Short-Term Interactive Effects of Experimental Heat Waves and Turbidity Pulses on the Foraging Success of a Subtropical Invertivorous Fish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studied Species and Animal Collection
2.2. General Experimental Design
2.3. Experiment #1: Assessment of Prey Behaviour in Experimental Clear Water Conditions
2.4. Experiment #2: Effects of Heat Waves and Turbidity Pulses on Fish Foraging Success
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. Experiment #1: Assessment of Prey Behaviour in Experimental Clear Water Conditions
2.5.2. Experiment #2: Effects of Heat Waves and Turbidity Pulses on Fish Foraging Success
3. Results
3.1. Experiment #1: Assessment of Experimental Prey Behaviour in Clear Water Conditions
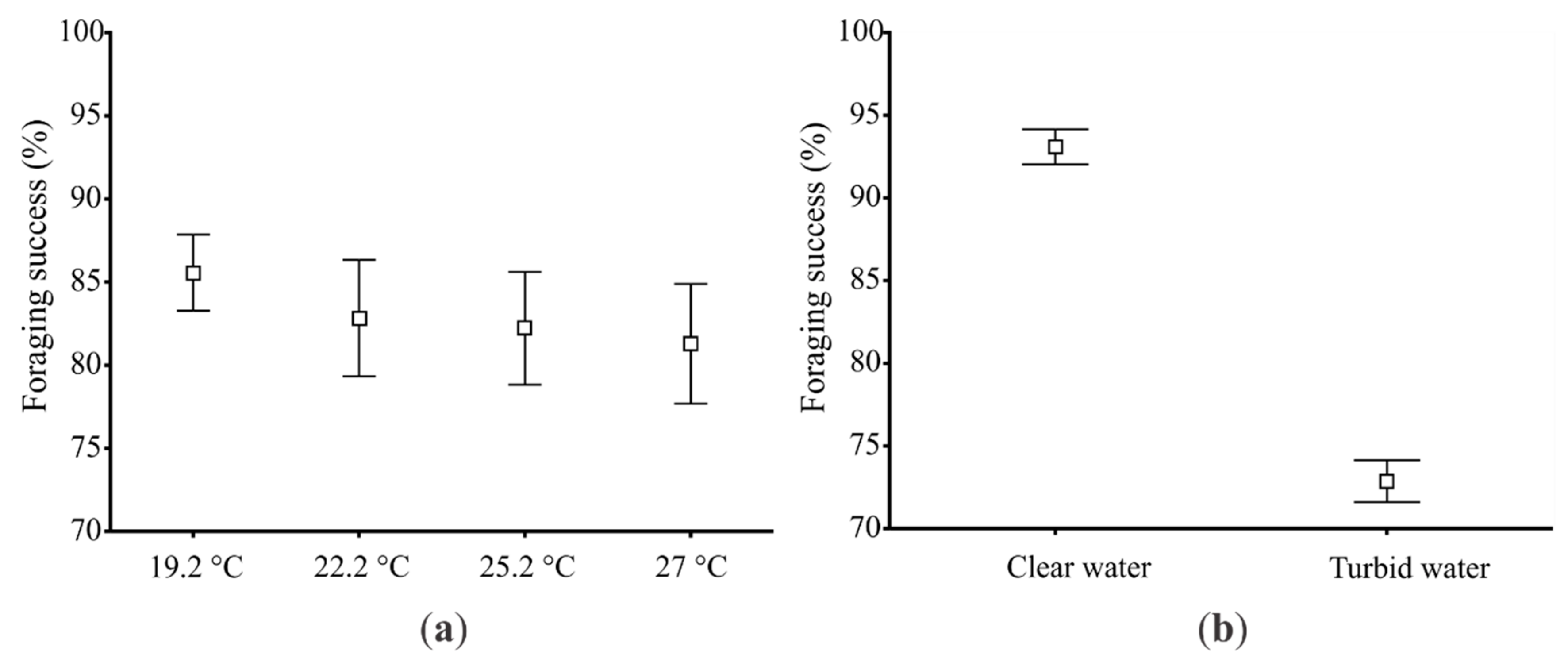
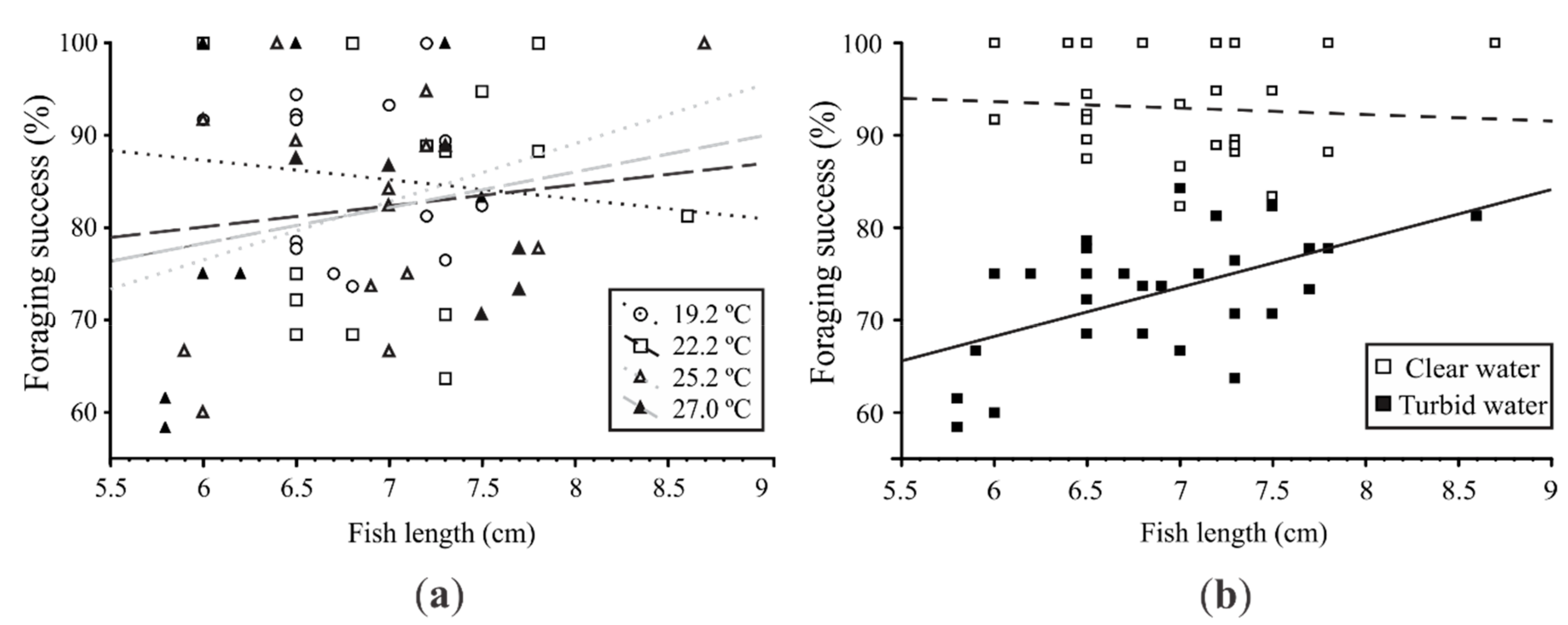
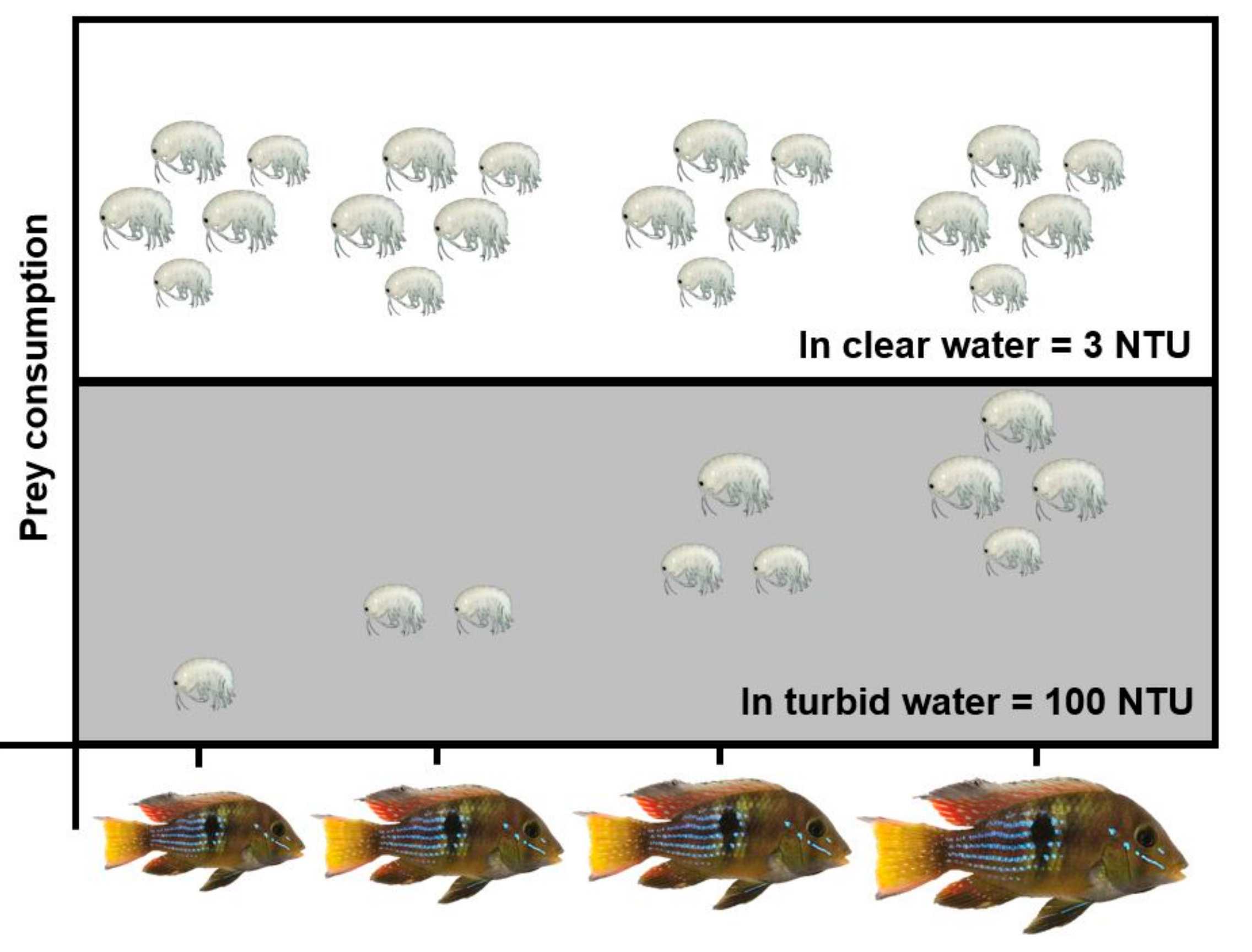
3.2. Experiment #2: Effects of Heat Waves and Turbidity Pulses on Fish Foraging Success
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers: Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation. A Special Report of Working Groups I and II of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; ISBN 9781139177245. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report.Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel in Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Marengo, J.A.; Chou, S.C.; Kay, G.; Alves, L.M.; Pesquero, J.F.; Soares, W.R.; Santos, D.C.; Lyra, A.A.; Sueiro, G.; Betts, R.; et al. Development of regional future climate change scenarios in South America using the Eta CPTEC/HadCM3 climate change projections: Climatology and regional analyses for the Amazon, São Francisco and the Paraná River basins. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 1829–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, F.; Huszar, V.; Farjalla, V.; Enrich-Prast, A.; Amado, A.; Ometto, J. Climate change in Brazil: perspective on the biogeochemistry of inland waters. Braz. J. Biol. 2012, 72, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellard, C.; Bertelsmeier, C.; Leadley, P.; Thuiller, W.; Courchamp, F. Impacts of climate change on the future of biodiversity. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, J.A.; Terborgh, J.; Brashares, J.S.; Power, M.E.; Berger, J.; Bond, W.J.; Carpenter, S.R.; Essington, T.E.; Holt, R.D.; Jackson, J.B.C.; et al. Trophic Downgrading of Planet Earth. Science 2011, 333, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.H.; Gillooly, J.F.; Allen, A.P.; Savage, V.M.; West, G.B. Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology 2004, 85, 1771–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, D.; Claireaux, G. The effects of environmental factors on the physiology of aerobic exercise. Fish Locomot. Eco-Ethol. Perspec. 2010, 296–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, J.P.; Miller, G.M.; Munday, P.L. Interactive effects of elevated temperature and CO2 on foraging behavior of juvenile coral reef fish. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 412, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, S.R.; Momo, F.R. Effects of body weight and temperature on the metabolic rate of Hyalella curvispina Shoemaker, 1942 (Amphipoda). Crustaceana 2009, 82, 1423–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pink, M.; Abrahams, M.V. Temperature and its impact on predation risk within aquatic ecosystems. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 73, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsolver, J.G.; Huey, R.B. Evolutionary analyses of morphological and physiological plasticity in thermally variable environments. Am. Zool. 1998, 38, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, J.G.; Loeschcke, V. Natural adaptation to environmental stress via physiological clock-regulation of stress resistance in Drosophila. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.M.; Kalbe, M.; Milinski, M.; Reusch, T. Mortality selection during the 2003 European heat wave in three-spined sticklebacks: Effects of parasites and MHC genotype. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leicht, K.; Jokela, J.; Seppälä, O. An experimental heat wave changes immune defense and life history traits in a freshwater snail. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 4861–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öhlund, G.; Hedström, P.; Norman, S.; Hein, C.L.; Englund, G. Temperature dependence of predation depends on the relative performance of predators and prey. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 282, 20142254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, L.I.; Castro, F.; Marquart, A.; Gaedke, U.; Weithoff, G.; Vos, M. Heated relations: Temperature-mediated shifts in consumption across trophic levels. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kirk, J.T.O. Effects of suspensoids (turbidity) on penetration of solar radiation in aquatic ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 1985, 125, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, K.A.; Winemiller, K.O. Hydrologic regime and turbidity influence entrance of terrestrial material into river food webs. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, W.T.Z.; Thomaz, S.M.; Murphy, K.J.; Silveira, M.J.; Mormul, R.P. Environmental predictors of the occurrence of exotic Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle and native Egeria najas Planch. in a sub-tropical river floodplain: The Upper River Paraná, Brazil. Hydrobiologia 2009, 632, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, B.R.S.; Mormul, R.P.; Chapman, B.B.; Lolis, L.A.; Fiori, L.F.; Benedito, E. Turbidity amplifies the non-lethal effects of predation and affects the foraging success of characid fish shoals. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksnes, D.L.; Utne, A.C.W. A revised model of visual range in fish. Sarsia 1997, 82, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horppila, J.; Nurminen, L. Effects of submerged macrophytes on sediment resuspension and internal phosphorus loading in Lake Hiidenvesi (southern Finland). Water Res. 2003, 37, 4468–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranåker, L.; Jönsson, M.; Nilsson, P.A.; Brönmark, C. Effects of brown and turbid water on piscivore-prey fish interactions along a visibility gradient. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, T.E.; Stewart, W.J.; Wainwright, P.C. Turbulence, Temperature, and Turbidity: The ecomechanics of predator–prey interactions in fishes. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2015, 55, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishingrad, V.; Musgrove, A.B.; Chivers, D.P.; Ferrari, M.C.O. Risk in a changing world: Environmental cues drive anti-predator behaviour in lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens) in the absence of predators. Behaviour 2015, 152, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, M.; Kattenfeld, M. The role of turbidity as a constraint on predator–prey interactions in aquatic environments. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1997, 40, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmesan, C.; Root, T.L.; Willig, M.R. Impacts of extreme weather and climate on terrestiral biota. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.C.O.; Ranåker, L.; Weinersmith, K.L.; Young, M.J.; Sih, A.; Conrad, J.L. Effects of turbidity and an invasive waterweed on predation by introduced largemouth bass. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2014, 97, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangles, O.; Magal, C.; Pierre, D.; Olivier, A.; Casas, J. Variation in morphology and performance of predator-sensing system in wild cricket populations. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlberger, J. Climate warming and ectotherm body size–from individual physiology to community ecology. Funct. Ecol. 2013, 27, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breck, J.E.; Gitter, M.J. Effect of fish size on the reactive distance of bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus) Sunfish. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1983, 40, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.J.; Crowder, L.B.; Rice, J.A.; Marschall, E.A. Larval size and recruitment mechanisms in fishes: Toward a conceptual framework. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1988, 45, 1657–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundvall, D.; Svanbäck, R.; Persson, L.; Byström, P. Size-dependent predation in piscivores: Interactions between predator foraging and prey avoidance abilities. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1999, 56, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, P.A.; Beckmann, C.; Stamps, J.A. Small within-day increases in temperature affects boldness and alters personality in coral reef fish. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira-de Mello, F.; de Oliveira, V.A.; Loverde-Oliveira, S.M.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Barquín, J.; Iglesias, C.; Silva, T.S.F.; Duque-Estrada, C.H.; Silió-Calzada, A.; Mazzeo, N. The structuring role of free-floating plants on the fish community in a tropical shallow lake: An experimental approach with natural and artificial plants. Hydrobiologia 2016, 778, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Vidal, N.; Eguren, G.; Loureiro, M. Length–weight relationships of 21 fish species from the lower section of the Santa Lucía river basin (Canelones-Montevideo, Uruguay). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2009, 25, 491–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rodríguez, A.; Silva, I.; de Ávila-Simas, S.; Stebniki, S.; Bastian, R.; Massaro, V.M.; Pais, J.; Tesitore, G.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; D’Anatro, A.; et al. Diets and trophic structure of fish assemblages in a large and unexplored subtropical river: The Uruguay River. Water 2019, 11, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, M.; Zarucki, M.; Malabarba, L.R.; González-Bergonzoni, I. A new species of Gymnogeophagus Miranda Ribeiro from Uruguay (Teleostei: Cichliformes). Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2016, 14, e150082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartz, S.M.; Bruschi, J.W.; Formehl, M.V. Idade e crescimento de Gymnogeophagus lacustris Reis & Malabarba, um Cichlidae endêmico da bacia hidrográfica do Rio Tramandaí, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Rev. Bras. Zool. 1998, 15, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.; Iglesias, C.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Clemente, J.M.; Jensen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Jeppesen, E. Effects of habitat complexity on community structure and predator avoidance behaviour of littoral zooplankton in temperate versus subtropical shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullander, S.O. Cichlidae (Cichlids). In Checklist of the Freshwater Fishes of South and Central America, 1st ed.; Reis, R.E., Kullander, S.O., Ferraris, C.J.J., Eds.; EDIPUCRS: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2003; pp. 605–654. [Google Scholar]
- Yafe, A.; Loureiro, M.; Scasso, F.; Quintans, F. Feeding of two cichlidae species (Perciformes) in an hypertrophic urban lake. Iheringia Sér. Zool. 2002, 92, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Bergonzoni, I.; Jeppesen, E.; Vidal, N.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Goyenola, G.; López-Rodriguez, A.; Meerhoff, M. Potential drivers of seasonal shifts in fish omnivory in a subtropical stream. Hydrobiologia 2016, 768, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, F.S.; Juanes, F. Predator size-prey size relationships of marine fish predators: Interspecific variation and effects of ontogeny and body size on trophic-niche breadth. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 208, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galassi, M.E.; Franceschini, M.C.; Neiff, A. Population estimates of Hyalella curvispina Shoemaker (Amphipoda) in aquatic vegetation of Northeastern Argentinian ponds. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2006, 18, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorojo Moreno, V.; García, I.; Maroñas, M.E.; Colautti, D.C. Feeding of Gymnogeophagus meridionalis (Osteichthyes, Cichlidae) in an urban stream. Rev. Mus. Argent. Cienc. Nat. Nueva Ser. 2017, 19, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Meerhoff, M.; Pekcan-Hekim, Z.; Jeppesen, E. Substantial differences in littoral fish community structure and dynamics in subtropical and temperate shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelós, M.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Goyenola, G.; Iglesias, C.; Fosalba, C.; García-Rodríguez, F.; Pacheco, J.P.; García, S.; Meerhoff, M. Seasonal and diel changes in fish activity and potential cascading effects in subtropical shallow lakes with different water transparency. Hydrobiologia 2010, 646, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, J.C.; Skorupka, C.N.; Bilos, C.; Tatone, L.; Cappelletti, N.; Carolina Migoya, M.; Astoviza, M.; Speranza, E. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of water quality in the Uruguay River, Argentina. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, B.; Torchiano, M. Package ′lmPerm′. 2016. Available online: ftp://ftp.math.ethz.ch/sfs/pub/Software/R-CRAN/web/packages/lmPerm/lmPerm.pdf (accessed on 4 July 2019).
- Dowdy, S.; Wearden, S.; Chilko, D. Statistics for research; John Wiley and Sons: Somerset, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, G.P.; Keough, M.J. Experimental Design and Data Analysis for Biologists; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe, M.A.B.; Bassett, D.K.; Webb, J.F. Feeding in the dark: Lateral-line-mediated prey detection in the peacock cichlid Aulonocara stuartgranti. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 2060–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, B.R.S.; Mormul, R.P.; Benedito, E. Non-additive effects of macrophyte cover and turbidity on predator–prey interactions involving an invertivorous fish and different prey types. Hydrobiologia 2013, 713, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemanse, N.J.; Both, C.; Drent, P.J.; Tinbergen, J.M. Fitness consequences of avian personalities in a fluctuating environment. Proc. R. Soc. Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, B.B.; Morrell, L.J.; Tosh, C.R.; Krause, J. Behavioural consequences of sensory plasticity in guppies. Proc. R. Soc. Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverino, G.; Ruberto, T.; Staaks, G.; Mehner, T. Tank size alters mean behaviours and individual rank orders in personality traits of fish depending on their life stage. Anim. Behav. 2016, 115, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothen, D.; Curtis, E.; Yanong, R. Tolerance of yolk sac and free-swimming fry of the zebra danio Brachydanio rerio, black tetra Gymnocorymbus ternetzi, Buenos Aires tetra Hemigrammus caudovittatus, and blue gourami Trichogaster trichopterus to therapeutic doses of formalin and sodium chloride. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2002, 14, 204–208. [Google Scholar]
- Kingsolver, J.G.; Pfennig, D.W. Individual-level selection as a cause of Cope’s rule of phyletic size increase. Evolution 2007, 58, 1608–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hone, D.W.E.; Benton, M.J. The evolution of large size: How does Cope’s Rule work? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vucic-Pestic, O.; Ehnes, R.B.; Rall, B.C.; Brose, U. Warming up the system: Higher predator feeding rates but lower energetic efficiencies. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.T.; Kiesecker, J.M.; Chivers, D.P.; Blaustein, A.R. The direct and indirect effects of temperature on a predator–prey relationship. Can. J. Zool. 2001, 79, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell, A.I.; Pawar, S.; Savage, V.M. Temperature dependence of trophic interactions are driven by asymmetry of species responses and foraging strategy. J. Anim. Ecol. 2013, 83, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.I.A.; Dossena, M.; Bohan, D.A.; Jeppesen, E.; Kordas, R.L.; Ledger, M.E.; Meerhoff, M.; Moss, B.; Mulder, C.; Shurin, J.B.; et al. Mesocosm experiments in ecological climate change research. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2013, 48, 71–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, W.E.; Graeb, B.D.S.; Chipps, S.R.; Klumb, R.A. Vulnerability of age-0 pallid sturgeon Scaphirhynchus albus to predation; effects of predator type, turbidity, body size, and prey density. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2014, 97, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Effects | Degrees of Freedom | Means of Squares | F | P | |
| Fish presence (FP) | 1 | 0.82 | 235.58 | < 0.001 | |
| Water temperature (WT) | 1 | 0.11 | 30.80 | < 0.001 | |
| Interaction FP × WT | 1 | 0.05 | 15.58 | < 0.001 | |
| Error | 24 | 0.01 | |||
| Treatment Combination | Amphipods out of Water Median (Mean ± SD) | Post-hoc Comparison | |||
| Fish absent at 19.2 °C | 1 (0.9 ± 0.7) | a | |||
| Fish absent at 27.0 °C | 2 (1.6 ± 0.5) | a | |||
| Fish present at 19.2 °C | 6 (5.9 ± 0.9) | b | |||
| Fish present at 27.0 °C | 9 (9.7 ± 1.7) | c | |||
| Main Effects | Degrees of Freedom | Means of Squares | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turbidity (TU) | 1 | 0.040 | 12.570 | 0.001 |
| Water temperature (WT) | 3 | 0.005 | 1.560 | 0.214 |
| Fish length (FL) | 1 | 0.005 | 1.686 | 0.201 |
| Interaction TU × WT | 3 | 0.002 | 0.490 | 0.691 |
| Interaction TU × FL | 1 | 0.020 | 6.247 | 0.017 |
| Interaction WT × FL | 3 | 0.005 | 1.608 | 0.203 |
| Interaction TU × WT × FL | 3 | 0.001 | 0.418 | 0.741 |
| Error | 40 | 0.003 | ||
| t | P | |||
| Clear Water | −0.383 | 0.703 | ||
| Turbid Water | 3.292 | 0.001 | ||
| 19.2 °C | −0.269 | 0.789 | ||
| 22.2 °C | 0.453 | 0.652 | ||
| 25.2 °C | 1.392 | 0.170 | ||
| 27.0 °C | 0.833 | 0.409 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Figueiredo, B.R.S.; Calvo, C.; López-Rodríguez, A.; Mormul, R.P.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Benedito, E.; Meerhoff, M. Short-Term Interactive Effects of Experimental Heat Waves and Turbidity Pulses on the Foraging Success of a Subtropical Invertivorous Fish. Water 2019, 11, 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102109
Figueiredo BRS, Calvo C, López-Rodríguez A, Mormul RP, Teixeira-de Mello F, Benedito E, Meerhoff M. Short-Term Interactive Effects of Experimental Heat Waves and Turbidity Pulses on the Foraging Success of a Subtropical Invertivorous Fish. Water. 2019; 11(10):2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102109
Chicago/Turabian StyleFigueiredo, Bruno R. S., Clementina Calvo, Anahí López-Rodríguez, Roger P. Mormul, Franco Teixeira-de Mello, Evanilde Benedito, and Mariana Meerhoff. 2019. "Short-Term Interactive Effects of Experimental Heat Waves and Turbidity Pulses on the Foraging Success of a Subtropical Invertivorous Fish" Water 11, no. 10: 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102109
APA StyleFigueiredo, B. R. S., Calvo, C., López-Rodríguez, A., Mormul, R. P., Teixeira-de Mello, F., Benedito, E., & Meerhoff, M. (2019). Short-Term Interactive Effects of Experimental Heat Waves and Turbidity Pulses on the Foraging Success of a Subtropical Invertivorous Fish. Water, 11(10), 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102109







