Effects of Different Irrigation Treatments on Aquaculture Purification and Soil Desalination of Paddy Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Experimental Design and Irrigation Management
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality Indexes
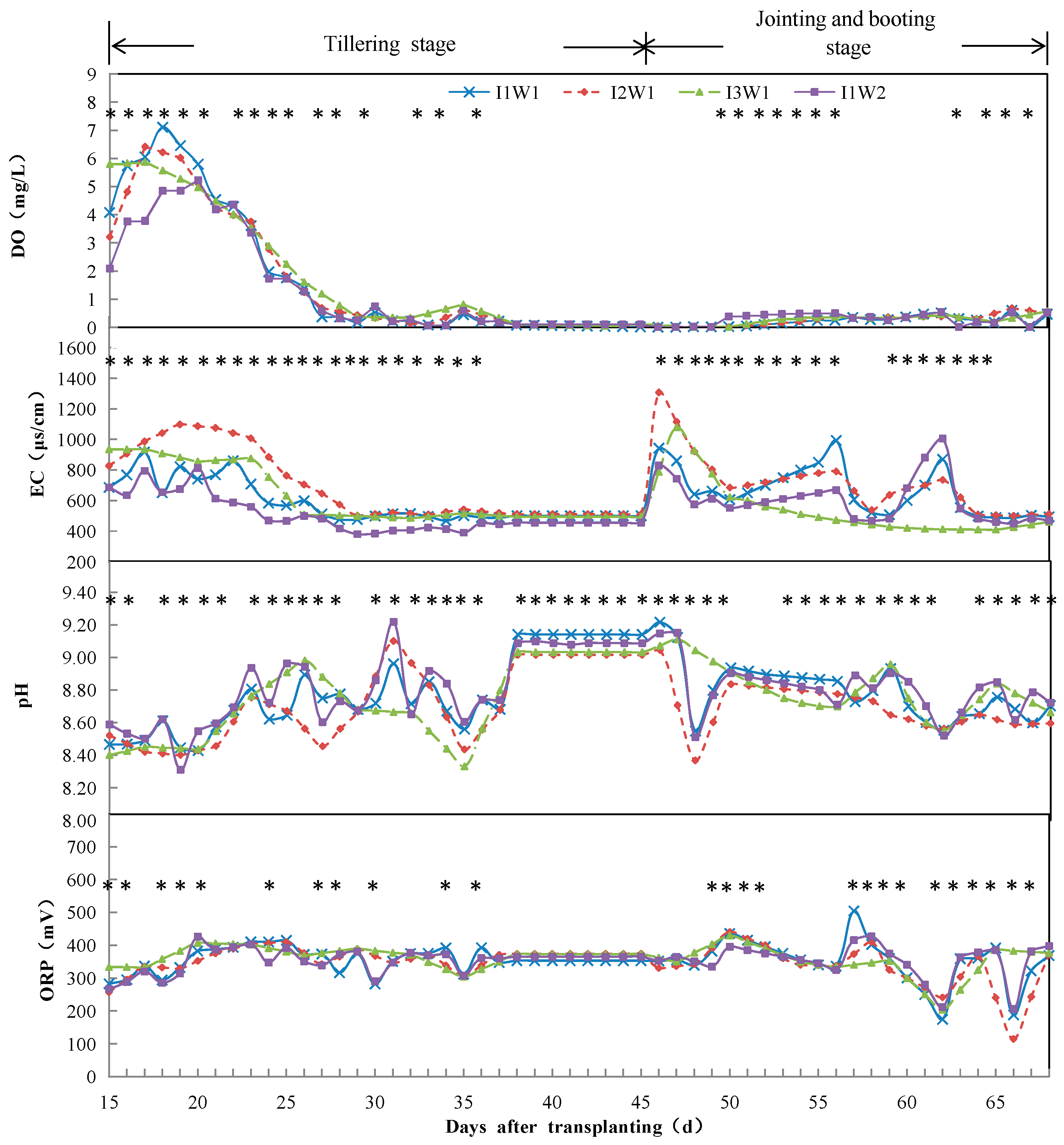
3.1.1. Temporal Variation of DO
3.1.2. Temporal Variation of EC
3.1.3. Temporal Variation of pH
3.1.4. Temporal Variation of ORP
3.2. The TN and TP Losses through Discharge
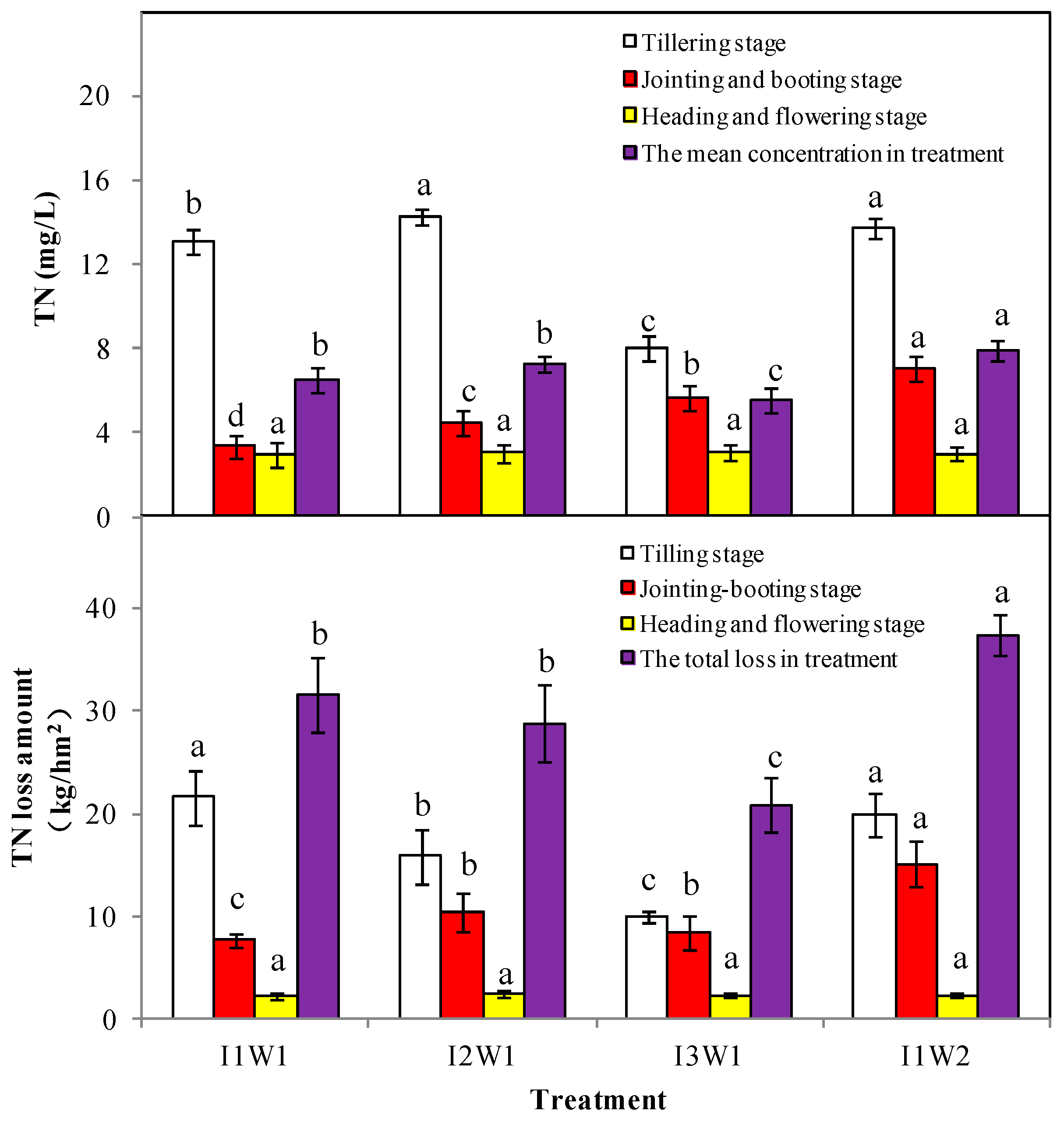
3.2.1. The TN Losses for Surface Discharge
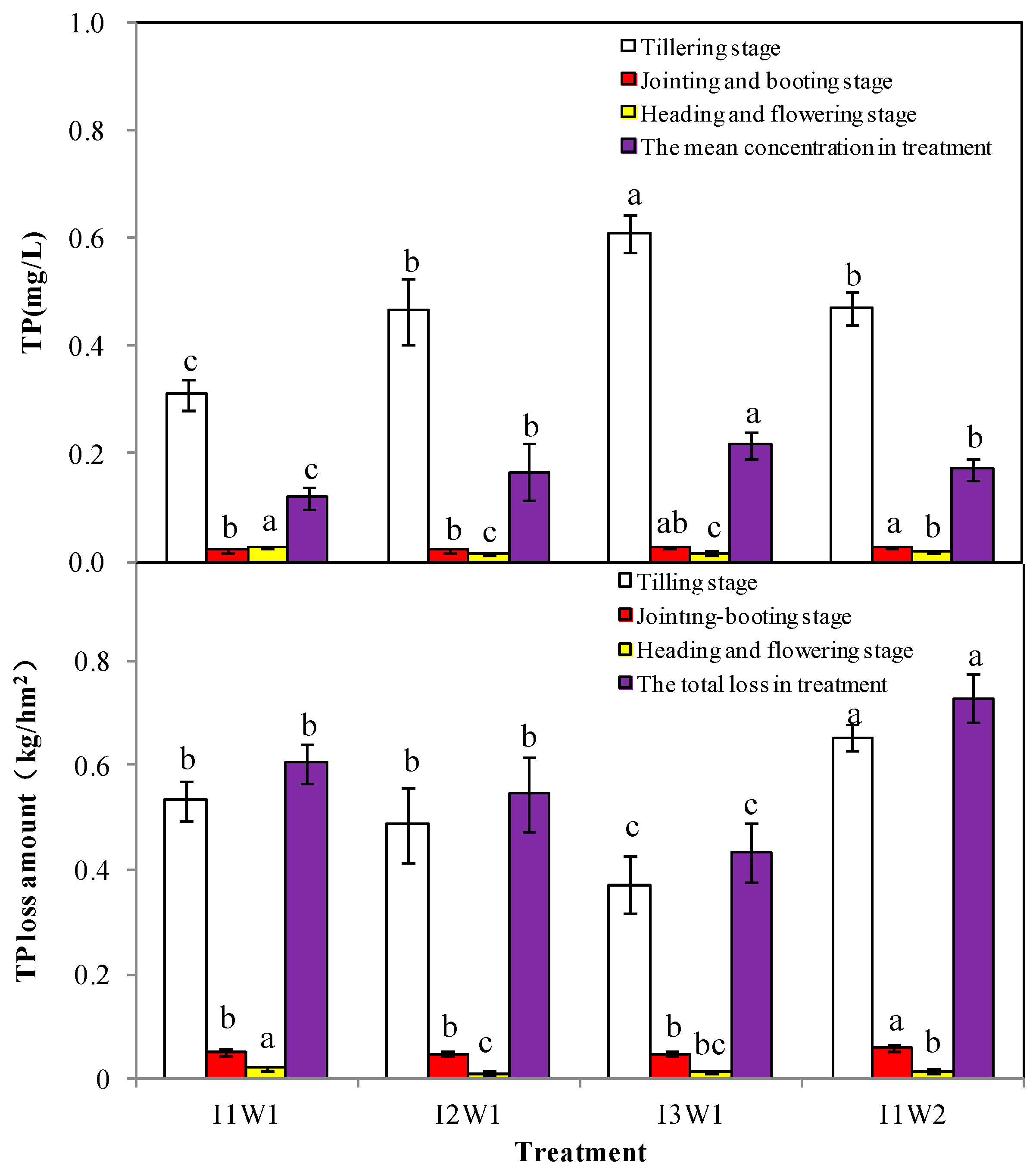
3.2.2. The TP Losses for Surface Discharge
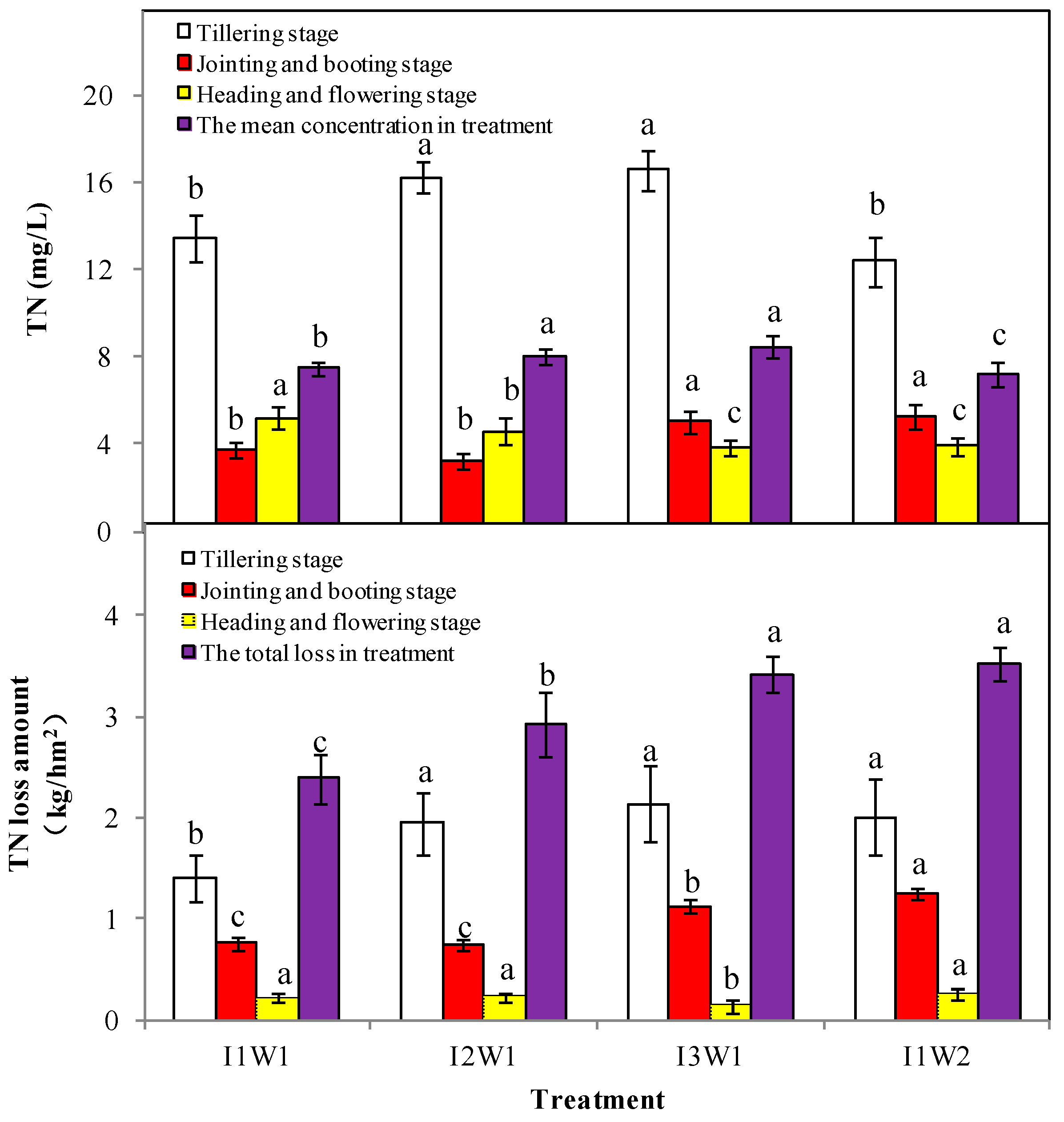
3.2.3. The TN Losses for Ground Discharge
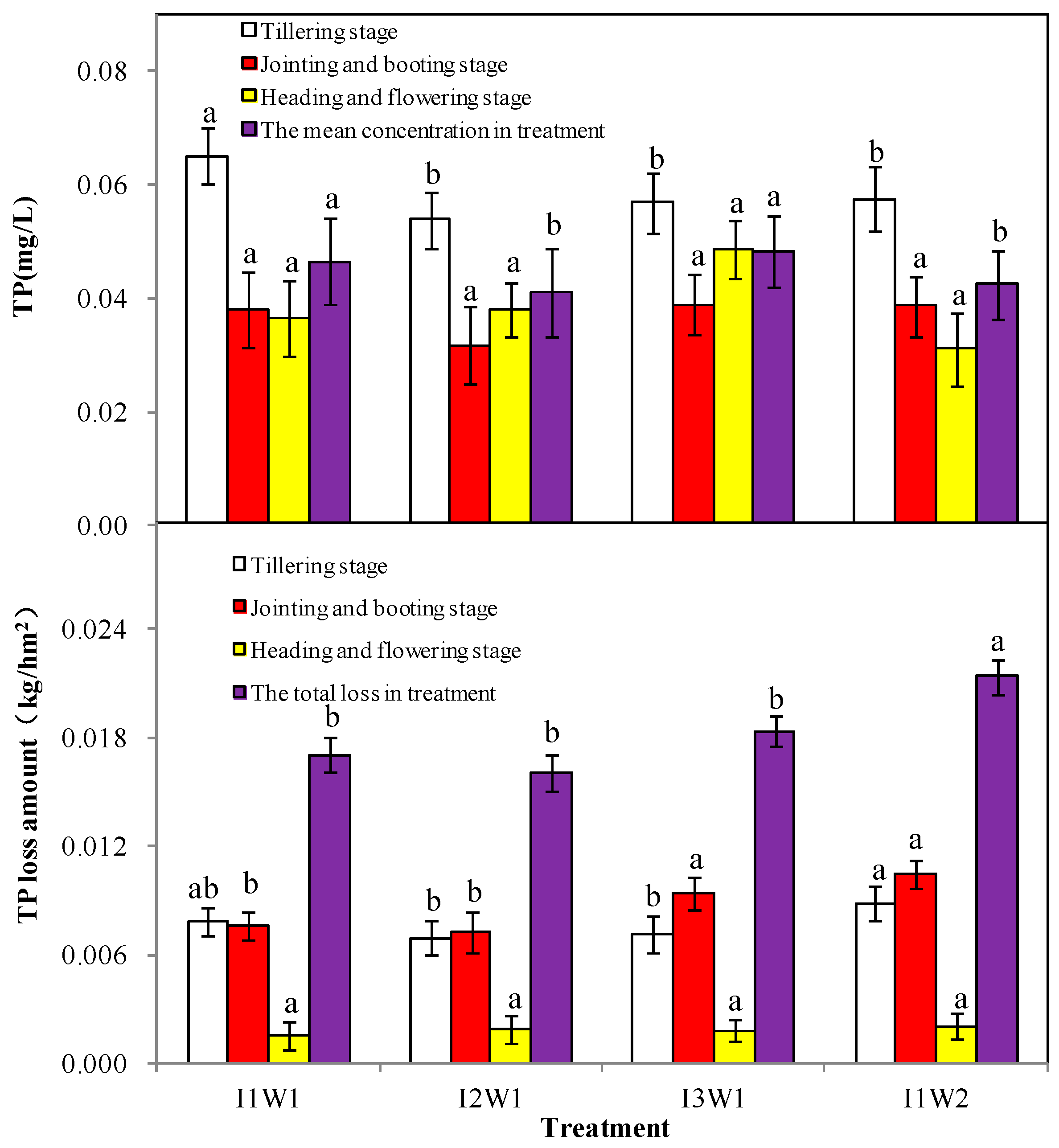
3.2.4. The TP Losses for Ground Discharge
3.3. The Change of Growth Indexes
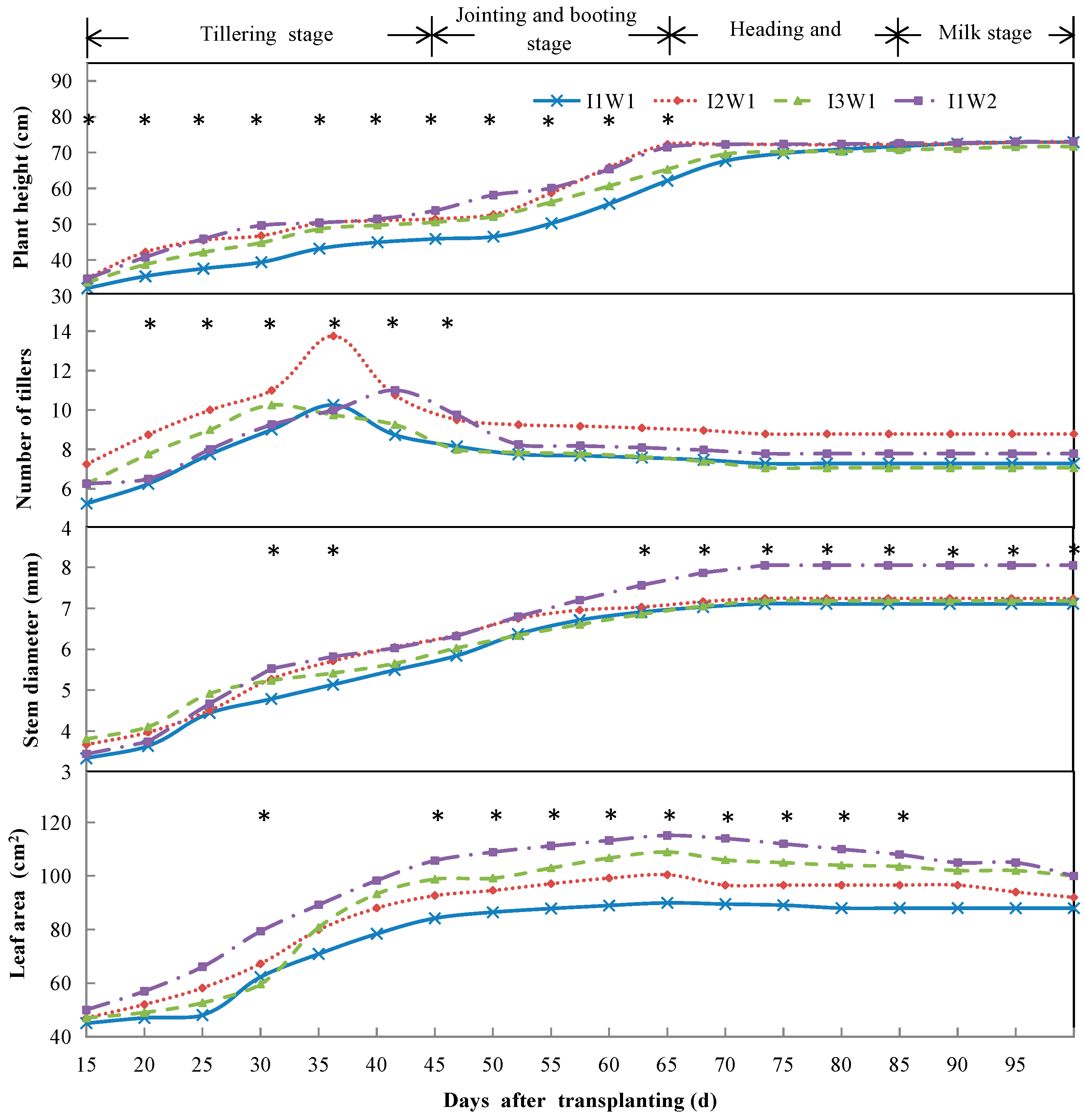
3.3.1. Temporal Variation of Plant Height
3.3.2. Temporal Variation in the Number of Tillers
3.3.3. Temporal Variation in Stem Diameters
3.3.4. Temporal Variation of Leaf Area
3.4. Grain Yields and Soil Salinity
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Quality Indexes
4.1.1. DO
4.1.2. EC
4.1.3. pH
4.1.4. ORP
4.2. The TN and TP Losses through Discharge
4.3. Growth Indexes
4.4. Grain Yields
4.5. Soil Salinity
4.6. Significance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations and Symbols
| TN | total nitrogen |
| TP | total phosphorus |
| I1 | shallow–frequent irrigation |
| I2 | shallow–wet irrigation |
| I3 | flooding irrigation |
| W1 | aquaculture wastewater |
| W2 | fresh water |
| CF | compound fertilizer |
| U | urea |
| DO | dissolved oxygen |
| EC | electrical conductivity |
| pH | potential of hydrogen |
| ORP | oxidation-reduction potential |
References
- Zhang, C.X.; Liu, W.D.; Luo, Y.L. Current Situation, Problems and Reflections on Sustainable Development and Utilization of Land Resources in China. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Education and Management, Dalian, China, 6–7 August 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Ho, S. China Land: Insights from the 1996 Land Survey. Land Use Policy 2003, 20, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, M.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Zheng, J.; Qiu, R. Effects of uneven vertical distribution of soil salinity under a buried straw layer on the growth, fruit yield, and fruit quality of tomato plants. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 203, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qun, L.; Yong, Y. The Tidal Flat Geomorphology of Jiangsu Coast Area and Ways of Resources Development and Exploitation. Henan Sci. 2010, 28, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindran, K.C.; Venkatesan, K.; Balakrishnan, V.; Chellappan, K.P.; Balasubramanian, T. Restoration of saline land by halophytes for Indian soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2661–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, F.M. Role of natural vegetation in improving salt affected soil in northern Egypt. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 64, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Chen, J.; Ge, X.; Meng, S.; Fan, L.; Hu, G. The Relationship between the Area of Aquaculture Pond and Purification Pond in Water Circulation Aquaculture System. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 61, 301–315. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Q. A study on regional difference of fresh water resources shortage in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2001, 16, 516–520. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, F.F.; Com, F. Nutrients Removal From Fish Pond by Rice Planting. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2015, 29, 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, G.Z. Pollution in Pounds at Side of Ehai Lake. Yunnan Environ. 2000, 19, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J. Experiments on nitrogen and phosphorus losses from paddy fields under different scales. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hamoud, Y.A.; Guo, X.P.; Wang, Z.C.; Chen, S.; Rasool, G. Effects of irrigation water regime, soil clay content and their combination on growth, yield, and water use efficiency of rice grown in South China. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 144–155. [Google Scholar]
- Carreres, R.; Tome, R.G.; Sendra, J.; Ballesteros, R.; Valiente, E.F.; Quesada, A.; Nieva, M.; Leganés, F. Effect of nitrogen rates on rice growth and biological nitrogen fixation. J. Agric. Sci. 1996, 127, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Piernas, A.B.; Plaza-Bolaños, P.; García-Gómez, E.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Agüera, A. Determination of organic microcontaminants in agricultural soils irrigated with reclaimed wastewater: Target and suspect approaches. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1030, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; An, P.; Li, X.; Guo, K.; Yang, C.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of soil water and salinity after establishment of dense-foliage Tamarix chinensis on coastal saline land. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 121, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.H. The knowledge of fish ponds changing water. Sci. Fish Farming 2004, 4, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Cao, C.L.; Ren, L.J.; Tian, S.; Li, N.; An, S.Q.; Leng, X. Research on Pollutants Removal Effect of Different Combined Substrate under Different Hydraulic Retention Time in Vertical Flow Constructed Wetlands. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 25, 292–299. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; APHA, AWWA, WEF: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.-J.; Zhu, L.-F.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, J.-H.; Cao, X.-C.; Yu, S.-M.; Allen, B.J.; Jin, Q.-Y. Effects of dissolved oxygen on nitrogen transformation in paddy soil and nitrogen metabolism of rice: A review. Chin. J. Ecology 2017, 36, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar]
- Reich, P.B.; Walters, M.B.; Tjoelker, M.G.; Vanderklein, D.; Buschena, C. Photosynthesis and respiration rates depend on leaf and root morphology and nitrogen concentration in nine boreal tree species varying in RGR. Funct. Ecol. 1998, 12, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.Q.; Lin, S.M. Study on dissolved oxygen in aquaculture. Feed Ind. 2007, 28, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Colt, J. Computation of Dissolved Gas Concentrations in Water as Functions of Temperature, Salinity, and Pressure. Am. Fish. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1984, 14, 154. [Google Scholar]
- Rixen, T.; Baum, A.; Sepryani, H.; Pohlmann, T.; Jose, C.; Samiaji, J. Dissolved oxygen and its response to eutrophication in a tropical black water river. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.F.; Peterson, M.L.; Solbau, R.D. Measurement and Interpretation of Low Levels of Dissolved Oxygen in Ground Water. Groundwater 2010, 28, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Shukla, A.; Mani, S.C.; Kumar, P. Hypoxia induced non-apoptotic cellular changes during aerenchyma formation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2010, 16, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ansa-Asare, O.D.; Marr, I.L.; Cresser, M.S. Evaluation of Modelled and Measured Patterns of Dissolved Oxygen in a Freshwater Lake as an Indicator of the Presence of Biodegradable Organic Pollution. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Luo, W.; Jia, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Y. Variation characteristics of salinity in water of drainage ditches in saline lands. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2013, 31, 811–815. [Google Scholar]
- Bhoades, J.D.; Chanduvi, F.; Leseh, S. Soil Salinity Assessment. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Papers. 1999, 57, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; He, J.; Peng, J.; Zhang, S. Correlation between Fertilized Amount and Solution Conductivity in Floating Pool and Effects on Culturing Robust Seedlings of Tobacco. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 25, 2167–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, D.F.; Yan, S.F.; Yang, Y.; Xu, B.; Shang, J. Desalination Experiment in Saline Soil of Jiangsu Province Coastal Area under Saturated Infiltration Condition. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 10, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, N.; Carranca, C.; Goufo, P.; Pereira, J.; Trindade, H.; Coutinho, J. Impact of agricultural practices, elevated temperature and atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration on nitrogen and pH dynamics in soil and floodwater during the seasonal rice growth in Portugal. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 145, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J. Greenhouse Gases Concentration, Emission and Influence Factors in Farming Waters. Master’s Degree Dissertation, Hua Zhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Haitao, W.; Xianguo, L.; Qing, Y.; Ming, J.; Shouzheng, T. Early-stage litter decomposition and its influencing factors in the wetland of the Sanjiang Plain, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 4027–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.C.; Niu, Y.Z.; Xu, Q.Z.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhang, X.Q. Relationship between plant type and canopy apparent photosynthesis in maize (Zea mays L.). Biol. Plant. (Prague) 1995, 37, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Ortiz, R.; Steele, T.W.; Stuckey, D.C. Toxicants inhibiting anaerobic digestion: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peddie, C.C.; Mavinic, D.S.; Jenkins, C.J. Use of ORP for Monitoring and Control of Aerobic Sludge Digestion. J. Environ. Eng. 1990, 116, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.G.; Bao, X.T.; Zu, H.; Zhou, H.Y.; Liang, C.; Liu, X.G. Typical correlation analysis was used for key factors of pond culture environment. Fish. Mod. 2015, 42, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bonaiti, G.; Borin, M. Efficiency of controlled drainage and subirrigation in reducing nitrogen losses from agricultural fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, A.P.; Li, Y.H.; Chen, C.; Hong, Y.; Yang, Z.L. Types of Fertilizers and Their Application Affect the Leaching of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Paddy Fields in Irrigation Districts of Yellow River. J. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 36, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacic, D.A.; David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E.; Starks, K.M.; Cooke, R.A. Effectiveness of Constructed Wetlands in Reducing Nitrogen and Phosphorus Export from Agricultural Tile Drainage. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Zhang, A.P.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, F.; Zhao, T.C.; Chen, C.; Hong, Y. Rice Yield, Nitrogen Use Efficiency(NUE) and Nitrogen Leaching Losses as Affected by Long-term Combined Applications of Manure and Chemical Fertilizers in Yellow River Irrigated Region of Ningxia, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 947–954. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Shao, D.; Gu, W.; Liu, H. Field analysis of water and nitrogen fate in lowland paddy fields under different water managements using HYDRUS-1D. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 150, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Kadlec, R.H.; Flaig, E.; Gale, P.M. Phosphorus Retention in Streams and Wetlands: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Control 1999, 29, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Sun, J.; Li, C.X.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, J.G.; Zhao, H.W.; Zou, D.T. Genetic dissection of the developmental behavior of plant height in rice under different water supply conditions. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2688–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyrouty, C.A.; Norman, R.J.; Wells, B.R.; Gbur, E.E.; Grigg, B.; Teo, Y.H. Water management and location effects on root and shoot growth of irrigated lowland rice. J. Plant Nutr. 1992, 15, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Song, D.T.; Zou, G.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Nie, J.H. Effect of Different Organic Fertilizers on Growth and Quality of Tomato. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2008, 24, 300–305. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.M.; Ladha, J.K.; Khan, S.R.; Khan, A.H.; Buresh, R.J. Leaf color chart for managing nitrogen fertilizer in lowland rice in Bangladesh. Agron. J. 1952, 97, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.; Bynum, E.D.; Archer, T.L.; Lascano, R.J.; Wilson, L.T.; Bordovosky, J.; Segarra, E.; Bronson, K.; Nesmith, D.M.; Xu, W. Spatial and temporal variability of corn growth and grain yield, implications for site-specific farming. Crop Sci. 2002, 42, 1564–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venuprasad, R.; Dalid, C.O.; Del Valle, M.; Zhao, D.; Espiritu, M.; Cruz, M.S.; Atlin, G.N. Identification and characterization of large-effect quantitative trait loci for grain yield under lowland drought stress in rice using bulk-segregant analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 120, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotera, A.; Nawata, E. Role of plant height in the submergence tolerance of rice: A simulation analysis using an empirical model. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Rasool, G.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Yousef, A.H.; Shao, G. Effects of vertically heterogeneous soil salinity on tomato photosynthesis and related physiological parameters. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 249, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.L.; Zhang, M.Y. Desalting Effect of Soil under Different Infiltration Conditions. J. Irrig. Drain. 2008, 27, 116–117. [Google Scholar]
| Irrigation Treatments | Limit | Re-Greening | Tillering | Jointing and Booting | Heading and Flowering | Milk Maturity | Yellow Maturity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Late | |||||||
| I1 1 | Upper limit of irrigation/mm | 20~30 | 15 | 35 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| The duration of aquaculture wastewater kept in the soil surface/d | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Naturally drying | ||
| I2 | Upper limit of irrigation/mm | 20~30 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| The duration of aquaculture wastewater kept in the soil surface/d | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Naturally drying | ||
| I3 | Upper limit of irrigation/mm | 20~30 | 35 | 65 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 0 |
| The duration of aquaculture wastewater kept in the soil surface/d | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Naturally drying | ||
| Year | Activity | W1 2 | W2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | Base fertilizer (21 June) 1 | 300.0 (CF) 3 | 300.0 (CF) |
| Re-greening fertilizer (4 July) | 75.0 (U) | 150.0 (U) | |
| Tillering fertilizer (15 July) | 62.5 (U) | 125.0 (U) | |
| Panicle fertilizer (18 August) | 75.0 (U) | 150.0 (U) | |
| Total nitrogen | 512.5 | 725 |
| Years | Treatments | Number of Grains per Panicle | Seed Setting Rate/% | Thousand Grain Weight/g | Grain Yield/kg·hm−2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | I1W1 1 | 74.92 a 2 | 75.01 a | 23.45 a | 3860.44 b |
| I2W1 | 70.00 a | 76.60 a | 23.11 a | 3942.59 a b | |
| I3W1 | 69.84 a | 75.63 a | 22.94 a | 3491.66 b | |
| I1W2 | 71.15 a | 78.75 a | 23.22 a | 4421.05 a |
| Treatments | I1W1 1 | I2W1 | I3W1 | I1W2 |
| Soil Salinity/‰ | 2.34 | 2.24 | 1.98 | 2.25 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Lakthan, S.; Chen, S.; Xiao, Z.; Alhaj Hamoud, Y. Effects of Different Irrigation Treatments on Aquaculture Purification and Soil Desalination of Paddy Fields. Water 2019, 11, 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071424
Xie Y, Wang Z, Guo X, Lakthan S, Chen S, Xiao Z, Alhaj Hamoud Y. Effects of Different Irrigation Treatments on Aquaculture Purification and Soil Desalination of Paddy Fields. Water. 2019; 11(7):1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071424
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yi, Zhenchang Wang, Xiangping Guo, Sirikanya Lakthan, Sheng Chen, Zhiming Xiao, and Yousef Alhaj Hamoud. 2019. "Effects of Different Irrigation Treatments on Aquaculture Purification and Soil Desalination of Paddy Fields" Water 11, no. 7: 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071424
APA StyleXie, Y., Wang, Z., Guo, X., Lakthan, S., Chen, S., Xiao, Z., & Alhaj Hamoud, Y. (2019). Effects of Different Irrigation Treatments on Aquaculture Purification and Soil Desalination of Paddy Fields. Water, 11(7), 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071424






