A Modified Green-Ampt Model and Parameter Determination for Water Infiltration in Fine-textured Soil with Coarse Interlayer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Description of the Modified Green-Ampt Model
3. Materials and Methods
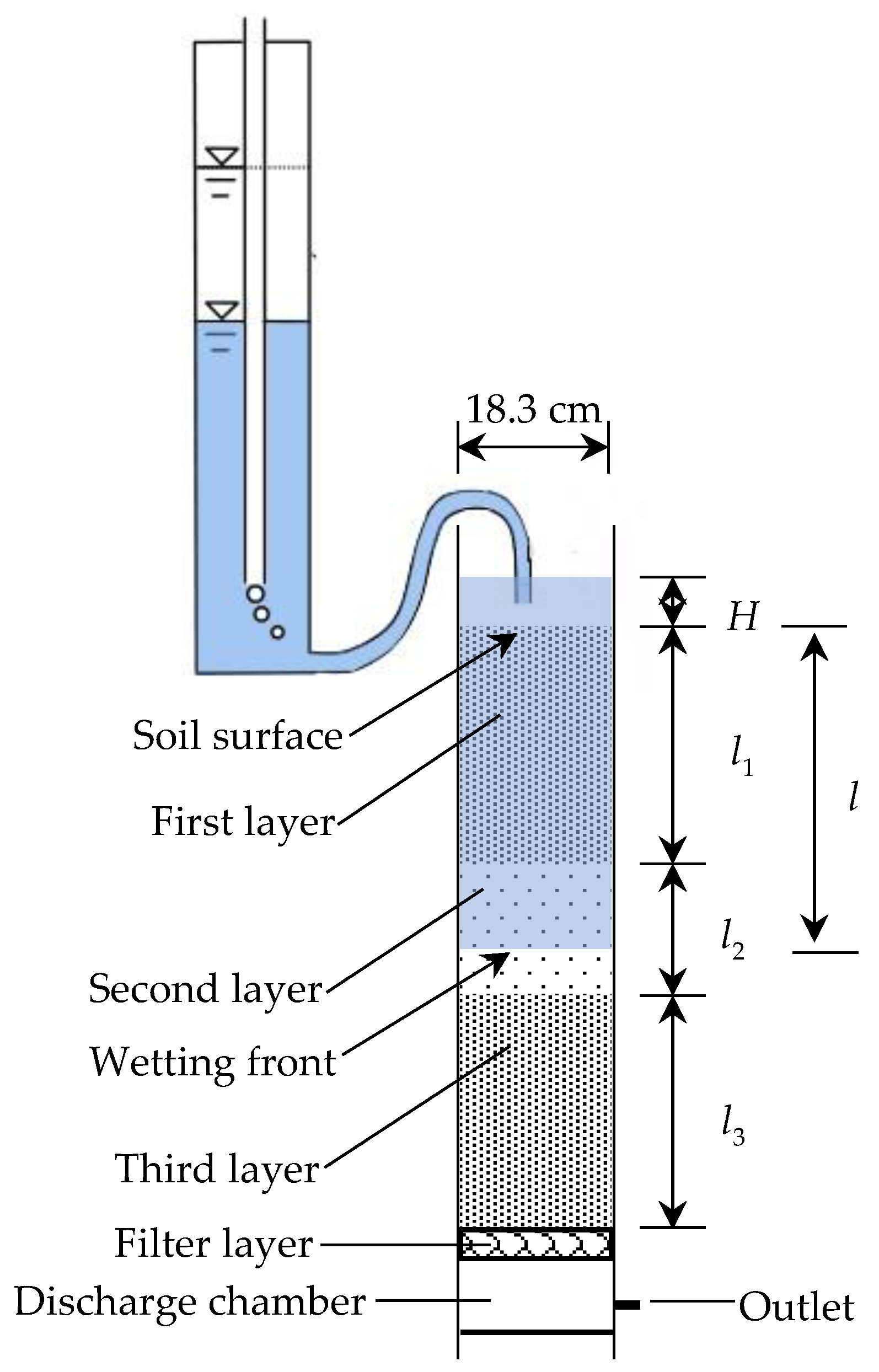
3.1. Infiltration Experiment
3.1.1. Experiment I
3.1.2. Experiment II
3.2. The Richards Equation-Based Infiltration Model
3.3. Scenario Analysis
3.4. The Test of the Proposed Green-Ampt Model
4. Results and Discussion
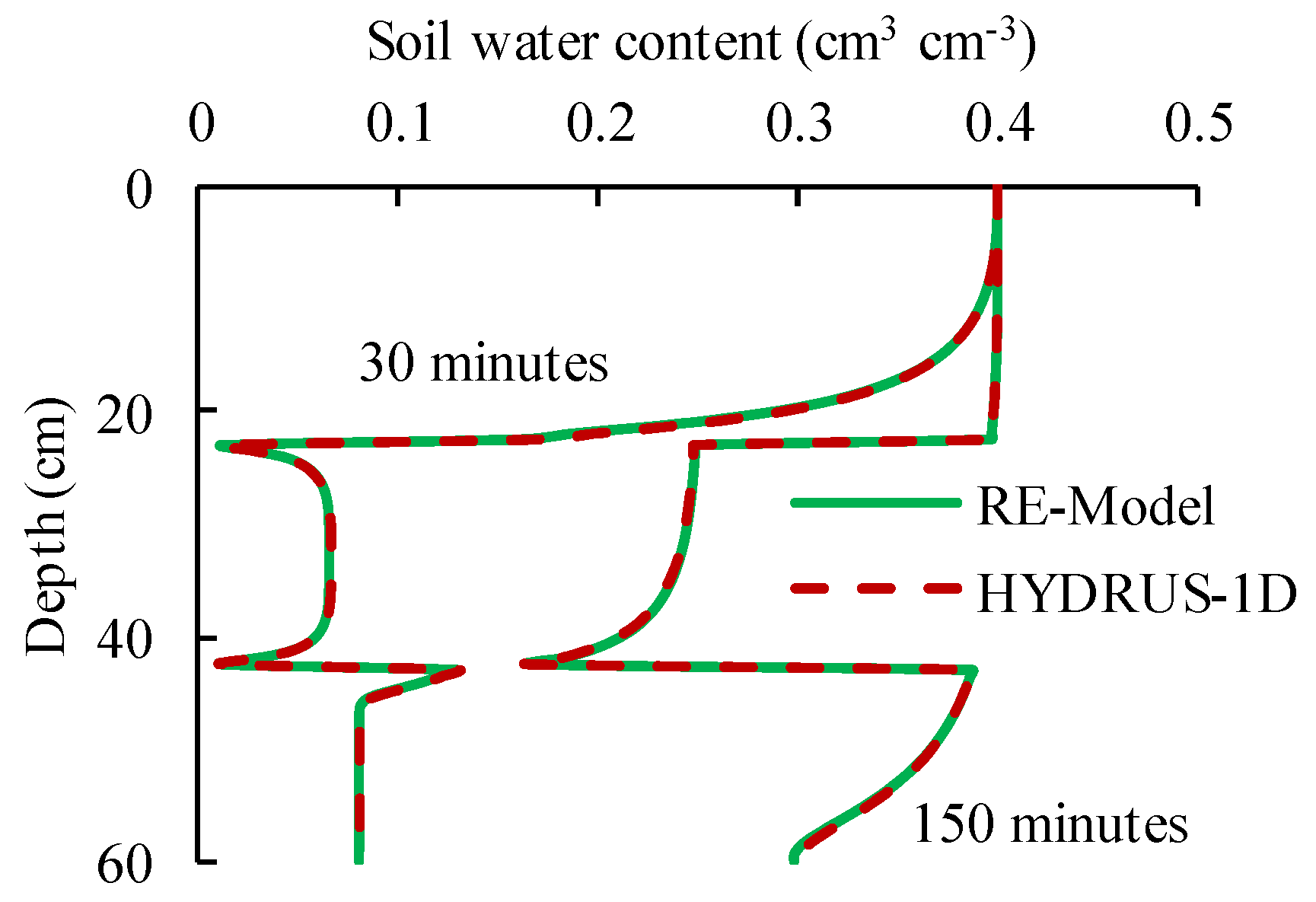
4.1. The Verification of the RE-Model
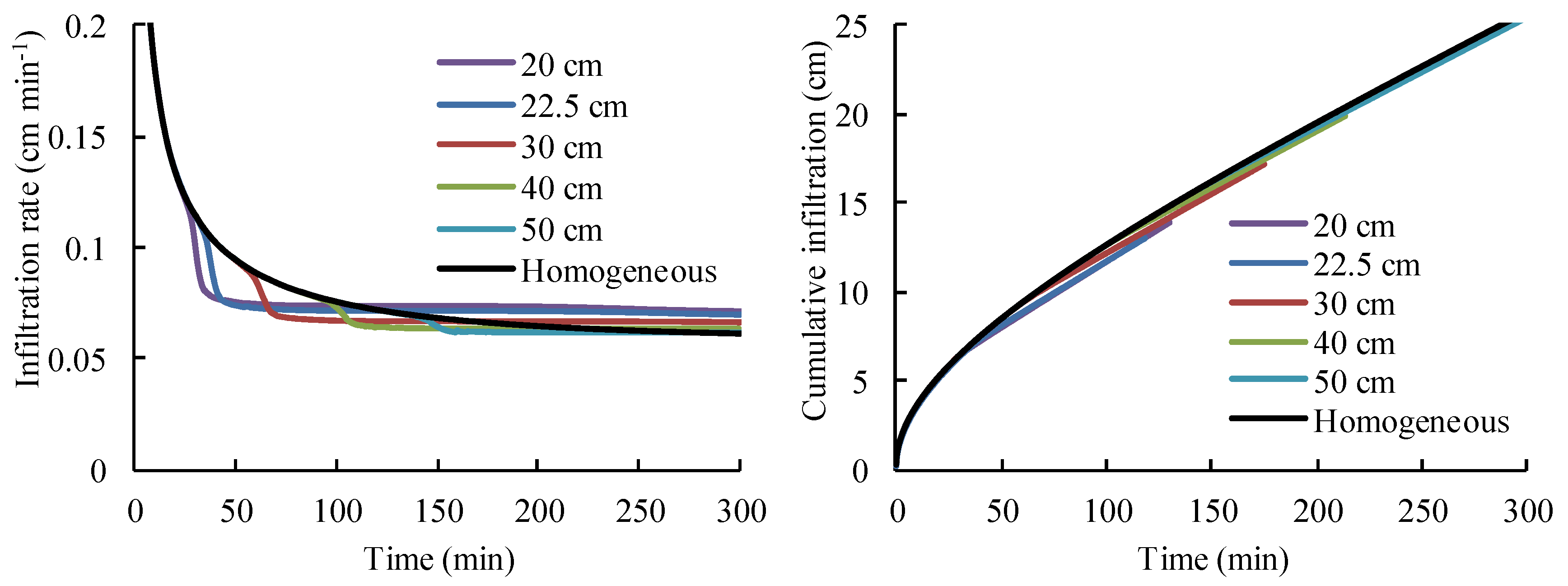
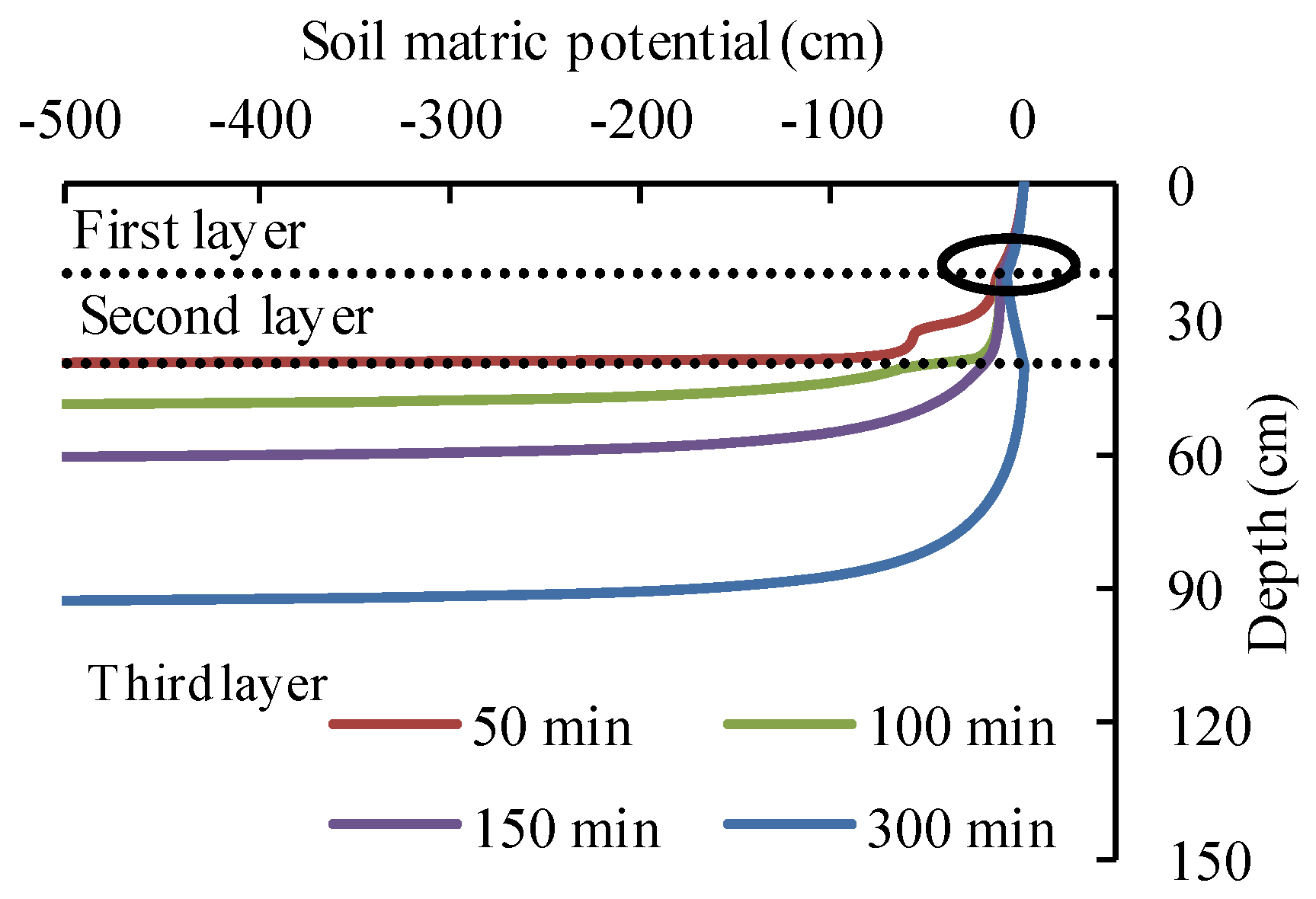
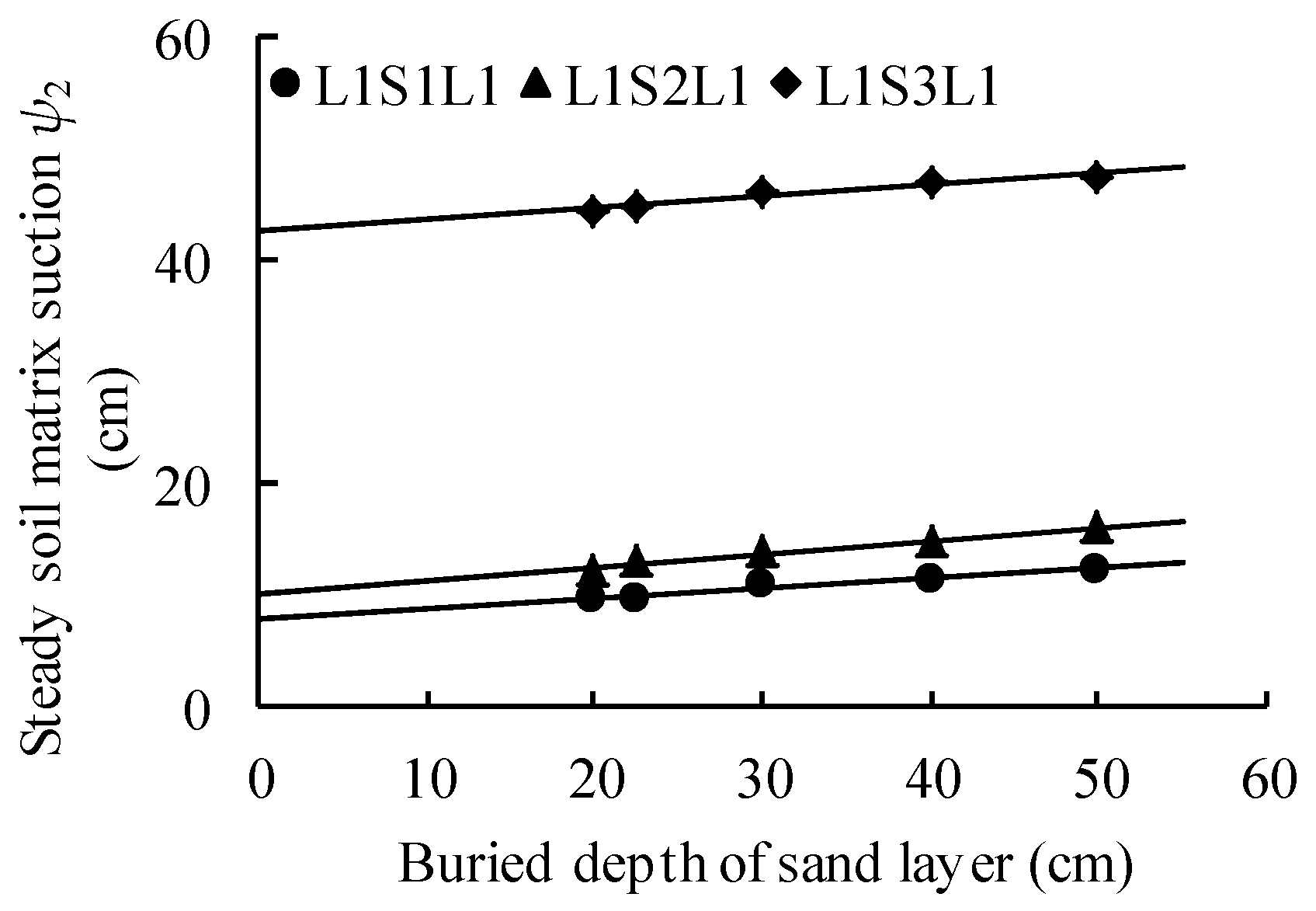
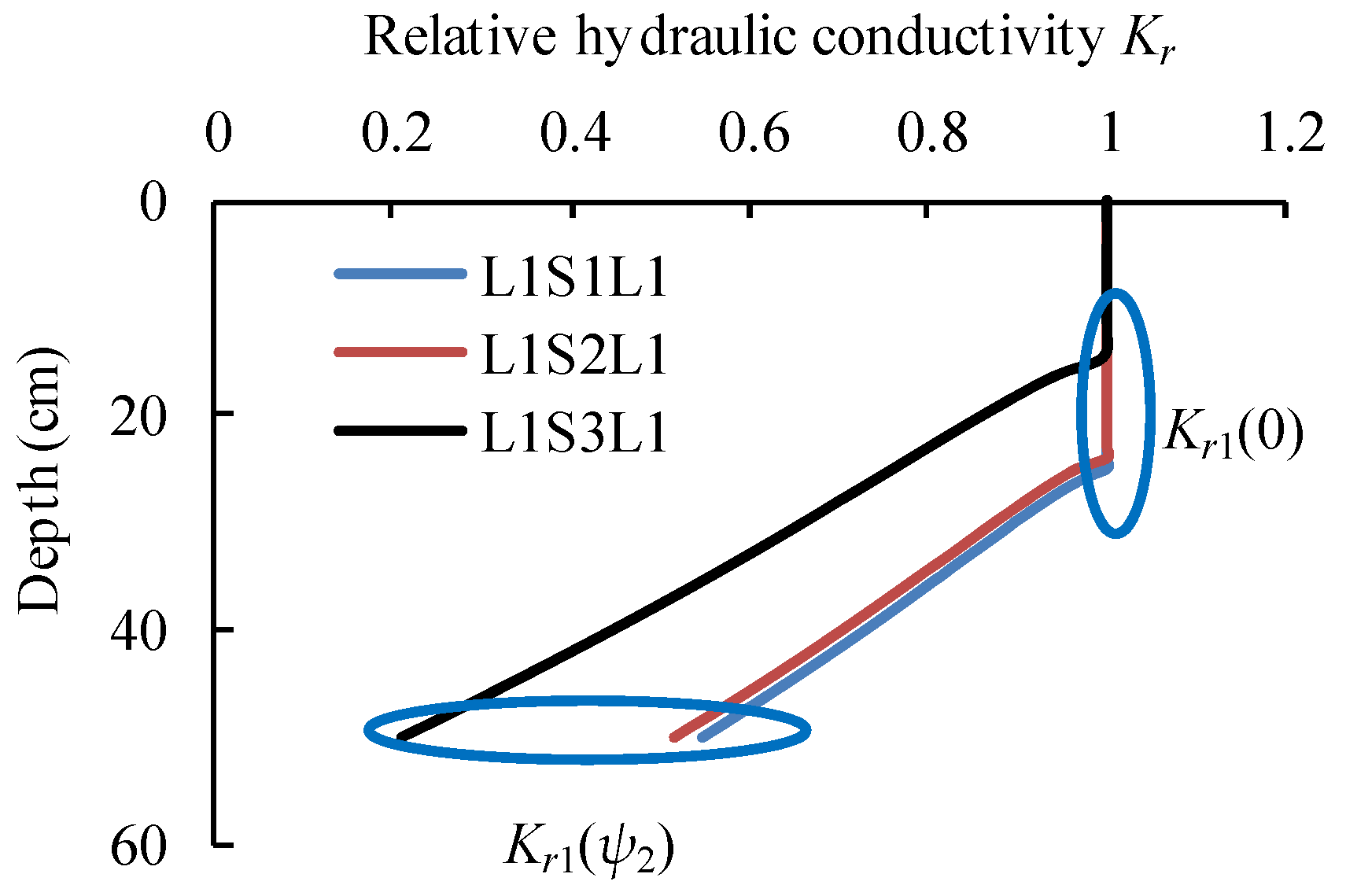
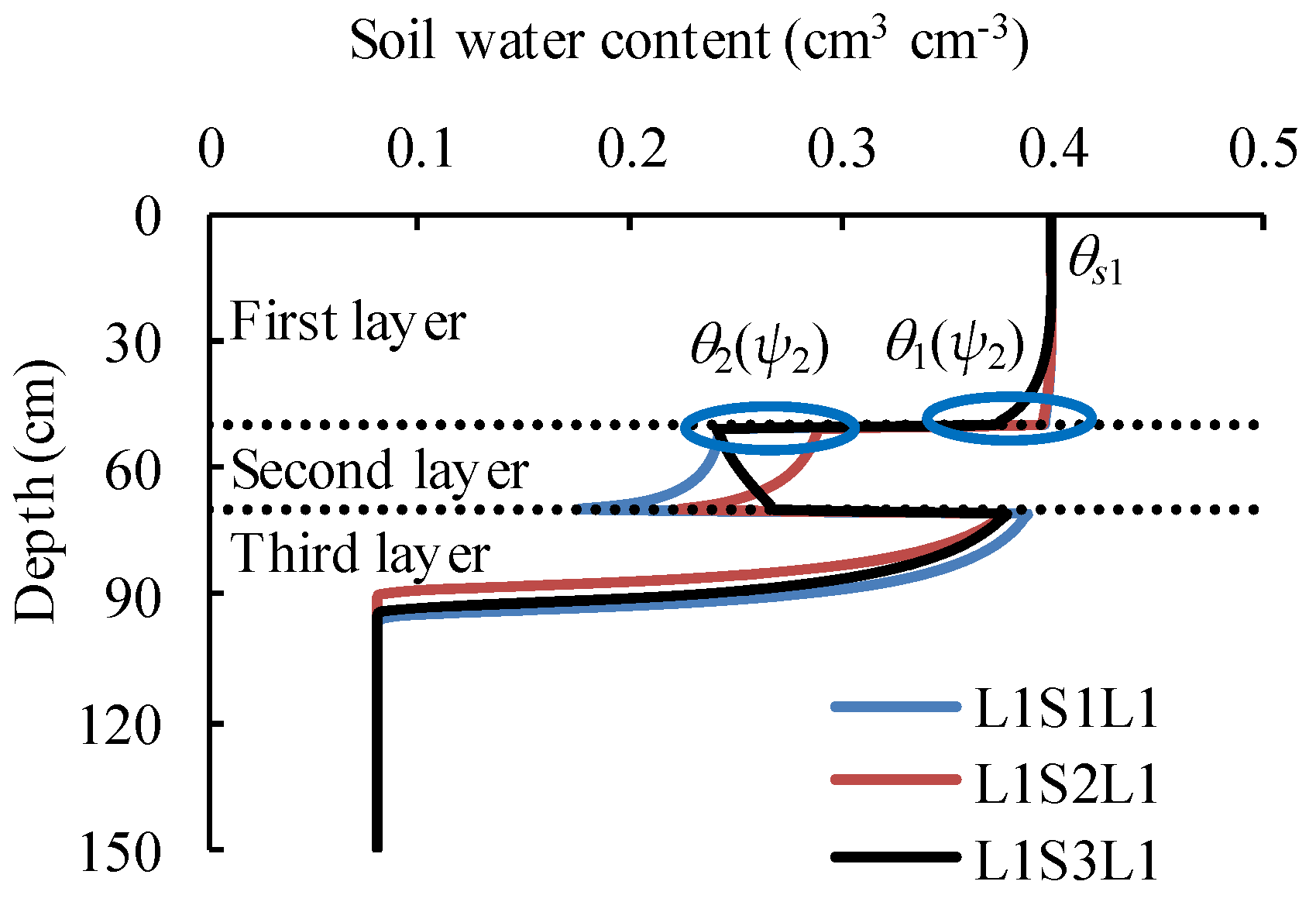
4.2. The Effect of Buried Depth of Coarse Interlayer on Water Infiltration
4.3. Parameter Determination for the MGA-2
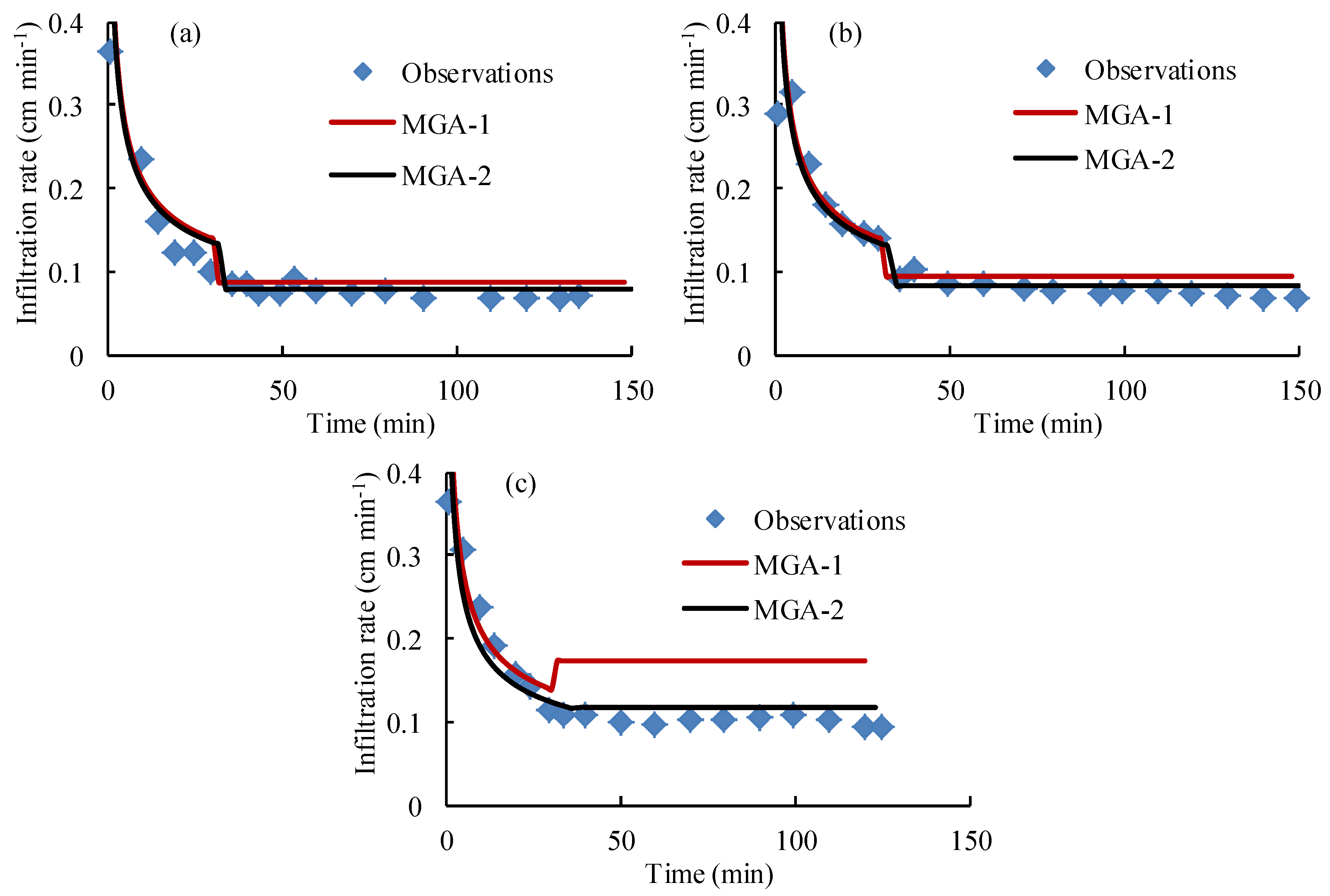
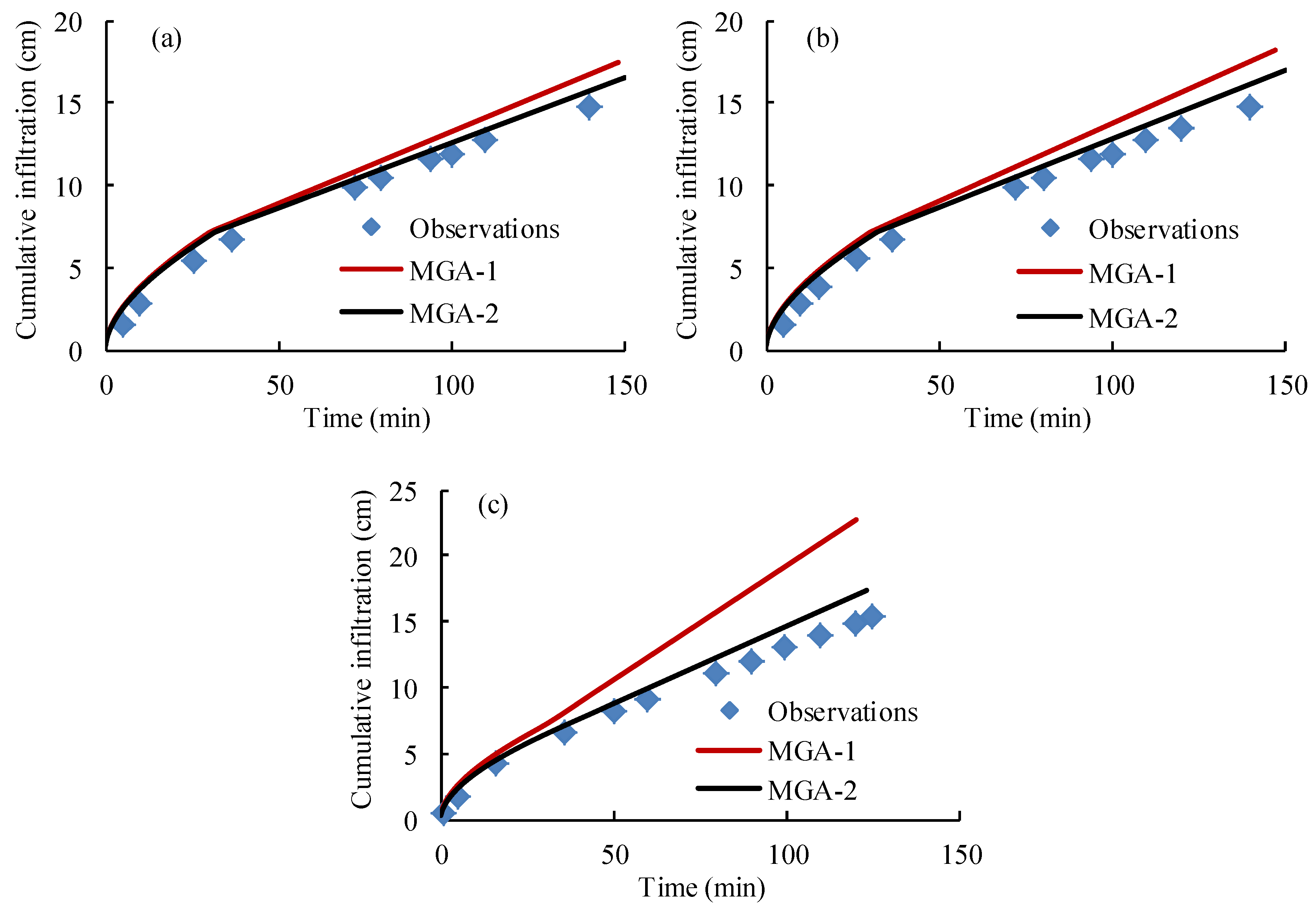
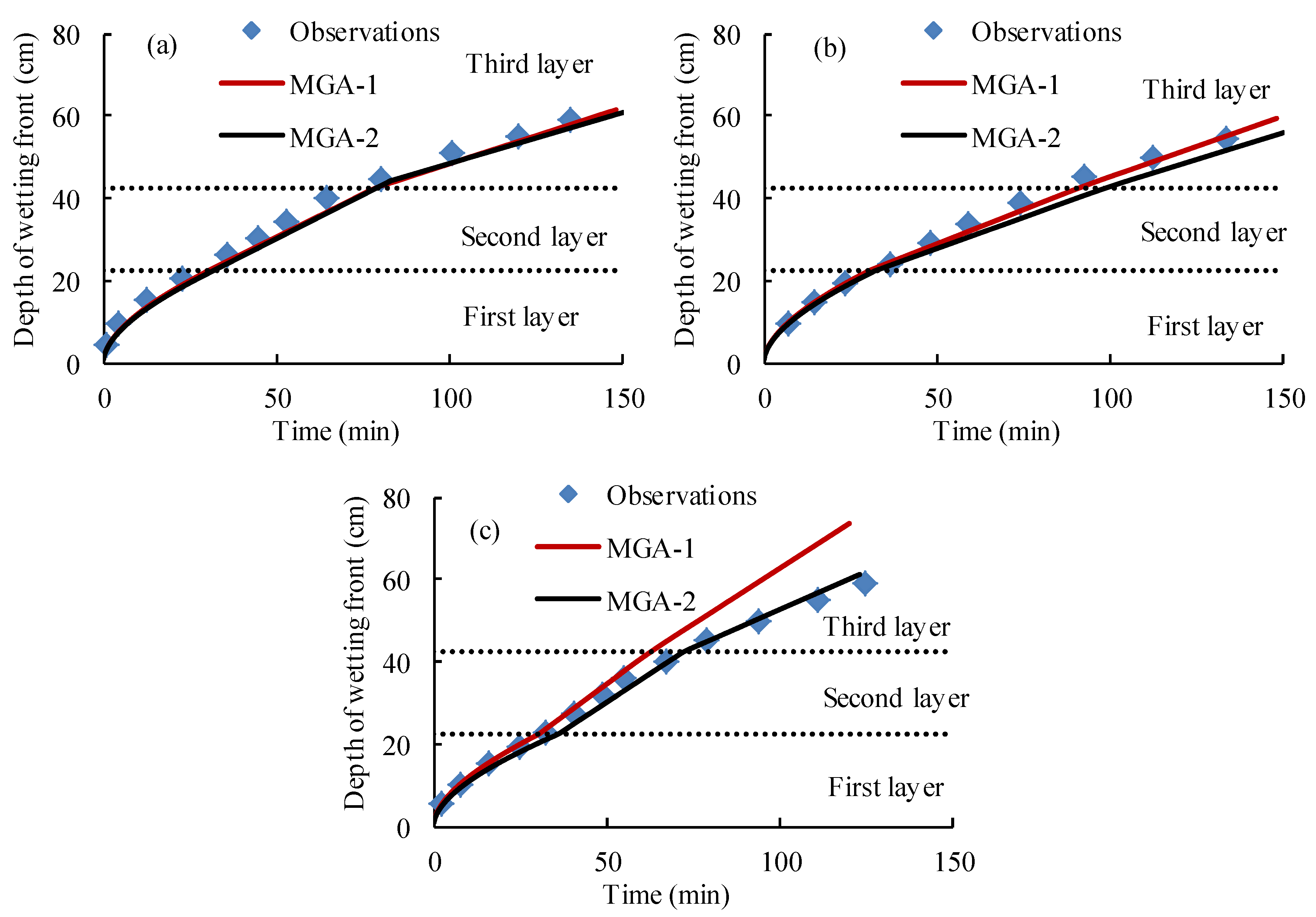
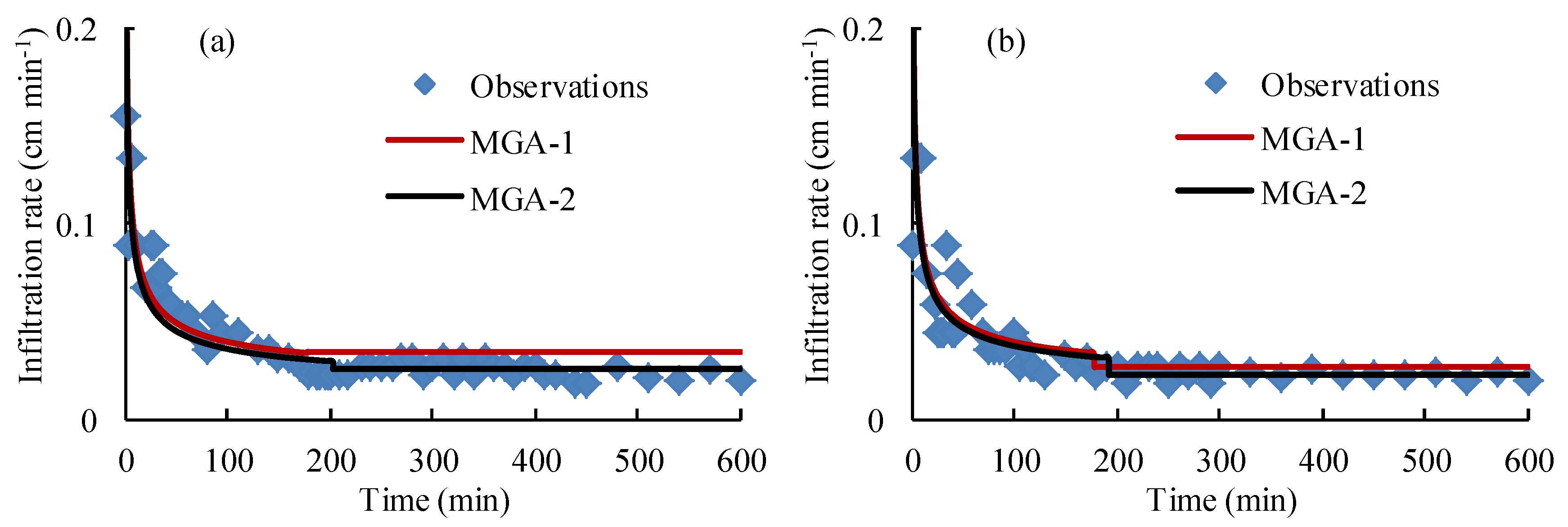
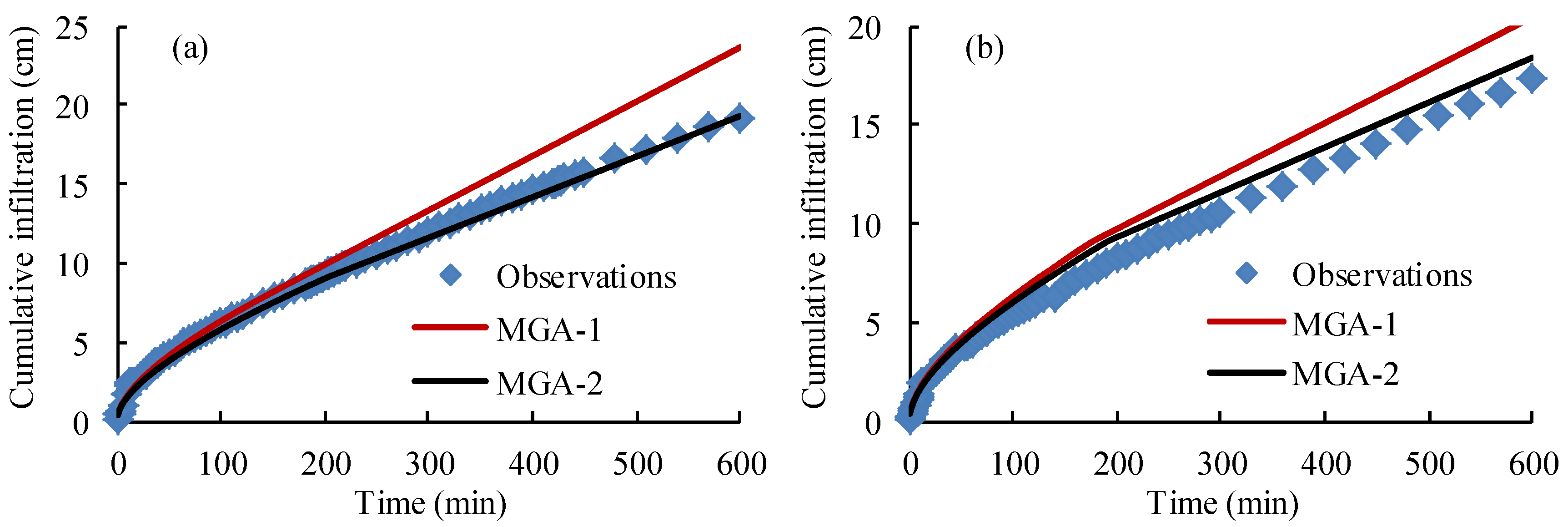
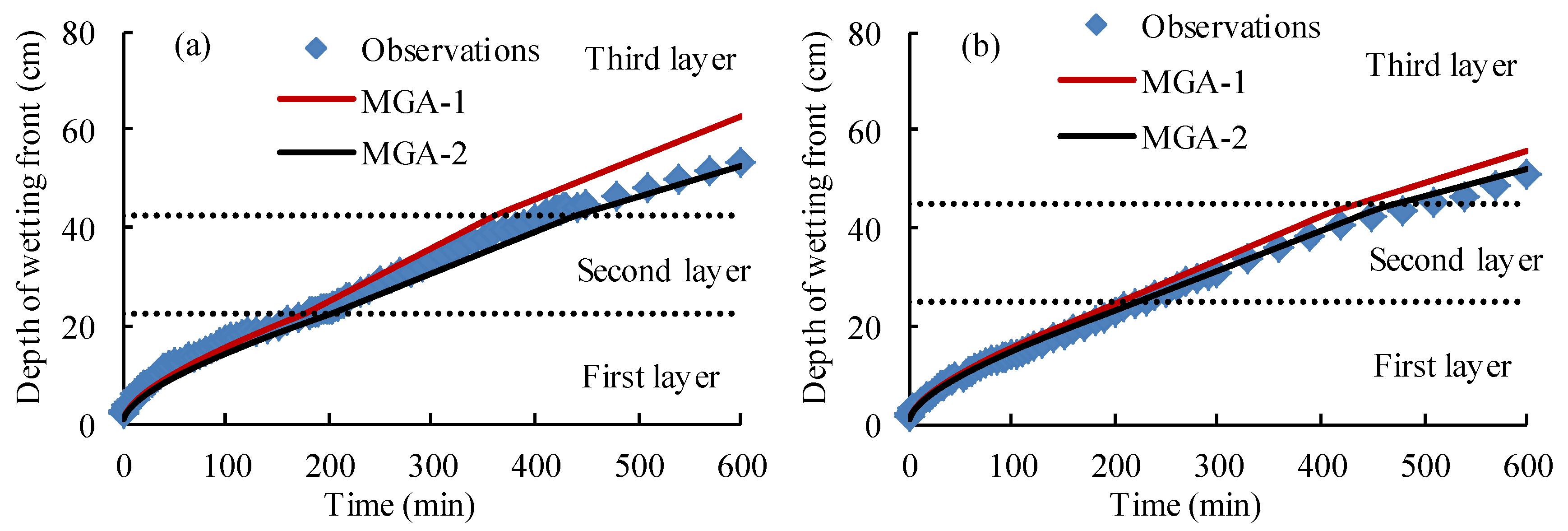
4.4. The Performance of the Proposed Green-Ampt Model
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Y.; Feng, S.; Su, D.; Gao, G.; Huo, Z. Modeling water infiltration in a large layered soil column with a modified Green-Ampt model and HYDRUS-1D. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 71 (Suppl. 1), S40–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Elshorbagy, A.; Barbour, S.L.; Zettl, J.D.; Si, B.C. System dynamics modeling of infiltration and drainage in layered coarse soil. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 91, 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- Pedretti, D.; Fernandez-Garcia, D.; Sanchez-Vila, X.; Barahona-Palomo, M.; Bolster, D. Combining physical-based models and satellite images for the spatio-temporal assessment of soil infiltration capacity. Stoch. Environ. Res. Assess. 2011, 25, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Pedretti, D.; Masetti, M.; Marangoni, T.; Beretta, G.P. Slurry wall containment performance: Monitoring and modeling of unsaturated and saturated flow. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 607–624. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Mao, X.; Hatano, R. Modeling ponded infiltration in fine-textured soils with coarse interlayer. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masetti, M.; Pedretti, D.; Sorichetta, A.; Stevenazzi, S.; Bacci, F. Impact of a storm-water infiltration basin on the recharge dynamics in a highly permeable aquifer. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagna, V.; Di Prima, S.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Iovino, M.; Pirastru, M.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A.; Cerdà, A. The impact of the age of vines on soil hydraulic conductivity in vineyards in eastern Spain. Water 2017, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.; Mol, G.; de Leeuw, J.; Okx, J.; de Cleen, M.; Visser, S. Soil-related sustainable development goals: Four concepts to make land degradation neutrality and restoration work. Land 2018, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, X.; Hill, R.; Malone, R.; Zhao, Y. Characteristics of water infiltration in layered water-repellent soils. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 775–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.E.; Gardner, W.H. Water infiltration into stratified soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1962, 26, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Di Prima, S.; Concialdi, P.; Lassabatere, L.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R.; Pirastru, M.; Cerda, A.; Keesstra, S. Laboratory testing of Beerkan infiltration experiments for assessing the role of soil sealing on water infiltration. Catena 2018, 167, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, R.; Wu, F.; Keesstra, S. Effect of soil surface roughness on infiltration water, ponding and runoff on tilled soils under rainfall simulation experiments. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 179, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shao, M.; Horton, R. Modified Green and Ampt models for layered soil infiltration and muddy water infiltration. Soil Sci. 1999, 164, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Marino, M.A. Determination of ponding condition and infiltration into layered soils under unsteady rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2005, 313, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y. Experiment and study on water-tightness and infiltration reduction of sand layer in loess soils. Trans. CSAE 1995, 11, 104–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fok, Y.S. One-dimensional infiltration into layered soils. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1970, 96, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.K.; Kumar, S.R.; Singh, V.P. Calibration and validation of a general infiltration model. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 1691–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, W.H.; Ampt, G.A. Studies on soil physics: Part I. The flow of air and water through soils. J. Agric. Sci. 1911, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J. Green–Ampt model for layered soils with nonuniform initial water content under unsteady infiltration. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mao, X.; Zhao, B. Experiments and simulation on infiltration into layered soil column with sand interlayer under ponding condition. Trans. CSAE 2010, 26, 61–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Van Mullem, J.A. Runoff and peak discharges using Green–Ampt infiltration model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1991, 117, 354–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, H. Rapid field measurement of air entry value and hydraulic conductivity of soil as significant parameters in flow system analysis. Water Resour. Res. 1966, 2, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Feng, S.; Zhan, H.; Liu, X.; Su, D.; Kang, S.; Song, X. Water infiltration in layered soils with air entrapment: Modified Green–Ampt model and experimental validation. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 16, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh-Habili, J.; Heidarpour, M. Estimating soil hydraulic parameters by using Green and Ampt infiltration equation. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 16, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, H.; Prasad, S.N.; Helweg, O.J. Air entrapment and water infiltration in two-layered soil column. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. ASCE 1994, 120, 871–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.H.; Corey, A.T. Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media; Hydrology Paper No. 3; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums. Physics 1931, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, J.; van Genuchten, M.Th.; Sejna, M. The HYDRUS-1D Software Package for Simulating the One-Dimensional Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes in Variably-Saturated Media Version 4.0; Department of Environmental Sciences, University of California Riverside: Riverside, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadzadeh-Habili, J.; Heidarpour, M. Application of the Green–Ampt model for infiltration into layered soils. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Pang, H.; Wang, J.; Huo, L.; Li, Y. Effects of straw mulch and buried straw on soil moisture and salinity in relation to sunflower growth and yield. Field Crop Res. 2014, 161, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Texture | Textural Fractions (%) | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Initial Water Content (cm3 cm−3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gravel (>2.0 mm) | Sand (2.0–0.05 mm) | Silt (0.05–0.002 mm) | Clay (<0.002 mm) | |||
| L1 | 0 | 42.2 | 45.8 | 12 | 1.40 | 0.080 |
| S1 | 0.95 | 97.85 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.65 | 0.065 |
| S2 | 14.3 | 83.7 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 1.65 | 0.015 |
| S3 | 0 | 96.9 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 1.65 | 0.020 |
| L2 | 0 | 41.9 | 50.4 | 7.7 | 1.50 | 0.014 |
| SL1 | 0 | 55.0 | 39.8 | 5.2 | 1.55 | 0.014 |
| SL2 | 0 | 67.8 | 28.0 | 4.2 | 1.60 | 0.011 |
| Soil | θr (cm3 cm−3) | θs (cm3 cm−3) | α (cm−1) | n | Ks (cm min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 0.014 | 0.400 | 0.009 | 1.58 | 0.057 |
| S1 | 0.010 | 0.275 | 0.050 | 2.50 | 0.160 |
| S2 | 0.005 | 0.300 | 0.025 | 2.50 | 0.070 |
| S3 | 0.005 | 0.300 | 0.018 | 4.30 | 0.194 |
| L2 | 0.010 | 0.420 | 0.012 | 1.40 | 0.021 |
| SL1 | 0.008 | 0.330 | 0.025 | 2.30 | 0.027 |
| SL2 | 0.005 | 0.310 | 0.046 | 2.20 | 0.031 |
| Soil | ψl in Equation (12) | ψ in Figure 5 | η |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 8.4 | 7.9 | 0.1 |
| S2 | 10.5 | 10.1 | |
| S3 | 41.0 | 42.6 | |
| SL1 | 10.7 | 10.2 | 0.14 |
| SL2 | 3.0 | 2.4 |
| Cases | a1 | b1 | a2 | b2 | ψ2 | ψl1 | θ1(ψ2) | θ2(ψ2) | Kr1(ψ2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1S1L1 | 0.953 | 1.000 | 0.907 | 0.911 | 9.9 | 30.4 | 0.397 | 0.251 | 0.568 |
| L1S2L1 | 0.941 | 1.000 | 0.881 | 0.968 | 12.8 | 0.395 | 0.290 | 0.513 | |
| L1S3L1 | 0.839 | 0.997 | 0.678 | 0.775 | 45.0 | 0.371 | 0.232 | 0.197 | |
| L2SL1L2 | 0.873 | 1.000 | 0.747 | 0.963 | 12.6 | 12.0 | 0.412 | 0.318 | 0.288 |
| L2SL2L2 | 0.925 | 1.000 | 0.849 | 0.935 | 5.1 | 0.418 | 0.290 | 0.451 |
| Case | Buried Depth of Sand (cm) | RE-Model | MGA-2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a2 | b1 | b2 | a2 | b1 | b2 | ||
| L1S1L1 | 20 | 0.845 | 0.999 | 0.944 | 0.910 | 1.000 | 0.918 |
| 30 | 0.852 | 0.999 | 0.900 | 0.898 | 1.000 | 0.892 | |
| 40 | 0.866 | 0.999 | 0.854 | 0.893 | 1.000 | 0.879 | |
| 50 | 0.879 | 0.999 | 0.821 | 0.884 | 1.000 | 0.858 | |
| L1S2L1 | 20 | 0.894 | 0.999 | 0.990 | 0.884 | 1.000 | 0.970 |
| 30 | 0.848 | 0.998 | 0.976 | 0.873 | 1.000 | 0.961 | |
| 40 | 0.841 | 0.998 | 0.933 | 0.864 | 1.000 | 0.954 | |
| 50 | 0.849 | 0.998 | 0.893 | 0.854 | 1.000 | 0.945 | |
| L1S3L1 | 20 | 0.715 | 0.991 | 0.841 | 0.680 | 0.997 | 0.784 |
| 30 | 0.680 | 0.989 | 0.840 | 0.673 | 0.997 | 0.756 | |
| 40 | 0.684 | 0.988 | 0.746 | 0.669 | 0.997 | 0.741 | |
| 50 | 0.708 | 0.989 | 0.665 | 0.667 | 0.997 | 0.732 | |
| Items | Cases | MGA-1 | MGA-2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infiltration rate (cm min−1) | L1S1L1 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| L1S2L1 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| L1S3L1 | 0.06 | 0.02 | |
| L2SL1L2 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| L2SL2L2 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Cumulative infiltration (cm) | L1S1L1 | 1.26 | 0.76 |
| L1S2L1 | 1.66 | 0.83 | |
| L1S3L1 | 4.72 | 1.26 | |
| L2SL1L2 | 1.81 | 0.35 | |
| L2SL2L2 | 1.91 | 0.87 | |
| Wetting front depth (cm) | L1S1L1 | 2.00 | 2.09 |
| L1S2L1 | 1.29 | 3.22 | |
| L1S3L1 | 5.20 | 1.51 | |
| L2SL1L2 | 3.65 | 2.18 | |
| L2SL2L2 | 2.80 | 0.43 |
| The Depth of Wetting Front l (cm) | L1S1L1 | L1S2L1 | L1S3L1 | L2SL1L2 | L2SL2L2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t1 | t2 | t1 | t2 | t1 | t2 | t1 | t2 | t1 | t2 | |
| 10 | 5.71 | 7.56 | 5.71 | 7.67 | 5.71 | 8.55 | 33.06 | 54.74 | 33.06 | 51.73 |
| 30 | 49.12 | 49.47 | 53.36 | 57.12 | 47.23 | 49.58 | 260.00 | 284.10 | 265.99 | 276.60 |
| 50 | 100.97 | 106.08 | 121.92 | 127.06 | 95.00 | 92.46 | 526.66 | 548.70 | 500.00 | 552.10 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Mao, X.; Wang, C. A Modified Green-Ampt Model and Parameter Determination for Water Infiltration in Fine-textured Soil with Coarse Interlayer. Water 2019, 11, 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040787
Chen S, Mao X, Wang C. A Modified Green-Ampt Model and Parameter Determination for Water Infiltration in Fine-textured Soil with Coarse Interlayer. Water. 2019; 11(4):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040787
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shuai, Xiaomin Mao, and Chunying Wang. 2019. "A Modified Green-Ampt Model and Parameter Determination for Water Infiltration in Fine-textured Soil with Coarse Interlayer" Water 11, no. 4: 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040787
APA StyleChen, S., Mao, X., & Wang, C. (2019). A Modified Green-Ampt Model and Parameter Determination for Water Infiltration in Fine-textured Soil with Coarse Interlayer. Water, 11(4), 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040787






