Driving Factors and Dynamics of Phytoplankton Community and Functional Groups in an Estuary Reservoir in the Yangtze River, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
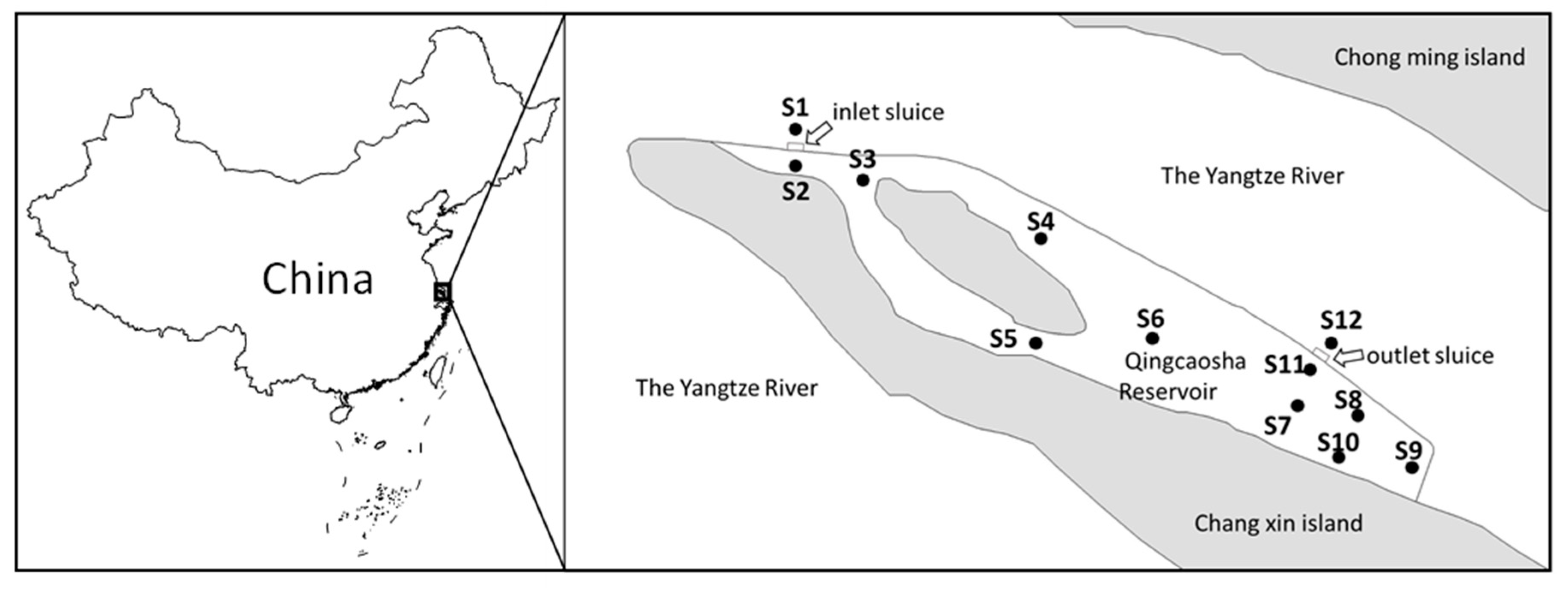
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Sample Analyses
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
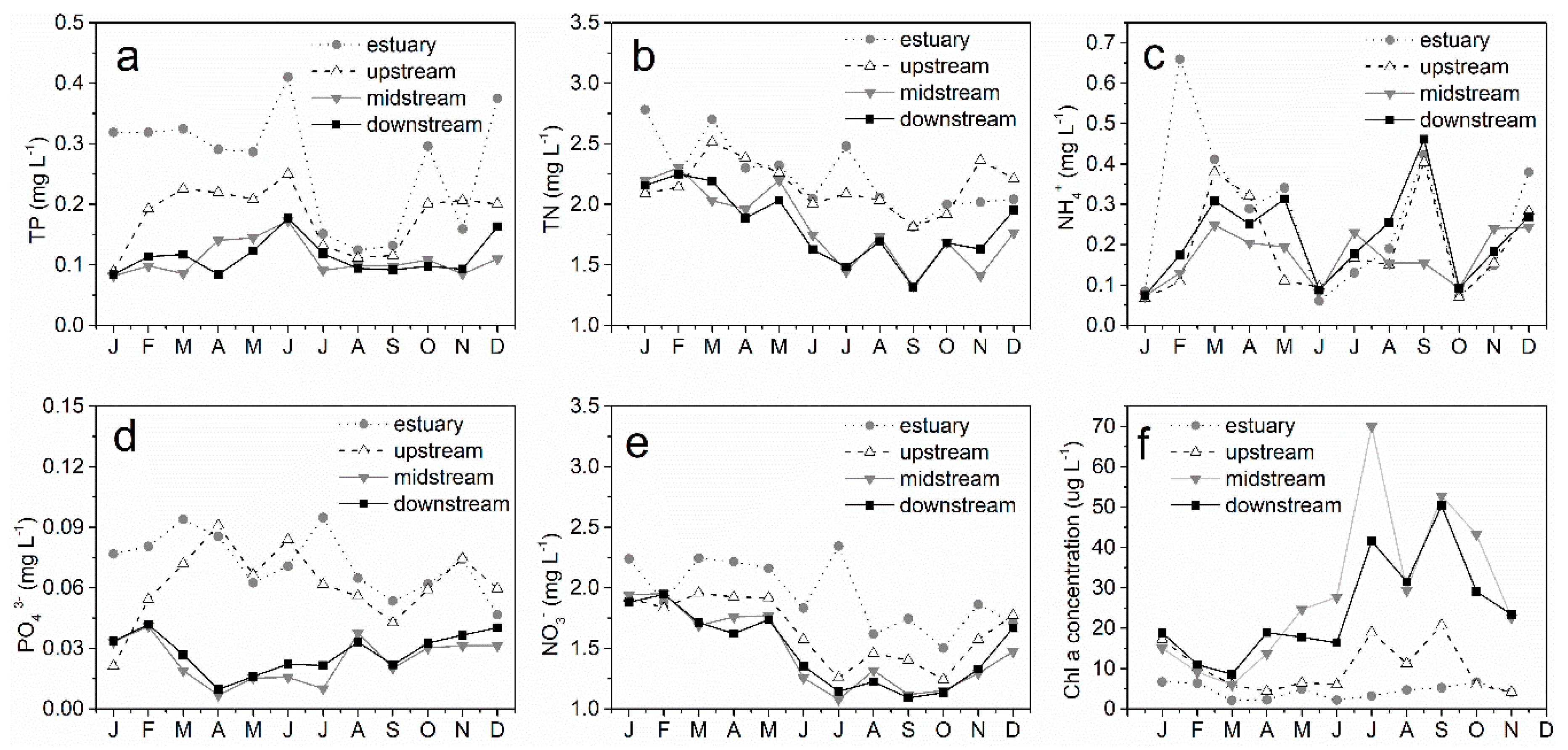
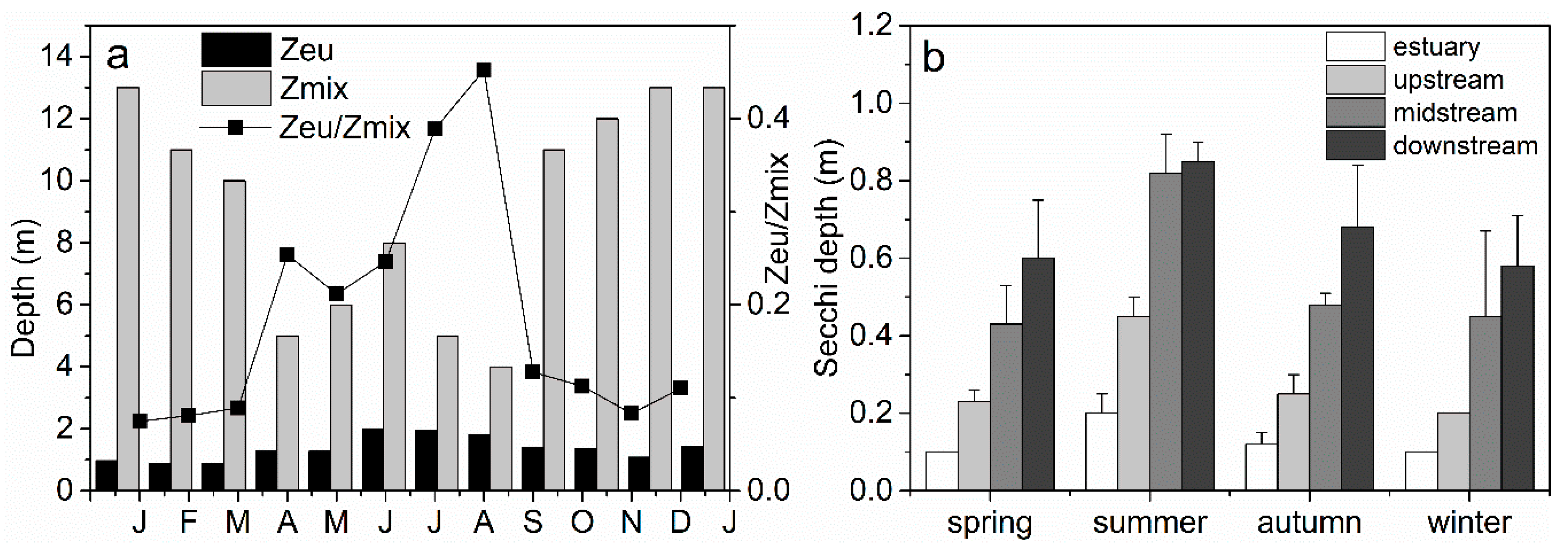
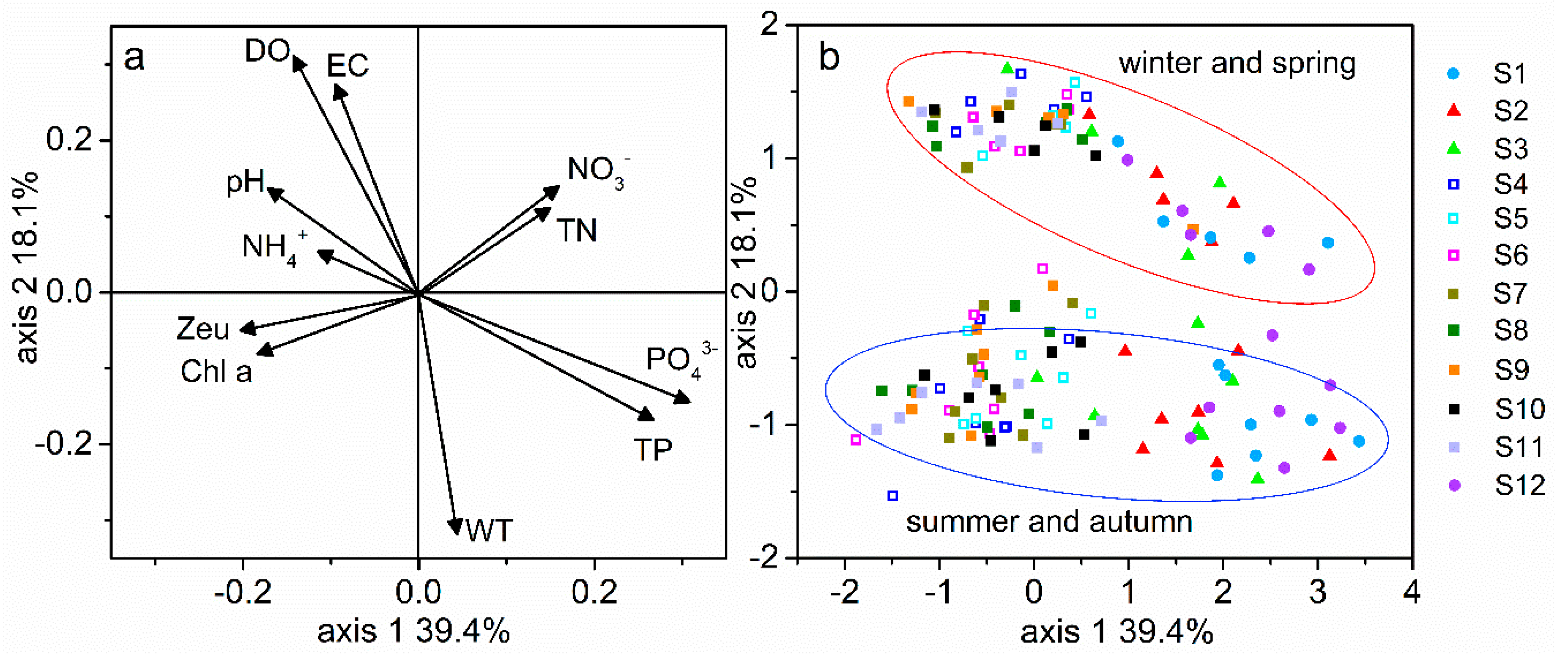
3.1. Variability of Physical and Chemical Factors Inside and Outside the Reservoir
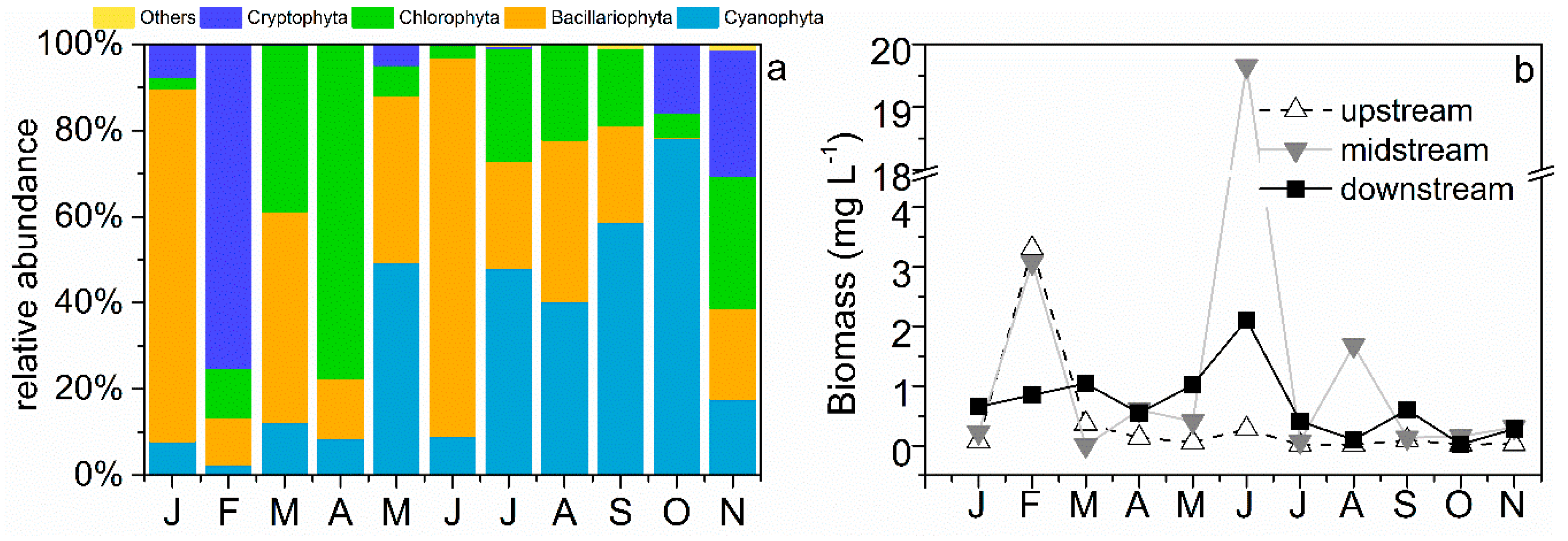
3.2. Phytoplankton Community Structure and Species Composition
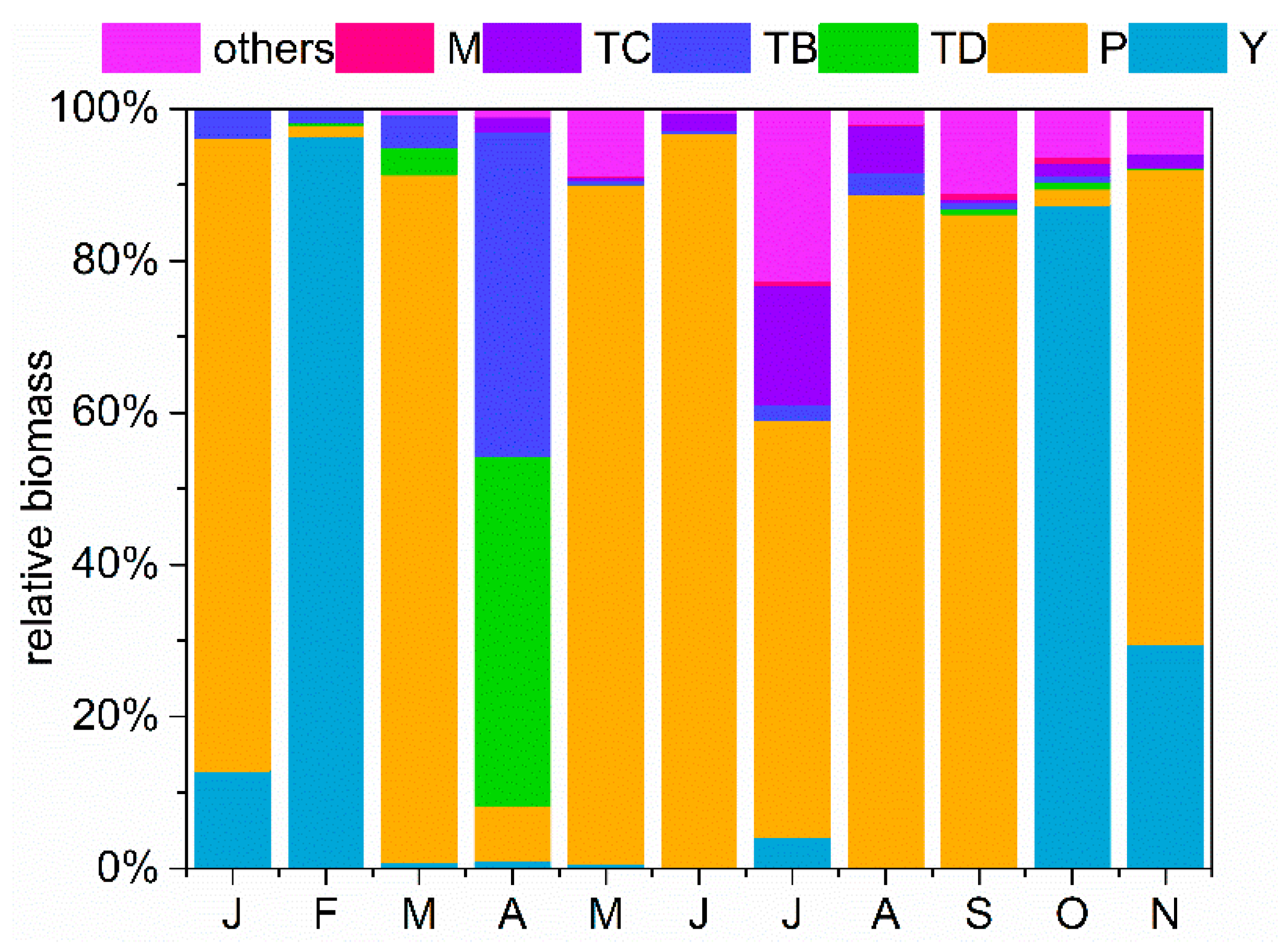
3.3. Functional Group Dynamic
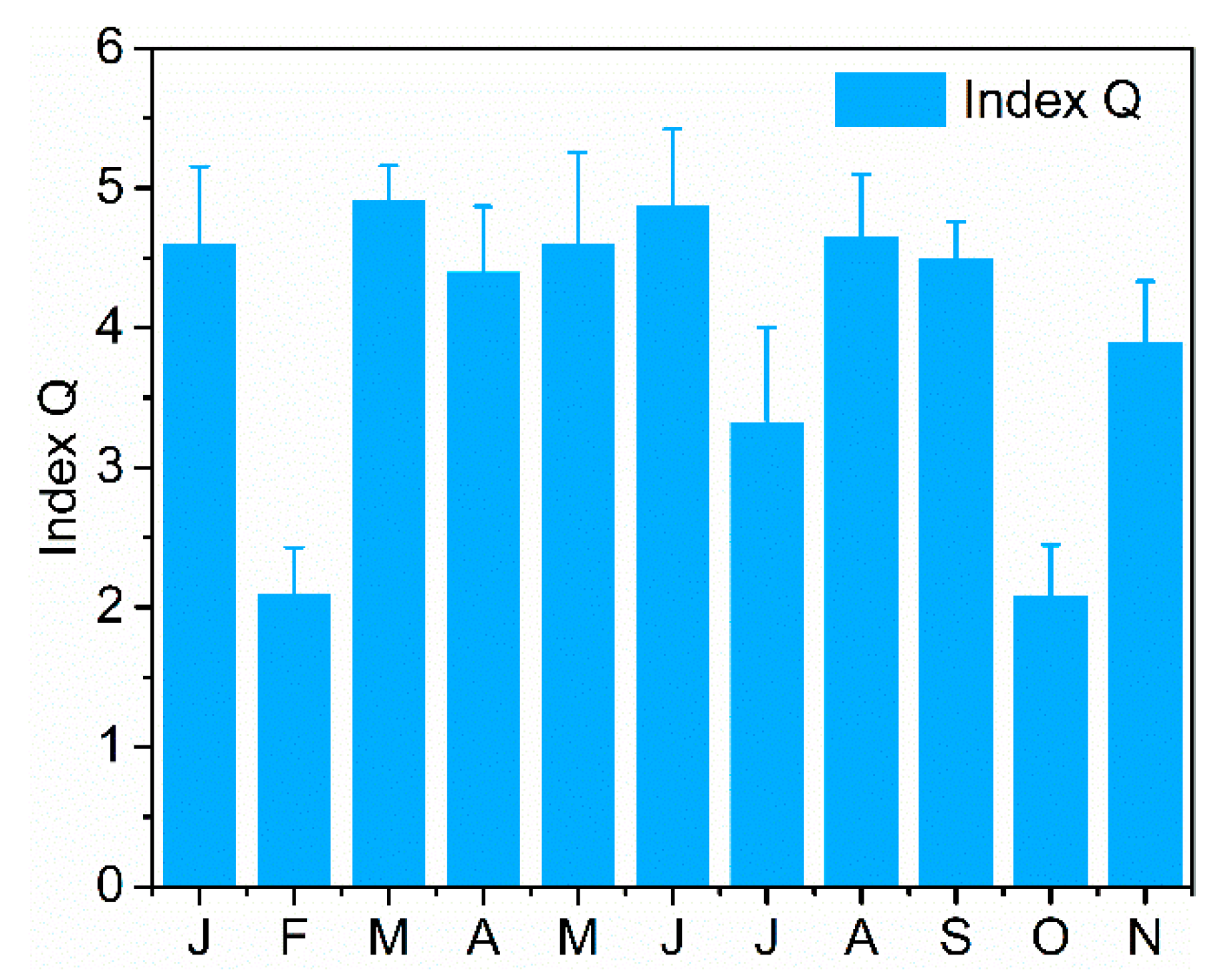
3.4. Q Index
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Nutrient and Light Availability on Phytoplankton Growth
4.2. Response of Phytoplankton Communities and Functional Groups to Environmental Driving Force
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeong, Y.H.; Yang, J.S.; Park, K. Changes in Water Quality After the Construction of an Estuary Dam in the Geum River Estuary Dam System, Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 30, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te, S.H.; Gin, K.Y.H. The dynamics of cyanobacteria and microcystin production in a tropical reservoir of Singapore. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, K.; Kuang, C.; Zhu, D.Z.; He, L.; Mao, X.; Liang, H.; Song, H. Influence of sea level rise on saline water intrusion in the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2016, 54, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.M.D.S.; Azevedo, M.T.D.P.; de Oliveira Azevedo, S.M.F.; Honda, R.Y.; Corrêa, B. Toxic cyanobacteria and microcystin concentrations in a public water supply reservoir in the Brazilian Amazonia region. Toxicon 2005, 45, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Xu, X.; Kong, F.; Zhang, S.; Kong, W.; Hao, J.; Shang, L. Two-Decade Reconstruction of Algal Blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3522–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.K.; Lin, T.F.; Tseng, I.C. Detection and quantification of major toxigenic Microcystis genotypes in Moo-Tan reservoir and associated water treatment plant. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, V.; Caputo, L.; Ordóñez, J.; Marcé, R.; Armengol, J.; Crossetti, L.O.; Huszar, V.L. Driving factors of the phytoplankton functional groups in a deep Mediterranean reservoir. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3345–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; Jing, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Community dynamics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes in an estuary reservoir. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, T.; Jephson, T.; Carlsson, P. Molecular size of riverine dissolved organic matter influences coastal phytoplankton communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 409, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.W.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; Tuttle, T.; McKay, R.M.; Watson, S.B. Effects of increasing nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on phytoplankton community growth and toxicity during Planktothrix blooms in Sandusky Bay, Lake Erie. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7197–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, X.; Yu, Z.; Chiang, P.-C.; Jun, Y. Temperature and nutrients are significant drivers of seasonal shift in phytoplankton community from a drinking water reservoir, subtropical China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 5917–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, L.M.; Soares, M.C.S.; Paiva, R.; Silva, L.H.S. Morphology-based functional groups as effective indicators of phytoplankton dynamics in a tropical cyanobacteria-dominated transitional river–reservoir system. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 64, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, P.A.F.; Train, S.; Rodrigues, L.C. Spatial and temporal variation of phytoplankton in two subtropical Brazilian reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 2008, 607, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciric, M.; Gavrilović, B.; Simić, G.S.; Krizmanic, J.; Vidović, M.; Zebic, G. Driving factors affecting spatial and temporal variations in the structure of phytoplankton functional groups in a temperate reservoir. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2015, 44, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León López, N.; Rivera Rondón, C.A.; Zapata, Á.; Jiménez, J.; Villamil, W.; Arenas, G.; Carlos, A.; Tulio, S. Factors controlling phytoplankton in tropical high-mountain drinking-water reservoirs. Limnetica 2012, 31, 305–321. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, V.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Crossetti, L.O. Responses of phytoplankton functional groups to the mixing regime in a deep subtropical reservoir. Hydrobiologia 2009, 628, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthaud, F.; Vallod, D.; Robin, J.; Wezel, A.; Bornette, G. Short-term succession of aquatic plant species richness along ecosystem productivity and dispersal gradients in shallow lakes. J. Veg. Sci. 2013, 24, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Bi, Y.; Hu, Z. Responses of phytoplankton functional groups to the hydrologic regime in the Daning River, a tributary of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 450–451, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Qin, X.; Shi, H.; Zhou, R.; Dai, M.; Ding, D. Distribution and controlling factors of phytoplankton assemblages in a semi-enclosed bay during spring and summer. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padisak, J.; Crossetti, L.O.; Naselli-Flores, L. Use and misuse in the application of the phytoplankton functional classification: A critical review with updates. Hydrobiologia 2009, 621, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.-J.; Wang, T.; Hu, R.; Han, B.-P.; Wang, S.; Qian, X.; Padisák, J. Succession of phytoplankton functional groups regulated by monsoonal hydrology in a large canyon-shaped reservoir. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5099–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, D.G.; Bueno, N.C.; Bortolini, J.C.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Bovo-Scomparin, V.M.; de Souza Franco, G.M. Phytoplankton functional groups in a subtropical Brazilian reservoir: Responses to impoundment. Hydrobiologia 2016, 779, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, B.; Cai, Q.; Han, Q.; Gu, Y.; Qu, Y. Phytoplankton functional groups in a high spatial heterogeneity subtropical reservoir in China. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, H.S.; Wei, C.H.; Deng, Y.; Gao, N.Y. Principal component analysis to assess the composition and fate of impurities in a large river-embedded reservoir: Qingcaosha Reservoir. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Pan, D.; Chen, P. A two-year field study and evaluation of water quality and trophic state of a large shallow drinking water reservoir in Shanghai, China. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 57, 13829–13838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xie, B.; Yuan, Q.; Xu, W.; Lu, J. Microbial community study in newly established Qingcaosha Reservoir of Shanghai, China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9849–9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Leng, F.; Liu, H.; Schmidt, W. Stage Variation of Phytoplankton and Environmental Factors in a Large Drinking Water Reservoir: From Construction to Full Operation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Te, S.H.; He, Y.; Gin, K.Y.-H. The Effects of Antibiotics on Microbial Community Composition in an Estuary Reservoir during Spring and Summer Seasons. Water 2018, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.; Rice, E.; Baird, R. Standard Methods for the Determination of Water and Wastewater; APHA Publication Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H. The Freshwater Algae of China: Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, G.A. Textbook of Limnology; Waveland Press Inc.: Long Grove, IL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kunz, T.J.; Diehl, S. Phytoplankton, light and nutrients along a gradient of mixing depth: A field test of producer-resource theory. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.A.; Diehl, S.; Kunz, T.J.; Albrecht, D.; Oucible, A.M.; Ritzer, S. Light supply, plankton biomass, and seston stoichiometry in a gradient of lake mixing depths. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1898–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E.; Olrik, K.; Kristensen, P. Impact of nutrients and physical factors on the shift from cyanobacterial to chlorophyte dominance in shallow Danish lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1994, 51, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H.; Dürselen, C.-D.; Kirschtel, D.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G.; Likens, G.E. Limnological Analyses; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Padisák, J.; Borics, G.; Grigorszky, I.; Soróczki-Pintér, É. Use of Phytoplankton Assemblages for Monitoring Ecological Status of Lakes within the Water Framework Directive: The Assemblage Index. Hydrobiologia 2006, 553, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cai, Q.; Tan, L.; Kong, L. Phytoplankton development and ecological status during a cyanobacterial bloom in a tributary bay of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3820–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, J. Reducing eutrophication risk of a reservoir by water replacement: A case study of the Qingcaosha reservoir in the Changjiang Estuary. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Internal phosphorus loading in shallow Danish lakes. In Shallow Lakes’ 98; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999; pp. 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C. Non-determinism to probability, or N: P in the community ecology of phytoplankton: Nutrient ratios. Arch. Für Hydrobiol. 1999, 146, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohary, T.; Padisák, J.; Naselli-Flores, L. Phytoplankton in the physical environment: Beyond nutrients, at the end, there is some light. Hydrobiologia 2010, 639, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filstrup, C.T.; Heathcote, A.J.; Kendall, D.L.; Downing, J.A. Phytoplankton taxonomic compositional shifts across nutrient and light gradients in temperate lakes. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Xu, D. Seasonal succession of phytoplankton functional groups in a reservoir in central China. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2018, 192, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, Q.; Yan, X.; Xuan, J.; Zeng, J. Responses of summer phytoplankton community to drastic environmental changes in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) estuary during the past 50 years. Water Res. 2014, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouterfas, R.; Belkoura, M.; Dauta, A. Light and temperature effects on the growth rate of three freshwater algae isolated from a eutrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 2002, 489, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Estrada, V.; Parodi, E.R. Factors Triggering Cyanobacteria Dominance and Succession During Blooms in a Hypereutrophic Drinking Water Supply Reservoir. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xiong, J.; Wang, X.C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, B.; Pan, P.; Liu, Y.; Ding, F. Relationship between phytoplankton community and environmental factors in landscape water with high salinity in a coastal city of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 28460–28470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalu, T.; Wasserman, R.J. Cyanobacteria dynamics in a small tropical reservoir: Understanding spatio-temporal variability and influence of environmental variables. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, B.; Teubner, K.; Dokulil, M.T. Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellamano-Oliveira, M.J.; Vieira, A.A.H.; Rocha, O.; Colombo, V.; Sant’Anna, C.L. Phytoplankton taxonomic composition and temporal changes in a tropical reservoir. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2008, 171, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro Medeiros, L.; Mattos, A.; Lürling, M.; Becker, V. Is the future blue-green or brown? The effects of extreme events on phytoplankton dynamics in a semi-arid man-made lake. Aquat. Ecol. 2015, 49, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Huang, B.; Yu, C.; Chen, N.; Hong, H. Dynamics of phytoplankton communities in the Jiangdong Reservoir of Jiulong River, Fujian, South China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2014, 32, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Reynolds, C.; Irish, A. An investigation of dominance in phytoplankton using the PROTECH model. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U.; Gliwicz, Z.M.; Lampert, W.; Duncan, A. The PEG-model of seasonal succession of planktonic events in fresh waters. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1986, 106, 433–471. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.; Huang, T.; Zeng, M. Differences in phytoplankton dynamics and community structure between a wet year and dry year in the Zhoucun Reservoir. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2016, 31, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, Y.; Jeong, B. Short-term variations of phytoplankton communities in response to anthropogenic stressors in a highly altered temperate estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 156, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Interval | Mean | Interval | Mean | Interval | Mean | Interval | |
| WT (°C) | 13.7 | 9.5–16.9 | 25.2 | 22.8–25.8 | 19.2 | 15.4–23.0 | 7.0 | 6.8–7.2 |
| pH | 7.8 | 7.3–8.3 | 8.1 | 7.8–8.2 | 8.1 | 7.9–8.2 | 8.1 | 7.8–8.2 |
| DO (mg L−1) | 9.4 | 8.7–9.8 | 8.8 | 8.2–9.5 | 8.9 | 8.7–9.1 | 11.2 | 10.4–11.9 |
| EC (μs cm−1) | 473 | 207–838 | 166 | 160–176 | 182 | 179–186 | 363 | 225–440 |
| TN (mg L−1) | 2.20 | 1.93–2.44 | 1.78 | 1.50–2.19 | 1.54 | 1.41–1.72 | 2.02 | 1.64–2.25 |
| TP (mg L−1) | 0.14 | 0.13–0.15 | 0.13 | 0.10–0.19 | 0.11 | 0.10–0.12 | 0.14 | 0.18–0.20 |
| TN/TP | 18.5 | 15.1–20.7 | 14.9 | 9.4–19.1 | 16.1 | 15.4–17.2 | 21.1 | 14.2–28.5 |
| Chla (μg L−1) | 13.1 | 7.3–17.6 | 30.1 | 17.8–45.6 | 31.1 | 19.3–45.2 | 13.9 | 10.4–17.4 |
| SS (mg L−1) | 21.4 | 7.0–45.4 | 13.2 | 3.4–25.4 | 18.2 | 7.6–42.0 | 19.0 | 8.3–63.0 |
| WT = water temperature; DO = dissolved oxygen; EC = conductivity; TN = total nitrogen; TP = total phosphorus; Chl a = chlorophyll a concentration; SS = suspended solids. | ||||||||
| TP | TN | PO43− | NO3− | Chl a | EC | WT | pH | TDP | SS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | ||||||||||
| TN | 0.51 ** | |||||||||
| PO43− | 0.69 ** | 0.64 ** | ||||||||
| NO3− | 0.88 ** | 0.53 ** | ||||||||
| NH4+ | ||||||||||
| Chl a | −0.66 ** | −0.71 ** | −0.75 ** | −0.70 ** | ||||||
| EC | 0.60 ** | |||||||||
| WT | −0.47 ** | −0.58 ** | −0.83 ** | |||||||
| pH | −0.50 ** | −0.51 ** | 0.49 ** | |||||||
| DO | 0.70 ** | −0.80 ** | ||||||||
| TDP | 0.67 ** | 0.54 ** | 0.84 ** | −0.64 ** | −0.59 ** | |||||
| SS | 0.61 ** | 0.64 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.63 ** | −0.73 ** | −0.57 ** | 0.55 ** | |||
| Zeu | −0.61 ** | −0.65 ** | −0.71 ** | −0.65 ** | 0.81 ** | 0.54 ** | −0.61 ** | −0.92 ** | ||
| * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01. | ||||||||||
| Variables | Estuary (n = 24) | Upstream (n = 24) | Midstream (n = 36) | Downstream (n = 60) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chl a | Zeu | Chl a | Zeu | Chl a | Zeu | Chl a | Zeu | |
| TP | ||||||||
| TN | −0.59 ** | −0.64 ** | −0.60 ** | |||||
| PO43− | ||||||||
| NO3− | −0.83 ** | −0.56 * | −0.77 ** | −0.69 ** | ||||
| NH4+ | ||||||||
| Chla | 0.50 ** | 0.61 ** | ||||||
| EC | −0.68 ** | −0.75 ** | −0.79 ** | −0.73 ** | −0.66 ** | −0.66 ** | ||
| WT | 0.64 ** | 0.88 ** | 0.81 ** | 0.56 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.84 ** | ||
| pH | ||||||||
| DO | −0.54 ** | −0.39 ** | ||||||
| TDP | ||||||||
| SS | −0.79 ** | −0.84 ** | −0.66 ** | −0.51 ** | ||||
| Zeu | 0.55 ** | 0.61 ** | ||||||
| * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01. | ||||||||
| Functional Groups | Species Included in the Group | Taxonomic Groups | F Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | Thalassiosira lacustris | Bacillariophyta | 4.0 |
| C | Cyclotella meneghiniana, Asterionella formosa | Bacillariophyta | 5.0 |
| D | Fragilaria acus, Nitzschia spp. | Bacillariophyta | 2.0 |
| N | Cosmarium laeve | Chlorophyta | 5.0 |
| P | Melosira granulata | Bacillariophyta | 5.0 |
| MP | Diploneis ovalis, Cocconeis placentula | Bacillariophyta | 3.5 |
| TC | Oscillatoria spp., Phormidium spp., Gloeobacter spp. | Cyanophyta | 1.0 |
| TD | Ulothrix spp. | Chlorophyta | 4.0 |
| TB | Melosira varians | Bacillariophyta | 5.0 |
| X2 | Chroomonas acuta | Cryptophyta | 3.5 |
| X1 | Chlorella spp., Ankistrodesmus spp., Chlamydomonas spp. ChlororcoccumChlororcoccumChlororcoccumChlororcoccumChlororcoccum | Chlorophyta | 4.0 |
| Y | Cryptomonas ovata, Cryptomonas erosa | Cryptophyta | 2.0 |
| F | Sphaerellocystis ampla, Selenastrum spp., Westellopsis linearis | Chlorophyta | 5.0 |
| G | Pandorina morum | Chlorophyta | 1.0 |
| J | Scenedesmus spp, Crucigenia quadrata | Chlorophyta | 1.0 |
| K | Synechocystis aquatilis, Dactylococcopsis spp. | Cyanophyta | 2.0 |
| LO | Chroococcus spp., Merismopedia spp. | Cyanophyta | 0 |
| M | Microcystis spp. | Cyanophyta | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Nan, J.; Li, J. Driving Factors and Dynamics of Phytoplankton Community and Functional Groups in an Estuary Reservoir in the Yangtze River, China. Water 2019, 11, 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061184
Yang C, Nan J, Li J. Driving Factors and Dynamics of Phytoplankton Community and Functional Groups in an Estuary Reservoir in the Yangtze River, China. Water. 2019; 11(6):1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061184
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Changtao, Jing Nan, and Jianhua Li. 2019. "Driving Factors and Dynamics of Phytoplankton Community and Functional Groups in an Estuary Reservoir in the Yangtze River, China" Water 11, no. 6: 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061184
APA StyleYang, C., Nan, J., & Li, J. (2019). Driving Factors and Dynamics of Phytoplankton Community and Functional Groups in an Estuary Reservoir in the Yangtze River, China. Water, 11(6), 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061184







