Abstract
Most water supply and hydropower generation is obtained from the river–reservoir system, and wastewater pollutants are also dumped into the system. Increasing water demand and consumption have caused the water supply, wastewater pollutant management and hydropower generation sectors to be interlinked and to reinforce each other in the system. A physical nexus across water supply, wastewater management and hydropower generation sectors for a river–reservoir system was developed based on the analytical water quality and hydropower generation equations. Considering the Jinghong hydropower reservoir, located in the middle and lower reaches of the Lancangjiang River Basin, as a case study, both the wastewater pollutant management target and water inflow from the upstream as the external and boundary conditions, were employed to establish the effects of the external and boundary conditions on the nexus. It was demonstrated that the nexus of water supply and hydropower generation sectors does not vary with the water quality indicators and its protection target, without the separation of environmental flow in hydropower generation flow. In addition, the amount of hydropower generation decreases with increasing water supply. However, the lapse rates of allowable wastewater pollutants–water supply differ based on the water inflow and the wastewater pollutant management sectors, while the efficiency of hydropower generation and the sensitivity of allowable wastewater pollutants per amount of water supply are considered to be unrelated to the water inflow and wastewater pollutant management target conditions. The quantitative nexus developed through the proposed equation not only contributes to a more complete understanding of the mechanism of cross-connections, but also in creation of specific water protection and utilization measures, which is also the focus of the water–energy nexus.
1. Introduction
‘Nexus thinking’ has been proposed as a conceptual tool for achieving sustainable development by the World Economic Forum [1]. It is considered an approach to simultaneously examine interactions among multiple sectors and promote integrated planning, management and governance [2]. Given that energy and water are essential resources of our natural environment [3] and are inextricably linked [4], the nexus of these entities is high on the world’s science and policy agenda with regard to global socioeconomic development and environmental change [5,6,7,8], and has gained increasing attention in the research and policy making communities [9]. Although integrated water resource management (IWRM) has been pervasive since the Harvard Water Program [10,11], the nexus approach can make the objectives of integrated water resource management more practical to satisfy stakeholders across political boundaries and for sector-specific governance of natural resource use [4,12,13]. It is critical for every traditional water community with an interest in water study, i.e., hydrologists, water resources engineers, economists, and policy analysts to engage each other to advance water–energy nexus understanding and management [4]. However, the nexus formed by physical water flow mechanism between every sector should be first understood.
As water can be used for water supply and wastewater management extracted from river or reservoir will conflict with hydropower generation projects [14] in attempting to achieve renewable energy targets. Increasing population, improving living standards, changing consumption patterns, and the expansion of economic development [15,16] have accelerated water supply and consumption. More water is supplied and consumed by human and, more wastewater pollutants are dump into rivers. Therefore, water quality protection need to be implemented. As such, water supply, water quality protection, and hydropower generation are interlinked and enhance each other. However, the water quality issue, which determines whether or not water can be utilized, is often overlooked in water–energy nexus studies, though significant efforts have been made to explore the water–energy nexus from water quantity and water availability. Meanwhile, hydropower is also always excluded from the energy–water nexus analysis [17,18,19,20], even it has played an irreplaceable role in the development of electric power industry especially for renewable energy and peak period power demands. Several works have already been published on policy related research to identify applications of nexus in water and energy resources management [12,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. However, few studies had characterized the interlinkages between nexus sectors, with a focus on the understanding of the underlying physical mechanism of the nexus and on conceptualizing relationships of nexus sectors [29]. Therefore, the nexus across water supply, wastewater management, and hydropower generation sectors based on the water quantity, quality and energy should be modeled for coordinating and sustainability of water use, water protection and energy sectors. The aim of this paper was to address a new way to develop a physical nexus across water supply, wastewater management and hydropower generation sectors in river–reservoir systems based on the physical law equations of water quantity, pollutant transport, and hydropower generation; the effects of boundary conditions on the nexus to support adaptive water resource management are also analyzed.
2. Methodology
2.1. A Generalized River–Reservoir System
As the source or sink of water supply, hydropower generation and wastewater management is the river or reservoir, their nexus, based on the physical relationship and cross-connections in a river–reservoir system, will be modeled for local water supply, water protection, and energy operation. We begin by considering that a river or a reservoir lake for water quality concentration is uniformly distributed through any cross-section so that the analytical water quality model is applicable. The river–reservoir system can then be assumed as the shown in Figure 1. The blue lines represent the water flow in the river, the green lines represent the supplied water, and the black arrows represent the allowable wastewater pollutant at the discharged location. The reservoir is also a hydropower generation plant which converts the water into energy. The inflow to the river–reservoir system is indicated by Q0 with a water quality given by C0. The water is considered to be supplied from (I) and (II) where the amounts of water are S1 and S2. The allowable wastewater pollutant is simplified to be discharged into A, B, C, and D points where the amount of the allowable wastewater pollutants are WA, WB, WC, and WD, respectively (their corresponding allowable wastewater pollutants are qA, qB, qC, and qD, respectively). The distances between the points along the river for the water intake or wastewater pollutant sewage are represented by l1, l2, l3, l4, and l5, respectively, as shown in Figure 1. ki=1,…,5 is the first-order decaying coefficient of the wastewater pollutants for the lith river, while ui is the corresponding average water velocity.
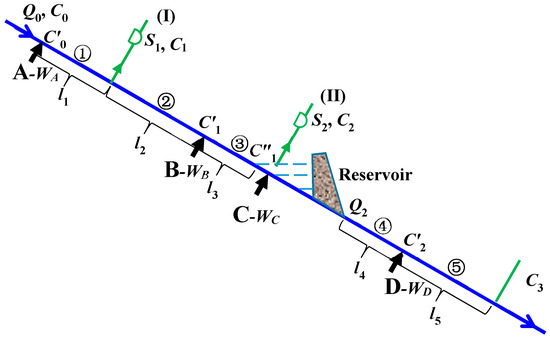
Figure 1.
An illustrative example of a river–reservoir system.
2.2. Physical Nexus Across Water Supply, Wastewater Management, and Hydropower Generation Sectors for the Generalized River–Reservoir System
The water quality at Ci or C′i can be expressed as shown in the following Equations (1)–(6). The water quality C0′at the allowable wastewater pollutant discharged point A is given as
The water quality C1 at water intake point (I) is given as
The water quality C1′ at the allowable wastewater pollutant discharged point B is
The water quality C2 at the water intake point (II) in the reservoir based on the complete mixing model is
where k′ is the sedimentation coefficient and V0 and CC′0 are the initial reservoir storage and water quality condition for the first time step of the simulation, respectively. These values are used as the parameters for the Equation (4). Q2 is the water flow released from the reservoir.
The water quality C2′ at the wastewater pollutant discharged point D is
and the water quality C3 at water intake point (III) is
By substituting the values of C2 in Equation (4), we can get the following.
According to the classification of the variables and the parameters, the Q2 in Equation (7) can be rewritten as
The hydropower energy generated from the reservoir can be expressed by
ΔH is the net water head and η is the coefficient of the output for hydropower generation from a reservoir. The average head available for the reservoir during period t is expressed as a non-linear function of the average storage during that period (shown as the equation g1(·)). The tailwater level can be determined using the function g2(·) between the discharge and the water level. Equation (9) can be rewritten as
According to the classification of the variables and parameters, the water flow released from the reservoir Q2 in Equation (9) can be expressed as f2 in Equation (11):
where θ(g1) and θ(g2) are the inverse functions of g1(·) and g2(·), respectively. Obviously, the generated output of the hydropower plant cannot exceed its installed capacity.
Now, if Q2 shown in Equation (11) is substituted in Equation (8), we obtain
Then Equation (12) can be transformed as
Since the water quality in the river or reservoir is essential to instream ecological systems and water utilization, it is often a requirement that it should not exceed the water protection target (CTi′ or CTi) set by the environmental agency as defined by the following constraints.
Ci′ or Ci ≤ CTi′ or CTi, i = 0, …, 3
Therefore, Equation (13) and the constraints (14) are called the nexus equations of the supplied water (S1, S2) allowable discharged wastewater pollutant (WA, WB, WC, and WD) hydropower generation (PW). If there is no water supply or wastewater pollutant at the points, the values of Si (i = 1, 2) or Wi (i = A, B, C, D) can be given as 0. If there are other water intake or allowable wastewater pollutant discharge points, then these points can be classified initially by distance and then be summed to the points as shown in Figure 1 using Equations (1)–(6). If there are other reservoirs, then these reservoir systems can be divided into subsystems. Every subsystem is only formed by one reservoir and its up-downstream rivers. So the illustrative example of the river–reservoir system shown in Figure 1 is a basic element of the river–reservoir system in a basin or regional scale.
3. Study Area and Data Collection
In this study, the Jinghong hydropower reservoir in the Lancang River was selected as a case study. The Jinghong hydropower dam located in the lower-middle area of the Lancang River, was commissioned in 2009, and is approximately 5 km upstream to (the north of) Jinghong City in the southwest of Yunnan Province. It serves as the source of water supply for Jinghong City. The locations of the Lancang River, Jinghong hydropower reservoir, and the allowable pollutant discharge points are shown in Figure 2.
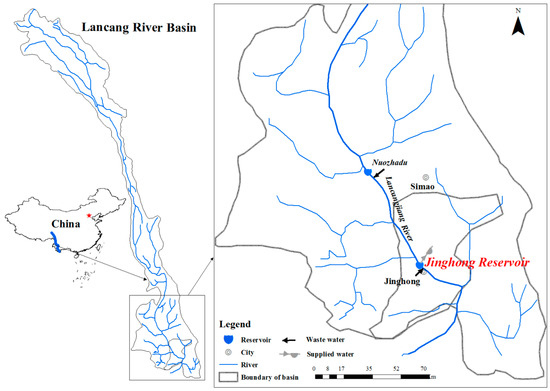
Figure 2.
Location of study area.
The catchment area at the Jinghong dam site is 149,100 km2 and the average yearly runoff is 1820 m3/s at the dam site. Rainfall provides most of the runoff and the division of dry season and wet season is distinct. Nearly 70% of the annual rainfall occurs from June to September during the wet season, while the dry season is from October to May. The distance of the backwater in the main stream is ~97.6 km with a water area of 32.8 km2. The total storage, the storage at normal water level, and the dead storage are 1.4, 1.04, and 0.81 billion m3, respectively. The installed capacity for hydropower generation is 1500 MW. The coefficient of output for hydropower generation from Jinghong reservoir η is 7.6. The functions g1(·) for the Jinghong reservoir and g2(·) for the tailwater at the Jinghong dam downstream site are determined via the measured and surveyed data, such as the topography map, and are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
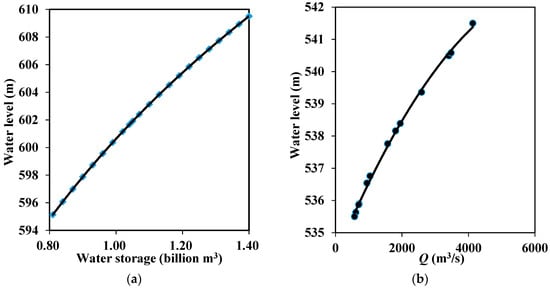
Figure 3.
The functions g1(·) (shown as (a)) for Jinghong reservoir and g2(·) (shown as (b)) for the tail water at the Jinghong dam downstream site.
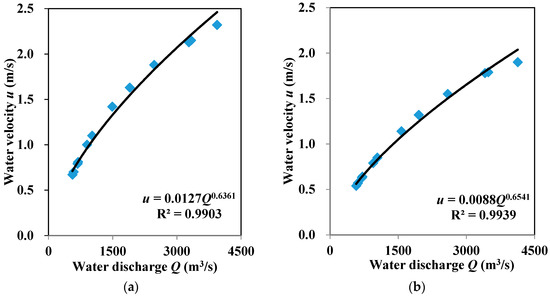
Figure 4.
The relationship between water discharge and water level for the upstream (a) and downstream (b) of Jinghong reservoir.
For the hydraulic parameters in this study area for Equations (8) and (13), the water velocity in the river can be approximated by Equations (15). The data associated with the water flow into the river–Jinghong Reservoir system are presented in Table 1. The initial water storage V0 in Equations (7) and (13) is set to be the storage at the normal water level according to the Jinghong reservoir operation rules.

Table 1.
Monthly water flow at different frequency levels (m3/s).
Since the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5) and ammonia as nitrogen (NH3-N) indicators in allowable wastewater are considered as a measure of water organic pollutants [30,31,32,33], their total amount is considered as indicators of the water quality variable (waste pollutants) in this study. According to the results from the report on the impact of cascade hydropower plants on the environment in the Lancang River [34], kBOD5 in Equation (7) was calibrated and validated as 0.042 day−1 in the wet season (from June to October), 0.054 day −1 in the dry season (from January to May), and 0.048 day−1 during the normal water season (November and December). The variable kNH3-N is calibrated and validated as 0.0474 day−1 in the wet season (from June to October), 0.0469 day−1 in the dry season (from January to May), and 0.0471 day−1 in the normal water season (from November and December). In the reservoir, k′BOD5 is 0.039 day−1 and k′NH3-N is 0.043 day−1. The input water quality conditions C0 are 0.0061 mg/L for NH3-N and 0.0096 mg/L for BOD5. The initial water quality conditions CC′0 in the Jinghong Reservoir are 0.0230 mg/L for NH3-N and 0.0606 mg/L for BOD5. According to the requirement of the surface water area functions in our study area [35], class is III is investigated. This represents water that is mainly used as a centralized potable water source in addition to protected areas for general fishing and swimming [36].
4. Results and Discussion
The nexus of across water supply, wastewater management and hydropower generation sectors for the Jinghong Hydropower Reservoir was tested by modeling Equation (13). The parameters (represented as the vector Ω) in Equations (13) are calibrated in the report on the impact of cascade hydropower plants on the environment in the Lancang River [34], and their values are presented in Section 3. The water quality protection target (denoted by CT′ in the nexus equations) and the water inflow to the river–reservoir system at the upstream boundary are the main two factors that impact the nexus. Their effects were tested and assessed respectively. Both BOD5 and NH3-N with the protection targets of classes III and I are employed to determine their effects on the nexus. The conditions of the water inflow to the Jinghong hydropower river–reservoir are from the dry year (frequency level p = 75%) and the extraordinarily dry year (frequency level p = 99%).
4.1. Effects of the Water Quality Protection Target on the Nexus
In order to present the effects of the water quality protection target, the amount of supplied water varied from 0.1 to 10 times the total water demand of the domesticity and industry in 2030. The corresponding allowable wastewater pollutants and hydropower generation are obtained from the analytical nexus equation. In order to show the nexus under the extraordinarily dry year (p = 99%), the relationships between water supply and allowable wastewater pollutants are presented in Figure 5a–c, and the relationship between water supply and hydropower generation is presented in Figure 5d. Both allowable wastewater pollutants and the hydropower generation are approximate declined lines with an increasing water supply. The more water is extracted from the river or reservoir, the less water is left for hydropower generation and the allowable wastewater pollutants that are a diluted or dispersion for the water quality protection target is reduced. The slope of the declining line indicates the speed or sensitivity of hydropower generation or the allowable wastewater pollutants. As the lengths and scales of the abscissa are set to be the same, the change of the ordinate represents the slope. The amount of allowable wastewater pollutants in the case of Class III water quality protection target (Figure 5a) is more than that for Class I (a stricter water quality protection than Class III) (Figure 5b). Although the water quality protection target C3 = 1.0 mg/L for N3H-N is two times larger than the target C3 = 0.5 mg/L, the amount of allowable wastewater discharge from the former (shown in Figure 5a) is not twice as much as the latter (shown in Figure 5b). The relationship between the amount of allowable wastewater and the water protection target is nonlinear. This can be established by examining Equation (7). Figure 5c including two different water quality indicator targets and also exhibits a nonlinear relationship. The C3 in Figure 5c are 4 and 3 times as much as the corresponding values in Figure 5a, respectively, the amount of allowable BOD5 shown in Figure 5c is larger than the allowable NH3-N shown in Figure 5a, however, the former is obviously not 4 or 3 times as much as the latter. The parameters that define several different water quality indicators such as the decaying coefficient, also impact the amount of allowable wastewater pollutant and their nexus. According to the changes of the ordinate value in Figure 5a–c, the slopes of Figure 5c are much steeper than those of Figure 5a,b, which refers to C3 according to Equation (7). All of the Pearson correlation coefficients of the relationship lines in Figure 5 are approximately −1.
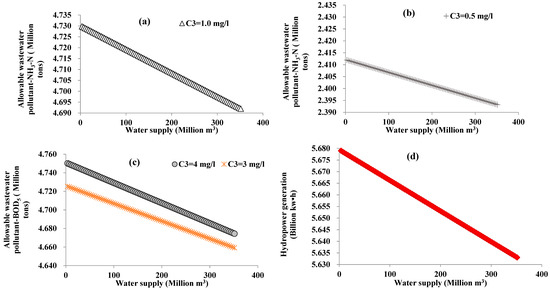
Figure 5.
The relationships between water supply and allowable wastewater pollutant under the inflow frequency level p = 99%: (a) for NH3-N with the Class III (C3 = 1.0 mg/L) water quality protection target, (b) for NH3-N with the Class I (C3 = 0.5 mg/L)water quality protection target, (c) for BOD5 with the Class III (C3 = 4.0 mg/L) and I (C3 = 3.0 mg/L) water quality protection target, and (d) for relationship between water supply and hydropower generation.
The nexus of supplied water and hydropower generation does not vary with the water quality indicators and their protection target. The amount of hydropower generation decreases with an increase of the water supply. If water is extracted from the upstream of the reservoir or from the reservoir, the hydropower generation will be reduced by both the amount of water and the head. Since the environmental flow is not separated from the water for hydropower generation, it was only reduced by approximately 50 million kw·h (0.9% of the hydropower generation without water supply) in the study area, even if the amount of supplied water is assumed to increase to 10 times as much as water demand in 2030. The nexus between water supply and hydropower generation shows that the contradiction between the two sectors is not irreconcilable. If the environmental water flow is separated from the flow for hydropower generation, or the water supply accounts for a high percentage of water flow in the river–reservoir, the nexus of the supplied water and hydropower generation will be close, especially in the dry season. Not only is there a decrease in hydropower generation, but also its assurance ratio decreases. This results in a loss of competitiveness and specific benefits in the electricity market.
4.2. Effects of the Inflow to the River–Reservoir System at the Upstream Boundary on the Nexus
The water inflow is more in dry years (p = 75%) than in extraordinarily dry years (p = 99%). The wastewater pollutants and hydropower generation will also increase since the water supply is the same as in the previous section. Figure 6 presents the relationship between allowable wastewater pollutants and water supply for different water quality protection targets (from Figure 6a–c), and the relationship between water supply and hydropower generation (in Figure 6d) for a dry year (p = 75%) boundary condition. All Pearson correlation coefficients of these relationship lines in Figure 6 are approximately −1. If the water quality C3 is set the same, the relationship lines in Figure 6 are moved upwards (the ordinate values increase) from Figure 5. Therefore, their slopes do not vary with an increase of the water inflow. The efficiency of hydropower generation and the sensitivity of the allowable wastewater pollutants for a given volume of supplied water are considered to not be related to the boundary conditions. Since the annual average water inflow in a dry year is 249 m3/s more than that of an extraordinarily dry year, the average allowable wastewater pollutants are increased by 1.87 million tons and 1.25 million tons for NH3-N or 2.33 and 1.19 million tons for BOD5. The increasing magnitude of the pollutants is different from their water quality protection targets. The stricter the target (e.g., water quality at Class I level is stricter than that of the Class III level), the smaller the increase of the magnitude. As indicated in Section 4.1, the nexus of supplied water hydropower generation is not impacted by the water quality indicator (with different parameters for water quality modeling) and their protection target. Hydropower generation can be increased by 1.45 billion kw·h.
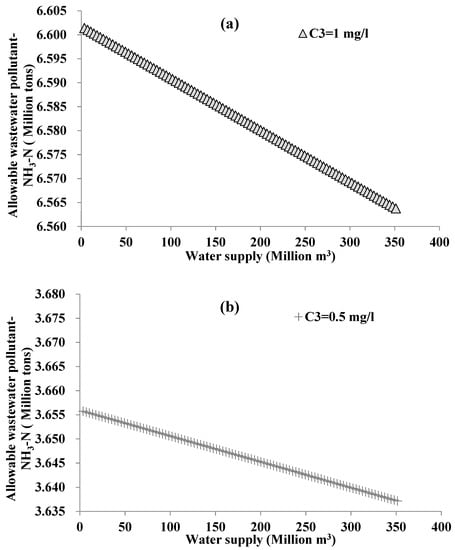
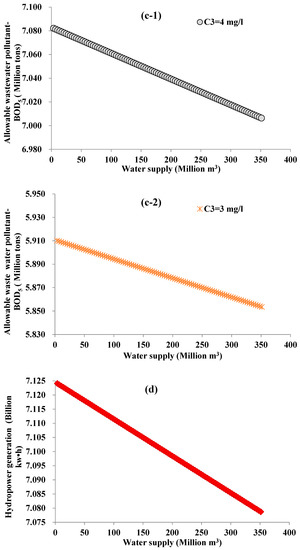
Figure 6.
The nexus between water supply and allowable wastewater pollutant under the inflow frequency level p = 75%: (a) for NH3-N with Class III (C3 = 1.0 mg/L) water quality protection target, (b) for NH3-N with Class I (C3 = 0.5 mg/L)water quality protection target, (c-1) and (c-2) for BOD5 with Class III (C3 = 4.0 mg/L) and I (C3 = 3.0 mg/L) water quality protection targets, respectively, and (d) for the nexus between water supply and hydropower generation.
In order to determine the nexus across water supply, wastewater management and hydropower generation sectors under high water stress conditions, the amount of water supply was increased to 60% of the average water inflow in a dry year, and 70% of the average water inflow in an extraordinarily dry year [7]. The nexuses are presented in Figure 7. Their abscissas represent the water supply. The main ordinates (on the left side) are hydropower generation and the subordinates (on the right side) are the allowable wastewater pollutants (NH3-N). Since the scales of the abscissas and ordinate values are set as the same, the slopes of the lines can be compared with each other. Although the relationship between water supply and hydropower generation is impacted by the water supply and water inflow, the slopes of the line represented by the rhombus symbols in Figure 7a–c are the same. All of the Pearson correlation coefficients of the relationship lines in Figure 7 are approximately −1. This indicates that the efficiency of conversion of the water supply to hydropower generation is constant. Water inflow and water quality protection target influence the lapse rates (slopes) of the lines identified by the triangle symbols; the lapse rates of these lines are shown in Figure 7, whereas the deepest lapse rates are shown in Figure 7a and the flattest one is represented in Figure 7c. Figure 7b depicts rates which are in the middle of the two, and the effects of the water quality protection targets and water inflow on the lapse rates are the same as discussed in the preceding section. That is, the lower the water inflow and water quality protection target (higher C3 value), the deeper the lapse rate, and vice versa. However, all of the lapse rates (slopes) for the lines identified by the triangles are flatter than those represented by the rhombus. The increasing water supply will reduce the hydropower generation and allowable wastewater pollutants, but the lapse rate of hydropower generation with units of billion kw·h/(Million m3), is higher than that of the allowable wastewater pollutants with units of million tons/(Million m3).
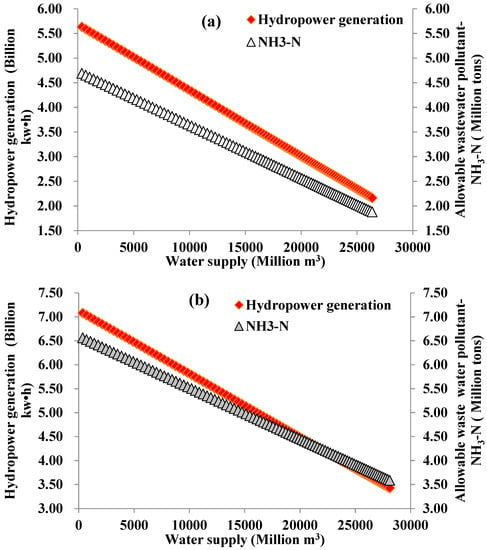
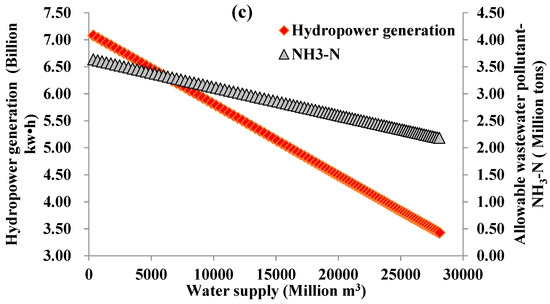
Figure 7.
The nexuses of supplied water-allowable wastewater pollutant (NH3-N)-hydropower generation: (a) p = 99%, C3 = 1.0 mg/L; (b) p = 75%, C3 = 1.0 mg/L; and (c) p = 75%, C3 = 0.5 mg/L.
4.3. Discussion
A detailed understanding of the physical nexus can point to some potential measures that can support adaptive water resource management in Jinghong area. For example, increasing supplied water will reduce the hydropower generation and the allowable wastewater pollutants. The investment for dealing with wastewater pollutants will increase while the hydropower generation company might obtain compensation from the water supply sector if their initial water rights had been allocated before. If a water pollutant event happened in an emergency situation in the study area, its impacts on supplied water and hydropower generation can be quantitatively estimated directly through the calibrated nexus; and an emergency water supply program to the emergency event will be implemented.
For the effects of boundary conditions including water inflow from the upstream and the water quality protection target, the physical nexus is sensitive to these conditions. The water inflow and water quality protection target are often belongs to the integrated water resources management at basin level. If there is more than one river–reservoir system in a basin, the physical nexus of the whole basin will be assembled by the ones proposed in our paper according to the river–reservoir networks in the basin. Based on the nexus, not only the impacts of adaptive measures on integrated water resource management can be assessed, but also the trade-offs between the water resources, the allowable wastewater pollutants, and hydropower generation can be optimized for planning or real-time operation, which will be beneficial for adaptive water resource management under the changing environment.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we have developed the nexus equations across water supply, wastewater management, and hydropower generation sectors for a river–reservoir system. Considering the Jinghong Hydropower Reservoir, located in the middle and lower reaches of the Lancang River basin, as a case study, both the water quality protection target and inflow, as the external and boundary conditions, respectively, can affect the nexus results. The incremental water supply can cause a linear decrease of the hydropower generation and allowable wastewater pollutant, while the incremental water inflow causes an increase of hydropower generation and allowable wastewater pollutants. The relationship between water supply and hydropower generation is not related to the water quality protection target since the environmental flow is not separated from the flow for hydropower generation. However, the lapse rates (slopes) of allowable wastewater pollutants–water supply are differed by the water inflow and the water quality protection target. The lower the water inflow and water quality protection target (higher value for the water quality concentration target C3), the deeper the lapse rate of allowable wastewater pollutants to water supply, and vice visa. The higher the water quality protection target (e.g., from class I to class III target), the smaller the amount of water extracted from the river, and more water is left for hydropower generation. If there is an increase in the required water supply, the amount of allowable wastewater pollutants is lower when the water inflow is higher or the water quality protection concentration is lower.
In our case study of the nexus equations in reference to a river–reservoir system, it is instructive to note that these should be added in an adaptive manner according to the network representation based on the area of research. This can be done by taking the input in our example as the output of another river–reservoir system in the upstream, or taking the output in our example as the input of another system in the downstream. The water quality indicators NH3-N and BOD5 are only adopted in our case study. Other water quality indicators can also be analyzed by replacing the corresponding parameters (e.g., the decaying coefficient and the protection concentration of the wastewater pollutants); our results from the nexus equations still clearly visually illustrate the physical cross-connections between the water supply sector, the environmental protection sector for allowable wastewater pollutants, and the energy sector for hydropower generation. In addition, the cross-connections will be very helpful for water protection and policymaking.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.L.; Methodology, D.L.; Software, D.L. and J.Z.; Validation, D.L., J.Z., Y.S. and Y.Z.; Formal Analysis, D.L..; Investigation, D.L. and J.Z.; Resources, D.L. and J.Z.; Data Curation, D.L., Y.Z.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, D.L.; Writing-Review & Editing, D.L.; Visualization, D.L. and Y.Z.; Supervision, D.L.; Project Administration, D.L.; Funding Acquisition, D.L.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 91647106, 51879194, and 51579183), 111 Project (No. B18037).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- World Economic Forum (WEF). Water Security: The Water–Food–Energy–Climate Nexus; World Economic Forum: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.G.; Hull, V.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Tilman, D.; Gleick, P.; Hoff, H.; Pahl-Wostl, C.; Xu, Z.C.; Chuang, M.G.; Sun, J.; et al. Nexus approaches to global sustainable development. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, F.; Avgerinopoulos, G.; Fazekas, D.; Laspidou, C.; Mercure, J.F.; Pollitt, H.; Ramos, E.P.; Howells, M. Energy modelling and the Nexus concept. Energy Strateg. Rev. 2018, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.M.; Wallington, K.; Shafiee-Jood, M.; Marston, L. Understanding and managing the food-energy-water nexus -opportunities for water resources research. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 111, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagmawi, M.D.; He, W.J.; Liao, Z.Y.; Yuan, L.; Huang, Z.W.; An, M. Mapping Monthly Water Scarcity in Global Transboundary Basins at Country-Basin Mesh Based Spatial Resolution. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernaat, D.E.H.J.; Bogaart, P.W.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Biemans, H.; Niessink, R. High-resolution assessment of global technical and economic hydropower potential. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munia, H.; Guillaume, J.H.A.; Mirumachi, N.; Porkka, M.; Wada, Y.; Kummu, M. Water stress in global transboundary river basin: Significance of upstream water use on downstream stress. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 14002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Zhao, D.D.; Gerbens-Leenes, P.W.; Guan, D.B. China’s rising hydropower demand challenges water sector. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, T.R.; Crootof, A.; Scott, C.A. The Water-Energy-Food Nexus: A systematic review of methods for nexus assessment. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 043002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Water Partnership. Integrated Water Resources Management; Global Water Partnership: Stockholm, Sweden, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Maass, A.; Hufschmidt, M.M.; Dorfman, R.; Thomas, H.A., Jr.; Marglin, S.A.; Fair, G.M. Design of Water-Resource Systems: New Techniques for Relating Economic Objectives, Engineering Analysis, and Governmental Planning; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, E.M.; Bruce, E.; Boruff, B.; Duncan, J.M.A.; Horsley, J.; Pauli, N.; McNeill, K.; Neef, A.; Van Ogtrop, F.; Curnow, J.; et al. Sustainable development and the water-energy-food nexus: A perspective on livelihoods. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, P.; Madel, R.; Olson-Sawyer, K.; Rabin, K.; Rose, J. Food, Water and Energy: Know the Nexus; GRACE Communications Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD); The International Energy Agency (IEA). World Energy Outlook 2012; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ercin, A.E.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Water footprint scenarios for 2050: A global analysis. Environ. Int. 2014, 64, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Green, P.; Salisbury, J.; Lammers, R.B. Global water resources: Vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 2000, 289, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, P.; van Vliet, M.T.H.; Nanninga, T.; Walsh, B.; Rodrigues, J.F.D. Climate change and the vulnerability of electricity generation to water stress in the European Union. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macknick, J.; Newmark, R.; Heath, G.; Hallett, K.C. Operational water consumption and withdrawal factors for electricity generating technologies: A review of existing literature. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 045802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spang, E.S.; Moomaw, W.R.; Gallagher, K.S.; Kirshen, P.H.; Marks, D.H. The water consumption of energy production: An international comparison. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elcock, D. Future US water consumption: The role of energy production. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 46, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrapon-Pfaff, J.; Ortiz, W.; Dienst, C.; Grone, M.C. Energising the WEF nexus to enhance sustainable development at local level. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.X.; Li, Y.; Ding, W.; Fu, G.T. Water-energy-food nexus: Concepts, questions and methodologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, A.; Tsurita, I.; Burnett, K.; Orencio, P.M. A review of the current state of research on the water, energy, and food nexus. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 11, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamo, J. Systems Thinking for Advancing a Nexus Approach to Water, Soil and Waste; United Nations University Institute for Integrated Management of Material Fluxes and of Resources (UNU-FLORES): Dresden, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- IRENA. Renewable Energy in the Water, Energy and Food Nexus; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, UAE, 2015; pp. 1–125. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, C.; Allouche, J.; Gyawali, D.; Allen, S. The rise and implications of the water-energy-food nexus in Southeast Asia through an environmental justice lens. Water Altern. (WaA) 2015, 8, 627–654. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.; Mehta, L. Nexus and Security Not Another Nexus? Critical Thinking on the New Security Convergence in Energy, Food, Climate and Water; STEPS Centre: Brighton, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Glassman, D.; Wucker, M.; Isaacman, T.; Champilou, C. The Water-Energy Nexus: Adding Water to the Energy Agenda; World Policy Institute: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- De Grenade, R.; House-Peters, L.; Scott, C.A.; Thapa, B.; Mills-Novoa, M.; Gerlak, A.; Verbist, K. The nexus: Reconsidering environmental security and adaptive capacity. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2016, 21, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, A.H.; Altouqi, S.; Karanjekar, R.V.; Hossain, M.D.S.; Chen, V.P.; Sattler, M.S. Preliminary regression models for estimating first-order rate constants for removal of BOD and COD from landfill leachate. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 5, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.D.; Jia, H.F.; Yang, C.; Melching, C.; Yuan, Y.P. A pollutant load hierarchical allocation method integrated in an environmental capacity management system for Zhushan Bay, Taihu Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.H.; Nikraz, H.; Hung, Y.T. Influence of waste age on landfill leachate quality. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2010, 1, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chian, E.S.K.; De Walle, F.B. Evaluation of Leachate Treatment, Volume II. Biological and Physical–Chemical Processes; EPA-600/2-77-186b; US EPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1977.
- Hydrochina Corporation. Report on the Impacts of Cascade Hydropower Plants on Environment in Lancangjiang River; Hydrochina Corporation: Bejin, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yunan Environmental Protection Department (YEPD). Classification for Surface Water Area Functions in Yunnan Province from 2010 to 2020. (YEPD-No.34); 2014. Available online: http://www.7c.gov.cn/zwxx/zfwj/yhf/201404/t20140417_47007.html (accessed on 8 September 2018). (In Chinese)
- General Bureau of China National Environmental Protection (GBCNEP). Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002); GBCNEP: Bejin, China, 2002.
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).