Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Water Table Depth Associated with Changing Agricultural Land Use in an Arid Zone Oasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
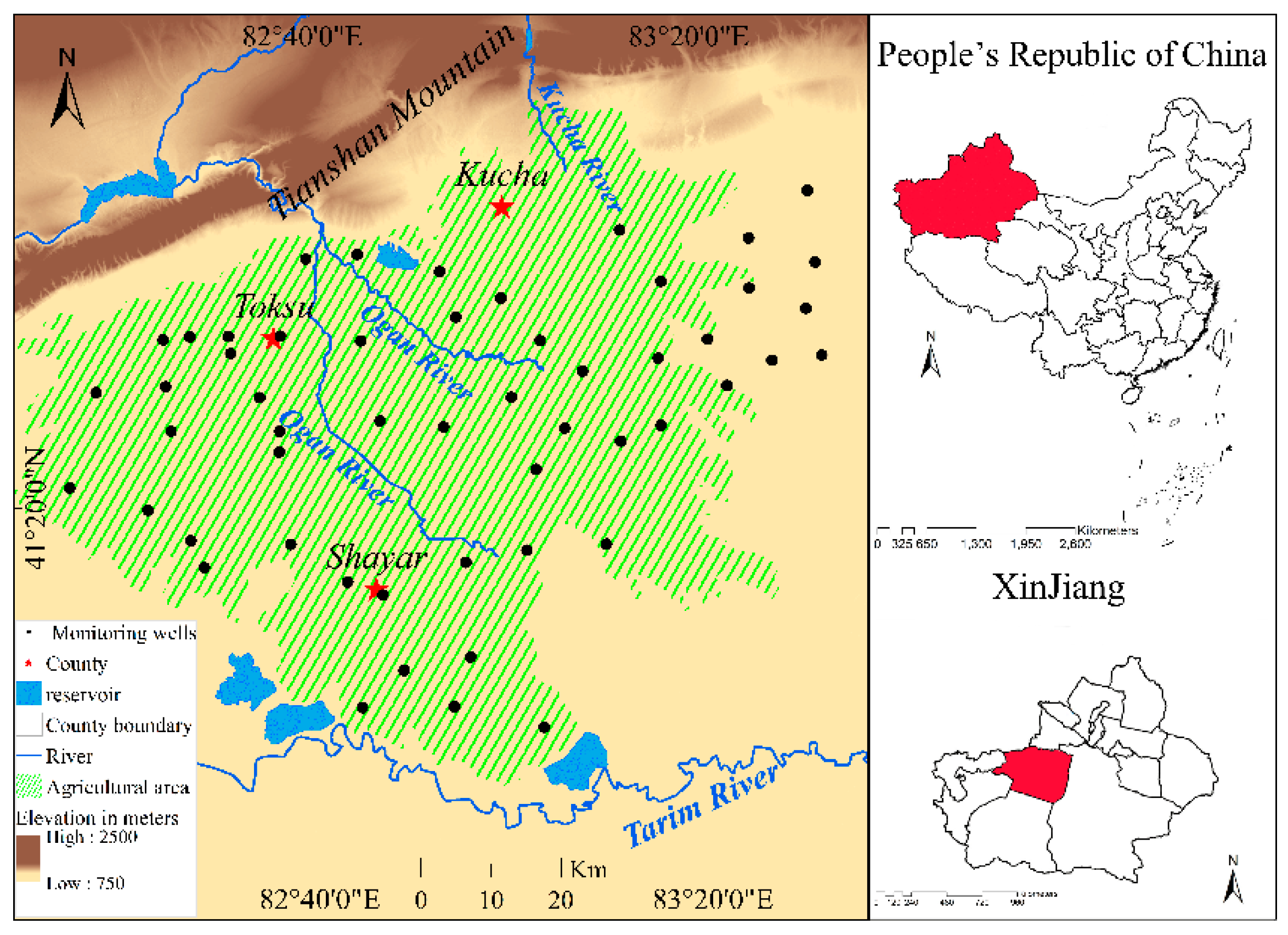
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Table Depth
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Geostatistical Analysis
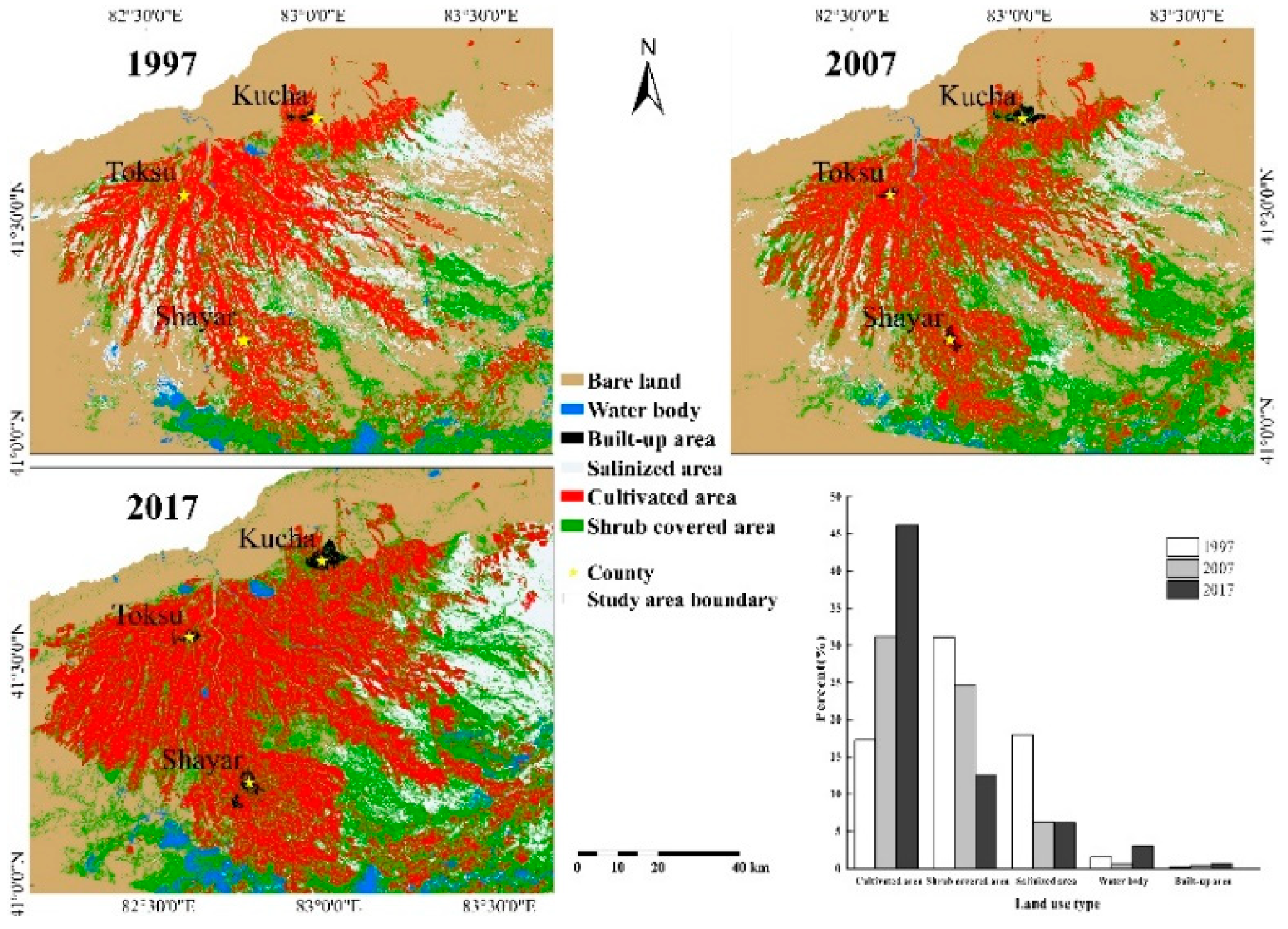
2.4.2. Mapping Land Cover and Land Use
2.4.3. Grid Cell Method
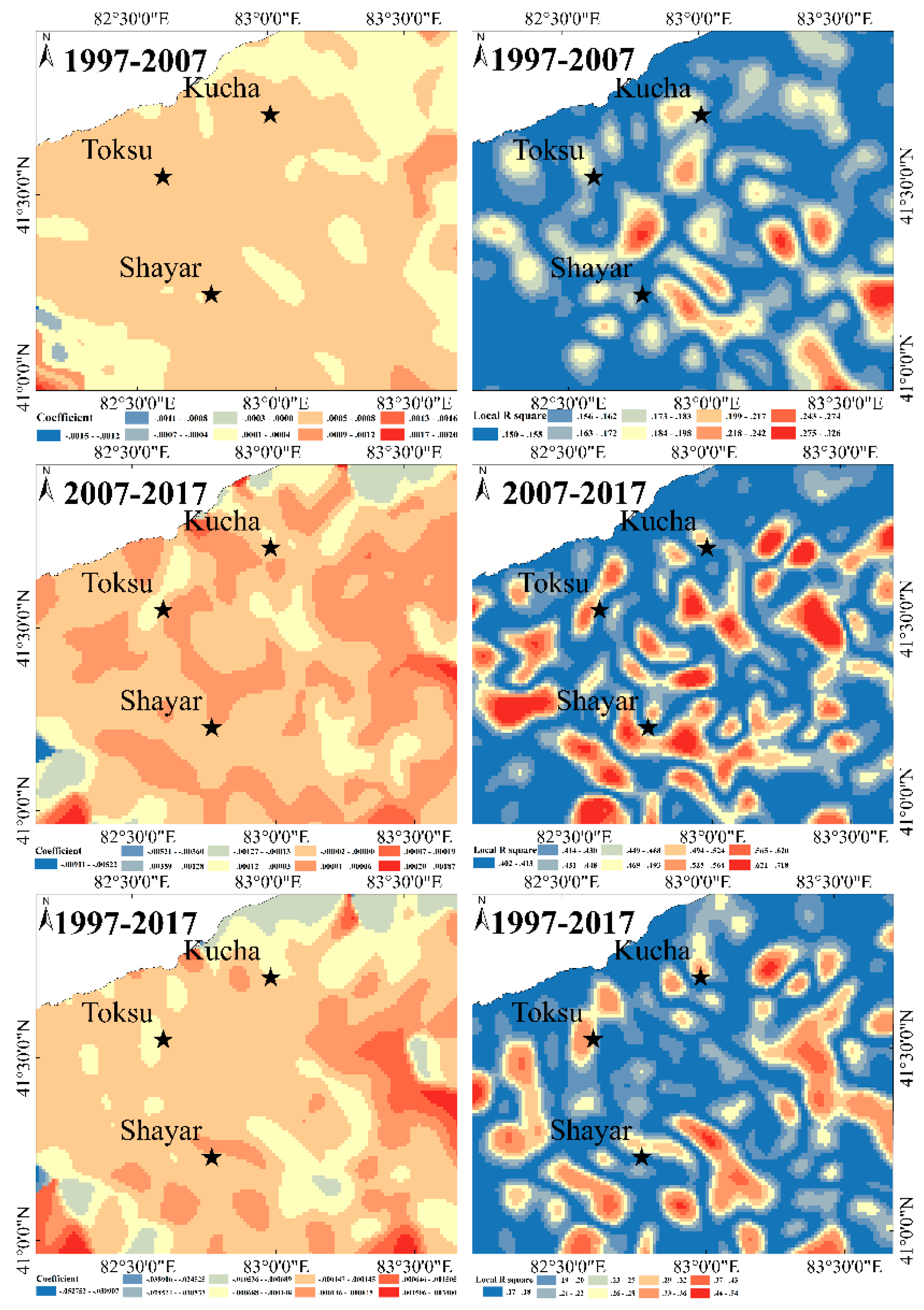
2.4.4. Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) Analysis
3. Results
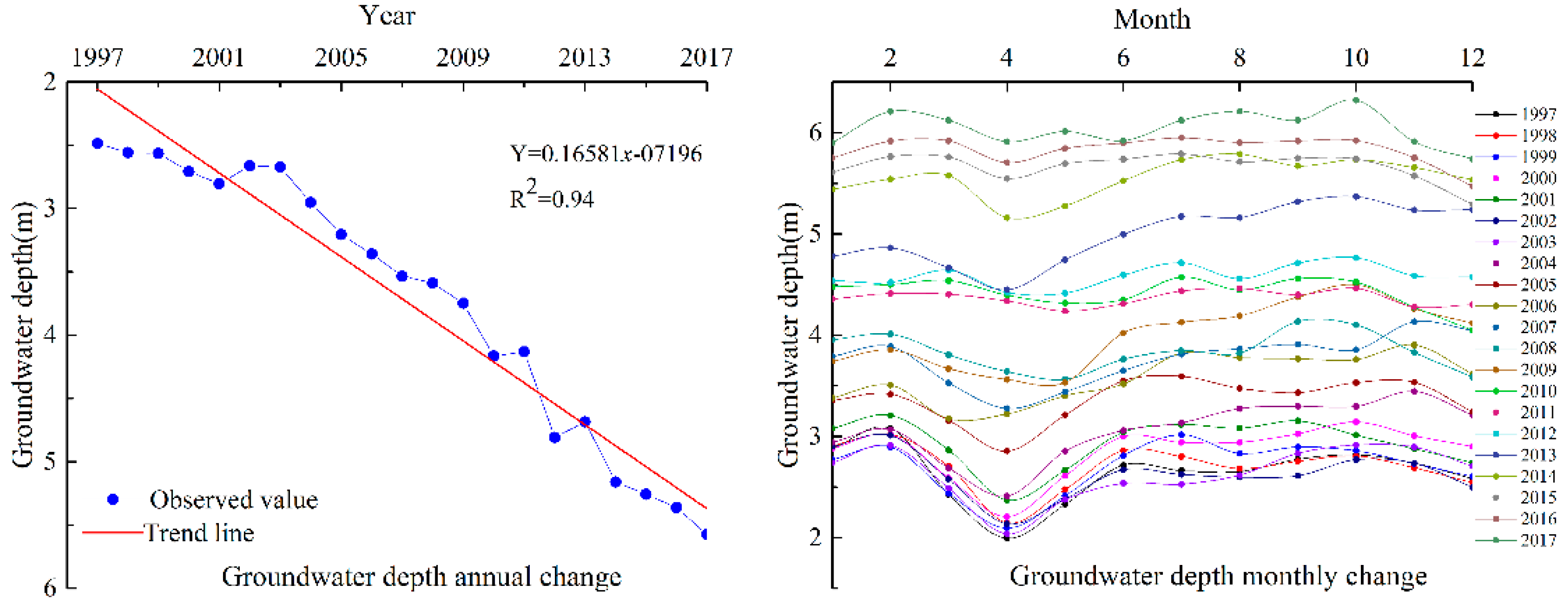
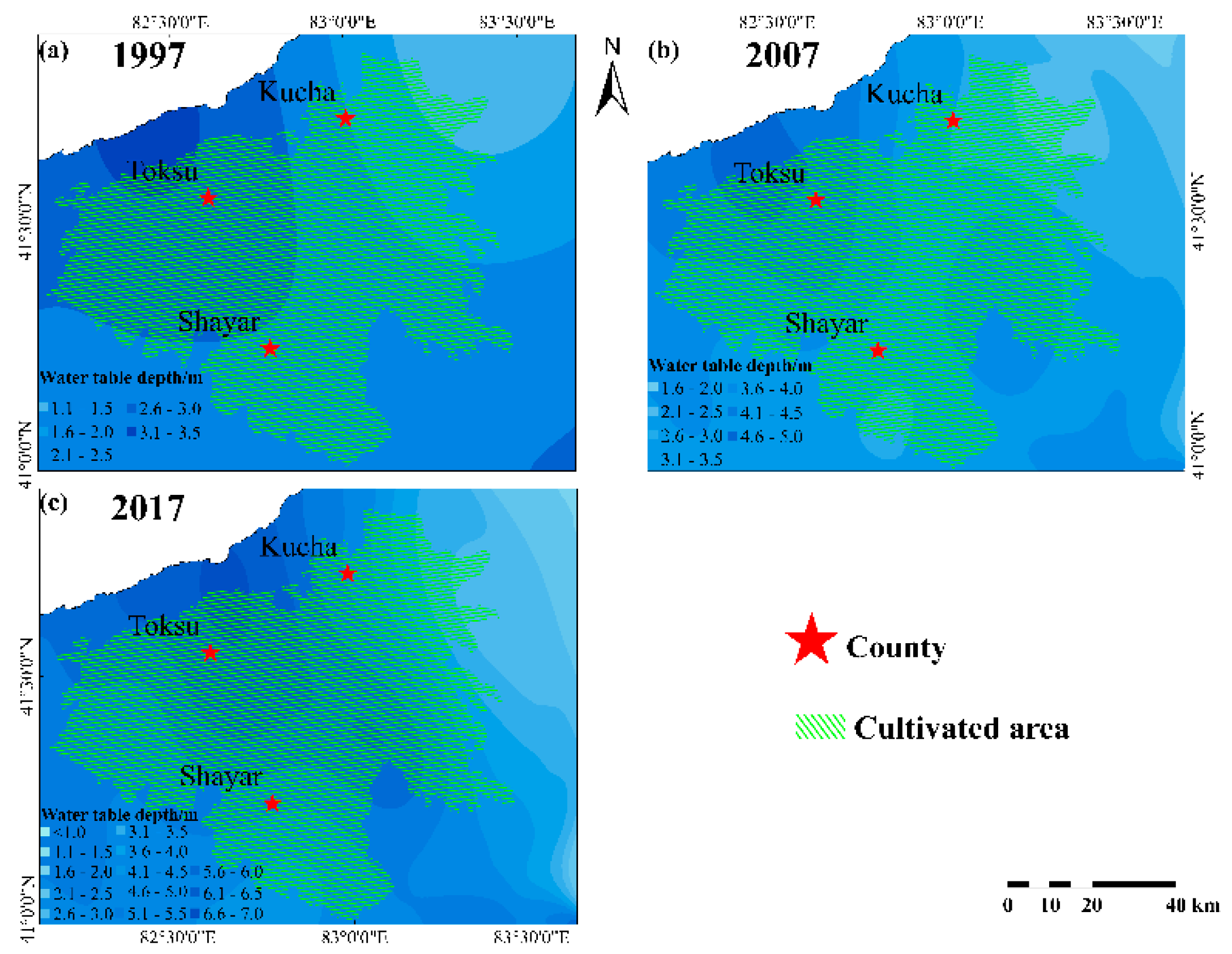
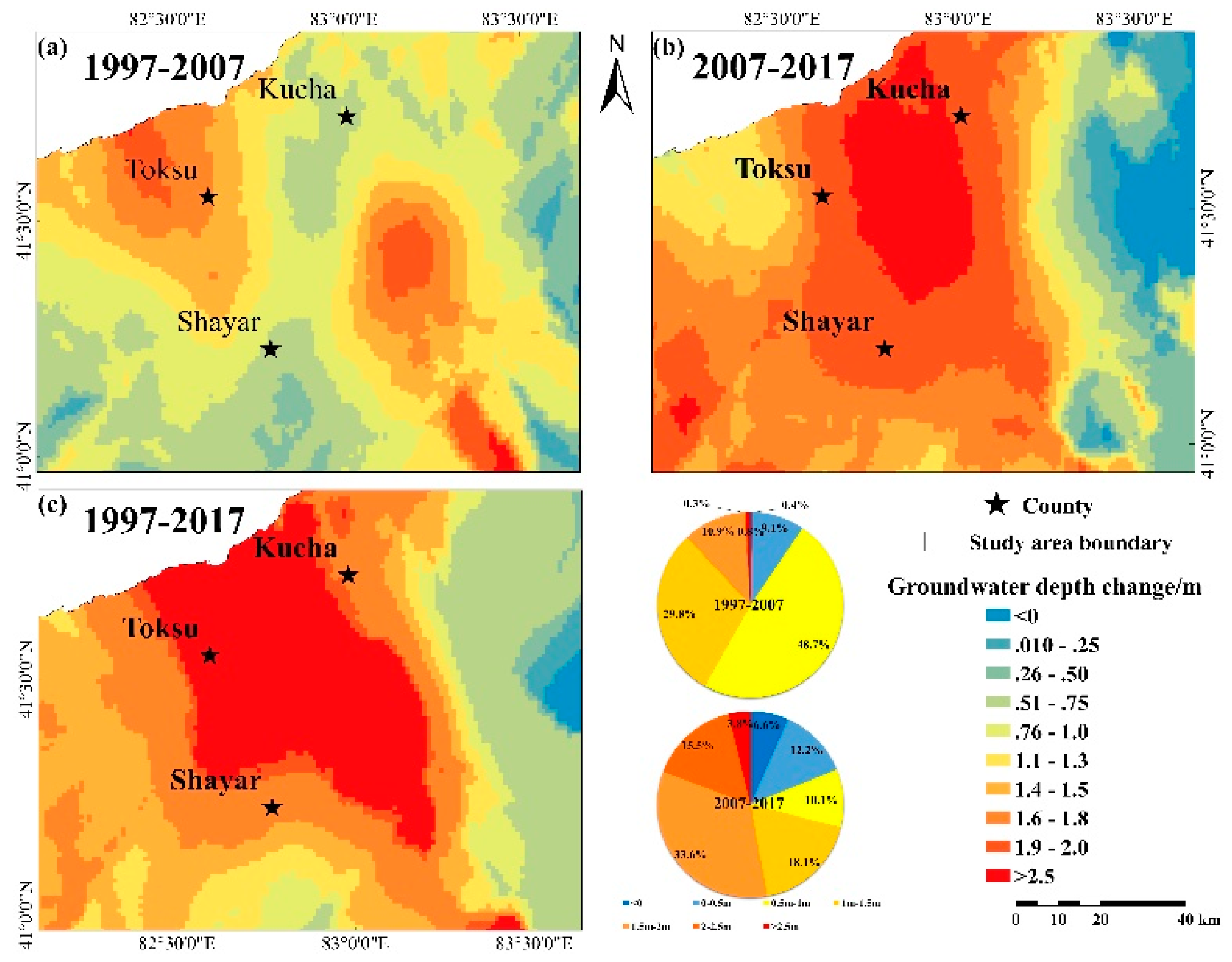
3.1. Water Table Depth Variations
3.2. Land Cover Change Patterns
3.3. Relationship between WTD Change and Land Cover Classes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, G. Effect of Polluted Surface Water on Groundwater: A Case Study of Budha Nullah. Science 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musaoglu, N.; Tanik, A.; Gumusay, M.U.; Dervisoglu, A.; Bilgilioglu, B.B.; Yagmur, N.; Bakirman, T.; Baran, D.; Gokdag, M.F. Long-term Monitoring of Wetlands via Remote Sensing and GIS: A case study from Turkey. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Climate Change, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 15–16 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- LaMoreaux, J.W. Thematic issue: Groundwater resources management. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.G.; Scanlon, B.; Döll, P.; Rodell, M.; Beek, R.V.; Wada, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Leblanc, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Edmunds, M. Ground water and climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Huo, Z.; Xu, X.; Qu, Z.; Huang, G.; Tang, P.; Bai, Y. Shallow groundwater plays an important role in enhancing irrigation water productivity in an arid area: The perspective from a regional agricultural hydrology simulation. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 208, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ling, H.; Xu, H.; Guo, B. Study of suitable oasis scales based on water resource availability in an arid region of China: A case study of Hotan River Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wenninger, J.; Uhlenbrook, S. A multi-method approach to quantify groundwater/surface water-interactions in the semi-arid Hailiutu River basin, northwest China. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschbachhertig, W.; Gleeson, T. Regional strategies for the accelerating global problem of groundwater depletion. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotterman, K.A.; Kendall, A.D.; Basso, B.; Hyndman, D.W. Groundwater depletion and climate change: Future prospects of crop production in the Central High Plains Aquifer. Clim. Chang. 2018, 146, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.J.; Yan, Q.L.; Song, L.N. Effects of land use changes on the groundwater table and the decline of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in southern Horqin Sandy Land, Northeast China. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 109, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J.; Wang, X.; Qi, P. Assessment of Shallow Groundwater Recharge from Extreme Rainfalls in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Water 2016, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Shashtri, S. Modeling impacts of change in Landuse/Landcover on groundwater system in Shiwaliks of Punjab using Remote Sensing and GIS. J. Mammal. 2009, 88, 1098–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Opp, C.; Hennig, T.; Marold, U. Impacts and Implications of Major Changes Caused by the Three Gorges Dam in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3367–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazavi, R. Impacts of land-use change on groundwater resources using remote sensing and numerical modeling. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Reedy, R.C.; Stonestrom, D.A.; Prudic, D.E.; Dennehy, K.F. Impact of land use and land cover change on groundwater recharge and quality in the southwestern US. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 11, 1577–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlhaus, P.G.; Evans, T.J.; Nathan, E.L.; Cox, J.W.; Simmons, C.T. Groundwater-level response to land-use change and the implications for salinity management in the West Moorabool River catchment, Victoria, Australia. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 1611–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhao, C.; Wei, H.; Peng, D. Simulation of the relationship between land use and groundwater level in Tailan River basin, Xinjiang, China. Quat. Int. 2011, 244, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, V.; Prajwal, M.; Shetty, A.; Srivastava, A.; Bhosale, R. Spatiotemporal Relationship Linking Land Use/Land Cover with Groundwater Level. In Groundwater; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S. Land Use/Cover Change Impacts on Water Table Change over 25 Years in a Desert-Oasis Transition Zone of the Heihe River Basin, China. Water 2016, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahdy, S.I.; Mohamed, M.M. Land use/land cover change impact on groundwater quantity and quality: A case study of Ajman Emirate, the United Arab Emirates, using remote sensing and GIS. Arabian J. Geosci. 2016, 19, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmillen, D.P. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2002, 86, 554–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellehumeur, C.; Legendre, P. Multiscale sources of variation in ecological variables: Modeling spatial dispersion, elaborating sampling designs. Landsc. Ecol. 1998, 13, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Xia, Z.G. Examining spatially varying relationships between land use and water quality using geographically weighted regression I: Model design and evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 407, 358–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.F.; Chen, X.; Luo, G.P.; Guo, Q.J. Temporal and spatial variability response of groundwater level to land use/land cover change in oases of and areas. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langroodi, S.H.M.; Masoum, M.G.; Nasiri, H.; Javi, S.T. Spatial and temporal variability analysis of groundwater quantity to land-use/land-cover change in the Khanmirza agricultural plain in Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 8385–8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moukana, J.A.; Asaue, H.; Koike, K. Co-kriging for modeling shallow groundwater level changes in consideration of land use/land cover pattern. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javi, S.T.; Malekmohammadi, B.; Mokhtari, H. Application of geographically weighted regression model to analysis of spatiotemporal varying relationships between groundwater quantity and land use changes (case study: Khanmirza Plain, Iran). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 3123–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically Weighted Regression: A Method for Exploring Spatial Nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Versace, V.L.; Laurenson, L.; Ierodiaconou, D.; Fawcett, J.; Salzman, S. Assessment of Spatiotemporal Varying Relationships Between Rainfall, Land Cover and Surface Water Area Using Geographically Weighted Regression. Environ. Model. Assess. 2012, 17, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, F.; Orange, D.; Williams, M.; Mulley, C.; Epprecht, M. Drivers of afforestation in Northern Vietnam: Assessing local variations using geographically weighted regression. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.Q.; Du, P.J.; Samat, A.; Xia, J.S.; Che, M.Q.; Xue, Z.H. Spatiotemporal Pattern of PM2.5 Concentrations in Mainland China and Analysis of Its Influencing Factors using Geographically Weighted Regression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, B.; McGill, B.J.; Wilson, A.M.; Regetz, J.; Jetz, W.; Guralnick, R.; Tuanmu, M.N.; Schildhauer, M. Using multi-timescale methods and satellite-derived land surface temperature for the interpolation of daily maximum air temperature in Oregon. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3862–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.B.; Charlton, M.; Harris, P.; Fotheringham, A.S. Geographically weighted regression with a non- Euclidean distance metric: A case study using hedonic house price data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 660–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes, N.B.P.; Sendra, J.B.; Delgado, M.G.; Plata, R.F. Exploring the driving forces behind deforestation in the state of Mexico (Mexico) using geographically weighted regression. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, M.; Bilal, M. Evaluation of Ordinary Least Square (OLS) and Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) for Water Quality Monitoring: A Case Study for the Estimation of Salinity. J. Ocean Univ. China 2018, 17, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabiti, M.; Yan-Hong, L.I. Analysis on Water-saving Potentiality and the Issue of Water Resources in the WeiGan-KuChe River Delta Oasis. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2007, 21, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Haiyang, Y.U.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis on the Hydrological and Ecological Characteristics Based on the LUCC in Weigan and Kuqa River. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 23, 236–242. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, W.; Ding, J.; Yang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Sensitivity analysis of soil salinity and vegetation indices to detect soil salinity variation by using Landsat series images: Applications in different oases in Xinjiang, China. Acta Ecol. Sinica. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Juan, Q.U.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. The retrieval model of soil salinization information in arid region based on MSAVI-WI feature space: A case study of the delta oasis in Weigan-Kuqa watershed. Geogr. Res. 2013, 32, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.L.; Yu, D.L. Monitoring and evaluating spatial variability of soil salinity in dry and wet seasons in the Werigan-Kuqa Oasis, China, using remote sensing and electromagnetic induction instruments. Geoderma 2014, 235, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jialaliding, A.; Tursun, T.; Mamat, R. Research on Water and Soil Resources in Weiganhe River Basin of Xinjiang. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2013, 52, 2532–2535. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Ding, J.; Yu, H. Relationship between multi-scale landscape pattern and salinity in Weigan and Kuqa rivers delta oasis. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, X.; Wang, X.; Chai, Z. Land Use/Cover Changes and Influencing Factors in Delta Oasis of Weigan-Kuqa River During Last 25 Years. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 36, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Litan, S.U.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Z. Study on the Spatio-temporal Variation of Groundwater Salt Content in Xinjiang Weigan Catchment. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 854–860. [Google Scholar]
- Moeck, C.; Brunner, P.; Hunkeler, D. The influence of model structure on groundwater recharge rates in climate-change impact studies. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinnirella, S.; Buttafuoco, G.; Pirrone, N. Stochastic analysis to assess the spatial distribution of groundwater nitrate concentrations in the Po catchment (Italy). Environ. Pollut. 2005, 133, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boken, V.K.; Hoogenboom, G.; Hook, J.E.; Thomas, D.L.; Guerra, L.C.; Harrison, K.A. Agricultural water use estimation using geospatial modeling and a geographic information system. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 67, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Kang, S.Z.; Li, F.S.; Zhang, L. Comparison of interpolation methods for depth to groundwater and its temporal and spatial variations in the Minqin oasis of northwest China. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2009, 24, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.Q.; Huo, Z.L.; Feng, S.Y.; Mao, X.M.; Kang, S.Z.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.J.; Steenhuis, T.S. Evaluation of spatial interpolation methods for groundwater level in an arid inland oasis, northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbasiouny, H.; Abowaly, M.; Abu Alkheir, A.; Gad, A. Spatial variation of soil carbon and nitrogen pools by using ordinary Kriging method in an area of north Nile Delta, Egypt. Catena 2014, 113, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phachomphon, K.; Dlamini, P.; Chaplot, V. Estimating carbon stocks at a regional level using soil information and easily accessible auxiliary variables. Geoderma 2010, 155, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Ye, H.C.; Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, S.W.; Shen, C.Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.F. Prediction of Soil Organic Matter Using Ordinary Kriging Combined with the Clustering of Self-organizing Map: A Case Study in Pinggu District, Beijing, China. Soil Sci. 2017, 182, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, T.G.; Pusuluri, N.B.; Mathias, K.K.; Cornelius, P.L.; Barnhisel, R.I.; Shearer, S.A. Map quality for ordinary kriging and inverse distance weighted interpolation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagan, H.; Yamagata, Y. Landsat analysis of urban growth: How Tokyo became the world’s largest megacity during the last 40 years. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 127, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, B. Geographically weighted regression: The analysis of spatially varying relationships. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2003, 17, 717–719. [Google Scholar]
- Georganos, S.; Abdi, A.M.; Tenenbaum, D.E.; Kalogirou, S. Examining the NDVI-rainfall relationship in the semi-arid Sahel using geographically weighted regression. J. Arid Environ. 2017, 146, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Crespo, R.; Charlton, M. The Use of Geographically Weighted Regression for Spatial Prediction: An Evaluation of Models Using Simulated Data Sets. Math. Geosci. 2011, 43, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabiti, M.; Jiang-Ling, H.U. Effects of Groundwater Characteristics on Vegetation in the Oasis on the Ugan-Kuqa River Delta, Xinjiang Region, China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2010, 32, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; He, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, L. Quantifying the impacts of land use/land cover change on groundwater depletion in Northwestern China—A case study of the Dunhuang oasis. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 146, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Velazquez, M.; Pena-Haro, S.; Garcia-Prats, A.; Mocholi-Almudever, A.F.; Henriquez-Dole, L.; Macian-Sorribes, H.; Lopez-Nicolas, A. Integrated assessment of the impact of climate and land use changes on groundwater quantity and quality in the Mancha Oriental system (Spain). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1677–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Mo, X.G.; Cai, Y.L.; Li, X.B. Analysis on groundwater table drawdown by land use and the quest for sustainable water use in the Hebei Plain in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 75, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettle, N.; Harrington, L.; Harrington, J. Groundwater depletion and agricultural land use change in the high plains: A case study from Wichita County, Kansas. Prof. Geogr. 2007, 59, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabit, M.; Yusuf, N.; Nasierding, N. Supply and demand analysis on water resources in Weigan river-Kuqa river delta oasis, Xinjiang. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2010, 24, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Qiao, X.N.; Tang, H. Temporal and spatial dynamic changes of land use and ecosystem service value in the Weigan River Basin in recent 20 years. Agric. Res. Arid Areas. 2013, 31, 213–223. [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani, Y.; Uesugi, Y.; Kitagawa, T. Characteristics of temporal and spatial dynamic changes of land use and their relationship with regional development—A case study in the Weigan River Basin. Agric. Res. Arid Areas. 2012, 38, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.D.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, C.Y.; Ding, J.L.; Zhang, X.L. Characteristics of soil salinity under different land use types in Weigan River Oasis. Arid Land Geogr. 2018, 41, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.W.; Ding, J.L.; Xie, X. Spatial Quantitative Research of Ecosystem Service Value Based on Land Use in the Delta Oasis of Weigan and Kuqa River. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2014, 10, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar]

| Year | Model | Nugget | Sill | GD | Range/m | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1997 | Gaussian | 0.42 | 2.228 | 0.18 | 19278 | 0.78 |
| 2007 | Gaussian | 1.48 | 5.969 | 0.25 | 25392 | 0.66 |
| 2017 | Gaussian | 3.22 | 10.449 | 0.31 | 22881 | 0.52 |
| Period | Land Use Type | OLS | R2 | Pearson Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1997–2007 | Bare land | y =0.00001845x + 0.962 | 0.06 | 0.11** |
| Water body | y = −0.000000246x + 0.969 | 0.23 | −0.04 | |
| Built-up area | y = 0.00001954x + 0.968 | 0.01 | 0.06* | |
| Salinized area | y = −0.00001558x + 0.961 | 0.28 | −0.16** | |
| Cultivated area | y = 0.00003652x + 0.965 | 0.3 | 0.31** | |
| Shrub covered area | y = −0.00002525x + 0.949 | 0.15 | −0.15** | |
| 2007–2017 | Bare land | y = 0.00009034x + 1.539 | 0.11 | 0.17** |
| Water body | y = −0.00000592x + 1.346 | 0.13 | −0.01 | |
| Built-up area | y = 0.00001103x + 1.344 | 0.08 | 0.05** | |
| Salinized area | y = −0.0000121x + 1.373 | 0.38 | −0.39** | |
| Cultivated area | y = 0.0000691x + 1.344 | 0.58 | 0.51** | |
| Shrub covered area | y = −0.00004784x + 1.364 | 0.34 | −0.25** | |
| 1997–2017 | Bare land | y = 0.0008145x + 2.515 | 0.12 | 0.18** |
| Water body | y = −0.0000072x + 2.320 | 0.12 | −0.05** | |
| Built-up area | y = 0.00009367x + 2.310 | 0.05 | 0.05** | |
| Salinized area | y = −0.00001412x + 2.285 | 0.36 | −0.39** | |
| Cultivated area | y = 0.00003355x + 2.266 | 0.48 | 0.59** | |
| Shrub covered area | y = −0.00003317x + 2.351 | 0.37 | −0.29** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ainiwaer, M.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Nasierding, N. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Water Table Depth Associated with Changing Agricultural Land Use in an Arid Zone Oasis. Water 2019, 11, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040673
Ainiwaer M, Ding J, Wang J, Nasierding N. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Water Table Depth Associated with Changing Agricultural Land Use in an Arid Zone Oasis. Water. 2019; 11(4):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040673
Chicago/Turabian StyleAiniwaer, Mireguli, Jianli Ding, Jingjie Wang, and Nasiman Nasierding. 2019. "Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Water Table Depth Associated with Changing Agricultural Land Use in an Arid Zone Oasis" Water 11, no. 4: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040673
APA StyleAiniwaer, M., Ding, J., Wang, J., & Nasierding, N. (2019). Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Water Table Depth Associated with Changing Agricultural Land Use in an Arid Zone Oasis. Water, 11(4), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040673






