Development of a Combined Aerobic–Anoxic and Methane Oxidation Bioreactor System Using Mixed Methanotrophs and Biogas for Wastewater Denitrification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methanotrophs and Activated Sludge
2.2. Methanotroph Culture Solution
2.3. Biogas Source
2.4. Analysis and Measurements
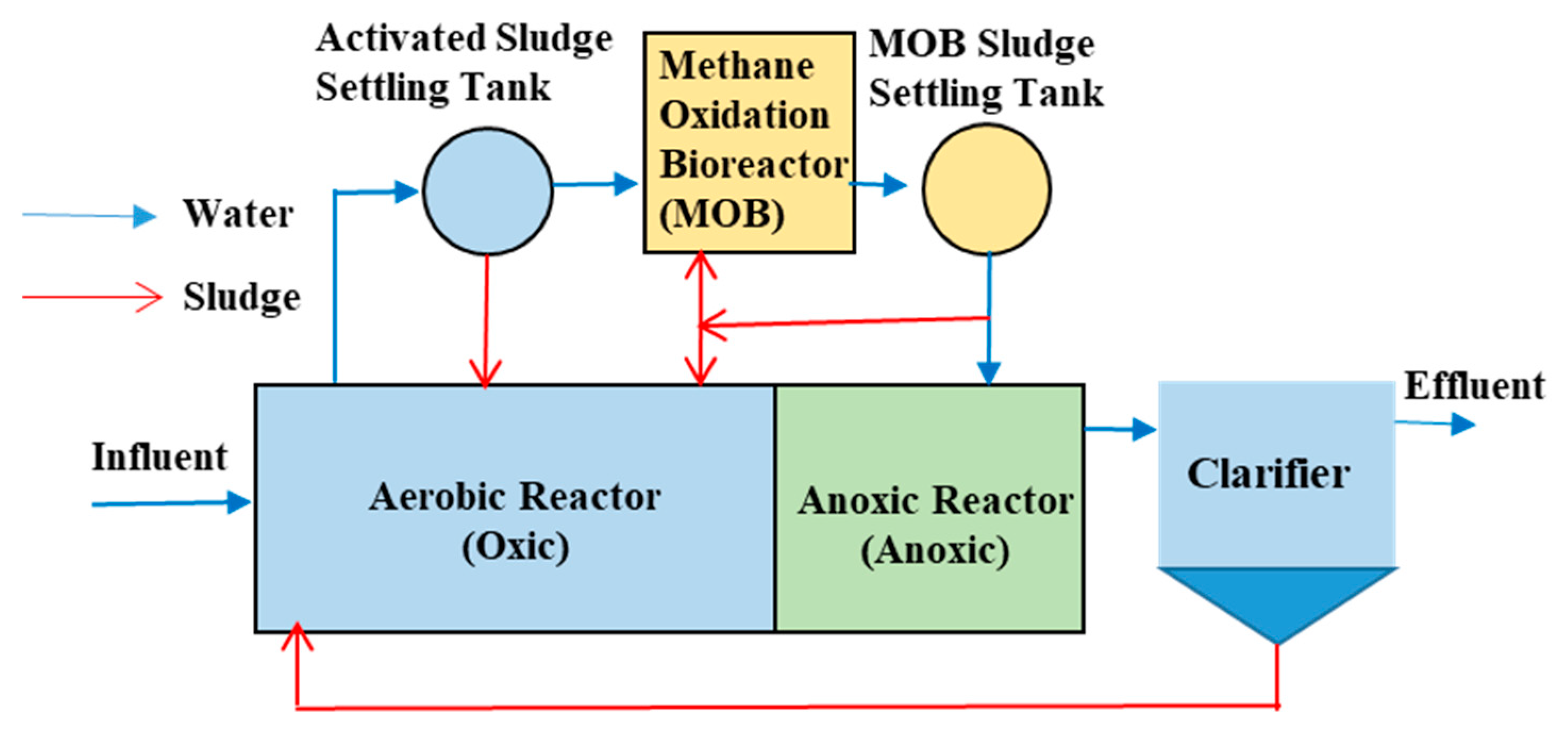
2.5. Treatment Process Composition
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Methanol Production in the MOB and Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal
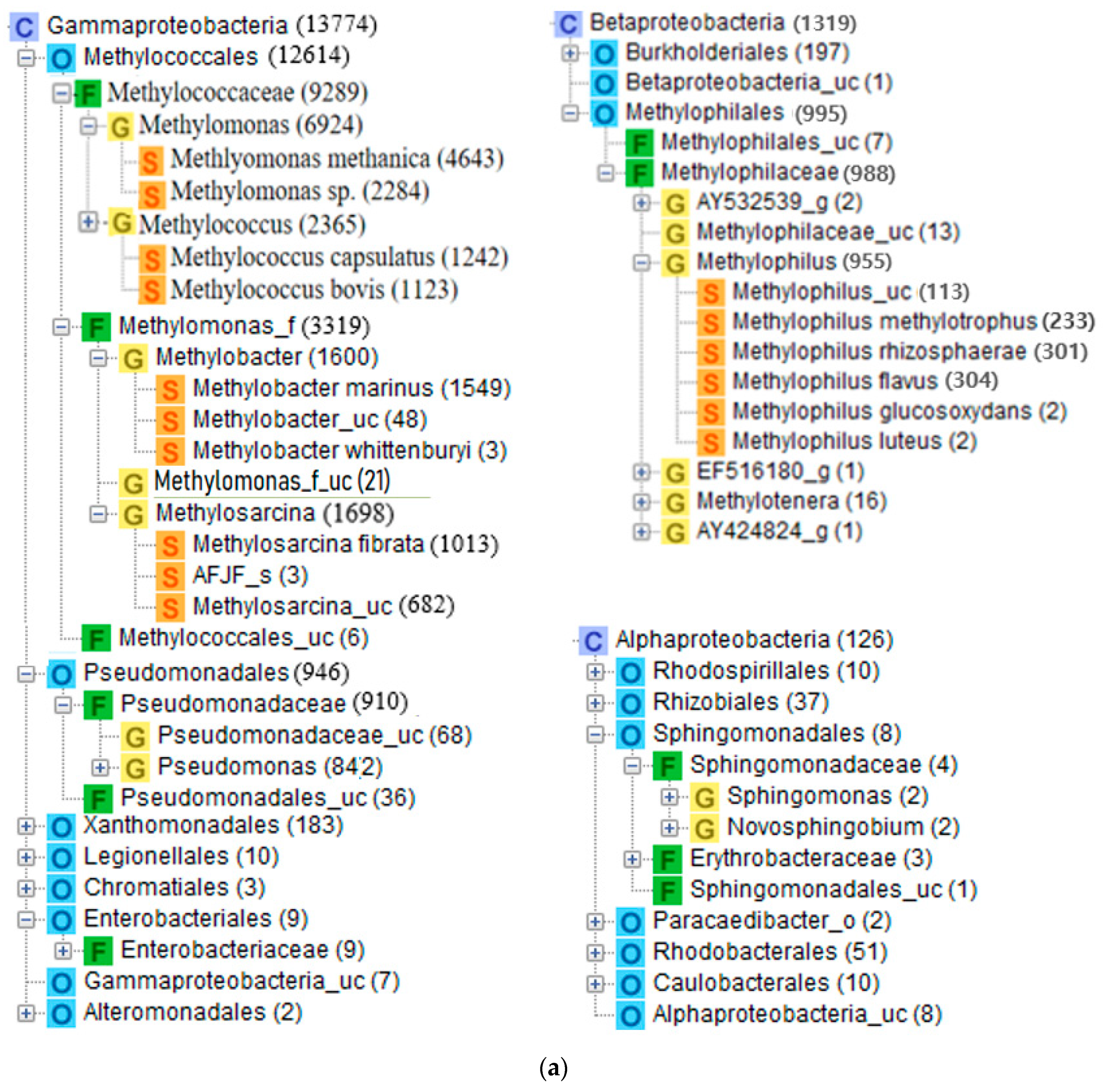
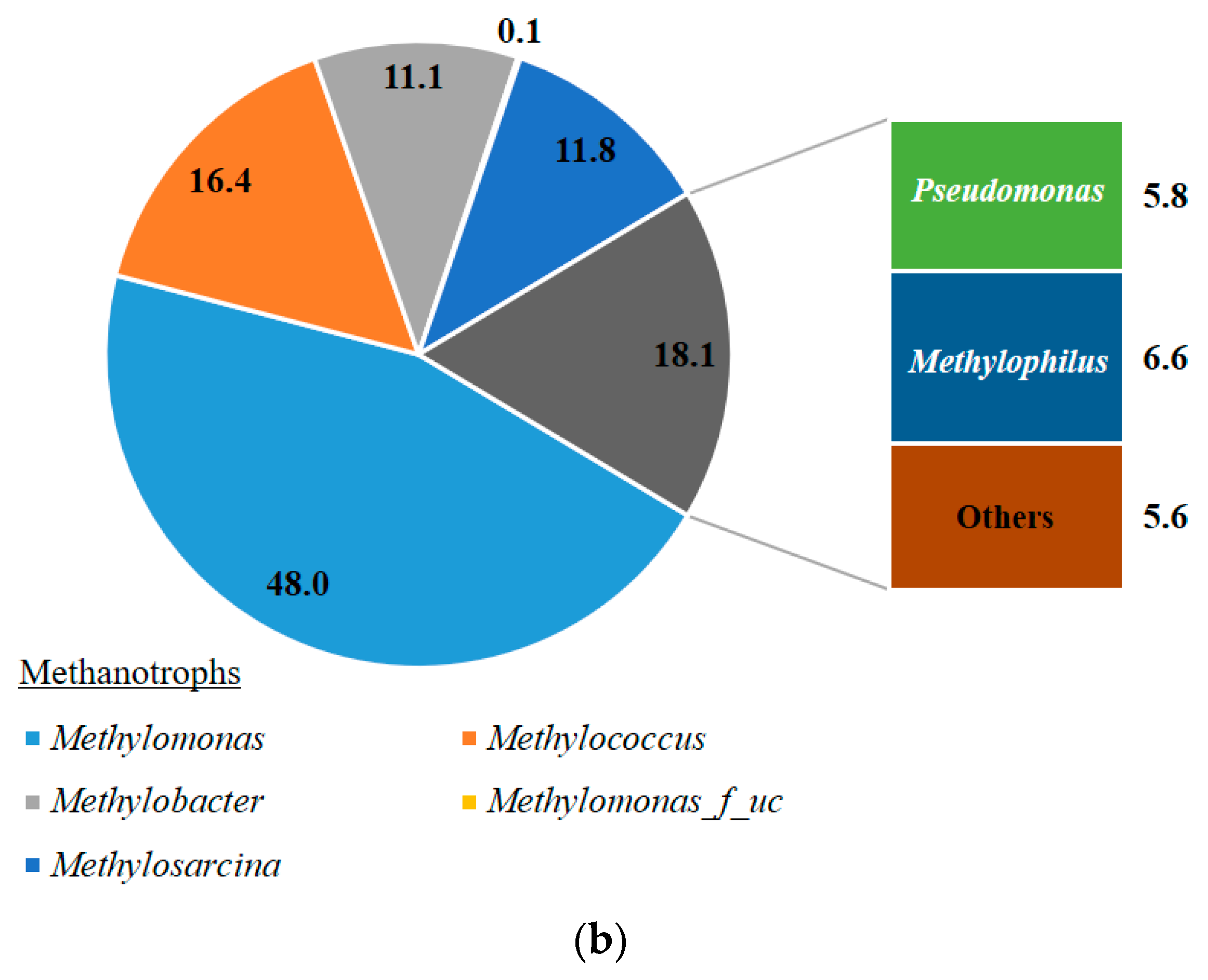
3.2. Microbial Consortium in the MOB
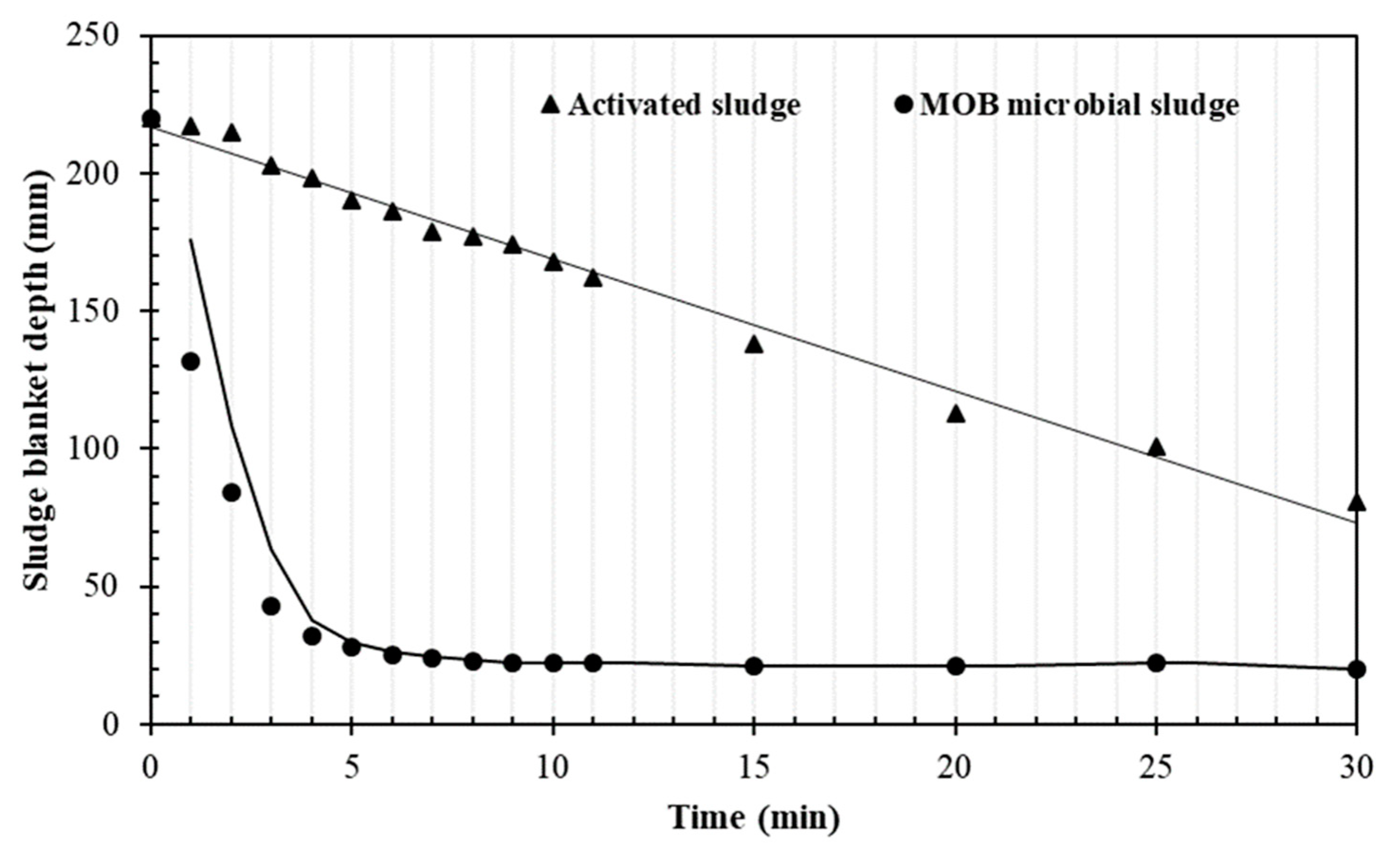
3.3. Sedimentation Properties of the Methanotrophic Microbial Consortium
3.4. Denitrification Efficiency
3.4.1. Aerobic–Anoxic Process
3.4.2. Aerobic–MOB–Anoxic Process
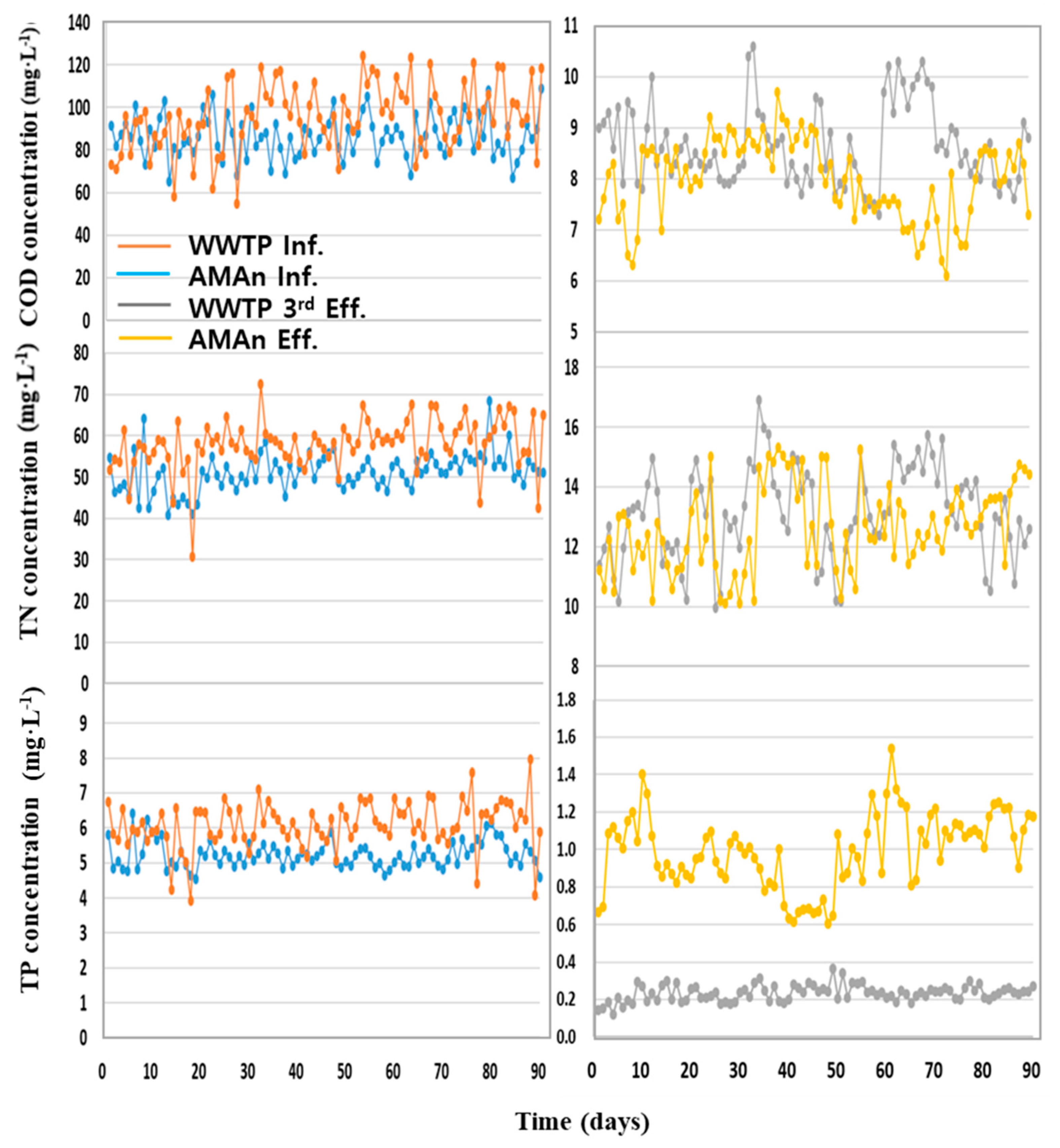
3.4.3. Comparison with a Tertiary Advanced WWTP Facility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mechsner, K.L.; Hamer, G. Denitrification by Methanotrophic, Methylotrophic Bacterial Associations in Aquatic Environments; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 257–271. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, M.; Kayser, R. Denitrification with Biogas as External Carbon Source. Water Sci. Technol. 1991, 23, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalasso, F.; Vallecillo, A.; Garcıa-Encina, P.; Fdz-Polanco, F. The use of methane as a sole carbon source for wastewater denitrification. Water Res. 1997, 31, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houbron, E.P.; Torrijos, M.; Capdeville, B. An Alternative Use of Biogas Applied at the Water Denitrification. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, J.P.; Scutt, J.E. Denitrification with natural gas and various new growth media. Water Res. 1999, 33, 3723–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, C.; Knowles, R. Physiology, biochemistry, and specific inhibitors of CH4, NH4+, and CO oxidation by methanotrophs and nitrifiers. Microbiol. Rev. 1989, 53, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calsen, H.N.; Joergensen, L.; Degn, H. Inhibition by ammonia of methane utilization in Methylococcus capsulatus (Bath). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1991, 35, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Applegate, C.S.; Wilder, B.; DeShaw, J.R. Total Nitrogen Removal in a Multichemical Oxidation System. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1980, 52, 568–577. [Google Scholar]
- Ludzack, F.J.; Ettinger, M.B. Controlling Operation to Minize Activated Sludge Effluent Nitrogen. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1962, 34, 920–931. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, I.J.; Best, D.J.; Hammond, R.C.; Scott, D. Methane-oxidizing microorganisms. capsularus (Bath). Its ability to oxygenate n-alkanes. Microbiol. Rev. 1981, 45, 556–590. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.K.; Mardina, P.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, I.W. Biological Methanol Production by a Type II Methanotroph Methylocystis bryophila. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardina, P.; Li, J.; Patel, S.K.S.; Kim, I.W.; Lee, J.K.; Selvara, C. Potential of Immobilized Whole-Cell Methylocella tundrae as a Biocatalyst for Methanol Production from Methane. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.T.; Yoo, Y.S.; Yoon, Y.H.; Lee, Y.E.; Jo, J.H.; Jeong, W.; Kim, K.-S. Bio-Methanol Production Using Treated Domestic Wastewater with Mixed Methanotroph Species and Anaerobic Digester Biogas. Water 2018, 10, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raunkjær, K.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.; Nielsen, P.H. Measurement of pools of protein, carbohydrate and lipid in domestic wastewater. Water Res. 1994, 28, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhiwei, W.Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, G.; Gu, G. Sludge rheological and physiological characteristics in a pilot-scale submerged membrane bioreactor. Desalination 2007, 212, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, C. The Biochemistry of Methylotrophs; Academic Press Ltd.: London, UK, 1982; pp. 235–279. [Google Scholar]
- Trotsenko, Y.A.; Shishkina, V.N. Studies on phosphate metabolism in obligate methanotrophs. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1990, 87, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaduraia, G.; Juangb, R.S.; Lee, D.J. Microbiological degradation of phenol using mixed liquors of Pseudomonas putida and activated sludge. Waste Manage. 2002, 22, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, T.; Okamoto, T.; Nishiyama, N. Biodegradation of didecyldimethyl ammonium chloride by Pseudomonas fluorescens TN4 isolated from activated sludge. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanya, V.; Usharani, M.V.; Jayadev, P. Biodegradation of cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone using mixed culture of Pseudomonas in activated sludge process. J. Environ. Res. Dev. 2016, 11, 324–331. [Google Scholar]
- Osaka, T.; Yoshie, S.; Tsuneda, S.; Hirata, A.; Iwami, N.; Inamori, Y. Identification of acetate- or methanol- assimilating bacteria under nitrate-reducing conditions by stable-isotope probing. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogleva, A.A.; Kaparullina, E.N.; Doronina, N.V.; Trotsenko, Y.A. Methylophilus flavus sp. nov. and Methylophilus luteus sp. nov., aerobic, methylotrophic bacteria associated with plants. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2623–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, D.A.C.; McTaggart, T.L.; Setboonsarng, U.; Vorobev, A.; Kalyuzhnaya, M.G.; Ivanova, N.; Goodwin, L.; Woyke, T.; Lidstrom, M.E.; Chistoserdova, L. The expanded diversity of Methylophilaceae from Lake Washington through cultivation and genomic sequencing of novel ecotypes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhaiyan, M.; Poonguzhali, S.; Kwon, S.; Sa, T. Methylophilus rhizosphaerae sp. nov., a restricted facultative methylotroph isolated from rice rhizosphere soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2904–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, P.L.; Beck, L.; Amant, P.S. Biological Denitrification of Wastewater by Addition of Organic Materials. In Proceedings of the 24th Industrial Waste Conference, Lafayette, IN, USA, 6–8 May 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf & Eddy Inc. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse, 4th ed.; Tchobanoglous, G., Burton, F.L., Stensel, H.D., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Concentration (mg·L−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Sewage | Treated Wastewater | |
| COD | 94.9 | 12.4 |
| NH3-N | 44.8 | 16.7 |
| NO3−-N | 4.6 | 15.3 |
| PO43−-P | 5.8 | 1.6 |
| Reactor | MLSS (mg·L−1) | Inflow (L·day−1) | HRT (h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerobic | 2200–2300 | 24 | 4.3 |
| Anoxic | 2300–2400 | – | 1.7 |
| MOB | 1000–1200 | – | 3 |
| Sludge Inoculant | Time (h) | Methanol (mg·L−1) | Formaldehyde (mg·L−1) | MLSS (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activated sludge | 3 | <0.52 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 520 |
| Methanotrophs | 1 | 12.13 ± 0.31 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | 520 |
| 3 | 35.23 ± 1.21 | 1.74 ± 0.08 | 520 |
| Parameter | Initial Concentration (mg·L−1) | Concentration after 3 h (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|
| COD | 12.42 ± 0.22 | 59.84 ± 0.62 |
| NH3-N | 16.75 ± 0.18 | 2.16 ± 0.06 |
| NO3−-N | 15.33 ± 0.21 | 1.23 ± 0.03 |
| PO4−3-P | 1.68 ± 0.02 | 0.62 ± 0.01 |
| Characteristic | Activated Sludge | MOB Sludge |
|---|---|---|
| EPS protein (mg·g VSS−1) | 76.8 ± 4.9 | 106.2 ± 9.4 |
| EPS polysaccharide (mg·g VSS−1) | 31.4 ± 3.2 | 46.5 ± 2.6 |
| Particle size (µm) | 107 ± 12 | 742 ± 22 |
| Parameter | Influent (mg·L−1) | Aerobic–Anoxic Process | Activated Sludge Process | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effluent Concentration (mg·L−1) | Removal Rate (%) | Effluent Concentration (mg·L−1) | Removal Rate (%) | ||
| COD | 106.3 | 11.1 ± 1.6 | 89.56 | 26.3 ± 2.6 | 75.25 |
| NH3-N | 17.2 | 0.68 ± 0.04 | 96.05 | 14.98 ± 1.5 | 10.30 |
| NO3−-N | 1.7 | 9.9 ± 1.3 | 41.92 (as TN) | 2.7 ± 0.4 | 2.95 (as TN) |
| PO4−3-P | 7.34 | 6.42 ± 0.76 | 12.53 | 6.24 ± 0.64 | 14.98 |
| Parameter | Influent (mg·L−1) | 0.1 Q 1 (2.4 L·day−1) | 0.2 Q 1 (4.8 L·day−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effluent Concentration (mg·L−1) | Removal Rate (%) | Effluent Concentration (mg·L−1) | Removal Rate (%) | ||
| COD | 129.3 | 9.4 ± 1.2 | 92.7 | 9.7 ± 0.8 | 92.5 |
| NH3-N | 27.93 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 99.9 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 99.9 |
| NO3−-N | 1.3 | 8.4 ± 0.6 | 71.21 (as TN) | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 85.87 (as TN) |
| PO4−3-P | 6.49 | 3.82 ± 0.06 | 41.14 | 2.0 ± 0.03 | 69.47 |
| COD | Total Nitrogen | Total Phosphorus | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | Effluent | Influent | Effluent | Influent | Effluent | |||||||
| WWTP | AMAn | WWTP | AMAn | WWTP | AMAn | WWTP | AMAn | WWTP | AMAn | WWTP | AMAn | |
| Conc. (mg·L−1) | 86.4 | 95.9 | 8.6 | 8.0 | 51.0 | 57.9 | 13.1 | 13.7 | 5.23 | 6.08 | 0.23 | 0.21 |
| SD | 9.77 | 16.63 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 4.56 | 6.10 | 1.54 | 1.23 | 0.38 | 0.67 | 0.04 | 0.20 |
| Removal rate (%) | 90.0 | 91.7 | – | – | 74.2 | 76.3 | – | – | 95.5 | 83.7 | – | – |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, I.-T.; Lee, Y.-E.; Yoo, Y.-S.; Jeong, W.; Yoon, Y.-H.; Shin, D.-C.; Jeong, Y. Development of a Combined Aerobic–Anoxic and Methane Oxidation Bioreactor System Using Mixed Methanotrophs and Biogas for Wastewater Denitrification. Water 2019, 11, 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071377
Kim I-T, Lee Y-E, Yoo Y-S, Jeong W, Yoon Y-H, Shin D-C, Jeong Y. Development of a Combined Aerobic–Anoxic and Methane Oxidation Bioreactor System Using Mixed Methanotrophs and Biogas for Wastewater Denitrification. Water. 2019; 11(7):1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071377
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, I-Tae, Ye-Eun Lee, Yeong-Seok Yoo, Wonsik Jeong, Young-Han Yoon, Dong-Chul Shin, and Yoonah Jeong. 2019. "Development of a Combined Aerobic–Anoxic and Methane Oxidation Bioreactor System Using Mixed Methanotrophs and Biogas for Wastewater Denitrification" Water 11, no. 7: 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071377
APA StyleKim, I.-T., Lee, Y.-E., Yoo, Y.-S., Jeong, W., Yoon, Y.-H., Shin, D.-C., & Jeong, Y. (2019). Development of a Combined Aerobic–Anoxic and Methane Oxidation Bioreactor System Using Mixed Methanotrophs and Biogas for Wastewater Denitrification. Water, 11(7), 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071377





