Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Water Access in Rural Areas of Low and Middle Income Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Countries Selected for the Analysis
2.2. Econometric Model
2.3. Dependent Variables
2.4. Independent Variables
3. Results
3.1. Global Results
3.2. Results for Middle-High Income Economies
3.3. Results for Middle-Low income Economies
3.4. Results for Low Income Economies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Afghanistan | Gambia, The | Niger |
| Benin | Guinea | Rwanda |
| Burkina Faso | Guinea-Bisau | Sierra Leone |
| Burundi | Haiti | Somalia |
| Cambodia | Korea, Dem People’s Rep | South Sudan |
| Central African Republic | Liberia | Tanzania |
| Chad | Madagascar | Togo |
| Comoros | Malawi | Uganda |
| Congo, Dem. Rep | Mali | Zimbabwe |
| Eritrea | Mozambique | |
| Ethiopia | Nepal |
| Armenia | Indonesia | Samoa |
| Bangladesh | Kenya | Sao Tomé and Principe |
| Bhutan | Kiribati | Senegal |
| Bolovia | Kosovo | Solomon Islands |
| Cabo Verde | Kyrgyz Republic | Sri Lanka |
| Cameroon | Lao PDR | Sudan |
| Congo Rep. | Lesotho | Swaziland |
| Côte d’Ivoire | Mauritania | Syrian Arab Republic |
| Djibouti | Micronesia, Fed. Sts. | Tajikistan |
| Egypt, Arab Rep. | Moldova | Timor-Leste |
| El Salvador | Morocco | Ukraine |
| Georgia | Myanmar | Uzbekistan |
| Ghana | Nicaragua | Vanuatu |
| Guatemala | Nigeria | Vietnam |
| Guyana | Pakistan | West Bank and Gaza |
| Honduras | Papua New Guinea | Yemen, Rep. |
| India | Philippines |
| Albania | Fiji | Namibia |
| Algeria | Gabon | Palau |
| American Samoa | Grenada | Panama |
| Angola | Iran, Islamic Rep. | Paraguay |
| Azerbaijan | Iraq | Peru |
| Belarus | Jamaica | Romania |
| Belize | Jordan | Serbia |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Kazakhstan | South Africa |
| Botswana | Lebanon | St. Lucia |
| Brazil | Libya | St. Vincent and the Grenadines |
| Bulgaria | Macedonia, FYR | Suriname |
| China | Malaysia | Thailand |
| Colombia | Maldives | Tonga |
| Costa Rica | Marshall Islands | Tunisia |
| Cuba | Mauritius | Turkey |
| Dominica | Mexico | Turkmenistan |
| Dominican Republic | Mongolia | Tuvalu |
| Ecuador | Montenegro |
| Total Improved Access | Piped Access | Other Improved Access | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rule of law | 3.47 * (0.0624) | 6.43 ** (0.0112) | 0.00 (0.9789) |
| Voice and accountability | 12.90 *** (0.0016) | 7.39 ** (0.0249) | 5.89 * (0.0526) |
| Political stability | 14.82 *** (0.0006) | 0.80 (0.6697) | 4.11 (0.1280) |
| Control of corruption | 1.40 (0.2359) | 0.96 (0.3277) | 1.62 (0.2034) |
| Government effectiveness | 1.46 (0.4819) | 1.36 (0.2444) | 2.72 (0.2567) |
| Regulatory quality | 0.39 (0.8245) | 2.21 (0.3307) | 15.46 *** (0.0004) |
| Total Improved Access | Piped Access | Other Improved Access | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rule of law | 5.21 * (0.0738) | 1.07 (0.5853) | 3.16 (0.2064) |
| Voice and accountability | 19.10 *** (0.0001) | 3.07 (0.2158) | 2.58 (0.2753) |
| Political stability | 4.28 (0.1178) | 1.34 (0.5106) | 0.29 (0.8658) |
| Control of corruption | 0.01 (0.9309) | 0.75 (0.3851) | 0.01 (0.9432) |
| Government effectiveness | 1.81 (0.4053) | 12.04 *** (0.0024) | 1.22 (0.5432) |
| Regulatory quality | 16.16 *** (0.0003) | 2.83 (0.2426) | 0.45 (0.7977) |
| Total improved Access | Piped Access | Other Improved Access | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rule of law | 0.01 (0.9964) | 5.00 * (0.0821) | 0.28 (0.8707) |
| Voice and accountability | 0.85 (0.6546) | 12.69 *** (0.0018) | 2.95 (0.2287) |
| Political stability | 1.08 (0.5814) | 2.22 (0.3296) | 0.69 (0.7084) |
| Control of corruption | 2.64 (0.1040) | 0.00 (0.9774) | 0.01 (0.9344) |
| Government effectiveness | 2.66 (0.2648) | 6.10 ** (0.0473) | 2.80 (0.2471) |
| Regulatory quality | 7.64 ** (0.0220) | 7.39 ** (0.0249) | 0.23 (0.8922) |
References
- WHO. Drinking Water Fact Sheet. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water (accessed on 9 December 2018).
- WHO; UNICEF. Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: 2017 Update and SDG Baselines; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.unicef.org/publications/index_96611.html (accessed on 9 December 2018).
- UNDP. The Millennium Development Goals Report 2015; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Available online: http://www.un.org/millenniumgoals/2015_MDG_Report/pdf/MDG%202015%20rev%20(July%201).pdf (accessed on 9 May 2016).
- UNDP. Support to the Implementation of Sustainable Development. Goal 6. Sustainable Management of Water and Sanitation; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alcamo, J.; Henrichs, T.; Rösch, T. World Water in 2025: Global Modeling and Scenario Analysis for the World Commission on Water for the 21st Century; Report A0002; Center for Environmental Systems Research, University of Kassel: Kassel, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Munamati, M.; Nhapi, I.; Misi, S. Exploring the determinants of sanitation success in Sub-Saharan Africa. Water Res. 2016, 103, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yao, W.; Fu, Y.; Wei, H.; Tao, Y.; Liu, J.; Yao, H. A spatio-temporal pattern and socio-economic factors analysis of improved sanitation in China, 2006–2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health 2018, 15, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luha, J.; Bartrama, J. Drinking water and sanitation: Progress in 73 countries in relation to socioeconomic indicators. Bull. World Health Organ. 2015, 94, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopewell, M.R.; Graham, J.P. Trends in access to water supply and sanitation in 31 major Sub-Saharan African cities: an analysis of DHS data from 2000 to 2012. BMC Publ. Health 2014, 14, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onda, K.; Crocker, J.; Kayser, G.L.; Bartram, J. Country clustering applied to the water and sanitation sector: A new tool with potential applications in research and policy. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, R.; Luyendijk, R.; Bartram, J. Universal access to drinking water: The role of aid. In WIDER Working Papers; No. 2013/088; World Institute for Development Economics Research (UNU-WIDER), United Nations University: Tokyo, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ndikumana, L.; Pickbourn, L. The Impact of Foreign Aid Allocation on Access to Social Services in Sub-Saharan Africa: The Case of Water and Sanitation; Political Economy Research Institute, University of Massachusetts Amherst: Amherst, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wayland, J. A Drop in the Bucket? The Effectiveness of Foreign Aid in the Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) Sector; American University: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, E.A.; Boateng, G.O.; Amoyaw, J.A. Socioeconomic and demographic predictors of potable water and sanitation access in Ghana. Soc. Indic. Res. 2016, 126, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskei, E.C.; Koskei, R.C.; Koske, M.C.; Koech, H.K. Effect of Socio-economic Factors on Access to Improved Water Sources and Basic Sanitation in Bomet Municipality, Kenya. Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 5, 714–719. [Google Scholar]
- Mulenga, J.N.; Bwalya, B.B.; Kaliba-Chishimba, K. Determinants and inequalities in access to improved water sources and sanitation among the Zambian households. Int. J. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 6, 746–762. [Google Scholar]
- Dondeynaz, C.; Carmona Moreno, C.; Céspedes Lorente, J. Analysing inter- relationships among water, governance, human development variables in developing countries. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3791–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, J. Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach; Nelson Education: Scarborough, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Webbink, E.; Smits, J.; de Jong, E. Household and context determinants of child labor in 221 districts of 18 developing countries. Soc. Indic. Res. 2013, 110, 819–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UN Water. UN-Water Factsheet on Water and Gender, World Water Day 2013; UN Water: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Demie, G.; Bekele, M.; Seyoum, B. Water accessibility impact on girl and women’s participation in education and other development activities: The case of Wuchale and Jidda Woreda, Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2016, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kookana, R.S.; Maheshwari, B.; Dillon, P.; Dave, S.H.; Soni, P.; Bohra, H.; Katara, P. Groundwater scarcity impact on inclusiveness and women empowerment: Insights from school absenteeism of female students in two watersheds in India. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 2016, 20, 1155–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Water Assessment Programme; UNESCO. Water for Women: Every Woman Counts. Every Second Counts; Stockholm International Water Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, I. Women, water, and development. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2007, 32, 421–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, J.; Iranzo, S.; Sanz, A. Community-Managed Water Services: The Case of Peru. J. Environ. Dev. 2017, 26, 400–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, P.; Perkins, P.E. Women and water management in times of climate change: Participatory and inclusive processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 60, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, M. Women’s Participation in Rural Water Projects: The Case of Kwaebibirem District in the Eastern Region of Ghana. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Ghana, Accra, Ghana, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Botting, M.J.; Porbeni, E.O.; Joffres, M.R.; Johnston, B.C.; Black, R.E.; Mills, E.J. Water and sanitation infrastructure for health: The impact of foreign aid. Glob. Health 2010, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J. Corruption in public service delivery: Experience from South Asia’s water and sanitation sector. World Dev. 2004, 32, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.K.; Tortajada, C. Future water governance: Problems and perspectives. Water Resour. Dev. 2010, 26, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, D.; Kraay, A.; Mastruzzi, M. The worldwide governance indicators: Methodology and analytical issues. Hague J. Rule Law 2011, 3, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

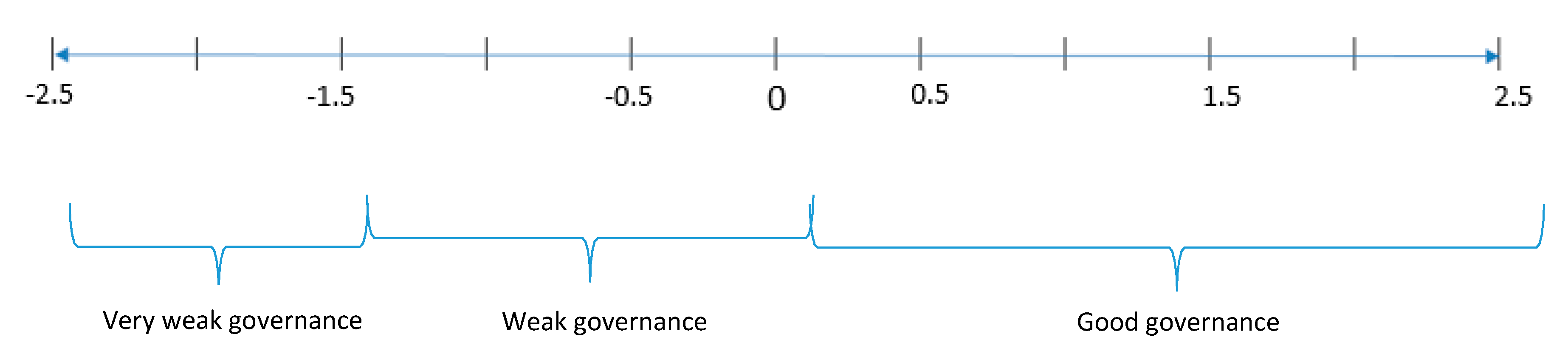
| Global Database | Middle-High Income | Middle-low Income | Low Income | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNI per capita | $2093.49 (2192,47) | $3889.46 (2420.69) | $1248.49 (886,35) | $374.94 (196.12) |
| Primary completion rate, female | 76.67% (28.02) | 96.14% (13.16) | 78.48% (22.50) | 43.41% (22.36) |
| Agriculture (%GDP) | 21.14% (13.46) | 11.40% (7.16) | 23.00% (10.88) | 36.76% (10.85) |
| Official level of development assistance (% GDP) | 0.018% (0.038) | 0.005% (0.014) | 0.019% (0.036) | 0.035% (0.055) |
| Rural population growth | 0.91 (1.60) | 0.10 (1.51) | 1.11 (1.20) | 1.97 (1.59) |
| Six governance indicators | ||||
| Rule of Law | −0.55 (0.58) | −0.24 (0.66) | −0.59 (0.56) | −1.01 (0.56) |
| Voice and accountability | −0.43 (0.83) | −0.11 (0.87) | −0.48 (0.75) | −0.91 (0.62) |
| Political Stability | −0.44 (0.93) | −0.07 (0.83) | −0.53 (0.90) | −0.91 (0.90) |
| Control of corruption | −0.54 (0.58) | −0.28 (0.59) | −0.60 (0.49) | −0.87 (0.47) |
| Government effectiveness | −0.56 (0.61) | −0.23 (0.60) | −0.58 (0.44) | −1.07 (0.52) |
| Regulatory quality | −0.53 (0.69) | −0.22 (0.71) | −0.59 (0.51) | −0.98 (0.64) |
| Total Improved | Total Improved | Total Improved | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LogGNI | 10.583 *** (0.425) | ||
| Female | 0.234 *** (0.020) | ||
| Agriculture | −0.391 *** (0.026) | ||
| Rural Growth | −0.614 *** (0.162) | −1.351 *** (0.230) | −0.017 (0.116) |
| Development Aid | 0.846 (1.472) | -1.773 (1.591) | −1.887 (1.469) |
| Weak Rule | −2.272 *** (0.312) | −1.637 *** (0.614) | −1.078 *** (0.358) |
| Very weak Rule | −2.276 *** (0.484) | −2.978 ** (1.230) | −0.170 (0.597) |
| Weak Voice | −0.631 ** (0.270) | −2.024 *** (0.357) | −0.982 *** (0.222) |
| Very weak Voice | −0.806 (0.625) | −2.720 *** (0.877) | −0.903 * (0.508) |
| Weak Stability | −0.621 *** (0.216) | −0.838 *** (0.304) | −0.381 ** (0.175) |
| Very weak Stability | −0.687 ** (0.323) | −1.632 *** (0.464) | 0.087 (0.290) |
| Weak Corruption | −0.080 (0.309) | −0.575 (0.463) | −0.350 (0.282) |
| Very weak Corruption | −0.362 (0.899) | 6.178 *** (2.166) | 0.172 (0.835) |
| Weak Effectiveness | −0.074 (0.280) | 0.147 (0.423) | 0.065 (0.195) |
| Very weak Effectiveness | −1.562 *** (0.554) | −1.234 (1.520) | −0.069 (0.902) |
| Weak Regulatory | 1.330 *** (0.367) | 0.648 (0.417) | 0.043 (0.260) |
| Very weak Regulatory | 0.716 (0.637) | 1.710 ** (0.660) | −0.511 (0.484) |
| N | 1713 | 1087 | 1593 |
| Piped | Piped | Piped | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LogGNI | 11.034 *** (0.563) | ||
| Female | 0.154 *** (0.024) | ||
| Agriculture | −0.409 *** (0.032) | ||
| Rural Growth | −0.260 * (0.152) | −0.266 (0.415) | 0.931 *** (0.170) |
| Development Aid | −2.654 * (1.289) | −8.421 ** (3.703) | −6.519 *** (1.798) |
| Weak Rule | 0.356 (0.293) | −1.296 * (0.707) | 0.352 (0.374) |
| Very weak Rule | 0.459 (0.568) | −3.932 ** (1.611) | 1.060 (0.680) |
| Weak Voice | 0.451 (0.283) | −2.429 *** (0.591) | −0.780 ** (0.328) |
| Very weak Voice | 0.727 (0.602) | −3.397 ** (1.402) | 0.048 (0.753) |
| Weak Stability | 0.377 * (0.202) | 0.274 (0.370) | −0.034 (0.220) |
| Very weak Stability | 0.247 (0.340) | −1.160 ** (0.520) | −0.537 * (0.322) |
| Weak Corruption | −0.079 (0.279) | −1.516 * (0.816) | −0.277 (0.367) |
| Very weak Corruption | 0.315 (0.723) | −4.589 (4.899) | −0.642 (1.092) |
| Weak Effectiveness | −0.014 (0.264) | −1.091 (1.278) | 0.322 (0.373) |
| Very weak Effectiveness | −1.438 ** (0.588) | −9.874 *** (2.494) | −1.045 (0.813) |
| Weak Regulatory | 0.126 (0.362) | −2.252 *** (0.834) | −1.809 *** (0.564) |
| Very weak Regulatory | 0.254 (0.642) | −1.930 (1.368) | −1.469 * (0.778) |
| N | 1691 | 1076 | 1573 |
| Other Improved | Other Improved | Other Improved | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LogGNI | −2.975 *** (0.454) | ||
| Female | 0.018 (0.023) | ||
| Agriculture | −0.023 (0.033) | ||
| Rural Growth | −0.062 (0.151) | −0.300 (0.509) | −0.206 (0.176) |
| Development Aid | 0.619 (1.428) | −1.230 (2.860) | 5.828 *** (2.172) |
| Weak Rule | −2.142 *** (0.472) | −0.385 (0.708) | −2.535 *** (0.611) |
| Very weak Rule | −1.978 *** (0.558) | −2.409 ** (1.219) | −2.306 *** (0.695) |
| Weak Voice | −1.079 *** (0.331) | 0.554 (0.424) | −0.720 * (0.380) |
| Very weak Voice | −1.750 *** (0.573) | −0.003 (1.058) | −2.080 *** (0.795) |
| Weak Stability | −0.864 *** (0.302) | −0.459 (0.373) | −0.797 *** (0.291) |
| Very weak Stability | −1.043 *** (0.379) | −0.906 * (0.500) | −0.649 * (0.388) |
| Weak Corruption | −0.018 (0.417) | 1.108 * (0.671) | −0.249 (0.475) |
| Very weak Corruption | 0.486 (0.818) | −2.055 (2.659) | 0.026 (1.354) |
| Weak Effectiveness | −0.515 (0.423) | 1.209 (1.032) | −0.488 (0.500) |
| Very weak Effectiveness | −0.608 (0.655) | 2.203 (2.062) | 0.349 (1.179) |
| Weak Regulatory | 2.017 *** (0.635) | 2.943 *** (0.915) | 3.368 *** (0.763) |
| Very weak Regulatory | 1.052 (0.848) | 1.979 (1.295) | 2.646 *** (0.989) |
| N | 1697 | 1083 | 1577 |
| Total Improved | Piped | Other Improved | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LogGNI | −1.174 (0.933) | 1.758 (1.528) | −2.154 (1.617) |
| Female | −0.012 (0.011) | 0.023 (0.017) | −0.023 (0.032) |
| Agriculture | 0.096 (0.080) | 0.574 *** (0.175) | 0.521 * (0.277) |
| Rural Growth | 0.332 ** (0.148) | 0.267 (0.236) | −0.646 ** (0.284) |
| Development Aid | 6.951 (17.375) | −12.302 (22.174) | −12.853 (29.625) |
| Weak Rule | −0.977 ** (0.490) | −1.707 *** (0.658) | |
| Weak Voice | −0.153 (0.449) | 2.089 ** (0.894) | −2.437 ** (1.058) |
| Very weak Voice | −3.415 *** (0.861) | −0.296 (0.894) | −6.866 ** (2.871) |
| Weak Stability | 0.579 * (0.349) | −1.578 * (0.957) | |
| Very weak Stability | 3.083 *** (0.738) | 0.773 (1.726) | |
| Weak Regulatory | 3.955 *** (1.074) | ||
| Very weak Regulatory | 4.028 ** (1.567) | ||
| N | 351 | 343 | 347 |
| Total Improved | Piped | Other Improved | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LogGNI | 2.094 ** (1.056) | 2.157 * (1.113) | 0.489 (1.062) |
| Female | 0.118 *** (0.018) | 0.030 * (0.017) | 0.052 *** (0.018) |
| Agriculture | −0.515 *** (0.064) | 0.042 (0.046) | −0.122 ** (0.050) |
| Rural Growth | 1.126 *** (0.289) | −0.523 * (0.297) | −0.017 (0.208) |
| Development Aid | 0.368 (4.370) | −5.379 (3.903) | 0.242 (3.162) |
| Weak Rule | −0.424 (0.498) | ||
| Very weak Rule | 1.416 (1.461) | ||
| Weak Voice | −0.090 (0.415) | ||
| Very weak Voice | −9.386 *** (2.059) | ||
| Weak Effectiveness | −1.123 ** (.567) | ||
| Very weak Effectiveness | −2.863 *** (0.750) | ||
| Weak Regulatory | 1.639 *** | ||
Very weak Regulatory | (0.504) −2.701 (2.160) | ||
| N | 408 | 408 | 458 |
| Total Improved | Piped | Other Improved | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LogGNI | 2.318 ** (1.180) | 0.622 *** (0.141) | 0.620 (1.008) |
| Female | 0.104 *** (0.030) | 0.021 *** (0.004) | 0.082 *** (0.026) |
| Agriculture | −0.240 *** (0.037) | −0.032 *** (0.005) | −0.153 *** (0.031) |
| Rural Growth | −0.055 (0.469) | −0.306 *** (0.065) | 0.011 (0.250) |
| Development Aid | −0.683 (1.970) | −0.595 * (0.311) | 0.422 (1.582) |
| Weak Rule | 0.125 (0.240) | ||
| Very weak Rule | 0.325 (0.258) | ||
| Weak Voice | −0.174 (0.133) | ||
| Very weak Voice | 0.313 (0.196) | ||
| Weak Corruption | 0.402 (0.626) | ||
| Weak Effectiveness | 0.486 ** (0.199) | ||
| Very Weak Effectiveness | 0.338 (0.240) | ||
| Weak Regulatory | 1.065 | 0.100 | |
Very weak Regulatory | (2.192) 0.024 (2.289) | (0.120) −0.636 ** (0.305) | |
| N | 262 | 260 | 294 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomez, M.; Perdiguero, J.; Sanz, A. Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Water Access in Rural Areas of Low and Middle Income Countries. Water 2019, 11, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020202
Gomez M, Perdiguero J, Sanz A. Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Water Access in Rural Areas of Low and Middle Income Countries. Water. 2019; 11(2):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020202
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomez, Mabel, Jordi Perdiguero, and Alex Sanz. 2019. "Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Water Access in Rural Areas of Low and Middle Income Countries" Water 11, no. 2: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020202
APA StyleGomez, M., Perdiguero, J., & Sanz, A. (2019). Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Water Access in Rural Areas of Low and Middle Income Countries. Water, 11(2), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020202





