Effects of Drought and Rehydration on the Physiological Responses of Artemisia halodendron
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Treatment Description
2.3. Analytical Methods and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
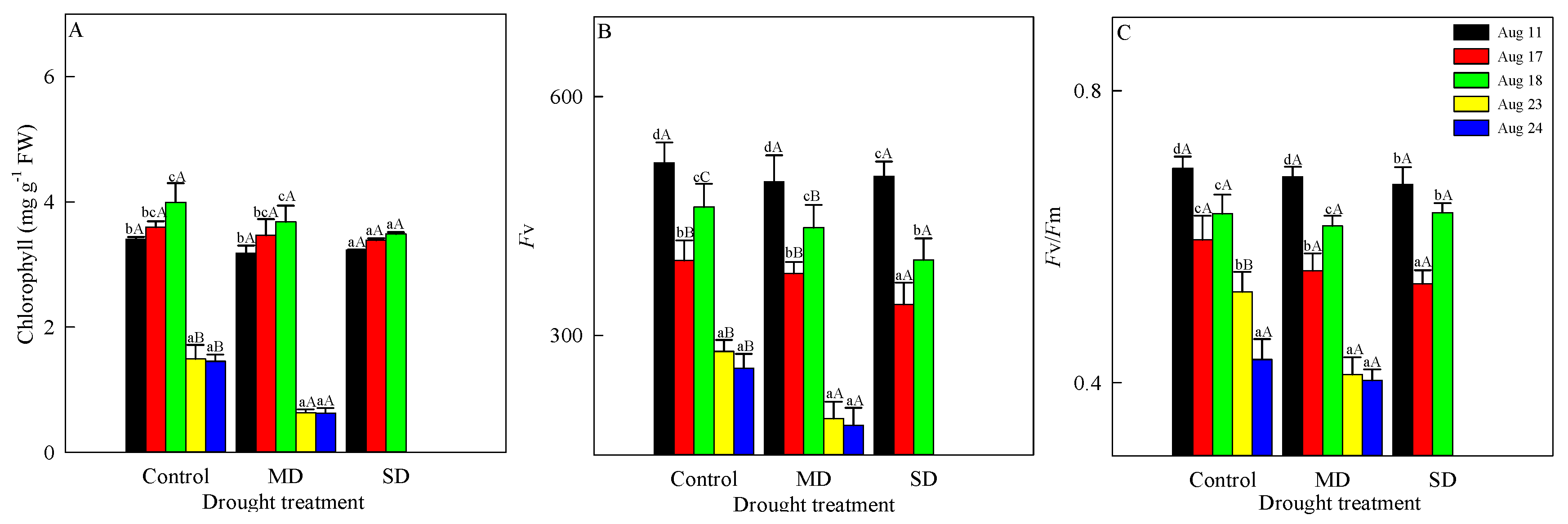
3.1. Changes in Chlorophyll Fluorescence
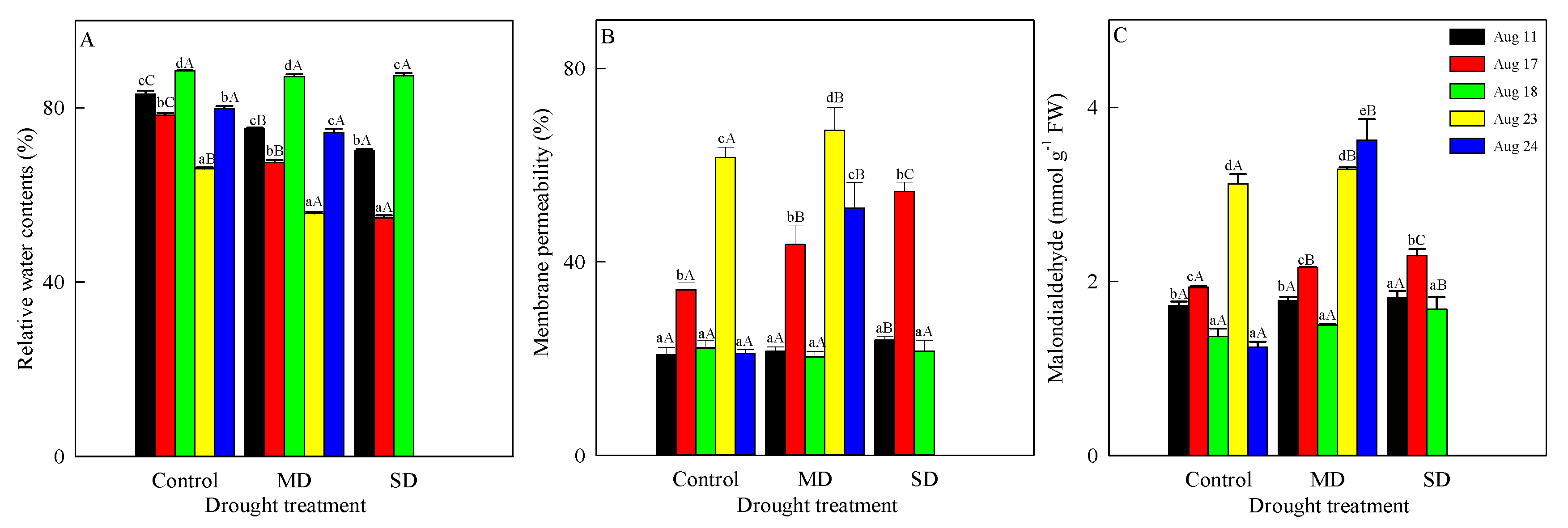
3.2. Changes in RWC, Membrane Permeability and Malondialdehyde Content
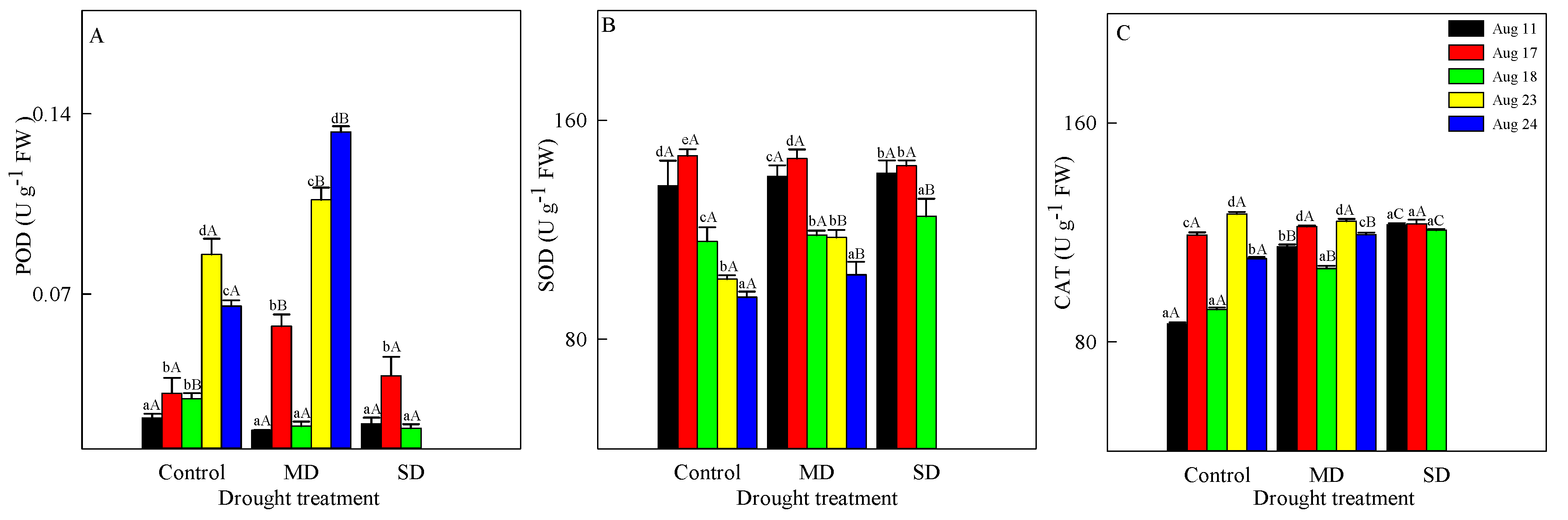
3.3. Changes in Antioxidant Enzymes Activity
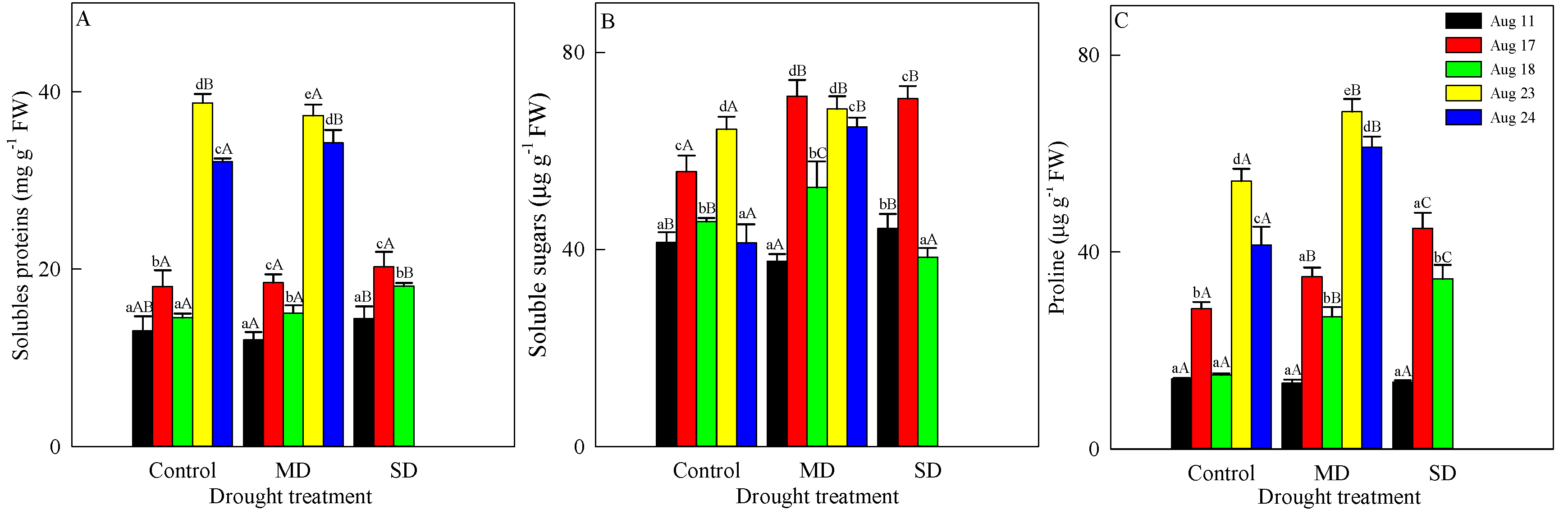
3.4. Changes in Osmoregulatory Substances
3.5. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, H.X.; Wang, B.C.; Adams, B. Water resources exploitation and sustaining development in arid area. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 1998, 18, 97–108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bray, E.A. Molecular responses to water deficit. Plant Physiol. 1993, 103, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, H.G.; Corlett, J.E. Current topics in drought physiology. J. Agric. Sci. 1992, 119, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, F.; Abdul, W.; Osamulto, D.L.; Siddique, K. Advances in drought resistance of rice. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2009, 28, 199–217. [Google Scholar]
- Goodale, C.L.; Davidson, E.A. Uncertain sinks in the shrubs. Nature 2002, 418, 593–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, D.L.; Scott, R.L.; Bayram, S.; Carbonara, J. Woody plants modulate the temporal dynamics of soil moisture in a semi-arid mesquite savanna. Ecohydrology 2010, 3, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullet, J.E.; Whitsitt, M.S. Plant cellular responses to water deficit. Plant Growth Regul. 1996, 20, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheokand, S.; Kumari, A.; Sawhney, V. Effect of nitric oxide and putrescine on antioxidative responses under NaCl stress in chickpea plants. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2008, 14, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demiral, T.; Türkan, I. Comparative lipid peroxidation, antioxidant defense systems and proline content in roots of two rice cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2005, 53, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delauney, A.J.; Verma, D.P.S. Proline biosynthesis and osmoregulation in plants. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 1993, 4, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, A.; Razzaq, A.; Ahmad, M.; Jenks, M.A. Water stress causes differential effects on germination indices, total soluble sugar and proline content in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 14038–14045. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.Y.; Liang, Z.S.; Zhao, R.K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.J. Organ-dependent responses of Periploca sepium to repeated dehydration and rehydration. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2011, 77, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anjum, F.; Yaseen, M.; Rasool, E.; Wahid, A.; Anjum, S. Water stress in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). II. Effect on chemical composition and chlorophyll contents. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2003, 40, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mafakheri, A.; Siosemardeh, A.; Bahramnejad, B.; Struik, P.C.; Sohrabi, Y. Effect of drought stress on yield, proline and chlorophyll contents in three chickpea cultivars. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2010, 4, 580–585. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.R.; Zhao, A.F.; Huang, Y.M.; Zhang, X.S.; Zhang, C.L. Water relations, gas exchange, photochemical efficiency, and peroxidative stress of four plant species in the Heihe drainage basin of northern China. Photosynthetica 2006, 44, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.R.; Zhang, L.X.; Zhao, A.F.; Bi, Y.R. Elementary studies on physiological and bio-chemical anti-drought features of Artemisia ordosica. J. Desert Res. 2002, 22, 387–392. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhou, R.L.; Zuo, X.A.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.Q. Physiological acclimation of two psammophytes to repeated soil drought and rewatering. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Zhao, H.L.; Su, Y.Z.; Sam, D. Comparison of seed germination of Agriophyllum squarrosum (L.) Moq. and Artemisia halodendron Turcz. Ex Bess, two dominant species of Horqin desert, China. Arid Soil Res. Rehabil. 2007, 21, 165–179. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Zhao, X.Y.; Padilla, F.; Zhao, H.L. Fine root dynamics and longevity of Artemisia halodendron reflect plant growth strategy in two contrasting habitats. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Z.; Zhang, T.H.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, F. Changes in soil properties after establishment of Artemisia halodendron and Caragana microphylla on shifting sand dunes in semiarid Horqin sandy land, northern China. Environ. Manag. 2005, 36, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.Q.; Zhao, X.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, T. Effects of foliage litter of a pioneer shrub (Artemisia halodendron) on germination from the soil seedbank in a semi-arid sandy grassland in China. J. Plant Res. 2017, 130, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.Q.; Zhao, X.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Zuo, X.A.; Lian, J.; Wang, T. Root decomposition of Artemisia halodendron and its effect on soil nitrogen and soil organic carbon in the Horqin Sandy Land, northeastern China. Ecol. Res. 2016, 31, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Y. Drought-resistant mechanism of two edificatos in Horqin sandy land of northeast China. Bull. Bot. Res. 2002, 22, 51–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.L.; Zhou, R.L.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhao, X.Y. Effects of desertification on soil and crop growth properties in Horqin sandy cropland of Inner Mongolia, North China. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovič, A. Photosynthetic characterization of Australian pitcher plant Cephalotus follicularis. Photosynthetica 2011, 49, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.R. Chlorophyll fluorescence: A probe of photosynthesis in vivo. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izanloo, A.; Condon, A.G.; Langridge, P.; Tester, M.; Schnurbusch, T. Different mechanisms of adaptation to cyclic water stress in two South Australian bread wheat cultivars. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 3327–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.L.; Packer, L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968, 125, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuveni, R. Peroxidase activity as a biochemical marker for resistance of muskmelon (Cucumis melo) to pseudoperonospora cubensis. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drazkiewicz, M.; Skórzyńska-Polit, E.; Krupa, Z. Copper-induced oxidative stress and antioxidant defence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biometals 2004, 17, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, D.; Perianayaguy, B.; Reddy, A.R. Localization of antioxidant enzymes in the cellular compartments of sorghum leaves. Plant Growth Regul. 2004, 44, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Liu, J.; Dai, T.; Jing, Q.; Cao, W.; Jiang, D. Alterations in photosynthesis and antioxidant enzyme activity in winter wheat subjected to post-anthesis water-logging. Photosynthetica 2008, 46, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, K.J. A water relations analysis of seed germination rates. Plant Physiol. 1990, 94, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yemm, E.W.; Cocking, E.C. The determination of amino-acids with ninhydrin. Analyst 1955, 80, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, G.H.; Weis, E. Chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthesis: The basics. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. 1991, 42, 313–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ommen, O.E.; Donnelly, A.; Vanhoutvin, S.; Oijen, V.M.; Manderscheid, R. Chlorophyll content of spring wheat flag leaves grown under elevated CO2 concentrations and other environmental stresses within the ‘ESPACE-wheat’ project. Eur. J. Agron. 1999, 10, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutraa, T. Effects of water stress on root growth, water use efficiency, leaf area and chlorophyll content in the desert shrub Calotropis procera. J. Int. Environ. Appl. Sci. 2010, 5, 124–132. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, O.H. Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool in cereal crop research. Photosynthetica 2003, 41, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooten, O.V.; Snel, J.F. The use of chlorophyll fluorescence nomenclature in plant stress physiology. Photosynth. Res. 1990, 25, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roháček, K. Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters: The definitions, photosynthetic meaning, and mutual relationships. Photosynthetica 2002, 40, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.X.; Zhang, S.Q.; Yan, X.J. Effects of drought and re-watering on photosynthetic characteristics of maize leaf. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 19, 278–283. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, M.D.; Shen, S.H. Effect of salt on malondialdehyde and antioxidant enzymes in seedling roots of Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, H.H.; Hadley, M. Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mittler, R. Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhami, K.; Lokman, Z.; Yavuz, D.; Ali, U.; Ahmet, K.; Oral, D. Alterations in antioxidant enzyme activities and proline content in pea leaves under long-term drought stress. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2012, 30, 693–700. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, J.M.; Condon, A.G. Water use, grain yield, and osmoregulation in wheat. Funct. Plant Biol. 1986, 13, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Chlorophyll | Fv | Fv/Fm | RWC | Membrane Permeability | MDA | POD | SOD | CAT | Soluble Proteins | Soluble Sugars |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fv | 0.868 ** | ||||||||||
| Fv/Fm | 0.865 ** | 0.984 ** | |||||||||
| RWC | 0.439 | 0.481 | 0.488 | ||||||||
| Membrane permeability | −0.625 * | −0.741 ** | −0.714 ** | −0.831 ** | |||||||
| MDA | −0.739 ** | −0.719 ** | −0.668 * | −0.643 * | 0.887 ** | ||||||
| POD | −0.911 ** | −0.909 ** | −0.912 ** | −0.471 | 0.758 ** | 0.851 ** | |||||
| SOD | 0.774 ** | 0.668 * | 0.594 * | −0.173 | −0.631 * | −0.844 ** | −0.789 ** | ||||
| CAT | 0.032 | −0.066 | 0.020 | −0.663 * | 0.401 | 0.240 | −0.069 | −0.130 | |||
| Soluble proteins | −0.924 ** | −0.932 ** | −0.925 ** | −0.474 | 0.739 ** | 0.730 ** | 0.895 ** | −0.731 ** | 0.197 | ||
| Soluble sugars | −0.369 | −0.614 * | −0.625 * | −0.735 ** | 0.884 ** | 0.725 ** | 0.627 * | −0.365 | 0.263 | 0.519 | |
| proline | −0.825 ** | −0.965 ** | −0.927 ** | −0.582 * | 0.846 ** | 0.807 ** | 0.879 ** | −0.732 ** | 0.227 | 0.911 ** | 0.709 ** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Ning, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, P.; Cong, A. Effects of Drought and Rehydration on the Physiological Responses of Artemisia halodendron. Water 2019, 11, 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040793
Chen J, Zhao X, Zhang Y, Li Y, Luo Y, Ning Z, Wang R, Wang P, Cong A. Effects of Drought and Rehydration on the Physiological Responses of Artemisia halodendron. Water. 2019; 11(4):793. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040793
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Juanli, Xueyong Zhao, Yaqiu Zhang, Yuqiang Li, Yongqing Luo, Zhiying Ning, Ruixiong Wang, Peiyu Wang, and Anqi Cong. 2019. "Effects of Drought and Rehydration on the Physiological Responses of Artemisia halodendron" Water 11, no. 4: 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040793
APA StyleChen, J., Zhao, X., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Luo, Y., Ning, Z., Wang, R., Wang, P., & Cong, A. (2019). Effects of Drought and Rehydration on the Physiological Responses of Artemisia halodendron. Water, 11(4), 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040793





