Inter-Seasonal Precipitation Variability over Southern China Associated with Commingling Effect of Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. IOD and ENSO Data
2.2. Precipitation Data
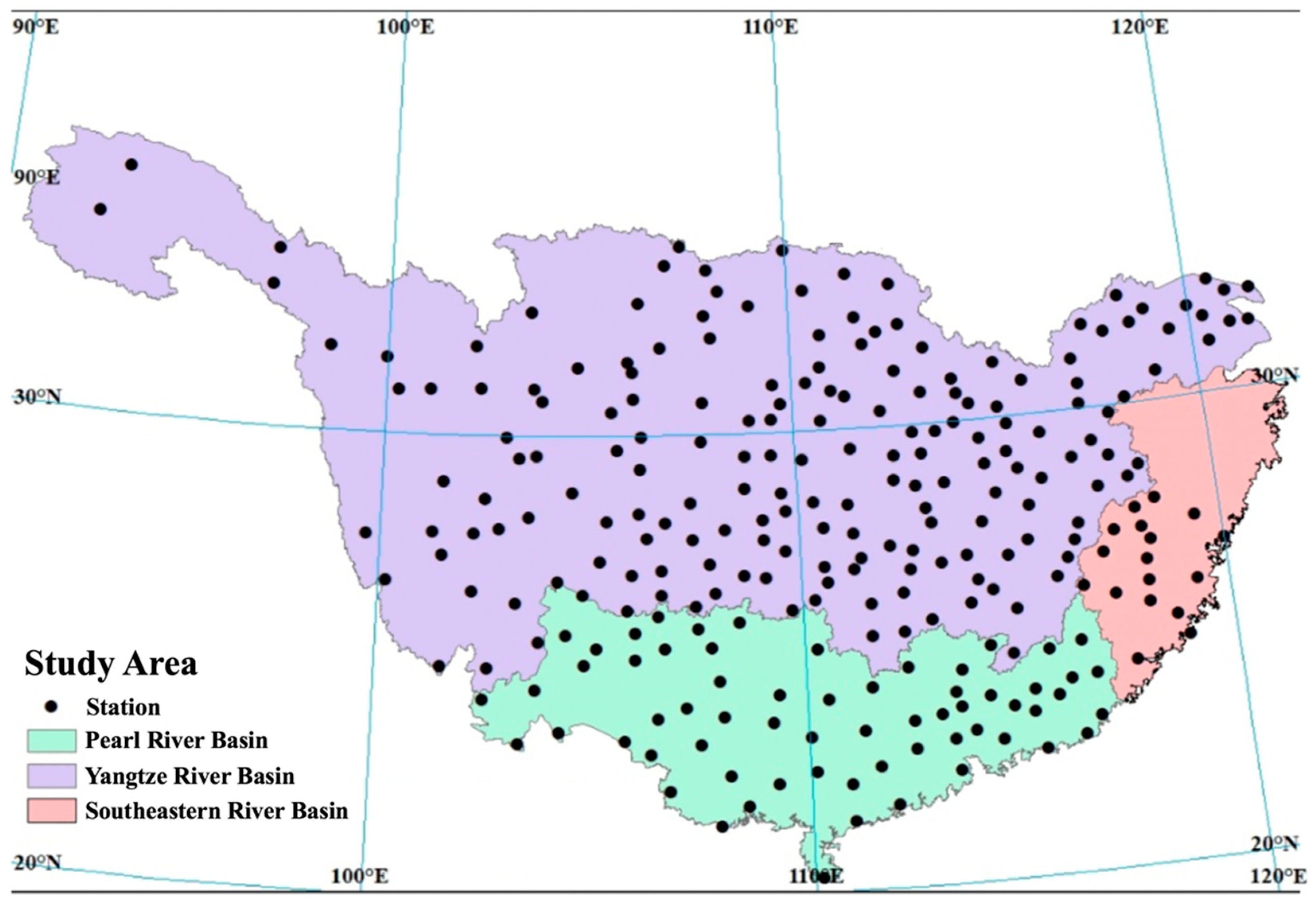
2.3. Study Area
2.4. Trend Detection
2.5. IBB Simulation
3. Analysis Results
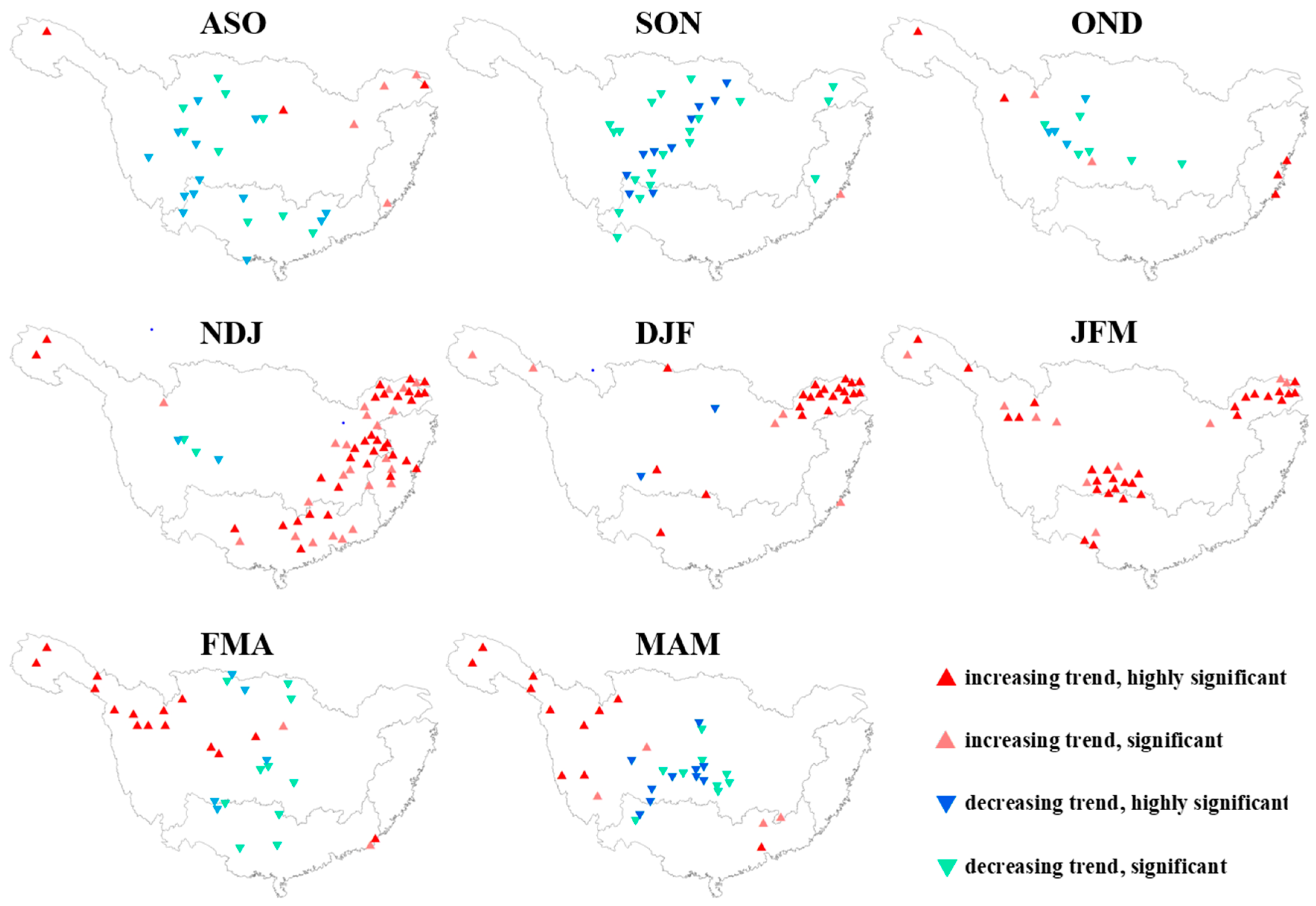
3.1. Trends in Seasonal Precipitation in SC
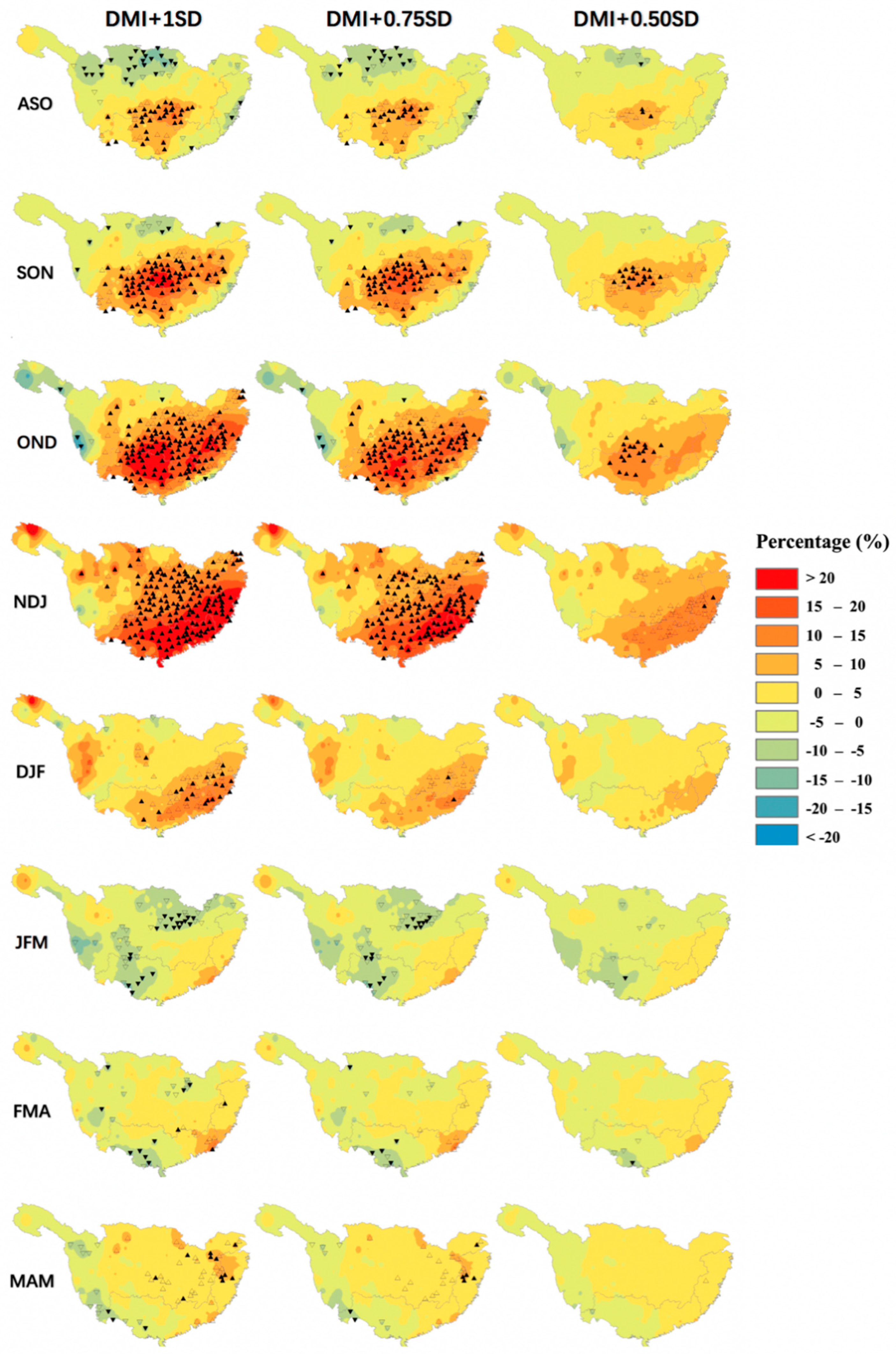
3.2. Inter-Seasonal Rainfall Variability Associated with IOD
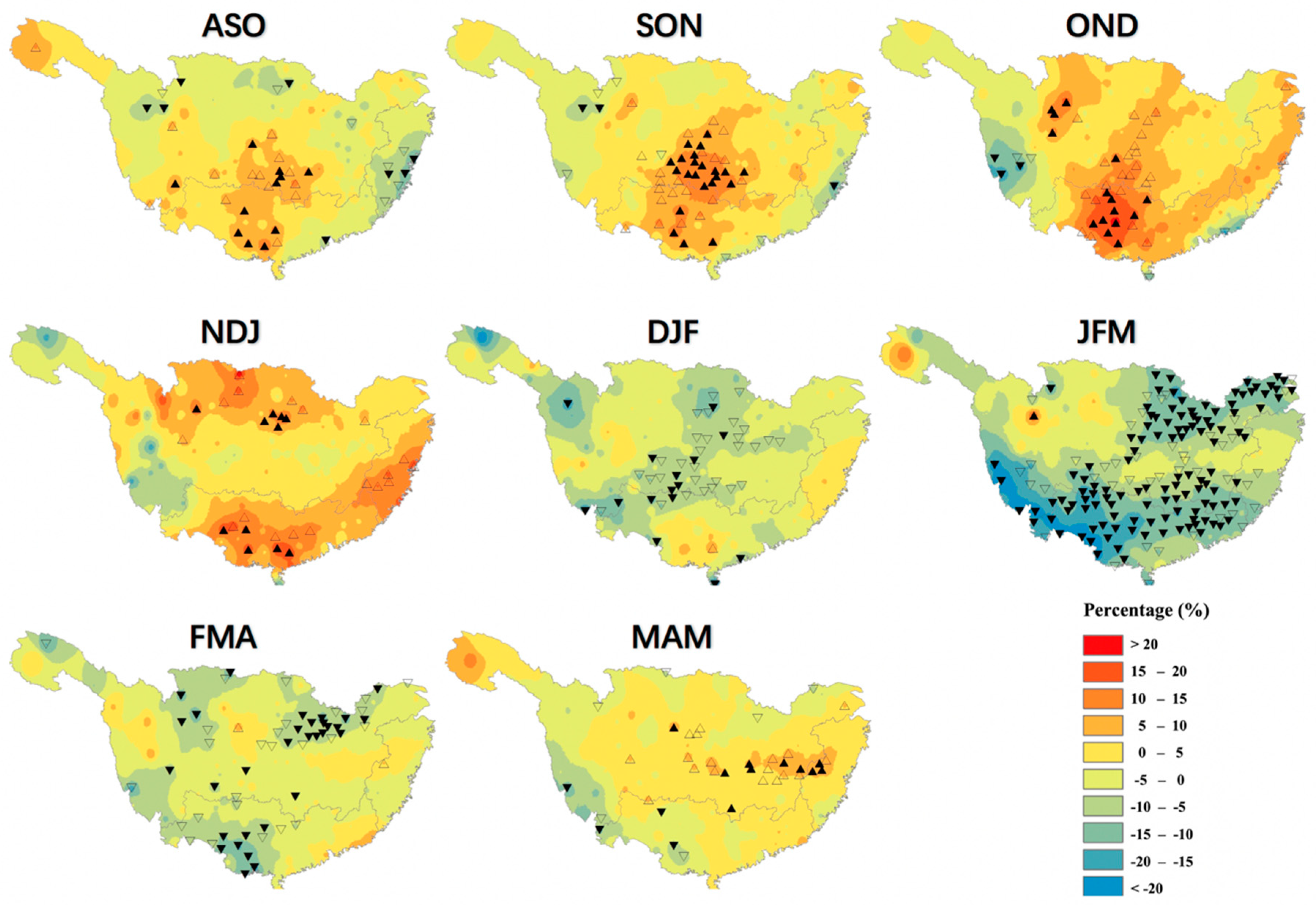
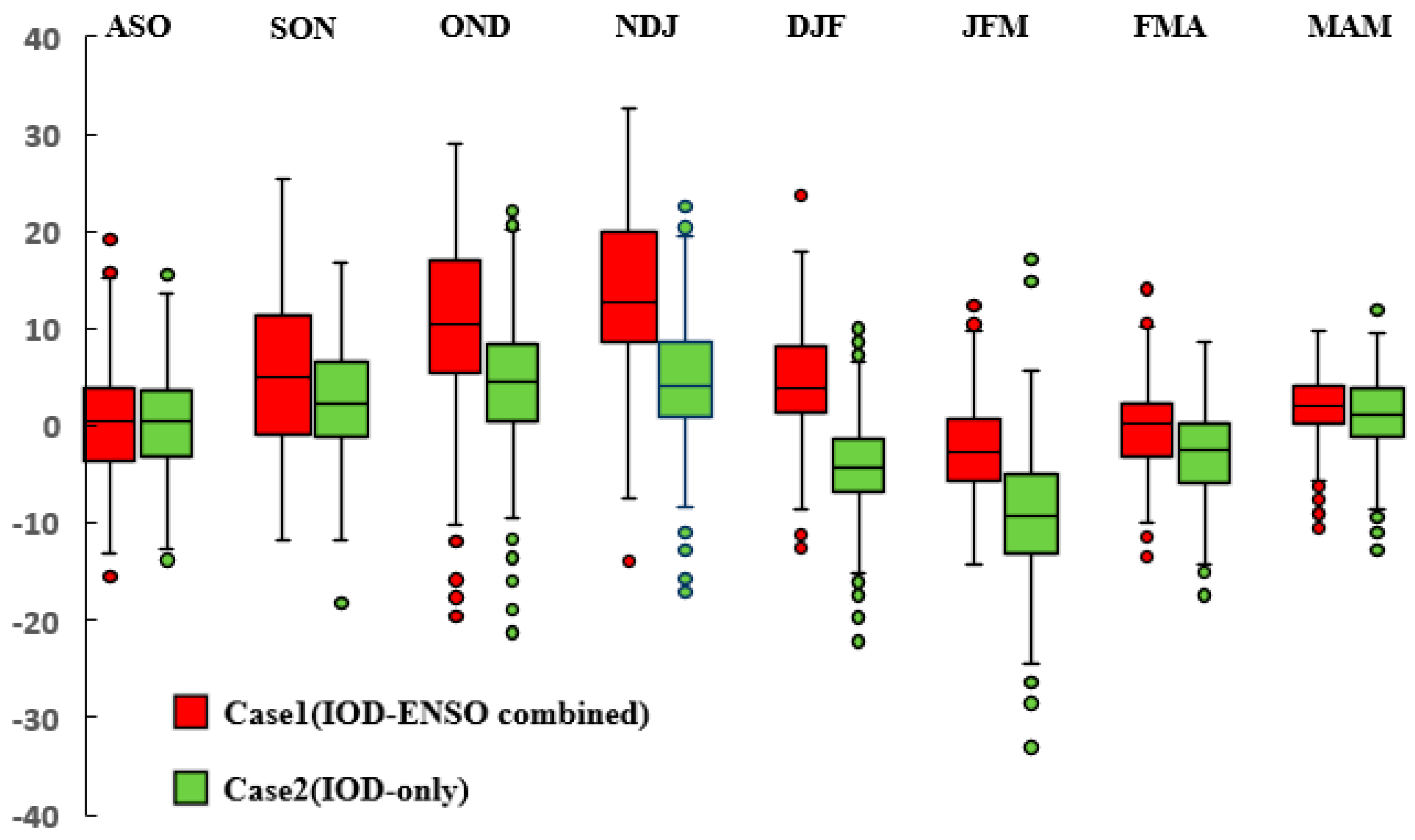
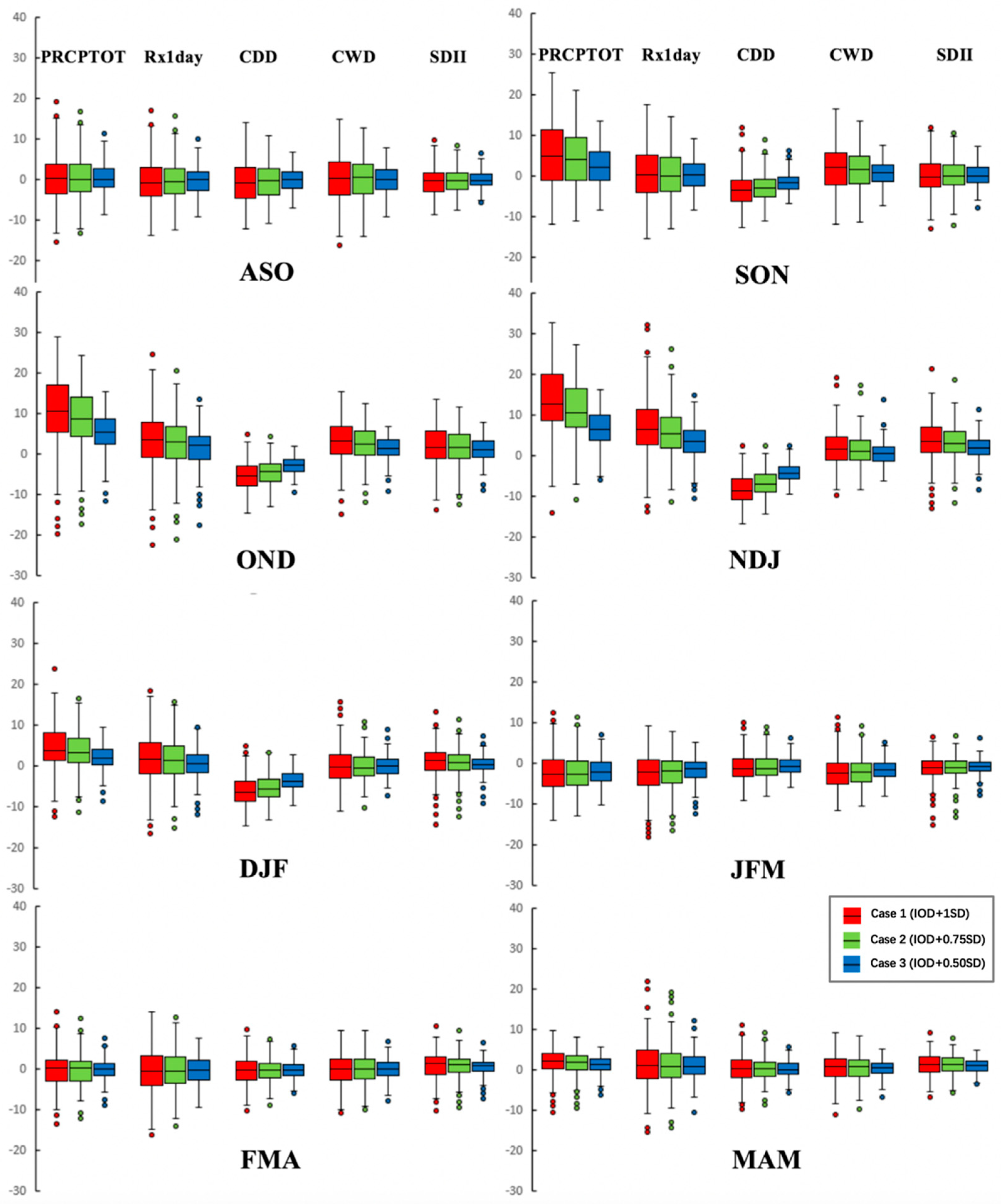
3.3. Commingling Effect of IOD and ENSO on Seasonal Precipitation
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behera, S.K.; Krishnan, R.; Yamagata, T. Unusual ocean-atmosphere conditions in the tropical Indian Ocean during 1994. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 3001–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.H.; Goswami, B.N.; Vinayachandran, P.N.; Yamagata, T. A dipole mode in the Tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 1999, 401, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, P.J.; Moore, A.M.; Loschnigg, J.P.; Leben, R.R. Coupled ocean-atmosphere dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98. Nature 1999, 401, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashok, K.; Guan, Z.; Yamagata, T. Influence of the Indian Ocean Dipole on the Australian winter rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, E.; Slingo, J.; Sperber, K.R. An Observational Study of the Relationship between Excessively Strong Short Rains in Coastal East Africa and Indian Ocean SST. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.C.; Behera, S.K.; Yamagata, T. Indian Ocean Dipole influence on South American rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L14S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.H.; Yamagata, T. Possible impacts of Indian Ocean Dipole mode events on global climate. Clim. Res. 2003, 25, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.; Guan, Z.; Yamagata, T. Impact of the Indian Ocean dipole on the relationship between the Indian monsoon rainfall and ENSO. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 4499–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Rensch, P.V.; Cowan, T.; Hendon, H.H. Teleconnection Pathways of ENSO and the IOD and the Mechanisms for Impacts on Australian Rainfall. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3910–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mu, M. The Influence of the Indian Ocean Dipole on Atmospheric Circulation and Climate. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 18, 830–843. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.; Rensch, P.V.; Cowan, T.; Hendon, H.H. An Asymmetry in the IOD and ENSO Teleconnection Pathway and Its Impact on Australian Climate. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6318–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Yamagata, T. The unusual summer of 1994 in East Asia: IOD teleconnections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Cai, W.; Guo, X.; Ng, B. The asymmetric influence of the positive and negative IOD events on China’s rainfall. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Y. Effects of Indian Ocean SSTA with ENSO on winter rainfall in China. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2014, 20, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, W.; Li, C. Influences of the Indian Ocean Dipole on the Asian summer monsoon in the following year. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Yuan, H.; Li, C. The relationship between Indian Ocean SSTA Dipole Index and the precipitation and temperature over China. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2012, 4, 732. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yuan, H.; Guan, Z. Effects of ENSO on the relationship between IOD and summer rainfall in China. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2009, 15, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, M. A Study of the Indian Ocean Dipole Influence on Climate Variations over East Asian Monsoon Region. Clim. Environ. Res. 2004, 3, 461–462. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Yu, L.; Hu, D. Influence of Indian Ocean subtropical dipole on spring rainfall over China. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Z.; Yang, S.; Xu, J. Relationship between Indian Ocean Dipole and Autumn Rainfall in West China. Plateau Meteorol. 2015, 4, 461–462. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, R.; Behera, S.K.; Masumoto, Y.; Jin, F.; Lukas, R.; Yamagata, T. Interaction between El Niño and Extreme Indian Ocean Dipole. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 726–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhu, C.; Wang, W. The cooperative impacts of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation and the Indian Ocean Dipole on the interannual variability of autumn rainfall in China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 1987–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, H.; Xie, S.P.; McCreary, J.P.; Murtugudde, R. Impact of Indian Ocean Sea Surface Temperature on Developing El Niño. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, T.; Behera, S.K.; Luo, J.; Masson, S.; Jury, M.R.; Rao, S.A. Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Variability in the Tropical Indian Ocean. Geophys. Monogr. Am. Geophys. Union 2004, 147, 189–212. [Google Scholar]
- Annamalai, H.; Murtugudde, R.; Potemra, J.; Xie, S.P.; Liu, P.; Wang, B. Coupled dynamics over the Indian Ocean: Spring initiation of the Zonal Mode. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2003, 50, 2305–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumo, T.; Vialard, J.; Lengaigne, M.; de Boyer Montegut, C.; Behera, S.K.; Luo, J.; Cravatte, S.; Masson, S.; Yamagata, T. Influence of the state of the Indian Ocean Dipole on the following year’s El Niño. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P. Influences of ENSO, NAO, IOD and PDO on seasonal precipitation regimes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3556–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, A.; Sharma, A.; Santoso, A.; Westra, S. Impact of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation, Indian Ocean Dipole, and Southern Annular Mode on Daily to Subdaily Rainfall Characteristics in East Australia. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 1665–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Knight, R.W.; Plummer, N. Trends in high-frequency climate variability in the twentieth century. Nature 1995, 377, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chao, B.; Chen, J.; Wilson, C. Terrestrial water storage anomalies of Yangtze River Basin droughts observed by GRACE and connections with ENSO. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 126, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, A.; Qu, B.; Jia, S.; Zhu, W. Influence of three phases of El Niño–Southern Oscillation on daily precipitation regimes in China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Stepaniak, D.P. Indices of El Nino evolution. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 1697–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Nicholls, N.; Ghazi, A. CLIVAR/GCOS/WMO Workshop on Indices and Indicators for Climate Extremes—Workshop summary. Clim. Chang. 1999, 42, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T.C. Climate Change Indices. WMO Bull. 2005, 54, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Non-parametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank correlation methods. Br. J. Psychol. 1990, 25, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P.; Presnell, B. Intentionally biased bootstrap methods. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1999, 61, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, A.C.; Hinkley, D.V.; Young, G.A. Recent developments in bootstrap methodology. Stat. Sci. 2003, 18, 141–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T. Climate change inspector with intentionally biased bootstrapping (CCIIBB ver. 1.0)—Methodology development. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinka, I. SOMA—self organizing migrating algorithm. In New Optimization Techniques in Engineering; Onwubolu, B.B., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 167–218. ISBN 3-540-20167X. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heng, C.; Yoon, S.-K.; Kim, J.-S.; Xiong, L. Inter-Seasonal Precipitation Variability over Southern China Associated with Commingling Effect of Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño. Water 2019, 11, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102023
Heng C, Yoon S-K, Kim J-S, Xiong L. Inter-Seasonal Precipitation Variability over Southern China Associated with Commingling Effect of Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño. Water. 2019; 11(10):2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102023
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeng, Chaizi, Sun-Kwon Yoon, Jong-Suk Kim, and Lihua Xiong. 2019. "Inter-Seasonal Precipitation Variability over Southern China Associated with Commingling Effect of Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño" Water 11, no. 10: 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102023
APA StyleHeng, C., Yoon, S.-K., Kim, J.-S., & Xiong, L. (2019). Inter-Seasonal Precipitation Variability over Southern China Associated with Commingling Effect of Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño. Water, 11(10), 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102023






