrid | 100 |
| Budget (€) | Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Actions declared of General Interest (involves actions of River Basin districts and State Societies) | 1114 | 5.7 |
| Actions without WTP or with WTP not in accordance | 2903 | 14.8 |
| Actions to recently declared Sensitive areas | 4782 | 24.3 |
| Actions to cover future needs | 5620 | 28.6 |
| Actions to achieve objectives of the WFD | 1938 | 9.9 |
| Actions in sanitation (without purification) | 2741 | 14.0 |
| Actions to promote R+D+I in sanitation and purification | 547 | 2.8 |
| Total | 19,645 | 100.0 |
| Priority: 1, 2 and 3 (AGE + Autonomous Communities) | AGE | Aut. Communities | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° Actions | Investment (M€) | N° Actions | Investment (M€) | |
| Infringement in “Normal Zones” (Populations > 15,000 equivalent inhabitants). Infringement procedure n° 2004/2031. | 3 | 115 | 2 | 15 |
| Infringement in “Sensitive Zones” (Populations > 10,000 equivalent inhabitants). Infringement procedure n° 2002/2123. | 2 | 70 | 13 | 31 |
| Infringement in “Normal Zones” (2000 < Populations < 15,000 equivalent inhabitants); in “Sensitive Zones” (2000 < Populations <10,000 eq.inhabitants). Infringement procedure n° 2012/2100. | 101 | 212 | 269 | 635 |
| Total | 106 | 397 | 284 | 681 |
| Total of Both Administrations | ||||
| N° actions | 390 | |||
| Investment (M€) | 1078 | |||
| Actions | Resources Provided (hm3/year) |
|---|---|
| Complementary reuse of wastewater in Campo de Dalías (Almería) | 20 |
| Wastewater reuse actions in Almería | 10 |
| Wastewater reuse in the city of Málaga | 30 |
| Wastewater reuse in the Mar Menor (Murcia) | 25 |
| Wastewater reuse and complementary works in Villajoyosa and other annexed areas (Alicante) | 10 |
| Wastewater reuse in the WTP of Novelda and Monforte del Cid (Alicante) | 5 |
| Wastewater reuse in the WTP of Sueca (Valencia) | 10 |
| Reuse of treated wastewaters in the Albufera Sur (Valencia) | 5 |
| Wastewater reuse in the Vinalopó-Alacantí system (Alicante) | 5 |
| Improvement of wastewater treatment and reuse in the Plana de Castellón (Castellón) | 20 |
| Completion of the wastewater reuse from Pinedo (Valencia) | 30 |
| Total | 170 |
| Total | Supply | Sanitation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Andalucía | 1.74 | 1.04 | 0.7 |
| Aragón | 1.46 | 0.7 | 0.76 |
| Asturias | 1.32 | 0.68 | 0.64 |
| Baleares | 2.21 | 1.11 | 1.1 |
| Canarias | 2.03 | 1.66 | 0.37 |
| Cantabria | 1.56 | 0.91 | 0.65 |
| Castilla y León | 1.0 | 0.54 | 0.46 |
| Castilla-La Mancha | 1.28 | 0.79 | 0.49 |
| Cataluña | 2.54 | 1.34 | 1.2 |
| Comunidad Valenciana | 2.03 | 1.23 | 0.8 |
| Extremadura | 1.49 | 1.04 | 0.45 |
| Galicia | 1.19 | 0.77 | 0.42 |
| Madrid | 2.02 | 1.28 | 0.74 |
| Murcia | 2.73 | 1.86 | 0.87 |
| Navarra | 1.47 | 0.73 | 0.74 |
| País Vasco | 1.52 | 0.75 | 0.77 |
| La Rioja | 1.06 | 0.5 | 0.56 |
| Ceuta y Melilla | 1.95 | 1.37 | 0.58 |
| Average unit cost | 1.83 | 1.09 | 0.74 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jodar-Abellan, A.; López-Ortiz, M.I.; Melgarejo-Moreno, J. Wastewater Treatment and Water Reuse in Spain. Current Situation and Perspectives. Water 2019, 11, 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081551
Jodar-Abellan A, López-Ortiz MI, Melgarejo-Moreno J. Wastewater Treatment and Water Reuse in Spain. Current Situation and Perspectives. Water. 2019; 11(8):1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081551
Chicago/Turabian StyleJodar-Abellan, Antonio, María Inmaculada López-Ortiz, and Joaquín Melgarejo-Moreno. 2019. "Wastewater Treatment and Water Reuse in Spain. Current Situation and Perspectives" Water 11, no. 8: 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081551
APA StyleJodar-Abellan, A., López-Ortiz, M. I., & Melgarejo-Moreno, J. (2019). Wastewater Treatment and Water Reuse in Spain. Current Situation and Perspectives. Water, 11(8), 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081551







