Abstract
Silicon (Si) has been recently reconsidered as a beneficial element due to its direct roles in stimulating the growth of many plant species and alleviating metal toxicity. This study aimed at validating the potential of an aquatic macrophyte Eleocharis acicularis for simultaneous removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions under different dissolved Si. The laboratory experiments designed for determining the removal efficiencies of heavy metals were conducted in the absence or presence of Si on a time scale up to 21 days. Eleocharis acicularis was transplanted into the solutions containing 0.5 mg L−1 of indium (In), gallium (Ga), silver (Ag), thallium (Tl), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), and lead (Pb) with various Si concentrations from 0 to 4.0 mg L−1. The results revealed that the increase of dissolved Si concentrations enhanced removal efficiencies of E. acicularis for Ga, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb, while this increase did not show a clear effect for In, Tl, and Ag. Our study presented a notable example of combining E. acicularis with dissolved Si for more efficient removals of Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, and Ga from aqueous solutions. The findings are applicable to develop phytoremediation or phytomining strategy for contaminated environment.
1. Introduction
Silicon (Si) is the second most abundant element in soil after oxygen. Almost all terrestrial plants contain Si in their tissues, although the content of Si varies considerably across species, ranging from 0.1% to 10% Si on a dry weight (wt) basis []. Monocots usually accumulate more Si than dicots []. Silicon has recently been reconsidered as a beneficial element for higher plants [], because of its roles in various bio-physio-mechanical functions [,]. Recent studies reported that the application of Si or fast-reacting silicates can not only enhance crop yield [] but also stimulate the tolerance and accumulation of heavy metals [,,]. This has encouraged more work on the combination of plant selection and Si application for more efficient heavy metal removal to develop phytoremediation or phytomining techniques.
Phytoremediation and phytomining or agromining [] have emerged as cost-effective, long-lasting, and environment-friendly technologies for the treatment of water contaminated with heavy metals [,] and for the economic exploitation of low-grade surface ores or mineralized soils that are too metal-poor for conventional mining [,], respectively. The economic return from heavy metal phytoextractions could turn out to be an additional source of finance for the phytoremediation process. Therefore, phytoremediation, in combination with phytomining, appears to be a strategy for ensuring the commercialization of these technologies. Previous studies have attempted to enhance these technologies in both laboratory and field trials [,,]. However, while Si is one of the most common elements in soil solution, its presence in and impact on the effectiveness of phytoremediation and phytomining has not been systematically studied.
Eleocharis is a member of the Cyperaceae family—monocots—which is widely known as an accumulator of Si []. The aquatic macrophyte Eleocharis acicularis (L.) Roem. et Schult. var. longiseta Svenson is an emergent herbaceous perennial with a worldwide distribution []. This species has been reported to accumulate multiple metals from mine drainage, water, and sediment, and shows a great potential for phytoremediation [,,,,,,,]. However, currently, there is no available information regarding the simultaneous accumulation of rare metals (i.e., gallium (Ga) and thallium (Tl)) in E. acicularis. Despite the fact that an application of materials containing easy-soluble Si together with E. acicularis showed great effects on increasing the accumulation of chromate (Cr), zinc (Zn), arsenic (As), and cadmium (Cd) [,], there have also been contrasting observations in which evidence on the relation between the concentration of dissolved Si in the solution and the removal of heavy metals by E. acicularis was not confirmed []. This suggests that more works on the accumulation of heavy metals in E. acicularis under the presence of different levels of Si are necessary.
In this study, E. acicularis was planted in pot experiments, with various levels of Si concentrations. Heavy metals (i.e., indium (In), Ga, silver (Ag), Tl, copper (Cu), Zn, Cd, and lead (Pb)) were introduced together and their concentrations from aqueous solutions to plants were examined on a time scale of up to 21 days. We aimed to clarify the effects of dissolved Si on either favoring or inhibiting the accumulation of heavy metals by E. acicularis. The findings of this study can help to establish phytoremediation and phytomining practices based on the combined utilization of E. acicularis and dissolved Si to remediate contaminated environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant and Solution Preparation
Nitrate salt solutions of In, Ag, Ga, Tl, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb (standard solutions for atomic absorption spectrometry; Kanto Chemical Co. Inc., Japan) were simultaneously added to the tanks until a concentration of 0.5 mg L−1 of each solution was achieved. The desired level of metals (0.5 mg L−1) was selected based on our previous study on the possible capacity of E. acicularis to simultaneously remove heavy metals from solutions []. Silicon (standard solutions of (NH4)2SiF6; Merck Corporation) was also added to these tanks until final concentrations of 0, 0.5, 1.0, or 4.0 mg L−1 were achieved. A minor amount of 1 M NaOH solution was added to adjust the pH of the final solutions to 5.5.
Eleocharis acicularis, which were about 20 cm high, were collected from a clump in an agricultural irrigation ditch in Northwestern Shikoku, Japan for pot experiments. The plant was washed thoroughly with tap water followed by Milli-Q water and placed into 20 L experimental tanks (20 × 40 × 25 cm3) filled with 15 L of solutions. The plant (85 g of fresh weight) was transplanted in the tanks containing the desired levels of mixed heavy metals (In, Ag, Ga, Tl, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb) and Si and held at the bottom of the tank by hard plastic net fix-aided tools. The same amount of the plant was also grown in a tank, without the addition of heavy metals or Si as the plant control. For the metal control, the same Si and metal concentrations were generated, but no plant was transplanted. All experiments were conducted in duplicate. The tanks were placed in a greenhouse with a controlled ambient condition: exposure of white fluorescent light was set up at 54 μmol m−2 s−1 for 16 h per day, and the ambient temperature was constantly kept at 24 ± 1 °C during the experiment.
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
To identify removal efficiencies of heavy metals from aqueous solutions to plants, from each pot experiment, 10 mL of aliquot was sampled after 8 h, 1 day, 2 days and 3 days, and then every 2 days until 21 days. To examine the chemical composition of the plant samples and accumulation of heavy metals, the original E. acicularis plant sample and those harvested from pot experiments after 21 days were separated into the root and shoot parts, well rinsed with deionized water by using an ultrasonic cleaner and dried in a ventilated oven at 80 °C for 48 h. The dried samples were ground into a fine powder using a mortar mill. Silicon concentrations in the plant were determined by particle-induced X-ray emission (PIXE) at the Cyclotron Research Center, Iwate Medical University, Japan. In addition, plant samples (50 mg) of each sample were digested with H2O2, HF, HNO3 mixture (2:5:10, v/v). Soluble heavy metals in water and plant were determined by ICP-MS (Varian 810/820–MS) at the Integrated Center for Sciences, Ehime University, Japan. Certified reference materials NIES CRM No. 1 provided by the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES) of Japan and SRM 1643e provided by the U.S. National Institute of Standards Technology were used for quality control of the analytical procedure of plant and water samples, respectively. The recoveries of elements ranged from 91% to 105% of the certified values. All analytical measurements were performed in at least triplicates and approximately 96% of the results fall within a 3% error margin.
2.3. Bioconcentration Factor
Bioconcentration factor (BCF) is used to estimate the potential of a plant for phytoremediation and calculated with the following Equation:
where, and were the concentrations of heavy metals in the whole plant of E. acicularis and those of the growing solution, respectively. The concentrations of heavy metals in the solutions at the start of the experiment were used to calculate the values. The values were calculated by average concentrations in the roots and the shoots at the end of the experiment.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
SPSS 15.0 software was used for all statistical analysis. All data were fitted with a Kolmogorov-Smirnov one-sample test. An independent t-test (Student’s t-test) was used to analyze significant differences in concentrations of heavy metals between root and shoot parts. Significant differences on the concentrations of Si and heavy metals in the roots and shoots, shoot/root ratios, and BCF values among different treatments were evaluated using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test at level p < 0.05. Pearson product moment correlation coefficient (r) was used to express possible relationships of quantitative variables. Since E. acicularis was exposed to various heavy metals together, principal component analysis (PCA) enabled us to identify possible correlations (supportive or competitive) between heavy metals.
3. Results
3.1. Kinetic Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions
In a time sequence up to 21 days, the concentrations of heavy metals within the control tanks showed a gradual increase (1.14 ± 0.11% day−1) as a result of combined effects of water evaporation and metal precipitation []. Accordingly, all the concentration data presented in this study were recalculated to eliminate these effects.
The removal efficiencies of heavy metals from aqueous solutions in the absence or presence of dissolved Si as a function of time are described in Figure 1. It is obvious that heavy metals were removed at different efficiencies and levels, and Si showed a clear effect as an enhancer for metal removal by E. acicularis. In the absence of Si, E. acicularis did not show clear responses for Cu, Zn, Cd, Tl, and Ga, while it showed high accumulation rates for Pb, Ag, and In. After 21 days, the concentrations of Pb, Ag, and In decreased from 500 to 288, 0, and 97 μg L−1, respectively. The removal efficiencies of these heavy metals by E. acicularis were in the following order: Ag > In > Pb > Tl > Ga > Cu > Zn > Cd. In the presence of Si, the acceleration of heavy metal accumulation was observed at different efficiencies and levels. While increasing concentration of Si up to 4.0 mg L−1 resulted in severe decreases in the concentrations of Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, and Ga, only small decreases in the concentration of Ag, In, and Tl, over the whole time span of the empirical experiment (21 days) were observed. In the presence of Si at 4 mg L−1, most of the heavy metals were transferred from aqueous solution to the plant within 21 days, indicating a high potential of E. acicularis for heavy metal removal when it is coupled with a Si amendment.
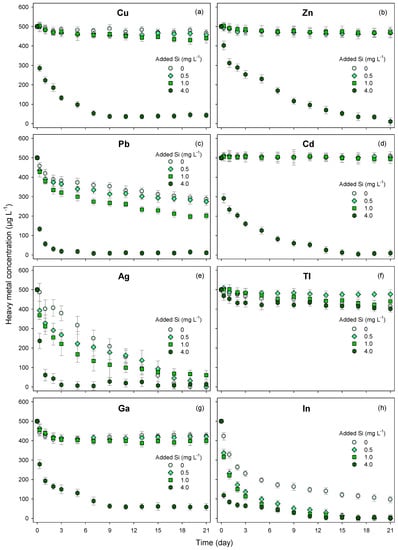
Figure 1.
Removal efficiencies of Cu (a), Zn (b), Pb (c), Cd (d), Ag (e), Tl (f), Ga (g), and In (h) from aqueous solutions by E. acicularis as functions of time and dissolved Si concentration.
3.2. Accumulation of Si and Heavy Metals in E. acicularis
There was almost no change in biomass including the root and shoot parts, over the 21 days, although the growth of some new shoots and roots of E. acicularis were observed. However, changes in the color of approximately 20%–30% of the plant shoots from green to yellowish brown were most obvious for all experiments with or without the presence of Si. The extent of chlorosis was more severe in plants grown at 4.0 mg Si L−1 than at other Si concentrations.
Table 1 shows the concentrations of Si and heavy metals in the roots and shoots under the absence and presence of Si at different concentrations. With an increase in the Si concentration of the growing solution from 0 to 4 mg L−1, corresponding increases of Si contents, from 1.28% to 1.54% and 4.33% to 5.22% were observed in roots and shoots, respectively. Significantly higher concentrations of Si were observed in the shoots than in the roots (p < 0.001), reflecting the ability of E. acicularis to transport Si from the roots to the shoots. Along with the decreasing concentrations of Si and heavy metals in the aqueous solutions, their accumulation in the roots and shoots were found at different efficiencies and levels. The concentrations of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, Ag, and Ga) in both the roots and shoots of the plant, correlated with the concentration of Si (r (32) = 0.69, p < 0.05). This indicated that dissolved Si had a strong effect in facilitating the accumulation of heavy metals in the roots and translocation to the shoots. However, there was no correlation between the concentrations of Tl and Si in the plant. It was likely that Tl translocated from the root to the shoot parts at higher efficiencies compared to other metals. After 21 days, the relative contents of Tl in the shoot parts ranged from 55% to 80%, while those of Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, Ag, Ga, and In were only 47%, 65%, 59%, 63%, 64%, 30%, and 35%, respectively.

Table 1.
Concentrations of Si and heavy metals (mg kg−1 dry wt) in the roots and shoots of E. acicularis before (initial) and after 21 days of the experiment.
The shoot/root ratios of Si, Ga, Cu, and Zn showed no significant differences in the entire Si range from 0 to 4.0 mg L−1 (Table 2, p < 0.05), indicating that the addition of Si did not affect the transport of these metals from the roots to the shoots. The shoot/root ratios after the addition of Si at 1.0 and 4.0 mg L−1 showed no significant difference, compared with those to which no Si was added (Table 2). In addition, we found significantly higher shoot/root ratios for Pb at the concentration of 4.0 mg Si L−1 in comparison with those at other Si levels. In contrast, the addition of Si at all levels inhibited the transport of In from the roots to the shoots.

Table 2.
The shoot/root ratios of E. acicularis after 21 d of the experiment
Bioconcentration factor values of In, Ga, Ag, Tl, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb in this study were higher than 100 (Table 3) [] which indicates that E. acicularis is a good accumulator of these heavy metals. The BCF values for E. acicularis for Ga, Ag, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb were significantly higher at 4.0 mg Si L−1 than at other Si concentrations (p < 0.05). In contrast, the addition of 4.0 mg Si L−1 significantly reduced the removal of In from the solution by E. acicularis (p < 0.001) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Bioconcentration factors of E. acicularis after 21 days of the experiment
3.3. Relation of Metal Removal by PCA Analysis
The PCA indicated the differentiation of removed heavy metals in the presence of Si at different levels (Figure 2). Herein, the first two principal components (PC1 and PC2) showed their different levels of association, in which PC1 explained at least 74% of the total variance. These similar loadings into PC1 mean that the heavy metals likely shared the same removal mechanism. For all experiments with or without the presence of Si, all heavy metals showed positive effects with the first PC, and the differentiations were closely associated with the time points of the time span within 3 days. This demonstrates that differences in the removal efficiencies can most probably be detected in the first 3 days. In the absence of Si, the association of Ag, Tl, Zn, Pb, In, and Cu was well recognized, indicating a similar removal mechanism for these heavy metals or at least that they were not opposed to the others. In contrast, Cd and Ga did not show associations with other heavy metals (Figure 2a). This implies that the removal of these two metals might be inhibited by the presence of other presenting metals or controlled by other removal mechanisms. The presence of Si tends to enhance the association of Ga and Cd with other heavy metals (Figure 2b–d), suggesting a possible role of Si to favor Cd and Ga removal from solutions and accumulation in the plant. At the concentration of 4.0 mg Si L−1, a cluster of Pb, Ag, and In can be seen, which demonstrates similar trends for these metals.
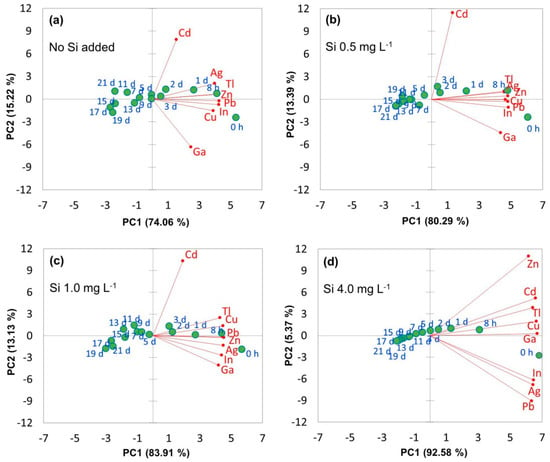
Figure 2.
Score plots of principal component 1 (PC1) versus PC2 indicating the differentiation of removal efficiencies of heavy metals.
4. Discussion
4.1. Combined Effects of E. acicularis and Dissolved Si on the Removal of Heavy Metals
Macrophyte E. acicularis was widely reported as a potential species to be transplanted into soil and water environments to remove various heavy metals [,,,,]. Positive responses were observed when it was "coupled" with a dissolved Si application. In this study, the highest content of Si in E. acicularis was 5.2% (dry wt) (Table 1). Therefore, E. acicularis is a Si accumulator because the plant accumulated more than 1% Si in its dry leaf matter []. This finding is consistent with that reported by Ha et al. []. Silicon in the form of monosilicic acid can be assimilated and transported to different parts of the plant and eventually precipitated throughout inter- and intracellular spaces. Two transporters (Lsi1 and Lsi2) might be responsible for the removal of Si from solutions cross root cell membranes [,], while Lsi6 controls the transportation and alternation of Si in the shoot (leaf) []. Excessive precipitation of Si might lead to the formation of a so-called phytolith structure in leaf or stem [], and this structure may be involved in the occlusion of dissolved substances in transport sap []. However, the formation of phytolith in E. acicularis, its morphotypes and possible compartmentations of heavy metals are beyond the scope of our study.
There has likely been a central debate regarding the role of Si for mediating metal stress [,]. Many studies stated the role of Si in diminishing plants’ metal absorption [,,], while some others reported a co-absorption of Si and metals into plants [,]. In our study, it was obvious that Si favored the absorption of heavy metals (except In and Tl) into E. acicularis (Table 1). It is possible that the exposure of heavy metals was conducted at low concentrations, which were 0.5 mg L−1 for single metal and 4.0 mg L−1 for multiple metals. At low exposure levels of heavy metals and dissolved Si, competition among metals for accumulation was not pronounced, while Si might not affect metal accumulation via complexation or co-precipitation []. The role of Si in facilitating metal absorption is supported by previous findings which focused on the relation between Mn and Si in other crop species such as bean [], barley [], and maize []. It was probable that Si increased the accumulation of heavy metals by enhancing the root activity [], increasing the water uptake [], and improving the hydraulic conductance of roots [].
PCA analysis revealed the removal trend for heavy metals and the effect of Si was identified. In the absence of Si, a close association of Ag, Tl, Zn, Pb, In, and Cu indicated that they have similar traits, being accumulated in E. acicularis or at least they were not opposed to the others (Figure 2a). Since Cd and Ga did not show that they had associations with other heavy metals (Figure 2a) and their removed amounts were low (Figure 1d,g). This may imply that the removal of these two metals might be inhibited by the presence of other metals or controlled by other removal and accumulation mechanisms. In the presence of Si, a significant acceleration of Cd and Ga absorption was observed (Figure 1d,g), thereby supporting the two possible mechanisms: (i) increasing co-absorption of Si and Cd, which is consistent with the finding of He et al. []; and (ii) mediating competitive effects from other metals. In increasing the presence of Si, two PCA clusters, i.e. (1) Zn, Cd, Tl, Cu and Ga, and (2) Pb, Ag and In (Figure 2d), demonstrated two absorption trends. The obtained results in this work, however, were insufficient for clarification, and there is also little available information that can help to elucidate this issue.
4.2. Suggestions for Suitable Practices for Phytoremediation and Phytomining
The characteristics of an ideal plant for phytoremediation and phytomining were discussed in Ha et al. []. Of these criteria, hyperaccumulators are defined as plants with leaves that can accumulate at least 100 mg kg−1 of Cd, Tl, Ag, In, or Ga; 1000 mg kg−1 of Cu or Pb; or 10,000 mg kg−1 of Zn (dry wt) when grown in a metal-rich environment [,]. In this study, E. acicularis was shown to be a hyperaccumulator of In, Ga, Tl, Ag, and Cd. There is very little available information regarding the accumulation of Ga in plants. Few works have mentioned Ga in lichens (2.2–60 mg kg−1 dry wt) and bryophytes (2.7–30 mg kg−1 dry wt) []. Therefore, to the best of our knowledge, E. acicularis is the first known hyperaccumulator of Ga in any plant group.
The concentrations of Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cd in E. acicularis in this study were still far below the thresholds of hyperaccumulation [,]. This is possibly due to the low concentrations of Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cd in the growing solutions (0.5 mg L−1). Therefore, although high BCF values were obtained for Pb, Cu, Cd, and Zn (Table 3), E. acicularis was not considered to have potential for phytoremediation based on data concerning the concentrations of these metals in the plant in this study.
The hyperaccumulation levels and BCF values of In, Ga, Tl, and Ag indicated that this plant species appears to be a good hyperaccumulator of these metals. However, phytomining alone does not appear to be commercially viable given the concentrations and the current price of these metals. This is inconsistent with a previous study, which indicated that commercial phytomining has not yet become a reality [].
While the present study does not show the potential and feasibility of E. acicularis for phytoremediation and phytomining, this plant has been reported to accumulate as much as 20,200, 14,200, 1,120, and 575 mg kg−1 dry wt of Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cd, respectively, in its shoots [,]. Lower concentrations of these metals in the mixed solutions in this study would result in lower concentrations of heavy metals in the plant than those found in previous studies [,]. In addition, E. acicularis is easily cultivated, grows rapidly, is widely distributed, and is well adapted to contaminated environments. It can, therefore, be suggested that E. acicularis has potential for the phytoremediation of Pb, Cu, Cd, and Zn. Moreover, the combination of phytoremediation and phytomining would be considered a more feasible approach meeting two needs: to clean up contaminated environments and to obtain extra income from phytomining, which would increase the applicability of these environmentally friendly technologies. Particularly, the effectiveness of phytoremediation and phytomining might be increased if E. acicularis was coupled with a Si application. In the concentration range of 0.5 to 4 mg Si L−1, we found a resonant effect of Si and E. acicularis in removing heavy metals (i.e., Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, and Ga) from aqueous solution as shown in Figure 1. A contrasting effect of Si in the removal of In and Tl suggests that the application of Si might not be a suitable practice for enhancing phytomining or phytoremediation for these metals.
5. Conclusions
This study reported the removal and accumulation of various heavy metals together from aqueous solutions to macrophyte E. acicularis and the role of dissolved Si was highlighted. In the presence of Si, the removal of metals (i.e., Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, and Ga) from solutions and their accumulation in the roots and the shoots of E. acicularis was enhanced, suggesting a possible supportive role of Si. A potential use of E. acicularis, coupled with a Si application, can be developed for removing heavy metals (i.e., Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, and Ga) from water. The polymerization and precipitation of Si in the inter- and intracellular space of E. acicularis might lead to possible compartmentations of heavy metals within its structure and this requires further investigation.
Author Contributions
H.T.H.N., M.S. designed the research, H.T.H.N. operated the experiment and analysis, H.N.T.N., M.N.N. wrote original draft preparation; M.S., N.T.M., V.T.N. reviewed and edited the paper.
Funding
This research is funded by the Grant for Environmental Research Projects from The Sumitomo Foundation (No. 083187) and Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 105.99-2017.313.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Epstein, E. The anomaly of silicon in plant biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyckx, M.; Hausman, J.F.; Lutts, S.; Guerriero, G. Impact of Silicon in Plant Biomass Production: Focus on Bast Fibres, Hypotheses, and Perspectives. Plants 2017, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, E.; A. Bloom, J. Mineral Nutrition of Plants: Principles and Perspectives; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, J.F.; Sullivan, L.A. Soil carbon sequestration in phytoliths. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yao, X.; Cai, K.; Chen, J. Silicon alleviates drought stress of rice plants by improving plant water status, photosynthesis and mineral nutrient absorption. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 142, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerling, D.J.; Leake, J.R.; Long, S.P.; Scholes, J.D.; Ton, J.; Nelson, P.N.; Bird, M.; Kantzas, E.; Taylor, L.L.; Sarkar, B.; et al. Farming with crops and rocks to address global climate, food and soil security. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haag-Kerwer, A.; Schäfer, H.J.; Heiss, S.; Walter, C.; Rausch, T. Cadmium exposure in Brassica juncea causes a decline in transpiration rate and leaf expansion without effect on photosynthesis. J. Exp. Bot. 1999, 341, 1827–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.C.; J. Wong, W.C.; Long, W. Silicon-mediated enhancement of cadmium tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Lin, Y.; Xu, F. Evidence for ‘silicon’ within the cell walls of suspension-cultured rice cells. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ent, A.; Baker, A.J.; Reeves, R.D.; Chaney, R.L.; Anderson, C.W.; Meech, J.A.; Erskine, P.D.; Simonnot, M.O.; Vaughan, J.; Morel, J.L.; et al. Agromining: Farming for metals in the future? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4773–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbisu, C.; Alkorta, I. Phytoextraction: a cost-effective plant based technology for the removal of metals from the environment. Biores. Technol. 2001, 77, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.T.H.; Sakakibara, M.; Sano, S. Accumulation of Indium and other heavy metals by Eleocharis acicularis: An option for phytoremediation and phytomining. Biores. Technol. 2011, 102, 2228–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.R.; Chambers, M.F.; Nicks, L.J.; Robinson, B.H. Phytomining. Perspectives 1998, 3, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boominathan, R.; Saha-Chaudhury, N.M.; Sahajwalla, V.; Doran, P.M. Production of nickel bio-ore from hyperaccumulator plant biomass: Applications in phytomining. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 86, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Nongkynrih, J.M. Metal hyperaccumulation and bioremediation. Biol. Plant. 2007, 51, 618–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K. Heavy metal phytoremediation from aquatic ecosystems with special reference to macrophytes. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 697–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, V.A.; Sheoran, S.; Poonia, P. Phytomining: A review. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, M.J.; White, P.J.; Mead, A.; Broadley, M.R. Phylogenetic variation in the silicon composition of plants. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 1027–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, L.; Doll, J.; Holm, E.; Pancho, J.V.; Herberger, J. World Weeds: Natural Histories and Distribution; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, N.T.H.; Sakakibara, M.; Sano, S.; Hori, R.S.; Sera, K. The potential of Eleocharis acicularis for phytoremediation: case study at an abandoned mine site. Clean-Soil Air Water 2009, 37, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, N.T.H.; Sakakibara, M.; Sano, S. Phytoremediation of Sb, As, Cu, and Zn from contaminated water by the aquatic macrophyte Eleocharis acicularis. Clean-Soil Air Water 2009, 37, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, S.; Ohmori, Y.; Ha, N.T.H.; Sano, S.; Sera, K. Phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated water and sediment by aquatic macrophyte Eleocharis acicularis. Clean-Soil Air Water 2011, 39, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, M.; Sugawara, M.; Sano, S.; Sera, K. Phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated river water by aquatic macrophyte Eleocharis acicularis in a mine site, southwestern Japan. NMCC Annu. Rep. 2013, 20, 226–233. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.; Goto, S.; Teraoka, S.; Takagaki, K.; Takehara, A.; Sano, S.; Sakakibara, M. Establishment of an aseptic culture system and analysis of the effective growth conditions for Eleocharis acicularis ramets for use in phytoremediation. Environments 2017, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurfitri, A.G.; Masayuki, S.; Koichiro, S. Phytoremediation of heavy metal polluted mine drainage by Eleocharis acicularis. Environ. Sci. Ind. J. 2017, 13, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, S.; Okazaki, K.; Kurahashi, T.; Sakakibara, M. Phytoremediation of arsenic- and molybdenum-contaminated alkaline wastewater by Eleocharis acicularis in winter in Japan. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 71, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramoto, S.; Sakakibara, M. Effects of clinker ash as Si fertilizer on phytoremediation for heavy metal contaminated water using Eleocharis acicularis. In Proceedings of the 1st International Seminar of Environmental Geoscience in Asia (ISEGA I), Bandung, Indonesia, 5–6 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki, K.; Yamazaki, S.; Kurahashi, T.; Sakakibara, M. An artificial channel experiment for purifying drainage water containing arsenic by using Eleocharis acicularis. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 71, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Yamaji, N. Silicon uptake and accumulation in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Yamaji, N.; Mitani, N.; Tamai, K.; Konishi, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Katsuhara, M.; Yano, M. An efflux transporter of silicon in rice. Nature 2007, 448, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaji, N.; Mitani, N.; Ma, J.F. A transporter regulating silicon distribution in rice shoots. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.M.; Dultz, S.; Picardal, F.; Bui, T.K.A.; Pham, Q.V.J. Schieber, Release of potassium accompanying the dissolution of rice straw phytolith. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, M.; Hausman, J.F.; Lutts, S.; Guerriero, G. Silicon and plants: current knowledge and technological perspectives. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesamia, H.; Jeong, B.R. Silicon (Si): Review and future prospects on the action mechanisms in alleviating biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.H.; Qiu, H.; Tian, T.; Zhan, S.S.; Deng, T.H.; Chaney, R.L.; Wang, S.Z.; Tang, Y.T.; Morel, J.L.; Qiu, R.L. Mitigation effects of silicon rich amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on multi-metal contaminated acidic soil. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, W.J.; Marschner, H. Effect of silicon on manganese tolerance of bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Soil 1978, 50, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Vlamis, J. The effect of silicon on yield and manganese-54 uptake and distribution in the leaves of barley plants grown in culture solutions. Plant Physiol. 1957, 32, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonobe, K.; Hattori, T.; An, P.; Tsuji, W.; Eneji, A.E.; Kobayashi, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Inanaga, S. Effect of silicon application on sorghum root responses to water stress. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 34, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Sonobe, K.; Araki, H.; Inanaga, S.; An, P.; Morita, S. Silicon application by sorghum through the alleviation of stress-induced increase in hydraulic resistance. J. Plant Nutr. 2008, 31, 1482–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, R.D.; Baker, A.J.M. Metal-accumulating plants. In Phytoremediation of Toxic Metals: Using Plants to Clean-up the Environment; Raskin, I., Ensley, B.D., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 193–230. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).