Abstract
Cattle slaughterhouse wastewater (CSWW) with an average chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biochemical oxygen demand of 32,000 mg/L and 17,000 mg/L, respectively, can cause a severe environmental hazard if discharged untreated. Conventional upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor is used in the treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater to meet the discharge standard limit of wastewater discharge set by the Department of Environment Malaysia (DOE). However, at higher loading rates the conventional systems are characterized by slow-growing microorganism resulting in long startup period, surface scum formation, and sludge washout. In this work, the performance of two laboratory scale (12 L) conventional (R1) and modified (R2) UASB reactors treating CSWW at mesophilic (36 ± 1 °C) condition were investigated. Both reactors were subjected to increasing organic loading rate (OLR) from 1.75 to 32 g L−1 day−1. The average COD, BOD5, and TSS removal efficiencies were ˃90%, at an OLR between 1.75 to 5 g L−1 day−1. The study revealed that R1 drastically reduced to 50, 53, and 43% with increasing OLR until 16 g L−1 day−1, whereas R2 maintained 76, 77, and 88% respectively, under the same OLR. Sign of reactor instability was very much pronounced in R1, showing poorly active Methanosaeta spp., whereas R2 showed a predominantly active Methanosarcina spp.
1. Introduction
The demand for effective treatment of high-strength industrial wastewater has increased over time, due to the effects related to environmental pollution. Cattle slaughterhouses are among the many food industries that are utilizing a considerable quantity of freshwater and generate a large volume of wastewater rich in organic contaminants and nutrients [1]. Wastewater produced during slaughter and cleaning processes usually consists of the animal fats, blood, urine, feces, soil from hides, soft tissue removed during trimming, and cleaning and sanitizing compounds [2]. Discharge of untreated slaughterhouse wastewater (SWW), especially in developing countries, constitutes a severe threat to public health and the environment [3]. Although rivers have natural cleansing capacity, the frequent release of such effluent without being adequately treated might overburden the receiving water body. The volume of water consumption per animal slaughtered varies according to the type of animals and the process used. Ahmadian et al. [4] and Caixeta et al. [5] reported values between 1.0 to 8.3 m3 and 0.4 to 3.1 m3, respectively. Furthermore, SWW usually contains high chemical oxygen demand (COD), biological oxygen demand (BOD5), suspended solids (SS), nitrogen, and phosphorus [6]. Rajab et al. [7] have found that the contaminant concentration have relatively high COD (3102 ± 688 mg L−1), fats, oil, and grease (FOG) (375 ± 151 mg L−1), suspended solids (SS) (872 ± 178 mg L−1), total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN) (186 ± 27 mg (N) L−1), and total phosphate (PO3−4) (76 ± 36 mg L−1). However, the strength could differ from one industry to another, owing to the number and type of animals slaughtered. Moreover, the high concentration of color and nitrogen in the SWW could also impede light penetration and encourage algal boom that could lead to eutrophication [8]. Discharge of improperly treated high-strength wastewater has mandated stakeholders at both national and international levels to intervene. Most of the interventions yield standard rules and regulatory discharge limit requirements. Malaysia is not an exception to this type of regulations. For instance, 120 mg/L and 200 mg/L are the COD standard A and B acceptable limits allowed for all intending investors capable of generating wastewater that could be discharged as sewage into the receiving water body [9]. Conventionally, slaughterhouse wastewater (SWW) treatment methods are similar to current technologies used in municipal wastewater treatment. These include lagoon and ponds systems, sedimentation and floatation, coagulation/flocculation, adsorption, membrane technology, dissolve air, and other advanced oxidation processes [10]. However, several researchers have specifically reported different methods of slaughterhouse wastewater treatment that works as an entity and a combined operation. Such work includes aerobic/anaerobic [11,12,13], fixed-bed reactor [14], anaerobic/aerobic (An/Ar) system (comprising an anaerobic filter (AF) coupled to anaerobic sequential batch reactor (SBR)) [15], and fixed-bed granular sludge with/without static activated sludge [16]. But most of the studies have consistently shown the numerous drawbacks, ranging from a large area of space requirement, the massive volume of sludge generation, intensive use of energy for aeration, and the high overall cost of maintenance [10,17].
However, anaerobic digestion using upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactors (UASB) have now become a promising technique for the treatment of wastewater from food processing industries [18]. This might be due to its efficiency, flexibility, smaller footprint with less maintenance, and high-quality effluent. Moreover, the condition at which the UASB reactor operates plays a vital role in the performance of the bioreactor. For instance, the study of Musa et al. [19] on SWW treatment under mesophilic temperature (35 °C) revealed a COD removal efficiency of 70% at an organic loading rate of 10 g L−1 day−1. Similarly, Mittal et al. [20] reported a UASB reactor with an average COD removal efficiency of 80–85% and is very much efficient when operated at an organic loading rate (OLR) of 2.7–10.8 kg COD m−3 day−1. In another development, slaughterhouse wastewater removal efficiency of 90% was revealed by Nacheva et al. [21] at a high OLR of 15 kg COD m−3 day−1. Most interestingly, the UASB reactor operation was carried out at ambient temperature (20.9–25.2 °C). Furthermore, a comparative study between hybrid UASB and anaerobic filter (AF) was revealed by Rajakumar et al. [22] using poultry wastewater under similar conditions of loading. The result of the experiment shows a high COD and soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) removal efficiencies of 80% and 86% in the UASB reactor as compared to 70% COD and 79% SCOD in the AF. However, reducing hydraulic retention time (HRT) of both reactors from an optimum of 12 h to 10 h resulted in sludge washout and lower COD removal efficiencies to less than 80% in the UASB and 66% in the AF.
The potential of UASB reactors in the treatment of mainly liquid wastewater was reported at full, pilot, and laboratory scales. The various types of wastewater tested ranged from the slaughterhouse wastewater (SWW), dairy, wine distillery, palm oil mill, and municipal wastewater [23]. However, researchers have consistently reported problems related to high suspended solids—sludge washed out along with the large population of the microbial community. Also, fats, oil, and grease (FOG) content of causing harm to human life and the environment. The overall aim is to examine the efficiency of the two systems in producing an effluent which is suitable for discharge and use the most effective result obtained to serve as the basis for UASB bioreactor design in cattle slaughterhouses.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate and Seed Inoculum
The slaughterhouse wastewater used as substrate was collected from a discharge point of abattoir Shah Alam, in the state of Selangor, Malaysia. The samples were then immediately transported to the public and environmental health laboratory in the faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia. The sample was screened to remove larger particles. The COD, BOD5, TSS, alkalinity, color, and turbidity of the sample were measured and subsequently stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C for further use. Table 1 present the characteristics of raw CSWW. The seed sludge used as inoculum was collected from a wastewater treatment plant in the faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia. Each reactor received a total of 6 kg (wet weight) sludge, and the reactors were acclimatized with synthetic wastewater prepared according to Idrus et al. [24]. The composition of the synthetic wastewater used was as follows: Full cream milk, 144 mL; ammonium phosphate (NH4)2HPO4, 3.4 g urea, 2.14 g; yeast, 23 g; dried blood, 5.75 g and filled up to 1 L with tap water.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the cattle slaughterhouse wastewater (CSWW) used in this study.
2.2. Experimental Setup
Figure 1 represents the schematic lab scale conventional UASB reactor R1 and the modified UASB reactor R2 used in this work. The cylindrical shaped UASB reactor columns were made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The reactors working and total volumes are 12 and 14 L. Each reactor, R1 and R2, has a diameter and height of 12 cm and 60 cm, respectively (Figure 1). A 3-mm synthetic grass was used vertically from bottom to top, with a height of 210 cm. R2 was equipped with a flat-round PVC mesh as a separator in the upper portion slightly above the sludge (5.08 cm) which separated the solid sludge from the liquid, thus preventing washout of the sludge from the reactor. Also, a manual flexible stirrer was attached to the top of R2 for scum displacement. Both R1 and R2 were fed six times per day using a dosing pump at a flow rate of 1.2 L/m. The two reactors were partially immersed in a water jacketed tank at a temperature of 35 ± 1 °C. The hydraulic retention time (HRT) of the reactors was maintained at 24-h HRT during acclimatization and subsequent operational period. The acclimatization period for R1 lasted for one month and R2 for three weeks with no supplemental addition of nutrient to set the level for anaerobic digestion. Feeding of the synthetic and CSWW was done from the bottom of the reactors to allow for sufficient contact between the biologically activated sludge containing microbes and the CSWW (Influent). After the acclimatization, both reactors were fed with influent COD of 3500 mg COD L−1 added, which corresponds to an organic loading rate (OLR) of 1.75 g L−1 day−1. Exclusive feeding of the reactors was achieved after each loading attained a stable state. Feed COD into the systems was done by reducing the dilution factor of CSWW until undiluted CSWW was fed into the systems. The feeding was done at an interval of time in 24 h throughout the operational period. This strategy of feeding was done to enhance smooth digestion and avoid overloading of food to the microbial population. The pH, influent, and effluent flows were monitored daily.
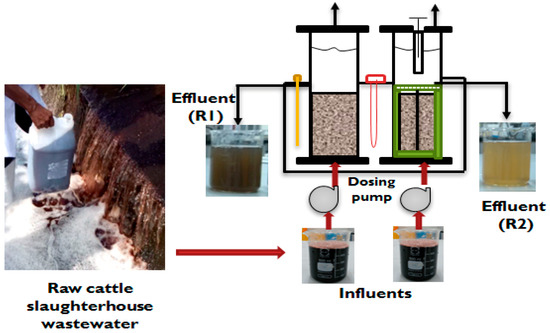
Figure 1.
The configuration of the conventional and the modified upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors setup.
Parameters like COD, BOD5, TSS, pH, FOG, Color, and Turbidity were measured at an interval of one day, except BOD5 of the reactor’s effluents, which were measured once at every stable state of organic loading. Table 2 represents the strategy employed during the reactor’s startup and operation.

Table 2.
Startup strategy of conventional and modified UASB reactors.
2.3. Analytical Methods
Analyses of the effluent sample from the two reactors were measured at the one-day intervals. Parameters such as chemical oxygen demand, total suspended solid (TSS), and volatile suspended solid (VSS) were analyzed according to the standard method for the Examination of Water and Wastewater APHA [25]. Fats, oil, and grease content were analyzed following the procedure reported by Cirne et al. [26]. However, TSS samples were filtered through a 0.47 μm filter paper placed on a vacuum pump before the examination. Other parameters like color, turbidity, and total nitrogen (TN) were determined using multi-parameter portable calorimeter HACH system (DR 900). The methods used for each of these parameters were Platinum-Cobalt Standard Method 8025 for color, Absorptometric method 8237 for turbidity measurements, and total nitrogen (TN) following persulfate Digestion Method for TN. The protein content of the wastewater was determined by multiplying TN by 6.24 [27]. The samples used for color measurements were filtered through 0.47 μm filter paper at a wavelength of 465 nm, and the blank was distilled water. A pH meter (Mettler-Toledo AG, Schwarzenbach, Switzerland) was used for daily pH measurement throughout the operation. Also, the sample sludge from R1 and the synthetic grass used as biofilm in R2 before and after anaerobic digestion were characterized to see the behavior of the materials. Sample sludge was dried and crushed to powder form using a mortar and pestle while the synthetic grass was peeled off from the main body and cut in 1 mm size using a sharp knife. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) was carried out using (S-3400N SEM HITACHI, Milpitas, CA, USA) to examine the surface morphology of the sludge in the conventional and modified reactor.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. COD Removal Efficiency
The performance of conventional R1 and modified R2 UASB reactors were operated continuously for 95 days and evaluated in terms of COD removal at various OLR, as shown in Figure 2. Both reactors were maintained at 24-h HRT and 36 ± 1 °C. The variation of OLR during the whole period of the study range from 1.75 g L−1 day−1 to 16 g L−1 day−1 and this corresponds to influent COD range of 3.5 g COD L−1 to 32 g COD L−1. The removal efficiencies of R1 and R2 at steady-state OLR of 5 g L−1 day−1 were ˃ 90% on the average. However, with the increase in OLR to 10 g L−1 day−1, the reactor R1 suffered a severe decline of COD removal to 58% while R2 maintained a significant COD removal of 95% at a stable state. The setback observed in R1 could be due to shock received by the microbial community to withstand the change in loading rate. Moreover, the formation scum coupled with insufficient bacterial population resulted in a decline in the microbial activity of R1 as compared to R2. The manual scum-displacement stirrer used intermittently vigorously opposed the formation of surface scum in the R2. Also, the synthetic grass bed in R2 was able to provide sufficient room for the microbial population to multiply. The average VSS and TSS measured at 10 g L−1 day−1 OLR in the R1 were 2340.25 and 4269.5 mg/L, and 0.53 was the VSS/TSS ratio within the same phase. This was the possible reason for the decline in the removal efficiency, while in R2 the ratio was 0.87 on the average. The subsequent increase in OLR to both reactors further deteriorated the rate of COD removal efficiency in R1 to an average 50% at OLR 14 and 16 g L−1 day−1, whereas R2 was able to retain the removal rate of 95%. The resilience of the R2 was ascribed to the high adaptability of the microbial community to the environment [28]. Furthermore, the studies of Fang and coworkers had shown that the UASB reactor could maintain a stable process once the operation is within the normal OLR boundaries which range between 1.5 and 16.0 kg COD m−3 day−1 [29,30]. Consequently, the evaluation of the two experimental results indicates that the modified UASB reactor showed excellent efficiency at reducing COD as compared to conventional UASB. Similar wastewater treatment was previously reported in the literature [31,32] using a UASB reactor. However, the results obtained were lower as compared to the modified reactor in this study. In general, the increase in OLR and maintaining 24-h HRT for both reactors negatively affected R1, whereas R2 was able to withstand high OLR with quality effluent at HRT of one day.
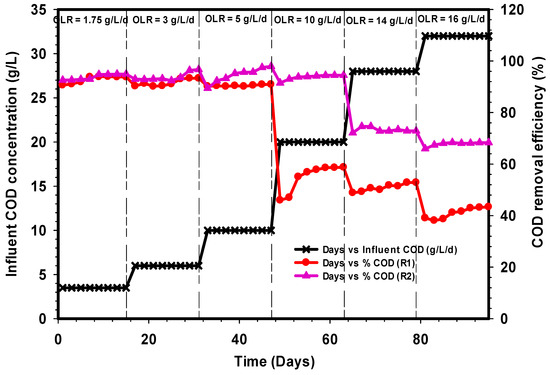
Figure 2.
Comparison of chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiencies of R1 and R2.
3.2. Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD5) Removal
Figure 3 illustrates the influent BOD5 concentration at various OLR with the respective BOD5 removal efficiency pattern of the R1 and R2. Despite the significant fluctuation in the influent BOD5 concentration of the CSWW, the characteristic of the effluent in R1 and R2 at influent OLR of 5 g L−1 day−1 was quite good. The average BOD5 removal efficiency of R1 at 1.75 g L−1 day−1 was 87%, and 62% at the higher OLR of 16 g L−1 day−1. For R2, the BOD5 removal efficiency stood at 95% and 84% at 1.75 g L−1 day−1 and 16 g L−1 day−1, respectively. This trend of BOD5 removals in R1 corresponds to the pattern of COD removal efficiency as shown in Figure 2, in which the COD removal drastically declined under shock loading due to the change in OLR from 10 to 16 g L−1 day−1. A similar trend of BOD5 and COD removal efficiencies was reported in the literature [33,34]. Although, the BOD5 result of Mustapha et al. [34] does not change drastically as the BOD5 does in R1. Furthermore, the study of Sreekanth et al. [35] also reveals a reduction of BOD5 similar to COD, which declined as a result of the shock loading. Consequently, the drop in the COD removal of R1 at 10 and 16 g L−1 day−1 OLR affected the BOD5 removal in the same phase and was transmitted to the subsequent stages of R1. This phenomenon could be due to inhibition of biomass activity at high concentration. However, the modified R2 yielded an effluent with high COD removal which, in turn, contributed significantly to achieving high BOD5 removal of the system.
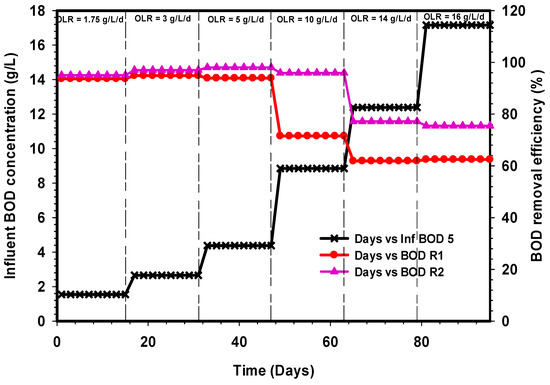
Figure 3.
Comparison of biological oxygen demand (BOD5) removal efficiencies of R1 and R2.
3.3. TSS Removal Profile
Effluent total suspended solids (TSS) concentrations of R1 and R2 were measured to know the insoluble organic matter present in the treated CSWW after one day. The TSS parameters are among the many parameters that were used in analyzing the reactor’s performance at various OLR and one-day HRT. Figure 4 depicts the TSS removal concentration of the treated CSWW effluents. Both reactors R1 and R2 demonstrated high TSS removal efficiencies of 90% and 92% at OLR of 1.75 on the average, and this OLR corresponds to influent COD of 3.5 g L−1. An average of 95% was achieved at 5 g L−1 day−1 corresponding to 10 g L−1 influent COD in both reactors. The excellent performance of the systems between 1.75 and 5 g L−1 day−1 OLR is an indication of sufficient microbial growth and good hydraulic contact between the substrates and the biomass. However, a sudden dropped in TSS removal efficiency was observed in R1 at 10 g L−1 day−1 OLR. During this period, the ratio of VSS/TSS became 0.5 on average, thus indicating insufficiency of the microbial population within the system. On the other hand, R2 maintained an average TSS removal of 92%, 91%, and 88% at the loading rates of 10, 14, and 16 g L−1 day−1, respectively. Likewise, the VSS/TSS in these phases was 0.87, 0.8, and 0.68, respectively, thus showing good microbial growth. It can be deduced that the reactor R1 suffered from a great shock with the increment of OLR, while its counterpart R2 showed a consistently steady-state performance. The performances of R2 further reveals a self-regulatory capability inherent in the biological system, making it possible for the microbial consortium to acclimate itself to the increasing OLR. The experiment of Sreekanth et al. [35] demonstrated similar behavior of TSS removal. However, their system was able to regain stabilization after reduction of OLR. But in this case, the OLR could not be reduced in R1 since the objective was to compare the performance between the conventional and the modified UASB reactors subjected to the same OLR, COD, and HRT.
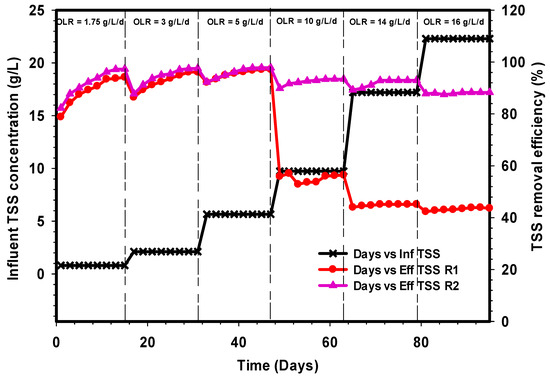
Figure 4.
Comparison of total suspended solids removal efficiencies of R1 and R2.
3.4. Fats, Oil, And Grease (FOG) Removal
Slaughterhouse wastewater is considered as high-strength waste stream, because of the oil, grease, and protein content that make it difficult to achieve high treatment performance using anaerobic digestion [36]. One major concern with this type of waste in an anaerobic digester is that at higher organic loading rates, FOG may cause significant digester foaming [37]. Jeganathan et al. [38] observed that FOG accumulation led to digester foaming and reduced degradation in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor at a loading rate of 5 kg COD/m3d. The effect of fats, oil, and grease removal efficiencies of the R1 and R2 is shown in Figure 5. The influent contained a high content of FOG and total protein (Table 1) which are the main components of this type of wastewater. The FOG removal efficiencies at 1.75, 3, and 5 g L−1 day−1 were 89%, 81%, and 74% in R1, while R2 presented 90%, 90%, and 84%, respectively. These results demonstrate that the two reactors were well adapted with biomass concentration. However, at a loading rate of 10 g L−1 day−1, the process appeared inhibitory in R1 as indicated in Figure 5. The reduction in the FOG removal of R1 could be attributed to the sudden change of OLR beyond the biomass degradation capacity, and this resulted in the accumulation of long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs). The efficiency of R2 slightly reduced, but not as significantly as R1, since the reduction was only from 84–73%, while R1 reduced to 48% from 74% at the same OLR concentration. Moreover, the increase in OLR to 14 g L−1 day−1 and subsequently to 16 g L−1 day−1 further deteriorated R1 to 42% and 34%, while R2 stood at 65% and 54% on average, with very little or no foaming; further, biomass washout was observed in the R2. Hence, the modified UASB reactor R2 was more robust than conventional R1. Alves et al. [39] suggest that the pattern of degradation observed in R1 was mainly due to the inhibition of propionate degradation by LCFAs and the inhibition of hydrolysis by a high propionate concentration. Furthermore, some studies have also shown that reactor failure is mainly due to the inhibition of methanogens and acetogens [40,41]. The inhibition process occurs when the LCFAs disappear from the solution and accumulates in solid biomass within 24 h and are subsequently adsorbed into the membrane/cell wall of bacteria which damages the microbial cell transport function or protective function [8].
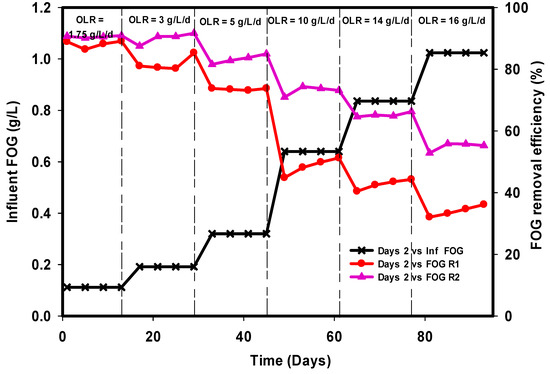
Figure 5.
Comparison of fats, oil, and grease removal efficiencies of R1 and R2.
3.5. pH
A functional anaerobic digestion system depends on the buffering capacity and the degree of adaptation of the microorganisms [19]. The high protein and lipid content of slaughterhouse wastewater makes it a challenging substrate for degradation by the microbial consortium. pH is an important parameter that defines the stability and performance of the anaerobic digestion processes [42]. The degradation of the substrate during anaerobic digestion largely depends on three phases namely hydrolysis, acidogenesis, and methanogenesis [43]. In anaerobic digestion, microorganisms have a working range of pH. Methanogens are sensitive to pH between 6.5 and 7.5 and have optimal pH of between 7.0 and 7.2 [44,45]. Figure 6 shows the effluent pH pattern of the convention R1 and the modified R2 UASB reactors treating the CSWW. The pH of the R1 was around 6.7 on average, while R2 was 6.8 and 7 at OLR 1.75, 3, and 5 g L−1 day−1 respectively. Subsequently, increasing the concentration of substrate COD to 10 g L−1 day−1 resulted to decrease in the pH of R1 to 6.2, while that of R2 maintained a neutral state. The behavior of R1 could be the result of volatile fatty acids (VFA) accumulation in the system beyond the microbial consumption. But, R2 depicts a system with a sufficient buffering capacity in which the VFAs were consumed by the microbial population. The pH of R1 further decreased to 5.7 and 5.2 at 14 and 16 g L−1 day−1 OLR and further deteriorated the performance of R1 to the lowest level.
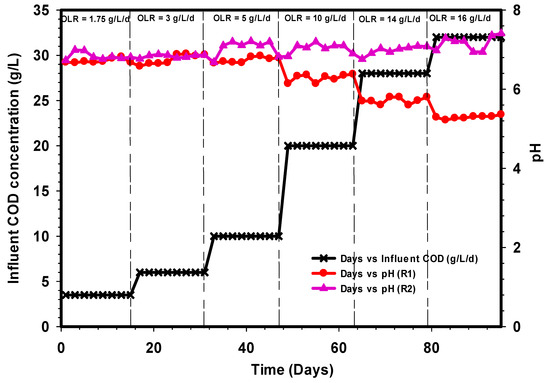
Figure 6.
Effect of pH on the on the conventional R1 and the modified R2 UASB reactors.
3.6. Color Removal Efficiency
Color measurements were reported as a true and apparent color, based on the APHA platinum-cobalt standard method using DR 900 portable calorimeter. The UV-visible spectra in influents and effluents were measured to identify the spectral changes. Color removal in a UASB reactor is usually the result of adsorption of the red pigment into the sludge, followed by biodegradation processes by anaerobic consortium bacteria. Figure 7 depicts the variation in color removal efficiency of the two UASB reactors (R1 and R2) with the same conditions of OLR and HRT. Decolorization efficiency increased from 90–91% in R1 and 91–97% in R2 at OLR 1.75–3 g L−1 day−1. Increasing the influent concentration to 5 g L−1 day−1 OLR decreased the rate of decolorization to 83% in R1 and 85% in R2. The subsequent increase in loading rate drastically affected the removal efficiency of R1 to 53% while R2 remained at 76%. Moreover, the removal efficiency continued to decrease with the increase in color-rich influent concentration until the efficiency of R1, on average, became 38% in the highest OLR. Also, with the stepwise increase of recalcitrant compound to R2, a similar trend of reduction was observed. However, R2 was able to record an average of more than 50% removal at the highest OLR. The high color removal in the efficiency at the beginning of the continuous operation seems to be due to adsorption/biodegradation on to the sludge. The modified UASB reactor R2 was well-adapted with anaerobic bacteria consortium, and this could be the reason for the high substrate degradability that resulted in high-quality effluent in terms of color removal as against R1.
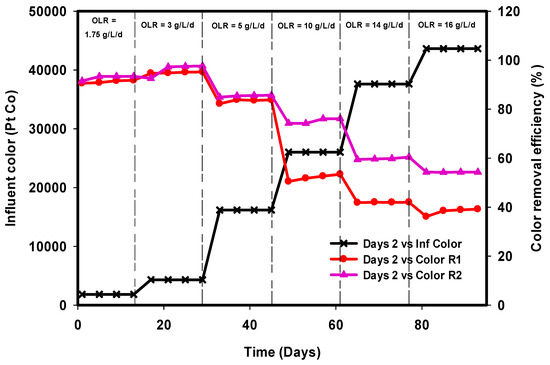
Figure 7.
Comparison of color removal efficiencies of R1 and R2.
3.7. Turbidity Removal
In evaluating the performance of wastewater treatment systems, turbidity is among the most important parameters considered in this work. Figure 8 portrays the removal efficiency of turbidity from the R1 and R2. The turbidity removal was significantly high at loading rates of 1.75, 3, and 5 g L−1 day−1, and this corresponds to an average of 92, 92, and 75% in R1, and 96, 94, and 90% in R2. However, a further increase in organic loading rate to 10 g L−1 day−1, corresponding to 20 g L−1 COD, resulted in a decrease in the turbidity removal efficiency to an average of 41% in R1 and 81% in R2. The drastic reduction in R1 was a result of aggressive shock received by the microbial population due to the continuous loading of organic matter, and thus limits the treatment efficiency of the system. Furthermore, the inefficiency of the reactor R1 to achieve high turbidity removal is an indication of the fact that part of the reactor volume was operating as a “dead zone”, decreasing the contact between the influent substrate and the active microbial population. However, the immobilization of biomass in R2 coupled with intermittent stirring was responsible for degrading the wastewater to ˃80% at 10 g L−1 day−1 OLR. Moreover, the middle perforated flat sheet PVC attached with synthetic grass in the R2 is an important part of the reactor design that was responsible for retaining maximum sludge from washout and ensuring smooth flow of effluent out of the reactor.
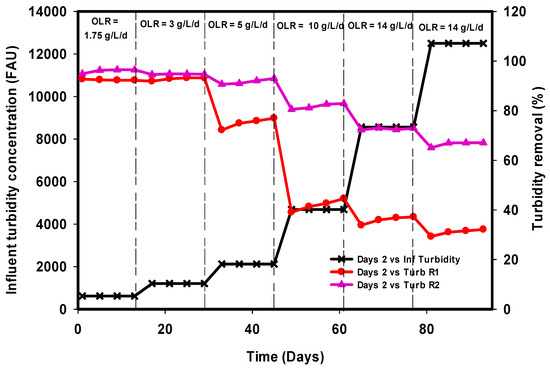
Figure 8.
Comparison of turbidity removal efficiencies of R1 and R2.
3.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
The scanning electron microscopic (SEM) images were observed in granules before and after treatment to find out the changes of the microbial community in the systems. Figure 9a,b represents the surface morphology of the sludge in R1 before and after contact with the CSWW, while Figure 9c,d showed the synthetic grass packing media in R2 before and after contact with CSWW. Rod-like structures with bigger pores were observed in Figure 9b, and this is an indication of the presence of methanosaeta. These microorganisms typically occurred in pairs and were often enmeshed in flocs of filaments. In reactor R2, an evenly distributed coccoid-shaped archaeal species was observed on the synthetic grass media surface which represents the typical characteristics of Methanosarcina spp. [46]. The morphology of the image in Figure 9b showed poorly active Methanosaeta spp., and these could be due to volatile acids and soluble microbial products (SMP) which accumulate and exceed the reactor buffering capacity.
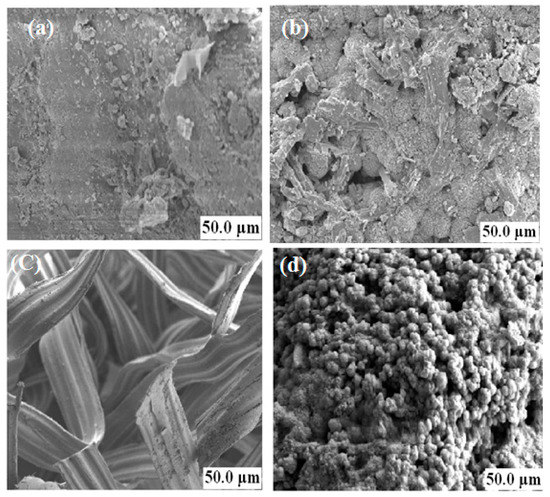
Figure 9.
The SEM image of a conventional UASB reactor R1 before (a) and after (b), and a modified UASB R2 reactor before (c) and after (d) contact with CSWW.
Furthermore, the poor performance of the R1 could also be due to the overloading of the fat-rich wastewater that resulted in low pH and triggered a high concentration of volatile acids [47]. Moreover, the Methanosaeta spp. in R1 seems inactive, and this was due to the presence of high concentration of acetate. Furthermore, Methanosarcina species can achieve stable growth at high organic loading rates (OLR) and high levels of ammonium and acetate. In contrast, high ammonium concentrations and elevated acetate levels were reported to suppress the growth of Methanosaeta species [48,49]. But, the reason for diversification of Methanosarcina species in R2 was due to the high maximum specific growth rate (μmax) and high half-saturation coefficient (KS) making it possible to utilize acetate, formate, H2, and CO2 for their growth, while Methanosaeta species have a low μmax and low KS value [50].
3.9. Overall Performance Study of the Conventional and Modified UASB Reactors
The overall average performance of the conventional and modified UASB reactors is listed in (Table 3). The runs in both reactors were aimed to examine the effect of a change in OLR at a constant hydraulic retention time of 24 h. The change of OLR to both reactors corresponds to changes in COD and TSS concentration as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Results of the average performance study of the conventional (R1) and modified (R2) UASB reactor.
During the comparative study, the OLR ranged from 1.75 g L−1 day−1 to 16 g L−1 day −1, corresponding to 3500 mg COD L−1 to 32,000 mg COD L−1 COD. Based on the runs I, II, and III in Table 3, the increases in OLR from 1.75, 3, and 5 g L−1 day −1 in both reactors showed a fluctuating trend in the COD and TSS removal efficiencies. However, the overall COD removals remained stable in R2 when the OLR increased to 10 g L−1 day −1 (run IV). Subsequently, increasing OLR to run IV caused a massive decline of COD and TSS removal in R1, while R2 remained stable, with 95% and 92% on the average. On the other hand, the overall BOD5 removal efficiency of the systems follows the trend of COD removal with average values of ˃ 90% for all the reactors at BOD5 runs in I–III Table 3. The decrease in the reactor performance, particularly in R1 at a higher OLR, was mainly due to an imbalance of the microbial population. According to Zhou et al. [51], granules formed more rapidly at high OLR. Therefore, modifying the reactor by providing a suitable environment for the microbes to strive better at a higher OLR is necessary when dealing with high-strength wastewater. The pH of the effluents in both reactors was significantly within the stable anaerobic digestion condition in runs I–III. However, with the increase in organic loading rate as shown in run IV, Table 3, the pH of R1 declined to an average of 6.2, whereas R2 maintained within a neutral (7) state. These implied that the microbial populations in R1 were not sufficient to consume the accumulated VFA, and thus resulted in inhibition.
Further increases in OLR, in the runs I–VI, resulted in decreases in pH of R1 to 5.7 and 5.2, but R2 remained at 6.9 and 7, on average, indicating a neutral state. Color is an important parameter to be considered during CSWW effluent discharge. The overall color removal efficiencies of the reactors were ˃90% at run I and ˃80% in run II, as seen in Table 3. Based on the results in Table 3, it was concluded that the color effluent quality of R1 and R2 decreased with increase in OLR, although the quality of R1 significantly reduced as compared to R2, which remained at an average ˃50% at the maximum OLR of 16 g L−1 day−1. Similarly, turbid effluent is also an indication of the presence of dissolved and suspended particles. Based on the results shown Table 3, R1 was highly characterized by a massive reduction in the reactor performance during run IV, V, and VI and thus, resulted in high turbid effluent which was due to the scum formation and the resulting sludge washout. The work of Halalsheh et al. [52] revealed that high organic loading at short HRT promotes scum formation, and oil and grease will tend to adsorb on the sludge. The case is entirely different in reactor R2; this is because no sludge washed out and very little or no scum formed in R2. These could be due to the presence of the middle-perforated flat PVC sheet attached with the synthetic grass slightly above the sludge level (2 inches) in the reactor (Figure 1), preventing sludge washout and subsiding the suspended solids. Another important observation made in both reactors was the presence of fats, oil, and grease. The high occurrence of scum in R1 at OLR 10 g L−1 day −1 is an indication of FOG with high lipid content. This case is more severe in R1 than R2, as shown in Figure 5 and Table 3.
Moreover, Musa et al. [53] showed that lower HRT gives room for shorter contact time between microorganisms and substrate and therefore might pave the way for a part of influent COD leaving the reactor without proper treatment. However, Halalsheh et al. [52] suggest that longer retention time could reduce the scum formation of a system as lipid removal was better achieved at longer HRT. From the results of the performance of the two reactors it was noticed that the high loading rate coupled with insufficiency of microbial population resulted in the decrease in efficiency of R1 at some points, but the modified UASB reactor achieved better and more efficient output under the same conditions of organic loading and HRT.
4. Conclusions
The examination of the conventional (R1) and the modified (R2) UASB reactors demonstrates that both reactors had comparably high COD removal efficiencies, being ˃90% on the average, at a loading rate of 5 g L−1 day −1 corresponding to 10,000 mg/L COD. On further increase of organic load to both reactors, the modified UASB reactor R2 exhibited high organic-matter removal efficiency accompanied by steady performance and shock loading tolerance as compared to R1. This is because a higher amount of granulated biomass was retained in R2 and this improves the overall performance of the R2 as against R1. Furthermore, the reactor R2 showed the capability of handling OLR up to 16 g L−1 day −1 corresponding to 32 COD g L−1. The drastic decline of the reactor R1 at 10 g L−1 day −1 OLR resulted in low removal efficiencies of the target parameters, and this affected all the subsequent stages of OLR. However, the optimum organic matter removal efficiency of the R2 was found at 10 g L−1 day −1 at 24 h HRT. Therefore, the configuration of R2 enhanced sludge stability and tolerated the shock loading occurrence by handling organic loading rate up to 16 g L−1 day −1 better than the conventional reactor R1. Nonetheless, HRT of one day was not sufficient enough to degrade the waste to 90% efficiency at the highest OLR of 16 g L−1 day −1 in R2 and as such the system will also require a minimum of two days to achieve a higher percentage of organic matter removal to comply with the discharge standard limits set by the department of environment (DOE) Malaysia. Future work will focus on the optimization and scale-up analysis of the modified UASB reactor to facilitate the implementation at a commercial scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.M. and S.I.; methodology, S.I., H.C.M., and N.N.N.D.; validation, S.I., H.C.M., and N.N.N.D.; formal analysis, M.A.M. and S.I.; investigation, M.A.M. data verification, H.C.M. and N.N.N.D.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.M., review and editing, S.I., H.C.M., and N.N.N.D. All authors have read and approved this article.
Funding
The authors thank Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) for the preparation, execution, and writing of this research with grant baseline funding GP-IPS/9633400 awarded to Mohammed Ali Musa.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledged the support received from Universiti Putra Malaysia, from the preparation, execution and writing of this research article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jensen, P.D.; Sullivan, T.; Carney, C.; Batstone, D.J. Analysis of the potential to recover energy and nutrient resources from cattle slaughterhouses in Australia by employing anaerobic digestion. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Technical Development Document for the Final Effluent Limitations Guidelines and Standards for the Meat and Poultry Products Point Source Category (40 CFR 432); USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Barrera, M.; Mehrvar, M.; Gilbride, K.A.; McCarthy, L.H.; Laursen, A.E.; Bostan, V.; Pushchak, R. Photolytic treatment of organic constituents and bacterial pathogens in secondary effluent of synthetic slaughterhouse wastewater. Chem. Eng. Des. 2012, 90, 1335–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Yousefi, N.; Van Ginkel, S.W.; Zare, M.R.; Rahimi, S.; Fatehizadeh, A. Kinetic study of slaughterhouse wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation using Fe electrodes. Water. Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caixeta, C.E.; Cammarota, M.C.; Xavier, A.M. Slaughterhouse wastewater treatment: Evaluation of a new three-phase separation system in a UASB reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 81, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo-Lecompte, C.F.; Mehrvar, M.; Quiñones, E.B. Combined anaerobic-aerobic and UV/H2O2 processes for the treatment of synthetic slaughterhouse wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2013, 48, 1122–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajab, A.R.; Salim, M.R.; Sohaili, J.; Anuar, A.N.; Lakkaboyana, S.K. Performance of integrated anaerobic/aerobic sequencing batch reactor treating poultry slaughterhouse wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Debsarkar, A.; Mukherjee, S. Treatment of slaughter house wastewater in a sequencing batch reactor: Performance evaluation and biodegradation kinetics. BioMed. Res. Int. 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Environmental Requirements: A Guide for Investors. Department of Environment, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment: Wisma Sumber Asli, Precinct 4 Federal Government Administrative Centre, 62574 Putrajaya, Malaysia. 2010. Available online: http://www.doe.gov.my/eia/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/A-Guide-For-Investors1.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2019).
- Bustillo-Lecompte, C.F.; Mehrvar, M. Slaughterhouse wastewater characteristics, treatment, and management in the meat processing industry: A review on trends and advances. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 161, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, M. Developments in wastewater treatment in the meat processing industry: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 1995, 54, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massé, D.I.; Masse, L. The effect of temperature on slaughterhouse wastewater treatment in anaerobic sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 76, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernet, N.; Delgenes, N.; Akunna, J.C.; Delgenes, J.P.; Moletta, R. Combined anaerobic–aerobic SBR for the treatment of piggery wastewater. Water Res. 2000, 34, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddoud, A.; Sayadi, S. Application of acidogenic fixed-bed reactor prior to anaerobic membrane bioreactor for sustainable slaughterhouse wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-López, A.; Vallejo-Rodríguez, R.; Méndez-Romero, D. Evaluation of a combined anaerobic and aerobic system for the treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debik, E.; Coskun, T. Use of the Static Granular Bed Reactor (SGBR) with anaerobic sludge to treat poultry slaughterhouse wastewater and kinetic modeling. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2777–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.J.; Fong, C.M.; Chung, L.L.; Hassell, D.G. A review on anaerobic–aerobic treatment of industrial and municipal wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, M.K.; Hina, R.; Muhammad, F.A.; Shafaqat, A.; Muhammad, M.N.; Zhu, J.S. Review of Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor Technology: Effect of Different Parameters and Developments for Domestic Wastewater Treatment. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1596319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.; Syazwani, I.; Hasfalina, C.M.; Daud, N.N. Effect of Organic Loading Rate on Anaerobic Digestion Performance of Mesophilic (UASB) Reactor Using Cattle Slaughterhouse Wastewater as Substrate. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, G.S. Treatment of wastewater from abattoirs before land application—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1119–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacheva, P.M.; Pantoja, M.R.; Serrano, E. Treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Water. Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakumar, R.; Meenambal, T. Comparative Study on Start-Up Performance of HUASB and AF Reactors Treating Poultry Slaughterhouse Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2008, 2, 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, M.A.; Rumana, G.; Zularisam, A.W.; Anwar, A. Integrated application of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor for the treatment of wastewaters. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4683–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idrus, S.; Banks, C.; Heaven, S. Assessment of the potential for biogas production from wheat straw leachate in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket digesters. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2737–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Cirne, I.; Jaime, B.; Yuri, G.; Elizabete, L. Methods for determination of oil and grease contents in wastewater from the petroleum industry. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2016, 10, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.M.; Seung, K.H.; Seung, Y.; Chang, H. Potential of anaerobic digestion for material recovery and energy production in waste biomass from a poultry slaughterhouse. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Jianzheng, L.; Yupeng, Z.; Antwi, P.; En, S.; Xue, C.; Jia, M. Influence of glucose fermentation on CO2 assimilation to acetate in homoacetogen Blautia coccoides GA-1. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 42, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Boe, K.; Angelidaki, I. Biogas production from potato-juice, a by-product from potato-starch processing, in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) and expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB) reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5734–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Yong, H.; Qigui, N.; Yuyu, L.; Yu, L.Y.; Xiaochang, C.W. UASB performance and electron competition between methane-producing archaea and sulfate-reducing bacteria in treating sulfate-rich wastewater containing ethanol and acetate. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 137, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendooven, L.; Escamilla, E.S. Poultry slaughter wastewater treatment with an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1730–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobya, M.; Senturk, E.; Bayramoglu, M. Treatment of poultry slaughterhouse wastewater by electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 133, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.; Wong, K. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of palm oil mill effluent. Water Res. 1983, 17, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.; Ashhuby, B.; Rashid, M.; Azni, I. Start-up strategy of a thermophilic upflow anaerobic filter for treating palm oil mill effluent. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2003, 81, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, D.; Sivaramakrishna, D.; Himabindu, V.; Anjaneyulu, Y. Thermophilic treatment of bulk drug pharmaceutical industrial wastewaters by using hybrid up flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2534–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, E.; Rintala, J. Anaerobic digestion of organic solid poultry slaughterhouse waste—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C.D.; Gough, H.L.; Nelson, D.; Ferguson, J.; Stensel, H.; David, H.; Randolph, P. Investigating the Process Constraints of the Addition of Co-digestion Substrates to Temperature Phased Anaerobic Digestion. Proc. Water Environ. Fed. 2009, 4810–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeganathan, J.; Nakhla, G.; Bassi, A. Long-term performance of high-rate anaerobic reactors for the treatment of oily wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6466–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.M.; Mota, J.A.; Álvares, R.M.; Pereira, M.A.; Mota, M. Effect of lipids and oleic acid on biomass development in anaerobic fixed-bed reactors. Part I: Biofilm growth and activity. Water Res. 2001, 35, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, Q.B.; Laurens, L.L.; Jarvis, E.E.; Nagle, N.J.; Chen, S.; Frear, C.S. Mechanism, kinetics and microbiology of inhibition caused by long-chain fatty acids in anaerobic digestion of algal biomass. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, B.; Peng, Y. Long-term effect of pH on short-chain fatty acids accumulation and microbial community in sludge fermentation systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudi, Z.N.; Hu, Z.; Sun, N.; Xiao, B.; Rajaa, N.; Liu, C.; Guo, D. Batch anaerobic co-digestion of OFMSW (organic fraction of municipal solid waste), TWAS (thickened waste activated sludge) and RS (rice straw): Influence of TWAS and RS pretreatment and mixing ratio. Energy 2016, 107, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Ren, L.; Jiang, B. Microbial characteristics in anaerobic digestion process of food waste for methane production—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.; Wang, J. An overview on biogas generation from anaerobic digestion of food waste. Int. J. Green Energy 2016, 13, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulsalam, M.; Hasfalina, C.M.; Aida, I.I.; Khairul, F.Y.; Zurina, Z.A. Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent Using Membrane Bioreactor: Novel Processes and Their Major Drawbacks. Water 2018, 10, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lier, J.B.; Mahmoud, N.; Zeeman, G. Anaerobic wastewater treatment. In Biological Wastewater Treatment, Principles, Modelling and Design; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2008; pp. 415–456. [Google Scholar]
- Lew, B.; Lustig, I.; Beliavski, M.; Tarre, S.; Green, M. An integrated UASB-sludge digester system for raw domestic wastewater treatment in temperate climates. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4921–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziganshin, A.M.; Schmidt, T.; Scholwin, F.; Il’inskaya, O.N.; Harms, H.; Kleinsteube, S. Bacteria and archaea involved in anaerobic digestion of distillers grains with solubles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 2039–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakashev, D.; Batstone, D.J.; Angelidaki, I. Influence of environmental conditions on methanogenic compositions in anaerobic biogas reactors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vrieze, J.; Hennebel, T.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. Methanosarcina: The rediscovered methanogen for heavy duty biomethanation. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; IImai, T.; Ukita, M.; Li, F.; Yuasa, A. Effect of loading rate on the granulation process and granular activity in a bench scale UASB reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.A.; Idrus, S.; Hasfalina, C.M.; Daud, N.N. Wastewater Treatment and Biogas Recovery Using Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors (AnMBRs): Strategies and Achievements. Energies 2018, 11, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halalsheh, M.; Koppes, J.; den Elzen, J.; Zeeman, G.; Fayyad, M.; Lettinga, G. Effect of SRT and temperature on biological conversions and the related scum-forming potential. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).