Hybrid Methodology for the Estimation of Crop Coefficients Based on Satellite Imagery and Ground-Based Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
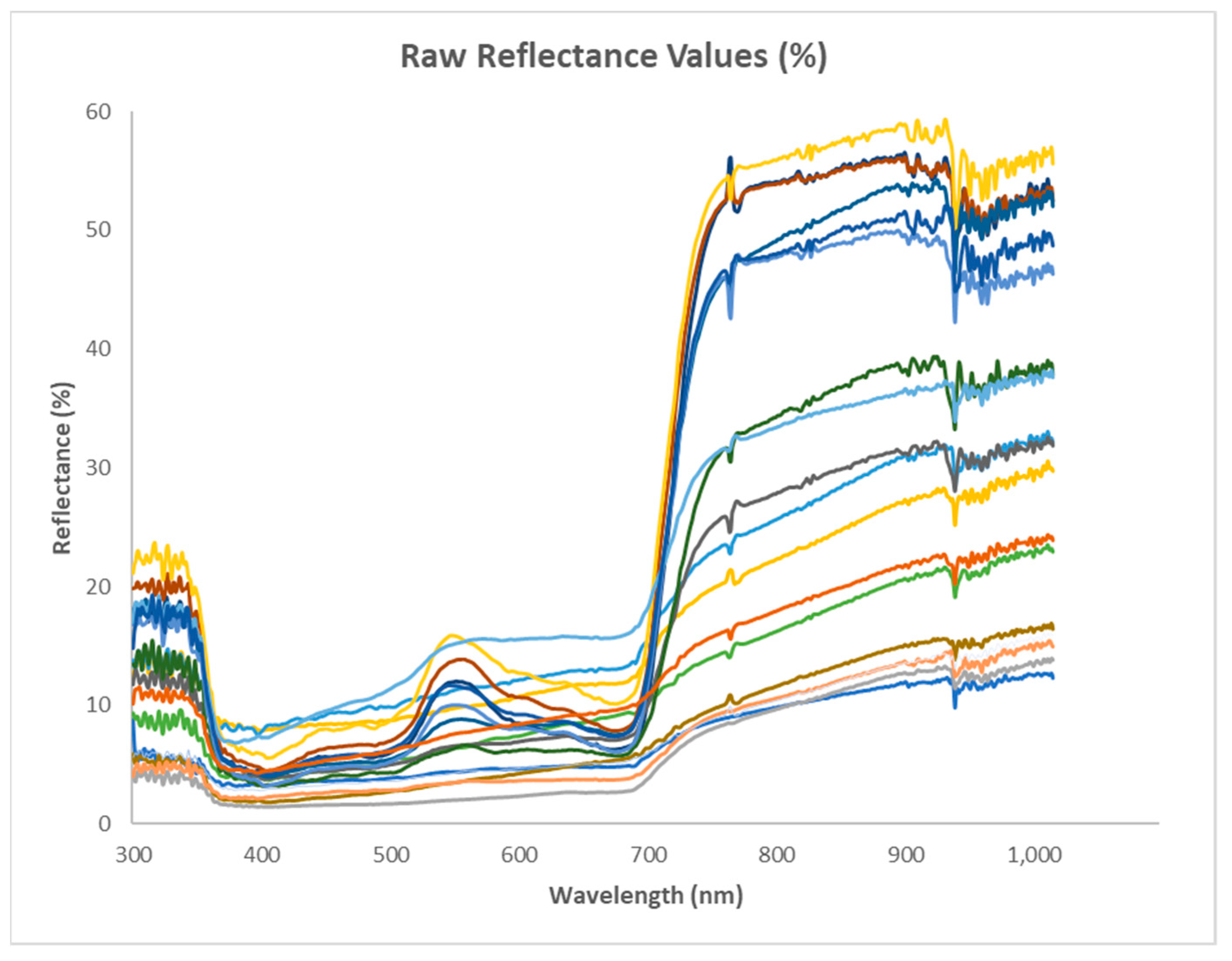
1.1. Field Spectroscopy
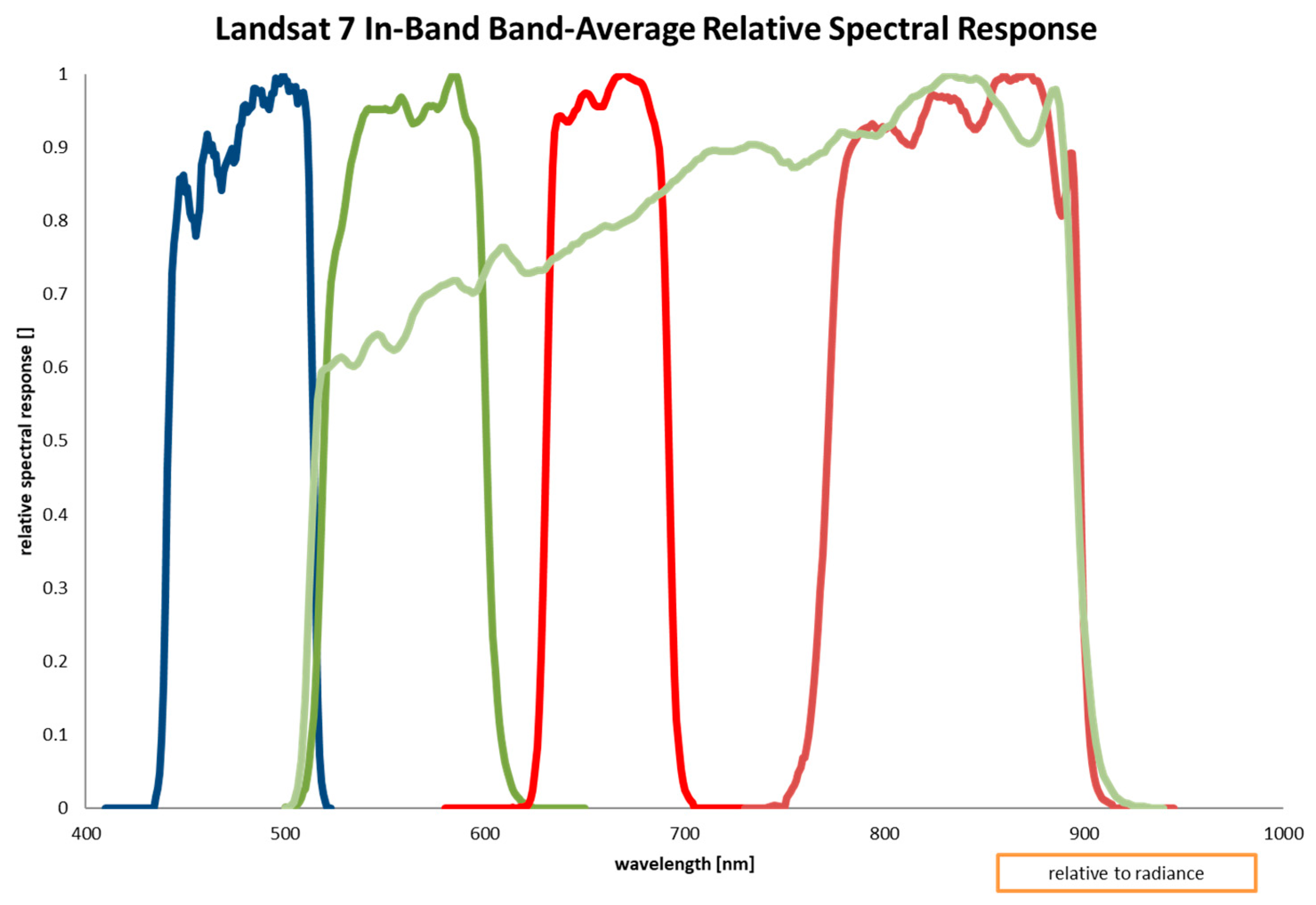
1.2. METRIC Model
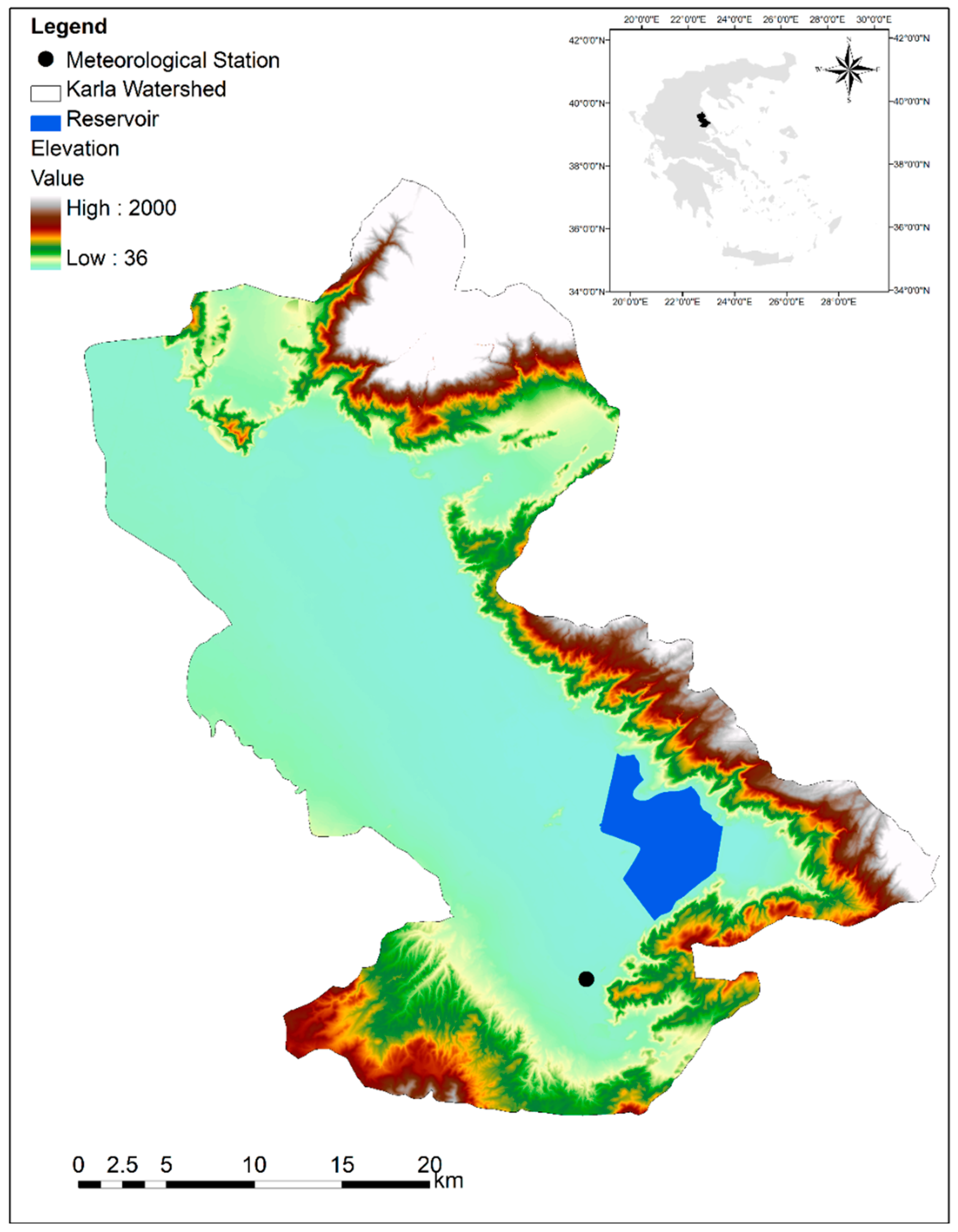
1.3. Study Area
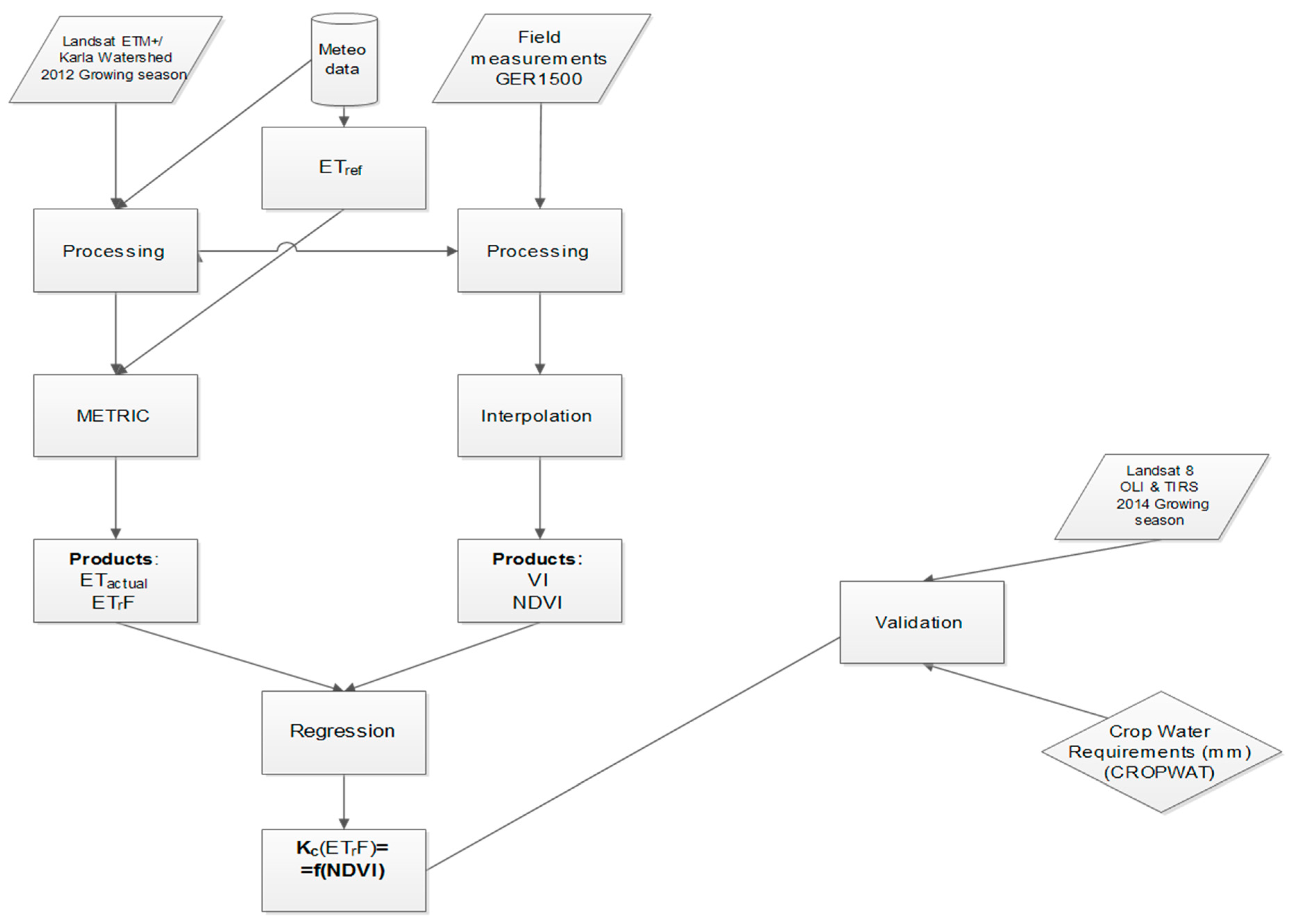
2. Materials and Methods
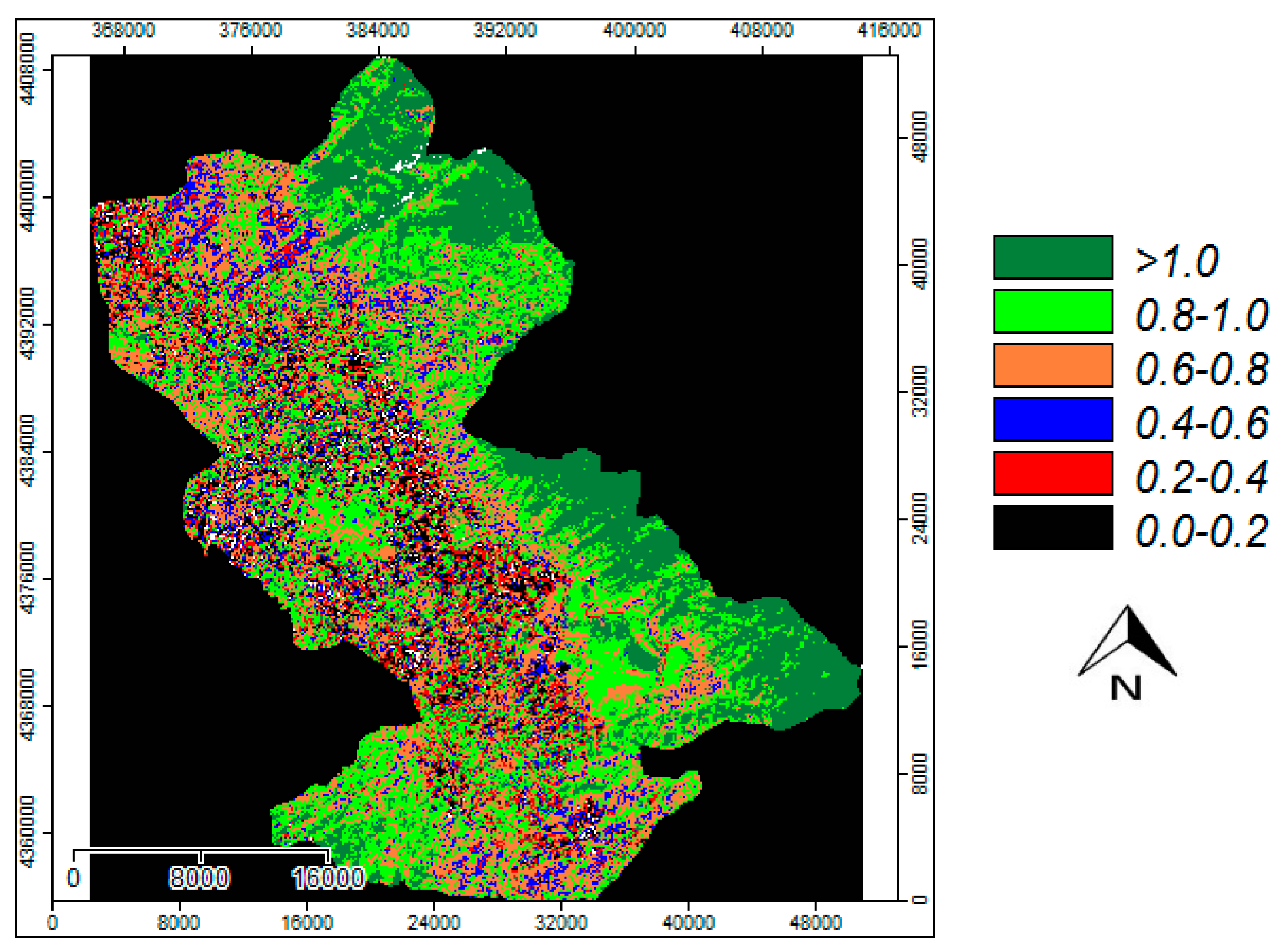
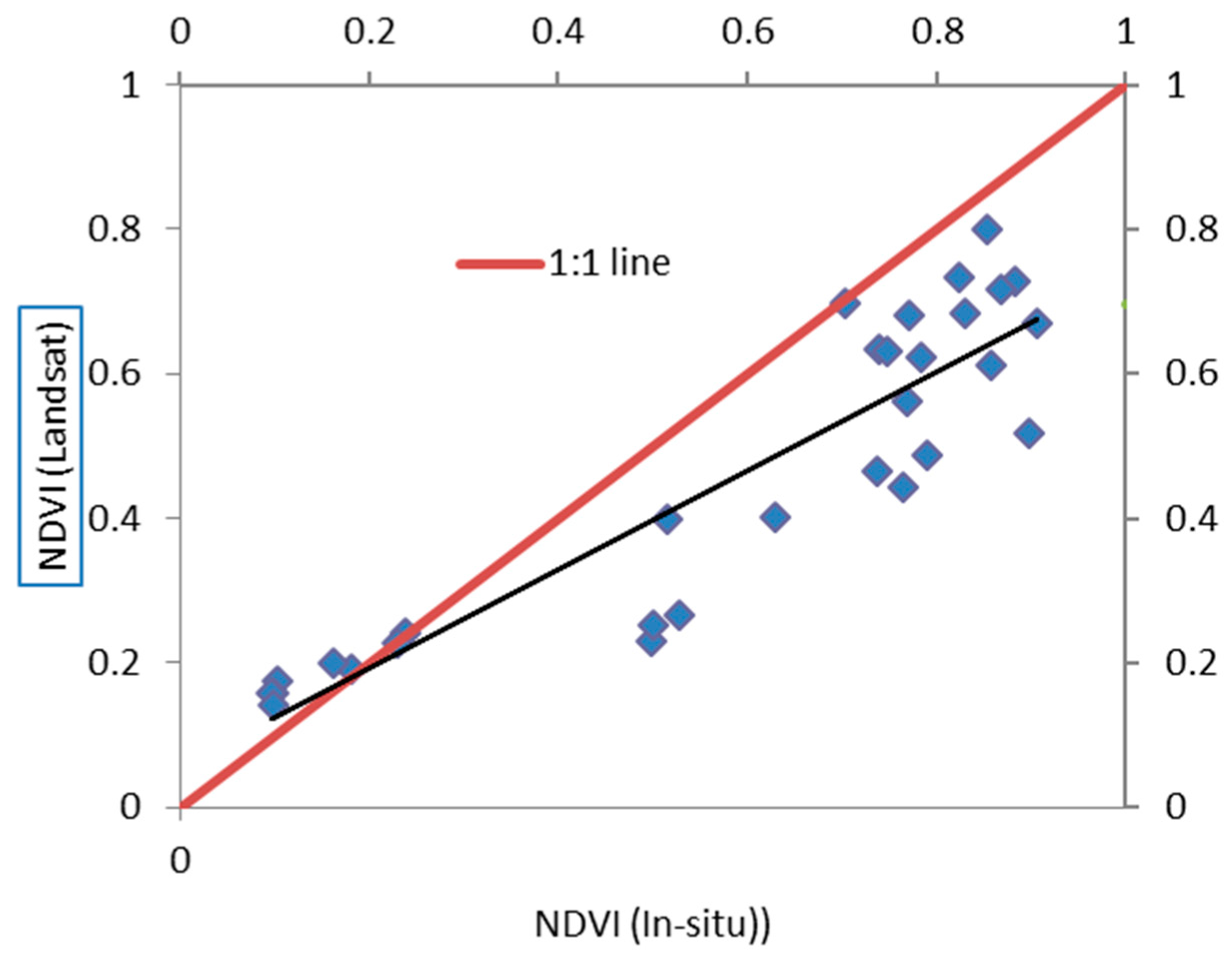
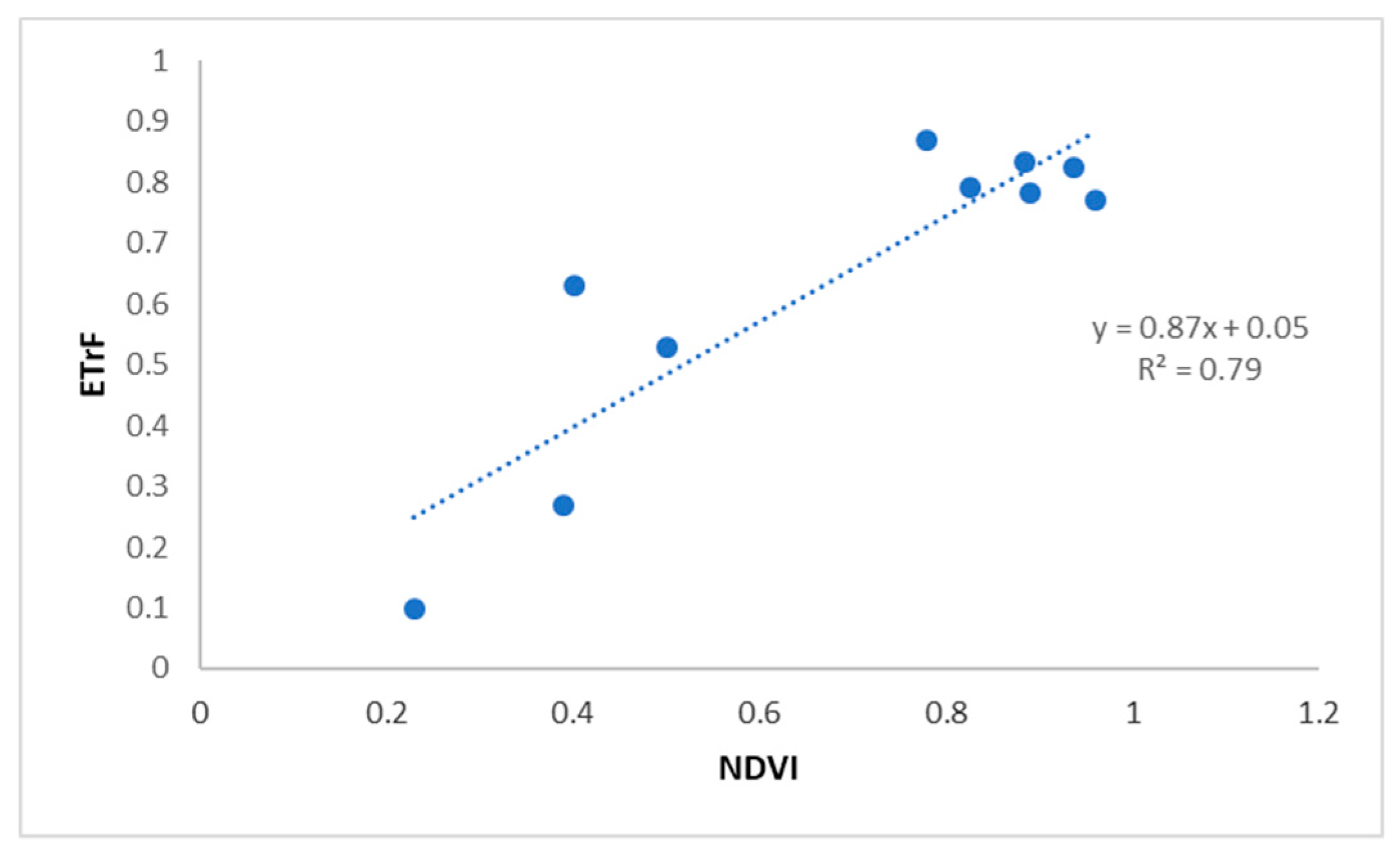
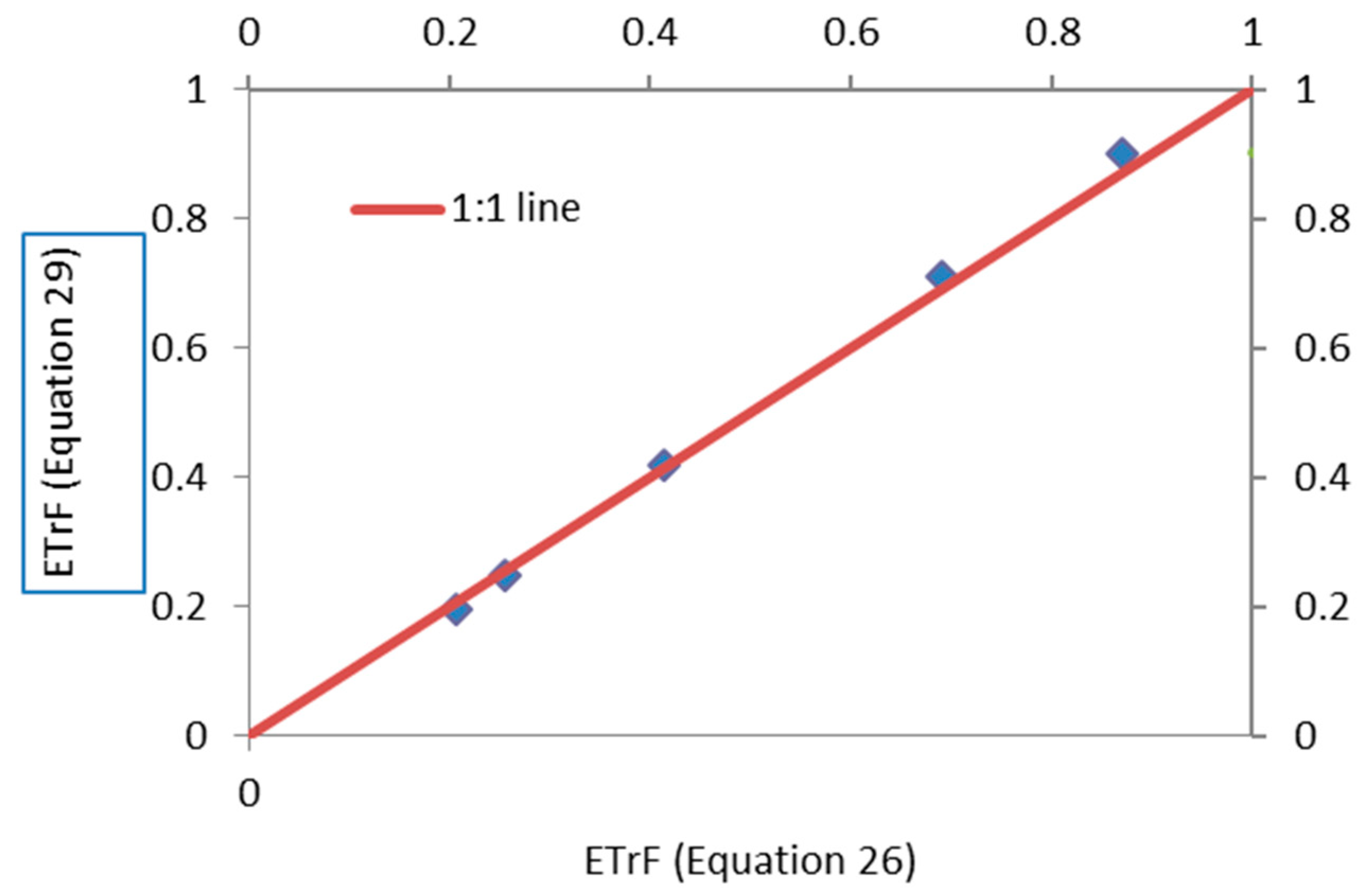
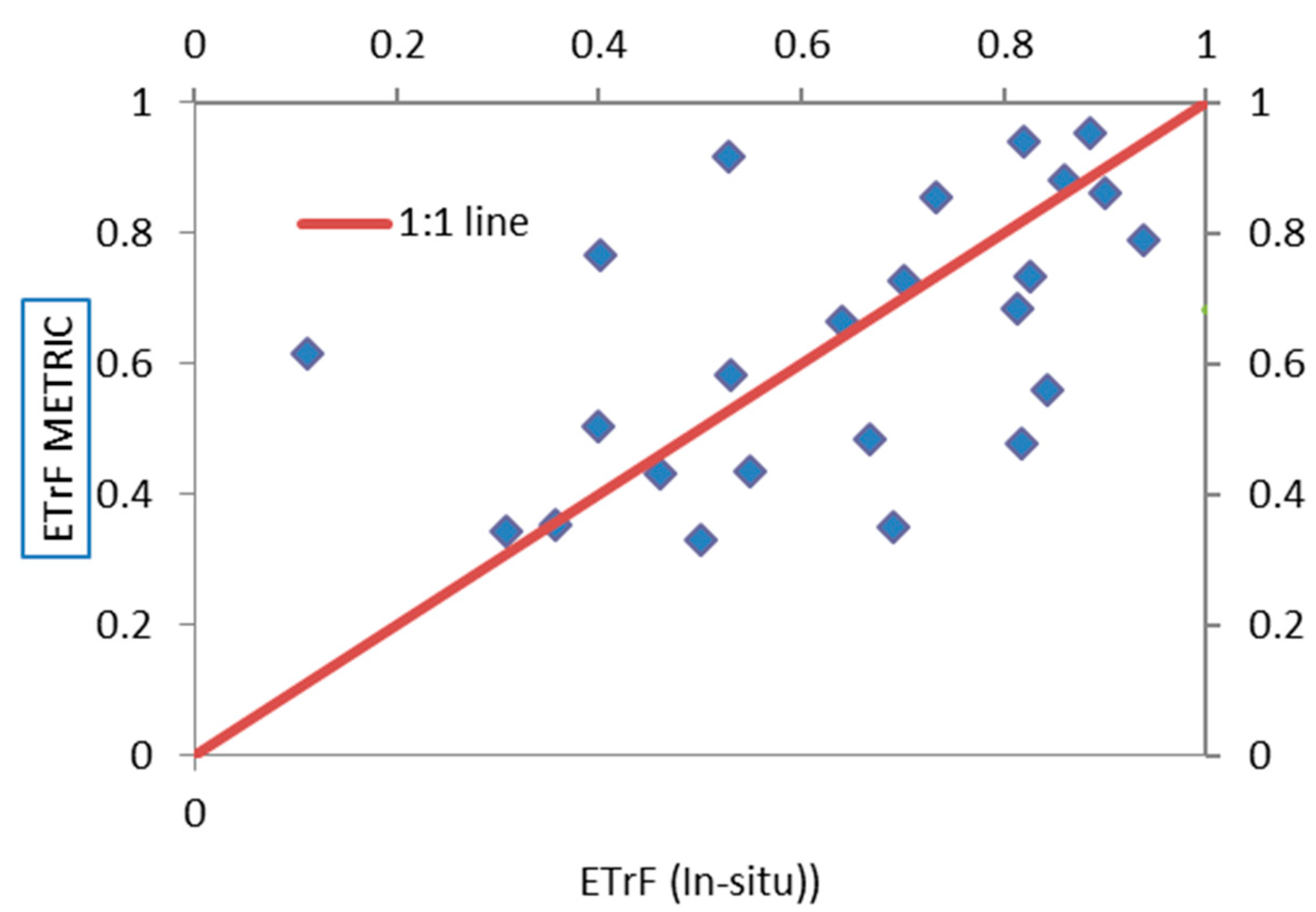
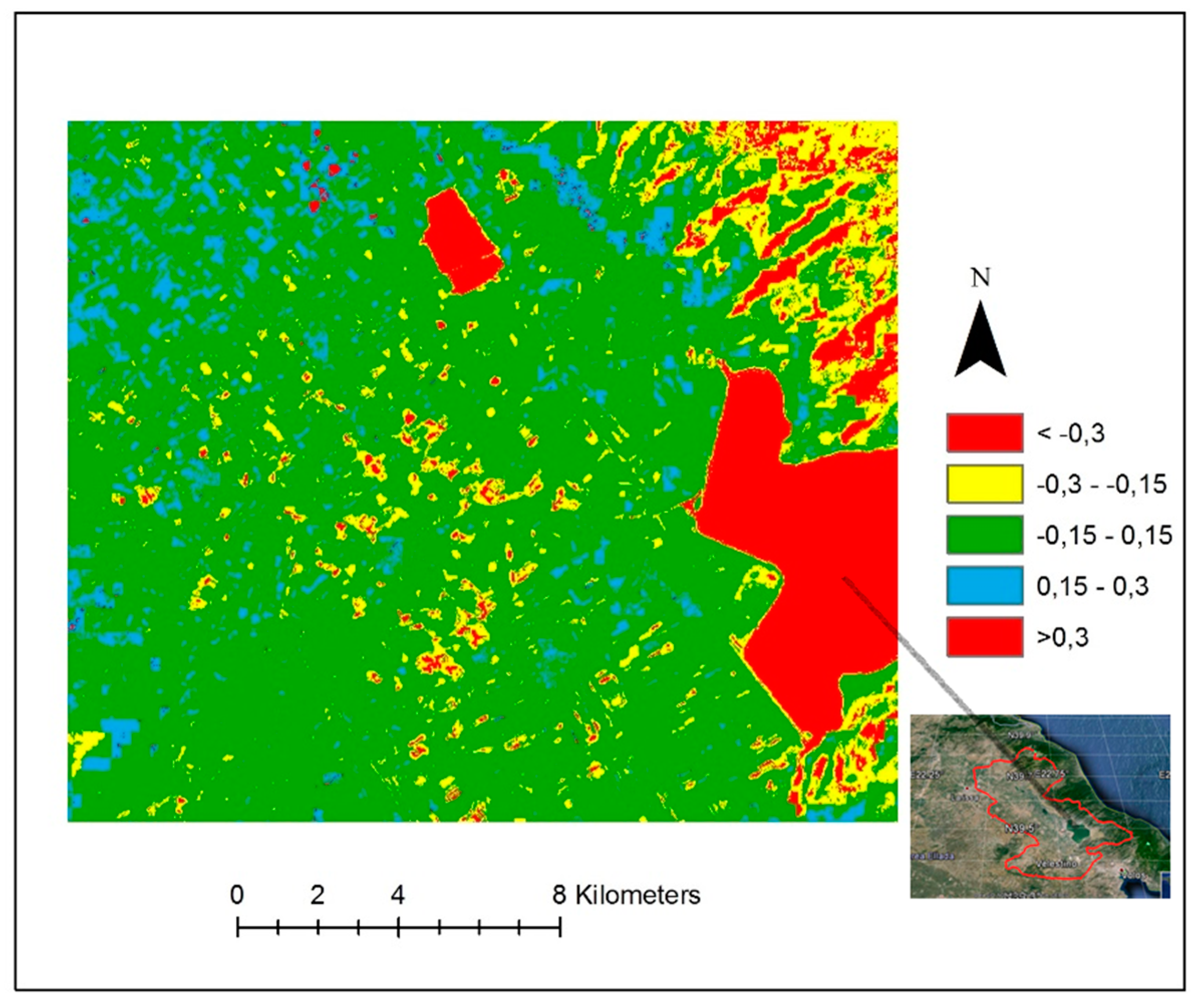
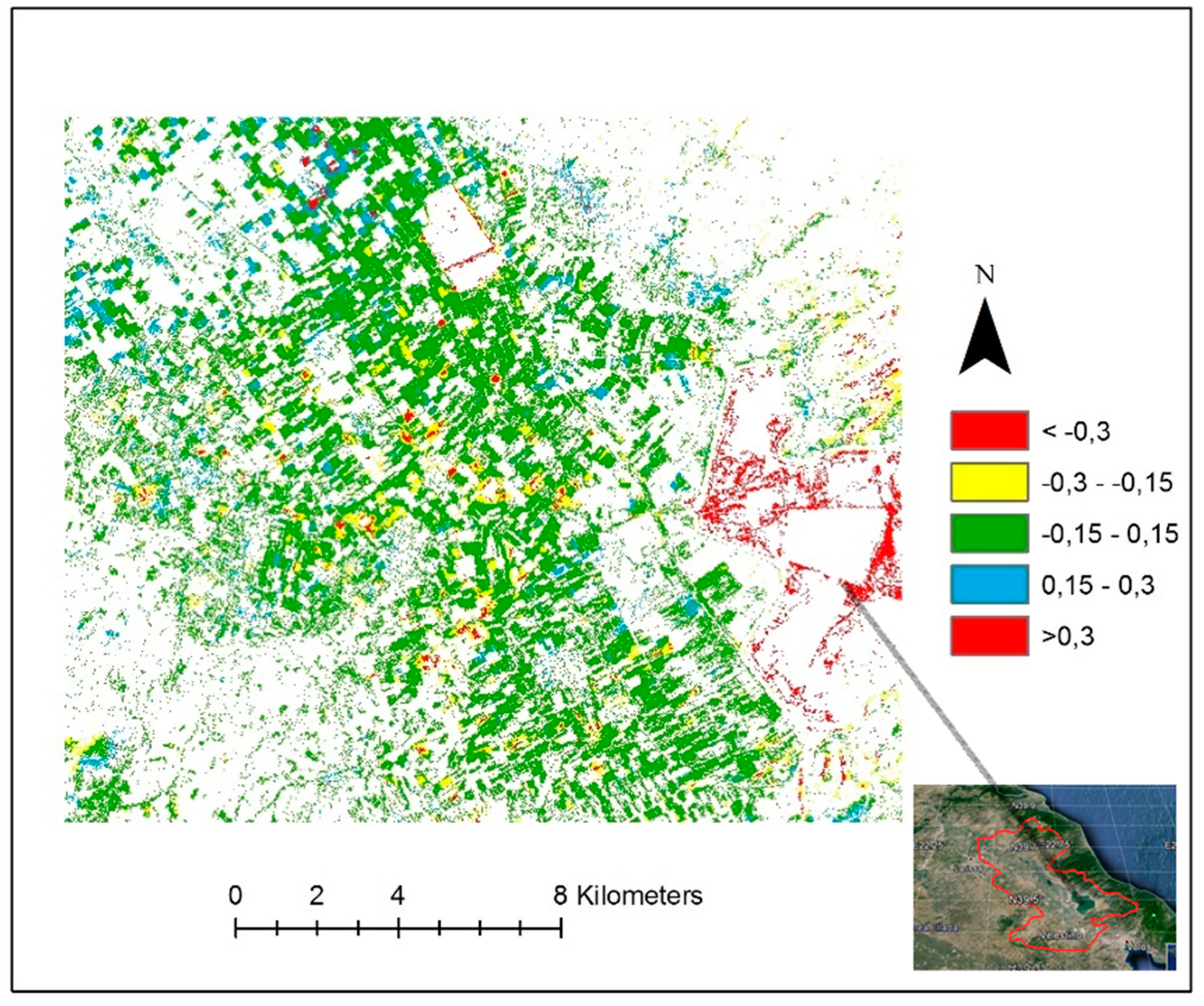
3. Results and Discussion
Validation of the Methodology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriquez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreria, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannari, A.; Morin, D.; Bonn, F.; Huete, A.R. A review of vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Rev. 1995, 13, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Chen, Z. Comparison of broad-band and narrow-band red and near-infrared vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Su, B. Significant remote sensing vegetation indices: A review of developments and applications. J. Sens. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Wessman, C.A.; Bateson, C.A.; Privette, J.L. Impact of Tissue, Canopy, and Landscape Factors on the Hyperspectral Reflectance Variability of Arid Ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlein, A.K.; Rumpf, T.; Welke, P. Development of spectral indices for detecting and identifying plant diseases. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration: Guidelines for computing crop water requirements. In United Nations FAO, Irrigation and Drainage; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; ISBN 92-5-104219-5. [Google Scholar]
- Townshend, J.R.G.; Justice, C.O. Towards operational monitoring of terrestrial systems by moderate-resolution remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, W.C.; Neale, C.M.U. Spectral Inputs Improve Corn Crop Coefficients and Irrigation Scheduling. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, C.M.U.; Bausch, W.C.; Heerman, D.F. Development of reflectance-based crop coefficients for corn. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.J.; Ahmed, N.U.; Idso, S.B.; Reginato, R.J.; Daughtry, C.S.T. Relations between evaporation coefficients and vegetation indices studied by model simulations. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchemin, B.; Hadria, R.; Erraki, S.; Boulet, G.; Maisongrande, P.; Chehbouni, A.; Escadafal, R.; Ezzahar, J.; Hoedjes, J.C.B.; Kharrou, M.H.; et al. Monitoring wheat phenology and irrigation in Central Morocco: On the use of relationships between evapotranspiration, crops coefficients, leaf area index and remotely-sensed vegetation indices. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 79, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunsaker, D.J.; Pinter, P.J., Jr.; Kimball, B.A. Wheat basal crop coefficients determined by normalized difference vegetation index. Irrig. Sci. J. 2005, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.E.; Burman, R.D.; Allen, R.G. Evapotranspiration and Irrigation Water Requirements. ASCE Manual No. 70; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Irmak, S. Nebraska water and energy flux measurement, modeling, and research network (NEBFLUX). Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 1097–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. SEBAL-based sensible and latent heat fluxes in the irrigated Gediz Basin, Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukal, M.; Irmak, S.; Kilic, A. Long-term spatial and temporal maize and soybean evapotranspiration trends derived from ground-based and satellite-based datasets over the great plains. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimpale, A.R.; Rajankar, P.B.; Wadatkar, S.B.; Wanjari, S.S.; Ramteke, I.K. Estimation of water requirement of wheat using multispectral vegetation indices. J. Agrometeorol. 2015, 17, 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn, E.P.; Neale, C.M.U.; Hunsaker, D.J.; Nagler, P.L. Vegetation index-based crop coefficients to estimate evapotranspiration by remote sensing in agricultural and natural ecosystems. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 4050–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdim, N.; Alfieri, S.M.; Habib, A.; Choukri, A.; Cheruiyot, E.; Labbassi, K.; Menenti, M. Monitoring of irrigation schemes by remote sensing: Phenology versus retrieval of biophysical variables. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5815–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, B.; Kilic, A.; Hubbard, K. Estimating crop coefficients using remote sensing-based vegetation index. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1588–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunink, J.E.; Eekhout, J.P.C.; de Vente, J.; Contreras, S.; Droogers, P.; Baille, A. Hydrological modelling using satellite-based crop coefficients: A comparison of methods at the basin scale. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Baik, J.; Choi, M. Satellite-based crop coefficient and evapotranspiration using surface soil moisture and vegetation indices in Northeast Asia. CATENA 2017, 156, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilman, J.L.; Heilman, W.E.; Moore, D.G. Evaluating the crop coefficient using spectral reflectance. Agron. J. 1982, 74, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, P.N.; Patel, J.N. Development of relationship between crop coefficient and NDVI using geospatial technology. J. Agrometeorol. 2016, 18, 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-González, A. Using Remote Sensing to Estimate Crop Water Use to Improve Irrigation Water Management. Ph.D. Thesis, South Dakota State University, Brookings, SD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.D.; Idso, S.B.; Regionato, R.J.; Pinter, P.J., Jr. Remotely sensed crop temperatures and reflectances as inputs to irrigation scheduling. In Proceedings of the Irrigation and Drainage Special Conference (ASCE), Boise, NY, USA, 23–25 July 1980; pp. 390–397. [Google Scholar]
- Sellers, P.J. Canopy reflectance, photosynthesis and transpiration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1985, 6, 1335–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, R.; Rossinni, P. On the use of NDVI profiles as a tool for agricultural statistics: The case study of wheat yield estimate and forecast in Emilia Romagna. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 45, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, K.G., Sivakumar, M.V.K., Eds.; Automated Weather Stations for Applications in Agriculture and Water Resources Management: Current Use and Future Perspectives. In Proceedings of the International Workshop, Lincoln, NE, USA, 6–10 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jayanthi, H.; Neale, C.M.U.; Wright, J.L. Seasonal Evapotranspiration Estimation Using Canopy Reflectance: A Case Study Involving Pink Beans. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing and Hydrology, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2–7 April 2000; pp. 302–305. [Google Scholar]
- Irmak, A.; Kamble, B. Evapotranspiration data assimilation with genetic algorithms and SWAP model for on-demand irrigation. Irrig. Sci. J. 2009, 28, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenikiotis, C.; Spiliotopoulos, M.; Tsiros, E.; Dalezios, N.R. Early cotton production assessment in Greece based on the combination of the drought vegetation condition index (VCI) and Bhalme and Mooley drought index (BMDI). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 5373–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenikiotis, C.; Spiliotopoulos, M.; Tsiros, E.; Dalezios, N.R. Early Cotton Yield Assessment by the use of the NOAA/AVHRR derived drought Vegetation Condition Index in Greece. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2807–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenikiotis, C.; Spiliotopoulos, M.; Tsiros, E.; Dalezios, N.R. Remotely sensed estimation of annual cotton production under different environmental conditions in Central Greece. Phys. Chem. Earth 2005, 30, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenikiotis, C.; Tsiros, E.; Spiliotopoulos, M.; Dalezios, N.R. Use of NOAA/AVHRR-based Vegetation Condition Index (VCI) and Temperature Condition Index (TCI) for drought monitoring in Thessaly, Greece. In Proceedings of the EWRA Symposium—Water Resources Management: Risks and Challenges for the 21st Century, Izmir, Turkey, 2–4 September 2004; Harmancioglu, N.B., Fistikoglu, O., Dalkilic, Y., Gul, A., Eds.; Sumer: Izmir, Turkey; pp. 769–782.
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, E.J. Principles of field spectroscopy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1987, 8, 1807–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, E.J.; Rollin, E.M.; Emery, D.R. Advances in field spectroscopy. In Advances in Environmental Remote Sensing; Danson, F.M., Plummer, S.E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- D’Urso, G.; Calera, B.A. Operative approaches to determinate crop water requirements from Earth Observation data: Methodologies and Applications. In Proceedings of the Earth Observation for Vegetation Monitoring and Water Management, Naples, Italy, 9–10 November 2005; pp. 14–25. [Google Scholar]
- Agapiou, A.; Papadavid, G.; Hadjimitsis, D. Surface reflectance retrieval from Landsat TM/ETM+ images for monitoring irrigation demand in Cyprus. In Proceedings of the 29th EARSeL Symposium, Chania, Greece, 15–18 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Labsphere, Technical Guide: Reference Materials. New Hampshire, USA. Available online: http://www.labsphere.com (accessed on 12 March 2017).
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL): 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–212, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Pelgrum, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Moreno, J.F.; Roerink, G.J.; van der Wal, T. The Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL): Part 2 validation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-based energy balance for mapping evapotranspiration with internalized calibration (METRIC)—Model. ASCE J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, I.; Khand, K.; Kjaersgaard, J.; Cochrane, M.; Silva, S. Evaluation of Landsat-Based METRIC modelling to provide high-spatial resolution evapotranspiration estimates for Amazonian forests. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R.; Waters, R.; Bastiaanssen, W. Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL)—Advanced Training and User’s Manual; Idaho Department of Water Resources, University of Idaho: Moscow, ID, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Monin, A.S.; Obukhov, A.M. Basic laws of turbulent mixing in the surface layer of the atmosphere. Contrib. Geophys. Inst. Slovak Acad. Sci. 1954, 24, 163–187. [Google Scholar]
- Spiliotopoulos, M.; Loukas, A.; Mylopoulos, N. A new remote sensing procedure for the estimation of crop water requirements. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment, Paphos, Cyprus, 16–19 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sidiropoulos, P.; Tziatzios, G.; Vasiliades, L.; Mylopoulos, N.; Loukas, A. Groundwater Nitrate Contamination Integrated Modeling for Climate and Water Resources Scenarios: The Case of Lake Karla Over-Exploited Aquifer. Water 2019, 11, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G. REF-ET: Reference Evapotranspiration Calculation Software for FAO and ASCE Standardized Equations. University of Idaho. 2000. Available online: www.kimberly.uidaho.edu/ref-et (accessed on 12 March 2017).
- Park, J.; Choi, M. Estimation of evapotranspiration from ground-based meteorological data and global land data assimilation system (GLDAS). Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 1963–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaersgaard, J.; Allen, R.G.; Irmak, A. Improved methods for estimating monthly and growing season ET using METRIC applied to moderate resolution satellite imagery. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 23, 4028–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, D.J. Effect of Relative Spectral Response on Multi-Spectral Measurements and NDVI from Different Remote Sensing Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Papadavid, G. Estimating Evapotranspiration for Annual Crops in Cyprus Using Remote Sensing. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering and Geomatics, Cyprus University of Technology, Lemesos, Cyprus, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T. Development of a Two-Band Enhanced Vegetation Index without a Blue Band. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, J.; Connolly, J.; Vermote, E.F.; Holden, N.M. Radiometric normalization for change detection in peatlands: A modified temporal invariant cluster approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2905–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiliotopoulos, M.; Holden, N.; Loukas, A. Mapping Evapotranspiration Coefficients in a Temperate Maritime Climate Using the METRIC Model and Landsat TM. Water 2017, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. CROPWAT, a Computer Program for Irrigation Planning and Management by M. Smith; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 26; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Tsouni, A.; Kontoes, C.; Koutsoyiannis, D.; Elias, P.; Mamassis, N. Estimation of Actual Evapotranspiration by Remote Sensing: Application in Thessaly Plain, Greece. Sensors 2008, 8, 3586–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalezios, N.R.; Mplanta, A.; Domenikiotis, C. Remotely sensed cotton evapotranspiration for irrigation water management in vulnerable agriculture of Central Greece. J. Inf. Technol. Agric. 2011, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliades, L.; Spiliotopoulos, M.; Tzabiras, J.; Loukas, A.; Mylopoulos, N. Estimation of crop water requirements using remote sensing for operational water resources management. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment, Paphos, Cyprus, 16–19 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Melton, F.S.; Johnson, L.F.; Lund, C.P.; Pierce, L.L.; Michaelis, A.R.; Hiatt, S.H.; Guzman, A.; Adhikari, D.D.; Purdy, A.J.; Rosevelt, C. Satellite irrigation management support with the terrestrial observation and prediction system: A framework for integration of satellite and surface observations to support improvements in agricultural water resource management. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Irmak, A. Estimation of crop coefficients using satellite remote sensing. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2009, 135, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calera, A.; Campos, I.; Osann, A.; D’Urso, G.; Menenti, M. Remote sensing for crop water management: From ET modelling to services for the end users. Sensors 2017, 17, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasumi, M.; Allen, R.G.; Trezza, R. Calibrating satellite-based vegetation indices to estimate evapotranspiration and crop coefficients. In Proceedings of the USCID Water Management Conference, Boise, ID, USA, 25–28 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, I.; Balbontin, C.; González-Piqueras, J.; González-Dugo, M.P.; Neale, C.; Calera, A. Combining water balance model with evapotranspiration measurements to estimate total available water soil water in irrigated and rain-fed vineyards. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 165, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Clemmens, A.J.; Burt, C.M.; Solomon, K.; O’Halloran, T. Prediction accuracy for project wide evapotranspiration using crop coefficients and reference evapotranspiration. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-González, A.; Kjaersgaard, J.; Trooien, T.; Hay, C.; Ahiablame, L. Estimation of Crop Evapotranspiration Using Satellite Remote Sensing-Based Vegetation Index. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 4525021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzar, M.; Whitfield, D.; McAllister, A.; Sheffield, K. Application of ET-NDVI-relationship approach and soil-water-balance modelling for the monitoring of irrigation performance of treed horticulture crops in a key fruit-growing district of Australia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 4724–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Morton, C.; Kamble, B.; Kilic, A.; Huntington, J.; Thau, D.; Gorelick, N.; Erickson, T.; Moore, R.; Trezza, R.; et al. EEFlux: A Landsat-based Evapotranspiration mapping tool on the Google Earth Engine. In Proceedings of the Joint ASABE/IA Irrigation Symposium 2015: Emerging Technologies for Sustainable Irrigation, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–12 November 2015; pp. 424–433. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Foody, G.M. What is the difference between two maps? A remote sensor’s view. J. Geogr. Syst. 2006, 8, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.W.; Yuan, M.; Cerveny, R.S.; Giri, C.P. Comparison of remote sensing image processing techniques to identify tornado damage areas from Landsat TM data. Sensors 2008, 8, 1128–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, D.J.; Sader, S.A. Comparison of change-detection techniques for monitoring tropical forest clearing and vegetation regrowth in a time series. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2001, 67, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Rafn, E.B.; Contor, B.; Ames, D.P. Evaluation of a Method for Estimating Irrigated Crop-Evapotranspiration Coefficients from Remotely Sensed Data in Idaho. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2008, 134, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorenbos, J.; Pruitt, W.O. Guidelines for Predicting Crop Water Requirements. In FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 24; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Doorenbos, J.; Kassam, A. Yield Response to Water. In FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 33; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Karioti, K. Land Use and Water Needs Mapping for Lake Karla Watershed. Master’s Thesis, University of Thessaly, Volos, Greece, 2013. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]

| Landsat 7 ETM+ and In-Situ GER1500 Data Availability | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition | Julian Day Acquisition | Path/Row | GER1500 Availability | ETM+ Availability |
| 26 April 2012 | 117 | 184/032 | NO | YES |
| 12 May 2012 | 133 | 184/032 | YES | YES |
| 22 May 2012 | 143 | 184/032 | YES | NO |
| 13 June 2012 | 165 | 184/032 | NO | YES |
| 29 June 2012 | 181 | 184/032 | YES | YES |
| 13 July 2012 | 195 | 184/032 | YES | NO |
| 15 July 2012 | 197 | 184/032 | NO | YES |
| 31 July 2012 | 213 | 184/032 | YES | YES |
| 16 August 2012 | 229 | 184/032 | YES | NO |
| 01 September 2012 | 245 | 184/032 | YES | YES |
| 03 October 2012 | 277 | 184/032 | NO | YES |
| 19 October 2012 | 293 | 184/032 | NO | YES |
| 26 April 2012 | 117 | 184/033 | NO | YES |
| 12 May 2012 | 133 | 184/033 | NO | YES |
| 13 June 2012 | 165 | 184/033 | NO | YES |
| 29 June 2012 | 181 | 184/033 | NO | YES |
| 15 July 2012 | 197 | 184/033 | NO | YES |
| 31 July 2012 | 213 | 184/033 | NO | YES |
| 01 September 2012 | 245 | 184/033 | NO | YES |
| 03 October 2012 | 277 | 184/033 | YES | YES |
| 19 October 2012 | 293 | 184/033 | NO | YES |
| Corn | |||||
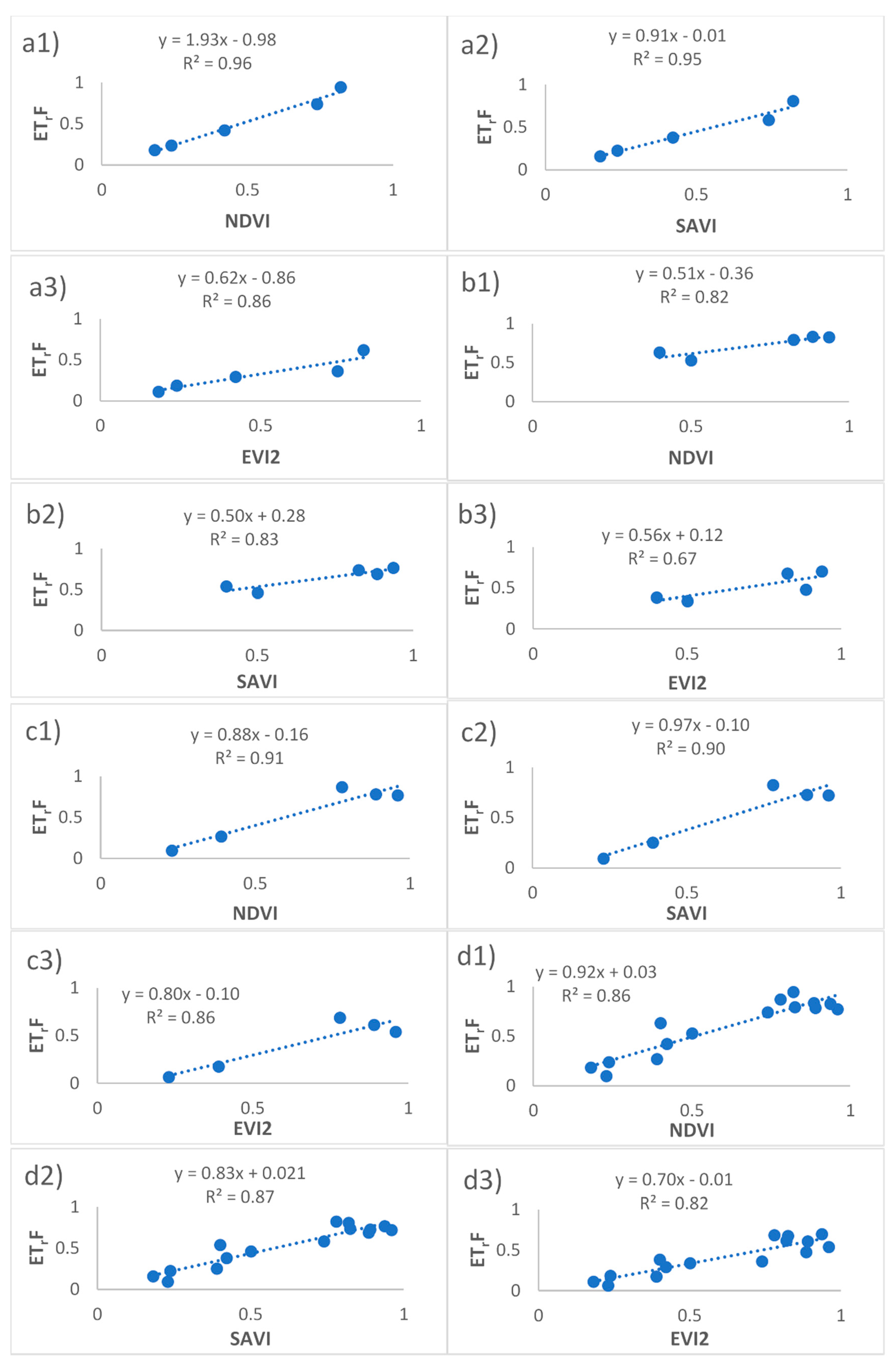
| Index | Equation | R2 | RMSE | MAE | CV |
| NDVI | y = 1.93x − 0.98 (Equation (17)) | 0.96 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.14 |
| SAVI | y = 0.91x − 0.01 (Equation (18)) | 0.95 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.40 |
| EVI2 | y = 0.62x − 0.86 (Equation (19)) | 0.86 | 0.32 | 0.40 | 1.33 |
| Cotton | |||||
| Index | Equation | R2 | RMSE | MAE | CV |
| NDVI | y = 0.51x + 0.36 (Equation (20)) | 0.82 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.23 |
| SAVI | y = 0.50 + 0.28 (Equation (21)) | 0.83 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.34 |
| EVI2 | y = 0.56x + 0.12 (Equation (22)) | 0.67 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.82 |
| Sugar Beet | |||||
| Index | Equation | R2 | RMSE | MAE | CV |
| NDVI | y = 0.88x − 0.16 (Equation (23)) | 0.91 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.54 |
| SAVI | y = 0.97x − 0.10 (Equation (24)) | 0.90 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.62 |
| EVI2 | y = 0.80x − 0.10 (Equation (25)) | 0.86 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 2.17 |
| General * | |||||
| Index | Equation | R2 | RMSE | MAE | CV |
| NDVI | y = 0.92x + 0.03 (Equation (26)) | 0.86 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.21 |
| SAVI | y = 0.83x + 0.021 (Equation (27)) | 0.87 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.46 |
| EVI2 | y = 0.70x − 0.01 (Equation (28)) | 0.82 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 1.45 |
| 24 June 2013 | METRIC Based Kc | Proposed Kc | CROPWAT’s Crop Water Irrigation Requirements (mm)—Using Proposed Kc | CROPWAT’s Crop Water Irrigation Requirements (mm)—Using Proposed Kc | Crop Irrigation Requirements Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | Average values | ||||
| 0.71 | 0.71 | 3.67 | 3.67 | 0 | |
| Sugar beet | Average values | ||||
| 0.75 | 0.75 | 4.05 | 4.03 | 0.49 | |
| Corn | Average values | ||||
| 0.77 | 0.76 | 4.06 | 4.01 | 1.23 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spiliotopoulos, M.; Loukas, A. Hybrid Methodology for the Estimation of Crop Coefficients Based on Satellite Imagery and Ground-Based Measurements. Water 2019, 11, 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071364
Spiliotopoulos M, Loukas A. Hybrid Methodology for the Estimation of Crop Coefficients Based on Satellite Imagery and Ground-Based Measurements. Water. 2019; 11(7):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071364
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpiliotopoulos, Marios, and Athanasios Loukas. 2019. "Hybrid Methodology for the Estimation of Crop Coefficients Based on Satellite Imagery and Ground-Based Measurements" Water 11, no. 7: 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071364
APA StyleSpiliotopoulos, M., & Loukas, A. (2019). Hybrid Methodology for the Estimation of Crop Coefficients Based on Satellite Imagery and Ground-Based Measurements. Water, 11(7), 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071364






