Precipitation Isotopes Associated with the Duration and Distance of Moisture Trajectory in a Westerly-Dominant Setting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
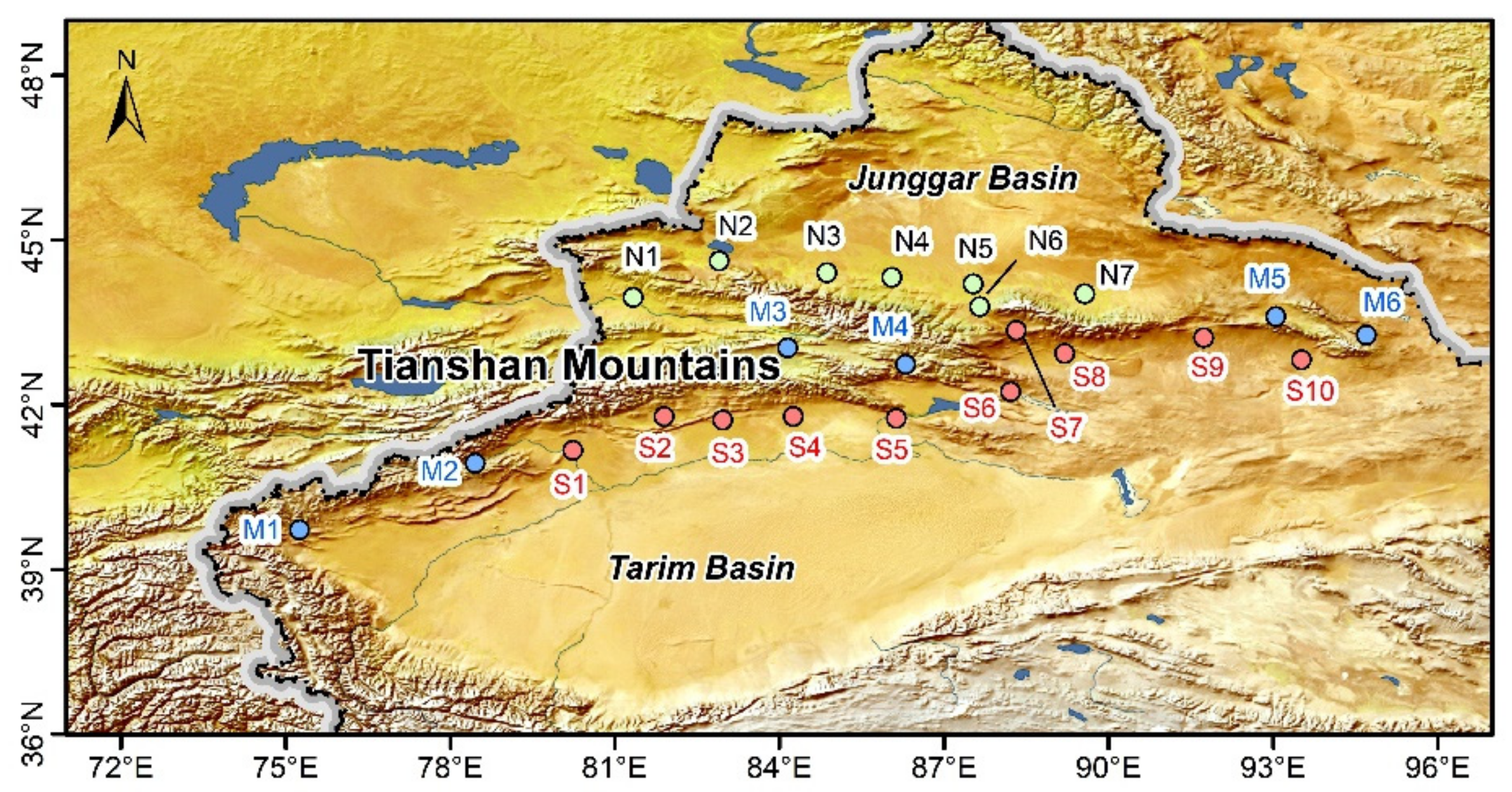
2. Data and Method
3. Results and Discussion
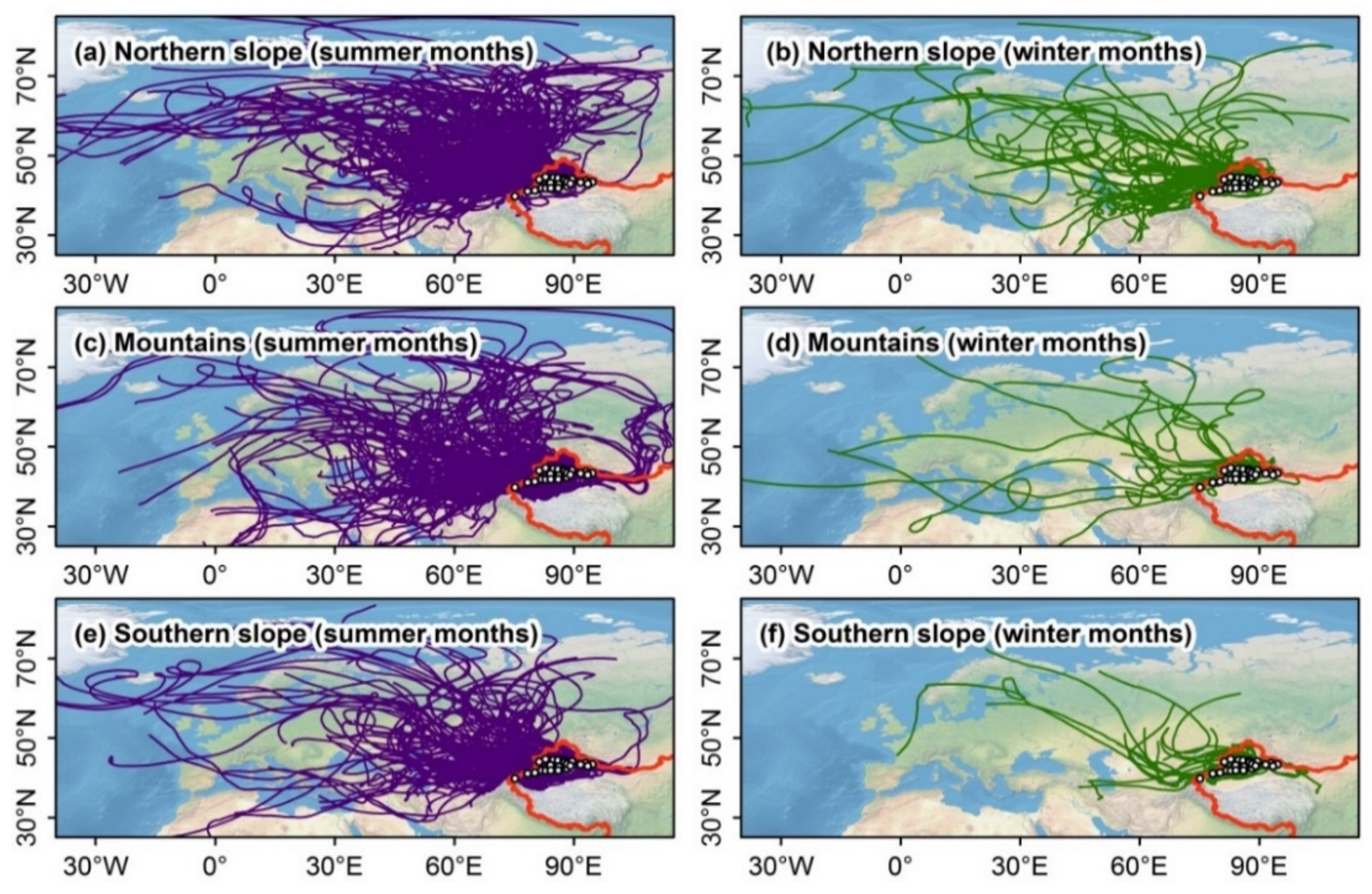
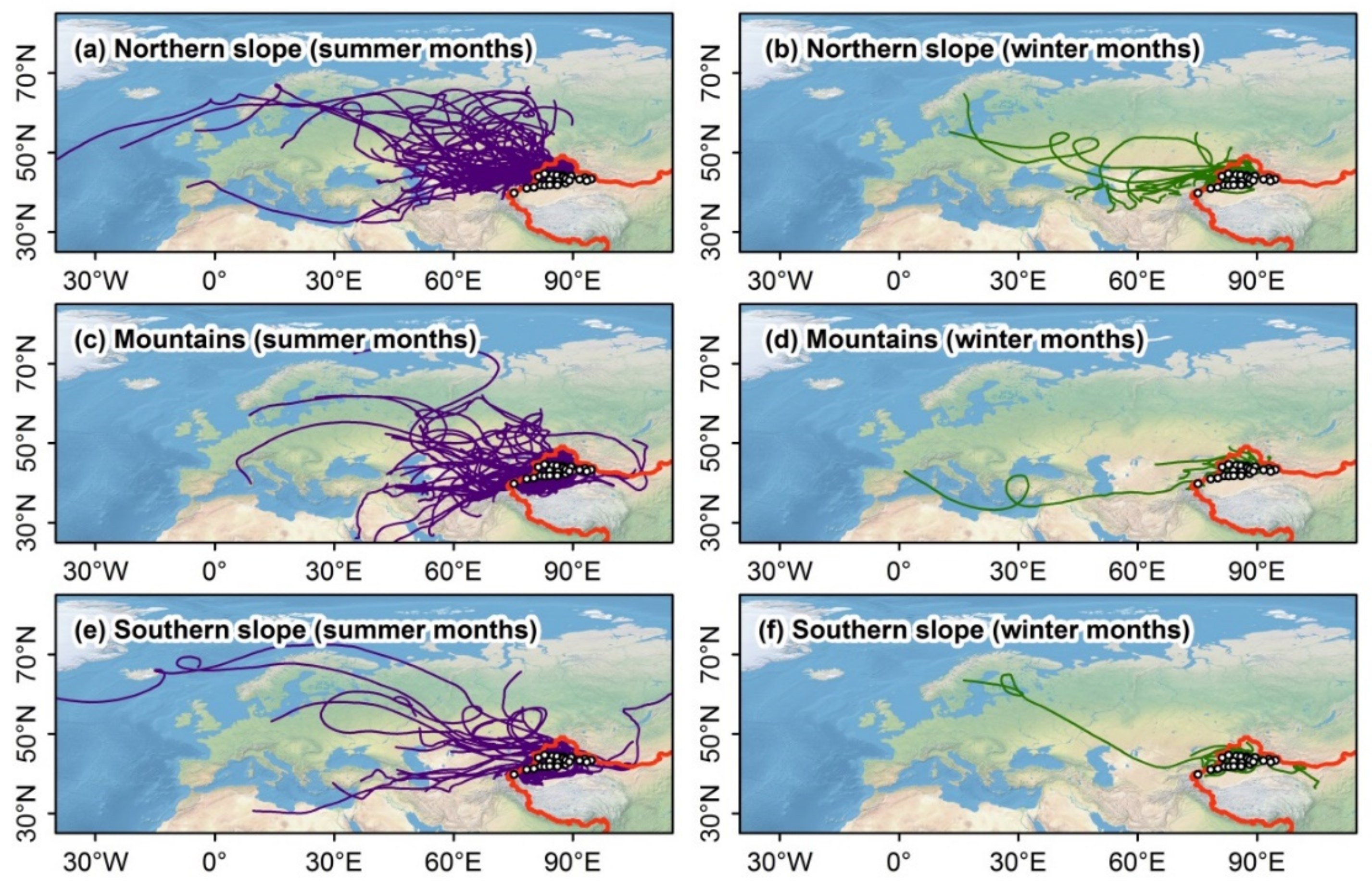
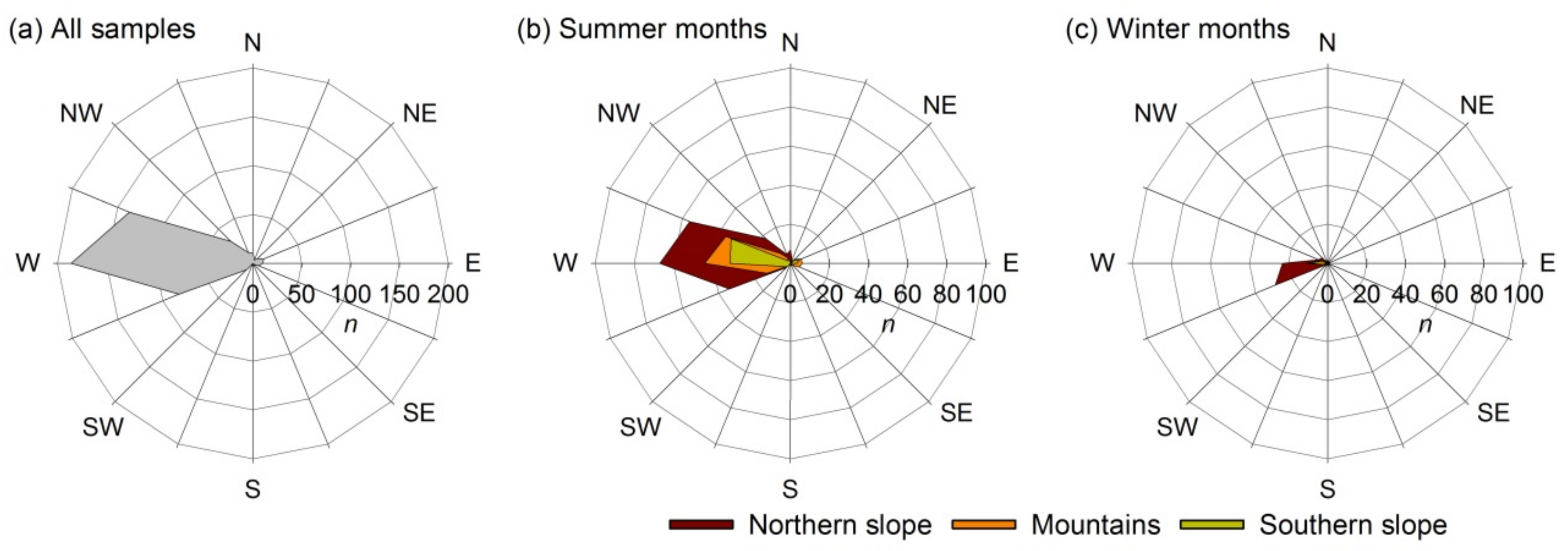
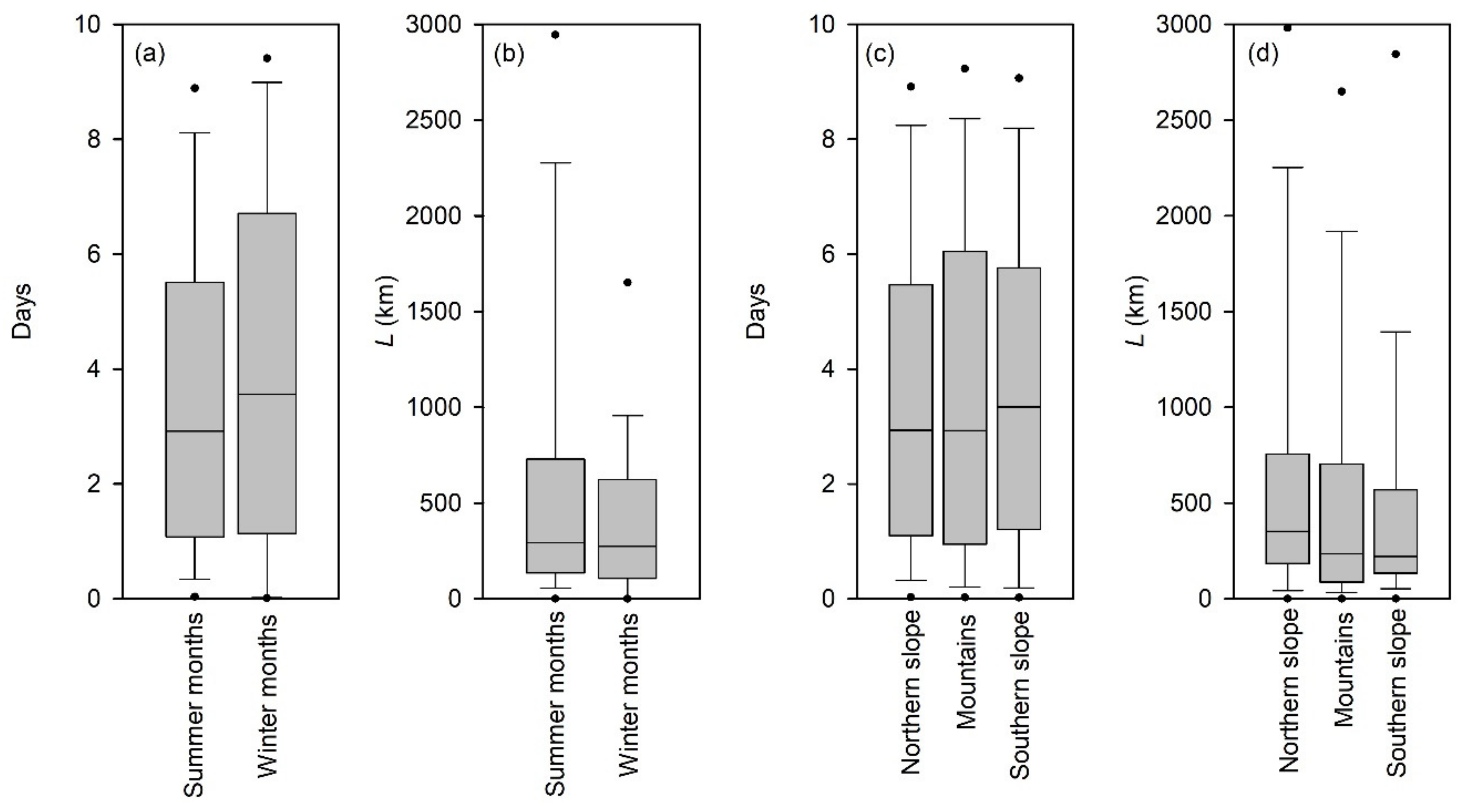
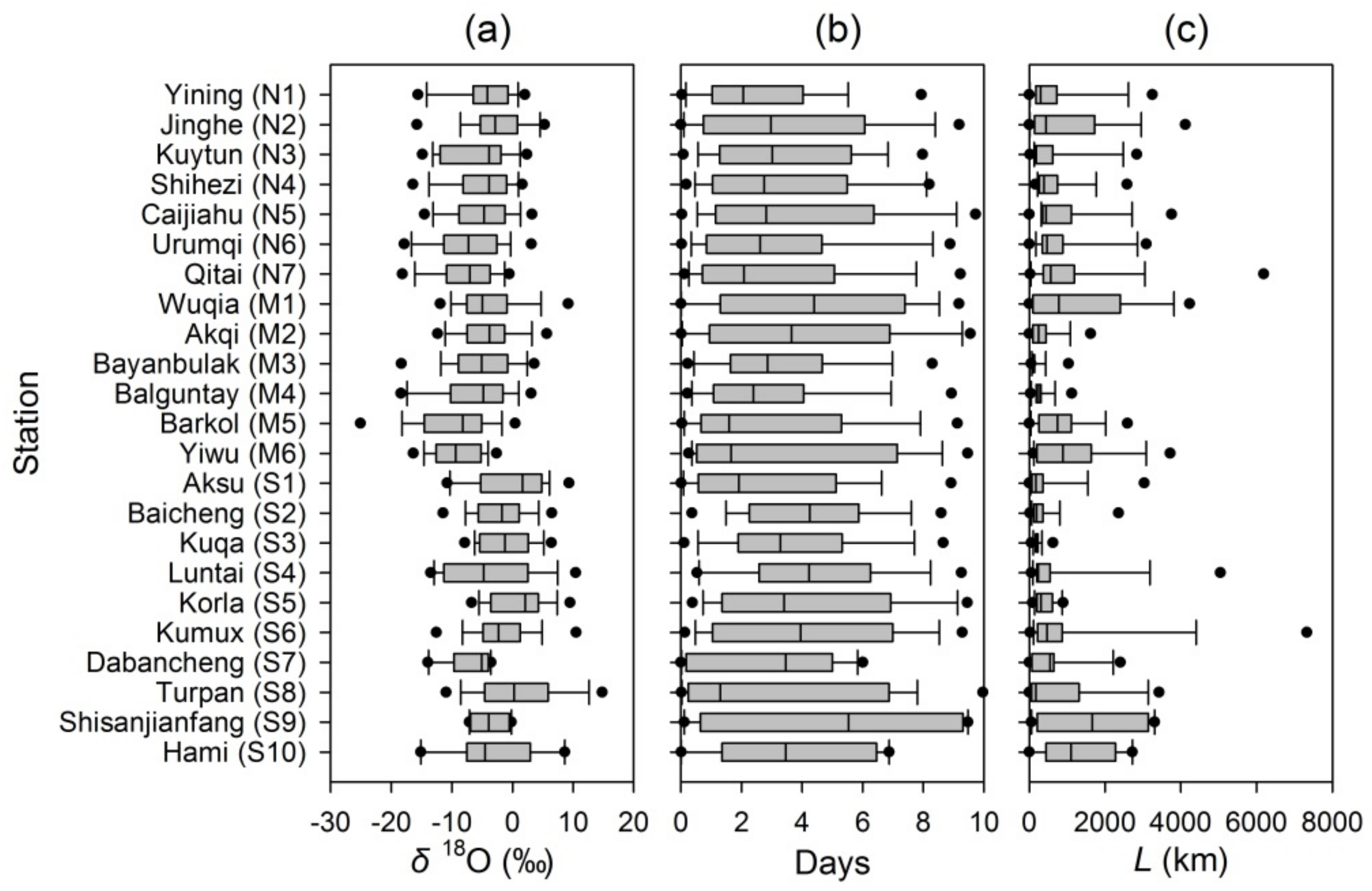
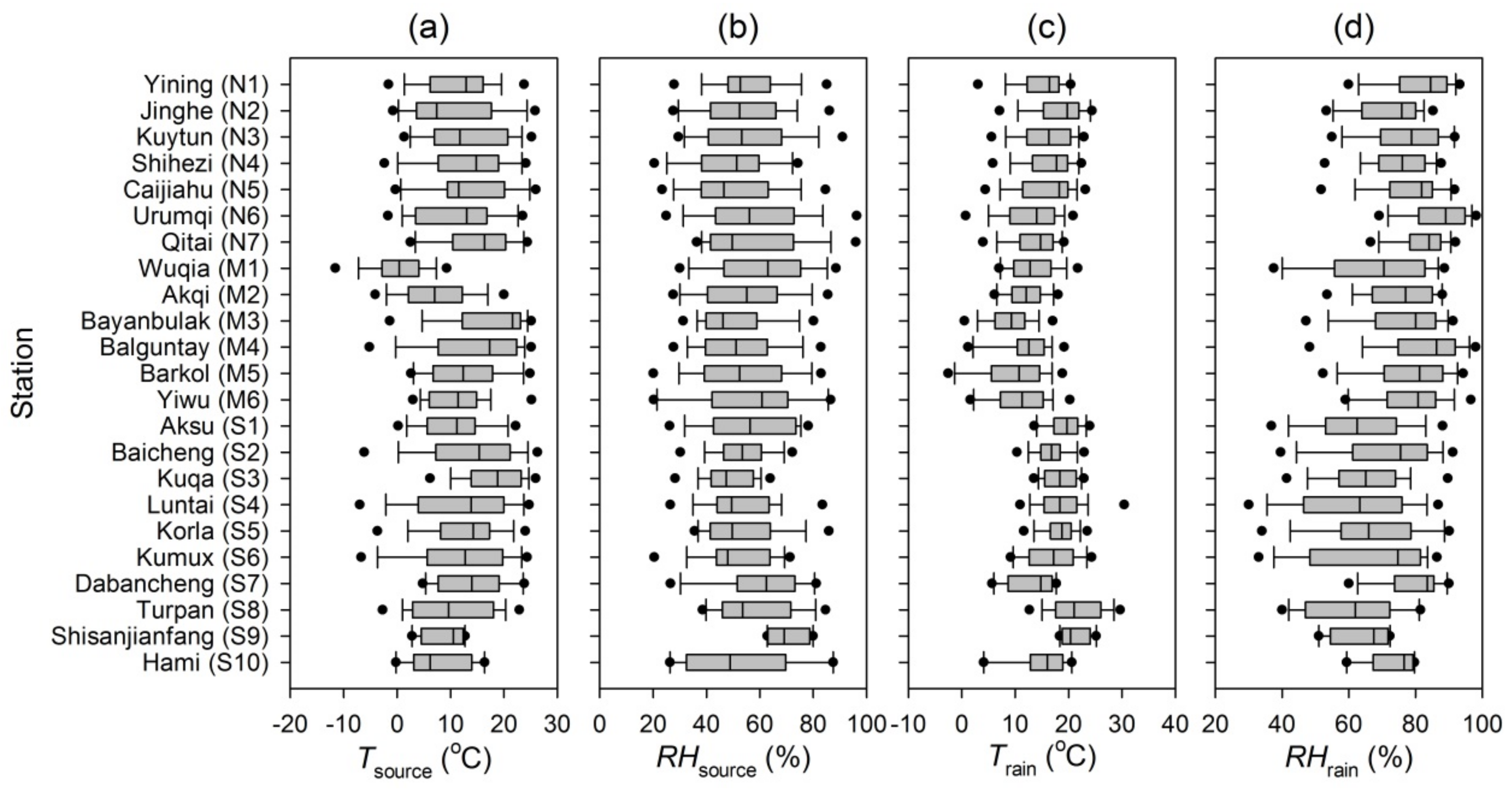
3.1. Lagrangian Diagnosed Moisture Sources
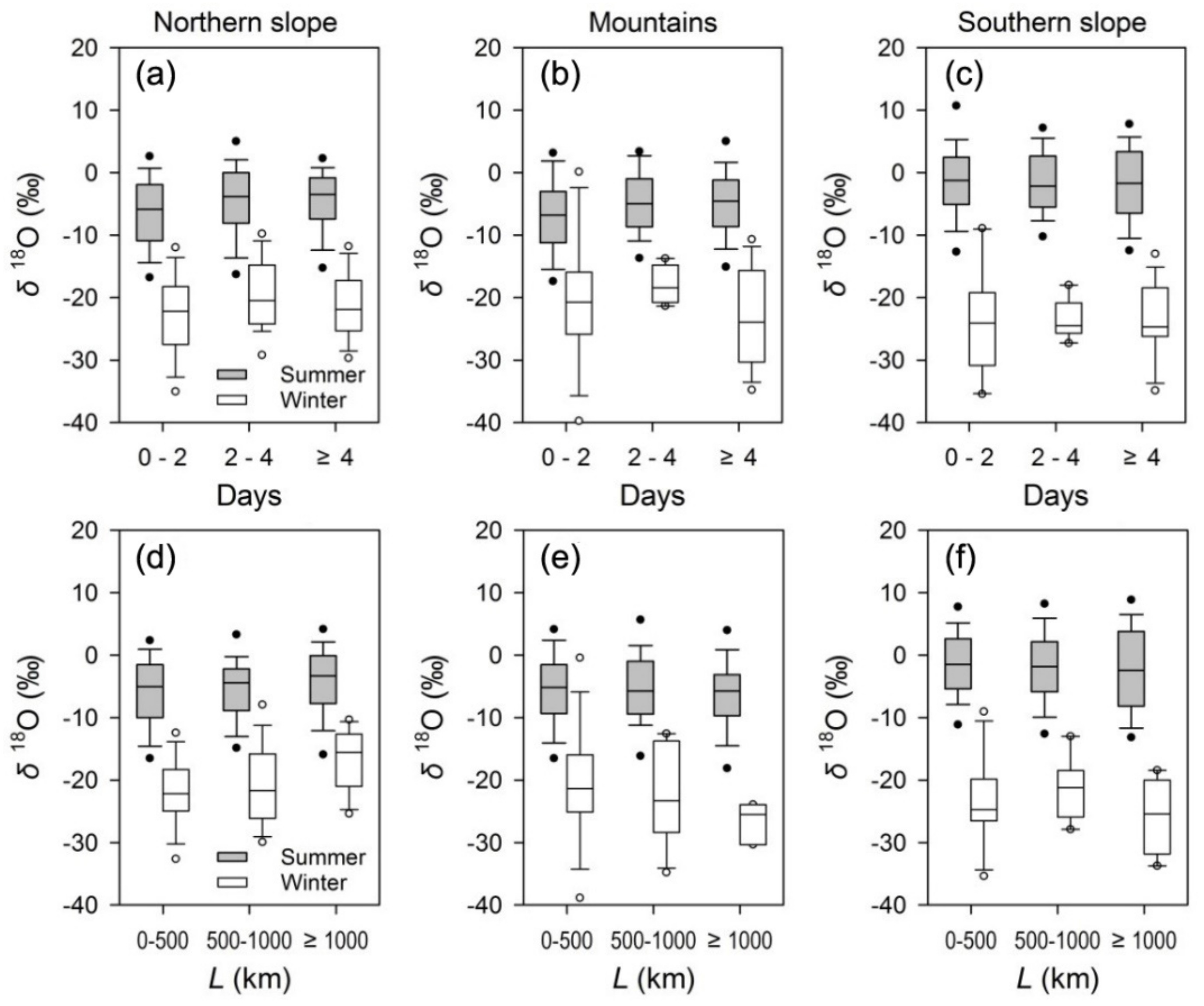
3.2. Relationship between Precipitation Isotope and Moisture Source
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, X.; Qian, C.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Variations and changes of annual precipitation in Central Asia over the last century. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, W.; Yang, Q. Hydro-climatic changes and their impacts on vegetation in Xinjiang, Central Asia. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 660, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, P.; Hamdi, R.; Luo, G.; He, H.; Zhang, M.; Termonia, P.; De Maeyer, P. Agriculture intensification increases summer precipitation in Tianshan Mountains, China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araguas-Araguas, L.; Froehlich, K.; Rozanski, K. Stable isotope composition of precipitation over Southeast Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 28721–28742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yao, T.; MacClune, K.; White, J.W.C.; Schilla, A.; Vaughn, B.; Vachon, R.; Ichiyanagi, K. Stable isotopic variations in west China: A consideration of moisture sources. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Pang, Z. Stable isotopes of precipitation in China: A consideration of moisture Sources. Water 2019, 11, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Masson, V.; Jouzel, J.; Stievenard, M.; Sun, W.; Jiao, K. Relationships between δ18O in precipitation and surface air temperature in the Urumqi River Basin, East Tianshan Mountains, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 3473–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Froehlich, K.; Huang, T.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, F. Processes affecting isotopes in precipitation of an arid region. Tellus B 2011, 63, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Hughes, C.E.; Zhu, X.; Dong, L.; Ren, Z.; Chen, F. Factors controlling stable isotope composition of precipitation in arid conditions: An observation network in the Tianshan Mountains, central Asia. Tellus B 2016, 68, 26206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, F.; Du, M.; Qiu, X.; Zhou, S. Meteoric water lines in arid Central Asia using event-based and monthly data. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, Y.; Han, D.; Xu, Z. Stable isotopic compositions in precipitation over wet island in Central Asia. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Tayier, R.; Wang, R. Characteristics of atmospheric precipitation isotopes and isotopic evidence for the moisture origin in Yushugou River basin, Eastern Tianshan Mountains, China. Quat. Int. 2015, 380–381, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S. Precipitation isotopes in the Tianshan Mountains as a key to water cycle in arid central Asia. Sci. Cold Arid. Reg. 2018, 10, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Che, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X. Influence of below-cloud evaporation on deuterium excess in precipitation of arid central Asia and its meteorological controls. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1973–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Che, Y.; Chen, F.; Qiang, F. Contribution of recycled moisture to precipitation in oases of arid central Asia: A stable isotope approach. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 3246–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Pang, Z. A positive altitude gradient of isotopes in the precipitation over the Tianshan Mountains: Effects of moisture recycling and sub-cloud evaporation. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Gao, J.; Yu, W.; Yang, X.; Risi, C.; Sturm, C.; Werner, M.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; et al. A review of climatic controls on δ18O in precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: Observations and simulations. Rev. Geophys. 2013, 51, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, F. Variations in the oxygen isotopic composition of precipitation in the Tianshan Mountains region and their significance for the Westerly circulation. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Crawford, J.; Hughes, C.E.; Du, M.; Liu, X. The effect of moisture source and synoptic conditions on precipitation isotopes in arid central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2667–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S. Affecting mechanism of moisture sources of isotopes in precipitation in the Tianshan Mountains based on GCMs and ice core. Arid. Zone Res. 2018, 35, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodemann, H.; Schwierz, C.; Wernli, H. Interannual variability of Greenland winter precipitation sources: Lagrangian moisture diagnostic and North Atlantic Oscillation influence. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D03107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodemann, H.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Schwierz, C.; Vinther, B.M.; Wernli, H. Interannual variability of Greenland winter precipitation sources: 2. Effects of North Atlantic Oscillation variability on stable isotopes in precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D12111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.; Hughes, C.E.; Parkes, S.D. Is the isotopic composition of event based precipitation driven by moisture source or synoptic scale weather in the Sydney Basin, Australia? J. Hydrol. 2013, 507, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krklec, K.; Domínguez-Villar, D.; Lojen, S. The impact of moisture sources on the oxygen isotope composition of precipitation at a continental site in central Europe. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of HYSPLIT_4 modelling system for trajectories, dispersion and deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Kleist, D.T.; Parrish, D.F.; Derber, J.C.; Treadon, R.; Wu, W.-S.; Lord, S. Introduction of the GSI into the NCEP Global Data Assimilation System. Weather Forecast. 2009, 24, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.M.M.; Miranda, P.M.A.; Siebesma, A.P.; Teixeira, J. An eddy-diffusivity/mass-flux parametrization for dry and shallow cumulus convection. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 130, 3365–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, A.K. Coupling of water vapor convergence, clouds, precipitation, and land-surface processes. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D10108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Herrmann, C.F. Problems in meteorology. Mon. Weather Rev. 1906, 34, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, J. Availability of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis at high altitudes: Theoretical considerations. Ecology 1972, 53, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.L. An empirical shortcut to the calculation of temperature and pressure at the lifted condensation level. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1968, 7, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Li, W.; Ma, Z.; Wang, P. Water-vapor source shift of Xinjiang region during the recent twenty years. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2007, 17, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Jin, S.; Dong, Z. Deuterium and oxygen 18 in precipitation and atmospheric moisture in the upper Urumqi River Basin, eastern Tianshan Mountains. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, X.; Sun, X.; Yuan, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Isotopic composition of precipitation over Arid Northwestern China and its implications for the water vapor origin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R. Physical Geography of the Tianshan Mountains in China; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Du, M.; Zhang, M.; Shi, M.; Jiao, R.; Wang, L. Precipitation Isotopes Associated with the Duration and Distance of Moisture Trajectory in a Westerly-Dominant Setting. Water 2019, 11, 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122434
Wang S, Du M, Zhang M, Shi M, Jiao R, Wang L. Precipitation Isotopes Associated with the Duration and Distance of Moisture Trajectory in a Westerly-Dominant Setting. Water. 2019; 11(12):2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122434
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shengjie, Mingxia Du, Mingjun Zhang, Mengyu Shi, Rong Jiao, and Liwei Wang. 2019. "Precipitation Isotopes Associated with the Duration and Distance of Moisture Trajectory in a Westerly-Dominant Setting" Water 11, no. 12: 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122434
APA StyleWang, S., Du, M., Zhang, M., Shi, M., Jiao, R., & Wang, L. (2019). Precipitation Isotopes Associated with the Duration and Distance of Moisture Trajectory in a Westerly-Dominant Setting. Water, 11(12), 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122434






