Abstract
The optimal design of Water Distribution Systems (WDSs) using multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (MOEAs) has received substantial attention in the past two decades. Many MOEAs have been proposed and applied successfully to this challenging problem. However, these tools are primarily considered black-boxes by end users, especially when the algorithm parameterization issues are taken into consideration. This paper presents a simple yet effective method for capturing the interrelationships among the five key parameters of the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II), which is one of the state-of-the-art MOEAs in this field. Two representative boundary values for each parameter are selected from a reasonable range, and all the possible combinations are tested on three benchmark design problems. Those benchmarks are based on two widely used small networks and a larger, real-world irrigation network. Results suggest that there is a hierarchy of impacts imposed by the five parameters of NSGA-II. The population size turns out to be the most important one, which implies that NSGA-II is sensitive to the initial population, especially for complex problems. A relatively large population size increases the diversity of a population; hence some key genes may be identified at the beginning (or early stage) of search. Furthermore, it transpires that the distribution indices of crossover and mutation have a more significant impact than their probabilities, where the former are generally overlooked by previous studies. Some useful guidelines are also provided, which can improve the efficacy of NSGA-II and increase the chance of identifying near-optimal solutions.
1. Introduction
A Water Distribution System (WDS) plays a crucial role in delivering potable drinking water from a treatment plant to households and other types of water utility customers, e.g., industrial and commercial users. The capital investments and maintenance costs of such underground infrastructure are large; hence a detailed cost-effectiveness analysis at the design stage is necessary to facilitate the decision-making. In the past, this task was usually given to experienced engineers who have a sound understanding of the entire system. As a WDS tends to grow larger and more complex over time due to urbanization and system expansion, it is challenging for engineers to design a large-scale network considering a number of performance measures by merely relying on domain-specific knowledge and experience.
Advances in WDS simulation and optimization techniques, which emerged in the mid-1970s [1], provide promising tools to support decision making for WDS design tasks. Initially, the optimal design of WDSs was often formulated as a single-objective optimization problem. This means minimizing the total costs while meeting all the design criteria including minimum nodal pressure heads at junctions and/or economical flow velocities within pipes [2,3,4]. However, this approach was often criticized for compromising on other essential aspects of WDS performance, such as reliability, water quality, and vulnerability [5,6,7]. An optimal least-cost solution is likely to result in less resilient infrastructure that cannot cope with unexpected conditions (e.g., pipe burst or power outage). Later, the multi-objective formulation (i.e., two or three objectives considered simultaneously) was introduced by the research community. This has the advantage of being able to identify the trade-off between costs and hydraulic performance (e.g., system reliability) explicitly [8]. As more advanced optimization tools have become available in recent years, the many-objective formulation (i.e., with more than three objectives concerned) became increasingly popular [9,10]. In this approach, the highly complex interrelationships among different goal attainments, also known as the hypersurface [11], can be visualized and analyzed, thus facilitating a better-informed decision-making process [12].
During the period when the focus changed from the single-objective to many-objective formulations, advances in optimization algorithms were the main driving force behind a series of breakthroughs in both the algorithmic framework and computational efficiency. In particular, multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (MOEAs) have attracted more attention as they can identify the Pareto front more efficiently than traditional operations research methods (e.g., linear and non-linear programming). MOEAs do not require the gradient or derivative information of the objective functions, and they start the optimization from multiple locations using the population-based search mechanism. Therefore, the pursuit of more powerful MOEAs has become an active and cutting-edge direction in the research community. From the mid-1980s to nowadays, many MOEAs have been created. Among those, the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) [13] has been extensively applied to a wide range of disciplines including water engineering. As the continuous development of more powerful MOEAs, some hybrid algorithms have gained growing attention in the last decade. The two most-cited such algorithms are a multialgorithm, genetically adaptive multiobjective (AMALGAM) method [14] and the Borg MOEA [15], which embed diversified search operators (four and six, respectively) to improve the robustness and accuracy of MOEAs. Inspired by AMALGAM and Borg, a tailored MOEA for the optimal design of WDSs called GALAXY was developed and validated on a range of benchmark design problems with increasing complexities [16]. These hybrid MOEAs have great potential in shaping the future of this research area.
Despite considerable success in the creation of more advanced MOEAs, there is a rare discussion of some fundamental questions regarding their applications to WDS optimization. That is, by developing new MOEAs and verifying them on selected benchmark design problems, do we really understand these tools well or have sufficient confidence in applying them on larger, real-world design problems? Currently, MOEAs are, to a large extent, black-box tools, which limits their utility to researchers and practitioners. This is particularly true when the parameterization issues are considered. Quite often they have a number of parameters that need to be tuned for best performance. The main challenges of applying MOEAs involve their reliability, robustness, and accuracy, which are profoundly influenced by the choices of the most appropriate algorithm and the corresponding parameter values [17]. The fine-tuning of these parameters before an application is a common rule-of-thumb, although further guidelines on how to do that are generally lacking.
Most recently, Cisty et al. [18] employed the NSGA-II to solve the optimal design of a large real-world irrigation network. They tested varying standard settings of associated parameters (i.e., crossover and mutation probabilities, as well as the population sizes), rather than adopting the recommended settings (fixed values) from literature. By using this approach, a new best-known least-cost solution was found for the problem they studied. Their work highlights the potential for obtaining equally good, if not better, solutions with existing optimization methods but with their parameters suitably selected to take full advantage of methods’ capabilities. More importantly, knowing the efficient value ranges for the parameters is necessary to avoid the time-consuming process of fine-tuning.
Motivated by the work mentioned above, this paper reverts to the classical NSGA-II rather than hybrid MOEAs in an attempt to explore the interrelationships among algorithm parameters and discover their impact on the performance. In particular, we aim to address the following two questions: (1) How do various parameters within NSGA-II influence its performance, and (2) can we develop practical guidelines for settings those parameters? By addressing the above questions, this paper contributes to the gaining of in-depth knowledge of NSGA-II applied to the optimal design of WDSs and an effective way for the research community to take full advantage of this optimization tool with improved performance. Furthermore, we also hope to influence the development of new MOEAs by opening the black-box and providing some insights into the behavior of the search operators.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 provides a moderate introduction to NSGA-II and a representative summary of its applications to the WDS design problems. Then, the proposed methodology of investigating the parameterization of NSGA-II is detailed in Section 3. Section 4 includes a short description of each case study and the experimental setup. The results obtained from three case studies and related discussion are demonstrated in Section 5. Finally, Section 6 draws key conclusions and identifies research limitations.
2. Current Understanding of NSGA-II
NSGA-II is arguably the most popular MOEA in the water research community. It is acknowledged as an “industry standard” algorithm that has been successfully applied to a variety of water resources optimization problems [12,17,19]. It features a fast non-dominated sorting approach to ranking solutions primarily based on the Pareto dominance relationship. Solutions with higher rankings survive and are selected to reproduce. For those solutions that are non-dominated to each other (i.e., with the same ranking), a secondary sorting criterion known as the crowding distance is used to further discriminate among solutions. Solutions with larger crowding distances are preferred in this approach. The standard NSGA-II implements a binary tournament selection to establish the mating pool (i.e., parents) and applies the Simulated Binary Crossover (SBX) and the Polynomial Mutation (PM) with designated probabilities to create children from parents [13]. The implicit elitism strategy ensures the best solutions ever found in the search history are always retained in the population. This allows a new population to be derived from the combination of parents and their offspring via the fast non-dominated sorting approach. NSGA-II also provides a constraint-handling technique to efficiently deal with constrained problems and supports both binary and real coding representations.
NSGA-II has various parameters which may have different impacts on its computational effectiveness. The most often studied are the population size (PS), the number of function evaluations (NFEs), the probability of SBX (Pc), and the probability of PM (Pm). PS and NFEs together determine the total computational budget applied to a given problem. That is, the ratio of NFEs to PS is equal to the number of generations over which NSGA-II will evolve. Note that a larger number of generations normally ensures better convergence of NSGA-II. However, the convergence rate declines significantly as the optimization proceeds, and only minor improvements may be achieved with an additional computational budget. However, it is also essential to pay particular attention to PS, as an inadequately small value may result in a crowded population, i.e., with a number of similar solutions, rather than a diversified set. This normally leads to premature convergence due to the insufficient exchange of new information in the gene pool of the population. Pc and Pm control the chance of each chromosome undergoing the crossover and mutation processes, respectively. A widely adopted strategy is to keep a high value of Pc (e.g., 0.9) and a low value of Pm (e.g., the inverse of the number of decision variables (NDVs), 1/NDVs). The crossover rate, as the predominant search driver, plays a critical role during optimization. The mutation rate contributes mainly to prevent the population from being trapped in local optima.
There are another two important parameters which may significantly affect the performance of NSGA-II, which are the distribution indices of SBX and PM (denoted as DIc and DIm, respectively). As previously mentioned, SBX and PM are the main search operators within NSGA-II, producing improved children from parents with designated probabilities (i.e., Pc and Pm). SBX mimics the search behavior of the single-point crossover used in binary-coded genetic algorithms and is suitable for optimization problems with real or discrete decision variables. The positions of children points are distributed around their parents following the exponential laws of DIc (for more details, see [20]). Similar to SBX, the search behavior of PM also depends on the exponential laws of DIm. As such, each distribution index directly influences the Euclidean distance of the offspring from their parents in the decision variable space (eventually reflected in the objective space). Explicitly, a larger value of DIc or DIm keeps the offspring similar (i.e., close) to their parents. In contrast, a smaller value increases the probability of generating offspring substantially different (i.e., far) from their parents (Figure 1). In short, DIc and DIm control the search step sizes, while Pc and Pm determine the likelihood of implementing such search steps in the decision variable space. Consequently, a proper combination of these five parameters (i.e., PS, Pc, Pm, DIc, and DIm), in addition to a sufficient computational budget, can lead to a better and more robust search behavior of NSGA-II, thus eventually improving the quality of Pareto fronts obtained.
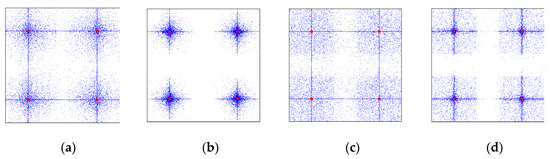
Figure 1.
Impact of DIc and DIm on the distribution of offspring in the decision variable space (The red dots indicate the four parents used in SBX and PM. The blue dots denote the ten thousand offspring generated randomly from these parents with specified DIc and DIm); (a) DIc = 1; DIm = 20; (b) DIc = 20; DIm = 20; (c) DIc = 1; DIm = 1; (d) DIc = 20; DIm = 1.
We have conducted an extensive literature survey regarding the applications of NSGA-II to WDS design problems (see Table 1) and found that fine-tuning of the NSGA-II parameters had often not been performed. Instead, authors followed the recommended settings from literature, mainly originated from Deb et al. [13]. The ranges of the three primary parameters—namely PS, Pc, and Pm—were found to be within the following bounds: PS ∈ [40,1000], Pc ∈ [0.80,0.98], and Pm ∈ o(1/NDVs). NFEs was often determined according to the size of the design problems, with larger cases using higher NFEs values. Surprisingly, only a few previous studies focused on the fine-tuning of DIc and DIm, which implies that the potential of NSGA-II might not be fully utilized in those applications.

Table 1.
Literature survey on the applications of the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) to Water Distribution Systems (WDS) design problems.
Though using different parameter combinations proved to be an effective way of eliminating the need for fine-tuning, Cisty et al. [18] did not elaborate on how various parameters were altered in their experiment. In other words, the two key questions related to the parameters setting and practical guidance for their selection were not adequately addressed. The current understanding and applications of NSGA-II reveal the gaps between the potential of this classic MOEA and the knowledge of its parameterization. Therefore, by improving our understanding of the complicated nexus among different parameters, we aim to provide guidance for future utilization of NSGA-II, i.e., by alleviating the criticism of the black-box characteristics of MOEAs to a great extent.
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Formulation
A mathematical definition of the optimal design of WDSs considered in this work is given in Equation (1). The optimization problem is formulated as the minimization of the total capital costs and the total hydraulic head deficit, with pipe diameter options as decision variables that can be chosen from a list of discrete sizes available in the market. This multi-objective formulation is a relaxed form of the least-cost design of WDSs, in which the constraints regarding the minimum nodal heads are converted to the other objective. The benefits of using this kind of formulation are twofold. Firstly, it eliminates the troublesome task (often time-consuming) of setting the penalty factor to discriminate the infeasible solutions from feasible ones. Secondly, in case of the insufficient budget, this formulation can provide many alternative solutions that marginally violate the head requirements but with significant investment savings. The latter point is probably a great advantage in dealing with practical projects.
where Ctotal is the total capital costs, U(Di) is the unit cost of pipe i which depends on its corresponding diameter (the relationship between sizes and unit costs is available from the manufacturer which is usually non-linear), Li is the length of pipe I, np is the number of pipes considered in the design stage, Hd is the total head deficit, Hmin is the minimum required head at node j, Hj is the actual head at node j, nn is the number of nodes within the network, Di is the diameter option for pipe i, and ns is the number of commercially available pipe sizes.
3.2. Proposed Methodology of Investigating the Parameterization of NSGA-II
The behavior of evolutionary algorithms depends on the underlying parameters. According to the “No Free Lunch” theorems [33], it is impossible to find a group of parameters which are always effective across various optimization problems. In other words, for a particular type of problem like the optimal design of WDS, which is the focus of this paper, there exist a set of highly effective parameter values that match NSGA-II capabilities to the characteristics of WDS design problems. When multiple parameters are involved, the interrelationships and interactions among them can be even more complex. Furthermore, the impact of randomness in the initialization of the population should also be taken into account. In particular, the number of possible interaction combinations increases exponentially with the number of parameters concerned as well as the sampling density within the associated ranges. On the other hand, it is essential to balance the computational effort of reducing the impact of uncertainty imposed by random seeds while implementing a sufficient number of independent runs.
In this paper, we select two representative values in the range of each parameter as an attempt to keep the numerical experiments manageable. More specifically, five NSGA-II parameters (i.e., PS, DIc, DIm, Pc, and Pm) are investigated, leading to 32 parameter combinations in total (i.e., 25 = 32). For each parameter combination, 100 independent runs are conducted for smaller benchmark design problems, while 50 runs are carried out for a larger design problem. Compared to the previous studies summarized in Table 1, we believe these choices can provide more reliable results. At least 2000 generations are allowed to ensure a sufficient convergence of NSGA-II. Total NFEs vary from case to case and are determined according to the search space size of each WDS design problem.
As mentioned earlier, the multi-objective formulation is used to identify a set of non-dominated solutions, presenting the trade-off between total capital costs and the total head deficit. In this paper, our focus is on the least-cost solutions which fully satisfy the nodal head requirements, rather than the convergence and diversity of the Pareto fronts. In this sense, the quality of solutions obtained by a specific parameter combination can be evaluated via the frequency of identifying the currently best-known solution to each benchmark design problem (denoted as Freq). This is a direct and objective indicator for assessing the reliability, robustness, and accuracy of NSGA-II for the problem formulation adopted in the current study. Another commonly used metric is also adopted: The averaged capital costs of solutions without head deficit over multiple independent runs (denoted as Avg). Equations (2)–(4) show how these two performance metrics are calculated. When ranking the effectiveness of all the parameter combinations of NSGA-II, we use the Freq as the primary indicator and the Avg as the secondary one. However, one needs to bear in mind that a marginal difference in Freq and/or Avg should not be overemphasized when interpreting the comparison results.
where Tj is a Boolean value, indicating whether the currently best-known solution for a specific case study is found at run j; is the best solution found at run j; is the total head deficit of the best solution found at run j; and nr is the number of independent runs.
The parameterization impact of NSGA-II is illustrated in the format of a compass plot initially used in [34]. Generally speaking, the compass plot is used to demonstrate how the performance of NSGA-II varies according to different combinations of its parameters. More specifically, each parameter is represented by an individual ring and an associated color. Different depths of the same color scheme indicate the two representative values selected for a specific parameter. For instance, PS is shown in the innermost ring with the salmon and red colors denoting PS = 40 and PS = 200, respectively. As such, the combinations of five controlling parameters of NSGA-II (i.e., PS, DIc, DIm, Pc, and Pm) are shown in five colored rings (in an outwards order), and their effectiveness in terms of Freq is shown in the outermost gray ring. Every five-colored-slot in the radial direction of the compass plot (from the red to purple schemes) denotes a particular combination of parameters, and the gray patch next to it in the outermost ring suggests its effectiveness. The whole plot is sorted by the performance of NSGA-II in descending order in the counter-clockwise direction. In this way, one can quickly identify how the highly effective parameter combinations are comprised. For example, in Figure 3 the most effective parameter combination for solving the first case study (i.e., PS = 200, DIc = 20, DIm = 1, Pc = 0.9, Pm = 0.0476) was able to identify the best-known solution with a Freq equal to 0.97 over 100 independent runs. Furthermore, using the compass plot facilitates the analysis on the “sweet spots” within the parameter space of NSGA-II, which in turn contributes to the identification of practical guidelines for setting those parameters.
4. Case Studies
We selected three benchmark networks from the literature to illustrate how the parameterization of NSGA-II affects its performance and which parameter(s) has a dominant impact on the quality of solutions obtained. In particular, two widely used small cases were chosen, namely the New York tunnel [35] and the Hanoi [36], as well as a larger irrigation network design problem [37]. Figure 2 shows the layout of each network. For detailed information including the available pipe sizes and the associated unit costs of these cases, readers are referred to the following website http://tinyurl.com/cwsbenchmarks/.
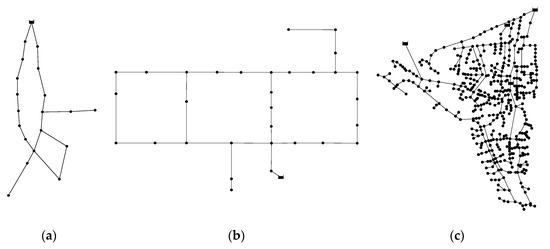
Figure 2.
The layout of each benchmark network. (a) NYT; (b) HAN; (c) BIN.
4.1. New York Tunnel Network (NYT)
The New York Tunnel Network (NYT) was first proposed as a rehabilitation activity undertaken in an existing tunnel system which was the primary water distribution system of the city of New York, USA. The NYT is comprised of twenty-one pipes organized in two loops, nineteen demand nodes, and one reservoir with a fixed head of 91.44 m (300 ft.). All the existing pipes are considered for duplication to meet the projected future demand. The Hazen-Williams roughness coefficient for both new and existing pipes is 100. The minimum pressure of all the demand nodes is fixed at 77.72 m (255 ft.) except for nodes 16 and 17 that are 79.25 m (260 ft.) and 83.15 m (272.8 ft.), respectively. A selection of fifteen diameter sizes is available as well as a ‘do nothing’ option. Therefore, the search space is equal to 1621 ≈ 1.93 × 1025 discrete combinations.
4.2. Hanoi Network (HAN)
The Hanoi Network (HAN) resembles a water distribution system in Hanoi, the capital of Vietnam. The HAN consists of thirty-four pipes organized in three loops, thirty-one demand nodes, and one reservoir with a fixed head of 100.0 m. The Hazen-Williams roughness coefficient for all pipes is 130. The minimum head above the ground elevation of each node is 30.0 m. There are six commercially available pipe sizes, ranging from 304.8 mm (12.0 in.) to 1016.0 mm (40.0 in.). Therefore, the search space is equal to 634 ≈ 2.87 × 1026 discrete combinations. Due to a very limited range of pipe sizes, the HAN has a vast region of infeasible solutions in the landscape of decision variables, thus increasing the level of difficulty to identify near-optimal solutions.
4.3. Balerma Irrigation Network (BIN)
The Balerma Irrigation Network (BIN) represents an adaptation of the existing irrigation system in the Sol-Poniente irrigation district, which is located in Balerma province of Almería, Spain. The distinguishing feature of this network is that all nodes have the same demand of 5.55 L/s across the network. The BIN has 454 relatively short pipes, 443 demand nodes (hydrants), and four reservoirs with fixed heads between 112.0 m and 127.0 m. The material of pipes is polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The Darcy-Weisbach roughness coefficient of 0.0025 mm is applied to all the pipes. The minimum pressure head above the ground elevation is 20.0 m for all the demand nodes. There are a total of ten commercially available sizes, ranging from 113.0 mm to 581.8 mm. Therefore, the search space is equal to 10454 discrete combinations.
4.4. Experimental Setup
The NYT and HAN have been widely used in most previous works as small and real-world WDS design problem. The currently best-known solutions to the least-cost design of NYT and HAN are $38.64 million and $6.081 million, respectively [38]. The BIN has also attracted the attention of optimization technique developers, and the recently updated least-cost solution is €1,921,400 [18]. With these best-known solutions, it is convenient to evaluate the performance of NSGA-II by the indicators of Freq and Avg under different parameter value combinations. The NFEs set for solving the NYT and HAN design problems are 0.5 and 0.6 million, respectively. Both design problems are solved 100 times independently using different random seeds with the designated NFEs. For the BIN problem, due to a significantly increased search space size, the NFEs are extended to five million which is ten times of that for the NYT problem. However, due to the excessive runtime for this problem, the number of independent optimization runs is reduced to 50 times.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. The NYT Design Problem
Figure 3 shows the compass plot obtained in solving the NYT design problem, with the boundary values selected for the five parameters indicated. Typically, we considered a minimum PS of 40 and a maximum PS of 200. This is believed to be contrasting enough. The DIc and DIm were both bounded by 1 and 20 due to the preliminary observations in which the values more than 20 significantly reduced the diversity of the offspring derived from their parents [20]. The most recommended Pc and Pm were adopted, i.e., 0.9 and 0.0476 (1/21), respectively. In contrast, a Pc of 0.45 and a Pm of 0.0952 were also used as choices of a much lower SBX rate and a much higher PM rate.
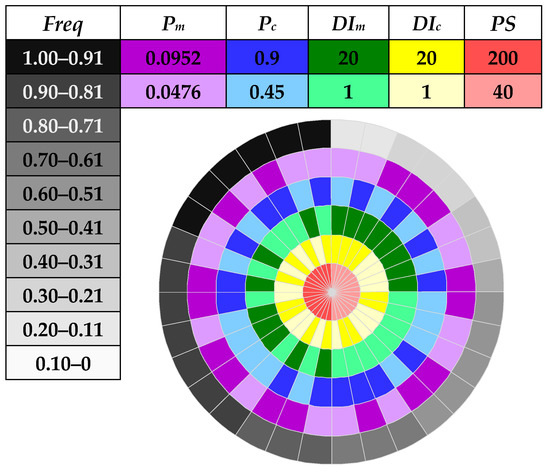
Figure 3.
Parameterization of NSGA-II applied to the New York Tunnel Network (NYT) design problem.
It is evident that different combinations led to dramatically varying performance, as the gray ring covered the whole spectrum of the designated intervals. Surprisingly, the combinations with a PS of 200 accounted for the top half (left) of the gray ring, suggesting that for this benchmark design problems PS was the dominating parameter. With a larger PS, no matter how the other four parameters were set, NSGA-II was able to identify the best-known solutions at a frequency higher than 0.75 out of 100 independent runs consistently. This was already a very high level of robustness and accuracy. Even for the topmost interval (i.e., Freq greater than 0.9), the other four parameters can be arbitrarily combined as long as DIc and DIm were not equal to 20 concurrently. From the right half of the compass plot, it is observed that DIm was probably the second important parameter since a larger DIm always resulted in worse performance. Pc and Pm turned out to have a minor impact on the behavior of NSGA-II. This is somewhat contradictory to what previous studies had concluded, in which Pc and Pm were fine-tuned but DIc and DIm were usually neglected.
5.2. The HAN Design Problem
Figure 4 shows the compass plot obtained in solving the HAN design problem. The boundary values selected for Pc, DIc, and DIm were the same as those used in NYT. PS was set to 60 and 300. The recommended Pm (i.e., 1/34) and a double of that setting were adopted again. From Figure 4, it is revealed that NSGA-II had difficulties in dealing with the HAN design problem, as the maximum Freq was less than 0.7 even if the search space size is quite close to that of NYT, and larger PS and NFEs were used. This is perhaps because HAN has a vast region of infeasible solutions; hence NSGA-II had to spend more effort in finding a feasible solution which fully satisfies the nodal head requirements, leading to less robust and accurate performance.
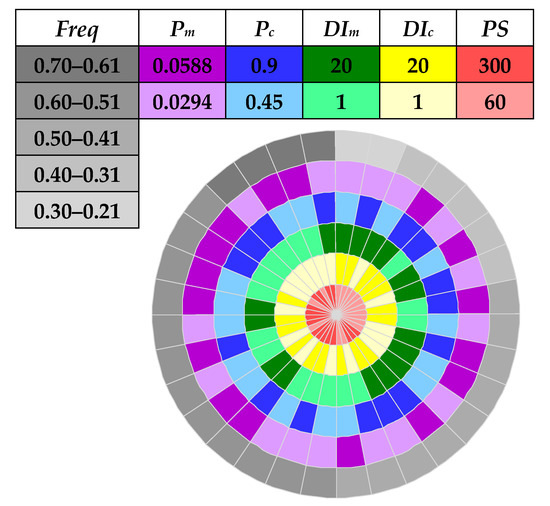
Figure 4.
Parameterization of NSGA-II applied to the Hanoi Network (HAN) design problem.
PS still turned out to be the most critical parameter, as the majority of parameter combinations (i.e., 13 out of 16) with a PS of 300 managed to achieve Freq values larger than 0.5. For the other three combinations, their Freq values were quite close to 0.5. On the contrary, only three combinations with a PS of 60 managed to obtain Freq values greater than 0.5, with the rest 69% of combinations obtained Freq values less than 0.5. DIc and DIm were less critical compared to PS but had a more significant impact than Pc and Pm. In particular, When DIc and DIm were both equal to 1, no matter what PS, Pc, and Pm were set, the Freq was consistently higher than or equal to 0.5. However, if both DIc and DIm were set to 20, the combinations of the other three parameters had only a 25% chance to obtain Freq values larger than 0.5. Again, Pc and Pm only had a marginal effect on the effectiveness of NSGA-II.
5.3. The BIN Design Problem
First of all, it is worth noting that the Freq indicator used for the BIN problem had a different definition. Precisely, the currently best-known solution, i.e., €1,921,400 million, was challenging due to insufficient NFEs adopted (The reported precision is given here only for comparison purposes as for any practical decision support this would indicate unrealistic certainty). This solution was obtained via 20 million NFEs [18], which was four times the NFEs used in this paper. Alternatively, we counted the number of solutions which cost no more than €1.93 million to yield the corresponding Freq for the following reasons: (1) This level of accuracy is believed to be reasonable from a practical perspective, and (2) most previous studies only found solutions greater than €1.94 million even ten to thirty million NFEs were used according to [18,38].
In this case, DIc and DIm seemed to have at least the same level of impact, if not higher, compared with PS (see Figure 5). In particular, six out of the top seven parameter combinations, which achieved Freq values larger than 0.8, had both parameters equal to 20. All the parameter combinations followed this setting were able to obtain Freq values no less than 0.5, implying a 50% chance to identify a least-cost solution that is less than €1.93 million. In contrast, if both DIc and DIm were set to 1, the majority of parameter combinations performed less competent or even resulting in complete failure (i.e., the Freq was equal to zero) no matter what PS was chosen. The values of Freq seem to be insensitive to Pc and Pm, and a Pc of 0.45 or a Pm of 0.011 (which was five times the most recommended mutation probability) had equally good performance compared with the generally used settings, which looks quite counterintuitive.
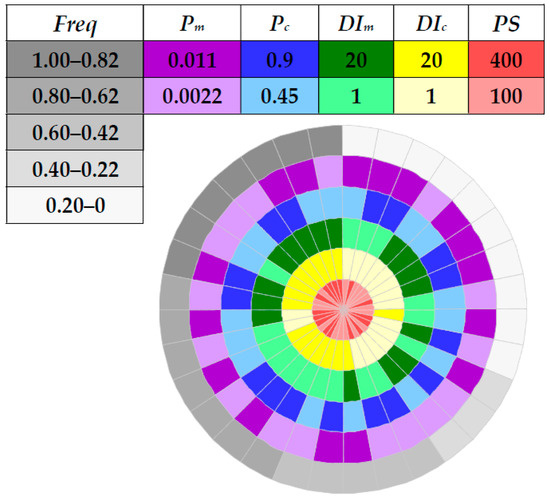
Figure 5.
Parameterization of NSGA-II applied to the Balerma Irrigation Network (BIN) design problem.
5.4. A Further Experiment on the BIN Design Problem
To enable a fair comparison, we increased the NFEs for the BIN problem up to 20 million, which was the same as used in Cisty et al. [18] and is the largest computational budget ever used in the literature for solving this benchmark design problem. We also conducted ten independent runs for statistical results. Two variants of the search space reduction strategies inspired by Cisty et al. [18] were employed. One was to use the common range of each decision variable derived from all the non-dominated solutions found after 10 million NFEs (marked as Strategy I), and the other was to use the common range of each decision variable derived from all the least-cost solutions (marked as Strategy II). The rest 10 million NFEs were then resumed with the updated ranges of decision variables following Strategies I and II. The former strategy achieved a similar level of search space reduction (i.e., 6.02 × 10213) compared with that (i.e., 10200) reported in [18], while the latter one dramatically decreased the search space size from 10454 to 2.26 × 10101. Hinted from the findings on three benchmark design problems, the population sizes were raised to 400 and 1000, and the two representative boundary values of DIc and DIm were both set to 10 and 30. In addition, Pc and Pm were kept at 0.9 and 0.0022 (i.e., most recommended settings), respectively.
Statistical results in Table 2 suggest that Strategy II consistently worked better than Strategy I by obtaining higher Freq and lower Avg and Min. In other words, Strategy II is more effective than that proposed in Cisty et al. [18] by reducing the search space size to a dramatically lower level. However, it should be noted that this effect may not be extended to other multi-objective problem formulations because using Strategy II can increase the risk of restricting the initial population to local optima. A very close least-cost solution (i.e., €1,921,455) was found with only a 0.05‰ difference from the currently best-known one (i.e., €1,921,400). The small discrepancy in the best solutions found by the two approaches is probably due to the differences in the computational precision used. On the other hand, a larger value of PS ensured better performance, which remained consistent with the observations as mentioned earlier.

Table 2.
Statistical results of solving the BIN design problem using 20 million number of function evaluations (NFEs).
6. Conclusions
This paper has proposed a simple yet effective methodology to capture the impact of various parameters on the performance of NSGA-II. In particular, by selecting two representative values from within the range of each key parameter and using the proposed compass plot, one can intuitively identify the interrelationship among different parameters and their influence on the behavior of NSGA-II, which in turn facilitates the identification of general guidelines for setting those parameters. As a spin-off, a more effective strategy of reducing the search space size has been realized when comparing the performance of NSGA-II with application to the design of a real-world irrigation network, following the derived guidelines of parameter settings.
The main conclusions are as follows. First, there is a hierarchy of impact imposed by the five NSGA-II parameters, which implies that their influences are not equally significant. Based on the results obtained in the selected benchmark design problems of WDSs, PS tends to be the paramount parameter that has a more profound impact on the performance of NSGA-II than the other ones, followed by DIc and DIm. In contrast, the values of Pc and Pm are of minor impact on the effectiveness of NSGA-II in this paper. These findings highlight some aspects that were often neglected in previous studies, with many papers cited in Table 1 having used a fixed PS of 100, a recommended Pc and Pm in combination with default or unknown DIc and DIm, no matter how large the search space size was.
Second, the interrelationships among the five key parameters are complex and are case by case dependent. Thus, it is highly recommended to fine-tune these five parameters, preferably following the method proposed in this paper, to confirm which combinations have great potential to identify the near-optimal solutions. This suggestion can save the computational budget and time substantially when dealing with larger, real-world design problems.
Last but not least, the key recommendation for applying NSGA-II to the optimal design of WDSs is to use a reasonably large PS, which usually depends on the scale of the design problem. This will significantly improve the diversity of the initial population, thus lowering the risk of getting trapped in local optima and increasing the probability of finding near-optimal solutions. The second recommendation is to pay particular attention to the choices of DIc and DIm, rather than Pc and Pm, since the former two parameters are more important to affect the positions of the offspring generated from their parents. Considering the discrete nature of WDS design problems and the monotonicity of DIc and DIm, their ranges should be kept between 1 and 20. By contrast, default values of Pc and Pm (i.e., 0.9 and 1/NDVs) are expected to be sufficient (no need of fine-tuning).
There are some limitations of the current work, which are elaborated as follows. First, since the impact of parameter settings on the performance of NSGA-II are usually non-linear, it is therefore unknown to what extent selecting two representative values within the range of each parameter can adequately reflect the underlying correlation among various parameters. Second, the characteristics of the design problems being solved and their effect on the parameterization of NSGA-II is not considered in this work. Several relevant studies have pointed out that the behavior of MOEAs has a close interrelationship with the landscape of the search space [12,15,39]. Therefore, possible changes to the problem formulations may be able to reveal more of the nature of the complicated nexus between optimization problems and MOEAs. Whether this underlying relationship can significantly affect the understanding and application of MOEAs is a worthy future direction for research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.W. and L.W.; methodology, Q.W., L.W., and S.L.; coding, L.W. and W.H.; formal analysis, L.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.W.; writing—review and editing, Z.W., S.L., and D.A.S.; visualization, Q.W.; funding acquisition, S.L.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 51879139.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Milan Cisty for sending the best solution he found in the format of EPANET2 input file, so that we were able to compare our solution with the currently best-known one in the literature.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mala-Jetmarova, H.; Barton, A.; Bagirov, A. A history of water distribution systems and their optimisation. Water Sci. Technol.-Water Supply 2015, 15, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, D.A.; Walters, G.A. Genetic Algorithms for Least-Cost Design of Water Distribution Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 1997, 123, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandy, G.C.; Simpson, A.R.; Murphy, L.J. An Improved Genetic Algorithm for Pipe Network Optimization. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, G.A.; Lohbeck, T. Optimal Layout of Tree Networks Using Genetic Algorithms. Eng. Optim. 1993, 22, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walski, T.M. The Wrong Paradigm, Why Water Distribution Optimization Doesn’t Work. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2001, 127, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, T.D.; Park, N.-S. Multiobjective Genetic Algorithms for Design of Water Distribution Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2004, 130, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakoudis, V.K. Vulnerability based management of water resources systems. J. Hydroinform. 2004, 6, 133–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halhal, D.; Walters, G.; Ouazar, D.; Savic, D. Water Network Rehabilitation with Structured Messy Genetic Algorithm. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 1997, 123, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khu, S.-T.; Keedwell, E. Introducing more choices (flexibility) in the upgrading of water distribution networks: the New York city tunnel network example. Eng. Optim. 2005, 37, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Kapelan, Z.; Kasprzyk, J.R.; Reed, P. Optimal Design of Water Distribution Systems Using Many-Objective Visual Analytics. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2013, 139, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, M.J.; Reed, P.M.; Simpson, T.W. Many objective visual analytics: rethinking the design of complex engineered systems. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2013, 48, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, P.M.; Hadka, D.; Herman, J.D.; Kasprzyk, J.R.; Kollat, J.B. Evolutionary multiobjective optimization in water resources: The past, present; future. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 438–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A Fast and Elitist Multiobjective Genetic Algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; Robinson, B.A. Improved Evolutionary Optimization from Genetically Adaptive Multimethod Search. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadka, D.; Reed, P. Borg: An Auto-Adaptive Many-Objective Evolutionary Computing Framework. Evol. Comput. 2013, 21, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Savić, D.A.; Kapelan, Z. GALAXY: A new hybrid MOEA for the optimal design of Water Distribution Systems. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 1997–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Kapelan, Z.; Kasprzyk, J.; Kollat, J.; Matott, L.S.; Cunha, M.C.; Dandy, G.C.; Gibbs, M.S.; Keedwell, E.; Marchi, A. Evolutionary algorithms and other metaheuristics in water resources: Current status, research challenges and future directions. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 62, 271–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisty, M.; Bajtek, Z.; Celar, L. A two-stage evolutionary optimization approach for an irrigation system design. J. Hydroinform. 2017, 19, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mala-Jetmarova, H.; Sultanova, N.; Savic, D. Lost in Optimisation of Water Distribution Systems? A Literature Review of System Design. Water 2018, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Agrawal, R.B. Simulated binary crossover for continuous search space. Complex Syst. 1995, 9, 115–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.; Qi, Z.; Bi, W.; Zhang, T.; Yu, T.; Shao, Y. Improved Understanding on the Searching Behavior of NSGA-II Operators Using Run-Time Measure Metrics with Application to Water Distribution System Design Problems. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 1121–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zecchin, A.C.; Maier, H.R.; Simpson, A.R. Comparison of the searching behavior of NSGA-II, SAMODE; borg MOEAs applied to water distribution system design problems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2016, 142, 04016017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Dandy, G.C.; Maier, H.R. Use of Domain Knowledge to Increase the Convergence Rate of Evolutionary Algorithms for Optimizing the Cost and Resilience of Water Distribution Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2016, 142, 04016027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guidolin, M.; Savic, D.; Kapelan, Z. Two-Objective Design of Benchmark Problems of a Water Distribution System via MOEAs: Towards the Best-Known Approximation of the True Pareto Front. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2015, 141, 04014060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh, M.; Tolson, B. Hybrid Pareto archived dynamically dimensioned search for multi-objective combinatorial optimization: application to water distribution network design. J. Hydroinform. 2012, 14, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raad, D.; Sinske, A.; van Vuuren, J. Robust multi-objective optimization for water distribution system design using a meta-metaheuristic. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2009, 16, 595–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, R.J.; Kapelan, Z.; Savic, D.A. Probabilistic building block identification for the optimal design and rehabilitation of water distribution systems. J. Hydroinform. 2009, 11, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, N.; Srinivasan, K. Performance Based Optimal Design and Rehabilitation of Water Distribution Networks Using Life-Cycle Costing. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W01417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelman, L.; Ostfeld, A.; Salomons, E. Cross Entropy multiobjective optimization for water distribution systems design. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W09413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmani, R.; Walters, G.; Savic, D. Evolutionary multi-objective optimization of the design and operation of water distribution network: total cost vs. reliability vs. water quality. J. Hydroinform. 2006, 8, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmani, R.; Walters, G.A.; Savic, D.A. Trade-Off between Total Cost and Reliability for Anytown Water Distribution Network. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2005, 131, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmani, R.; Savic, D.A.; Walters, G.A. Evolutionary multi-objective optimization in water distribution network design. Eng. Optim. 2005, 37, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G. No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Lei, X.; Savić, D.A. Comparison of multi-objective optimization methods applied to urban drainage adaptation problems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. ASCE 2018, 144, 04018070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaake, J.C.; Lai, D. Linear Programming and Dynamic Programming Application to Water Distribution Network Design; Report No. 116; Hydrodynamics Laboratory, Department of Civil Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, O.; Khang, D.A. Two-phase decomposition method for optimal design of looped water distribution networks. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reca, J.; Martínez, J. Genetic algorithms for the design of looped irrigation water distribution networks. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W05416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zecchin, A.C.; Simpson, A.R. Self-Adaptive Differential Evolution Algorithm Applied to Water Distribution System Optimization. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2013, 27, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadka, D.; Reed, P. Diagnostic Assessment of Search Controls and Failure Modes in Many-Objective Evolutionary Optimization. Evol. Comput. 2012, 20, 423–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).