Inactivation and Loss of Infectivity of Enterovirus 70 by Solar Irradiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Simulated Solar Inactivation Trials
2.3. Virus Inactivation Kinetics Evaluated by Means of Infectious Assay
2.4. Virus Inactivation Kinetics Evaluated by Means of RNA Concentration Decay
2.5. Growth Curve Analysis
2.6. Virus Absorption Assay
2.7. EV70 Genome Sequencing
3. Results
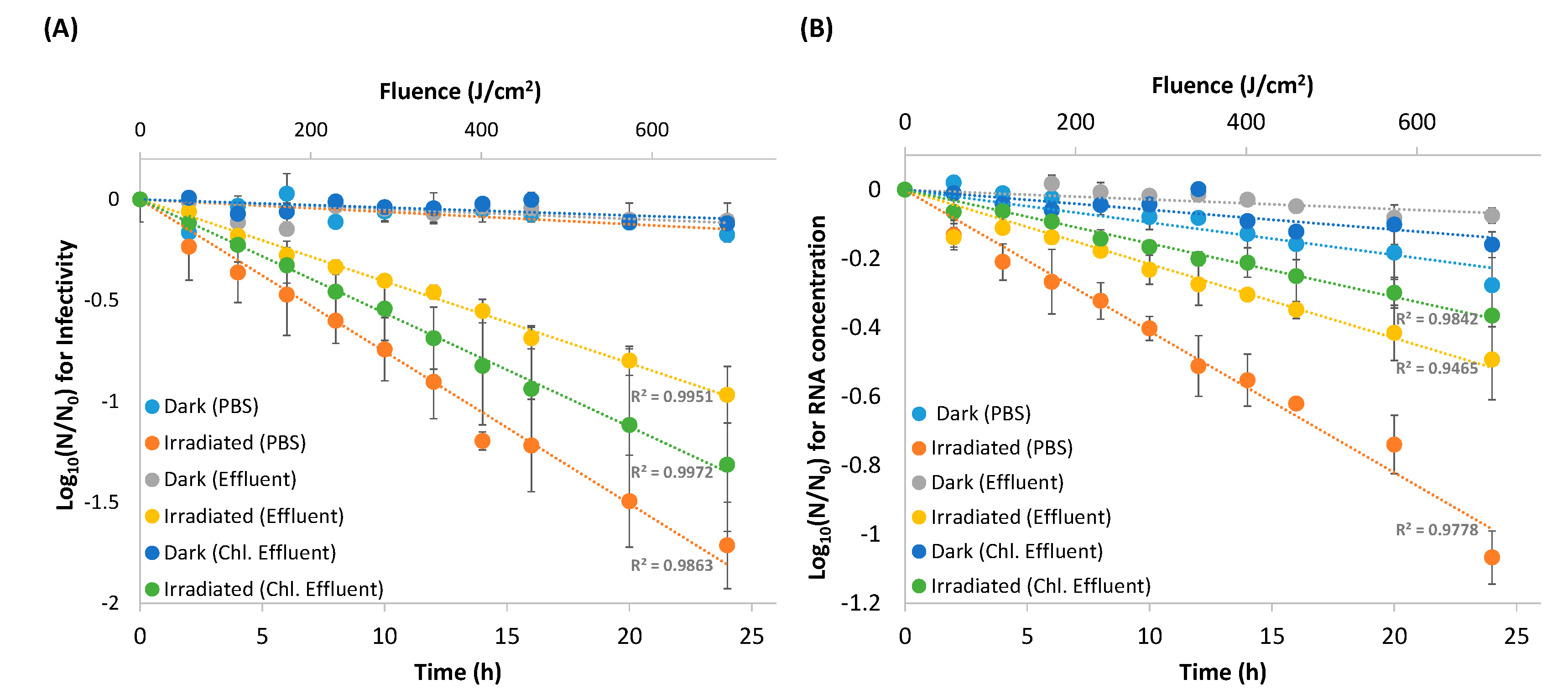
3.1. Viral Inactivation Upon Solar Irradiation
3.2. RNA Decay
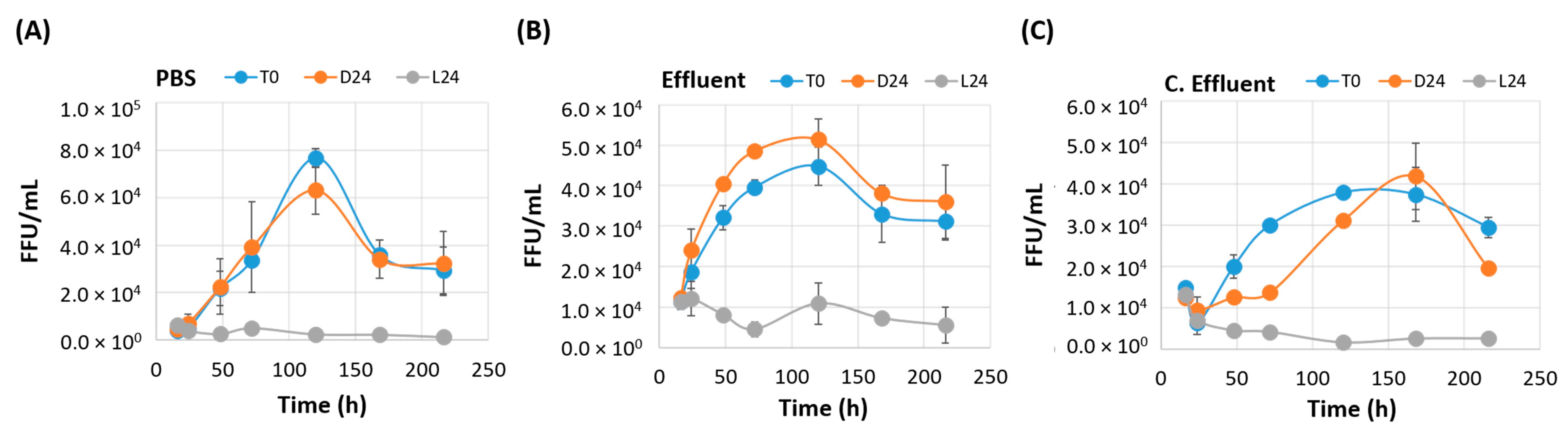
3.3. Irradiated EV70 Displays Inhibited Viral Replication
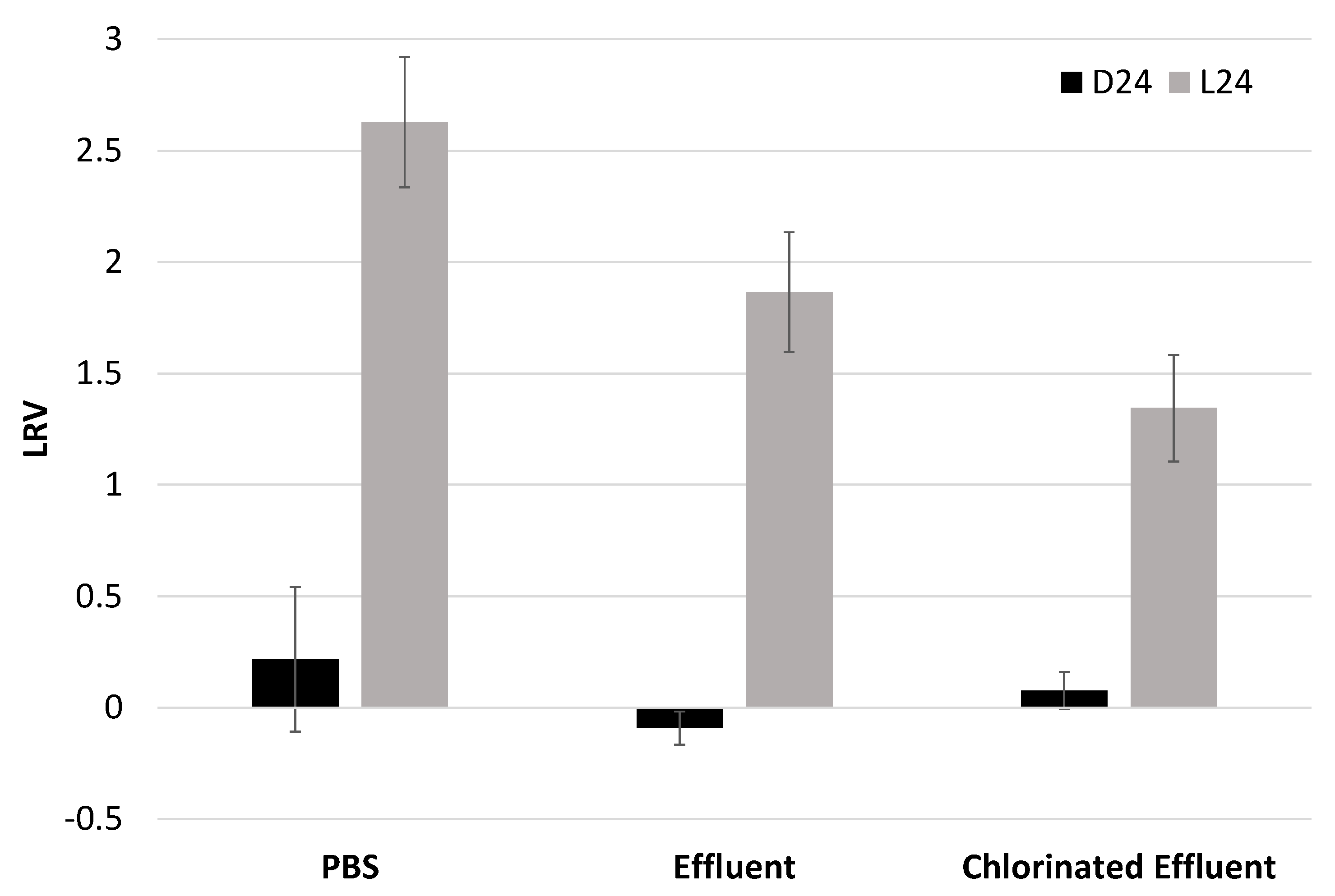
3.4. Irradiated EV70 Displayed Reduced Binding Capability
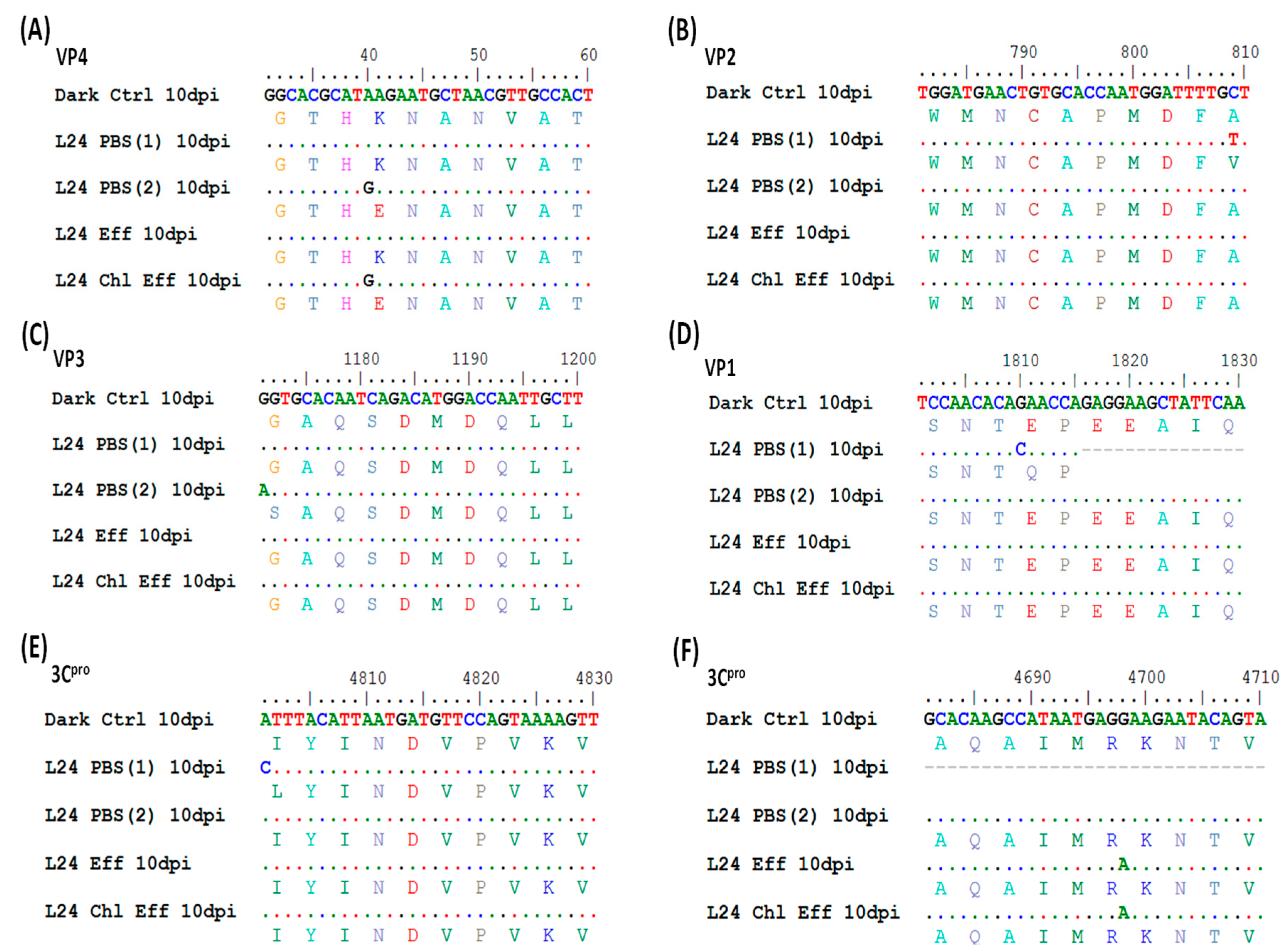
3.5. Irradiated Viruses Select for Five Nonsynonymous Mutations
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AghaKouchak, A.; Feldman, D.; Hoerling, M.; Huxman, T.; Lund, J. Water and climate: Recognize anthropogenic drought. Nature 2015, 524, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Da, L.; Song, K.; Li, B.-L. Temporal variations of surface water quality in urban, suburban and rural areas during rapid urbanization in shanghai, china. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liyanage, C.; Yamada, K. Impact of population growth on the water quality of natural water bodies. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, M. Chapter 19—Disinfection. In Wetlands for Water Pollution Control, 2nd ed.; Scholz, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Q.; Carratalà, A.; Ossola, R.; Bachmann, V.; Kohn, T. Cross-resistance of uv- or chlorine dioxide-resistant echovirus 11 to other disinfectants. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumat, M.; Hasan, N.; Subramanian, P.; Heberling, C.; Colwell, R.; Hong, P.-Y. Membrane bioreactor-based wastewater treatment plant in saudi arabia: Reduction of viral diversity, load, and infectious capacity. Water 2017, 9, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-L.; Nakajima, S.; Ma, L.; Walter, B.; Yasui, A.; Ethell, D.W.; Owen, L.B. Differential biologic effects of cpd and 6-4pp uv-induced DNA damage on the induction of apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest. BMC Cancer 2005, 5, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, R.; Therrien, J.P. Uvb-induced cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer frequency correlates with skin cancer mutational hotspots in p53. Photochem. Photobiol. 1997, 66, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, Y.; Rzeżutka, A.; Anderson, J.; MacGregor, S.; Given, M.; Deppe, C.; Cook, N. Pulsed uv-light inactivation of poliovirus and adenovirus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizasoain, A.; Tort, L.F.L.; García, M.; Gillman, L.; Alberti, A.; Leite, J.P.G.; Miagostovich, M.P.; Pou, S.A.; Cagiao, A.; Razsap, A.; et al. Human enteric viruses in a wastewater treatment plant: Evaluation of activated sludge combined with uv disinfection process reveals different removal performances for viruses with different features. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 66, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrefils, G.; Caron, É.; Wright, H.; Sakamoto, G.; Payment, P.; Barbeau, B.; Cairns, B. Uv dose required to achieve incremental log inactivation of bacteria, protozoa and viruses. IUVA News 2006, 8, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lytle, C.D.; Sagripanti, J.L. Predicted inactivation of viruses of relevance to biodefense by solar radiation. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14244–14252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racaniello, V.R. Picornaviridae: The viruses and their replication. In Fields virology, sixth edition; Wolters Klewer/Lippincott Williams Wilkinspp: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 453–489. [Google Scholar]
- Heaselgrave, W.; Patel, N.; Kilvington, S.; Kehoe, S.; McGuigan, K. Solar disinfection of poliovirus and acanthamoeba polyphaga cysts in water—A laboratory study using simulated sunlight. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaselgrave, W.; Kilvington, S. The efficacy of simulated solar disinfection (sodis) against coxsackievirus, poliovirus and hepatitis a virus. J. Water Health 2012, 10, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerba, C.P.; Gramos, D.M.; Nwachuku, N. Comparative inactivation of enteroviruses and adenovirus 2 by uv light. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5167–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirkovic, R.R.; Kono, R.; Yin-Murphy, M.; Sohier, R.; Schmidt, N.J.; Melnick, J.L. Enterovirus type 70: The etiologic agent of pandemic acute haemorrhagic conjunctivitis. Bull. World Health Organ. 1973, 49, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Khetsuriani, N.; Lamonte-Fowlkes, A.; Oberst, S.; Pallansch, M.A. Enterovirus surveillance—United States, 1970–2005. MMWR Surveill Summ 2006, 55, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roivainen, M. Enteroviruses: New findings on the role of enteroviruses in type 1 diabetes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylipaasto, P.; Klingel, K.; Lindberg, A.M.; Otonkoski, T.; Kandolf, R.; Hovi, T.; Roivainen, M. Enterovirus infection in human pancreatic islet cells, islet tropism in vivo and receptor involvement in cultured islet beta cells. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomqvist, S.; Savolainen, C.; Raman, L.; Roivainen, M.; Hovi, T. Humanrhinovirus 87 and enterovirus 68 represent a unique serotype with rhinovirus and enterovirus features. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4218–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Li, D.; Xie, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, X.; Guo, N.; Li, Y.; Duan, Z. Inactivation of ev71 by exposure to heat and ultraviolet light. Bing Du Xue Bao 2015, 31, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ottoson, J.; Hansen, A.; Westrell, T.; Johansen, K.; Norder, H.; Stenstrom, T.A. Removal of noro- and enteroviruses, giardia cysts, cryptosporidium oocysts, and fecal indicators at four secondary wastewater treatment plants in sweden. Water Environ. Res. 2006, 78, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Lee, B.E.; Neumann, N.; Ashbolt, N.; Craik, S.; Maal-Bared, R.; Pang, X.L. Assessment of human virus removal during municipal wastewater treatment in edmonton, canada. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, F.J.; Xagoraraki, I. Release of infectious human enteric viruses by full-scale wastewater utilities. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3590–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Gastaminza, P.; Cheng, G.; Kapadia, S.; Kato, T.; Burton, D.R.; Wieland, S.F.; Uprichard, S.L.; Wakita, T.; Chisari, F.V. Robust hepatitis c virus infection in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9294–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jassim, N.; Mantilla-Calderon, D.; Wang, T.; Hong, P.-Y. Inactivation and gene expression of a virulent wastewater escherichia coli strain and the nonvirulent commensal escherichia coli dsm1103 strain upon solar irradiation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3649–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. Bioedit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/nt. Nucleic Acids Sympos. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L.; Lam, J.W. Pymol: A communications tool for computational models. Abstr. ACS 2005, 230, U1371–U1372. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, E.D.; Plewa, M.J. Cho cell cytotoxicity and genotoxicity analyses of disinfection by-products: An updated review. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 58, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.D.; Jenkins, O.; Hughes, P.J.; Brown, A.; Knowles, N.J.; Booth, D.; Minor, P.D.; Almond, J.W. The complete nucleotide sequence of enterovirus type 70: Relationships with other members of the picornaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 2291–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cliver, D.O. Experimental infection by waterborne enteroviruses. J. Food Prot. 1981, 44, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogle, J.M. Poliovirus cell entry: Common structural themes in viral cell entry pathways. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56, 677–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.R.; McCormick, M.J. Electron microscopy of poliomyelitis virus. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1956, 28, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yang, H.; Feng, Q.-J.; Yao, X.-J.; Zhang, H.-L.; Zhang, R.-L.; He, Y.-Q. Complete genome sequence of a coxsackievirus a16 strain, isolated from a fatal case in Shenzhen, Southern China, in 2014. Gen. Ann. 2015, 3, e00391-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowell, R.L.; Landau, B.J. A short history and introductory b. In The Coxsackie B Viruses; Tracy, S., Chapman, N.M., Mahy, B.W.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dahllund, L.; Nissinen, L.; Pulli, T.; Hyttinen, V.P.; Stanway, G.; Hyypia, T. The genome of echovirus 11. Virus Res. 1995, 35, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, A.I.; Peterson, B.M.; Boehm, A.B.; McNeill, K.; Nelson, K.L. Sunlight inactivation of human viruses and bacteriophages in coastal waters containing natural photosensitizers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenwick, M.L.; Wall, M.J. Factors determining the site of synthesis of poliovirus proteins: The early attachment of virus particles to endoplasmic membranes. J. Cell Sci. 1973, 13, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.D.; Semler, B.L. Bridging ires elements in mrnas to the eukaryotic translation apparatus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1789, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Li, M.L.; Huang, P.N.; Chien, K.Y.; Horng, J.T.; Shih, S.R. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonuclear protein k interacts with the enterovirus 71 5′ untranslated region and participates in virus replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.I.; Chang, Y.Y.; Lin, J.Y.; Kuo, R.L.; Liu, H.P.; Shih, S.R.; Wu, C.C. Interactome analysis of the ev71 5′ untranslated region in differentiated neuronal cells sh-sy5y and regulatory role of fbp3 in viral replication. Proteomics 2016, 16, 2351–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.-T.; Kung, Y.-A.; Li, M.-L.; Brewer, G.; Lee, K.-M.; Liu, S.-T.; Shih, S.-R. Additive promotion of viral internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation by far upstream element-binding protein 1 and an enterovirus 71-induced cleavage product. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Shih, S.-R.; Pan, M.; Li, C.; Lue, C.-F.; Stollar, V.; Li, M.-L. Hnrnp a1 interacts with the 5′ untranslated regions of enterovirus 71 and sindbis virus rna and is required for viral replication. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6106–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noah, J.W.; Shapkina, T.; Wollenzien, P. Uv-induced crosslinks in the 16s rrnas of escherichia coli, bacillus subtilis and thermus aquaticus and their implications for ribosome structure and photochemistry. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 3785–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, M.; Fry, E.; Stuart, D.; Lyons, C.; Hoey, E.; Martin, S.J. Preliminary crystallographic analysis of bovine enterovirus. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 231, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poyry, T.; Kinnunen, L.; Hyypia, T.; Brown, B.; Horsnell, C.; Hovi, T.; Stanway, G. Genetic and phylogenetic clustering of enteroviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 1699–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, M.; Tate, J.; Hoey, E.; Lyons, C.; Martin, S.; Stuart, D. Implications for viral uncoating from the structure of bovine enterovirus. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1995, 2, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Racaniello, V.R. Enterovirus 70 receptor utilization is controlled by capsid residues that also regulate host range and cytopathogenicity. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 8648–8655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, N.H.; Kolatkar, P.R.; Oliveira, M.A.; Cheng, R.H.; Greve, J.M.; McClelland, A.; Baker, T.S.; Rossmann, M.G. Structure of a human rhinovirus complexed with its receptor molecule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnauchow, T.M.; Tolson, D.L.; Harrison, B.A.; Altman, E.; Lublin, D.M.; Dimock, K. The hela cell receptor for enterovirus 70 is decay-accelerating factor (cd55). J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5143–5152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smyth, M.S.; Trudgett, A.; Hoey, E.M.; Martin, S.J.; Brown, F. Characterization of neutralizing antibodies to bovine enterovirus elicited by synthetic peptides. Arch. Virol. 1992, 126, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.J.; Kremer, M.J.; Luo, M.; Vriend, G.; Arnold, E.; Kamer, G.; Rossmann, M.G.; McKinlay, M.A.; Diana, G.D.; Otto, M.J. The site of attachment in human rhinovirus 14 for antiviral agents that inhibit uncoating. Science 1986, 233, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, E.; Rossmann, M.G. The use of molecular-replacement phases for the refinement of the human rhinovirus 14 structure. Acta Cryst. 1988, 44, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Smith, T.J.; Chapman, M.S.; Rossmann, M.C.; Pevear, D.C.; Dutko, F.J.; Felock, P.J.; Diana, G.D.; McKinlay, M.A. Crystal structure of human rhinovirus serotype 1a (hrv1a). J. Mol. Biol. 1989, 210, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Chen, S.; Cheng, A.; Wang, M. Roles of the picornaviral 3c proteinase in the viral life cycle and host cells. Viruses 2016, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Wang, J.; Fan, T.; Qin, B.; Guo, L.; Lei, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Jin, Q. Crystal structure of human enterovirus 71 3c protease. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 408, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, D.; Pathak, H.B.; Cameron, C.E.; Rombaut, B.; Wimmer, E.; Paul, A.V. Stimulation of poliovirus synthesis in a hela cell-free in vitro translation-rna replication system by viral protein 3cdpro. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6358–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, W.S.; Parsley, T.B.; Bogerd, H.P.; Towner, J.S.; Semler, B.L.; Cullen, B.R. Utilization of a mammalian cell-based rna binding assay to characterize the rna binding properties of picornavirus 3c proteinases. RNA 1998, 4, 215–225. [Google Scholar]
- Pecson, B.M.; Martin, L.V.; Kohn, T. Quantitative pcr for determining the infectivity of bacteriophage ms2 upon inactivation by heat, uv-b radiation, and singlet oxygen: Advantages and limitations of an enzymatic treatment to reduce false-positive results. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5544–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, M.R.; Andrews, R.C.; Hofmann, R. Inactivation of particle-associated viral surrogates by ultraviolet light. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3487–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, M.; Fitzhenry, K.; O'Flaherty, V.; Dore, W.; Keaveney, S.; Cormican, M.; Rowan, N.; Clifford, E. Detection, fate and inactivation of pathogenic norovirus employing settlement and uv treatment in wastewater treatment facilities. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöcking, R.; Felber, Y.; Guhr, M.; Meyer, G.; Schubert, R.; Schoenherr, J.I. Development of an innovative peat lipstick based on the uv-b protective effect of humic substances. Mires Peat 2013, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Westerhoff, P.; Aiken, G.; Amy, G.; Debroux, J. Relationships between the structure of natural organic matter and its reactivity towards molecular ozone and hydroxyl radicals. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2265–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-X.; Kitajima, M.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Sunlight inactivation of somatic coliphage in the presence of natural organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symonds, E.M.; Griffin, D.W.; Breitbart, M. Eukaryotic viruses in wastewater samples from the united states. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bofill-Mas, S.; Albinana-Gimenez, N.; Clemente-Casares, P.; Hundesa, A.; Rodriguez-Manzano, J.; Allard, A.; Calvo, M.; Girones, R. Quantification and stability of human adenoviruses and polyomavirus jcpyv in wastewater matrices. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7894–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuigan, K.G.; Conroy, R.M.; Mosler, H.-J.; Preez, M.d.; Ubomba-Jaswa, E.; Fernandez-Ibañez, P. Solar water disinfection (sodis): A review from bench-top to roof-top. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonica, S.; Kohn, T.; Mac, M.; Real, F.J.; Wirz, J.; von Gunten, U. Photosensitizer method to determine rate constants for the reaction of carbonate radical with organic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9182–9188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PBS | Effluent | Chlorinated Effluent | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kobs | t1/2 | kobs | t1/2 | kobs | t1/2 | ||
| (A) | Dark Control | 0.014 ± 0.003 | 52 ± 12 h | 0.010 ± 5 × 10−5 | 70 ± 0.4 h | 0.009 ± 0.001 | 77 ± 3.8 h |
| Irradiated EV70 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 30 ± 3 min | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 47 ± 5 min | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 41 ± 3 min | |
| (B) | Dark Control | 0.002 ± 0.006 | 34.8 ± 11.2 h | 0.007± 0.001 | 101.8 ± 8.2 h | 0.013 ± 0.006 | 67.0 ± 29.3 h |
| Irradiated EV70 | 0.77 ± 0.16 | 57 ± 14 min | 0.48 ± 0.05 | 88 ± 9 min | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 145 ± 7 min | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jumat, M.R.; Hong, P.-Y. Inactivation and Loss of Infectivity of Enterovirus 70 by Solar Irradiation. Water 2019, 11, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010064
Jumat MR, Hong P-Y. Inactivation and Loss of Infectivity of Enterovirus 70 by Solar Irradiation. Water. 2019; 11(1):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010064
Chicago/Turabian StyleJumat, Muhammad Raihan, and Pei-Ying Hong. 2019. "Inactivation and Loss of Infectivity of Enterovirus 70 by Solar Irradiation" Water 11, no. 1: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010064
APA StyleJumat, M. R., & Hong, P.-Y. (2019). Inactivation and Loss of Infectivity of Enterovirus 70 by Solar Irradiation. Water, 11(1), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010064





